6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Formula Sheet for the Final Exam, Fall " de(x) dx % d&(x) dx %" d 2 &(x) (x,t) J e
|
|
|
- Charlene Wilcox
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 6.0 Mcroelectronc Devces and Crcuts Formula Sheet for the Fnal Exam Fall 009 Parameter Values: q.6x0 "9 Coul # o 8.854x0 "4 F/cm # rs.7 # S $0 " F/cm n [ S@R.T ] $0 0 cm "3 kt /q $ 0.05 V; kt /q Еm x0 "4 cm Drft/Dffuson: ln0 $ 0.06 V Perodc Table: III IV V B C N Al S P Ga Ge As In Sn Sb Electrostatcs: Drft velocty : Conductvty : Dffuson flux : Ensten relaton : s x БЕ m E x " q Е e n Е h p $C F m #D m m $x D m kt Е m q " dex dx dx dx " d x #x Ex #xdx " Ex x $ Exdx dx #x x " $ $$ #xdxdx The Fve Basc Equatons: Electron contnuty : Hole contnuty : Electron current densty : Hole current densty : Possons equaton : "nxt "t "pxt "t # q q "J e xt "J h xt g L xt # [ nxt $ pxt # n ]rt g L xt # [ nxt $ pxt # n ]rt "nxt J e xt qе e nxtext q "pxt J h xt qе h pxtext # qd h "Ext q pxt # nxt N d x # N # a x Unform dopng full onzaton TE n - type N d >> N a n o " N d # N a $ N D p o n n o n kt q ln N D n p - type N a >> N d p o " N a # N d $ N A n o n Unform optcal exctaton unform dopng p o p # kt q ln N A n dn n n o n p p o p n p dt g t " p n n nr l o o dn Low level njecton np<< p o n o : dt n g l t wth # mn $ p o r " # mn
2 Flow problems unformly doped quas-neutral regons wth quas-statc exctaton and low level njecton; p-type example: d nx Mnorty carrer excess: " nx " g dx L x L e # $ e L e dnt Mnorty carrer current densty: J e x q dx Majorty carrer current densty : J h x J Tot " J e x Electrc feld : E x x Majorty carrer excess: Short base nfnte lfetme lmt: Mnorty carrer excess: px nx q J h x D h J e x qе h p o de x x dx d nx " # g dx L x nx " # $$ g L xdxdx Non-unformly doped semconductor sample n thermal equlbrum d dx { $ [ N d x $ N a x]} q # n e q kt $ e $q kt n o x n e q kt p o x n e $q kt p o xn o x n Depleton approxmaton for abrupt p-n juncton: $ 0 #qn Ap qn Dn 0 for for for for x < #x p #x p < x < 0 0 < x < x n x n < x x p N Dn x n b n # p kt q ln N Dn n wv AB S b # v AB q N Dn E pk q # v b AB N Dn N Dn S N Dn q DP v AB #Ap x p Ideal p-n juncton dode -v relaton: n-x p n e qv AB / kt # D D Aqn h D e e qv AB / kt - $ N Dn w neff w peff -x p v AB #A q S b # v AB N Dn N Dn n-x p n e qv AB / kt "; px n n e qv AB / kt N Dn w meff w m " x m L m tanh w m " x m L m px n n e qv AB / kt " N Dn f L m >> w m f L m ~ w m q QNRp -sde Aq - nxdx q QNRn -sde Aq - pxdx Note : px. nx n QNRs -w p w n x n L m f L m << w m
3 Large sgnal BJT Model n Forward Actve Regon FAR: npn wth base wdth modulaton B C wth : I BS I BS e qv BE / kt " v BE v CE v BE v BC # F B v BE v CE I ES # F Also F "- B - E Aqn # F When - B. 0 then F. MOS Capactor: 3 $v CE [ $v CE ] # F I BS e qv BE / kt " and # F. D h D e N DE w Eeff N AB w # F Beff - E "- B - E - B wth - E D h / N AB N DE / w Beff w Eeff and # F. - E F " F and $ and - B w Beff L eb Flat - band voltage : V FB " v GB at whch #0 # p$s [# 0 n S] V FB # p$s $ # m Threshold voltage : V T " v GC at whch #0 $ # p$s $ v BC # # p$s $ v BC n S { } / V T v BC V FB $ # p$s S # p$s $ v BC Depleton regon wdth at threshold : x DT v BC S # p$s $ v BC Oxde capactance per unt area : Inverson layer sheet charge densty : q N $ Accumulaton layer sheet charge densty: C ox ox [ rso 3.9 SO 3.5x0 $3 F /cm] q P $ [ v GC $V T v BC ] [ v GB $V FB ] Gradual Channel Approxmaton for MOSFET Characterstcs: n-channel; strong nverson; wth channel length modulaton; no velocty saturaton Only vald for v BS В 0 v DS Г 0. G 0 B 0 K D # [ v "V v GS T BS $ v DS " v DSsat ] for 0 < v GS K v GS "# v DS v DS for 0 < # v DS < v GS wth V T V FB " - p"s. S - p"s " v BS K W L Е e C ox C ox. ox # 0 for [ v GS ] < 0 < # v DS < # v DS { } / v DSsat # v "V v GS T BS. S [ - p"s " v BS ] / $
4 Large Sgnal Model for MOSFETs Operated below Threshold weak nverson: n-channel Only vald for for v GS В V T v DS Г 0 v BS В 0. 4 G 0 B " 0 Ds#t " I Ss#t e q{ v GS #V T } n kt # e #qv DS / kt where I Ss#t $ W L Е e kt q S p # v BS K o V t - p # v BS wth V t $ kt q K o $ W L Е ec ox - $ S - n " p # v BS Large Sgnal Model for MOSFETs Reachng Velocty Saturaton at Small v DS : n-channel Only vald for v BS В 0 v DS Г 0. Neglects v DS / relatve to -V T. Saturaton model: s y E y Е e E y f E y " E crt s y E y Е e E crt # s sat f E y $ E crt G 0 B 0 0 for v GS V T < 0 < v DS D W s sat [ v GS V T ][ v DS crt L ] for 0 < v GS V T crt L < v DS W L Е C e ox[ v GS V T ]v DS for 0 < v GS V T v DS < crt L wth # CMOS Performance Transfer characterstc: In general : V LO 0 V HI V DD I ON 0 I OFF 0 Symmetry : V M V DD and NM LO NM HI " K n K p and V Tp V Tn Mnmum sze gate : L n L p W n W mn W p Е n Е p W n or W p s satn s satp W n Swtchng tmes and gate delay no velocty saturaton: C " Ch arg e " Dsch arg e L V DD K n [ V DD #V Tn ] C L n W n L n W p L p C ox 3nW mn " Mn.Cycle " Ch arg e " Dsch arg e nl mnv DD Е e [ V DD #V Tn ] Dynamc power dsspaton no velocty saturaton: P fmax PD fmax C L V DD f max " C LV DD " Е W e mn$ V V V ox DD DD Tn # Mn.Cycle assumes Е e Е h P fmax InverterArea " P f max " Е e$ V V V ox DD DD Tn W mn
5 Swtchng tmes and gate delay full velocty saturaton: 5 C " Ch arg e " Dsch arg e L V DD W mn s sat [ V DD #V Tn ] C L n W n L n W p L p C ox nw mn assumes s sate s sath " Mn.Cycle " Ch arg e " Dsch arg e 4nV DD s sat [ V DD #V Tn ] Dynamc power dsspaton per gate full velocty saturaton: P fmax PD fmax C L V DD Statc power dsspaton per gate f max " C V L DD " s W sat mn$ V V V ox DD DD Tn # Mn.Cycle P fmax InverterArea " P f max " s sat$ V V V ox DD DD Tn W mn L P statc V DD I Doff W " V mn # DD Е e V S { t e $V T } nv t V BS P statc PD statc Inverter Area V DD # Е e V S t e $V T V BS CMOS Scalng Rules - Constant electrc feld scalng { } nv t Scaled Dmensons : " s W " W s " s N A " sn A Scaled Voltages : V DD " V DD s V BS " V BS s Consequences : C ox " s Devce transt tmes K " sk V T " V T s # " # s P dyn " P dyn s PD fmax " PD fmax PD statc " s e s$v T sn V t PD statc Short Base Dode transt tme : " b w B D mnb w B Е mnb V thermal Channel transt tme MOSFET w.o. velocty saturaton : " Ch 3 Е Ch V GS #V T Channel transt tme MOSFET wth velocty saturaton : " Ch L s sat L
6 6 Small Sgnal Lnear Equvalent Crcuts: Ѕ p-n Dode n -p dopng assumed for C d g d " # D q #v AB kt I S eqb / kt $ Q where C dp B A q I D kt C d C dp C df q S and C V qi D df AB kt b B Ѕ BJT n FAR q kt " oi BS e qv kt BE [ #V CE ] $ qi C kt # $ # I C or $ I C " o I BS e qv BE kt C b B-E depleton cap. wth b - w B [ w p x p ] g " o q I C " o kt g d d wth d " w x p p C Е : B-C depleton cap. Ѕ MOSFET strong nverson; n saturaton no velocty saturaton K[ V GS V BS ][ #V DS ] $ K I D K [ V "V V GS T BS ] # $ # I D or $ I D b K I D wth " -V T -v BS Q 3 W LC ox C sb C gb C db : depleton capactances C gd W C gd where C gd. S q/ p "V BS s the G-D frngng and overlap capactance per unt gate length parastc Ѕ MOSFET strong nverson; n saturaton wth full velocty saturaton W s sat C ox " I D I D b # wth # $ V T v BS Q S q p V BS W LC ox C sb C gb C db : depleton capactances C gd W C gd where C gd s the G-D frngng and overlap capactance per unt gate length parastc Ѕ MOSFET operated sub-threshold; n forward actve regon; only vald for v bs 0 q I D n kt " I D I D # W L C gd W C gd where C gd C # ox V GS $V FB C db : dran regon depleton capactance S s the G-D frngng and overlap capactance per unt gate length parastc
7 7 Sngle transstor analog crcut buldng block stages Note: g l g sl g el ; g l е g l BIPOLAR Common emtter " Common base Emtter follower Emtter degeneracy Shunt feedback Voltage Current gan A v gan A # " r l " $ g l g l g l Input r # g [ g l ] m r l # # [ $ ] [ g ] # $ g l # $ r $ g g l " g " G m F G F g l Output resstance R resstance R o r r o # [ $ ]r o r r t r l $ # " r l # $ # r [ $ ]R F # r o R F # " R F " g l G F g G F " A v r o R F G F MOSFET Common source " Common gate Source follower Source degeneracy seres feedback Shunt feedback Voltage Current Input Output gan A v gan A resstance R resstance R o " r l g # # r $ o g l o [ [ b ] r l r [ b ] o g g mb o]. / - g t 0 [ ] [ g l ] # # [ g l ] " " G F G F " r l R F # # r o " R F " g l G F G F " A v OCTC/SCTC Methods for Estmatng Amplfer Bandwdth OCTC estmate of " HI : " HI # " $ - R C - $ r o R F G F wth R defned as the equvalent resstance n parallel wth C wth all other parastc devce capactors C s C Е s s C gd s etc. open crcuted. SCTC estmate of " LO : " LO # $ " j $ R j C j j j wth R j defned as the equvalent resstance n parallel wth C j wth all other basng and couplng capactors C s C O s C E s C S s etc. short crcuted.
8 8 Dfference- and Common-mode sgnals Gven two sgnals v and v we can decompose them nto two new sgnals one v C that s common to both v and v and the other v D that makes an equal but opposte polarty contrbuton to v and v : [ v D " v # v and v C " v v ] $ v v C v D and v v C # v D Short crcut current gan unty gan frequency f T " t # 3Е Ch V GS $V T L 3s Ch L MOSFET no vel. sat. W s sat W LC ox s sat L MOSFET w. vel. sat. - C C Е ; lm g I c [ m C C Е ] # D mnb w B BJT large I C. / tr Revsed /9/09
9 MIT OpenCourseWare Mcroelectronc Devces and Crcuts Fall 009 For nformaton about ctng these materals or our Terms of Use vst:
Section C2: BJT Structure and Operational Modes
 Secton 2: JT Structure and Operatonal Modes Recall that the semconductor dode s smply a pn juncton. Dependng on how the juncton s based, current may easly flow between the dode termnals (forward bas, v
Secton 2: JT Structure and Operatonal Modes Recall that the semconductor dode s smply a pn juncton. Dependng on how the juncton s based, current may easly flow between the dode termnals (forward bas, v
The circuit shown on Figure 1 is called the common emitter amplifier circuit. The important subsystems of this circuit are:
 polar Juncton Transstor rcuts Voltage and Power Amplfer rcuts ommon mtter Amplfer The crcut shown on Fgure 1 s called the common emtter amplfer crcut. The mportant subsystems of ths crcut are: 1. The basng
polar Juncton Transstor rcuts Voltage and Power Amplfer rcuts ommon mtter Amplfer The crcut shown on Fgure 1 s called the common emtter amplfer crcut. The mportant subsystems of ths crcut are: 1. The basng
Lecture #21. MOS Capacitor Structure
 Lecture #21 OUTLINE The MOS apactor Electrotatc Readng: oure Reader EE130 Lecture 21, Slde 1 MOS apactor Structure MOS capactor (croectonal vew _ TE x EE130 Lecture 21, Slde 2 Typcal MOS capactor and trantor
Lecture #21 OUTLINE The MOS apactor Electrotatc Readng: oure Reader EE130 Lecture 21, Slde 1 MOS apactor Structure MOS capactor (croectonal vew _ TE x EE130 Lecture 21, Slde 2 Typcal MOS capactor and trantor
Multiple stage amplifiers
 Multple stage amplfers Ams: Examne a few common 2-transstor amplfers: -- Dfferental amplfers -- Cascode amplfers -- Darlngton pars -- current mrrors Introduce formal methods for exactly analysng multple
Multple stage amplfers Ams: Examne a few common 2-transstor amplfers: -- Dfferental amplfers -- Cascode amplfers -- Darlngton pars -- current mrrors Introduce formal methods for exactly analysng multple
Transconductance. (Saturated) MOSFET Small-Signal Model. The small-signal drain current due to v gs is therefore given by
 11 (Saturated) MOSFET Small-Signal Model Transconductance Concept: find an equivalent circuit which interrelates the incremental changes in i D v GS v DS etc. for the MOSFET in saturation The small-signal
11 (Saturated) MOSFET Small-Signal Model Transconductance Concept: find an equivalent circuit which interrelates the incremental changes in i D v GS v DS etc. for the MOSFET in saturation The small-signal
Victims Compensation Claim Status of All Pending Claims and Claims Decided Within the Last Three Years
 Claim#:021914-174 Initials: J.T. Last4SSN: 6996 DOB: 5/3/1970 Crime Date: 4/30/2013 Status: Claim is currently under review. Decision expected within 7 days Claim#:041715-334 Initials: M.S. Last4SSN: 2957
Claim#:021914-174 Initials: J.T. Last4SSN: 6996 DOB: 5/3/1970 Crime Date: 4/30/2013 Status: Claim is currently under review. Decision expected within 7 days Claim#:041715-334 Initials: M.S. Last4SSN: 2957
Chapter 6 Inductance, Capacitance, and Mutual Inductance
 Chapter 6 Inductance Capactance and Mutual Inductance 6. The nductor 6. The capactor 6.3 Seres-parallel combnatons of nductance and capactance 6.4 Mutual nductance 6.5 Closer look at mutual nductance Oerew
Chapter 6 Inductance Capactance and Mutual Inductance 6. The nductor 6. The capactor 6.3 Seres-parallel combnatons of nductance and capactance 6.4 Mutual nductance 6.5 Closer look at mutual nductance Oerew
Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime
 Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime Outline The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): structure and basic operation I-V characteristics in forward active regime Reading Assignment:
Lecture 17 The Bipolar Junction Transistor (I) Forward Active Regime Outline The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): structure and basic operation I-V characteristics in forward active regime Reading Assignment:
Mean Molecular Weight
 Mean Molecular Weght The thermodynamc relatons between P, ρ, and T, as well as the calculaton of stellar opacty requres knowledge of the system s mean molecular weght defned as the mass per unt mole of
Mean Molecular Weght The thermodynamc relatons between P, ρ, and T, as well as the calculaton of stellar opacty requres knowledge of the system s mean molecular weght defned as the mass per unt mole of
EDC Lesson 12: Transistor and FET Characteristics. 2008 EDCLesson12- ", Raj Kamal, 1
 EDC Lesson 12: Transistor and FET Characteristics Lesson-12: MOSFET (enhancement and depletion mode) Characteristics and Symbols 2008 EDCLesson12- ", Raj Kamal, 1 1. Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect
EDC Lesson 12: Transistor and FET Characteristics Lesson-12: MOSFET (enhancement and depletion mode) Characteristics and Symbols 2008 EDCLesson12- ", Raj Kamal, 1 1. Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect
The difference between voltage and potential difference
 Slavko Vjevć 1, Tonć Modrć 1 and Dno Lovrć 1 1 Unversty of Splt, Faclty of electrcal engneerng, mechancal engneerng and naval archtectre Splt, Croata The dfference between voltage and potental dfference
Slavko Vjevć 1, Tonć Modrć 1 and Dno Lovrć 1 1 Unversty of Splt, Faclty of electrcal engneerng, mechancal engneerng and naval archtectre Splt, Croata The dfference between voltage and potental dfference
Lecture 060 Push-Pull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 060-1. ECE 6412 - Analog Integrated Circuits and Systems II P.E. Allen - 2002
 Lecture 060 PushPull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 0601 LECTURE 060 PUSHPULL OUTPUT STAGES (READING: GHLM 362384, AH 226229) Objective The objective of this presentation is: Show how to design stages that
Lecture 060 PushPull Output Stages (1/11/04) Page 0601 LECTURE 060 PUSHPULL OUTPUT STAGES (READING: GHLM 362384, AH 226229) Objective The objective of this presentation is: Show how to design stages that
Lecture 8 MOSFET(I) MOSFET I-V CHARACTERISTICS
 Lecture 8 MOSFET(I) MOSFET I-V CHARACTERISTICS Outline 1. MOSFET: cross-section, layout, symbols 2. Qualitative operation 3. I-V characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Sections
Lecture 8 MOSFET(I) MOSFET I-V CHARACTERISTICS Outline 1. MOSFET: cross-section, layout, symbols 2. Qualitative operation 3. I-V characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Sections
NOTE: The Flatpak version has the same pinouts (Connection Diagram) as the Dual In-Line Package. *MR for LS160A and LS161A *SR for LS162A and LS163A
 BCD DECADE COUNTERS/ 4-BIT BINARY COUNTERS The LS160A/ 161A/ 162A/ 163A are hgh-speed 4-bt synchronous counters. They are edge-trggered, synchronously presettable, and cascadable MSI buldng blocks for
BCD DECADE COUNTERS/ 4-BIT BINARY COUNTERS The LS160A/ 161A/ 162A/ 163A are hgh-speed 4-bt synchronous counters. They are edge-trggered, synchronously presettable, and cascadable MSI buldng blocks for
SMA5111 - Compound Semiconductors Lecture 2 - Metal-Semiconductor Junctions - Outline Introduction
 SMA5111 - Compound Semiconductors Lecture 2 - Metal-Semiconductor Junctions - Outline Introduction Structure - What are we talking about? Behaviors: Ohmic, rectifying, neither Band picture in thermal equilibrium
SMA5111 - Compound Semiconductors Lecture 2 - Metal-Semiconductor Junctions - Outline Introduction Structure - What are we talking about? Behaviors: Ohmic, rectifying, neither Band picture in thermal equilibrium
BJT Ebers-Moll Model and SPICE MOSFET model
 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering mperial College London EE 2.3: Semiconductor Modelling in SPCE Course homepage: http://www.imperial.ac.uk/people/paul.mitcheson/teaching BJT Ebers-Moll
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering mperial College London EE 2.3: Semiconductor Modelling in SPCE Course homepage: http://www.imperial.ac.uk/people/paul.mitcheson/teaching BJT Ebers-Moll
CHAPTER 10 Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor
 CHAPTER 10 Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor Study the characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage in the metal oxide semiconductor structure known
CHAPTER 10 Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor Study the characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage in the metal oxide semiconductor structure known
Faraday's Law of Induction
 Introducton Faraday's Law o Inducton In ths lab, you wll study Faraday's Law o nducton usng a wand wth col whch swngs through a magnetc eld. You wll also examne converson o mechanc energy nto electrc energy
Introducton Faraday's Law o Inducton In ths lab, you wll study Faraday's Law o nducton usng a wand wth col whch swngs through a magnetc eld. You wll also examne converson o mechanc energy nto electrc energy
Time Domain simulation of PD Propagation in XLPE Cables Considering Frequency Dependent Parameters
 Internatonal Journal of Smart Grd and Clean Energy Tme Doman smulaton of PD Propagaton n XLPE Cables Consderng Frequency Dependent Parameters We Zhang a, Jan He b, Ln Tan b, Xuejun Lv b, Hong-Je L a *
Internatonal Journal of Smart Grd and Clean Energy Tme Doman smulaton of PD Propagaton n XLPE Cables Consderng Frequency Dependent Parameters We Zhang a, Jan He b, Ln Tan b, Xuejun Lv b, Hong-Je L a *
CO2005: Electronics I (FET) Electronics I, Neamen 3th Ed. 1
 CO2005: Electronics I The Field-Effect Transistor (FET) Electronics I, Neamen 3th Ed. 1 MOSFET The metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) becomes a practical reality in the 1970s. The
CO2005: Electronics I The Field-Effect Transistor (FET) Electronics I, Neamen 3th Ed. 1 MOSFET The metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) becomes a practical reality in the 1970s. The
Lecture 9 - MOSFET (I) MOSFET I-V Characteristics. March 6, 2003
 6.12 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits - Spring 23 Lecture 9-1 Lecture 9 - MOSFET (I) MOSFET I-V Characteristics March 6, 23 Contents: 1. MOSFET: cross-section, layout, symbols 2. Qualitative operation
6.12 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits - Spring 23 Lecture 9-1 Lecture 9 - MOSFET (I) MOSFET I-V Characteristics March 6, 23 Contents: 1. MOSFET: cross-section, layout, symbols 2. Qualitative operation
Portfolio Loss Distribution
 Portfolo Loss Dstrbuton Rsky assets n loan ortfolo hghly llqud assets hold-to-maturty n the bank s balance sheet Outstandngs The orton of the bank asset that has already been extended to borrowers. Commtment
Portfolo Loss Dstrbuton Rsky assets n loan ortfolo hghly llqud assets hold-to-maturty n the bank s balance sheet Outstandngs The orton of the bank asset that has already been extended to borrowers. Commtment
Topical Workshop for PhD students Adsorption and Diffusion in MOFs Institut für Nichtklassische Chemie, Germany, www.uni-leipzig.
 Gas Separaton and Purfcaton Measurement of Breakthrough Curves Topcal Workshop for PhD students Adsorpton and Dffuson n MOFs Adsorpton on Surfaces / Separaton effects Useful features Thermodynamc effect
Gas Separaton and Purfcaton Measurement of Breakthrough Curves Topcal Workshop for PhD students Adsorpton and Dffuson n MOFs Adsorpton on Surfaces / Separaton effects Useful features Thermodynamc effect
EQUIVALENT ELECTRIC CIRCUIT MATLAB SIMULINK OF A BIFACIAL SOLAR CELL IN TRANSIENT STATE: APPLIED MAGNETIC FIELD EFFECT
 Journal des Scences EQUIVAENT EECTRIC CIRCUIT MATAB SIMUINK OF A BIFACIA SOAR CE IN TRANSIENT STATE: APPIED MAGNETIC FIED EFFECT S.MBODJI, A.Y DIAO, I. Y. F. I. BARRO, F. ZOUGMORE, G.SISSOKO (gsssoko@yahoo.com)
Journal des Scences EQUIVAENT EECTRIC CIRCUIT MATAB SIMUINK OF A BIFACIA SOAR CE IN TRANSIENT STATE: APPIED MAGNETIC FIED EFFECT S.MBODJI, A.Y DIAO, I. Y. F. I. BARRO, F. ZOUGMORE, G.SISSOKO (gsssoko@yahoo.com)
Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I-V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.)
 Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I-V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.) Outline 1. The saturation regime 2. Backgate characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Section 4.4 Announcements: 1. Quiz#1:
Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I-V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.) Outline 1. The saturation regime 2. Backgate characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Section 4.4 Announcements: 1. Quiz#1:
Quantization Effects in Digital Filters
 Quantzaton Effects n Dgtal Flters Dstrbuton of Truncaton Errors In two's complement representaton an exact number would have nfntely many bts (n general). When we lmt the number of bts to some fnte value
Quantzaton Effects n Dgtal Flters Dstrbuton of Truncaton Errors In two's complement representaton an exact number would have nfntely many bts (n general). When we lmt the number of bts to some fnte value
MOSFET DEVICE MODELING FOR ANALOG CIRCUITS DESIGN
 MOSFET DEVICE MODELING FOR ANALOG CIRCUITS DESIGN Student name: Truong, Long Giang Student #: 970304580 Course: ECE1352F 1. INTRODUCTION The technological trend towards deep sub-micrometer dimensions,
MOSFET DEVICE MODELING FOR ANALOG CIRCUITS DESIGN Student name: Truong, Long Giang Student #: 970304580 Course: ECE1352F 1. INTRODUCTION The technological trend towards deep sub-micrometer dimensions,
RESEARCH ON DUAL-SHAKER SINE VIBRATION CONTROL. Yaoqi FENG 1, Hanping QIU 1. China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) yaoqi.feng@yahoo.
 ICSV4 Carns Australa 9- July, 007 RESEARCH ON DUAL-SHAKER SINE VIBRATION CONTROL Yaoq FENG, Hanpng QIU Dynamc Test Laboratory, BISEE Chna Academy of Space Technology (CAST) yaoq.feng@yahoo.com Abstract
ICSV4 Carns Australa 9- July, 007 RESEARCH ON DUAL-SHAKER SINE VIBRATION CONTROL Yaoq FENG, Hanpng QIU Dynamc Test Laboratory, BISEE Chna Academy of Space Technology (CAST) yaoq.feng@yahoo.com Abstract
Chapter 10 Advanced CMOS Circuits
 Transmission Gates Chapter 10 Advanced CMOS Circuits NMOS Transmission Gate The active pull-up inverter circuit leads one to thinking about alternate uses of NMOS devices. Consider the circuit shown in
Transmission Gates Chapter 10 Advanced CMOS Circuits NMOS Transmission Gate The active pull-up inverter circuit leads one to thinking about alternate uses of NMOS devices. Consider the circuit shown in
Computational Fluid Dynamics II
 Computatonal Flud Dynamcs II Eercse 2 1. Gven s the PDE: u tt a 2 ou Formulate the CFL-condton for two possble eplct schemes. 2. The Euler equatons for 1-dmensonal, unsteady flows s dscretsed n the followng
Computatonal Flud Dynamcs II Eercse 2 1. Gven s the PDE: u tt a 2 ou Formulate the CFL-condton for two possble eplct schemes. 2. The Euler equatons for 1-dmensonal, unsteady flows s dscretsed n the followng
s-domain Circuit Analysis
 S-Doman naly -Doman rcut naly Tme doman t doman near rcut aplace Tranform omplex frequency doman doman Tranformed rcut Dfferental equaton lacal technque epone waveform aplace Tranform nvere Tranform -
S-Doman naly -Doman rcut naly Tme doman t doman near rcut aplace Tranform omplex frequency doman doman Tranformed rcut Dfferental equaton lacal technque epone waveform aplace Tranform nvere Tranform -
Comparison of Control Strategies for Shunt Active Power Filter under Different Load Conditions
 Comparson of Control Strateges for Shunt Actve Power Flter under Dfferent Load Condtons Sanjay C. Patel 1, Tushar A. Patel 2 Lecturer, Electrcal Department, Government Polytechnc, alsad, Gujarat, Inda
Comparson of Control Strateges for Shunt Actve Power Flter under Dfferent Load Condtons Sanjay C. Patel 1, Tushar A. Patel 2 Lecturer, Electrcal Department, Government Polytechnc, alsad, Gujarat, Inda
Chapter 8 Differential and Multistage Amplifiers. EE 3120 Microelectronics II
 1 Chapter 8 Differential and Multistage Amplifiers Operational Amplifier Circuit Components 2 1. Ch 7: Current Mirrors and Biasing 2. Ch 9: Frequency Response 3. Ch 8: Active-Loaded Differential Pair 4.
1 Chapter 8 Differential and Multistage Amplifiers Operational Amplifier Circuit Components 2 1. Ch 7: Current Mirrors and Biasing 2. Ch 9: Frequency Response 3. Ch 8: Active-Loaded Differential Pair 4.
5.74 Introductory Quantum Mechanics II
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mt.edu 5.74 Introductory Quantum Mechancs II Sprng 9 For nformaton about ctng these materals or our Terms of Use, vst: http://ocw.mt.edu/terms. 4-1 4.1. INTERACTION OF LIGHT
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mt.edu 5.74 Introductory Quantum Mechancs II Sprng 9 For nformaton about ctng these materals or our Terms of Use, vst: http://ocw.mt.edu/terms. 4-1 4.1. INTERACTION OF LIGHT
Bob York. Transistor Basics - MOSFETs
 Bob York Transistor Basics - MOSFETs Transistors, Conceptually So far we have considered two-terminal devices that are described by a current-voltage relationship I=f(V Resistors: Capacitors: Inductors:
Bob York Transistor Basics - MOSFETs Transistors, Conceptually So far we have considered two-terminal devices that are described by a current-voltage relationship I=f(V Resistors: Capacitors: Inductors:
Lecture 23 - Frequency Response of Amplifiers (I) Common-Source Amplifier. December 1, 2005
 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Fall 2005 Lecture 231 Lecture 23 Frequency Response of Amplifiers (I) CommonSource Amplifier December 1, 2005 Contents: 1. Introduction 2. Intrinsic frequency
6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Fall 2005 Lecture 231 Lecture 23 Frequency Response of Amplifiers (I) CommonSource Amplifier December 1, 2005 Contents: 1. Introduction 2. Intrinsic frequency
(6)(2) (-6)(-4) (-4)(6) + (-2)(-3) + (4)(3) + (2)(-3) = -12-24 + 24 + 6 + 12 6 = 0
 Chapter 3 Homework Soluton P3.-, 4, 6, 0, 3, 7, P3.3-, 4, 6, P3.4-, 3, 6, 9, P3.5- P3.6-, 4, 9, 4,, 3, 40 ---------------------------------------------------- P 3.- Determne the alues of, 4,, 3, and 6
Chapter 3 Homework Soluton P3.-, 4, 6, 0, 3, 7, P3.3-, 4, 6, P3.4-, 3, 6, 9, P3.5- P3.6-, 4, 9, 4,, 3, 40 ---------------------------------------------------- P 3.- Determne the alues of, 4,, 3, and 6
Rotation Kinematics, Moment of Inertia, and Torque
 Rotaton Knematcs, Moment of Inerta, and Torque Mathematcally, rotaton of a rgd body about a fxed axs s analogous to a lnear moton n one dmenson. Although the physcal quanttes nvolved n rotaton are qute
Rotaton Knematcs, Moment of Inerta, and Torque Mathematcally, rotaton of a rgd body about a fxed axs s analogous to a lnear moton n one dmenson. Although the physcal quanttes nvolved n rotaton are qute
Chapter 31B - Transient Currents and Inductance
 Chapter 31B - Transent Currents and Inductance A PowerPont Presentaton by Paul E. Tppens, Professor of Physcs Southern Polytechnc State Unversty 007 Objectves: After completng ths module, you should be
Chapter 31B - Transent Currents and Inductance A PowerPont Presentaton by Paul E. Tppens, Professor of Physcs Southern Polytechnc State Unversty 007 Objectves: After completng ths module, you should be
Simulating injection moulding of microfeatured components
 Smulatng njecton mouldng of mcrofeatured components T. Tofteberg 1 * and E. Andreassen 1 1 SINTEF Materals and Chemstry, Oslo, Norway terje.tofteberg@sntef.no; erk.andreassen@sntef.no Numercal smulaton
Smulatng njecton mouldng of mcrofeatured components T. Tofteberg 1 * and E. Andreassen 1 1 SINTEF Materals and Chemstry, Oslo, Norway terje.tofteberg@sntef.no; erk.andreassen@sntef.no Numercal smulaton
Jet Engine. Figure 1 Jet engine
 Jet Engne Prof. Dr. Mustafa Cavcar Anadolu Unversty, School of Cvl Avaton Esksehr, urkey GROSS HRUS INAKE MOMENUM DRAG NE HRUS Fgure 1 Jet engne he thrust for a turboet engne can be derved from Newton
Jet Engne Prof. Dr. Mustafa Cavcar Anadolu Unversty, School of Cvl Avaton Esksehr, urkey GROSS HRUS INAKE MOMENUM DRAG NE HRUS Fgure 1 Jet engne he thrust for a turboet engne can be derved from Newton
EE-612: Nanoscale Transistors (Advanced VLSI Devices) Spring 2005
 EE-612: Nanoscale Transistors (Advanced VLSI Devices) Spring 2005 Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA 765-494-3515 lundstro@purdue.edu 1 evolution
EE-612: Nanoscale Transistors (Advanced VLSI Devices) Spring 2005 Mark Lundstrom Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN USA 765-494-3515 lundstro@purdue.edu 1 evolution
AMPLIFIERS BJT BJT TRANSISTOR. Types of BJT BJT. devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level
 AMPLFERS Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Floyd devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level have at least three terminals with one controlling the flow between
AMPLFERS Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Electronic Devices by Floyd devices that increase the voltage, current, or power level have at least three terminals with one controlling the flow between
Correlated Noise Modeling - An Implementation into HICUM
 Correlated ose Modelng - An Implementaton nto HICUM A. Chakravorty, M. chroter, P. akalas, J. Herrcht Char for Electron Devces and Integrated Crcuts (CEDIC) Unversty of Technology Dresden Germany Dept.
Correlated ose Modelng - An Implementaton nto HICUM A. Chakravorty, M. chroter, P. akalas, J. Herrcht Char for Electron Devces and Integrated Crcuts (CEDIC) Unversty of Technology Dresden Germany Dept.
Chapter 12 Inductors and AC Circuits
 hapter Inductors and A rcuts awrence B. ees 6. You may make a sngle copy of ths document for personal use wthout wrtten permsson. Hstory oncepts from prevous physcs and math courses that you wll need for
hapter Inductors and A rcuts awrence B. ees 6. You may make a sngle copy of ths document for personal use wthout wrtten permsson. Hstory oncepts from prevous physcs and math courses that you wll need for
Transient Voltage Suppressor SMBJ5.0 - SMBJ440CA
 Features: Glass passivated junction Low incremental surge resistance, excellent clamping capability 600W peak pulse power capability with a 10/1,000μs waveform, repetition rate (duty cycle): 0.01% Very
Features: Glass passivated junction Low incremental surge resistance, excellent clamping capability 600W peak pulse power capability with a 10/1,000μs waveform, repetition rate (duty cycle): 0.01% Very
http://www.springer.com/0-387-25742-x
 http://www.sprnger.com/0-387-25742-x Chapter 2 FAULT AND FAULT MODELLING 2.1 Introducton The rse of system-on-chp (SOC) technology has dramatcally boosted the mportance of analog crcutry, movng t more
http://www.sprnger.com/0-387-25742-x Chapter 2 FAULT AND FAULT MODELLING 2.1 Introducton The rse of system-on-chp (SOC) technology has dramatcally boosted the mportance of analog crcutry, movng t more
Linear Circuits Analysis. Superposition, Thevenin /Norton Equivalent circuits
 Lnear Crcuts Analyss. Superposton, Theenn /Norton Equalent crcuts So far we hae explored tmendependent (resste) elements that are also lnear. A tmendependent elements s one for whch we can plot an / cure.
Lnear Crcuts Analyss. Superposton, Theenn /Norton Equalent crcuts So far we hae explored tmendependent (resste) elements that are also lnear. A tmendependent elements s one for whch we can plot an / cure.
Lecture 9 - MOSFET (I) MOSFET I-V Characteristics. October 6, 2005
 6.12 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits - Fall 25 Lecture 9-1 Lecture 9 - MOSFET (I) MOSFET I-V Characteristics October 6, 25 Contents: 1. MOSFET: cross-section, layout, symbols 2. Qualitative operation
6.12 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits - Fall 25 Lecture 9-1 Lecture 9 - MOSFET (I) MOSFET I-V Characteristics October 6, 25 Contents: 1. MOSFET: cross-section, layout, symbols 2. Qualitative operation
Analysis and Modeling of Buck Converter in Discontinuous-Output-Inductor-Current Mode Operation *
 Energy and Power Engneerng, 3, 5, 85-856 do:.436/ee.3.54b63 Publshed Onlne July 3 (htt://www.scr.org/journal/ee) Analyss and Modelng of Buck Converter n Dscontnuous-Outut-Inductor-Current Mode Oeraton
Energy and Power Engneerng, 3, 5, 85-856 do:.436/ee.3.54b63 Publshed Onlne July 3 (htt://www.scr.org/journal/ee) Analyss and Modelng of Buck Converter n Dscontnuous-Outut-Inductor-Current Mode Oeraton
Loudspeaker Voice-Coil Inductance Losses: Circuit Models, Parameter Estimation, and Effect on Frequency Response
 44 JOURAL OF THE AUDIO EGIEERIG SOCIETY, VOL. 50, O. 6, 00 JUE Loudspeaker Voce-Col Inductance Losses: Crcut Models, Parameter Estmaton, and Effect on Frequency Response W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor
44 JOURAL OF THE AUDIO EGIEERIG SOCIETY, VOL. 50, O. 6, 00 JUE Loudspeaker Voce-Col Inductance Losses: Crcut Models, Parameter Estmaton, and Effect on Frequency Response W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor
Lecture 3: Force of Interest, Real Interest Rate, Annuity
 Lecture 3: Force of Interest, Real Interest Rate, Annuty Goals: Study contnuous compoundng and force of nterest Dscuss real nterest rate Learn annuty-mmedate, and ts present value Study annuty-due, and
Lecture 3: Force of Interest, Real Interest Rate, Annuty Goals: Study contnuous compoundng and force of nterest Dscuss real nterest rate Learn annuty-mmedate, and ts present value Study annuty-due, and
OptiMOS Power-Transistor Product Summary
 OptiMOS Power-Transistor Product Summary V DS 55 V R DS(on),max 4) 35 mω Features Dual N-channel Logic Level - Enhancement mode AEC Q11 qualified I D 2 A PG-TDSON-8-4 MSL1 up to 26 C peak reflow 175 C
OptiMOS Power-Transistor Product Summary V DS 55 V R DS(on),max 4) 35 mω Features Dual N-channel Logic Level - Enhancement mode AEC Q11 qualified I D 2 A PG-TDSON-8-4 MSL1 up to 26 C peak reflow 175 C
NPAR TESTS. One-Sample Chi-Square Test. Cell Specification. Observed Frequencies 1O i 6. Expected Frequencies 1EXP i 6
 PAR TESTS If a WEIGHT varable s specfed, t s used to replcate a case as many tmes as ndcated by the weght value rounded to the nearest nteger. If the workspace requrements are exceeded and samplng has
PAR TESTS If a WEIGHT varable s specfed, t s used to replcate a case as many tmes as ndcated by the weght value rounded to the nearest nteger. If the workspace requrements are exceeded and samplng has
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 11 MOSFET part 2 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br I D -V DS Characteristics
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 11 MOSFET part 2 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br I D -V DS Characteristics
ESPOO 2005 VTT PUBLICATIONS 570. Kari J. Kataja. Numerical modelling of near field optical data storage
 ESPOO 005 VTT PUBLICATIONS 570 Kar J. Kataja Numercal modellng of near feld optcal data storage VTT PUBLICATIONS 570 Numercal modellng of near feld optcal data storage Kar J. Kataja VTT Electroncs Academc
ESPOO 005 VTT PUBLICATIONS 570 Kar J. Kataja Numercal modellng of near feld optcal data storage VTT PUBLICATIONS 570 Numercal modellng of near feld optcal data storage Kar J. Kataja VTT Electroncs Academc
Interlude: Interphase Mass Transfer
 Interlude: Interphase Mass Transfer The transport of mass wthn a sngle phase depends drectly on the concentraton gradent of the transportng speces n that phase. Mass may also transport from one phase to
Interlude: Interphase Mass Transfer The transport of mass wthn a sngle phase depends drectly on the concentraton gradent of the transportng speces n that phase. Mass may also transport from one phase to
Field-Effect (FET) transistors
 Field-Effect (FET) transistors References: Hayes & Horowitz (pp 142-162 and 244-266), Rizzoni (chapters 8 & 9) In a field-effect transistor (FET), the width of a conducting channel in a semiconductor and,
Field-Effect (FET) transistors References: Hayes & Horowitz (pp 142-162 and 244-266), Rizzoni (chapters 8 & 9) In a field-effect transistor (FET), the width of a conducting channel in a semiconductor and,
Design Issues for Low Power Integrated Thermal Flow Sensors with Ultra-Wide Dynamic Range and Low Insertion Loss
 Mcromachnes 01, 3, 95-314; do:10.3390/m30095 Artcle OPEN ACCESS mcromachnes ISSN 07-666X www.mdp.com/journal/mcromachnes Desgn Issues for Low Power Integrated Thermal Flow Sensors wth Ultra-Wde Dynamc
Mcromachnes 01, 3, 95-314; do:10.3390/m30095 Artcle OPEN ACCESS mcromachnes ISSN 07-666X www.mdp.com/journal/mcromachnes Desgn Issues for Low Power Integrated Thermal Flow Sensors wth Ultra-Wde Dynamc
I-V Characteristics of BJT Common-Emitter Output Characteristics
 I-V Characteristics of BJT Common-Emitter Output Characteristics C i C C i C B v CE B v EC i B E i B E Lecture 26 26-1 To illustrate the I C -V CE characteristics, we use an enlarged β R Collector Current
I-V Characteristics of BJT Common-Emitter Output Characteristics C i C C i C B v CE B v EC i B E i B E Lecture 26 26-1 To illustrate the I C -V CE characteristics, we use an enlarged β R Collector Current
Section 2 Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
 Secton 2 Introducton to Statstcal Mechancs 2.1 Introducng entropy 2.1.1 Boltzmann s formula A very mportant thermodynamc concept s that of entropy S. Entropy s a functon of state, lke the nternal energy.
Secton 2 Introducton to Statstcal Mechancs 2.1 Introducng entropy 2.1.1 Boltzmann s formula A very mportant thermodynamc concept s that of entropy S. Entropy s a functon of state, lke the nternal energy.
Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57]
![Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57] Fig6-22 CB configuration. Z i [6-54] Z o [6-55] A v [6-56] Assuming R E >> r e. A i [6-57]](/thumbs/40/21338705.jpg) Common-Base Configuration (CB) The CB configuration having a low input and high output impedance and a current gain less than 1, the voltage gain can be quite large, r o in MΩ so that ignored in parallel
Common-Base Configuration (CB) The CB configuration having a low input and high output impedance and a current gain less than 1, the voltage gain can be quite large, r o in MΩ so that ignored in parallel
UGF09030. 30W, 1 GHz, 26V Broadband RF Power N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Lateral MOSFET
 30W, 1 GHz, 26V Broadband RF Power N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Lateral MOSFET Designed for base station applications in the frequency band 800MHz to 1000MHz. Rated with a minimum output power of 30W, it
30W, 1 GHz, 26V Broadband RF Power N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Lateral MOSFET Designed for base station applications in the frequency band 800MHz to 1000MHz. Rated with a minimum output power of 30W, it
Derivation of Humidty and NOx Humidty Correction Factors
 (Ths document follows the presentatons n "Vapor Pressure Equaton for Water n the Range 0 to 00 C", by Arnold Wexler and Lews Greenspan, February 9, 97 JOURNAL OF RESEARCH of the Natonal Bureau of Standards
(Ths document follows the presentatons n "Vapor Pressure Equaton for Water n the Range 0 to 00 C", by Arnold Wexler and Lews Greenspan, February 9, 97 JOURNAL OF RESEARCH of the Natonal Bureau of Standards
CHOLESTEROL REFERENCE METHOD LABORATORY NETWORK. Sample Stability Protocol
 CHOLESTEROL REFERENCE METHOD LABORATORY NETWORK Sample Stablty Protocol Background The Cholesterol Reference Method Laboratory Network (CRMLN) developed certfcaton protocols for total cholesterol, HDL
CHOLESTEROL REFERENCE METHOD LABORATORY NETWORK Sample Stablty Protocol Background The Cholesterol Reference Method Laboratory Network (CRMLN) developed certfcaton protocols for total cholesterol, HDL
ALTRONIC 24VDC Al TERNATOR ENGINE DRIVEN POWER PACKAGES. INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS!FORM Al T H 2m01 1.0 DESCRIPTION
 ALTRONC 4VDC Al TERNATOR ENGNE DRVEN POWER PACKAGES NSTALLATON NSTRUCTONS!FORM Al T H m1 WARNNG: DEVATON FROM THESE NSTALLATON NSTRUCTONS MAY LEAD TO MPROPER ENGNE OPERATON WHCH COULD CAUSE PERSONAL NJURY
ALTRONC 4VDC Al TERNATOR ENGNE DRVEN POWER PACKAGES NSTALLATON NSTRUCTONS!FORM Al T H m1 WARNNG: DEVATON FROM THESE NSTALLATON NSTRUCTONS MAY LEAD TO MPROPER ENGNE OPERATON WHCH COULD CAUSE PERSONAL NJURY
MOSFET N-channel enhancement switching transistor IMPORTANT NOTICE. http://www.philips.semiconductors.com use http://www.nxp.com
 Rev. 3 21 November 27 Product data sheet Dear customer, IMPORTANT NOTICE As from October 1st, 26 Philips Semiconductors has a new trade name - NXP Semiconductors, which will be used in future data sheets
Rev. 3 21 November 27 Product data sheet Dear customer, IMPORTANT NOTICE As from October 1st, 26 Philips Semiconductors has a new trade name - NXP Semiconductors, which will be used in future data sheets
Realistic Image Synthesis
 Realstc Image Synthess - Combned Samplng and Path Tracng - Phlpp Slusallek Karol Myszkowsk Vncent Pegoraro Overvew: Today Combned Samplng (Multple Importance Samplng) Renderng and Measurng Equaton Random
Realstc Image Synthess - Combned Samplng and Path Tracng - Phlpp Slusallek Karol Myszkowsk Vncent Pegoraro Overvew: Today Combned Samplng (Multple Importance Samplng) Renderng and Measurng Equaton Random
Viscosity of Solutions of Macromolecules
 Vscosty of Solutons of Macromolecules When a lqud flows, whether through a tube or as the result of pourng from a vessel, layers of lqud slde over each other. The force f requred s drectly proportonal
Vscosty of Solutons of Macromolecules When a lqud flows, whether through a tube or as the result of pourng from a vessel, layers of lqud slde over each other. The force f requred s drectly proportonal
An Introduction to the EKV Model and a Comparison of EKV to BSIM
 An Introduction to the EKV Model and a Comparison of EKV to BSIM Stephen C. Terry 2. 3.2005 Integrated Circuits & Systems Laboratory 1 Overview Characterizing MOSFET operating regions EKV model fundamentals
An Introduction to the EKV Model and a Comparison of EKV to BSIM Stephen C. Terry 2. 3.2005 Integrated Circuits & Systems Laboratory 1 Overview Characterizing MOSFET operating regions EKV model fundamentals
Lecture 090 Large Signal MOSFET Model (3/24/10) Page 090-1
 Lecture 9 Large Signal MOSFET Model (3/24/1) Page 9-1 LECTURE 9 LARGE SIGNAL MOSFET MODEL LECTURE ORGANIZATION Outline Introduction to modeling Operation of the MOS transistor Simple large signal model
Lecture 9 Large Signal MOSFET Model (3/24/1) Page 9-1 LECTURE 9 LARGE SIGNAL MOSFET MODEL LECTURE ORGANIZATION Outline Introduction to modeling Operation of the MOS transistor Simple large signal model
CIRCUITS AND ELECTRONICS. Filters
 6.00 IUITS AND EETONIS Flters te as: Anant Agarwal and Jeffrey ang, course materals for 6.00 rcuts and Electroncs, Sprng 007. MIT 6.00 Fall 000 ecture 8 evew v I v c c c j j j eadng: Secton 4.5, 4.6, 5.3
6.00 IUITS AND EETONIS Flters te as: Anant Agarwal and Jeffrey ang, course materals for 6.00 rcuts and Electroncs, Sprng 007. MIT 6.00 Fall 000 ecture 8 evew v I v c c c j j j eadng: Secton 4.5, 4.6, 5.3
Lecture 3: Annuity. Study annuities whose payments form a geometric progression or a arithmetic progression.
 Lecture 3: Annuty Goals: Learn contnuous annuty and perpetuty. Study annutes whose payments form a geometrc progresson or a arthmetc progresson. Dscuss yeld rates. Introduce Amortzaton Suggested Textbook
Lecture 3: Annuty Goals: Learn contnuous annuty and perpetuty. Study annutes whose payments form a geometrc progresson or a arthmetc progresson. Dscuss yeld rates. Introduce Amortzaton Suggested Textbook
OptiMOS 3 Power-Transistor
 Type IPD36N4L G OptiMOS 3 Power-Transistor Features Fast switching MOSFET for SMPS Optimized technology for DC/DC converters Qualified according to JEDEC ) for target applications Product Summary V DS
Type IPD36N4L G OptiMOS 3 Power-Transistor Features Fast switching MOSFET for SMPS Optimized technology for DC/DC converters Qualified according to JEDEC ) for target applications Product Summary V DS
Recurrence. 1 Definitions and main statements
 Recurrence 1 Defntons and man statements Let X n, n = 0, 1, 2,... be a MC wth the state space S = (1, 2,...), transton probabltes p j = P {X n+1 = j X n = }, and the transton matrx P = (p j ),j S def.
Recurrence 1 Defntons and man statements Let X n, n = 0, 1, 2,... be a MC wth the state space S = (1, 2,...), transton probabltes p j = P {X n+1 = j X n = }, and the transton matrx P = (p j ),j S def.
QUANTIZATION. Outlines. Joseph RONSIN. Definition Scalar quantization. Vector quantization. Definition Distortion Non uniform quantization
 QUANTIZATION by Joseph RONSIN Outlnes Scalar quantzaton Dstorton Non unform quantzaton Vector quantzaton Quantzaton 3 : Dscretsaton of color space One value for a set of values on an nterval Defnng number
QUANTIZATION by Joseph RONSIN Outlnes Scalar quantzaton Dstorton Non unform quantzaton Vector quantzaton Quantzaton 3 : Dscretsaton of color space One value for a set of values on an nterval Defnng number
 C o a t i a n P u b l i c D e b tm a n a g e m e n t a n d C h a l l e n g e s o f M a k e t D e v e l o p m e n t Z a g e bo 8 t h A p i l 2 0 1 1 h t t pdd w w wp i j fp h D p u b l i c2 d e b td S t
C o a t i a n P u b l i c D e b tm a n a g e m e n t a n d C h a l l e n g e s o f M a k e t D e v e l o p m e n t Z a g e bo 8 t h A p i l 2 0 1 1 h t t pdd w w wp i j fp h D p u b l i c2 d e b td S t
Consider a 1-D stationary state diffusion-type equation, which we will call the generalized diffusion equation from now on:
 Chapter 1 Boundary value problems Numercal lnear algebra technques can be used for many physcal problems. In ths chapter we wll gve some examples of how these technques can be used to solve certan boundary
Chapter 1 Boundary value problems Numercal lnear algebra technques can be used for many physcal problems. In ths chapter we wll gve some examples of how these technques can be used to solve certan boundary
Reduced magnetohydrodynamic equations with coupled Alfvén and sound wave dynamics
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS 14, 10906 007 Reduced magnetohydrodynamc equatons wth coupled Alfvén and sound wave dynamcs R. E. Denton and B. Rogers Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Dartmouth College, Hanover,
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS 14, 10906 007 Reduced magnetohydrodynamc equatons wth coupled Alfvén and sound wave dynamcs R. E. Denton and B. Rogers Department of Physcs and Astronomy, Dartmouth College, Hanover,
where the coordinates are related to those in the old frame as follows.
 Chapter 2 - Cartesan Vectors and Tensors: Ther Algebra Defnton of a vector Examples of vectors Scalar multplcaton Addton of vectors coplanar vectors Unt vectors A bass of non-coplanar vectors Scalar product
Chapter 2 - Cartesan Vectors and Tensors: Ther Algebra Defnton of a vector Examples of vectors Scalar multplcaton Addton of vectors coplanar vectors Unt vectors A bass of non-coplanar vectors Scalar product
1 Battery Technology and Markets, Spring 2010 26 January 2010 Lecture 1: Introduction to Electrochemistry
 1 Battery Technology and Markets, Sprng 2010 Lecture 1: Introducton to Electrochemstry 1. Defnton of battery 2. Energy storage devce: voltage and capacty 3. Descrpton of electrochemcal cell and standard
1 Battery Technology and Markets, Sprng 2010 Lecture 1: Introducton to Electrochemstry 1. Defnton of battery 2. Energy storage devce: voltage and capacty 3. Descrpton of electrochemcal cell and standard
Calculating the high frequency transmission line parameters of power cables
 < ' Calculatng the hgh frequency transmsson lne parameters of power cables Authors: Dr. John Dcknson, Laboratory Servces Manager, N 0 RW E B Communcatons Mr. Peter J. Ncholson, Project Assgnment Manager,
< ' Calculatng the hgh frequency transmsson lne parameters of power cables Authors: Dr. John Dcknson, Laboratory Servces Manager, N 0 RW E B Communcatons Mr. Peter J. Ncholson, Project Assgnment Manager,
OptiMOS 3 Power-Transistor
 Type IPD6N3L G OptiMOS 3 Power-Transistor Features Fast switching MOSFET for SMPS Optimized technology for DC/DC converters Qualified according to JEDEC 1) for target applications Product Summary V DS
Type IPD6N3L G OptiMOS 3 Power-Transistor Features Fast switching MOSFET for SMPS Optimized technology for DC/DC converters Qualified according to JEDEC 1) for target applications Product Summary V DS
substances (among other variables as well). ( ) Thus the change in volume of a mixture can be written as
 Mxtures and Solutons Partal Molar Quanttes Partal molar volume he total volume of a mxture of substances s a functon of the amounts of both V V n,n substances (among other varables as well). hus the change
Mxtures and Solutons Partal Molar Quanttes Partal molar volume he total volume of a mxture of substances s a functon of the amounts of both V V n,n substances (among other varables as well). hus the change
BJT Circuit Configurations
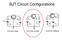 BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
BJT Circuit Configurations V be ~ ~ ~ v s R L v s R L V Vcc R s cc R s v s R s R L V cc Common base Common emitter Common collector Common emitter current gain BJT Current-Voltage Characteristics V CE,
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 15. BJT Structure and Fabrication
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 15 Lecture Outline Now move on to bipolar junction transistor (BJT) Strategy for next few lectures similar to diode: structure and processing, basic operation,
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 15 Lecture Outline Now move on to bipolar junction transistor (BJT) Strategy for next few lectures similar to diode: structure and processing, basic operation,
FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS. A Practical Guide for Actuaries. and other Business Professionals
 FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS A Practcal Gude for Actuares and other Busness Professonals Second Edton CHRIS RUCKMAN, FSA, MAAA JOE FRANCIS, FSA, MAAA, CFA Study Notes Prepared by Kevn Shand, FSA, FCIA Assstant
FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS A Practcal Gude for Actuares and other Busness Professonals Second Edton CHRIS RUCKMAN, FSA, MAAA JOE FRANCIS, FSA, MAAA, CFA Study Notes Prepared by Kevn Shand, FSA, FCIA Assstant
STANDING WAVE TUBE TECHNIQUES FOR MEASURING THE NORMAL INCIDENCE ABSORPTION COEFFICIENT: COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT EXPERIMENTAL SETUPS.
 STADIG WAVE TUBE TECHIQUES FOR MEASURIG THE ORMAL ICIDECE ABSORPTIO COEFFICIET: COMPARISO OF DIFFERET EXPERIMETAL SETUPS. Angelo Farna (*), Patrzo Faust (**) (*) Dpart. d Ing. Industrale, Unverstà d Parma,
STADIG WAVE TUBE TECHIQUES FOR MEASURIG THE ORMAL ICIDECE ABSORPTIO COEFFICIET: COMPARISO OF DIFFERET EXPERIMETAL SETUPS. Angelo Farna (*), Patrzo Faust (**) (*) Dpart. d Ing. Industrale, Unverstà d Parma,
Active Compensation of Transducer Nonlinearities
 Actve Compensaton of Transducer Nonlneartes Wolfgang Klppel Klppel GmbH, Dresden, 01277, Germany, www.klppel.de ABSTRACT Nonlneartes nherent n electromechancal and electroacoustcal transducers produce
Actve Compensaton of Transducer Nonlneartes Wolfgang Klppel Klppel GmbH, Dresden, 01277, Germany, www.klppel.de ABSTRACT Nonlneartes nherent n electromechancal and electroacoustcal transducers produce
Calculation of Sampling Weights
 Perre Foy Statstcs Canada 4 Calculaton of Samplng Weghts 4.1 OVERVIEW The basc sample desgn used n TIMSS Populatons 1 and 2 was a two-stage stratfed cluster desgn. 1 The frst stage conssted of a sample
Perre Foy Statstcs Canada 4 Calculaton of Samplng Weghts 4.1 OVERVIEW The basc sample desgn used n TIMSS Populatons 1 and 2 was a two-stage stratfed cluster desgn. 1 The frst stage conssted of a sample
Laddered Multilevel DC/AC Inverters used in Solar Panel Energy Systems
 Proceedngs of the nd Internatonal Conference on Computer Scence and Electroncs Engneerng (ICCSEE 03) Laddered Multlevel DC/AC Inverters used n Solar Panel Energy Systems Fang Ln Luo, Senor Member IEEE
Proceedngs of the nd Internatonal Conference on Computer Scence and Electroncs Engneerng (ICCSEE 03) Laddered Multlevel DC/AC Inverters used n Solar Panel Energy Systems Fang Ln Luo, Senor Member IEEE
IRF150 [REF:MIL-PRF-19500/543] 100V, N-CHANNEL. Absolute Maximum Ratings
![IRF150 [REF:MIL-PRF-19500/543] 100V, N-CHANNEL. Absolute Maximum Ratings IRF150 [REF:MIL-PRF-19500/543] 100V, N-CHANNEL. Absolute Maximum Ratings](/thumbs/40/21333646.jpg) PD - 90337G REPETITIVE AVALANCHE AND dv/dt RATED HEXFET TRANSISTORS THRU-HOLE (TO-204AA/AE) Product Summary Part Number BVDSS RDS(on) ID IRF150 100V 0.055Ω 38A IRF150 JANTX2N6764 JANTXV2N6764 [REF:MIL-PRF-19500/543]
PD - 90337G REPETITIVE AVALANCHE AND dv/dt RATED HEXFET TRANSISTORS THRU-HOLE (TO-204AA/AE) Product Summary Part Number BVDSS RDS(on) ID IRF150 100V 0.055Ω 38A IRF150 JANTX2N6764 JANTXV2N6764 [REF:MIL-PRF-19500/543]
Technical Note on the MTF of CCD Sensors
 Techncal Note on the MTF of CCD Sensors A unque MTF cannot be defned for a CCD usng the mathematcal structure of the classcal theory, whch s only applcable to lnearly and unformly respondng devces wth
Techncal Note on the MTF of CCD Sensors A unque MTF cannot be defned for a CCD usng the mathematcal structure of the classcal theory, whch s only applcable to lnearly and unformly respondng devces wth
Equivalent Electrical Simulation of High -Power Ultrasonic Piezoelectric Transducers by Using Finite Element Analysis
 Equvalent Electrcal Smulaton of Hgh -Power Ultrasonc Pezoelectrc Transducers by Usng Fnte Element Analyss Amr Abdullah 1, Abbas Pak, Alreza Shahd 3 1Department of Mechancal Engneerng, Amrkabr Unversty
Equvalent Electrcal Smulaton of Hgh -Power Ultrasonc Pezoelectrc Transducers by Usng Fnte Element Analyss Amr Abdullah 1, Abbas Pak, Alreza Shahd 3 1Department of Mechancal Engneerng, Amrkabr Unversty
Energy-balance and Sliding Mode Control Strategies of a Cascade H-Bridge Multilevel Converter for Grid-connected PV Systems
 Energy-balance and Sldng Mode Control Strateges of a Cascade H-Brdge Multlevel Converter for Grd-connected PV Systems Juan José Negron Domngo Bel Francesc Gunjoan Carlos Meza Unversdad Tecnológca Metropoltana,
Energy-balance and Sldng Mode Control Strateges of a Cascade H-Brdge Multlevel Converter for Grd-connected PV Systems Juan José Negron Domngo Bel Francesc Gunjoan Carlos Meza Unversdad Tecnológca Metropoltana,
We are now ready to answer the question: What are the possible cardinalities for finite fields?
 Chapter 3 Fnte felds We have seen, n the prevous chapters, some examples of fnte felds. For example, the resdue class rng Z/pZ (when p s a prme) forms a feld wth p elements whch may be dentfed wth the
Chapter 3 Fnte felds We have seen, n the prevous chapters, some examples of fnte felds. For example, the resdue class rng Z/pZ (when p s a prme) forms a feld wth p elements whch may be dentfed wth the
"Research Note" APPLICATION OF CHARGE SIMULATION METHOD TO ELECTRIC FIELD CALCULATION IN THE POWER CABLES *
 Iranan Journal of Scence & Technology, Transacton B, Engneerng, ol. 30, No. B6, 789-794 rnted n The Islamc Republc of Iran, 006 Shraz Unversty "Research Note" ALICATION OF CHARGE SIMULATION METHOD TO ELECTRIC
Iranan Journal of Scence & Technology, Transacton B, Engneerng, ol. 30, No. B6, 789-794 rnted n The Islamc Republc of Iran, 006 Shraz Unversty "Research Note" ALICATION OF CHARGE SIMULATION METHOD TO ELECTRIC
IRFP460LC PD - 9.1232. HEXFET Power MOSFET V DSS = 500V. R DS(on) = 0.27Ω I D = 20A
 HEXFET Power MOSFET PD - 9.232 IRFP460LC Ultra Low Gate Charge Reduced Gate Drive Requirement Enhanced 30V V gs Rating Reduced C iss, C oss, C rss Isolated Central Mounting Hole Dynamic dv/dt Rated Repetitive
HEXFET Power MOSFET PD - 9.232 IRFP460LC Ultra Low Gate Charge Reduced Gate Drive Requirement Enhanced 30V V gs Rating Reduced C iss, C oss, C rss Isolated Central Mounting Hole Dynamic dv/dt Rated Repetitive
How To Understand An Outut Stage
 CHATE 3 OUTUT STAGES AND OE AMFES Chapter Outline 3. Classificatin f Output Stages 3. Class A Output Stage 3.3 Class B Output Stage 3.4 Class AB Output Stage 3.5 Biasing the Class AB Circuit 3.6 CMOS Class
CHATE 3 OUTUT STAGES AND OE AMFES Chapter Outline 3. Classificatin f Output Stages 3. Class A Output Stage 3.3 Class B Output Stage 3.4 Class AB Output Stage 3.5 Biasing the Class AB Circuit 3.6 CMOS Class
SIMULATION OF THERMAL AND CHEMICAL RELAXATION IN A POST-DISCHARGE AIR CORONA REACTOR
 XVIII Internatonal Conference on Gas Dscharges and Ther Applcatons (GD 2010) Grefswald - Germany SIMULATION OF THERMAL AND CHEMICAL RELAXATION IN A POST-DISCHARGE AIR CORONA REACTOR M. Mezane, J.P. Sarrette,
XVIII Internatonal Conference on Gas Dscharges and Ther Applcatons (GD 2010) Grefswald - Germany SIMULATION OF THERMAL AND CHEMICAL RELAXATION IN A POST-DISCHARGE AIR CORONA REACTOR M. Mezane, J.P. Sarrette,
