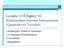
3. For the density curve displayed below, what is the mean?
|
|
|
- Clifford Wood
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following statements about a density curve are FALSE? A) A density curve always has area beneath it equal to 1. B) A density curve can adequately describe outliers observed in data. C) A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis. D) A density curve comes in many shapes, some of which are symmetric while others are skewed. E) The area under a density curve above any range of values is the proportion of all observations that fall in that range. 2. Which of the following statements about the mean and the median of a density curve are FALSE? A) The median is the point on the axis that divides the area under the density curve in two equal halves. B) The median and the mean have the same value if the density curve is symmetric. C) The mean is the balance point of the density curve. D) The median of a skewed density curve is pulled away from the mean in the direction of the long tail. E) For a symmetric density curve, both the mean and the median are at the center of the curve. 3. For the density curve displayed below, what is the mean? A) 0.25 B) 0.50 C) 0.71 D) 0.75 Page 1
2 4. A study is conducted on students taking a statistics class. Several variables are recorded in the survey. Identify each variable as categorical or quantitative. A) Type of car the student owns. B) Number of credit hours taken during that semester. C) The time the student waited in line at the bookstore to pay for his/her textbooks. D) Home state of the student. Use the following to answer question 5: Many residents of suburban neighborhoods own more than one car but consider one of their cars to be the main family vehicle. The age of these family vehicles can be modeled by a Normal distribution with a mean of 2 years and a standard deviation of 6 months. 5. What percentage of family vehicles is between 1 and 3 years old? A) Cannot be determined based on the information given. B) 68% C) 95% D) 99.7% 6. The time to complete an exam is approximately Normal with a mean of 70 minutes and a standard deviation of 10 minutes. Using the rule, what percentage of students will complete the exam in under an hour? A) 68% B) 32% C) 16% D) 5% Use the following to answer question 7: The number of Facebook friends students at a university have are Normally distributed with a mean of 1,200 and a standard deviation of What percent of students have at least 1000 Facebook friends? A) 84.13% B) 15.86% C) 42.07% D) None of the above. Page 2
3 8. The variable Z has a standard Normal distribution. Find the value z such that 85% of the observations fall below z. A) z = 1.04 B) z = 0.80 C) z = 0.85 D) z = When examining a scatterplot for strength, you are looking to see. A) how close the points in the scatterplot follow a line B) how close the points in the scatterplot follow a curve C) All of the above. D) None of the above. 10. An outlier is. A) a point in a scatterplot that follows the same pattern as the other points B) a point in a scatterplot that does not follow the same pattern as the other points C) All of the above. D) None of the above. 11. If you have two quantitative variables, one way to study them is to use a. A) Scatterplot B) Two way table C) None of the above. 12. When the explanatory variable is categorical and the response variable is quantitative, what type of plot would be appropriate? A) Boxplot B) Time plot C) Scatterplot Page 3
4 Use the following to answer questions 13-15: Malaria is a leading cause of infectious disease and death worldwide. It is also a popular example of a vector-borne disease that could be greatly affected by the influence of climate change. The scatterplot shows total precipitation (in mm) in select cities in West Africa on the x- axis and the percent of people tested positive for malaria in the select cities on the y-axis in Precipitation is the variable. A) independent B) dependent C) response D) explanatory E) A and B F) A and D Page 4
5 14. Percent tested positive for malaria is the variable. A) independent B) dependent C) response D) explanatory E) B and C F) A and B 15. The correlation between precipitation and percent tested positive for malaria is probably close to. A) 1 B) 0 C) Can't tell 16. Which one of the following statements is true? A) The correlation, r, measures the strength of the linear relationship between two quantitative variables. B) The correlation, r, measures the strength of the linear relationship between two categorical variables. C) The correlation, r, measures the strength between one quantitative variable and one categorical variable. 17. Positive linear relationships are represented by values of the correlation, r, that are. A) greater than zero B) less than zero C) zero 18. Negative linear relationships are represented by values of the correlation, r, that are. A) greater than zero B) less than zero C) zero 19. The lack of a linear relationship between two quantitative variables is represented by the correlation, r, with values A) greater than zero. B) less than zero. C) equal to zero. D) equal to 1 or -1. Page 5
6 20. As Swiss cheese matures, a variety of chemical processes take place. The taste of matured cheese is related to the concentration of several chemicals in the final product. In a study of cheese in a certain region of Switzerland, samples of cheese were analyzed for lactic acid concentration and were subjected to taste tests. The numerical taste scores were obtained by combining the scores from several tasters. A scatterplot of the observed data is shown below: Taste Rating Lactic Acid What is a plausible value for the correlation between lactic acid concentration and taste rating? A) B) 0.7 C) 0.07 D) In a study of 1991 model cars, a researcher computed the least-squares regression line of price (in dollars) on horsepower. He obtained the following equation for this line. price = horsepower Based on the least-squares regression line, what would we predict the cost to be of a 1991 model car with horsepower equal to 200? A) $41,677 B) $35,000 C) $28,323 D) $13,354 Page 6
7 22. Which of the following statements about least-squares regression involving two quantitative variables, x and y, is (are) TRUE? A) A change of one standard deviation in x corresponds to a change of r standard deviations in y. B) The least-squares regression line always passes through the point ( x, y ). 2 C) The square of the correlation, r, is the fraction of the variation in the values of y that is explained by the least-squares regression of y on x. D) The least-squares regression line of y on x is the line that makes the sum of the squares of the vertical distances of the data points from the line as small as possible. E) All of the above are true. 23. A(n) is an observation that is substantially different from the other observations. A) outlier B) lurking variable C) confounding variable D) None of the above. 24. If you have two categorical variables, one way to study them is to use a. A) Scatterplot B) Regression line C) Two way table Use the following to answer questions 25-26: Suppose you want to determine if there are differences in the average prices among items at three local supermarket chains. 25. What type of study would work best? A) An observational study B) An experiment 26. To reduce bias, how should you select the items to use in your study? A) Choose items which you know are commonly purchased. B) Randomly select an appropriate number of times from a list of all possible items in the supermarket. C) Choose only brand named items. Page 7
8 Use the following to answer questions 27-28: A television station is interested in predicting whether or not voters in its listening area are in favor of federal funding for abortions. It asks its viewers to phone in and indicate whether they are in favor of or opposed to this. Of the 2241 viewers who phoned in, 1574 (70.24%) were opposed to federal funding for abortions. 27. Fill in the blank. The number 70.24% is a. A) statistic B) parameter C) sample D) population 28. What type of sampling method was used to collect the data? A) A simple random sample. B) A stratified random sample. C) A probability sample in which each person in the population has the same chance of being in the sample. D) Voluntary response. Use the following to answer question 29: Olivia is planning to take a foreign language class. To research how satisfied other students are with their foreign language classes, she decides to take a sample of 20 such students. The university offers classes in four languages: Spanish, German, French, and Japanese. She will select a simple random sample of five students from each language. 29. What sampling technique is Olivia using? A) A simple random sample. B) A stratified sample. C) A multistage sample. D) None of the above. Page 8
9 30. A sample is to be selected from a large population using simple random sampling. The proportion of subjects in the sample that have a given characteristic is to be calculated. Which of the following best describes the sample proportion? A) It is a parameter. B) It is a statistic, which is unbiased for the population parameter only if the population is at least 100 times larger than the sample. C) It is a statistic that is unbiased and its variability does not depend on the population size provided the population is at least 100 times larger than the sample. D) It is a lurking variable whose value is unknown. E) It is a statistic, but its behavior cannot be determined because only one sample is to be taken. Page 9
10 Answer Key 1. B 2. D 3. B 4. A) categorical, B) quantitative, C) quantitative, D) categorical 5. C 6. C 7. A 8. D 9. C 10. B 11. A 12. A 13. F 14. E 15. B 16. A 17. A 18. B 19. C 20. B 21. C 22. E 23. A 24. C 25. A 26. B 27. A 28. D 29. B 30. C Page 10
Name: Date: Use the following to answer questions 2-3:
 Name: Date: 1. A study is conducted on students taking a statistics class. Several variables are recorded in the survey. Identify each variable as categorical or quantitative. A) Type of car the student
Name: Date: 1. A study is conducted on students taking a statistics class. Several variables are recorded in the survey. Identify each variable as categorical or quantitative. A) Type of car the student
2. Here is a small part of a data set that describes the fuel economy (in miles per gallon) of 2006 model motor vehicles.
 Math 1530-017 Exam 1 February 19, 2009 Name Student Number E There are five possible responses to each of the following multiple choice questions. There is only on BEST answer. Be sure to read all possible
Math 1530-017 Exam 1 February 19, 2009 Name Student Number E There are five possible responses to each of the following multiple choice questions. There is only on BEST answer. Be sure to read all possible
Exercise 1.12 (Pg. 22-23)
 Individuals: The objects that are described by a set of data. They may be people, animals, things, etc. (Also referred to as Cases or Records) Variables: The characteristics recorded about each individual.
Individuals: The objects that are described by a set of data. They may be people, animals, things, etc. (Also referred to as Cases or Records) Variables: The characteristics recorded about each individual.
Relationships Between Two Variables: Scatterplots and Correlation
 Relationships Between Two Variables: Scatterplots and Correlation Example: Consider the population of cars manufactured in the U.S. What is the relationship (1) between engine size and horsepower? (2)
Relationships Between Two Variables: Scatterplots and Correlation Example: Consider the population of cars manufactured in the U.S. What is the relationship (1) between engine size and horsepower? (2)
AP STATISTICS REVIEW (YMS Chapters 1-8)
 AP STATISTICS REVIEW (YMS Chapters 1-8) Exploring Data (Chapter 1) Categorical Data nominal scale, names e.g. male/female or eye color or breeds of dogs Quantitative Data rational scale (can +,,, with
AP STATISTICS REVIEW (YMS Chapters 1-8) Exploring Data (Chapter 1) Categorical Data nominal scale, names e.g. male/female or eye color or breeds of dogs Quantitative Data rational scale (can +,,, with
c. Construct a boxplot for the data. Write a one sentence interpretation of your graph.
 MBA/MIB 5315 Sample Test Problems Page 1 of 1 1. An English survey of 3000 medical records showed that smokers are more inclined to get depressed than non-smokers. Does this imply that smoking causes depression?
MBA/MIB 5315 Sample Test Problems Page 1 of 1 1. An English survey of 3000 medical records showed that smokers are more inclined to get depressed than non-smokers. Does this imply that smoking causes depression?
Statistics 151 Practice Midterm 1 Mike Kowalski
 Statistics 151 Practice Midterm 1 Mike Kowalski Statistics 151 Practice Midterm 1 Multiple Choice (50 minutes) Instructions: 1. This is a closed book exam. 2. You may use the STAT 151 formula sheets and
Statistics 151 Practice Midterm 1 Mike Kowalski Statistics 151 Practice Midterm 1 Multiple Choice (50 minutes) Instructions: 1. This is a closed book exam. 2. You may use the STAT 151 formula sheets and
MTH 140 Statistics Videos
 MTH 140 Statistics Videos Chapter 1 Picturing Distributions with Graphs Individuals and Variables Categorical Variables: Pie Charts and Bar Graphs Categorical Variables: Pie Charts and Bar Graphs Quantitative
MTH 140 Statistics Videos Chapter 1 Picturing Distributions with Graphs Individuals and Variables Categorical Variables: Pie Charts and Bar Graphs Categorical Variables: Pie Charts and Bar Graphs Quantitative
Descriptive Statistics
 Descriptive Statistics Descriptive statistics consist of methods for organizing and summarizing data. It includes the construction of graphs, charts and tables, as well various descriptive measures such
Descriptive Statistics Descriptive statistics consist of methods for organizing and summarizing data. It includes the construction of graphs, charts and tables, as well various descriptive measures such
1) Write the following as an algebraic expression using x as the variable: Triple a number subtracted from the number
 1) Write the following as an algebraic expression using x as the variable: Triple a number subtracted from the number A. 3(x - x) B. x 3 x C. 3x - x D. x - 3x 2) Write the following as an algebraic expression
1) Write the following as an algebraic expression using x as the variable: Triple a number subtracted from the number A. 3(x - x) B. x 3 x C. 3x - x D. x - 3x 2) Write the following as an algebraic expression
Linear Regression. Chapter 5. Prediction via Regression Line Number of new birds and Percent returning. Least Squares
 Linear Regression Chapter 5 Regression Objective: To quantify the linear relationship between an explanatory variable (x) and response variable (y). We can then predict the average response for all subjects
Linear Regression Chapter 5 Regression Objective: To quantify the linear relationship between an explanatory variable (x) and response variable (y). We can then predict the average response for all subjects
Lecture 11: Chapter 5, Section 3 Relationships between Two Quantitative Variables; Correlation
 Lecture 11: Chapter 5, Section 3 Relationships between Two Quantitative Variables; Correlation Display and Summarize Correlation for Direction and Strength Properties of Correlation Regression Line Cengage
Lecture 11: Chapter 5, Section 3 Relationships between Two Quantitative Variables; Correlation Display and Summarize Correlation for Direction and Strength Properties of Correlation Regression Line Cengage
Section 14 Simple Linear Regression: Introduction to Least Squares Regression
 Slide 1 Section 14 Simple Linear Regression: Introduction to Least Squares Regression There are several different measures of statistical association used for understanding the quantitative relationship
Slide 1 Section 14 Simple Linear Regression: Introduction to Least Squares Regression There are several different measures of statistical association used for understanding the quantitative relationship
DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS. The purpose of statistics is to condense raw data to make it easier to answer specific questions; test hypotheses.
 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS The purpose of statistics is to condense raw data to make it easier to answer specific questions; test hypotheses. DESCRIPTIVE VS. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Descriptive To organize,
DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS The purpose of statistics is to condense raw data to make it easier to answer specific questions; test hypotheses. DESCRIPTIVE VS. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Descriptive To organize,
Chapter 10. Key Ideas Correlation, Correlation Coefficient (r),
 Chapter 0 Key Ideas Correlation, Correlation Coefficient (r), Section 0-: Overview We have already explored the basics of describing single variable data sets. However, when two quantitative variables
Chapter 0 Key Ideas Correlation, Correlation Coefficient (r), Section 0-: Overview We have already explored the basics of describing single variable data sets. However, when two quantitative variables
Statistics 2014 Scoring Guidelines
 AP Statistics 2014 Scoring Guidelines College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online home
AP Statistics 2014 Scoring Guidelines College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online home
Descriptive Statistics and Measurement Scales
 Descriptive Statistics 1 Descriptive Statistics and Measurement Scales Descriptive statistics are used to describe the basic features of the data in a study. They provide simple summaries about the sample
Descriptive Statistics 1 Descriptive Statistics and Measurement Scales Descriptive statistics are used to describe the basic features of the data in a study. They provide simple summaries about the sample
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences Midterm Test March 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences Midterm Test March 2014 STAB22H3 Statistics I Duration: 1 hour and 45 minutes Last Name: First Name: Student number: Aids
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Department of Computer and Mathematical Sciences Midterm Test March 2014 STAB22H3 Statistics I Duration: 1 hour and 45 minutes Last Name: First Name: Student number: Aids
a) Find the five point summary for the home runs of the National League teams. b) What is the mean number of home runs by the American League teams?
 1. Phone surveys are sometimes used to rate TV shows. Such a survey records several variables listed below. Which ones of them are categorical and which are quantitative? - the number of people watching
1. Phone surveys are sometimes used to rate TV shows. Such a survey records several variables listed below. Which ones of them are categorical and which are quantitative? - the number of people watching
Simple linear regression
 Simple linear regression Introduction Simple linear regression is a statistical method for obtaining a formula to predict values of one variable from another where there is a causal relationship between
Simple linear regression Introduction Simple linear regression is a statistical method for obtaining a formula to predict values of one variable from another where there is a causal relationship between
Correlation and Regression
 Correlation and Regression Scatterplots Correlation Explanatory and response variables Simple linear regression General Principles of Data Analysis First plot the data, then add numerical summaries Look
Correlation and Regression Scatterplots Correlation Explanatory and response variables Simple linear regression General Principles of Data Analysis First plot the data, then add numerical summaries Look
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A recent report stated ʺBased on a sample of 90 truck drivers, there is evidence to indicate that, on average, independent truck drivers earn more than company -hired truck drivers.ʺ Does
Exam Name 1) A recent report stated ʺBased on a sample of 90 truck drivers, there is evidence to indicate that, on average, independent truck drivers earn more than company -hired truck drivers.ʺ Does
Fairfield Public Schools
 Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools AP Statistics AP Statistics BOE Approved 04/08/2014 1 AP STATISTICS Critical Areas of Focus AP Statistics is a rigorous course that offers advanced students an opportunity
Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools AP Statistics AP Statistics BOE Approved 04/08/2014 1 AP STATISTICS Critical Areas of Focus AP Statistics is a rigorous course that offers advanced students an opportunity
Lesson 4 Measures of Central Tendency
 Outline Measures of a distribution s shape -modality and skewness -the normal distribution Measures of central tendency -mean, median, and mode Skewness and Central Tendency Lesson 4 Measures of Central
Outline Measures of a distribution s shape -modality and skewness -the normal distribution Measures of central tendency -mean, median, and mode Skewness and Central Tendency Lesson 4 Measures of Central
What Does the Normal Distribution Sound Like?
 What Does the Normal Distribution Sound Like? Ananda Jayawardhana Pittsburg State University ananda@pittstate.edu Published: June 2013 Overview of Lesson In this activity, students conduct an investigation
What Does the Normal Distribution Sound Like? Ananda Jayawardhana Pittsburg State University ananda@pittstate.edu Published: June 2013 Overview of Lesson In this activity, students conduct an investigation
Univariate Regression
 Univariate Regression Correlation and Regression The regression line summarizes the linear relationship between 2 variables Correlation coefficient, r, measures strength of relationship: the closer r is
Univariate Regression Correlation and Regression The regression line summarizes the linear relationship between 2 variables Correlation coefficient, r, measures strength of relationship: the closer r is
Introduction to Quantitative Methods
 Introduction to Quantitative Methods October 15, 2009 Contents 1 Definition of Key Terms 2 2 Descriptive Statistics 3 2.1 Frequency Tables......................... 4 2.2 Measures of Central Tendencies.................
Introduction to Quantitative Methods October 15, 2009 Contents 1 Definition of Key Terms 2 2 Descriptive Statistics 3 2.1 Frequency Tables......................... 4 2.2 Measures of Central Tendencies.................
STAT 350 Practice Final Exam Solution (Spring 2015)
 PART 1: Multiple Choice Questions: 1) A study was conducted to compare five different training programs for improving endurance. Forty subjects were randomly divided into five groups of eight subjects
PART 1: Multiple Choice Questions: 1) A study was conducted to compare five different training programs for improving endurance. Forty subjects were randomly divided into five groups of eight subjects
ch12 practice test SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 ch12 practice test 1) The null hypothesis that x and y are is H0: = 0. 1) 2) When a two-sided significance test about a population slope has a P-value below 0.05, the 95% confidence interval for A) does
ch12 practice test 1) The null hypothesis that x and y are is H0: = 0. 1) 2) When a two-sided significance test about a population slope has a P-value below 0.05, the 95% confidence interval for A) does
ELEMENTARY STATISTICS
 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS Study Guide Dr. Shinemin Lin Table of Contents 1. Introduction to Statistics. Descriptive Statistics 3. Probabilities and Standard Normal Distribution 4. Estimates and Sample Sizes
ELEMENTARY STATISTICS Study Guide Dr. Shinemin Lin Table of Contents 1. Introduction to Statistics. Descriptive Statistics 3. Probabilities and Standard Normal Distribution 4. Estimates and Sample Sizes
X X X a) perfect linear correlation b) no correlation c) positive correlation (r = 1) (r = 0) (0 < r < 1)
 CORRELATION AND REGRESSION / 47 CHAPTER EIGHT CORRELATION AND REGRESSION Correlation and regression are statistical methods that are commonly used in the medical literature to compare two or more variables.
CORRELATION AND REGRESSION / 47 CHAPTER EIGHT CORRELATION AND REGRESSION Correlation and regression are statistical methods that are commonly used in the medical literature to compare two or more variables.
Box-and-Whisker Plots
 Learning Standards HSS-ID.A. HSS-ID.A.3 3 9 23 62 3 COMMON CORE.2 Numbers of First Cousins 0 3 9 3 45 24 8 0 3 3 6 8 32 8 0 5 4 Box-and-Whisker Plots Essential Question How can you use a box-and-whisker
Learning Standards HSS-ID.A. HSS-ID.A.3 3 9 23 62 3 COMMON CORE.2 Numbers of First Cousins 0 3 9 3 45 24 8 0 3 3 6 8 32 8 0 5 4 Box-and-Whisker Plots Essential Question How can you use a box-and-whisker
The Effect of Dropping a Ball from Different Heights on the Number of Times the Ball Bounces
 The Effect of Dropping a Ball from Different Heights on the Number of Times the Ball Bounces Or: How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Ball Comment [DP1]: Titles, headings, and figure/table captions
The Effect of Dropping a Ball from Different Heights on the Number of Times the Ball Bounces Or: How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Ball Comment [DP1]: Titles, headings, and figure/table captions
Chapter 1: Looking at Data Section 1.1: Displaying Distributions with Graphs
 Types of Variables Chapter 1: Looking at Data Section 1.1: Displaying Distributions with Graphs Quantitative (numerical)variables: take numerical values for which arithmetic operations make sense (addition/averaging)
Types of Variables Chapter 1: Looking at Data Section 1.1: Displaying Distributions with Graphs Quantitative (numerical)variables: take numerical values for which arithmetic operations make sense (addition/averaging)
Mind on Statistics. Chapter 2
 Mind on Statistics Chapter 2 Sections 2.1 2.3 1. Tallies and cross-tabulations are used to summarize which of these variable types? A. Quantitative B. Mathematical C. Continuous D. Categorical 2. The table
Mind on Statistics Chapter 2 Sections 2.1 2.3 1. Tallies and cross-tabulations are used to summarize which of these variable types? A. Quantitative B. Mathematical C. Continuous D. Categorical 2. The table
MEASURES OF VARIATION
 NORMAL DISTRIBTIONS MEASURES OF VARIATION In statistics, it is important to measure the spread of data. A simple way to measure spread is to find the range. But statisticians want to know if the data are
NORMAL DISTRIBTIONS MEASURES OF VARIATION In statistics, it is important to measure the spread of data. A simple way to measure spread is to find the range. But statisticians want to know if the data are
Statistics 100 Sample Final Questions (Note: These are mostly multiple choice, for extra practice. Your Final Exam will NOT have any multiple choice!
 Statistics 100 Sample Final Questions (Note: These are mostly multiple choice, for extra practice. Your Final Exam will NOT have any multiple choice!) Part A - Multiple Choice Indicate the best choice
Statistics 100 Sample Final Questions (Note: These are mostly multiple choice, for extra practice. Your Final Exam will NOT have any multiple choice!) Part A - Multiple Choice Indicate the best choice
Business Statistics. Successful completion of Introductory and/or Intermediate Algebra courses is recommended before taking Business Statistics.
 Business Course Text Bowerman, Bruce L., Richard T. O'Connell, J. B. Orris, and Dawn C. Porter. Essentials of Business, 2nd edition, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2008, ISBN: 978-0-07-331988-9. Required Computing
Business Course Text Bowerman, Bruce L., Richard T. O'Connell, J. B. Orris, and Dawn C. Porter. Essentials of Business, 2nd edition, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2008, ISBN: 978-0-07-331988-9. Required Computing
6.4 Normal Distribution
 Contents 6.4 Normal Distribution....................... 381 6.4.1 Characteristics of the Normal Distribution....... 381 6.4.2 The Standardized Normal Distribution......... 385 6.4.3 Meaning of Areas under
Contents 6.4 Normal Distribution....................... 381 6.4.1 Characteristics of the Normal Distribution....... 381 6.4.2 The Standardized Normal Distribution......... 385 6.4.3 Meaning of Areas under
Descriptive statistics Statistical inference statistical inference, statistical induction and inferential statistics
 Descriptive statistics is the discipline of quantitatively describing the main features of a collection of data. Descriptive statistics are distinguished from inferential statistics (or inductive statistics),
Descriptive statistics is the discipline of quantitatively describing the main features of a collection of data. Descriptive statistics are distinguished from inferential statistics (or inductive statistics),
Course Objective This course is designed to give you a basic understanding of how to run regressions in SPSS.
 SPSS Regressions Social Science Research Lab American University, Washington, D.C. Web. www.american.edu/provost/ctrl/pclabs.cfm Tel. x3862 Email. SSRL@American.edu Course Objective This course is designed
SPSS Regressions Social Science Research Lab American University, Washington, D.C. Web. www.american.edu/provost/ctrl/pclabs.cfm Tel. x3862 Email. SSRL@American.edu Course Objective This course is designed
Good luck! BUSINESS STATISTICS FINAL EXAM INSTRUCTIONS. Name:
 Glo bal Leadership M BA BUSINESS STATISTICS FINAL EXAM Name: INSTRUCTIONS 1. Do not open this exam until instructed to do so. 2. Be sure to fill in your name before starting the exam. 3. You have two hours
Glo bal Leadership M BA BUSINESS STATISTICS FINAL EXAM Name: INSTRUCTIONS 1. Do not open this exam until instructed to do so. 2. Be sure to fill in your name before starting the exam. 3. You have two hours
AP * Statistics Review. Descriptive Statistics
 AP * Statistics Review Descriptive Statistics Teacher Packet Advanced Placement and AP are registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Board was not involved in the production
AP * Statistics Review Descriptive Statistics Teacher Packet Advanced Placement and AP are registered trademark of the College Entrance Examination Board. The College Board was not involved in the production
Week 3&4: Z tables and the Sampling Distribution of X
 Week 3&4: Z tables and the Sampling Distribution of X 2 / 36 The Standard Normal Distribution, or Z Distribution, is the distribution of a random variable, Z N(0, 1 2 ). The distribution of any other normal
Week 3&4: Z tables and the Sampling Distribution of X 2 / 36 The Standard Normal Distribution, or Z Distribution, is the distribution of a random variable, Z N(0, 1 2 ). The distribution of any other normal
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Final Exam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A researcher for an airline interviews all of the passengers on five randomly
Final Exam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A researcher for an airline interviews all of the passengers on five randomly
Lecture 13/Chapter 10 Relationships between Measurement (Quantitative) Variables
 Lecture 13/Chapter 10 Relationships between Measurement (Quantitative) Variables Scatterplot; Roles of Variables 3 Features of Relationship Correlation Regression Definition Scatterplot displays relationship
Lecture 13/Chapter 10 Relationships between Measurement (Quantitative) Variables Scatterplot; Roles of Variables 3 Features of Relationship Correlation Regression Definition Scatterplot displays relationship
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All but one of these statements contain a mistake. Which could be true? A) There is a correlation
Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All but one of these statements contain a mistake. Which could be true? A) There is a correlation
The Importance of Statistics Education
 The Importance of Statistics Education Professor Jessica Utts Department of Statistics University of California, Irvine http://www.ics.uci.edu/~jutts jutts@uci.edu Outline of Talk What is Statistics? Four
The Importance of Statistics Education Professor Jessica Utts Department of Statistics University of California, Irvine http://www.ics.uci.edu/~jutts jutts@uci.edu Outline of Talk What is Statistics? Four
Def: The standard normal distribution is a normal probability distribution that has a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.
 Lecture 6: Chapter 6: Normal Probability Distributions A normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution for a random variable x. The graph of a normal distribution is called the normal curve.
Lecture 6: Chapter 6: Normal Probability Distributions A normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution for a random variable x. The graph of a normal distribution is called the normal curve.
Regression III: Advanced Methods
 Lecture 4: Transformations Regression III: Advanced Methods William G. Jacoby Michigan State University Goals of the lecture The Ladder of Roots and Powers Changing the shape of distributions Transforming
Lecture 4: Transformations Regression III: Advanced Methods William G. Jacoby Michigan State University Goals of the lecture The Ladder of Roots and Powers Changing the shape of distributions Transforming
Statistics courses often teach the two-sample t-test, linear regression, and analysis of variance
 2 Making Connections: The Two-Sample t-test, Regression, and ANOVA In theory, there s no difference between theory and practice. In practice, there is. Yogi Berra 1 Statistics courses often teach the two-sample
2 Making Connections: The Two-Sample t-test, Regression, and ANOVA In theory, there s no difference between theory and practice. In practice, there is. Yogi Berra 1 Statistics courses often teach the two-sample
How To Write A Data Analysis
 Mathematics Probability and Statistics Curriculum Guide Revised 2010 This page is intentionally left blank. Introduction The Mathematics Curriculum Guide serves as a guide for teachers when planning instruction
Mathematics Probability and Statistics Curriculum Guide Revised 2010 This page is intentionally left blank. Introduction The Mathematics Curriculum Guide serves as a guide for teachers when planning instruction
Course Text. Required Computing Software. Course Description. Course Objectives. StraighterLine. Business Statistics
 Course Text Business Statistics Lind, Douglas A., Marchal, William A. and Samuel A. Wathen. Basic Statistics for Business and Economics, 7th edition, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2010, ISBN: 9780077384470 [This
Course Text Business Statistics Lind, Douglas A., Marchal, William A. and Samuel A. Wathen. Basic Statistics for Business and Economics, 7th edition, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2010, ISBN: 9780077384470 [This
Simple Regression Theory II 2010 Samuel L. Baker
 SIMPLE REGRESSION THEORY II 1 Simple Regression Theory II 2010 Samuel L. Baker Assessing how good the regression equation is likely to be Assignment 1A gets into drawing inferences about how close the
SIMPLE REGRESSION THEORY II 1 Simple Regression Theory II 2010 Samuel L. Baker Assessing how good the regression equation is likely to be Assignment 1A gets into drawing inferences about how close the
2) The three categories of forecasting models are time series, quantitative, and qualitative. 2)
 Exam Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Regression is always a superior forecasting method to exponential smoothing, so regression should be used
Exam Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Regression is always a superior forecasting method to exponential smoothing, so regression should be used
Second Midterm Exam (MATH1070 Spring 2012)
 Second Midterm Exam (MATH1070 Spring 2012) Instructions: This is a one hour exam. You can use a notecard. Calculators are allowed, but other electronics are prohibited. 1. [60pts] Multiple Choice Problems
Second Midterm Exam (MATH1070 Spring 2012) Instructions: This is a one hour exam. You can use a notecard. Calculators are allowed, but other electronics are prohibited. 1. [60pts] Multiple Choice Problems
MBA 611 STATISTICS AND QUANTITATIVE METHODS
 MBA 611 STATISTICS AND QUANTITATIVE METHODS Part I. Review of Basic Statistics (Chapters 1-11) A. Introduction (Chapter 1) Uncertainty: Decisions are often based on incomplete information from uncertain
MBA 611 STATISTICS AND QUANTITATIVE METHODS Part I. Review of Basic Statistics (Chapters 1-11) A. Introduction (Chapter 1) Uncertainty: Decisions are often based on incomplete information from uncertain
Center: Finding the Median. Median. Spread: Home on the Range. Center: Finding the Median (cont.)
 Center: Finding the Median When we think of a typical value, we usually look for the center of the distribution. For a unimodal, symmetric distribution, it s easy to find the center it s just the center
Center: Finding the Median When we think of a typical value, we usually look for the center of the distribution. For a unimodal, symmetric distribution, it s easy to find the center it s just the center
Midterm Review Problems
 Midterm Review Problems October 19, 2013 1. Consider the following research title: Cooperation among nursery school children under two types of instruction. In this study, what is the independent variable?
Midterm Review Problems October 19, 2013 1. Consider the following research title: Cooperation among nursery school children under two types of instruction. In this study, what is the independent variable?
HISTOGRAMS, CUMULATIVE FREQUENCY AND BOX PLOTS
 Mathematics Revision Guides Histograms, Cumulative Frequency and Box Plots Page 1 of 25 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Higher Tier HISTOGRAMS, CUMULATIVE FREQUENCY AND BOX PLOTS
Mathematics Revision Guides Histograms, Cumulative Frequency and Box Plots Page 1 of 25 M.K. HOME TUITION Mathematics Revision Guides Level: GCSE Higher Tier HISTOGRAMS, CUMULATIVE FREQUENCY AND BOX PLOTS
Density Curve. A density curve is the graph of a continuous probability distribution. It must satisfy the following properties:
 Density Curve A density curve is the graph of a continuous probability distribution. It must satisfy the following properties: 1. The total area under the curve must equal 1. 2. Every point on the curve
Density Curve A density curve is the graph of a continuous probability distribution. It must satisfy the following properties: 1. The total area under the curve must equal 1. 2. Every point on the curve
Section 1.3 Exercises (Solutions)
 Section 1.3 Exercises (s) 1.109, 1.110, 1.111, 1.114*, 1.115, 1.119*, 1.122, 1.125, 1.127*, 1.128*, 1.131*, 1.133*, 1.135*, 1.137*, 1.139*, 1.145*, 1.146-148. 1.109 Sketch some normal curves. (a) Sketch
Section 1.3 Exercises (s) 1.109, 1.110, 1.111, 1.114*, 1.115, 1.119*, 1.122, 1.125, 1.127*, 1.128*, 1.131*, 1.133*, 1.135*, 1.137*, 1.139*, 1.145*, 1.146-148. 1.109 Sketch some normal curves. (a) Sketch
List of Examples. Examples 319
 Examples 319 List of Examples DiMaggio and Mantle. 6 Weed seeds. 6, 23, 37, 38 Vole reproduction. 7, 24, 37 Wooly bear caterpillar cocoons. 7 Homophone confusion and Alzheimer s disease. 8 Gear tooth strength.
Examples 319 List of Examples DiMaggio and Mantle. 6 Weed seeds. 6, 23, 37, 38 Vole reproduction. 7, 24, 37 Wooly bear caterpillar cocoons. 7 Homophone confusion and Alzheimer s disease. 8 Gear tooth strength.
List the elements of the given set that are natural numbers, integers, rational numbers, and irrational numbers. (Enter your answers as commaseparated
 MATH 142 Review #1 (4717995) Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 Description This is the review for Exam #1. Please work as many problems as possible
MATH 142 Review #1 (4717995) Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 Description This is the review for Exam #1. Please work as many problems as possible
3. There are three senior citizens in a room, ages 68, 70, and 72. If a seventy-year-old person enters the room, the
 TMTA Statistics Exam 2011 1. Last month, the mean and standard deviation of the paychecks of 10 employees of a small company were $1250 and $150, respectively. This month, each one of the 10 employees
TMTA Statistics Exam 2011 1. Last month, the mean and standard deviation of the paychecks of 10 employees of a small company were $1250 and $150, respectively. This month, each one of the 10 employees
Diagrams and Graphs of Statistical Data
 Diagrams and Graphs of Statistical Data One of the most effective and interesting alternative way in which a statistical data may be presented is through diagrams and graphs. There are several ways in
Diagrams and Graphs of Statistical Data One of the most effective and interesting alternative way in which a statistical data may be presented is through diagrams and graphs. There are several ways in
5/31/2013. 6.1 Normal Distributions. Normal Distributions. Chapter 6. Distribution. The Normal Distribution. Outline. Objectives.
 The Normal Distribution C H 6A P T E R The Normal Distribution Outline 6 1 6 2 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6 3 The Central Limit Theorem 6 4 The Normal Approximation to the Binomial Distribution
The Normal Distribution C H 6A P T E R The Normal Distribution Outline 6 1 6 2 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6 3 The Central Limit Theorem 6 4 The Normal Approximation to the Binomial Distribution
A full analysis example Multiple correlations Partial correlations
 A full analysis example Multiple correlations Partial correlations New Dataset: Confidence This is a dataset taken of the confidence scales of 41 employees some years ago using 4 facets of confidence (Physical,
A full analysis example Multiple correlations Partial correlations New Dataset: Confidence This is a dataset taken of the confidence scales of 41 employees some years ago using 4 facets of confidence (Physical,
Summary of Formulas and Concepts. Descriptive Statistics (Ch. 1-4)
 Summary of Formulas and Concepts Descriptive Statistics (Ch. 1-4) Definitions Population: The complete set of numerical information on a particular quantity in which an investigator is interested. We assume
Summary of Formulas and Concepts Descriptive Statistics (Ch. 1-4) Definitions Population: The complete set of numerical information on a particular quantity in which an investigator is interested. We assume
= 2.0702 N(280, 2.0702)
 Name Test 10 Confidence Intervals Homework (Chpt 10.1, 11.1, 12.1) Period For 1 & 2, determine the point estimator you would use and calculate its value. 1. How many pairs of shoes, on average, do female
Name Test 10 Confidence Intervals Homework (Chpt 10.1, 11.1, 12.1) Period For 1 & 2, determine the point estimator you would use and calculate its value. 1. How many pairs of shoes, on average, do female
 T O P I C 1 2 Techniques and tools for data analysis Preview Introduction In chapter 3 of Statistics In A Day different combinations of numbers and types of variables are presented. We go through these
T O P I C 1 2 Techniques and tools for data analysis Preview Introduction In chapter 3 of Statistics In A Day different combinations of numbers and types of variables are presented. We go through these
4. Continuous Random Variables, the Pareto and Normal Distributions
 4. Continuous Random Variables, the Pareto and Normal Distributions A continuous random variable X can take any value in a given range (e.g. height, weight, age). The distribution of a continuous random
4. Continuous Random Variables, the Pareto and Normal Distributions A continuous random variable X can take any value in a given range (e.g. height, weight, age). The distribution of a continuous random
Chapter 4. Probability and Probability Distributions
 Chapter 4. robability and robability Distributions Importance of Knowing robability To know whether a sample is not identical to the population from which it was selected, it is necessary to assess the
Chapter 4. robability and robability Distributions Importance of Knowing robability To know whether a sample is not identical to the population from which it was selected, it is necessary to assess the
The right edge of the box is the third quartile, Q 3, which is the median of the data values above the median. Maximum Median
 CONDENSED LESSON 2.1 Box Plots In this lesson you will create and interpret box plots for sets of data use the interquartile range (IQR) to identify potential outliers and graph them on a modified box
CONDENSED LESSON 2.1 Box Plots In this lesson you will create and interpret box plots for sets of data use the interquartile range (IQR) to identify potential outliers and graph them on a modified box
MATH 103/GRACEY PRACTICE EXAM/CHAPTERS 2-3. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MATH 3/GRACEY PRACTICE EXAM/CHAPTERS 2-3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Provide an appropriate response. 1) The frequency distribution
MATH 3/GRACEY PRACTICE EXAM/CHAPTERS 2-3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Provide an appropriate response. 1) The frequency distribution
Unit 31 A Hypothesis Test about Correlation and Slope in a Simple Linear Regression
 Unit 31 A Hypothesis Test about Correlation and Slope in a Simple Linear Regression Objectives: To perform a hypothesis test concerning the slope of a least squares line To recognize that testing for a
Unit 31 A Hypothesis Test about Correlation and Slope in a Simple Linear Regression Objectives: To perform a hypothesis test concerning the slope of a least squares line To recognize that testing for a
STA-201-TE. 5. Measures of relationship: correlation (5%) Correlation coefficient; Pearson r; correlation and causation; proportion of common variance
 Principles of Statistics STA-201-TE This TECEP is an introduction to descriptive and inferential statistics. Topics include: measures of central tendency, variability, correlation, regression, hypothesis
Principles of Statistics STA-201-TE This TECEP is an introduction to descriptive and inferential statistics. Topics include: measures of central tendency, variability, correlation, regression, hypothesis
Measures of Central Tendency and Variability: Summarizing your Data for Others
 Measures of Central Tendency and Variability: Summarizing your Data for Others 1 I. Measures of Central Tendency: -Allow us to summarize an entire data set with a single value (the midpoint). 1. Mode :
Measures of Central Tendency and Variability: Summarizing your Data for Others 1 I. Measures of Central Tendency: -Allow us to summarize an entire data set with a single value (the midpoint). 1. Mode :
Homework 8 Solutions
 Math 17, Section 2 Spring 2011 Homework 8 Solutions Assignment Chapter 7: 7.36, 7.40 Chapter 8: 8.14, 8.16, 8.28, 8.36 (a-d), 8.38, 8.62 Chapter 9: 9.4, 9.14 Chapter 7 7.36] a) A scatterplot is given below.
Math 17, Section 2 Spring 2011 Homework 8 Solutions Assignment Chapter 7: 7.36, 7.40 Chapter 8: 8.14, 8.16, 8.28, 8.36 (a-d), 8.38, 8.62 Chapter 9: 9.4, 9.14 Chapter 7 7.36] a) A scatterplot is given below.
Descriptive statistics; Correlation and regression
 Descriptive statistics; and regression Patrick Breheny September 16 Patrick Breheny STA 580: Biostatistics I 1/59 Tables and figures Descriptive statistics Histograms Numerical summaries Percentiles Human
Descriptive statistics; and regression Patrick Breheny September 16 Patrick Breheny STA 580: Biostatistics I 1/59 Tables and figures Descriptive statistics Histograms Numerical summaries Percentiles Human
1. The parameters to be estimated in the simple linear regression model Y=α+βx+ε ε~n(0,σ) are: a) α, β, σ b) α, β, ε c) a, b, s d) ε, 0, σ
 STA 3024 Practice Problems Exam 2 NOTE: These are just Practice Problems. This is NOT meant to look just like the test, and it is NOT the only thing that you should study. Make sure you know all the material
STA 3024 Practice Problems Exam 2 NOTE: These are just Practice Problems. This is NOT meant to look just like the test, and it is NOT the only thing that you should study. Make sure you know all the material
AP Statistics. Chapter 4 Review
 Name AP Statistics Chapter 4 Review 1. In a study of the link between high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease, a group of white males aged 35 to 64 was followed for 5 years. At the beginning of
Name AP Statistics Chapter 4 Review 1. In a study of the link between high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease, a group of white males aged 35 to 64 was followed for 5 years. At the beginning of
Summarizing and Displaying Categorical Data
 Summarizing and Displaying Categorical Data Categorical data can be summarized in a frequency distribution which counts the number of cases, or frequency, that fall into each category, or a relative frequency
Summarizing and Displaying Categorical Data Categorical data can be summarized in a frequency distribution which counts the number of cases, or frequency, that fall into each category, or a relative frequency
Geostatistics Exploratory Analysis
 Instituto Superior de Estatística e Gestão de Informação Universidade Nova de Lisboa Master of Science in Geospatial Technologies Geostatistics Exploratory Analysis Carlos Alberto Felgueiras cfelgueiras@isegi.unl.pt
Instituto Superior de Estatística e Gestão de Informação Universidade Nova de Lisboa Master of Science in Geospatial Technologies Geostatistics Exploratory Analysis Carlos Alberto Felgueiras cfelgueiras@isegi.unl.pt
Scatter Plots with Error Bars
 Chapter 165 Scatter Plots with Error Bars Introduction The procedure extends the capability of the basic scatter plot by allowing you to plot the variability in Y and X corresponding to each point. Each
Chapter 165 Scatter Plots with Error Bars Introduction The procedure extends the capability of the basic scatter plot by allowing you to plot the variability in Y and X corresponding to each point. Each
The Big Picture. Describing Data: Categorical and Quantitative Variables Population. Descriptive Statistics. Community Coalitions (n = 175)
 Describing Data: Categorical and Quantitative Variables Population The Big Picture Sampling Statistical Inference Sample Exploratory Data Analysis Descriptive Statistics In order to make sense of data,
Describing Data: Categorical and Quantitative Variables Population The Big Picture Sampling Statistical Inference Sample Exploratory Data Analysis Descriptive Statistics In order to make sense of data,
Lesson 17: Margin of Error When Estimating a Population Proportion
 Margin of Error When Estimating a Population Proportion Classwork In this lesson, you will find and interpret the standard deviation of a simulated distribution for a sample proportion and use this information
Margin of Error When Estimating a Population Proportion Classwork In this lesson, you will find and interpret the standard deviation of a simulated distribution for a sample proportion and use this information
FREE FALL. Introduction. Reference Young and Freedman, University Physics, 12 th Edition: Chapter 2, section 2.5
 Physics 161 FREE FALL Introduction This experiment is designed to study the motion of an object that is accelerated by the force of gravity. It also serves as an introduction to the data analysis capabilities
Physics 161 FREE FALL Introduction This experiment is designed to study the motion of an object that is accelerated by the force of gravity. It also serves as an introduction to the data analysis capabilities
Interpreting Data in Normal Distributions
 Interpreting Data in Normal Distributions This curve is kind of a big deal. It shows the distribution of a set of test scores, the results of rolling a die a million times, the heights of people on Earth,
Interpreting Data in Normal Distributions This curve is kind of a big deal. It shows the distribution of a set of test scores, the results of rolling a die a million times, the heights of people on Earth,
Descriptive Statistics
 Y520 Robert S Michael Goal: Learn to calculate indicators and construct graphs that summarize and describe a large quantity of values. Using the textbook readings and other resources listed on the web
Y520 Robert S Michael Goal: Learn to calculate indicators and construct graphs that summarize and describe a large quantity of values. Using the textbook readings and other resources listed on the web
Introduction. Chapter 1. 1.1 Before you start. 1.1.1 Formulation
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Before you start Statistics starts with a problem, continues with the collection of data, proceeds with the data analysis and finishes with conclusions. It is a common mistake
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Before you start Statistics starts with a problem, continues with the collection of data, proceeds with the data analysis and finishes with conclusions. It is a common mistake
Descriptive Methods Ch. 6 and 7
 Descriptive Methods Ch. 6 and 7 Purpose of Descriptive Research Purely descriptive research describes the characteristics or behaviors of a given population in a systematic and accurate fashion. Correlational
Descriptive Methods Ch. 6 and 7 Purpose of Descriptive Research Purely descriptive research describes the characteristics or behaviors of a given population in a systematic and accurate fashion. Correlational
Lecture 2: Descriptive Statistics and Exploratory Data Analysis
 Lecture 2: Descriptive Statistics and Exploratory Data Analysis Further Thoughts on Experimental Design 16 Individuals (8 each from two populations) with replicates Pop 1 Pop 2 Randomly sample 4 individuals
Lecture 2: Descriptive Statistics and Exploratory Data Analysis Further Thoughts on Experimental Design 16 Individuals (8 each from two populations) with replicates Pop 1 Pop 2 Randomly sample 4 individuals
Algebra II EOC Practice Test
 Algebra II EOC Practice Test Name Date 1. Suppose point A is on the unit circle shown above. What is the value of sin? (A) 0.736 (B) 0.677 (C) (D) (E) none of these 2. Convert to radians. (A) (B) (C) (D)
Algebra II EOC Practice Test Name Date 1. Suppose point A is on the unit circle shown above. What is the value of sin? (A) 0.736 (B) 0.677 (C) (D) (E) none of these 2. Convert to radians. (A) (B) (C) (D)
Classify the data as either discrete or continuous. 2) An athlete runs 100 meters in 10.5 seconds. 2) A) Discrete B) Continuous
 Chapter 2 Overview Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Classify as categorical or qualitative data. 1) A survey of autos parked in
Chapter 2 Overview Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Classify as categorical or qualitative data. 1) A survey of autos parked in
The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution 6.1 The Normal Distribution 1 6.1.1 Student Learning Objectives By the end of this chapter, the student should be able to: Recognize the normal probability distribution
Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution 6.1 The Normal Distribution 1 6.1.1 Student Learning Objectives By the end of this chapter, the student should be able to: Recognize the normal probability distribution
Linear Regression. use http://www.stat.columbia.edu/~martin/w1111/data/body_fat. 30 35 40 45 waist
 Linear Regression In this tutorial we will explore fitting linear regression models using STATA. We will also cover ways of re-expressing variables in a data set if the conditions for linear regression
Linear Regression In this tutorial we will explore fitting linear regression models using STATA. We will also cover ways of re-expressing variables in a data set if the conditions for linear regression
Statistics. Measurement. Scales of Measurement 7/18/2012
 Statistics Measurement Measurement is defined as a set of rules for assigning numbers to represent objects, traits, attributes, or behaviors A variableis something that varies (eye color), a constant does
Statistics Measurement Measurement is defined as a set of rules for assigning numbers to represent objects, traits, attributes, or behaviors A variableis something that varies (eye color), a constant does
Correlation key concepts:
 CORRELATION Correlation key concepts: Types of correlation Methods of studying correlation a) Scatter diagram b) Karl pearson s coefficient of correlation c) Spearman s Rank correlation coefficient d)
CORRELATION Correlation key concepts: Types of correlation Methods of studying correlation a) Scatter diagram b) Karl pearson s coefficient of correlation c) Spearman s Rank correlation coefficient d)
