On the Realization of Asymmetric High Radix Signed Digital Adder using Neural Network
|
|
|
- Todd Walsh
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 On the Realization of Asymmetric High Radix Signed Digital Adder using Neural Network Md Sumon Shahriar Tofail Ahammad Hafiz Md Hasan Babu Dept of Computer and Information science Dept of Computer Science and Engg Dept of Comp Sc and Engg University of South Australia BRAC University, Dhaka, Bangladesh University of Dhaka,Bangladesh Abstract This paper presents an asymmetric high-radix signed-digital (AHSD) adder that performs addition on the basis of neural network (NN) and also shows that the AHSD number system supports carry-free (CF) addition by using NN Besides, NN implies the simple construction in high-speed operation The signed-digit number system represent the binary numbers that uses only one redundant digit for any radix r 2, the high-speed adder in the processor can be realized in the signed-digit system without a delay of the carry propagation A Novel NN design has been constructed for CF adder based on the AHSD (4) number system is also presented Moreover, if the radix is specified as r = 2 m, where m is any positive integer, the binary-to-ahsd (r) conversion can be done in constant time regardless of the word-length Hence, the AHSD-to-binary conversion dominates the performance of an AHSD based arithmetic system In order to investigate how the AHSD number system based on NN design achieves its functions, computer simulations for key circuits of conversion from binary to AHSD (4) based arithmetic systems are made The result shows the proposed NN design can perform the operations in higher speed than existing CF addition for AHSD 1 Introduction Addition is the most important and frequently used arithmetic operation in computer systems Generally, a few methods can be used to speed up the addition operation One is by using neural network design convert the operands from the binary number system to a redundant number system, eg, the signed-digit number system [2][3] or the residue number system, so that the addition becomes carryfree (CF) This Neural Network (NN) design implies fast addition can be done, at the expense of conversion between the binary number system and the redundant number system In this paper we focus on exploring high radix signed-digit (SD) numbers and we also present the asymmetric high-radix signeddigit (AHSD) number system using NN [4][5] The idea of AHSD is not new Instead of proposing a new number representation, our purpose is to explore the inherent CF property of AHSD by using NN The CF addition in AHSD based on NN is the basis for our high-speed addition circuits The conversion of AHSD to and from binary will be discussed in detail By choosing r = 2 m, where m is any positive integer, a binary number can be converted to its canonical AHSD representation in constant time We will also present one simple algorithm for converting binary bit pattern to make pairs in AHSD for radix-r NN design for converting AHSD numbers to binary: the first stresses high speed and the other provide hardware reusability Since the conversion from AHSD to binary has been considered the bottleneck of AHSD-based arithmetic computation based on NN, these NN design greatly improve the performance of AHSD systems For illustration, we will discuss in detail the example on AHSD (4), ie, the radix-4 AHSD number system The proposed approach is practical thanks to the simple conversion 2 Basic definitions Here, few basic definitions will be discussed 21 Neural Network A neural network is a powerful data-modelling tool that is able to capture and represent complex input/output relationships The motivation for the development of neural network technology stemmed from the desire to develop an artificial system that could perform "intelligent" tasks similar to those
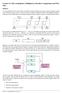
2 performed by the human brain Neural networks resemble the human brain in the following two ways: 1 A neural network acquires knowledge through learning 2 A neural network's knowledge is stored within inter-neuron connection strengths known as synaptic weights Figure 1: Neural Network prototype for AHSD number system addition In the figure, the simple prototype for NN is shown 22 Asymmetric Number System [1][3] The radix-r asymmetric high-radix signed-digit (AHSD) number system, denoted AHSD(r), is a positional weighted number system with the digit set S r = {- 1, 0,, r -1}, where r > 1 The AHSD number system is a minimally redundant system with only one redundant digit in the digit set We will explore the inherent carry-free property in AHSD and develop systematic approaches for conversion of AHSD numbers from binary ones An n-digit number X in AHSD (r) is represented as X = (x n-1, x n-2,, x 0) r, Where x i S r for i = 0, 1,, n - 1, and S r = {- 1, 0, 1,, r - 1} is the digit set of AHSD (r) The value of X can be represented as n 1 = X i= 0 Output Layer Hidden Layer Input Layer i x i r 0/1 0/ 1 n [ 1 1, r 1] n Clearly, the range of X is ( r )/( r ) 23 Binary to Asymmetric Number System conversion 0/2 Since the binary number system is the most widely used, we have to consider the conversion between the AHSD and binary number systems Although the radix r may be any positive integer, simple binary-to-ahsd conversion can be achieved if r = 2 m for any positive integer m The reason for such simple conversion will be explained later We assume r = 2 m in what follows, unless otherwise specified Note that there may be more than one AHSD (r) number representation for a binary number For instance, the binary number (0, 1, 1, 0, 0) 2 can be converted to two different AHSD (4) numbers, ie, (1, - 1, 0) 4 and (0, 3, 0) 4 Hence, the binary-to- AHSD(r) conversion, being a one-to-many mapping, may be performed by several different methods We would like to find an efficient and systematic conversion method that takes advantage of the carry-free property Here we follow a general algorithm to make pairs to convert Binary to AHSD (r) Algorithm for the conversion of AHSD from binary number system: Step 1 Suppose given binary #bits=n Step 2 If radix=2 m, where m is any positive integer then 2 p <m<2 p+1 Where p=1,2,3 Step 3 # Zero (0) will be padded in front of binary bits pattern 2 p+1 -n Step 4 Divide the array by m Step 5 If each sub array is =m Then stop Step 6 Else Divide each sub array by m Proof: Recurrence relation for the conversion from binaryto- AHSD numbers system is: c if n=m where c is a constant & m>2 T(n)= m T (n/m m T (n/m) if n>m T(n)=mT(n/m) (1) If n=n/m Replace it into (1) T(n/2)=mT(n/m^2) So, T(n)=m^2T(n/m^2) T (n) =m k T (n/m k ) where k=1,2,3 Assume n=m k T(n)=m k T(m k /m k ) T(n)=m k T(1 ) T(n)= m k n=m k Log m n = Log m m k =k Complexity of the algorithm to make pairs to convert Binary to AHSD (r) : O (log m n)
3 24 Addition of AHSD (4) number system [1] Here the addition process will be shown for AHSD number system This addition process can be for 1- bit to n-bit adder design without considering the carry propagation and its delay as well Example: Here two 4-bit AHSD (4) numbers are added X Y X (ahsd (4) ) ( ) 4 Y (ahsd (4) ) ( ) 4 X+Y(Z): Transfer digit: c Interim sum: µ Final sum S: ( ) 4 Result=( ) 2=(453) 10 The final result is in binary format The given example illustrates the addition process without carry propagation 3 Proposed Design of adder using Neural Network The neuron will work on the basis of feed-forward network with parallel processing This technique can be viewed as doing addition in adder in parallel The concept of parallel addition using neural network can be shown as the block diagram below Figure 3: N-bit adder generalization The N-bit adder generalization is shown in figure 3 Lemma: The total number of neurons for generating interim sum and carry of a radix-n asymmetric q-bit adder design is q 2(n-1) Proof: As n is the radix, so each bit will contain the value of n-1 So the interim sum will be in the range of 0 to 2(n-1) The total number of neurons for 1-bit adder design will be 2(n-1) For the design of a q-bit adder, the total number of neurons will be q 2(n-1) Here we proposed an algorithm for n-bit adder from binary to AHSD (4) using NN Algorithm: Step 1: Create 4 n input vectors (2n elements each) that represent all possible input combinations For example, for 1-bit addition, there will be 4 input vectors (2 elements each): {0, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {1, 1} Step 2: Create 4 n output vectors (ceiling of [ n / 2 + 1] elements) that represent the corresponding target combinations For example, for 1-bit addition, there will be 4 output vectors (2 elements each): {0, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, 1}, {0, 2} Step 3: Create a feed-forward back propagation neural network Step 4: Train the neural network for the input and output vectors of steps 1and step2 Step 5: Simulate the neural network with the input vectors of step 1, getting the sum in AHSD (4) as the target Figure 2: Trivial 1-bit AHSD radix-4 adder using NN The figure 2 shows the atomic view of the adder using Neural Network If we make it more generalized then the figure will be just like the following 4 AHSD addition for Radix-5 The asymmetric high radix number system considering radix-5 is not well suited for addition The first conversion from binary to AHSD requires pairing bits by 3-bit binary It will convey the values from 0 to 7 in decimal But radix-5 will need 0 to 4 values So we will get 5, 6, 7 as undetermined values Hence the addition process will not be possible as well Thus radix-4 AHSD is best suited for addition that is carry free and fast
4 5 Simulations Here the few simulations are described We performed the simulation using Matlab 71 neural network tools in a computer with Pentium IV processor At first conversion from binary- to- AHSD numbers is done for the manual simulation, then to get self-consistent adjustment (SCA) and adjacent digit modification (ADM) two AHSD numbers is added Then arithmetic addition of SCA and ADM is done Now NN design for addition of AHSD is considered Finally by using Mathlab-71 simulation tool simulation is performing for NN design and getting addition result of AHSD numbers In the figure 4 this workflow procedure is shown Binary to AHSD Conversion Training-Blue Performance is e-018, Goal is Epochs Figure 5-1:(TF- Logsig) 1-bit adder simulation and epoch is 100 Find out SCA and Get ADM in AHSD Simulate NN design for AHSD Numbers Using Matlab-71 Addition of AHSD Neural Network Design for Addition of AHSD Get result of Addition in AHSD Numbers Figure 5-2: (TF-Tansig) 1-bit adder for simulation and epoch is 12 Figure4: The Workflow of simulation procedure for AHSD numbers Figure 5-3: (TF-Purelin) 1-bit adder for simulation and epoch is 8
5 6 Experimental Results The table1 is summarized here from the experiments done Table 1: NN experimental results for AHSD adder design Figure 6-1: (TF-Tansig) 2-bit adder for simulation and epoch is 100 epochs Bit Layer Neuron numbers Activation Function 1- bit 2 I=2/O=2 Tansig/Logsig/Purelin 2-2 I=4/O=2 Tansig/Logsig bit 3- bit 2 I=6/O=3 Logsig Satisfactory performance is found in the design of AHSD-radix-4 adder using NN This performance shows the better implementation of the adder of redundant number system than radix-2 signed digital adder using NN [5] 7 Conclusion Figure 6-2: (TF-Logsig) 2-bit adder for simulation and epoch is 100 epochs In this paper one CF digital adder for AHSD (4) number system based on NN has been proposed Additionally, if r = 2 m for any positive integer m, the interface between AHSD and the binary number system can be realized and it can be easily implement able To make pairs at the time of conversion from binary to-ahsd, an algorithm has also been proposed Besides, NN design with Matlab-71 simulation tool is used to achieve high speed for addition on AHSD Even though hardware implementation is not done here but realization shows, the proposed NN design can be flexible Since both the binary-to-ahsd and AHSD-to-binary converter CF adder operate in a constant time, we can conclude that the AHSD-to-binary converter dominates the performance of the entire AHSD based on NN design system The time complexity of the entire AHSD CF adder is O (log m n) Finally, it is appealed that additional studies is necessary including not only the implementation of CF adder with different design skills, but also the applications of various CF adders to design fast arithmetic Hopefully, in future this paper can be extended for the digital adder of AHSD number system based on NN and which can be realized by using hardware, using current mode CMOS or voltage mode CMOS [6] and using SPICE simulation tool for hardware realization Figure 7: (TF-Logsig) 3-bit adder for simulation and epoch is 100 epochs
6 References [1] SH Sheih, and CW Wu, Asymmetric highradix signed-digit number systems for carry-free addition, Journal of information science and engineering 19, 2003, pp [2] B Parhami, Generalized signed-digit number sys tems: a unifying framework for redundant number representations, IEEE Transac tions on Computers, vol 39, 1990,pp89-98 [3]SH Sheih, and CW Wu, Carry-free adder design using asymmetric high- radix signed-digit number sys tem, in the Proceedings of 11 th VLSI De sign/cad Symposium, 2000, pp [4] M Sakamoto, D Hamano and M Morisue, A study of a radix-2 signed-digit al fuzzy processor using the logic oriented neural networks, IEEE International Systems Conference Proceedings, 1999, pp [5] T Kamio, H Fujisaka, and M Morisue, Back propagation algorithm for logic oriented neural networks with quantized weights and multilevel threshold neurons, IEICE Trans Fundamentals, vol E84-A, no3, 2001 [6] A Moushizuki, and T Hanyu, Low-power multi ple-valued current-mode logic using sub strate bias control, IEICE Trans Electron, vol E87-C, no 4, pp , 2004
An Efficient RNS to Binary Converter Using the Moduli Set {2n + 1, 2n, 2n 1}
 An Efficient RNS to Binary Converter Using the oduli Set {n + 1, n, n 1} Kazeem Alagbe Gbolagade 1,, ember, IEEE and Sorin Dan Cotofana 1, Senior ember IEEE, 1. Computer Engineering Laboratory, Delft University
An Efficient RNS to Binary Converter Using the oduli Set {n + 1, n, n 1} Kazeem Alagbe Gbolagade 1,, ember, IEEE and Sorin Dan Cotofana 1, Senior ember IEEE, 1. Computer Engineering Laboratory, Delft University
Implementation of Modified Booth Algorithm (Radix 4) and its Comparison with Booth Algorithm (Radix-2)
 Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 6 (2013), pp. 683-690 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Implementation of Modified Booth
Advance in Electronic and Electric Engineering. ISSN 2231-1297, Volume 3, Number 6 (2013), pp. 683-690 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aeee.htm Implementation of Modified Booth
A New Algorithm for Carry-Free Addition of Binary Signed-Digit Numbers
 2014 IEEE 22nd International Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines A New Algorithm for Carry-Free Addition of Binary Signed-Digit Numbers Klaus Schneider and Adrian Willenbücher Embedded
2014 IEEE 22nd International Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines A New Algorithm for Carry-Free Addition of Binary Signed-Digit Numbers Klaus Schneider and Adrian Willenbücher Embedded
RN-Codings: New Insights and Some Applications
 RN-Codings: New Insights and Some Applications Abstract During any composite computation there is a constant need for rounding intermediate results before they can participate in further processing. Recently
RN-Codings: New Insights and Some Applications Abstract During any composite computation there is a constant need for rounding intermediate results before they can participate in further processing. Recently
ANN Based Fault Classifier and Fault Locator for Double Circuit Transmission Line
 International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Open Access Research Paper Volume-4, Special Issue-2, April 2016 E-ISSN: 2347-2693 ANN Based Fault Classifier and Fault Locator for Double Circuit
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Open Access Research Paper Volume-4, Special Issue-2, April 2016 E-ISSN: 2347-2693 ANN Based Fault Classifier and Fault Locator for Double Circuit
Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders
 Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders In this set of slides, we present the two basic types of adders: 1. Half adders, and 2. Full adders. Each type of adder functions to add two binary bits. In order
Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders In this set of slides, we present the two basic types of adders: 1. Half adders, and 2. Full adders. Each type of adder functions to add two binary bits. In order
To convert an arbitrary power of 2 into its English equivalent, remember the rules of exponential arithmetic:
 Binary Numbers In computer science we deal almost exclusively with binary numbers. it will be very helpful to memorize some binary constants and their decimal and English equivalents. By English equivalents
Binary Numbers In computer science we deal almost exclusively with binary numbers. it will be very helpful to memorize some binary constants and their decimal and English equivalents. By English equivalents
A New Reversible TSG Gate and Its Application For Designing Efficient Adder Circuits
 A New Reversible TSG Gate and Its Application For Designing Efficient Adder s Himanshu Thapliyal Center for VLSI and Embedded System Technologies International Institute of Information Technology Hyderabad-500019,
A New Reversible TSG Gate and Its Application For Designing Efficient Adder s Himanshu Thapliyal Center for VLSI and Embedded System Technologies International Institute of Information Technology Hyderabad-500019,
Performance Comparison of an Algorithmic Current- Mode ADC Implemented using Different Current Comparators
 Performance Comparison of an Algorithmic Current- Mode ADC Implemented using Different Current Comparators Veepsa Bhatia Indira Gandhi Delhi Technical University for Women Delhi, India Neeta Pandey Delhi
Performance Comparison of an Algorithmic Current- Mode ADC Implemented using Different Current Comparators Veepsa Bhatia Indira Gandhi Delhi Technical University for Women Delhi, India Neeta Pandey Delhi
Lecture 2. Binary and Hexadecimal Numbers
 Lecture 2 Binary and Hexadecimal Numbers Purpose: Review binary and hexadecimal number representations Convert directly from one base to another base Review addition and subtraction in binary representations
Lecture 2 Binary and Hexadecimal Numbers Purpose: Review binary and hexadecimal number representations Convert directly from one base to another base Review addition and subtraction in binary representations
Let s put together a Manual Processor
 Lecture 14 Let s put together a Manual Processor Hardware Lecture 14 Slide 1 The processor Inside every computer there is at least one processor which can take an instruction, some operands and produce
Lecture 14 Let s put together a Manual Processor Hardware Lecture 14 Slide 1 The processor Inside every computer there is at least one processor which can take an instruction, some operands and produce
RN-coding of Numbers: New Insights and Some Applications
 RN-coding of Numbers: New Insights and Some Applications Peter Kornerup Dept. of Mathematics and Computer Science SDU, Odense, Denmark & Jean-Michel Muller LIP/Arénaire (CRNS-ENS Lyon-INRIA-UCBL) Lyon,
RN-coding of Numbers: New Insights and Some Applications Peter Kornerup Dept. of Mathematics and Computer Science SDU, Odense, Denmark & Jean-Michel Muller LIP/Arénaire (CRNS-ENS Lyon-INRIA-UCBL) Lyon,
Neural network software tool development: exploring programming language options
 INEB- PSI Technical Report 2006-1 Neural network software tool development: exploring programming language options Alexandra Oliveira aao@fe.up.pt Supervisor: Professor Joaquim Marques de Sá June 2006
INEB- PSI Technical Report 2006-1 Neural network software tool development: exploring programming language options Alexandra Oliveira aao@fe.up.pt Supervisor: Professor Joaquim Marques de Sá June 2006
Design Methods for Binary to Decimal Converters Using Arithmetic Decompositions
 J. of Mult.-Valued Logic & Soft Computing, Vol., pp. 8 7 Old City Publishing, Inc. Reprints available directly from the publisher Published by license under the OCP Science imprint, Photocopying permitted
J. of Mult.-Valued Logic & Soft Computing, Vol., pp. 8 7 Old City Publishing, Inc. Reprints available directly from the publisher Published by license under the OCP Science imprint, Photocopying permitted
Solution for Homework 2
 Solution for Homework 2 Problem 1 a. What is the minimum number of bits that are required to uniquely represent the characters of English alphabet? (Consider upper case characters alone) The number of
Solution for Homework 2 Problem 1 a. What is the minimum number of bits that are required to uniquely represent the characters of English alphabet? (Consider upper case characters alone) The number of
Stock Prediction using Artificial Neural Networks
 Stock Prediction using Artificial Neural Networks Abhishek Kar (Y8021), Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, IIT Kanpur Abstract In this work we present an Artificial Neural Network approach to predict
Stock Prediction using Artificial Neural Networks Abhishek Kar (Y8021), Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, IIT Kanpur Abstract In this work we present an Artificial Neural Network approach to predict
3.Basic Gate Combinations
 3.Basic Gate Combinations 3.1 TTL NAND Gate In logic circuits transistors play the role of switches. For those in the TTL gate the conducting state (on) occurs when the baseemmiter signal is high, and
3.Basic Gate Combinations 3.1 TTL NAND Gate In logic circuits transistors play the role of switches. For those in the TTL gate the conducting state (on) occurs when the baseemmiter signal is high, and
An Effective Deterministic BIST Scheme for Shifter/Accumulator Pairs in Datapaths
 An Effective Deterministic BIST Scheme for Shifter/Accumulator Pairs in Datapaths N. KRANITIS M. PSARAKIS D. GIZOPOULOS 2 A. PASCHALIS 3 Y. ZORIAN 4 Institute of Informatics & Telecommunications, NCSR
An Effective Deterministic BIST Scheme for Shifter/Accumulator Pairs in Datapaths N. KRANITIS M. PSARAKIS D. GIZOPOULOS 2 A. PASCHALIS 3 Y. ZORIAN 4 Institute of Informatics & Telecommunications, NCSR
A single register, called the accumulator, stores the. operand before the operation, and stores the result. Add y # add y from memory to the acc
 Other architectures Example. Accumulator-based machines A single register, called the accumulator, stores the operand before the operation, and stores the result after the operation. Load x # into acc
Other architectures Example. Accumulator-based machines A single register, called the accumulator, stores the operand before the operation, and stores the result after the operation. Load x # into acc
AN IMPROVED DESIGN OF REVERSIBLE BINARY TO BINARY CODED DECIMAL CONVERTER FOR BINARY CODED DECIMAL MULTIPLICATION
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (1): 69-73, 2014 ISSN: 1546-9239 2014 Science Publication doi:10.3844/ajassp.2014.69.73 Published Online 11 (1) 2014 (http://www.thescipub.com/ajas.toc) AN IMPROVED
American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (1): 69-73, 2014 ISSN: 1546-9239 2014 Science Publication doi:10.3844/ajassp.2014.69.73 Published Online 11 (1) 2014 (http://www.thescipub.com/ajas.toc) AN IMPROVED
Method of Combining the Degrees of Similarity in Handwritten Signature Authentication Using Neural Networks
 Method of Combining the Degrees of Similarity in Handwritten Signature Authentication Using Neural Networks Ph. D. Student, Eng. Eusebiu Marcu Abstract This paper introduces a new method of combining the
Method of Combining the Degrees of Similarity in Handwritten Signature Authentication Using Neural Networks Ph. D. Student, Eng. Eusebiu Marcu Abstract This paper introduces a new method of combining the
SAD computation based on online arithmetic for motion. estimation
 SAD computation based on online arithmetic for motion estimation J. Olivares a, J. Hormigo b, J. Villalba b, I. Benavides a and E. L. Zapata b a Dept. of Electrics and Electronics, University of Córdoba,
SAD computation based on online arithmetic for motion estimation J. Olivares a, J. Hormigo b, J. Villalba b, I. Benavides a and E. L. Zapata b a Dept. of Electrics and Electronics, University of Córdoba,
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications
 Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications TRIPTI SHARMA, K. G. SHARMA, B. P. SINGH, NEHA ARORA Electronics & Communication Department MITS Deemed University,
Efficient Interconnect Design with Novel Repeater Insertion for Low Power Applications TRIPTI SHARMA, K. G. SHARMA, B. P. SINGH, NEHA ARORA Electronics & Communication Department MITS Deemed University,
Recurrent Neural Networks
 Recurrent Neural Networks Neural Computation : Lecture 12 John A. Bullinaria, 2015 1. Recurrent Neural Network Architectures 2. State Space Models and Dynamical Systems 3. Backpropagation Through Time
Recurrent Neural Networks Neural Computation : Lecture 12 John A. Bullinaria, 2015 1. Recurrent Neural Network Architectures 2. State Space Models and Dynamical Systems 3. Backpropagation Through Time
COMP 250 Fall 2012 lecture 2 binary representations Sept. 11, 2012
 Binary numbers The reason humans represent numbers using decimal (the ten digits from 0,1,... 9) is that we have ten fingers. There is no other reason than that. There is nothing special otherwise about
Binary numbers The reason humans represent numbers using decimal (the ten digits from 0,1,... 9) is that we have ten fingers. There is no other reason than that. There is nothing special otherwise about
Multipliers. Introduction
 Multipliers Introduction Multipliers play an important role in today s digital signal processing and various other applications. With advances in technology, many researchers have tried and are trying
Multipliers Introduction Multipliers play an important role in today s digital signal processing and various other applications. With advances in technology, many researchers have tried and are trying
Floating Point Fused Add-Subtract and Fused Dot-Product Units
 Floating Point Fused Add-Subtract and Fused Dot-Product Units S. Kishor [1], S. P. Prakash [2] PG Scholar (VLSI DESIGN), Department of ECE Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam, Tamil Nadu,
Floating Point Fused Add-Subtract and Fused Dot-Product Units S. Kishor [1], S. P. Prakash [2] PG Scholar (VLSI DESIGN), Department of ECE Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam, Tamil Nadu,
Divide: Paper & Pencil. Computer Architecture ALU Design : Division and Floating Point. Divide algorithm. DIVIDE HARDWARE Version 1
 Divide: Paper & Pencil Computer Architecture ALU Design : Division and Floating Point 1001 Quotient Divisor 1000 1001010 Dividend 1000 10 101 1010 1000 10 (or Modulo result) See how big a number can be
Divide: Paper & Pencil Computer Architecture ALU Design : Division and Floating Point 1001 Quotient Divisor 1000 1001010 Dividend 1000 10 101 1010 1000 10 (or Modulo result) See how big a number can be
Analecta Vol. 8, No. 2 ISSN 2064-7964
 EXPERIMENTAL APPLICATIONS OF ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS IN ENGINEERING PROCESSING SYSTEM S. Dadvandipour Institute of Information Engineering, University of Miskolc, Egyetemváros, 3515, Miskolc, Hungary,
EXPERIMENTAL APPLICATIONS OF ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS IN ENGINEERING PROCESSING SYSTEM S. Dadvandipour Institute of Information Engineering, University of Miskolc, Egyetemváros, 3515, Miskolc, Hungary,
Lab 1: Full Adder 0.0
 Lab 1: Full Adder 0.0 Introduction In this lab you will design a simple digital circuit called a full adder. You will then use logic gates to draw a schematic for the circuit. Finally, you will verify
Lab 1: Full Adder 0.0 Introduction In this lab you will design a simple digital circuit called a full adder. You will then use logic gates to draw a schematic for the circuit. Finally, you will verify
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations. Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language
 Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
Chapter 4 Register Transfer and Microoperations Section 4.1 Register Transfer Language Digital systems are composed of modules that are constructed from digital components, such as registers, decoders,
INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS. IMPLEMENTATION: MODULES (ICs) AND NETWORKS IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHMS IN HARDWARE
 INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS 1 DESCRIPTION AND DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS FORMAL BASIS: SWITCHING ALGEBRA IMPLEMENTATION: MODULES (ICs) AND NETWORKS IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHMS IN HARDWARE COURSE EMPHASIS:
INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS 1 DESCRIPTION AND DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTEMS FORMAL BASIS: SWITCHING ALGEBRA IMPLEMENTATION: MODULES (ICs) AND NETWORKS IMPLEMENTATION OF ALGORITHMS IN HARDWARE COURSE EMPHASIS:
Neural Networks and Support Vector Machines
 INF5390 - Kunstig intelligens Neural Networks and Support Vector Machines Roar Fjellheim INF5390-13 Neural Networks and SVM 1 Outline Neural networks Perceptrons Neural networks Support vector machines
INF5390 - Kunstig intelligens Neural Networks and Support Vector Machines Roar Fjellheim INF5390-13 Neural Networks and SVM 1 Outline Neural networks Perceptrons Neural networks Support vector machines
NEW adder cells are useful for designing larger circuits despite increase in transistor count by four per cell.
 CHAPTER 4 THE ADDER The adder is one of the most critical components of a processor, as it is used in the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), in the floating-point unit and for address generation in case of cache
CHAPTER 4 THE ADDER The adder is one of the most critical components of a processor, as it is used in the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), in the floating-point unit and for address generation in case of cache
A Novel Low Power Fault Tolerant Full Adder for Deep Submicron Technology
 International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Open Access Research Paper Volume-4, Issue-1 E-ISSN: 2347-2693 A Novel Low Power Fault Tolerant Full Adder for Deep Submicron Technology Zahra
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Open Access Research Paper Volume-4, Issue-1 E-ISSN: 2347-2693 A Novel Low Power Fault Tolerant Full Adder for Deep Submicron Technology Zahra
A Simple Feature Extraction Technique of a Pattern By Hopfield Network
 A Simple Feature Extraction Technique of a Pattern By Hopfield Network A.Nag!, S. Biswas *, D. Sarkar *, P.P. Sarkar *, B. Gupta **! Academy of Technology, Hoogly - 722 *USIC, University of Kalyani, Kalyani
A Simple Feature Extraction Technique of a Pattern By Hopfield Network A.Nag!, S. Biswas *, D. Sarkar *, P.P. Sarkar *, B. Gupta **! Academy of Technology, Hoogly - 722 *USIC, University of Kalyani, Kalyani
Load balancing in a heterogeneous computer system by self-organizing Kohonen network
 Bull. Nov. Comp. Center, Comp. Science, 25 (2006), 69 74 c 2006 NCC Publisher Load balancing in a heterogeneous computer system by self-organizing Kohonen network Mikhail S. Tarkov, Yakov S. Bezrukov Abstract.
Bull. Nov. Comp. Center, Comp. Science, 25 (2006), 69 74 c 2006 NCC Publisher Load balancing in a heterogeneous computer system by self-organizing Kohonen network Mikhail S. Tarkov, Yakov S. Bezrukov Abstract.
Binary Numbering Systems
 Binary Numbering Systems April 1997, ver. 1 Application Note 83 Introduction Binary numbering systems are used in virtually all digital systems, including digital signal processing (DSP), networking, and
Binary Numbering Systems April 1997, ver. 1 Application Note 83 Introduction Binary numbering systems are used in virtually all digital systems, including digital signal processing (DSP), networking, and
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA & LOGIC GATES
 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA & LOGIC GATES Logic gates are electronic circuits that can be used to implement the most elementary logic expressions, also known as Boolean expressions. The logic gate is the most basic
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA & LOGIC GATES Logic gates are electronic circuits that can be used to implement the most elementary logic expressions, also known as Boolean expressions. The logic gate is the most basic
A Parallel Processor for Distributed Genetic Algorithm with Redundant Binary Number
 A Parallel Processor for Distributed Genetic Algorithm with Redundant Binary Number 1 Tomohiro KAMIMURA, 2 Akinori KANASUGI 1 Department of Electronics, Tokyo Denki University, 07ee055@ms.dendai.ac.jp
A Parallel Processor for Distributed Genetic Algorithm with Redundant Binary Number 1 Tomohiro KAMIMURA, 2 Akinori KANASUGI 1 Department of Electronics, Tokyo Denki University, 07ee055@ms.dendai.ac.jp
Performance Evaluation of Artificial Neural. Networks for Spatial Data Analysis
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 4, 2011, no. 4, 149-163 Performance Evaluation of Artificial Neural Networks for Spatial Data Analysis Akram A. Moustafa Department of Computer Science Al al-bayt
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 4, 2011, no. 4, 149-163 Performance Evaluation of Artificial Neural Networks for Spatial Data Analysis Akram A. Moustafa Department of Computer Science Al al-bayt
10 BIT s Current Mode Pipelined ADC
 10 BIT s Current Mode Pipelined ADC K.BHARANI VLSI DEPARTMENT VIT UNIVERSITY VELLORE, INDIA kothareddybharani@yahoo.com P.JAYAKRISHNAN VLSI DEPARTMENT VIT UNIVERSITY VELLORE, INDIA pjayakrishnan@vit.ac.in
10 BIT s Current Mode Pipelined ADC K.BHARANI VLSI DEPARTMENT VIT UNIVERSITY VELLORE, INDIA kothareddybharani@yahoo.com P.JAYAKRISHNAN VLSI DEPARTMENT VIT UNIVERSITY VELLORE, INDIA pjayakrishnan@vit.ac.in
SIM-PL: Software for teaching computer hardware at secondary schools in the Netherlands
 SIM-PL: Software for teaching computer hardware at secondary schools in the Netherlands Ben Bruidegom, benb@science.uva.nl AMSTEL Instituut Universiteit van Amsterdam Kruislaan 404 NL-1098 SM Amsterdam
SIM-PL: Software for teaching computer hardware at secondary schools in the Netherlands Ben Bruidegom, benb@science.uva.nl AMSTEL Instituut Universiteit van Amsterdam Kruislaan 404 NL-1098 SM Amsterdam
MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS
 Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Introduction MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCOMPUTER BASICS At present there are many types and sizes of computers available. These computers are designed and constructed based on digital and Integrated Circuit
Data Mining Techniques Chapter 7: Artificial Neural Networks
 Data Mining Techniques Chapter 7: Artificial Neural Networks Artificial Neural Networks.................................................. 2 Neural network example...................................................
Data Mining Techniques Chapter 7: Artificial Neural Networks Artificial Neural Networks.................................................. 2 Neural network example...................................................
This Unit: Floating Point Arithmetic. CIS 371 Computer Organization and Design. Readings. Floating Point (FP) Numbers
 This Unit: Floating Point Arithmetic CIS 371 Computer Organization and Design Unit 7: Floating Point App App App System software Mem CPU I/O Formats Precision and range IEEE 754 standard Operations Addition
This Unit: Floating Point Arithmetic CIS 371 Computer Organization and Design Unit 7: Floating Point App App App System software Mem CPU I/O Formats Precision and range IEEE 754 standard Operations Addition
Role of Neural network in data mining
 Role of Neural network in data mining Chitranjanjit kaur Associate Prof Guru Nanak College, Sukhchainana Phagwara,(GNDU) Punjab, India Pooja kapoor Associate Prof Swami Sarvanand Group Of Institutes Dinanagar(PTU)
Role of Neural network in data mining Chitranjanjit kaur Associate Prof Guru Nanak College, Sukhchainana Phagwara,(GNDU) Punjab, India Pooja kapoor Associate Prof Swami Sarvanand Group Of Institutes Dinanagar(PTU)
Properties of Stabilizing Computations
 Theory and Applications of Mathematics & Computer Science 5 (1) (2015) 71 93 Properties of Stabilizing Computations Mark Burgin a a University of California, Los Angeles 405 Hilgard Ave. Los Angeles, CA
Theory and Applications of Mathematics & Computer Science 5 (1) (2015) 71 93 Properties of Stabilizing Computations Mark Burgin a a University of California, Los Angeles 405 Hilgard Ave. Los Angeles, CA
A Novel Low Power, High Speed 14 Transistor CMOS Full Adder Cell with 50% Improvement in Threshold Loss Problem
 A Novel Low Power, High Speed 4 Transistor CMOS Full Adder Cell with 5% Improvement in Threshold Loss Problem T. Vigneswaran, B. Mukundhan, and P. Subbarami Reddy Abstract Full adders are important components
A Novel Low Power, High Speed 4 Transistor CMOS Full Adder Cell with 5% Improvement in Threshold Loss Problem T. Vigneswaran, B. Mukundhan, and P. Subbarami Reddy Abstract Full adders are important components
Stabilization by Conceptual Duplication in Adaptive Resonance Theory
 Stabilization by Conceptual Duplication in Adaptive Resonance Theory Louis Massey Royal Military College of Canada Department of Mathematics and Computer Science PO Box 17000 Station Forces Kingston, Ontario,
Stabilization by Conceptual Duplication in Adaptive Resonance Theory Louis Massey Royal Military College of Canada Department of Mathematics and Computer Science PO Box 17000 Station Forces Kingston, Ontario,
The string of digits 101101 in the binary number system represents the quantity
 Data Representation Section 3.1 Data Types Registers contain either data or control information Control information is a bit or group of bits used to specify the sequence of command signals needed for
Data Representation Section 3.1 Data Types Registers contain either data or control information Control information is a bit or group of bits used to specify the sequence of command signals needed for
Circuits and Boolean Expressions
 Circuits and Boolean Expressions Provided by TryEngineering - Lesson Focus Boolean logic is essential to understanding computer architecture. It is also useful in program construction and Artificial Intelligence.
Circuits and Boolean Expressions Provided by TryEngineering - Lesson Focus Boolean logic is essential to understanding computer architecture. It is also useful in program construction and Artificial Intelligence.
Implementing the Functional Model of High Accuracy Fixed Width Modified Booth Multiplier
 International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 393 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN: 2277-1956 Implementing the Functional Model of High Accuracy Fixed Width Modified Booth
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 393 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN: 2277-1956 Implementing the Functional Model of High Accuracy Fixed Width Modified Booth
SELECTING NEURAL NETWORK ARCHITECTURE FOR INVESTMENT PROFITABILITY PREDICTIONS
 UDC: 004.8 Original scientific paper SELECTING NEURAL NETWORK ARCHITECTURE FOR INVESTMENT PROFITABILITY PREDICTIONS Tonimir Kišasondi, Alen Lovren i University of Zagreb, Faculty of Organization and Informatics,
UDC: 004.8 Original scientific paper SELECTING NEURAL NETWORK ARCHITECTURE FOR INVESTMENT PROFITABILITY PREDICTIONS Tonimir Kišasondi, Alen Lovren i University of Zagreb, Faculty of Organization and Informatics,
Design of Energy Efficient Low Power Full Adder using Supply Voltage Gating
 Design of Energy Efficient Low Power Full Adder using Supply Voltage Gating S.Nandhini 1, T.G.Dhaarani 2, P.Kokila 3, P.Premkumar 4 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Nandha Engineering College, Erode,
Design of Energy Efficient Low Power Full Adder using Supply Voltage Gating S.Nandhini 1, T.G.Dhaarani 2, P.Kokila 3, P.Premkumar 4 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Nandha Engineering College, Erode,
Comparison of Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Classifiers for Travel Recommendations
 Volume 3, No. 8, August 2012 Journal of Global Research in Computer Science REVIEW ARTICLE Available Online at www.jgrcs.info Comparison of Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Classifiers for Travel Recommendations
Volume 3, No. 8, August 2012 Journal of Global Research in Computer Science REVIEW ARTICLE Available Online at www.jgrcs.info Comparison of Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Classifiers for Travel Recommendations
CSI 333 Lecture 1 Number Systems
 CSI 333 Lecture 1 Number Systems 1 1 / 23 Basics of Number Systems Ref: Appendix C of Deitel & Deitel. Weighted Positional Notation: 192 = 2 10 0 + 9 10 1 + 1 10 2 General: Digit sequence : d n 1 d n 2...
CSI 333 Lecture 1 Number Systems 1 1 / 23 Basics of Number Systems Ref: Appendix C of Deitel & Deitel. Weighted Positional Notation: 192 = 2 10 0 + 9 10 1 + 1 10 2 General: Digit sequence : d n 1 d n 2...
Method for Multiplier Verication Employing Boolean Equivalence Checking and Arithmetic Bit Level Description
 Method for Multiplier Verication Employing Boolean ing and Arithmetic Bit Level Description U. Krautz 1, M. Wedler 1, W. Kunz 1 & K. Weber 2, C. Jacobi 2, M. Panz 2 1 University of Kaiserslautern - Germany
Method for Multiplier Verication Employing Boolean ing and Arithmetic Bit Level Description U. Krautz 1, M. Wedler 1, W. Kunz 1 & K. Weber 2, C. Jacobi 2, M. Panz 2 1 University of Kaiserslautern - Germany
GOAL-BASED INTELLIGENT AGENTS
 International Journal of Information Technology, Vol. 9 No. 1 GOAL-BASED INTELLIGENT AGENTS Zhiqi Shen, Robert Gay and Xuehong Tao ICIS, School of EEE, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798
International Journal of Information Technology, Vol. 9 No. 1 GOAL-BASED INTELLIGENT AGENTS Zhiqi Shen, Robert Gay and Xuehong Tao ICIS, School of EEE, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798
Two's Complement Adder/Subtractor Lab L03
 Two's Complement Adder/Subtractor Lab L03 Introduction Computers are usually designed to perform indirect subtraction instead of direct subtraction. Adding -B to A is equivalent to subtracting B from A,
Two's Complement Adder/Subtractor Lab L03 Introduction Computers are usually designed to perform indirect subtraction instead of direct subtraction. Adding -B to A is equivalent to subtracting B from A,
DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNLOGY
 DRONACHARYA GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS, GREATER NOIDA Affiliated to Mahamaya Technical University, Noida Approved by AICTE DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNLOGY Lab Manual for Computer Organization Lab ECS-453
DRONACHARYA GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS, GREATER NOIDA Affiliated to Mahamaya Technical University, Noida Approved by AICTE DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNLOGY Lab Manual for Computer Organization Lab ECS-453
FPGA Implementation of an Advanced Traffic Light Controller using Verilog HDL
 FPGA Implementation of an Advanced Traffic Light Controller using Verilog HDL B. Dilip, Y. Alekhya, P. Divya Bharathi Abstract Traffic lights are the signaling devices used to manage traffic on multi-way
FPGA Implementation of an Advanced Traffic Light Controller using Verilog HDL B. Dilip, Y. Alekhya, P. Divya Bharathi Abstract Traffic lights are the signaling devices used to manage traffic on multi-way
what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored?
 Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
Inside the CPU how does the CPU work? what operations can it perform? how does it perform them? on what kind of data? where are instructions and data stored? some short, boring programs to illustrate the
Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots
 Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots Registers As you probably know (if you don t then you should consider changing your course), data processing is usually
Lecture 12: More on Registers, Multiplexers, Decoders, Comparators and Wot- Nots Registers As you probably know (if you don t then you should consider changing your course), data processing is usually
FPGA Implementation of an Extended Binary GCD Algorithm for Systolic Reduction of Rational Numbers
 FPGA Implementation of an Extended Binary GCD Algorithm for Systolic Reduction of Rational Numbers Bogdan Mătăsaru and Tudor Jebelean RISC-Linz, A 4040 Linz, Austria email: bmatasar@risc.uni-linz.ac.at
FPGA Implementation of an Extended Binary GCD Algorithm for Systolic Reduction of Rational Numbers Bogdan Mătăsaru and Tudor Jebelean RISC-Linz, A 4040 Linz, Austria email: bmatasar@risc.uni-linz.ac.at
Forecasting of Economic Quantities using Fuzzy Autoregressive Model and Fuzzy Neural Network
 Forecasting of Economic Quantities using Fuzzy Autoregressive Model and Fuzzy Neural Network Dušan Marček 1 Abstract Most models for the time series of stock prices have centered on autoregressive (AR)
Forecasting of Economic Quantities using Fuzzy Autoregressive Model and Fuzzy Neural Network Dušan Marček 1 Abstract Most models for the time series of stock prices have centered on autoregressive (AR)
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482
 International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Behavioral Analysis of Different ALU Architectures G.V.V.S.R.Krishna Assistant
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1482 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Behavioral Analysis of Different ALU Architectures G.V.V.S.R.Krishna Assistant
Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano
 Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano Lesson 6 - Combinational Design Practices Prof. João Miguel Fernandes (miguel@di.uminho.pt) Dept. Informática UNIVERSIDADE DO MINHO ESCOLA DE ENGENHARIA - PLDs (1) - The
Sistemas Digitais I LESI - 2º ano Lesson 6 - Combinational Design Practices Prof. João Miguel Fernandes (miguel@di.uminho.pt) Dept. Informática UNIVERSIDADE DO MINHO ESCOLA DE ENGENHARIA - PLDs (1) - The
Cash Forecasting: An Application of Artificial Neural Networks in Finance
 International Journal of Computer Science & Applications Vol. III, No. I, pp. 61-77 2006 Technomathematics Research Foundation Cash Forecasting: An Application of Artificial Neural Networks in Finance
International Journal of Computer Science & Applications Vol. III, No. I, pp. 61-77 2006 Technomathematics Research Foundation Cash Forecasting: An Application of Artificial Neural Networks in Finance
Automatic Detection of PCB Defects
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 6 November 2014 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Automatic Detection of PCB Defects Ashish Singh PG Student Vimal H.
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 6 November 2014 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Automatic Detection of PCB Defects Ashish Singh PG Student Vimal H.
A High Performance Binary to BCD Converter
 A High Performance Binary to BCD Converter A. Hari Priya 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Indur Institute of Engineering. and Technology, Siddipet, Medak, India 1 ABSTRACT: Decimal data processing
A High Performance Binary to BCD Converter A. Hari Priya 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Indur Institute of Engineering. and Technology, Siddipet, Medak, India 1 ABSTRACT: Decimal data processing
Cloud Computing for Agent-based Traffic Management Systems
 Cloud Computing for Agent-based Traffic Management Systems Manoj A Patil Asst.Prof. IT Dept. Khyamling A Parane Asst.Prof. CSE Dept. D. Rajesh Asst.Prof. IT Dept. ABSTRACT Increased traffic congestion
Cloud Computing for Agent-based Traffic Management Systems Manoj A Patil Asst.Prof. IT Dept. Khyamling A Parane Asst.Prof. CSE Dept. D. Rajesh Asst.Prof. IT Dept. ABSTRACT Increased traffic congestion
Design and Simulation of Soft Switched Converter Fed DC Servo Drive
 International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) ISSN: 2231-237, Volume-1, Issue-5, November 211 Design and Simulation of Soft Switched Converter Fed DC Servo Drive Bal Mukund Sharma, A.
International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) ISSN: 2231-237, Volume-1, Issue-5, November 211 Design and Simulation of Soft Switched Converter Fed DC Servo Drive Bal Mukund Sharma, A.
Digital System Design Prof. D Roychoudhry Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Digital System Design Prof. D Roychoudhry Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 04 Digital Logic II May, I before starting the today s lecture
Digital System Design Prof. D Roychoudhry Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 04 Digital Logic II May, I before starting the today s lecture
Chapter 2 The Research on Fault Diagnosis of Building Electrical System Based on RBF Neural Network
 Chapter 2 The Research on Fault Diagnosis of Building Electrical System Based on RBF Neural Network Qian Wu, Yahui Wang, Long Zhang and Li Shen Abstract Building electrical system fault diagnosis is the
Chapter 2 The Research on Fault Diagnosis of Building Electrical System Based on RBF Neural Network Qian Wu, Yahui Wang, Long Zhang and Li Shen Abstract Building electrical system fault diagnosis is the
Keywords: Image complexity, PSNR, Levenberg-Marquardt, Multi-layer neural network.
 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Volume 11 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 0975-4172
Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Volume 11 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 0975-4172
C H A P T E R. Logic Circuits
 C H A P T E R Logic Circuits Many important functions are naturally computed with straight-line programs, programs without loops or branches. Such computations are conveniently described with circuits,
C H A P T E R Logic Circuits Many important functions are naturally computed with straight-line programs, programs without loops or branches. Such computations are conveniently described with circuits,
Design and FPGA Implementation of a Novel Square Root Evaluator based on Vedic Mathematics
 International Journal of Information & Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 15 (2014), pp. 1531-1537 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com Design and FPGA
International Journal of Information & Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 4, Number 15 (2014), pp. 1531-1537 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com Design and FPGA
DIGITAL-TO-ANALOGUE AND ANALOGUE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION
 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOGUE AND ANALOGUE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION Introduction The outputs from sensors and communications receivers are analogue signals that have continuously varying amplitudes. In many systems
DIGITAL-TO-ANALOGUE AND ANALOGUE-TO-DIGITAL CONVERSION Introduction The outputs from sensors and communications receivers are analogue signals that have continuously varying amplitudes. In many systems
EE 261 Introduction to Logic Circuits. Module #2 Number Systems
 EE 261 Introduction to Logic Circuits Module #2 Number Systems Topics A. Number System Formation B. Base Conversions C. Binary Arithmetic D. Signed Numbers E. Signed Arithmetic F. Binary Codes Textbook
EE 261 Introduction to Logic Circuits Module #2 Number Systems Topics A. Number System Formation B. Base Conversions C. Binary Arithmetic D. Signed Numbers E. Signed Arithmetic F. Binary Codes Textbook
COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS
 COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/combinational_circuits.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Combinational circuit is a circuit in which we combine the different
COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/combinational_circuits.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Combinational circuit is a circuit in which we combine the different
TRAINING A LIMITED-INTERCONNECT, SYNTHETIC NEURAL IC
 777 TRAINING A LIMITED-INTERCONNECT, SYNTHETIC NEURAL IC M.R. Walker. S. Haghighi. A. Afghan. and L.A. Akers Center for Solid State Electronics Research Arizona State University Tempe. AZ 85287-6206 mwalker@enuxha.eas.asu.edu
777 TRAINING A LIMITED-INTERCONNECT, SYNTHETIC NEURAL IC M.R. Walker. S. Haghighi. A. Afghan. and L.A. Akers Center for Solid State Electronics Research Arizona State University Tempe. AZ 85287-6206 mwalker@enuxha.eas.asu.edu
Lecture 6. Artificial Neural Networks
 Lecture 6 Artificial Neural Networks 1 1 Artificial Neural Networks In this note we provide an overview of the key concepts that have led to the emergence of Artificial Neural Networks as a major paradigm
Lecture 6 Artificial Neural Networks 1 1 Artificial Neural Networks In this note we provide an overview of the key concepts that have led to the emergence of Artificial Neural Networks as a major paradigm
Binary Division. Decimal Division. Hardware for Binary Division. Simple 16-bit Divider Circuit
 Decimal Division Remember 4th grade long division? 43 // quotient 12 521 // divisor dividend -480 41-36 5 // remainder Shift divisor left (multiply by 10) until MSB lines up with dividend s Repeat until
Decimal Division Remember 4th grade long division? 43 // quotient 12 521 // divisor dividend -480 41-36 5 // remainder Shift divisor left (multiply by 10) until MSB lines up with dividend s Repeat until
An Introduction to Neural Networks
 An Introduction to Vincent Cheung Kevin Cannons Signal & Data Compression Laboratory Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Manitoba Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada Advisor: Dr. W. Kinsner May 27,
An Introduction to Vincent Cheung Kevin Cannons Signal & Data Compression Laboratory Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Manitoba Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada Advisor: Dr. W. Kinsner May 27,
Combinational Logic Design
 Chapter 4 Combinational Logic Design The foundations for the design of digital logic circuits were established in the preceding chapters. The elements of Boolean algebra (two-element switching algebra
Chapter 4 Combinational Logic Design The foundations for the design of digital logic circuits were established in the preceding chapters. The elements of Boolean algebra (two-element switching algebra
The Goldberg Rao Algorithm for the Maximum Flow Problem
 The Goldberg Rao Algorithm for the Maximum Flow Problem COS 528 class notes October 18, 2006 Scribe: Dávid Papp Main idea: use of the blocking flow paradigm to achieve essentially O(min{m 2/3, n 1/2 }
The Goldberg Rao Algorithm for the Maximum Flow Problem COS 528 class notes October 18, 2006 Scribe: Dávid Papp Main idea: use of the blocking flow paradigm to achieve essentially O(min{m 2/3, n 1/2 }
American International Journal of Research in Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics
 American International Journal of Research in Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics Available online at http://www.iasir.net ISSN (Print): 2328-349, ISSN (Online): 2328-3580, ISSN (CD-ROM): 2328-3629
American International Journal of Research in Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics Available online at http://www.iasir.net ISSN (Print): 2328-349, ISSN (Online): 2328-3580, ISSN (CD-ROM): 2328-3629
Today. Binary addition Representing negative numbers. Andrew H. Fagg: Embedded Real- Time Systems: Binary Arithmetic
 Today Binary addition Representing negative numbers 2 Binary Addition Consider the following binary numbers: 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 How do we add these numbers? 3 Binary Addition 0 0 1 0 0 1 1
Today Binary addition Representing negative numbers 2 Binary Addition Consider the following binary numbers: 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 How do we add these numbers? 3 Binary Addition 0 0 1 0 0 1 1
Some Computer Organizations and Their Effectiveness. Michael J Flynn. IEEE Transactions on Computers. Vol. c-21, No.
 Some Computer Organizations and Their Effectiveness Michael J Flynn IEEE Transactions on Computers. Vol. c-21, No.9, September 1972 Introduction Attempts to codify a computer have been from three points
Some Computer Organizations and Their Effectiveness Michael J Flynn IEEE Transactions on Computers. Vol. c-21, No.9, September 1972 Introduction Attempts to codify a computer have been from three points
File sharing using IP-Multicast
 File sharing using IP-Multicast Kai Trojahner, Peter Sobe University of Luebeck, Germany Institute of Computer Engineering email: sobe@iti.uni-luebeck.de Abstract: File sharing systems cause a huge portion
File sharing using IP-Multicast Kai Trojahner, Peter Sobe University of Luebeck, Germany Institute of Computer Engineering email: sobe@iti.uni-luebeck.de Abstract: File sharing systems cause a huge portion
Tolerance of Radial Basis Functions against Stuck-At-Faults
 Tolerance of Radial Basis Functions against Stuck-At-Faults Ralf Eickhoff 1 and Ulrich Rückert 1 Heinz Nixdorf Institute System and Circuit Technology University of Paderborn, Germany eickhoff,rueckert@hni.upb.de
Tolerance of Radial Basis Functions against Stuck-At-Faults Ralf Eickhoff 1 and Ulrich Rückert 1 Heinz Nixdorf Institute System and Circuit Technology University of Paderborn, Germany eickhoff,rueckert@hni.upb.de
Data Mining and Neural Networks in Stata
 Data Mining and Neural Networks in Stata 2 nd Italian Stata Users Group Meeting Milano, 10 October 2005 Mario Lucchini e Maurizo Pisati Università di Milano-Bicocca mario.lucchini@unimib.it maurizio.pisati@unimib.it
Data Mining and Neural Networks in Stata 2 nd Italian Stata Users Group Meeting Milano, 10 October 2005 Mario Lucchini e Maurizo Pisati Università di Milano-Bicocca mario.lucchini@unimib.it maurizio.pisati@unimib.it
MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS AND PROGRAMS
 CHAPTER 2 MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS AND PROGRAMS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn about: Machine instructions and program execution, including branching and subroutine call and return operations
CHAPTER 2 MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS AND PROGRAMS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn about: Machine instructions and program execution, including branching and subroutine call and return operations
EXPERIMENT 4. Parallel Adders, Subtractors, and Complementors
 EXPERIMENT 4. Parallel Adders, Subtractors, and Complementors I. Introduction I.a. Objectives In this experiment, parallel adders, subtractors and complementors will be designed and investigated. In the
EXPERIMENT 4. Parallel Adders, Subtractors, and Complementors I. Introduction I.a. Objectives In this experiment, parallel adders, subtractors and complementors will be designed and investigated. In the
HIGH SPEED AREA EFFICIENT 1-BIT HYBRID FULL ADDER
 HIGH SPEED AREA EFFICIENT 1-BIT HYBRID FULL ADDER Sachin Kumar *1, Aman Kumar #2, Puneet Bansal #3 * Department of Electronic Science, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra, Haryana, India # University Institute
HIGH SPEED AREA EFFICIENT 1-BIT HYBRID FULL ADDER Sachin Kumar *1, Aman Kumar #2, Puneet Bansal #3 * Department of Electronic Science, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra, Haryana, India # University Institute
ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT
 216 ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT *P.Nirmalkumar, **J.Raja Paul Perinbam, @S.Ravi and #B.Rajan *Research Scholar,
216 ON SUITABILITY OF FPGA BASED EVOLVABLE HARDWARE SYSTEMS TO INTEGRATE RECONFIGURABLE CIRCUITS WITH HOST PROCESSING UNIT *P.Nirmalkumar, **J.Raja Paul Perinbam, @S.Ravi and #B.Rajan *Research Scholar,
