U N IT 6: DIGESTION & H U M AN O R G AN I Z AT I O N REVIEW 1. Tissue lining the esophagus is A. nervous. B. muscular. C. epithelial. D. connective.
|
|
|
- Randolf McDonald
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 U N IT 6: DIGESTION & H U M AN O R G AN I Z AT I O N REVIEW 1. Tissue lining the esophagus is A. nervous. B. muscular. C. epithelial. D. connective. 2. Which of the following is a connective tissue? A. Skin. B. Brain. C. Blood. D. Muscle. 3. Similar cells which are joined together form A. a tissue. B. an organ. C. cytoplasm. D. an organ system. 4. Tissues that hold structures together and provide support and protection are A. nerve tissues. B. epithelial tissues. C. epidermis tissues. D. connective tissues Organ 2. Cell 3. Organ system 4. Tissue From left to right, the sequence that represents increasing complexity is A. 1, 3, 2, 4 B. 2, 1, 3, 4 C. 2, 4, 1, 3 D. 2, 4, 3, 1 6. Blood is a type of A. nervous tissue. B. epithelial tissue. C. muscular tissue. D. connective tissue. 7. Digestion is defined as the process whereby A. glucose is converted to glycogen. B. carbon dioxide is reduced to carbohydrate. C. proteins are absorbed into the bloodstream. D. food is chemically and physically broken down. 8. Which of the following describes peristalsis? A. the physical breakdown of fats B. production of vitamins by E. coli C. release of enzymes by the pancreas D. muscle contractions of the digestive tract 9. A patient complains of a burning sensation in the chest. This was found to be caused by gastric juice in the esophagus. The structure most likely not functioning properly is the A. pharynx. B. epiglottis. C. pyloric sphincter. D. cardiac sphincter. 10. Chewing food aids digestion by A. stimulating the release of bile. B. increasing the surface area of the food. C. breaking up large protein molecules into peptides. D. completing the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates. 11. The purpose of physical digestion is to A. hydrolyze large molecules. B. increase the amount of feces. C. increase the surface area of food. D. slow the action of digestive enzymes. 12. The purpose of physical digestion is to A. hydrolyze large molecules. B. increase the amount of feces. C. increase the surface area of food. D. slow the action of digestive enzymes. 13. Which of the following structures prevents food from entering the trachea? A. Larynx. B. Pharynx. C. Epiglottis. D. Cardiac sphincter. 14. The part of the digestive tract where starch first undergoes chemical digestion is the A. mouth. B. stomach. C. large intestine. D. small intestine. 15. Saliva contains an enzyme that partially digests A. fat. B. starch. C. protein. D. nucleic acids.
2 16. Eating which of the following would slow the rate of chemical digestion in the mouth? A. Cheese. B. Ice cream. C. Potato chips. D. Bread with butter. 17. Which of the following is required to convert pepsinogen into pepsin? A. Mucus secretions. B. Hydrochloric acid. C. Sodium bicarbonate. D. Lipid in the stomach. 18. A role of hydrochloric acid in the stomach is to A. kill bacteria. B. hydrolyze fat. C. digest protein. D. activate trypsin. 19. Sodium bicarbonate ( NaHCO3 ) in pancreatic juice A. emulsifies fats. B. activates pepsin. C. neutralizes acid chyme. D. stimulates the release of insulin. 20. Which of the following would inhibit trypsin s ability to form an enzyme-substrate complex? mbers of villi. 21. Which of the following is not a function of pancreatic juice? A. Raising ph. B. Emulsifying. C. Starch digestion. D. Protein digestion. 22. Which of the following is a function of pancreatic juice? A. lowering ph. B. Emulsifying. C. fat digestion. D. Protein absorption. 23. If sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3 ) is not released as part of the pancreatic juice, the ph of the A. stomach will remain basic. B. pancreas will become acidic. C. large intestine will become basic. D. small intestine will remain acidic. 24. Pancreatic juices are A. basic. B. acidic. C. the source of secretin. D. unnecessary for the digestion of fat. 25. The chemical digestion of fats is a result of the release of secretions from the A. pancreas. B. gall bladder. C. small intestine. D. salivary glands. 26. Trypsin functions best in which of the following conditions? A. basic B. acidic C. neutral D. low ph 27. Which organ has a large surface area and has special adaptations for the absorption of fats? A. mouth B. stomach C. esophagus D. small intestine 28. Peristalsis in the esophagus A. moves food to the stomach. B. opens the pyloric sphincter. C. activates the salivary glands. D. causes the secretion of pepsinogen. 29. The function of the pyloric sphincter is to prevent the backflow of material from the A. esophagus to the mouth. B. duodenum to the stomach. C. stomach to the esophagus. D. colon to the small intestine. 30. A function of the small intestine is to A. secrete bile. B. filter wastes. C. make vitamins. D. absorb nutrients. 31. Which of the following enzymes is correctly matched with its site of production? A. Pepsin liver. B. Lipase stomach. C. Amylase pancreas. D. Trypsin salivary glands. 32. The enzyme amylase is produced by which organs? A. Liver and duodenum. B. Duodenum and pancreas. C. Salivary glands and liver. D. Pancreas and salivary glands. 33. Which pair of enzymes have similar substrates? A. Pepsin and trypsin. B. Pepsin and maltase. C. Amylase and lipase. D. Maltase and peptidase.
3 34. Which of the following carries out chemical digestion? A. Insulin. B. Gastrin. C. Trypsin. D. Secretin. 35. An example of absorption is the A. movement of food by peristalsis. B. active transport of glucose into a villus. C. hydrolysis of a peptide into amino acids. D. release of secretin in the presence of HCl. 36. Which of the following is an example of physical digestion? A. Hydrolysis. B. Release of gastrin. C. Churning in the stomach. D. Action of lipase in the small intestine. 37. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells lining the small intestine allows it to A. release HCl. B. produce bile. C. absorb glucose. D. synthesize vitamins. 38. Which of the following enzymes is correctly matched with its source? A. Amylase stomach. B. Peptidase pancreas. C. Trypsin small intestine. D. Maltase small intestine. 39. Structures of the small intestine that aid in the absorption of nutrients include A. villi. B. cilia. C. E. Coli. D. sphincters. 40. High levels of toxins in the blood may indicate a problem with the function of the A. liver. B. stomach. C. pancreas. D. small intestine. 41. The liver plays vital roles in all of the following systems except the A. nervous system. B. digestive system. C. excretory system. D. circulatory system. 42. Vitamins and amino acids are produced in the large intestine by A. feces. B. bacteria. C. the cells of the villi. D. the reabsorption of water. 43. A function of the liver is to A. produce glucagon. B. break down blood cells. C. regulate sodium and potassium levels. D. secrete enzymes into the small intestine. 44. Products of the liver include A. pepsin, gastrin and bile. B. bile, proteases and urea. C. bile, urea and blood proteins. D. proteases, amylases and lipase. 45. If a person s liver fails, which process listed below would stop? A. Digestion of proteins. B. Destruction of red blood cells. C. Storage of starch between meals. D. Reabsorption of water from the digestive tract. 46. The emulsification of fats is a result of the release of secretions from the A. pancreas. B. gall bladder. C. small intestine. D. salivary glands. 47. The emulsification of fat is carried out by A. bile. B. lipase. C. pepsin. D. bicarbonate ions. 48. Bile causes the emulsification of A. lipids. B. proteins. C. nucleic acids. D. carbohydrates. 49. People who have their gall bladder removed have the most difficulty digesting A. butter. B. apples. C. vitamins. D. egg whites.
4 50. The gall bladder functions to A. store bile. B. digest fats. C. store urine. D. release sodium bicarbonate. 51. Emulsification of fat is the function of A. bile. B. lipase. C. pepsin. D. sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3). 52. Removal of the gall bladder would affect a person s ability to digest A. lipids. B. sugars. C. proteins. D. carbohydrates. 53. The release of cholecystokinin (CCK) would most likely be triggered after a meal of A. fruit. B. meat. C. bread. D. lettuce. 54. One function of the lymphatic system is to A. deliver oxygen to body tissues. B. store fluids during dehydration. C. absorb fats from the digestive system. D. carry platelets to sites of vessel injury. 55. Lacteals primarily absorb A. lipids. B. proteins. C. minerals. D. carbohydrates. 56. Bile is released as a result of A. gastrin entering the blood. B. sympathetic nerves being stimulated. C. the duodenum secreting CCK (cholecystokinin). D. the presence of carbohydrates in the digestive tract. 57. Which of the following supports the idea that the secretion of enzymes from the pancreas is controlled by hormones? A. The sight and smell of food causes the pancreas to secrete enzymes. B. If the nerves leading to the pancreas are cut, no enzymes are secreted. C. If there is no food in the stomach, the pancreas will not secrete enzymes. D. If the nerves leading to the pancreas are cut and weak acid is placed in the intestine, the pancreas secretes enzymes. 58. The secretion of cholecystokinin (CCK) will be stimulated by the presence of A. polypeptides and glucose. B. partially digested protein and fats. C. partially digested starch and water. D. completely digested carbohydrates and water. 59. What would occur if sodium bicarbonate ions were removed from pancreatic juice? A. Decreased amounts of bile would be released. B. Increased H 2 O absorption would occur in the colon. C. The cells lining the small intestine would be damaged. D. Digestion of nutrients in the small intestine would increase. 60. The absorption of water from the digestive tract occurs mainly in the A. colon. B. kidneys. C. stomach. D. duodenum. 61. Populations of E. coli are found in the A. liver. B. colon. C. pancreas. D. gall bladder. 62. The main source of energy for the body s metabolic processes comes from the breakdown of A. lipids. B. proteins. C. nucleic acids. D. carbohydrates. 63. Which of the following are absorbed into the lymphatic system from the small intestine? A. Lipids. B. Nucleotides. C. Amino acids. D. Monosaccharides. 64. Absorption of most nutrients from the digestive tract occurs in the A. liver. B. stomach. C. pancreas. D. small intestine.
5 65. An example of absorption is the A. movement of food by peristalsis. B. active transport of glucose into a villus. C. hydrolysis of a peptide into amino acids. D. release of secretin in the presence of HCl. 66. E. coli are beneficial to humans because they A. convert pepsinogen to pepsin. B. produce vitamins and amino acids. C. absorb water from the large intestine. D. synthesize urea from the breakdown of amino acids. 67. In humans, the bacteria E. coli are normally found within the A. colon. B. mouth. C. pancreas. D. small intestine. 68. colon pancreas gall bladder small intestine salivary glands How many of the structures above produce enzymes that digest carbohydrates? A. two B. three C. four D. five 69. Which organelles are found in greater amounts in a cell that produces enzymes for the digestion of starches? A. Golgi bodies and nuclei B. lysosomes and smooth endoplasmic reticulum C. Golgi bodies and rough endoplasmic reticulum D. smooth endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria 70. Which two enzymes break down the same substrate? A. trypsin and pepsin B. pepsin and peptidase C. lipase and salivary amylase D. pancreatic amylase and maltase 71. Increasing the secretion of insulin would have which of the following effects? A. decreased blood sugar B. decreased metabolic rate C. increased protein synthesis D. increased digestion of carbohydrate 72. When salivary amylase enters the stomach, it becomes A. basic. B. buffered. C. activated. D. denatured. 73. Which of the following correctly matches a digestive enzyme with its source? A. Pepsin / pancreas. B. Bile / gall bladder. C. Trypsin / stomach. D. Amylase / pancreas. 74. Secretions from the salivary glands catalyze which of the following reactions? A. protein H2O peptides B. peptides H2O amino acids C. carbohydrates H2O maltose D. fats H2O fatty acids and glycerol 75. Which of the following would prevent maltase from forming an enzyme-substrate complex? A. ph of 8.5 B. a competitive inhibitor C. increased production of bile D. an increase in substrate concentration 76. Two glands that are responsible for secreting protein-digesting enzymes are A. salivary and gastric. B. gastric and pancreas. C. thyroid and pancreas. D. intestinal and thyroid.
6 77. Blood glucose levels are lowered by insulin because it stimulates A. gluconeogenesis. B. the uptake of glucose by cells. C. the conversion of glucose to fatty acids. D. the conversion of glucose to amino acids. 78. Amylase is synthesized at the A. nucleus. B. ribosome. C. lysosome. D. mitochondrion. 79. The following events take place after eating a protein-rich meal. 1. The pancreas releases sodium bicarbonate(nahco3). 2. Pepsinogen is converted into pepsin. 3. Gastrin is released into the bloodstream. 4. Acid chyme stimulates the release of secretin. Place these events in the correct order for digestion. A. 3, 2, 4, 1. B. 3, 4, 2, 1. C. 4, 2, 3, 1. D. 2, 4, 1, Difficulty in absorbing glucose could indicate malfunctioning of the A. colon. B. stomach. C. gall bladder. D. small intestine. 81. The main source of energy in food is A. proteins. B. vitamins. C. nucleic acids. D. carbohydrates. 82. Bread that has been partially digested by saliva tends to have a sweet taste. Which enzyme and substrate are involved? A. Pepsin and starch. B. Pepsin and protein. C. Amylase and starch. D. Amylase and protein. 83. The digestion of starch is catalyzed by a polymer made up of A. fatty acids. B. nucleotides. C. amino acids. D. monosaccharides. 84. In a demonstration, 10 grams of raw meat were suspended in an enzyme solution. After several hours the meat was weighed and was found to have a mass of 3 grams. The solution most likely contained A. bile. B. pepsin. C. maltase. D. amylase. 85. The role of bile during digestion is to A. stimulate the release of glycogen. B. hydrolyze neutral fats into fatty acids. C. catalyze the breakdown of peptides into amino acids. D. break fat into droplets thereby increasing surface area. 86. Abnormal liver function in humans affects the digestion of A. fats. B. sugars. C. proteins. D. starches. 87. Glucose levels in the blood are lowered by the hormone A. insulin. B. glucagon. C. oxytocin. D. cholecystokinin (CCK). 88. Which of the following enzymes is correctly matched with its substrate? A. Amylase fat. B Lipase starch. C. Pepsin protein. D. Trypsin glycogen. 89. A piece of stomach wall is grafted into the skin of a mammal. The presence of food in the stomach causes this patch of stomach wall on the skin to produce gastric juices. This is evidence that the secretion of gastric juice is most likely brought about by A. peristalsis. B. nervous stimulation. C. the secretion of a hormone. D. mechanical stimulation of the stomach wall 90. Which of the following is a function of insulin? A. Initiating the fight or flight response. B. Decreasing glucose concentration in the blood. C. Increasing the calcium ions concentration in the blood. D. Decreasing the sodium ions concentration in the blood
7 Answers: DIGESTION & HUMAN ORGANIZATION 1. C 46. B 2. C 47. A 3. A 48. A 4. D 49. A 5. C 50. A 6. D 51. A 7. D 52. A 8. D 53. B 9. D 54. C 10. B 55. A 11. C 56. C 12. C 57. D 13. C 58. B 14. A 59. C 15. B 60. A 16. B 61. B 17. B 62. D 18. A 63. A 19. C 64. D 20. A 65. B 21. B 66. B 22. C 67. A 23. D 68. B 24. A 69. C 25. A 70. A 26. A 71. A 27. D 72. D 28. A 73. D 29. B 74. C 30. D 75. B 31. C 76. B 32. D 77. B 33. A 78. B 34. C 79. A 35. B 80. D 36. C 81. D 37. C 82. C 38. D 83. C 39. A 84. B 40. A 85. D 41. A 86. A 42. B 87. A 43. B 88. C 44. C 89. C 45. B 90. B
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
Digestive System Functions
 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
GI TRACT ORGANS ACCESSORY ORGANS
 Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestive System GI TRACT ORGANS Oral cavity Oropharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large Intestine Anus ACCESSORY ORGANS Salivary glands Pancreas Liver Gall bladder GI TRACT LAYERS Mucosa Submucosa
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly)
 Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
Chapter 49 - Nutrients and the Digestive System I. Nutrients (chemical substances necessary for organisms to grow and function properly) 6 basic nutrients - 4 food groups (milk, meat, fruit and vegetable,
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System
 The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
The Vertebrate (mostly human) Digestive System Mouth - mastication, lubrication, digestion Pharynx and Esophagus - swallowing Stomach - some digestion Small intestine - most digestion and absorption Large
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestive System Why is digestion important? How is food digested? Physical Digestion and Movement
 Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
Digestive System The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to the anus and other organs that help the body break down
The Human Digestive System
 The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
The Human Digestive System Name: Section: Date: Page 1 of 10 Page 2 of 10 Page 3 of 10 Page 4 of 10 Page 5 of 10 Page 6 of 10 Putting it All Together Digestive Enzymes Page 7 of 10 Page 8 of 10 Page 9
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive system Review
 Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
Digestive system Review 1. Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion. The physical breakdown of food begins in the mouth with two types of processes. The mouth is a complex structure
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
Chapter 15 Digestive System.
 Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Chapter 15 Digestive System. I. The Gastrointestinal Tract. a. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food into molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream or lymph. Residues
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Outline Digestive System
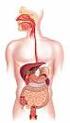 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients
 Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Jenny Kim Professor Rosario Nutrition: Macronutrients Project June 26, 2014 1. Essay: The Digestive and Absorption Processes of Macronutrients Whenever we eat, the foods we ingest in our bodies undergo
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014
 Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
Digestive System Lecture 5 Winter 2014 This lecture tells the story of the Flow of Matter from Food to Cells. The pictures are only there to help you visualize structures don t worry about names of structures
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Special organ structures and functions conduct these tasks through the successive parts of the overall system.
 Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
Chapter 5 Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Chapter 5 Lesson 5.1 Key Concepts Through a balanced system of mechanical and chemical digestion, food is broken down into smaller substances and the nutrients
8. Be able to label a diagram of an earthworm. Know the function of each of the major parts of the earthworm.
 Review for Unit Test: The Digestive System 1. Know the meaning of these terms: heterotrophs digestion peristalsis microvilli autotrophs chemical digestion chyme lacteal intracellular digestion mechanical
Review for Unit Test: The Digestive System 1. Know the meaning of these terms: heterotrophs digestion peristalsis microvilli autotrophs chemical digestion chyme lacteal intracellular digestion mechanical
Chapter 17 Digestive System. Alimentary Canal. Movements of the Tube
 Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM What is digestion? Digestion is the process of breaking down food so that it's small enough to be absorbed and used by the body for energy or in other bodily functions. Digestion involves
Absorption and Transport of Nutrients
 Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Page1 Digestion Food travels from mouth esophagus stomach small intestine colon rectum anus. Food mixes with digestive juices, moving it through the digestive tract Large molecules of food are broken into
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
Topic 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Organ Systems Organ systems must have the ability to to changes within and outside of your body to maintain life
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS
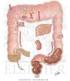 SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
SMALL AND LARGE INTESTINE SECRETIONS Objectives At the end of lecture student should be able to know, Digestive system Digestive system secretions Small intestine Component of small intestine Intestinal
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
30.3 The Digestive System
 30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 1 Understanding Animal Digestion 1 Terms Absorption Amino acids Anus Avian Bile Cecum Chyme Crop Cud Digestion Digestive system Enzymes Eructated Feces Gizzard
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Functions of the GI Tract. Chapter 18. Functions of the GI Tract (continued)
 Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Functions of the GI Tract Chapter 18 The Digestive System Motility: Movement of of food through the GI tract. Ingestion: Taking food into the mouth. Mastication: Chewing the food and mixing it with saliva.
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline
 Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
Chapter 2 Digestion and Absorption Chapter Outline I. Anatomy of the Digestive Tract A. The Digestive Organs 1. Mouth to the Esophagus 2. Esophagus to the Stomach 3. The Small Intestine 4. The Large Intestine
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
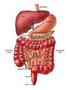 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Secretion Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1: Title Page Digestive system secretion involves
Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
OpenStax-CNX module: m49457 1 Digestive System Module 7: Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Donna Browne Based on Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look by OpenStax This work is
The digestive system, also called the gastrointestinal
 exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
exercise 8 Chemical and Physical Processes of Digestion Objectives 1. To define digestive tract, accessory glands, digestion, hydrolases, salivary amylase, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, bile salts,
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES
 LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
LAB 3: DIGESTION OF ORGANIC MACROMOLECULES INTRODUCTION Enzymes are a special class of proteins that lower the activation energy of biological reactions. These biological catalysts change the rate of chemical
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
Digestion in the small and Large Intestines
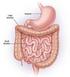 9.5 Digestion in the small and Large Intestines Do some foods keep you feeling full for a long time? Do you ever feel that after eating certain foods, you are hungry again in a short time? Some foods stay
9.5 Digestion in the small and Large Intestines Do some foods keep you feeling full for a long time? Do you ever feel that after eating certain foods, you are hungry again in a short time? Some foods stay
H.W. 1 Bio 101 Prof. Fournier
 H.W. 1 Bio 101 Prof. Fournier 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a
H.W. 1 Bio 101 Prof. Fournier 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a
Weds 5/20/15. Membranes - finish last lecture outline. Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system
 Membranes - finish last lecture outline Weds 5/20/15 Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system structures and functions // accessory organs mechanism
Membranes - finish last lecture outline Weds 5/20/15 Digestive System Nutrition Types of digestion & digestive systems Vertebrate digestive system structures and functions // accessory organs mechanism
Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW A. Gross anatomy (Fig. 24.1) and functions (Table 24.1) B. "You are what you eat." 1. The problem: Ingestion (eating) is not the same as absorption. 2. The solution:
Chapter 24: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW A. Gross anatomy (Fig. 24.1) and functions (Table 24.1) B. "You are what you eat." 1. The problem: Ingestion (eating) is not the same as absorption. 2. The solution:
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA
 Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
AP Biology. What do animals need to live? Animal Nutrition. Nutritional requirements. How do animals get their food? Different diets; different lives
 Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Animal Nutrition What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, fats, nucleotides O 2 ATP energy for synthesis
Digestive system. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College
 Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions Motility ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis Secretion exocrine endocrine Digestion Absorption Tunics Innervation
Digestive system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Functions Motility ingestion mastication deglutition peristalsis Secretion exocrine endocrine Digestion Absorption Tunics Innervation
1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit
 Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
Chapter 3 Digestion and Absorption Key Terms 1. gustatory cells: Surface cells in the throat and on the taste buds in the mouth that transmit taste information. 2. absorption: The movement of substances
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. Consists of the canal which is all of
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System What do you know?? quiz-digestive-health Digestion Videos The Digestive System Inside-Dr-Ozs-Digestive-System-Video Now it is your turn to recreate the digestive system. How is food
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System. Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism. Metabolism. Organs of the Digestive System. Digestion.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Chapter 14 The Digestive System The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Digestion of ingested food of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of Constructive and degradative cellular activities
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System
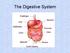 The Digestive System Objectives Name and locate the digestive organs and the accessory organs of digestion. List the general function of the digestive system and the function of each organ. Define mechanical
The Digestive System Objectives Name and locate the digestive organs and the accessory organs of digestion. List the general function of the digestive system and the function of each organ. Define mechanical
Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15
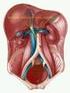 Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15 Digestive system processes the food used as fuel and nutrients for the body. Composed of a tube through the body (digestive tract,
Biology 2402 Anatomy &Physiology II - Digestive system notes - Ch. 15 Digestive system processes the food used as fuel and nutrients for the body. Composed of a tube through the body (digestive tract,
Name Date Period. Keystone Review Enzymes
 Name Date Period Keystone Review Enzymes 1. In order for cells to function properly, the enzymes that they contain must also function properly. What can be inferred using the above information? A. Cells
Name Date Period Keystone Review Enzymes 1. In order for cells to function properly, the enzymes that they contain must also function properly. What can be inferred using the above information? A. Cells
Enzymes. A. a lipid B. a protein C. a carbohydrate D. a mineral
 Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of different kinds of enzymes that are specialized to catalyze different chemical reactions. Given this information, which of the following
Enzymes 1. All cells in multicellular organisms contain thousands of different kinds of enzymes that are specialized to catalyze different chemical reactions. Given this information, which of the following
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
VII. Metabolism Overview and Digestion. A. Introduction
 VII. Metabolism verview and Digestion A. Introduction 1. All living organisms require a constant supply of energy a. Basic problem (1) Living organisms are working against natural tendency for things to
VII. Metabolism verview and Digestion A. Introduction 1. All living organisms require a constant supply of energy a. Basic problem (1) Living organisms are working against natural tendency for things to
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series
 from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Digestive System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3206 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100
from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Digestive System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3206 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes The Gastrointestinal tract (alimentary canal)
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Movement of the food along the G.I. tract. 3. Digestion- chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. 4. Absorption of the breakdown products
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Five Basic Processes 1. Ingestion - eating 2. Movement of the food along the G.I. tract. 3. Digestion- chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. 4. Absorption of the breakdown products
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition
 Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Chapter 25: Metabolism and Nutrition Chapter Objectives INTRODUCTION 1. Generalize the way in which nutrients are processed through the three major metabolic fates in order to perform various energetic
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3
 Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Horse Science: The Digestive System of the Horse Page 3 The digestive system of the horse is different from that Mastication (chewing) is the mechanical reduction of of the other farm animals. Although
Learning Objectives. Introduction to Medical Careers. Vocabulary: Chapter 16 FACTS. Functions. Organs. Digestive System Chapter 16
 Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Learning Objectives Introduction to Medical Careers Digestive System Chapter 16 Define at least 10 terms relating to the digestive Describe the four functions of the digestive Identify different structures
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
The chemical reactions inside cells are controlled by enzymes. Cells may be specialised to carry out a particular function.
 12.1 What are animals and plants built from? All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. to relate the structure of different types
12.1 What are animals and plants built from? All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. to relate the structure of different types
Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14
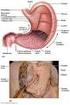 Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy ( ) Constructive and degradative
Name Digestive System and Body Metabolism Notes Ch 14 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy ( ) Constructive and degradative
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme
 The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
The 6 th International Junior Science Olympiad Training Programme KEEPING HEALTHY SECTION 2: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Notes to Teachers Learning Objectives: Processes of nutrition in human (0.25 hr) General plan
Anatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice with Answers at End!
 Anatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice with Answers at End! General Chemical Principles 1. bonds are characterized by the sharing of electrons between the participating atoms. a. hydrogen b.
Anatomy and Physiology Placement Exam 2 Practice with Answers at End! General Chemical Principles 1. bonds are characterized by the sharing of electrons between the participating atoms. a. hydrogen b.
glucose and fatty acids to raise your blood sugar levels.
 Endocrine & Cell Communication Part IV: Maintaining Balance (Homeostasis) TEACHER NOTES needs coding 1 Endocrine & Cell Communication Part IV: Maintaining Balance (Homeostasis) 2 AP Biology Curriculum
Endocrine & Cell Communication Part IV: Maintaining Balance (Homeostasis) TEACHER NOTES needs coding 1 Endocrine & Cell Communication Part IV: Maintaining Balance (Homeostasis) 2 AP Biology Curriculum
CHAPTER 17: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. 2. Distinguish between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion.
 CHAPTER 17: SYSTEM OBJECTIVES 1. Define the term digestion and explain its significance. 2. Distinguish between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. 3. Discuss the five digestive processes that
CHAPTER 17: SYSTEM OBJECTIVES 1. Define the term digestion and explain its significance. 2. Distinguish between mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. 3. Discuss the five digestive processes that
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes. 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
 Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Keystone Review Practice Test Module A Cells and Cell Processes 1. Which characteristic is shared by all prokaryotes and eukaryotes? a. Ability to store hereditary information b. Use of organelles to control
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1
 Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Endocrine System: Practice Questions #1 1. Removing part of gland D would most likely result in A. a decrease in the secretions of other glands B. a decrease in the blood calcium level C. an increase in
Lesson 2: Digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates
 Lesson 2: Digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates Inquiry Focus: How does the body get energy from food? Student Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson, students will be able to do the following:
Lesson 2: Digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates Inquiry Focus: How does the body get energy from food? Student Learning Objectives: By the end of the lesson, students will be able to do the following:
The Digestive System 24-1
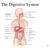 The Digestive System 24-1 Overview of GI tract Functions Mouth---bite, chew, swallow Pharynx and esophagus---- transport Stomach----mechanical disruption; absorption of water & alcohol Small intestine--chemical
The Digestive System 24-1 Overview of GI tract Functions Mouth---bite, chew, swallow Pharynx and esophagus---- transport Stomach----mechanical disruption; absorption of water & alcohol Small intestine--chemical
Lab 18 The Digestive System
 Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
Lab 18 The Digestive System Laboratory Objectives Identify on a diagram, model or cadaver the parts of the digestive system and accessory organs. Describe the general histology of the digestive system.
The Digestive System
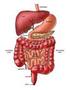 The Digestive System Digestive Structures Mouth including teeth and tongue Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Accessory structures - salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas Digestive
The Digestive System Digestive Structures Mouth including teeth and tongue Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Accessory structures - salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, & pancreas Digestive
Functions of the digestive system
 Digestive system Functions of the digestive system Digestion-mechanical and chemical breakdown of material Motility-movement of material from the oral cavity to the anus-swallowing / peristalsis Secretion-exocrine
Digestive system Functions of the digestive system Digestion-mechanical and chemical breakdown of material Motility-movement of material from the oral cavity to the anus-swallowing / peristalsis Secretion-exocrine
A comparison of the different livestock systems. By: Kristy Baird
 A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
A comparison of the different livestock systems By: Kristy Baird Describe the basic function of the primary components of the digestive system. Compare the function and location of the digestive organs
OVERVIEW OF LIPID METABOLISM
 VERVIEW F LIPID METABLISM Date: September 20, 2005 * Time: 8:00 am 8:50 am * Room: G202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Steve Chaney 515A Mary Ellen Jones Building stephen_chaney@med.unc.edu 9663286 *Please
VERVIEW F LIPID METABLISM Date: September 20, 2005 * Time: 8:00 am 8:50 am * Room: G202 Biomolecular Building Lecturer: Steve Chaney 515A Mary Ellen Jones Building stephen_chaney@med.unc.edu 9663286 *Please
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
Note Taking Guide. Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems
 Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
Note Taking Guide Topic # 3024 Comparative Digestive Systems Digestive Systems Overview 1. Digestion Digestion: Food enters the mouth and goes through mechanical and chemical changes as it passes through
26. Digestive System
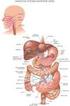 26. Digestive System Your body needs food for two primary purposes: growth and maintenance. Molecules and atoms in the food you eat are generally used to either build new molecules in your body or to provide
26. Digestive System Your body needs food for two primary purposes: growth and maintenance. Molecules and atoms in the food you eat are generally used to either build new molecules in your body or to provide
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
DIGESTION is the physical and
 Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
Digestion DIGESTION is the physical and chemical breakdown of feeds as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract. The structures of the gastrointestinal tract include the mouth, the esophagus, the stomach,
ANSWERS AND MARK SCHEMES. (a) 5 correct plots with bars labelled;;; (-1 each incorrect plot) 3
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) 5 correct plots with bars labelled;;; (-1 each incorrect plot) 3 (b) 200 grams of beans contains 2 x 3.6 = 7.2 grams of fibre. 2/3s of 7.2 = 4.8 grams;; (correct answer scores 2. Allow
QUESTIONSHEET 1 (a) 5 correct plots with bars labelled;;; (-1 each incorrect plot) 3 (b) 200 grams of beans contains 2 x 3.6 = 7.2 grams of fibre. 2/3s of 7.2 = 4.8 grams;; (correct answer scores 2. Allow
SEER Training Modules
 http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/digestive/ WiRED International wishes to thank the National Cancer Institute for use of this information. SEER Training Modules Introduction to the Digestive System
http://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/digestive/ WiRED International wishes to thank the National Cancer Institute for use of this information. SEER Training Modules Introduction to the Digestive System
6023-1 - Page 1. Name: 4) The diagram below represents a beaker containing a solution of various molecules involved in digestion.
 Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
II. General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 17 Be sure to watch the Video: The Digestive System. Digestive System URLs http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookDIGEST.html http://yahooligans.yahoo.com/reference/gray/244.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 17 Be sure to watch the Video: The Digestive System. Digestive System URLs http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookDIGEST.html http://yahooligans.yahoo.com/reference/gray/244.html
Regulation of Metabolism. By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College
 Regulation of Metabolism By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Energy Constant need in living cells Measured in kcal carbohydrates and proteins = 4kcal/g Fats = 9kcal/g Most diets are
Regulation of Metabolism By Dr. Carmen Rexach Physiology Mt San Antonio College Energy Constant need in living cells Measured in kcal carbohydrates and proteins = 4kcal/g Fats = 9kcal/g Most diets are
