Integumentary System Lab Purpose: Materials: Introduction: Procedure:
|
|
|
- Bethanie Wood
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Date: Integumentary System Lab Purpose: To observe the organs and tissues of the integumentary system and to review the functions of these parts. Materials: textbook, hand magnifier or dissecting scope, forceps, microscope slide and cover slip, pipette and water, compound light microscope, prepared microscope slide of scalp, prepared slide of thick skin Introduction: The integumentary system includes the skin, hair, nails, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. These organs provide a protective covering for deeper tissues, aid in regulating body temperature, retard, water loss, house sensory receptors, synthesize various chemicals, and excrete small quantities of wastes. Procedure: 1. Review the sections entitled Skin and its Tissues and Accessory Organs of the Skin in chapter 6 of your textbook. 2. As a review activity, label figures A, B and C. Figure A 1
2 Figure B 2 Figure C 3. Complete part A of the conclusion questions. 4. Use a hand magnifier or dissecting scope and proceed as follows: a. Observe the skin, hair, and nails of your hand. b. Compare the type and distribution of hairs on the front and back of your forearm.
3 3 5. Use low-power magnification of the compound light microscope and proceed as follows: a. Pull out a single hair with forceps and mount it on a microscope slide. Place a drop of water on top of the hair then cover it with a cover slip being careful not to have any air bubbles around the hair. b. Observe the root and shaft of the hair and note the scale-like parts that makeup the shaft. 6. Complete Part B of the conclusion questions. 7. As vertical sections of skin are observed, remember that the lenses of the microscope invert and reverse images. It is important to orient the position of the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layers using low power before continuing with additional observations. Compare all of your skin observations to the Figures D-H. Use low-power magnification of the compound light microscope and proceed as follows: a. Observe the prepared slide of skin with hair. b. Locate the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer, a hair follicle, a sebaceous gland, and a sweat gland. You may be able to locate an arrector pili muscle as well. c. Focus on the epidermis with high power and locate the stratum corneum and stratum basale (stratum germinativum). Note how the shapes of the cells in these two layers differ. d. Observe the dense connective tissue (irregular collagenous connective tissue) that makes up the bulk of the dermis. e. Observe the adipose tissue that composes most of the subcutaneous layer. 8. Observe the prepared slide of thick skin. Locate the stratum lucidum. Note how the stratum corneum compares to your observation of the human scalp. 9. Complete part C of the conclusion questions. 10. Using low-power magnification, locate a hair follicle that has been sectioned longitudinally through its bulblike base. Also locate a sebaceous gland close to the follicle and find a sweat gland. Observe the detailed structure of these parts with high power magnification. 11. Complete parts D and E of the conclusion questions.
4 4 Figure D (prickle layer = stratum spinosum) Figure E (hypodermis = subcutaneous) Figure F Figure G
5 Figure H: Sweat Gland and Ducts 5 Conclusion: Part A: Match the structures in Column A with the description and functions in column B. Place the letter of your choice in the space provided. 1. Apocrine sweat gland a. an oily secretion that helps to waterproof body surfaces 2. Arrector pili muscle b. outermost layer of the epidermis 3. Dermis c. Becomes active during puberty 4. Eccrine sweat gland d. Epidermal pigment 5. Epidermis e. Inner layer of skin 6. Hair follicle f. Responds to elevated body temperature 7. Keratin g. pigment-producing cell 8. Melanin h. general name of entire superficial layer of the skin 9. Melanocyte i. gland that secretes an oily substance 10. Sebaceous gland j. Hard protein of nails and hair 11. Sebum k. Binds skin to underlying organs 12. Stratum basale (stratum germinativum) l. Cell division and deepest layer of epidermis 13. Stratum corneum m. Tube-like part that contains the root of the hair 14. Subcutaneous layer n. Causes hair to stand on end and goose bumps to appear
6 Part B Complete the following using complete sentences: 1. How does the skin of your palm differ from that on the back (posterior) of your hand? 6 2. Describe the differences you observed in the type and distribution of hair on the anterior and posterior of your forearm. 3. Explain how hair is formed. Part C 1. Distinguish among the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer. 2. How do the cells of the stratum corneum and stratum basale (stratum germinativum) differ?
7 3. What special qualities does the connective tissue of the dermis have? 7 Part D 1. What part of the hair extends from the hair papilla to the body surface? 2. In which layer of skin are sebaceous glands found? 3. How are sebaceous glands associated with hair follicles? 4. In which layer of skin are sweat glands usually located? Part E Sketch and label a vertical section of skin using the low power objective. You must label the epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous, dermal papilla, adipose tissue, hair follicle, sebaceous gland, stratum basale, stratum corneum. Be sure to draw it to scale.
CHAPTER 6: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial. Cutaneous Mucous Serous
 Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Protective Functions. Functions in Sensation. Functions in Excretion. Functions in Temperature Regulation
 Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System. What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system?
 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system? 1 Size of the Integument The integument is the largest system of the body: 16% of body weight 1.5
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system? 1 Size of the Integument The integument is the largest system of the body: 16% of body weight 1.5
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN
 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN The skin is an amazing structure; it is the largest organ of the body containing many structures such as capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, glands and
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN The skin is an amazing structure; it is the largest organ of the body containing many structures such as capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, glands and
The Integumentary System
 5 The Integumentary System FOCUS: The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, nails, and a variety of glands. The epidermis of the skin provides protection against abrasion, ultraviolet light,
5 The Integumentary System FOCUS: The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, nails, and a variety of glands. The epidermis of the skin provides protection against abrasion, ultraviolet light,
Thick and Thin Evaluating layers of the skin
 Overview Thick and Thin Evaluating layers of the skin Understanding the layered structure of skin is essential to understanding how it functions. The focus of this lesson is for students to discover and
Overview Thick and Thin Evaluating layers of the skin Understanding the layered structure of skin is essential to understanding how it functions. The focus of this lesson is for students to discover and
Integumentary System CHAPTER. Overview CHAPTER SUMMARY
 CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Overview CHAPTER SUMMARY Skin, the largest organ in the body, forms the integumentary system in conjunction with its accessory structures. The skin consists of two layers:
CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Overview CHAPTER SUMMARY Skin, the largest organ in the body, forms the integumentary system in conjunction with its accessory structures. The skin consists of two layers:
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure
 Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Consists of the skin and its accessory organs; hair, nails, and cutaneous glands Inspection of the skin, hair, and nails is significant part of a physical exam Skin is the most
The Integumentary System Consists of the skin and its accessory organs; hair, nails, and cutaneous glands Inspection of the skin, hair, and nails is significant part of a physical exam Skin is the most
Approved for use September 2015 August 2016 (VERSION 2 ISSUED 16 OCTOBER 2015) Guidance
 Assignment brief Qualification Unit code/title AM20530 VTCT Level 2 Certificate in Hairdressing and Beauty Therapy (VRQ) UV21582 Hair and beauty science Approved for use September 2015 August 2016 (VERSION
Assignment brief Qualification Unit code/title AM20530 VTCT Level 2 Certificate in Hairdressing and Beauty Therapy (VRQ) UV21582 Hair and beauty science Approved for use September 2015 August 2016 (VERSION
The Integumentary System Chapter 6. Skin Functions Skin Layers Skin Color Hair Nails Cutaneous Glands Burns
 The Integumentary System Chapter 6 Skin Functions Skin Layers Skin Color Hair Nails Cutaneous Glands Burns Functions of the Skin Skin is a barrier to microbes, chemical irritants, water loss. Vitamin D
The Integumentary System Chapter 6 Skin Functions Skin Layers Skin Color Hair Nails Cutaneous Glands Burns Functions of the Skin Skin is a barrier to microbes, chemical irritants, water loss. Vitamin D
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System. Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology: Tissues and Integumentary System Biology 105 Lecture 7 Chapter 4 Outline I. Tissues A. Epithelial B. Connective C. Muscle D. Nervous tissues II. Cell-to-cell contact
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam #2
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
The Epidermis. Provides mechanical protection. Helps keep micoorganisms out of the body. Consists of stratified squamous epithelium
 Components of the Integumentary System include 1. cutaneous membrane (skin) a. epidermis (superficial epithelium) b. dermis (under lying connective tissue layer) 2. hair 3. nails } 2,3,4 accessory structures
Components of the Integumentary System include 1. cutaneous membrane (skin) a. epidermis (superficial epithelium) b. dermis (under lying connective tissue layer) 2. hair 3. nails } 2,3,4 accessory structures
Integumentary System (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Integumentary System (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Integument = covering ~16% of body mass: ~2 meter 2 Primary Sources for figures
Integumentary System (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Integument = covering ~16% of body mass: ~2 meter 2 Primary Sources for figures
Skin (Integumentary System)
 Skin (Integumentary System) considered an organ or an organ system body s largest organ organ of greatest surface area:15-20 sq ft. (1.5-2 m 2 ) General Functions: 1. protection mechanical chemical bacterial
Skin (Integumentary System) considered an organ or an organ system body s largest organ organ of greatest surface area:15-20 sq ft. (1.5-2 m 2 ) General Functions: 1. protection mechanical chemical bacterial
Integumentary System Digestive System. Outline. Integumentary System 11/4/2008. Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND
 Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Integumentary System Digestive System Week 11 BA & BP November 4, 2008 Nadia Arora, ND Outline Integumentary system and body membranes Types of body membranes and their function General structure and main
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
PROPERTIES OF THE HAIR AND SCALP
 PROPERTIES OF THE HAIR AND SCALP 1. The scientific study of hair, its diseases and care is called: a. dermatology c. biology b. trichology d. cosmetology 2. The two parts of a mature hair strand are the
PROPERTIES OF THE HAIR AND SCALP 1. The scientific study of hair, its diseases and care is called: a. dermatology c. biology b. trichology d. cosmetology 2. The two parts of a mature hair strand are the
Notes on Hair Analysis
 Notes on Hair Analysis I have found local veterinarians very uncooperative when trying to get samples of dog and cat fur. I have found neighbors, friends and relatives a much better source of fur. There
Notes on Hair Analysis I have found local veterinarians very uncooperative when trying to get samples of dog and cat fur. I have found neighbors, friends and relatives a much better source of fur. There
Anatomy and Functions of Skin
 3 The Anatomy and Functions of Skin 3.1 Introduction Skin is considered to be the largest organ of the human body with an average surface area of 1.6 2 m 2 and accounts for about 15% of the total body
3 The Anatomy and Functions of Skin 3.1 Introduction Skin is considered to be the largest organ of the human body with an average surface area of 1.6 2 m 2 and accounts for about 15% of the total body
SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY
 SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY 1. The subcutaneous layer consists mostly of. a. smooth muscle c. areolar and adipose connective tissues d. melanin e. keratin 2. Which of the following statements
SAMPLE LECTURE EXAM 1 -- HUMAN ANATOMY 1. The subcutaneous layer consists mostly of. a. smooth muscle c. areolar and adipose connective tissues d. melanin e. keratin 2. Which of the following statements
2014 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament
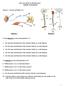 2014 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Neurons and Reflex Arc Diagram 1 Diagram 2 Use the Diagram 1 in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A
2014 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Neurons and Reflex Arc Diagram 1 Diagram 2 Use the Diagram 1 in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Membranes, Glands & Skin. Membranes. cells! tissues! organs. different from cell membranes
 Membranes, Glands & Skin cells! tissues! organs Organs! groups of tissues working together to perform a common function by definition, some of the simplest organs are membranes and glands neither fits
Membranes, Glands & Skin cells! tissues! organs Organs! groups of tissues working together to perform a common function by definition, some of the simplest organs are membranes and glands neither fits
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
PPx System Comprehensive Treatment Options Including: Acne, Skin Rejuvenation & Permanent Hair Reduction
 The Technology The PPx System combines pneumatic energy and broadband light, hence Photopneumatic (PPx ). Photo meaning light and pneumatic meaning vacuum. Most conventional laser and light based systems
The Technology The PPx System combines pneumatic energy and broadband light, hence Photopneumatic (PPx ). Photo meaning light and pneumatic meaning vacuum. Most conventional laser and light based systems
Skin Self-Study Module
 Skin Self-Study Module This self-study module will provide a foundation for clinicians to develop ongoing learning relating to skin and wound management Objectives After completing this module you should
Skin Self-Study Module This self-study module will provide a foundation for clinicians to develop ongoing learning relating to skin and wound management Objectives After completing this module you should
Integumentary System Answer Key
 Answer Key Free PDF ebook Download: Answer Key Download or Read Online ebook integumentary system answer key in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database the major organs and functions of the integumentary
Answer Key Free PDF ebook Download: Answer Key Download or Read Online ebook integumentary system answer key in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database the major organs and functions of the integumentary
Chapter 3 The Study of Hair By the end of the chapter you will be able to:
 Chapter 3 The Study of Hair By the end of the chapter you will be able to: identify the various parts of a hair describe variations in the structure of the medulla, cortex, and cuticle distinguish between
Chapter 3 The Study of Hair By the end of the chapter you will be able to: identify the various parts of a hair describe variations in the structure of the medulla, cortex, and cuticle distinguish between
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Lecture Exam One Material: Anatomy and Physiology 121 Introduction to Human Body, the Tissue Level of Organization and the Integumentary System
 Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy and physiology are absolutely interrelated subjects in which structures at all levels are defined and also used to understand the dynamic function of a living organism.
Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy and physiology are absolutely interrelated subjects in which structures at all levels are defined and also used to understand the dynamic function of a living organism.
GRADE 7: Life science 1. UNIT 7L.1 7 hours. Specialised cells. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Key vocabulary and technical terms
 GRADE 7: Life science 1 Specialised cells UNIT 7L.1 7 hours About this unit This unit is the first of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of
GRADE 7: Life science 1 Specialised cells UNIT 7L.1 7 hours About this unit This unit is the first of six units on life science for Grade 7. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, nails, the subcutaneous tissue below the skin, and assorted glands. Functions of the Integumentary System Protection against
The Integumentary System The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, nails, the subcutaneous tissue below the skin, and assorted glands. Functions of the Integumentary System Protection against
SKIN CARE AND COSMETIC INGREDIENTS DICTIONARY
 Milady s SKIN CARE AND COSMETIC INGREDIENTS DICTIONARY Third Edition Natalia Michalun and M. Varinia Michalun Australia Brazil Japan Korea Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom Milady s Skin Care & Cosmetic
Milady s SKIN CARE AND COSMETIC INGREDIENTS DICTIONARY Third Edition Natalia Michalun and M. Varinia Michalun Australia Brazil Japan Korea Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom Milady s Skin Care & Cosmetic
Melanoma The Skin Understanding Cancer
 Melanoma A form of cancer that begins in melanocytes (cells that make the pigment melanin). It may begin in a mole (skin melanoma), but can also begin in other pigmented tissues, such as in the eye or
Melanoma A form of cancer that begins in melanocytes (cells that make the pigment melanin). It may begin in a mole (skin melanoma), but can also begin in other pigmented tissues, such as in the eye or
PROVIDE EYELASH AND EYEBROW TREATMENTS
 PROVIDE EYELASH AND EYEBROW TREATMENTS aim and purpose This is a preparation for work unit which is based on capability and knowledge. The unit is about eyelash and eyebrow treatments. To carry out this
PROVIDE EYELASH AND EYEBROW TREATMENTS aim and purpose This is a preparation for work unit which is based on capability and knowledge. The unit is about eyelash and eyebrow treatments. To carry out this
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Hair Chemistry. Chapter 1. Hair Relaxers Science, Design, and Application www.alluredbooks.com
 Hair Relaxers Science, Design, and Application www.alluredbooks.com Chapter 1 Hair Chemistry We all know that the hair on our head is dead, but underneath the scalp, within the hair follicle, is a surprisingly
Hair Relaxers Science, Design, and Application www.alluredbooks.com Chapter 1 Hair Chemistry We all know that the hair on our head is dead, but underneath the scalp, within the hair follicle, is a surprisingly
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56
 Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN Skin is the largest organ of the body. The average adult has 18 square feet of skin which account for 16% of the total body weight. Skin acts as a physical barrier for you to the
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN Skin is the largest organ of the body. The average adult has 18 square feet of skin which account for 16% of the total body weight. Skin acts as a physical barrier for you to the
Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot
 Chapter 1 All you need to know about hair almost Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot Typically
Chapter 1 All you need to know about hair almost Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot Typically
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Acne (Acne Vulgaris) A common type of bacteria that lives on the skin, known as Propionibacterium acnes, sometimes
 Acne (Acne Vulgaris) Acne, clinically known as acne vulgaris, is the most common skin disease. It affects 85% of teenagers, some as young as 12, and often continues into adulthood. It is also called pimples,
Acne (Acne Vulgaris) Acne, clinically known as acne vulgaris, is the most common skin disease. It affects 85% of teenagers, some as young as 12, and often continues into adulthood. It is also called pimples,
Facts About Skin Appearance
 The Appearance of Human Skin Takanori Igarashi, Ko Nishino, and Shree K. Nayar Technical Report: CUCS-024-05 Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY 10027, USA June 2005 Takanori
The Appearance of Human Skin Takanori Igarashi, Ko Nishino, and Shree K. Nayar Technical Report: CUCS-024-05 Department of Computer Science Columbia University New York, NY 10027, USA June 2005 Takanori
Camouflage make-up UV30409 D/601/4355 VRQ. Learner name: Learner number:
 Camouflage make-up UV30409 D/601/4355 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy and Sport and Active Leisure sectors,
Camouflage make-up UV30409 D/601/4355 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy and Sport and Active Leisure sectors,
CHEM 107. Hair handout. Basic Structure of Hair. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05
 CHEM 107 Hair handout. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05 Basic Structure of Hair A hair can be defined as a slender, thread-like outgrowth from a follicle in the skin of mammals. Composed mainly of keratin, it has three
CHEM 107 Hair handout. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05 Basic Structure of Hair A hair can be defined as a slender, thread-like outgrowth from a follicle in the skin of mammals. Composed mainly of keratin, it has three
Please visit your examination provider s website for the most current bulletin prior to testing. IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS
 NATIONAL BARBER THEORY EXAMINATION CANDIDATE INFORMATION BULLETIN Please visit your examination provider s website for the most current bulletin prior to testing. The National Barber Theory Examination
NATIONAL BARBER THEORY EXAMINATION CANDIDATE INFORMATION BULLETIN Please visit your examination provider s website for the most current bulletin prior to testing. The National Barber Theory Examination
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
Students will identify these animal cell structures: Students should properly answer the pre-activity cell membrane, nucleus. questions.
 WHAT DO PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS LOOK LIKE? Grade Levels: 10-12 Time Frame: 2 periods Big Idea: Students will compare various plant epithelial cells (onion and elodea) with human epithelial cells (cheek lining
WHAT DO PLANT & ANIMAL CELLS LOOK LIKE? Grade Levels: 10-12 Time Frame: 2 periods Big Idea: Students will compare various plant epithelial cells (onion and elodea) with human epithelial cells (cheek lining
3.1 Cells and cell function
 BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
BTEC s own resources 3.1 Cells and cell function In this section: P1 How you are made Key terms Tissue a group of similar cells acting together to perform a particular function. Epithelial cells one of
Anatomy and Physiology
 Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Higher Beauty: Skills for Work Specification (Code C262 76)
 Higher Beauty: Skills for Work Specification (Code C262 76) Valid from August 2014 This edition, August 2014 version 1.0 This specification may be reproduced in whole or in part for educational purposes
Higher Beauty: Skills for Work Specification (Code C262 76) Valid from August 2014 This edition, August 2014 version 1.0 This specification may be reproduced in whole or in part for educational purposes
Secrets of Your. Skin & Hair. sweat gland. hair. dermis epidermis. muscle subdermis. by Michael Bono. www.bonoelectrolysis.com
 Secrets of Your Skin & Hair hair sweat gland dermis epidermis muscle subdermis by Michael Bono 1 2 Preface... I ve been in the business of hair removal (electrolysis) since 1975 and have seen countless
Secrets of Your Skin & Hair hair sweat gland dermis epidermis muscle subdermis by Michael Bono 1 2 Preface... I ve been in the business of hair removal (electrolysis) since 1975 and have seen countless
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
 1.2 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Plant and animal cell structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells perform some similar functions,
1.2 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Plant and animal cell structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells perform some similar functions,
Waxing for Cosmetologists
 Waxing for Cosmetologists Waxing This module introduces cosmetology continuing education students to the principles of hair removal and waxing. Topics include general facts about and structure of hair;
Waxing for Cosmetologists Waxing This module introduces cosmetology continuing education students to the principles of hair removal and waxing. Topics include general facts about and structure of hair;
Hair Analysis Notes. Hair s Anatomy
 Hair Analysis Notes Human hair is one of the most frequently found pieces of physical evidence located at the scene of a violent crime and can provide a substantive link between the criminal and their
Hair Analysis Notes Human hair is one of the most frequently found pieces of physical evidence located at the scene of a violent crime and can provide a substantive link between the criminal and their
OBJECTIVES PROCEDURE. Lab 2- Bio 160. Name:
 Lab 2- Bio 160 Name: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope. To obtain a better
Lab 2- Bio 160 Name: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope. To obtain a better
Lab Exercise 4. Epithelial Tissues. Connective Tissue Proper. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Fingerprinting Information Sheet
 Fingerprinting Information Sheet HISTORY Fingerprints weren t always used as a means to identify criminals. One of the first methods used to compare physical characteristics was developed in 1883 by Alphonse
Fingerprinting Information Sheet HISTORY Fingerprints weren t always used as a means to identify criminals. One of the first methods used to compare physical characteristics was developed in 1883 by Alphonse
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SYLLABUS FOR COMMUNITY COLLEGES. Leslie Dawn Schulz, B.S. Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SYLLABUS FOR COMMUNITY COLLEGES Leslie Dawn Schulz, B.S. Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS May 2000 APPROVED: Gerard A O Donovan, Major
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SYLLABUS FOR COMMUNITY COLLEGES Leslie Dawn Schulz, B.S. Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS May 2000 APPROVED: Gerard A O Donovan, Major
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 4B Chapter 4: Cell Structure
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 4B Chapter 4: Cell Structure The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist You may refer to pages 66-67, 72-73 in your textbook for a general discussion of microscopes.
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 4B Chapter 4: Cell Structure The Microscope: A Tool of the Scientist You may refer to pages 66-67, 72-73 in your textbook for a general discussion of microscopes.
Forensic Science Lesson 3: Trace Evidence Analysis
 Forensic Science Lesson 3: Trace Evidence Analysis History Alphonse Bertillon 1883 Created the first systematic system of individual classification & identification Detailed description of subject, full-length
Forensic Science Lesson 3: Trace Evidence Analysis History Alphonse Bertillon 1883 Created the first systematic system of individual classification & identification Detailed description of subject, full-length
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Specialized Tissues, Stem Cells, and Tissue Renewal
 Chapter 23 Specialized Tissues, Stem Cells, and Tissue Renewal 23 Cells evolved originally as free-living individuals, but the cells that matter most to us, as human beings, are specialized members of
Chapter 23 Specialized Tissues, Stem Cells, and Tissue Renewal 23 Cells evolved originally as free-living individuals, but the cells that matter most to us, as human beings, are specialized members of
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
 Lab 2- Bio 201 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Name: OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope, and in particular,
Lab 2- Bio 201 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Name: OBJECTIVES To explore cell structure and morphology in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. To gain more experience using the microscope, and in particular,
How To Understand The Skin
 THE SRUCTURE AND THE FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN Dr D. Tenea Department of Dermatology University of Pretoria BASIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY EMBRIOLOGY Ectoderm---Epidermis +Skin appendages Neural crest
THE SRUCTURE AND THE FUNCTIONS OF THE SKIN Dr D. Tenea Department of Dermatology University of Pretoria BASIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY EMBRIOLOGY Ectoderm---Epidermis +Skin appendages Neural crest
Hair Loss (Alopecia) Alopecia. Anatomy and Physiology of Hair. The Active Follicle
 Dr. Sahni BS DHMS Hons, PGRT (BOM), FF Hom Deputy Chief Medical Officer (H), ONGC Hospital Panvel-410221, Navi Mumbai, INDIA Hair Loss (Alopecia) Website: http://www.homoeopathyclinic.com Email: [email protected]
Dr. Sahni BS DHMS Hons, PGRT (BOM), FF Hom Deputy Chief Medical Officer (H), ONGC Hospital Panvel-410221, Navi Mumbai, INDIA Hair Loss (Alopecia) Website: http://www.homoeopathyclinic.com Email: [email protected]
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
 Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Cell Biology Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Observation of cells and organelles In this lab you will be looking at an example of a Prokaryotic cell (Bacillus cereus) and a some examples of Eukaryotic
Looking after your moles
 GenoMEL the Melanoma Genetics Consortium GenoMEL 2011. First published 2006. Revised February 2011. This leaflet is designed to help you look after your own moles. It is hoped that it will be useful for
GenoMEL the Melanoma Genetics Consortium GenoMEL 2011. First published 2006. Revised February 2011. This leaflet is designed to help you look after your own moles. It is hoped that it will be useful for
SECOND GRADE HUMAN BIOLOGY
 SECOND GRADE HUMAN BIOLOGY 2 WEEKS LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES LIFE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE ORGANISMS WEEK 1. PRE: Distinguishing characteristics of vertebrates. LAB: Discovering characteristics
SECOND GRADE HUMAN BIOLOGY 2 WEEKS LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES LIFE CYCLE OVERVIEW OF SECOND GRADE ORGANISMS WEEK 1. PRE: Distinguishing characteristics of vertebrates. LAB: Discovering characteristics
Hair. *credit to Anthony and Patti Bertino for image. Dec 2 8:10 PM
 Hair *credit to Anthony and Patti Bertino for image Dec 2 8:10 PM 1 Essential Question: How can hair be used to solve a crime? Dec 2 8:12 PM 2 History of hair evidence criminal evidence in 1800's 1883
Hair *credit to Anthony and Patti Bertino for image Dec 2 8:10 PM 1 Essential Question: How can hair be used to solve a crime? Dec 2 8:12 PM 2 History of hair evidence criminal evidence in 1800's 1883
Second Grade The Human Body-Cells Assessment
 Second Grade The Human Body-Cells Assessment 1a. The basic unit of all life is: a. a tree b. a cell 1b. The basic unit of all life is: a. a tree b. a cell c. an egg d. a phone 1c. The basic unit of all
Second Grade The Human Body-Cells Assessment 1a. The basic unit of all life is: a. a tree b. a cell 1b. The basic unit of all life is: a. a tree b. a cell c. an egg d. a phone 1c. The basic unit of all
Ground substance is the component of connective tissue between the cells and the fibers
 Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives.
 Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Smooth Muscle. Learning Objectives. At the end of this course, you should be able to : 1. describe the structure of smooth muscle 2. describe where smooth muscle occurs within the body 3. discuss the structural
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School. Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Your Skin. Name: Your Largest Organ
 Your Largest Organ What is the largest organ in your body? Your heart? It is the largest muscle in your body, but you do have larger organs. Your brain? The brain inside your skull is pretty big, but it's
Your Largest Organ What is the largest organ in your body? Your heart? It is the largest muscle in your body, but you do have larger organs. Your brain? The brain inside your skull is pretty big, but it's
Urinary System Lab Guide
 Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Exploring Creation with Advanced Biology ~ Schedule for 2015-2016 Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Date:
 Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Mon., Aug. 31 Tue., Sep. 1 Wed., Sept. 2 Thurs., Sept. 3 Fri., Sept. 4 Reading Pgs. 1-4; Introduction, Heart of the matter, Pgs. 5-8; Organization
Apologia ~ Exploring Creation with Biology ~ Module 1 (Week 1) Mon., Aug. 31 Tue., Sep. 1 Wed., Sept. 2 Thurs., Sept. 3 Fri., Sept. 4 Reading Pgs. 1-4; Introduction, Heart of the matter, Pgs. 5-8; Organization
SCHEME OF WORK APPLICATION FORM
 SCHEME OF WORK APPLICATION FORM For each ITEC qualification, the lecturer/centre must complete a Scheme of Work indicating how the lecturer is planning to cover the ITEC syllabus throughout the course.
SCHEME OF WORK APPLICATION FORM For each ITEC qualification, the lecturer/centre must complete a Scheme of Work indicating how the lecturer is planning to cover the ITEC syllabus throughout the course.
Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012
 Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012 Instructor: Dr. Elaine Chapman. Parker 130. Text/Atlas: Junqueira and Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 12th edition. McGraw Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163020-7
Biology 321. Mammalian Histology. Fall, 2012 Instructor: Dr. Elaine Chapman. Parker 130. Text/Atlas: Junqueira and Carneiro. Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 12th edition. McGraw Hill, 2010. ISBN 978-0-07-163020-7
about Why You Should Know Melanoma
 about Why You Should Know Melanoma Why You Should Know about Melanoma Each year, more than 3 million Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer. This is the most common form of cancer. Of these, more than
about Why You Should Know Melanoma Why You Should Know about Melanoma Each year, more than 3 million Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer. This is the most common form of cancer. Of these, more than
A Fishy Tale. Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope
 A Fishy Tale Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope A Fishy Tale About this Lesson In this lesson, students will explore a computer animation of the human body
A Fishy Tale Observing the Circulatory System of a Goldfish with a Compound Light Microscope A Fishy Tale About this Lesson In this lesson, students will explore a computer animation of the human body
Microscope Lab Introduction to the Microscope Lab Activity
 Microscope Lab Introduction to the Microscope Lab Activity Wendy Kim 3B 24 Sep 2010 http://www.mainsgate.com/spacebio/modules/gs_resource/ CellDivisionMetaphase.jpeg 1 Introduction Microscope is a tool
Microscope Lab Introduction to the Microscope Lab Activity Wendy Kim 3B 24 Sep 2010 http://www.mainsgate.com/spacebio/modules/gs_resource/ CellDivisionMetaphase.jpeg 1 Introduction Microscope is a tool
Thomas T. Jeneby, M.D. 7272 Wurzbach Suite 801 San Antonio, TX. 78240 210-782-8269/210 270 8595
 Laser hair removal is one of the most popular cosmetic procedures performed. Unwanted hair grows on various regions of the body. Often, individuals find the presence of hair in certain regions of the body
Laser hair removal is one of the most popular cosmetic procedures performed. Unwanted hair grows on various regions of the body. Often, individuals find the presence of hair in certain regions of the body
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
Unit 4: The Autonomic Nervous System 254 CHAPTER 16: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Read: Chapter 16, pages 517-534. Read only the topics covered in lecture. We will not cover this chapter in detail. Complete
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
