Transmission Line Equations
|
|
|
- Juliana Hollie Jacobs
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Transmission Line Equations A typical engineering problem involves the transmission of a signal from a generator to a load. A transmission line is the part of the circuit that provides the direct link between generator and load. Transmission lines can be realized in a number of ways. Common examples are the parallel-wire line and the coaxial cable. For simplicity, we use in most diagrams the parallel-wire line to represent circuit connections, but the theory applies to all types of transmission lines. Generator Load V G Z G Transmission line Z R Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 39
2 Examples of transmission lines d d D d Two-wire line D Coaxial cable w t h Microstrip Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 40
3 If you are only familiar with low frequency circuits, you are used to treat all lines connecting the various circuit elements as perfect wires, with no voltage drop and no impedance associated to them (lumped impedance circuits). This is a reasonable procedure as long as the length of the wires is much smaller than the wavelength of the signal. At any given time, the measured voltage and current are the same for each location on the same wire. Generator Load Z G V G V R V R V R Z R V V Z Z Z R R = G G + R L << λ Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 41
4 Let s look at some examples. The electricity supplied to households consists of high power sinusoidal signals, with frequency of 60Hz or 50Hz, depending on the country. Assuming that the insulator between wires is air (ε ε 0 ), the wavelength for 60Hz is: 8 c λ= = m= 5, 000 f 60 km which is the about the distance between S. Francisco and Boston! Let s compare to a frequency in the microwave range, for instance 60 GHz. The wavelength is given by 8 c λ= = m= 5.0 f mm which is comparable to the size of a microprocessor chip. Which conclusions do you draw? Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 42
5 For sufficiently high frequencies the wavelength is comparable with the length of conductors in a transmission line. The signal propagates as a wave of voltage and current along the line, because it cannot change instantaneously at all locations. Therefore, we cannot neglect the impedance properties of the wires (distributed impedance circuits). Generator + jβz jβz V(z) = V e + V e Load Z G V G V( 0 ) V( z ) V( L ) Z R L Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 43
6 Note that the equivalent circuit of a generator consists of an ideal alternating voltage generator in series with its actual internal impedance. When the generator is open ( ZR ) we have: I = = in 0 and Vin VG If the generator is connected to a load I V in in = = G ( Z + Z ) G V G ( Z + Z ) G V Z R R R If the load is a short ( Z R = 0) V I G in = and Vin = Z G 0 Z R V G Z G Generator V in I in Z R Load Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 44
7 The simplest circuit problem that we can study consists of a voltage generator connected to a load through a uniform transmission line. In general, the impedance seen by the generator is not the same as the impedance of the load, because of the presence of the transmission line, except for some very particular cases: Z in = ZR Z in only if λ L= n = 2 [ n integer ] Transmission line L Z R Our first goal is to determine the equivalent impedance seen by the generator, that is, the input impedance of a line terminated by the load. Once that is known, standard circuit theory can be used. Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 45
8 Generator Z G Load V G Transmission line Z R Generator Z G Equivalent Load V G Z in Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 46
9 A uniform transmission line is a distributed circuit that we can describe as a cascade of identical cells with infinitesimal length. The conductors used to realize the line possess a certain series inductance and resistance. In addition, there is a shunt capacitance between the conductors, and even a shunt conductance if the medium insulating the wires is not perfect. We use the concept of shunt conductance, rather than resistance, because it is more convenient for adding the parallel elements of the shunt. We can represent the uniform transmission line with the distributed circuit below (general lossy line) L R L R C G C G Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 47
10 The impedance parameters L, R, C, and G represent: L = series inductance per unit length R = series resistance per unit length C = shunt capacitance per unit length G = shunt conductance per unit length. Each cell of the distributed circuit will have impedance elements with values: L, R, C, and G, where is the infinitesimal length of the cells. If we can determine the differential behavior of an elementary cell of the distributed circuit, in terms of voltage and current, we can find a global differential equation that describes the entire transmission line. We can do so, because we assume the line to be uniform along its length. So, all we need to do is to study how voltage and current vary in a single elementary cell of the distributed circuit. Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 48
11 Loss-less Transmission Line In many cases, it is possible to neglect resistive effects in the line. In this approximation there is no Joule effect loss because only reactive elements are present. The equivalent circuit for the elementary cell of a loss-less transmission line is shown in the figure below. I (z) L I (z)+di V (z) C V (z)+dv Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 49
12 The series inductance determines the variation of the voltage from input to output of the cell, according to the sub-circuit below L V (z) I (z) V (z)+dv The corresponding circuit equation is ( V+ d V) V = jω L I which gives a first order differential equation for the voltage dv = jω L I Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 50
13 The current flowing through the shunt capacitance determines the variation of the current from input to output of the cell. I (z) C di I (z)+di V (z)+dv The circuit equation for the sub-circuit above is di = jω C( V+ d V) = jωcv jω CdV The second term (including dv ) tends to zero very rapidly in the limit of infinitesimal length leaving a first order differential equation for the current di = jω CV Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 51
14 We have obtained a system of two coupled first order differential equations that describe the behavior of voltage and current on the uniform loss-less transmission line. The equations must be solved simultaneously. dv = jωl I di = jωcv These are often called telegraphers equations of the loss-less transmission line. Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 52
15 One can easily obtain a set of uncoupled equations by differentiating with respect to the space coordinate. The first order differential terms are eliminated by using the corresponding telegraphers equation d 2 d 2 V 2 I 2 di = jω CV di 2 = jω L = jωl jω CV= ω LCV dv 2 = jω C = jωc jω L I= ω LC I dv = jω L I These are often called telephonists equations. Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 53
16 We have now two uncoupled second order differential equations for voltage and current, which give an equivalent description of the loss-less transmission line. Mathematically, these are wave equations and can be solved independently. The general solution for the voltage equation is + jβz jβz V(z) = V e + V e where the wave propagation constant is β=ω LC Note that the complex exponential terms including β have unitary magnitude and purely imaginary argument, therefore they only affect the phase of the wave in space. Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 54
17 We have the following useful relations: 2π 2π f ω β= = = λ v v v p p ω ε r µ = r =ω ε 0 µ 0 ε r µ r =ω εµ c f Here, λ= p is the wavelength of the dielectric medium surrounding the conductors of the transmission line and 1 1 v p = = ε ε µ µ εµ 0 r 0 is the phase velocity of an electromagnetic wave in the dielectric. As you can see, the propagation constant β can be written in many different, equivalent ways. r Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 55
18 The current distribution on the transmission line can be readily obtained by differentiation of the result for the voltage dv + jβz jβz = jβ V e + jβ V e = jω L I which gives C 1 I(z) = V e V e = V e V e L Z The real quantity ( + jβz jβ z) ( + jβz jβz) 0 Z 0 = L C is the characteristic impedance of the loss-less transmission line. Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 56
19 Lossy Transmission Line The solution for a uniform lossy transmission line can be obtained with a very similar procedure, using the equivalent circuit for the elementary cell shown in the figure below. I (z) L R I (z)+di V (z) C G V (z)+dv Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 57
20 The series impedance determines the variation of the voltage from input to output of the cell, according to the sub-circuit L R V (z) I (z) V (z)+dv The corresponding circuit equation is ( V+ d V) V = ( jω L + R) I from which we obtain a first order differential equation for the voltage dv = ( jω L+ R) I Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 58
21 The current flowing through the shunt admittance determines the input-output variation of the current, according to the sub-circuit I (z) di I (z)+di C G V (z)+dv The corresponding circuit equation is d I = ( jω C + G)( V+ d V) = ( jω C+ G) V ( jω C+ G)dV The second term (including dv ) can be ignored, giving a first order differential equation for the current di = ( jω C+ G) V Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 59
22 We have again a system of coupled first order differential equations that describe the behavior of voltage and current on the lossy transmission line dv = ( jω L+ R) I di = ( jω C+ G) V These are the telegraphers equations for the lossy transmission line case. Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 60
23 One can easily obtain a set of uncoupled equations by differentiating with respect to the coordinate z as done earlier d 2 d 2 V 2 I 2 di = ( jω C+ G) V di = ( jω L+ R) = ( jω L+ R)( jω C+ G) V dv = ( jω C+ G) = ( jω C+ G)( jω L+ R) I dv = ( jω L+ R) I These are the telephonists equations for the lossy line. Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 61
24 The telephonists equations for the lossy transmission line are uncoupled second order differential equations and are again wave equations. The general solution for the voltage equation is + γz γ z + αz jβ z αz jβ z V(z) = V e + V e = V e e + V e e where the wave propagation constant is now the complex quantity γ= ( jω L+ R)( jω C+ G) =α+ jβ The real part α of the propagation constant γ describes the attenuation of the signal due to resistive losses. The imaginary part β describes the propagation properties of the signal waves as in loss-less lines. The exponential terms including α are real, therefore, they only affect the magnitude of the voltage phasor. The exponential terms including β have unitary magnitude and purely imaginary argument, affecting only the phase of the waves in space. Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 62
25 The current distribution on a lossy transmission line can be readily obtained by differentiation of the result for the voltage which gives dv + γz γz = ( jω L+ R) I = γ V e +γ V e ( jω C+ G) + γz γz I(z) = ( V e V e ) ( jω L+ R) 1 ( + γz γz V e V e ) 0 = Z with the characteristic impedance of the lossy transmission line Z 0 = ( jω L+ R) ( jω C+ G) Note: the characteristic impedance is now complex! Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 63
26 For both loss-less and lossy transmission lines the characteristic impedance does not depend on the line length but only on the metal of the conductors, the dielectric material surrounding the conductors and the geometry of the line crosssection, which determine L, R, C, and G. One must be careful not to interpret the characteristic impedance as some lumped impedance that can replace the transmission line in an equivalent circuit. This is a very common mistake! Z 0 Z R Z 0 Z R Amanogawa, 2006 Digital Maestro Series 64
Transmission Lines. Smith Chart
 Smith Chart The Smith chart is one of the most useful graphical tools for high frequency circuit applications. The chart provides a clever way to visualize complex functions and it continues to endure
Smith Chart The Smith chart is one of the most useful graphical tools for high frequency circuit applications. The chart provides a clever way to visualize complex functions and it continues to endure
PHY3128 / PHYM203 (Electronics / Instrumentation) Transmission Lines. Repeated n times I L
 Transmission Lines Introduction A transmission line guides energy from one place to another. Optical fibres, waveguides, telephone lines and power cables are all electromagnetic transmission lines. are
Transmission Lines Introduction A transmission line guides energy from one place to another. Optical fibres, waveguides, telephone lines and power cables are all electromagnetic transmission lines. are
A wave lab inside a coaxial cable
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Eur. J. Phys. 25 (2004) 581 591 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS PII: S0143-0807(04)76273-X A wave lab inside a coaxial cable JoãoMSerra,MiguelCBrito,JMaiaAlves and A M Vallera
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Eur. J. Phys. 25 (2004) 581 591 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICS PII: S0143-0807(04)76273-X A wave lab inside a coaxial cable JoãoMSerra,MiguelCBrito,JMaiaAlves and A M Vallera
L stub Z A = Z 0 Z R Z 0S. Single stub impedance matching
 Single stub impedance matching Impedance matching can be achieved by inserting another transmission line (stub) as shown in the diagram below Z A = Z 0 Z 0 Z R Z 0S d stub L stub Amanogawa, 006 Digital
Single stub impedance matching Impedance matching can be achieved by inserting another transmission line (stub) as shown in the diagram below Z A = Z 0 Z 0 Z R Z 0S d stub L stub Amanogawa, 006 Digital
RLC Resonant Circuits
 C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
C esonant Circuits Andrew McHutchon April 20, 203 Capacitors and Inductors There is a lot of inconsistency when it comes to dealing with reactances of complex components. The format followed in this document
Digital Systems Ribbon Cables I CMPE 650. Ribbon Cables A ribbon cable is any cable having multiple conductors bound together in a flat, wide strip.
 Ribbon Cables A ribbon cable is any cable having multiple conductors bound together in a flat, wide strip. Each dielectric configuration has different high-frequency characteristics. All configurations
Ribbon Cables A ribbon cable is any cable having multiple conductors bound together in a flat, wide strip. Each dielectric configuration has different high-frequency characteristics. All configurations
Determining wave propagation characteristics of MV XLPE power cable using time domain reflectometry technique
 Turk J Elec Eng & Comp Sci, Vol.19, No.2, 2011, c TÜBİTAK doi:10.3906/elk-1001-371 Determining wave propagation characteristics of MV XLPE power cable using time domain reflectometry technique Ghulam Murtaza
Turk J Elec Eng & Comp Sci, Vol.19, No.2, 2011, c TÜBİTAK doi:10.3906/elk-1001-371 Determining wave propagation characteristics of MV XLPE power cable using time domain reflectometry technique Ghulam Murtaza
Eatman Associates 2014 Rockwall TX 800-388-4036 rev. October 1, 2014. Striplines and Microstrips (PCB Transmission Lines)
 Eatman Associates 2014 Rockwall TX 800-388-4036 rev. October 1, 2014 Striplines and Microstrips (PCB Transmission Lines) Disclaimer: This presentation is merely a compilation of information from public
Eatman Associates 2014 Rockwall TX 800-388-4036 rev. October 1, 2014 Striplines and Microstrips (PCB Transmission Lines) Disclaimer: This presentation is merely a compilation of information from public
DRAFT. University of Pennsylvania Moore School of Electrical Engineering ESE319 Electronic Circuits - Modeling and Measurement Techniques
 University of Pennsylvania Moore School of Electrical Engineering ESE319 Electronic Circuits - Modeling and Measurement Techniques 1. Introduction. Students are often frustrated in their attempts to execute
University of Pennsylvania Moore School of Electrical Engineering ESE319 Electronic Circuits - Modeling and Measurement Techniques 1. Introduction. Students are often frustrated in their attempts to execute
Three phase circuits
 Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
Three phase circuits THREE PHASE CIRCUITS THREE-PHASE ADVANTAGES 1. The horsepower rating of three-phase motors and the kva rating of three-phase transformers are 150% greater than single-phase motors
G019.A (4/99) UNDERSTANDING COMMON MODE NOISE
 UNDERSTANDING COMMON MODE NOISE PAGE 2 OF 7 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION 2 DIFFERENTIAL MODE AND COMMON MODE SIGNALS 2.1 Differential Mode signals 2.2 Common Mode signals 3 DIFFERENTIAL AND COMMON
UNDERSTANDING COMMON MODE NOISE PAGE 2 OF 7 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION 2 DIFFERENTIAL MODE AND COMMON MODE SIGNALS 2.1 Differential Mode signals 2.2 Common Mode signals 3 DIFFERENTIAL AND COMMON
Impedance Matching and Matching Networks. Valentin Todorow, December, 2009
 Impedance Matching and Matching Networks Valentin Todorow, December, 2009 RF for Plasma Processing - Definition of RF What is RF? The IEEE Standard Dictionary of Electrical and Electronics Terms defines
Impedance Matching and Matching Networks Valentin Todorow, December, 2009 RF for Plasma Processing - Definition of RF What is RF? The IEEE Standard Dictionary of Electrical and Electronics Terms defines
IFI5481: RF Circuits, Theory and Design
 IFI5481: RF Circuits, Theory and Design Lecturer: Prof. Tor A. Fjeldly, UiO og NTNU/UNIK [torfj@unik.no] Assistant: Malihe Zarre Dooghabadi [malihezd@ifi.uio.no] Syllabus: Lectured material and examples,
IFI5481: RF Circuits, Theory and Design Lecturer: Prof. Tor A. Fjeldly, UiO og NTNU/UNIK [torfj@unik.no] Assistant: Malihe Zarre Dooghabadi [malihezd@ifi.uio.no] Syllabus: Lectured material and examples,
Modeling of Transmission Lines
 Modeling of Transmission Lines Electric Power Transmission The electric energy produced at generating stations is transported over high-voltage transmission lines to utilization points. The trend toward
Modeling of Transmission Lines Electric Power Transmission The electric energy produced at generating stations is transported over high-voltage transmission lines to utilization points. The trend toward
Transmission Line Transformers
 Radio Frequency Circuit Design. W. Alan Davis, Krishna Agarwal Copyright 2001 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Print ISBN 0-471-35052-4 Electronic ISBN 0-471-20068-9 CHAPTER SIX Transmission Line Transformers 6.1
Radio Frequency Circuit Design. W. Alan Davis, Krishna Agarwal Copyright 2001 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Print ISBN 0-471-35052-4 Electronic ISBN 0-471-20068-9 CHAPTER SIX Transmission Line Transformers 6.1
The Critical Length of a Transmission Line
 Page 1 of 9 The Critical Length of a Transmission Line Dr. Eric Bogatin President, Bogatin Enterprises Oct 1, 2004 Abstract A transmission line is always a transmission line. However, if it is physically
Page 1 of 9 The Critical Length of a Transmission Line Dr. Eric Bogatin President, Bogatin Enterprises Oct 1, 2004 Abstract A transmission line is always a transmission line. However, if it is physically
APPLICATION NOTES POWER DIVIDERS. Things to consider
 Internet Copy Rev A Overview Various RF applications require power to be distributed among various paths. The simplest way this can be done is by using a power splitter/divider. Power dividers are reciprocal
Internet Copy Rev A Overview Various RF applications require power to be distributed among various paths. The simplest way this can be done is by using a power splitter/divider. Power dividers are reciprocal
Critical thin-film processes such as deposition and etching take place in a vacuum
 WHITEPAPER INTRODUCING POWER SUPPLIES AND PLASMA Critical thin-film processes such as deposition and etching take place in a vacuum SYSTEMS chamber in the presence of a plasma. A plasma is an electrically
WHITEPAPER INTRODUCING POWER SUPPLIES AND PLASMA Critical thin-film processes such as deposition and etching take place in a vacuum SYSTEMS chamber in the presence of a plasma. A plasma is an electrically
Agilent De-embedding and Embedding S-Parameter Networks Using a Vector Network Analyzer. Application Note 1364-1
 Agilent De-embedding and Embedding S-Parameter Networks Using a Vector Network Analyzer Application Note 1364-1 Introduction Traditionally RF and microwave components have been designed in packages with
Agilent De-embedding and Embedding S-Parameter Networks Using a Vector Network Analyzer Application Note 1364-1 Introduction Traditionally RF and microwave components have been designed in packages with
Cable Solutions for Servo and Variable Frequency Drives (VFD)
 Cable Solutions for Servo and Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) Electric drive systems with continuous torque and speed control are widespread today. They allow an optimal adjustment of the drive with respect
Cable Solutions for Servo and Variable Frequency Drives (VFD) Electric drive systems with continuous torque and speed control are widespread today. They allow an optimal adjustment of the drive with respect
EMI and t Layout Fundamentals for Switched-Mode Circuits
 v sg (t) (t) DT s V pp = n - 1 2 V pp V g n V T s t EE core insulation primary return secondary return Supplementary notes on EMI and t Layout Fundamentals for Switched-Mode Circuits secondary primary
v sg (t) (t) DT s V pp = n - 1 2 V pp V g n V T s t EE core insulation primary return secondary return Supplementary notes on EMI and t Layout Fundamentals for Switched-Mode Circuits secondary primary
WAVEGUIDE-COAXIAL LINE TRANSITIONS
 WAVEGUIDE-COAXIAL LINE TRANSITIONS 1. Overview Equipment at microwave frequencies is usually based on a combination of PCB and waveguide components. Filters and antennas often use waveguide techniques,
WAVEGUIDE-COAXIAL LINE TRANSITIONS 1. Overview Equipment at microwave frequencies is usually based on a combination of PCB and waveguide components. Filters and antennas often use waveguide techniques,
Chapter 10. RC Circuits ISU EE. C.Y. Lee
 Chapter 10 RC Circuits Objectives Describe the relationship between current and voltage in an RC circuit Determine impedance and phase angle in a series RC circuit Analyze a series RC circuit Determine
Chapter 10 RC Circuits Objectives Describe the relationship between current and voltage in an RC circuit Determine impedance and phase angle in a series RC circuit Analyze a series RC circuit Determine
LOW COST MOTOR PROTECTION FILTERS FOR PWM DRIVE APPLICATIONS STOPS MOTOR DAMAGE
 LOW COST MOTOR PROTECTION FILTERS FOR PWM DRIVE APPLICATIONS STOPS MOTOR DAMAGE Karl M. Hink, Executive Vice President Originally presented at the Power Quality 99 Conference ABSTRACT Motor protection
LOW COST MOTOR PROTECTION FILTERS FOR PWM DRIVE APPLICATIONS STOPS MOTOR DAMAGE Karl M. Hink, Executive Vice President Originally presented at the Power Quality 99 Conference ABSTRACT Motor protection
Current and Temperature Ratings
 Document 361-1 Current and Temperature Ratings Introduction This application note describes: How to interpret Coilcraft inductor current and temperature ratings Our current ratings measurement method and
Document 361-1 Current and Temperature Ratings Introduction This application note describes: How to interpret Coilcraft inductor current and temperature ratings Our current ratings measurement method and
Antennas. Antennas are transducers that transfer electromagnetic energy between a transmission line and free space. Electromagnetic Wave
 Antennas Transmitter I Transmitting Antenna Transmission Line Electromagnetic Wave I Receiver I Receiving Antenna Transmission Line Electromagnetic Wave I Antennas are transducers that transfer electromagnetic
Antennas Transmitter I Transmitting Antenna Transmission Line Electromagnetic Wave I Receiver I Receiving Antenna Transmission Line Electromagnetic Wave I Antennas are transducers that transfer electromagnetic
Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement. 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits. Experiment no 1
 Experiment no 1 Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits Let v = m cos(ωt) = cos(ωt) is the voltage applied to a R-L circuit and i =
Experiment no 1 Power measurement in balanced 3 phase circuits and power factor improvement 1 Power in Single Phase Circuits Let v = m cos(ωt) = cos(ωt) is the voltage applied to a R-L circuit and i =
Mode Patterns of Parallel plates &Rectangular wave guides Mr.K.Chandrashekhar, Dr.Girish V Attimarad
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 8, August-2012 1 Mode Patterns of Parallel plates &Rectangular wave guides Mr.K.Chandrashekhar, Dr.Girish V Attimarad Abstract-Parallel
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 8, August-2012 1 Mode Patterns of Parallel plates &Rectangular wave guides Mr.K.Chandrashekhar, Dr.Girish V Attimarad Abstract-Parallel
High Voltage Transient Analysis
 High Voltage Transient Analysis 4. Surges on Transmission Lines Due to a variety of reasons, such as a direct stroke of lightning on the line, or by indirect strokes, or by switching operations or by faults,
High Voltage Transient Analysis 4. Surges on Transmission Lines Due to a variety of reasons, such as a direct stroke of lightning on the line, or by indirect strokes, or by switching operations or by faults,
2/20/2009 3 Transmission Lines and Waveguides.doc 1/3. and Waveguides. Transmission Line A two conductor structure that can support a TEM wave.
 2/20/2009 3 Transmission Lines and Waveguides.doc 1/3 Chapter 3 Transmission Lines and Waveguides First, some definitions: Transmission Line A two conductor structure that can support a TEM wave. Waveguide
2/20/2009 3 Transmission Lines and Waveguides.doc 1/3 Chapter 3 Transmission Lines and Waveguides First, some definitions: Transmission Line A two conductor structure that can support a TEM wave. Waveguide
An equivalent circuit of a loop antenna.
 3.2.1. Circuit Modeling: Loop Impedance A loop antenna can be represented by a lumped circuit when its dimension is small with respect to a wavelength. In this representation, the circuit parameters (generally
3.2.1. Circuit Modeling: Loop Impedance A loop antenna can be represented by a lumped circuit when its dimension is small with respect to a wavelength. In this representation, the circuit parameters (generally
Connectivity in a Wireless World. Cables Connectors 2014. A Special Supplement to
 Connectivity in a Wireless World Cables Connectors 204 A Special Supplement to Signal Launch Methods for RF/Microwave PCBs John Coonrod Rogers Corp., Chandler, AZ COAX CABLE MICROSTRIP TRANSMISSION LINE
Connectivity in a Wireless World Cables Connectors 204 A Special Supplement to Signal Launch Methods for RF/Microwave PCBs John Coonrod Rogers Corp., Chandler, AZ COAX CABLE MICROSTRIP TRANSMISSION LINE
Engineering Sciences 151. Electromagnetic Communication Laboratory Assignment 3 Fall Term 1998-99
 Engineering Sciences 151 Electromagnetic Communication Laboratory Assignment 3 Fall Term 1998-99 WAVE PROPAGATION II: HIGH FREQUENCY SLOTTED LINE AND REFLECTOMETER MEASUREMENTS OBJECTIVES: To build greater
Engineering Sciences 151 Electromagnetic Communication Laboratory Assignment 3 Fall Term 1998-99 WAVE PROPAGATION II: HIGH FREQUENCY SLOTTED LINE AND REFLECTOMETER MEASUREMENTS OBJECTIVES: To build greater
Chapter 11. Inductors ISU EE. C.Y. Lee
 Chapter 11 Inductors Objectives Describe the basic structure and characteristics of an inductor Discuss various types of inductors Analyze series inductors Analyze parallel inductors Analyze inductive
Chapter 11 Inductors Objectives Describe the basic structure and characteristics of an inductor Discuss various types of inductors Analyze series inductors Analyze parallel inductors Analyze inductive
An Overview of Practical Capacitance Bridge Functioning. by Paul Moses
 An Overview of Practical Capacitance Bridge Functioning by Paul Moses INTRODUCTION The laboratory has a variety of bridges, both automatic and manual which can be used to measure the capacitance and dielectric
An Overview of Practical Capacitance Bridge Functioning by Paul Moses INTRODUCTION The laboratory has a variety of bridges, both automatic and manual which can be used to measure the capacitance and dielectric
Transmission-Line Essentials for Digital Electronics
 Transmission-Line Essentials for Digital Electronics Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University EM II / Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu 1 Introduction 6.1 Transmission
Transmission-Line Essentials for Digital Electronics Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University EM II / Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu 1 Introduction 6.1 Transmission
PHY114 S11 Term Exam 3
 PHY4 S Term Exam S. G. Rajeev Mar 2 20 2:0 pm to :45 pm PLEASE write your workshop number and your workshop leader s name at the top of your book, so that you can collect your graded exams at the workshop.
PHY4 S Term Exam S. G. Rajeev Mar 2 20 2:0 pm to :45 pm PLEASE write your workshop number and your workshop leader s name at the top of your book, so that you can collect your graded exams at the workshop.
Oscar E. Morel UtilX Corporation
 Oscar E. Morel UtilX Corporation Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) has been the preferred technique to assess: Cable length Splice number and spatial location, and Metallic neutral condition Tests for neutral
Oscar E. Morel UtilX Corporation Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) has been the preferred technique to assess: Cable length Splice number and spatial location, and Metallic neutral condition Tests for neutral
Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007
 [ Assignment View ] [ Print ] Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 30. Inductance Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, March 14, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after the deadline has
[ Assignment View ] [ Print ] Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 30. Inductance Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, March 14, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after the deadline has
Understanding SWR by Example
 Understanding SWR by Example Take the mystery and mystique out of standing wave ratio. Darrin Walraven, K5DVW It sometimes seems that one of the most mysterious creatures in the world of Amateur Radio
Understanding SWR by Example Take the mystery and mystique out of standing wave ratio. Darrin Walraven, K5DVW It sometimes seems that one of the most mysterious creatures in the world of Amateur Radio
Fundamentals of Electromagnetic Fields and Waves: I
 Fundamentals of Electromagnetic Fields and Waves: I Fall 2007, EE 30348, Electrical Engineering, University of Notre Dame Mid Term II: Solutions Please show your steps clearly and sketch figures wherever
Fundamentals of Electromagnetic Fields and Waves: I Fall 2007, EE 30348, Electrical Engineering, University of Notre Dame Mid Term II: Solutions Please show your steps clearly and sketch figures wherever
Alternating Current and Direct Current
 K Hinds 2012 1 Alternating Current and Direct Current Direct Current This is a Current or Voltage which has a constant polarity. That is, either a positive or negative value. K Hinds 2012 2 Alternating
K Hinds 2012 1 Alternating Current and Direct Current Direct Current This is a Current or Voltage which has a constant polarity. That is, either a positive or negative value. K Hinds 2012 2 Alternating
Transmission Lines in Communication Systems FACET
 Computer-Based Electronics Training System Transmission Lines in Communication Systems FACET 36970- Order no.: 36970-00 First Edition Revision level: 02/2015 By the staff of Festo Didactic Festo Didactic
Computer-Based Electronics Training System Transmission Lines in Communication Systems FACET 36970- Order no.: 36970-00 First Edition Revision level: 02/2015 By the staff of Festo Didactic Festo Didactic
The Importance of the X/R Ratio in Low-Voltage Short Circuit Studies
 The Importance of the X/R Ratio in Low-Voltage Short Circuit Studies DATE: November 17, 1999 REVISION: AUTHOR: John Merrell Introduction In some short circuit studies, the X/R ratio is ignored when comparing
The Importance of the X/R Ratio in Low-Voltage Short Circuit Studies DATE: November 17, 1999 REVISION: AUTHOR: John Merrell Introduction In some short circuit studies, the X/R ratio is ignored when comparing
potential in the centre of the sphere with respect to infinity.
 Umeå Universitet, Fysik 1 Vitaly Bychkov Prov i fysik, Electricity and Waves, 2006-09-27, kl 16.00-22.00 Hjälpmedel: Students can use any book. Define the notations you are using properly. Present your
Umeå Universitet, Fysik 1 Vitaly Bychkov Prov i fysik, Electricity and Waves, 2006-09-27, kl 16.00-22.00 Hjälpmedel: Students can use any book. Define the notations you are using properly. Present your
Experiment 3- Transmission Lines, Part 1
 Experiment 3- Transmission Lines, Part 1 Dr. Haim Matzner& Shimshon Levy. August, 2008. Contents Introduction 1 0.1 PrelabExercise.......................... 1 0.2 BackgroundTheory........................
Experiment 3- Transmission Lines, Part 1 Dr. Haim Matzner& Shimshon Levy. August, 2008. Contents Introduction 1 0.1 PrelabExercise.......................... 1 0.2 BackgroundTheory........................
High Frequency Characteristics of. Medium Voltage XLPE Power Cables. Gavita Mugala
 High Frequency Characteristics of Medium Voltage XLPE Power Cables Gavita Mugala Doctoral Thesis Stockholm, Sweden 2005 Akademisk avhandling som med tillstånd av Kungl Tekniska Högskolan framlägges till
High Frequency Characteristics of Medium Voltage XLPE Power Cables Gavita Mugala Doctoral Thesis Stockholm, Sweden 2005 Akademisk avhandling som med tillstånd av Kungl Tekniska Högskolan framlägges till
Unit2: Resistor/Capacitor-Filters
 Unit2: Resistor/Capacitor-Filters Physics335 Student October 3, 27 Physics 335-Section Professor J. Hobbs Partner: Physics335 Student2 Abstract Basic RC-filters were constructed and properties such as
Unit2: Resistor/Capacitor-Filters Physics335 Student October 3, 27 Physics 335-Section Professor J. Hobbs Partner: Physics335 Student2 Abstract Basic RC-filters were constructed and properties such as
zcable Model for Frequency Dependent Modelling of Cable Transmission Systems
 zcable Model for Frequency Dependent Modelling of Cable Transmission Systems T. C. Yu Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of British Columbia 356 Main Mall, Vancouver, B.C., Canada
zcable Model for Frequency Dependent Modelling of Cable Transmission Systems T. C. Yu Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of British Columbia 356 Main Mall, Vancouver, B.C., Canada
Inductors & Inductance. Electronic Components
 Electronic Components Induction In 1824, Oersted discovered that current passing though a coil created a magnetic field capable of shifting a compass needle. Seven years later, Faraday and Henry discovered
Electronic Components Induction In 1824, Oersted discovered that current passing though a coil created a magnetic field capable of shifting a compass needle. Seven years later, Faraday and Henry discovered
Grounding Demystified
 Grounding Demystified 3-1 Importance Of Grounding Techniques 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Grounding 42% Case 22% Cable 18% Percent Used Filter 12% PCB 6% Grounding 42% Case Shield 22% Cable Shielding 18%
Grounding Demystified 3-1 Importance Of Grounding Techniques 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Grounding 42% Case 22% Cable 18% Percent Used Filter 12% PCB 6% Grounding 42% Case Shield 22% Cable Shielding 18%
AND8200/D. Design Considerations for ESD/EMI Filters: I (Almost Everything You Wanted to Know About EMI Filters and Were Afraid to Ask)
 Design Considerations for ESD/EMI Filters: I (Almost Everything You Wanted to Know About EMI Filters and Were Afraid to Ask) Prepared by: Ryan Hurley Applications Engineer ON Semiconductor APPLICATION
Design Considerations for ESD/EMI Filters: I (Almost Everything You Wanted to Know About EMI Filters and Were Afraid to Ask) Prepared by: Ryan Hurley Applications Engineer ON Semiconductor APPLICATION
Fundamentals of radio communication
 Fundamentals of radio communication This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Fundamentals of radio communication This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Nexus Technology Review -- Exhibit A
 Nexus Technology Review -- Exhibit A Background A. Types of DSL Lines DSL comes in many flavors: ADSL, ADSL2, ADSL2+, VDSL and VDSL2. Each DSL variant respectively operates up a higher frequency level.
Nexus Technology Review -- Exhibit A Background A. Types of DSL Lines DSL comes in many flavors: ADSL, ADSL2, ADSL2+, VDSL and VDSL2. Each DSL variant respectively operates up a higher frequency level.
Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits
 Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits 12.1 What Is a Three Phase Circuit? 12.2 Balance Three Phase Voltages 12.3 Balance Three Phase Y to Y Connection 12.4 Other Balance Three Phase Connections 12.5 Power in
Chapter 12: Three Phase Circuits 12.1 What Is a Three Phase Circuit? 12.2 Balance Three Phase Voltages 12.3 Balance Three Phase Y to Y Connection 12.4 Other Balance Three Phase Connections 12.5 Power in
Capacitor Self-Resonance
 Capacitor Self-Resonance By: Dr. Mike Blewett University of Surrey United Kingdom Objective This Experiment will demonstrate some of the limitations of capacitors when used in Radio Frequency circuits.
Capacitor Self-Resonance By: Dr. Mike Blewett University of Surrey United Kingdom Objective This Experiment will demonstrate some of the limitations of capacitors when used in Radio Frequency circuits.
Lecture 24. Inductance and Switching Power Supplies (how your solar charger voltage converter works)
 Lecture 24 Inductance and Switching Power Supplies (how your solar charger voltage converter works) Copyright 2014 by Mark Horowitz 1 Roadmap: How Does This Work? 2 Processor Board 3 More Detailed Roadmap
Lecture 24 Inductance and Switching Power Supplies (how your solar charger voltage converter works) Copyright 2014 by Mark Horowitz 1 Roadmap: How Does This Work? 2 Processor Board 3 More Detailed Roadmap
Antenna Properties and their impact on Wireless System Performance. Dr. Steven R. Best. Cushcraft Corporation 48 Perimeter Road Manchester, NH 03013
 Antenna Properties and their impact on Wireless System Performance Dr. Steven R. Best Cushcraft Corporation 48 Perimeter Road Manchester, NH 03013 Phone (603) 627-7877 FAX: (603) 627-1764 Email: sbest@cushcraft.com
Antenna Properties and their impact on Wireless System Performance Dr. Steven R. Best Cushcraft Corporation 48 Perimeter Road Manchester, NH 03013 Phone (603) 627-7877 FAX: (603) 627-1764 Email: sbest@cushcraft.com
Vector Network Analyzer Techniques to Measure WR340 Waveguide Windows
 LS-296 Vector Network Analyzer Techniques to Measure WR340 Waveguide Windows T. L. Smith ASD / RF Group Advanced Photon Source Argonne National Laboratory June 26, 2002 Table of Contents 1) Introduction
LS-296 Vector Network Analyzer Techniques to Measure WR340 Waveguide Windows T. L. Smith ASD / RF Group Advanced Photon Source Argonne National Laboratory June 26, 2002 Table of Contents 1) Introduction
ANALYSIS AND VERIFICATION OF A PROPOSED ANTENNA DESIGN FOR AN IMPLANTABLE. RFID TAG AT 915 MHz RAHUL BAKORE
 ANALYSIS AND VERIFICATION OF A PROPOSED ANTENNA DESIGN FOR AN IMPLANTABLE RFID TAG AT 915 MHz By RAHUL BAKORE Bachelor of Engineering in Electronics and Communication University Of Rajasthan Jaipur, Rajasthan,
ANALYSIS AND VERIFICATION OF A PROPOSED ANTENNA DESIGN FOR AN IMPLANTABLE RFID TAG AT 915 MHz By RAHUL BAKORE Bachelor of Engineering in Electronics and Communication University Of Rajasthan Jaipur, Rajasthan,
Measuring Parasitic Capacitance and Inductance Using TDR
 Measuring Parasitic apacitance and Inductance Using TDR Time-domain reflectometry (TDR) is commonly used as a convenient method of determining the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or quantifying
Measuring Parasitic apacitance and Inductance Using TDR Time-domain reflectometry (TDR) is commonly used as a convenient method of determining the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or quantifying
6 J - vector electric current density (A/m2 )
 Determination of Antenna Radiation Fields Using Potential Functions Sources of Antenna Radiation Fields 6 J - vector electric current density (A/m2 ) M - vector magnetic current density (V/m 2 ) Some problems
Determination of Antenna Radiation Fields Using Potential Functions Sources of Antenna Radiation Fields 6 J - vector electric current density (A/m2 ) M - vector magnetic current density (V/m 2 ) Some problems
EXTENDING THE LIFE OF POWER FACTOR CAPACITORS
 by John Houdek, President, Allied Industrial Marketing, Inc., and Cesar Chavez, Engineering Manager, ARTECHE / Inelap Abstract: The addition of power factor improvement capacitors to individual motors
by John Houdek, President, Allied Industrial Marketing, Inc., and Cesar Chavez, Engineering Manager, ARTECHE / Inelap Abstract: The addition of power factor improvement capacitors to individual motors
Examples of Uniform EM Plane Waves
 Examples of Uniform EM Plane Waves Outline Reminder of Wave Equation Reminder of Relation Between E & H Energy Transported by EM Waves (Poynting Vector) Examples of Energy Transport by EM Waves 1 Coupling
Examples of Uniform EM Plane Waves Outline Reminder of Wave Equation Reminder of Relation Between E & H Energy Transported by EM Waves (Poynting Vector) Examples of Energy Transport by EM Waves 1 Coupling
EMC STANDARDS STANDARDS AND STANDARD MAKING BODIES. International. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) http://www.iec.
 EMC STANDARDS The EMC standards that a particular electronic product must meet depend on the product application (commercial or military) and the country in which the product is to be used. These EMC regulatory
EMC STANDARDS The EMC standards that a particular electronic product must meet depend on the product application (commercial or military) and the country in which the product is to be used. These EMC regulatory
DSL LINE TESTER USING WIDEBAND FREQUENCY DOMAIN REFLECTOMETRY
 DSL LINE TESTER USING WIDEBAND FREQUENCY DOMAIN REFLECTOMETRY A Thesis Submitted to the College of Graduate Studies and Research in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science
DSL LINE TESTER USING WIDEBAND FREQUENCY DOMAIN REFLECTOMETRY A Thesis Submitted to the College of Graduate Studies and Research in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science
How To Understand And Understand The Theory Of Electricity
 DIRECT CURRENT AND ALTERNATING CURRENT SYSTEMS N. Rajkumar, Research Fellow, Energy Systems Group, City University Northampton Square, London EC1V 0HB, UK Keywords: Electrical energy, direct current, alternating
DIRECT CURRENT AND ALTERNATING CURRENT SYSTEMS N. Rajkumar, Research Fellow, Energy Systems Group, City University Northampton Square, London EC1V 0HB, UK Keywords: Electrical energy, direct current, alternating
Experiment 7: Familiarization with the Network Analyzer
 Experiment 7: Familiarization with the Network Analyzer Measurements to characterize networks at high frequencies (RF and microwave frequencies) are usually done in terms of scattering parameters (S parameters).
Experiment 7: Familiarization with the Network Analyzer Measurements to characterize networks at high frequencies (RF and microwave frequencies) are usually done in terms of scattering parameters (S parameters).
Coupled Inductors. Introducing Coupled Inductors
 Coupled Inductors From power distribution across large distances to radio transmissions, coupled inductors are used extensively in electrical applications. Their properties allow for increasing or decreasing
Coupled Inductors From power distribution across large distances to radio transmissions, coupled inductors are used extensively in electrical applications. Their properties allow for increasing or decreasing
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA UNIT 5 - ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 4 - ALTERNATING CURRENT 4 Understand single-phase alternating current (ac) theory Single phase AC
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents. Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49
 Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
Circuits with inductors and alternating currents Chapter 20 #45, 46, 47, 49 RL circuits Ch. 20 (last section) Symbol for inductor looks like a spring. An inductor is a circuit element that has a large
Crosstalk effects of shielded twisted pairs
 This article deals with the modeling and simulation of shielded twisted pairs with CST CABLE STUDIO. The quality of braided shields is investigated with respect to perfect solid shields. Crosstalk effects
This article deals with the modeling and simulation of shielded twisted pairs with CST CABLE STUDIO. The quality of braided shields is investigated with respect to perfect solid shields. Crosstalk effects
EM Noise Mitigation in Circuit Boards and Cavities
 EM Noise Mitigation in Circuit Boards and Cavities Faculty (UMD): Omar M. Ramahi, Neil Goldsman and John Rodgers Visiting Professors (Finland): Fad Seydou Graduate Students (UMD): Xin Wu, Lin Li, Baharak
EM Noise Mitigation in Circuit Boards and Cavities Faculty (UMD): Omar M. Ramahi, Neil Goldsman and John Rodgers Visiting Professors (Finland): Fad Seydou Graduate Students (UMD): Xin Wu, Lin Li, Baharak
Designing the NEWCARD Connector Interface to Extend PCI Express Serial Architecture to the PC Card Modular Form Factor
 Designing the NEWCARD Connector Interface to Extend PCI Express Serial Architecture to the PC Card Modular Form Factor Abstract This paper provides information about the NEWCARD connector and board design
Designing the NEWCARD Connector Interface to Extend PCI Express Serial Architecture to the PC Card Modular Form Factor Abstract This paper provides information about the NEWCARD connector and board design
Subject: Glenair MIL-PRF 24758 Conduit Surface Transfer Impedance Test
 Lothar O. Hoeft, Ph.D. Consultant, Electromagnetic Effects 5012 San Pedro Ct., NE Albuquerque, New Mexico 87109-2515 Phone: (505)-889-9705 E-mail: bud.hoeft@ieee.org 1 February 24, 2006 Subject: Glenair
Lothar O. Hoeft, Ph.D. Consultant, Electromagnetic Effects 5012 San Pedro Ct., NE Albuquerque, New Mexico 87109-2515 Phone: (505)-889-9705 E-mail: bud.hoeft@ieee.org 1 February 24, 2006 Subject: Glenair
Selecting Current Transformers Part 1 By Darrell G. Broussard, P.E.
 By Darrell G. Broussard, P.E. Introduction: As engineers, we are aware that electrical power systems have grown. How much have they grown? When was the last time you specified a 2400-volt system, a 4160-volt
By Darrell G. Broussard, P.E. Introduction: As engineers, we are aware that electrical power systems have grown. How much have they grown? When was the last time you specified a 2400-volt system, a 4160-volt
S-Parameters and Related Quantities Sam Wetterlin 10/20/09
 S-Parameters and Related Quantities Sam Wetterlin 10/20/09 Basic Concept of S-Parameters S-Parameters are a type of network parameter, based on the concept of scattering. The more familiar network parameters
S-Parameters and Related Quantities Sam Wetterlin 10/20/09 Basic Concept of S-Parameters S-Parameters are a type of network parameter, based on the concept of scattering. The more familiar network parameters
Human Exposure to Outdoor PLC System
 1602 PIERS Proceedings, Marrakesh, MOROCCO, March 20 23, 2011 Human Exposure to Outdoor PLC System Vicko Doric 1, Dragan Poljak 1, and Khalil El Khamlichi Drissi 2 1 University of Split, Croatia 2 Blaise
1602 PIERS Proceedings, Marrakesh, MOROCCO, March 20 23, 2011 Human Exposure to Outdoor PLC System Vicko Doric 1, Dragan Poljak 1, and Khalil El Khamlichi Drissi 2 1 University of Split, Croatia 2 Blaise
Copyright 2000 IEEE. Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 2000
 Copyright 2000 IEEE Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 2000 This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE does not in any way imply IEEE
Copyright 2000 IEEE Reprinted from IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium 2000 This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE does not in any way imply IEEE
Lecture 22. Inductance. Magnetic Field Energy. Outline:
 Lecture 22. Inductance. Magnetic Field Energy. Outline: Self-induction and self-inductance. Inductance of a solenoid. The energy of a magnetic field. Alternative definition of inductance. Mutual Inductance.
Lecture 22. Inductance. Magnetic Field Energy. Outline: Self-induction and self-inductance. Inductance of a solenoid. The energy of a magnetic field. Alternative definition of inductance. Mutual Inductance.
MOBILE SYSTEM FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HIGH VOLTAGE CABLES (132KV/220KV) VLF-200 HVCD
 MOBILE SYSTEM FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HIGH VOLTAGE CABLES (132KV/220KV) VLF-200 HVCD VERY LOW FREQUENCY (VLF) - PARTIAL DISCHARGES AND TANGENT DELTA HV/EHV POWER CABLES DIAGNOSTIC AND ON-SITE FIELD TESTING WITH
MOBILE SYSTEM FOR DIAGNOSIS OF HIGH VOLTAGE CABLES (132KV/220KV) VLF-200 HVCD VERY LOW FREQUENCY (VLF) - PARTIAL DISCHARGES AND TANGENT DELTA HV/EHV POWER CABLES DIAGNOSTIC AND ON-SITE FIELD TESTING WITH
Diode Applications. by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 1, 2008. This note illustrates some common applications of diodes.
 by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 1, 2008 This note illustrates some common applications of diodes. Power supply applications A common application for diodes is converting AC to DC. Although half-wave rectification
by Kenneth A. Kuhn Sept. 1, 2008 This note illustrates some common applications of diodes. Power supply applications A common application for diodes is converting AC to DC. Although half-wave rectification
(3 )Three Phase Alternating Voltage and Current
 EEE 2015 EECTRCS (3) Monophase 1 Three phase Three phase electric power is a common method of alternating current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. t is a type of polyphase system
EEE 2015 EECTRCS (3) Monophase 1 Three phase Three phase electric power is a common method of alternating current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. t is a type of polyphase system
Various Technics of Liquids and Solids Level Measurements. (Part 3)
 (Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
(Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
Antenna A mean for radiating and receiving radio waves Transitional structure between free-space and a guiding device. Application: Radiation
 Antenna A mean for radiating and receiving radio waves Transitional structure between free-space and a guiding device Application: adiation Introduction An antenna is designed to radiate or receive electromagnetic
Antenna A mean for radiating and receiving radio waves Transitional structure between free-space and a guiding device Application: adiation Introduction An antenna is designed to radiate or receive electromagnetic
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 1 (Lectures 1 & 2)
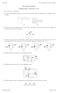 Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Ver 3537 E. Analysis of Circuits () Key: [A]= easy... [E]=hard E. Circuit Analysis Problem Sheet (Lectures & ). [A] One of the following circuits is a series circuit and the other is a parallel circuit.
Cable Size Selection for Energy Efficiency
 Cable Size Selection for Energy Efficiency Introduction The traditional method for determining the appropriate cable size for a particular installation involves the selection of the smallest size conductor
Cable Size Selection for Energy Efficiency Introduction The traditional method for determining the appropriate cable size for a particular installation involves the selection of the smallest size conductor
WHITEPAPER. Cable and Connector for Hiperface dsl motor drive applications
 WHITEPAPER Cable and Connector for Hiperface dsl motor drive applications information for cable manufacturers Version 02 Content Information for cable manufacturers...3 Communication...3 Crosstalk & shielding...3
WHITEPAPER Cable and Connector for Hiperface dsl motor drive applications information for cable manufacturers Version 02 Content Information for cable manufacturers...3 Communication...3 Crosstalk & shielding...3
Common Mode Choke Filtering Improves CMRR in Ethernet Transformer Applications. Application Note. June 2011
 Common Mode Choke Filtering Improves CMRR in Ethernet Transformer Applications June 2011 Application Note Common mode chokes provide an effective EMI filtering solution for Ethernet transformer applications.
Common Mode Choke Filtering Improves CMRR in Ethernet Transformer Applications June 2011 Application Note Common mode chokes provide an effective EMI filtering solution for Ethernet transformer applications.
Amplification of the Radiation from Two Collocated Cellular System Antennas by the Ground Wave of an AM Broadcast Station
 Amplification of the Radiation from Two Collocated Cellular System Antennas by the Ground Wave of an AM Broadcast Station Dr. Bill P. Curry EMSciTek Consulting Co., W101 McCarron Road Glen Ellyn, IL 60137,
Amplification of the Radiation from Two Collocated Cellular System Antennas by the Ground Wave of an AM Broadcast Station Dr. Bill P. Curry EMSciTek Consulting Co., W101 McCarron Road Glen Ellyn, IL 60137,
Keysight Technologies Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Vector Network Analysis. Application Note
 Keysight Technologies Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Vector Network Analysis Application Note Introduction Network analysis is the process by which designers and manufacturers measure the
Keysight Technologies Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Vector Network Analysis Application Note Introduction Network analysis is the process by which designers and manufacturers measure the
EECC694 - Shaaban. Transmission Channel
 The Physical Layer: Data Transmission Basics Encode data as energy at the data (information) source and transmit the encoded energy using transmitter hardware: Possible Energy Forms: Electrical, light,
The Physical Layer: Data Transmission Basics Encode data as energy at the data (information) source and transmit the encoded energy using transmitter hardware: Possible Energy Forms: Electrical, light,
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 8 CAPACITOR CURRENT-VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP
 1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 8 CAPACITOR CURRENT-VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP Purpose: To demonstrate the relationship between the voltage and current of a capacitor. Theory: A capacitor is a linear circuit element whose
1 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 8 CAPACITOR CURRENT-VOLTAGE RELATIONSHIP Purpose: To demonstrate the relationship between the voltage and current of a capacitor. Theory: A capacitor is a linear circuit element whose
Objectives. Electric Current
 Objectives Define electrical current as a rate. Describe what is measured by ammeters and voltmeters. Explain how to connect an ammeter and a voltmeter in an electrical circuit. Explain why electrons travel
Objectives Define electrical current as a rate. Describe what is measured by ammeters and voltmeters. Explain how to connect an ammeter and a voltmeter in an electrical circuit. Explain why electrons travel
Chapter 35 Alternating Current Circuits
 hapter 35 Alternating urrent ircuits ac-ircuits Phasor Diagrams Resistors, apacitors and nductors in ac-ircuits R ac-ircuits ac-ircuit power. Resonance Transformers ac ircuits Alternating currents and
hapter 35 Alternating urrent ircuits ac-ircuits Phasor Diagrams Resistors, apacitors and nductors in ac-ircuits R ac-ircuits ac-ircuit power. Resonance Transformers ac ircuits Alternating currents and
Physics 6C, Summer 2006 Homework 2 Solutions
 Physics 6C, Summer 006 Homework Solutions All problems are from the nd edition of Walker. Numerical values are different for each student. Chapter 3 Problems. Figure 3-30 below shows a circuit containing
Physics 6C, Summer 006 Homework Solutions All problems are from the nd edition of Walker. Numerical values are different for each student. Chapter 3 Problems. Figure 3-30 below shows a circuit containing
SECTION 2 Transmission Line Theory
 SEMICONDUCTOR DESIGN GUIDE Transmission Line Theory SECTION 2 Transmission Line Theory Introduction The ECLinPS family has pushed the world of ECL into the realm of picoseconds. When output transitions
SEMICONDUCTOR DESIGN GUIDE Transmission Line Theory SECTION 2 Transmission Line Theory Introduction The ECLinPS family has pushed the world of ECL into the realm of picoseconds. When output transitions
Characterization of Spatial Power Waveguide Amplifiers
 Characterization of Spatial Power Waveguide Amplifiers Authored by: Matthew H. Commens Ansoft Corporation Ansoft 003 / Global Seminars: Delivering Performance Presentation # Outline What is a Spatial Waveguide
Characterization of Spatial Power Waveguide Amplifiers Authored by: Matthew H. Commens Ansoft Corporation Ansoft 003 / Global Seminars: Delivering Performance Presentation # Outline What is a Spatial Waveguide
Errors Due to Shared Leadwires in Parallel Strain Gage Circuits
 Micro-Measurements Strain Gages and Instruments Errors Due to Shared Leadwires in Parallel Strain Gage Circuits TN-516 1. Introduction The usual, and preferred, practice with multiple quarterbridge strain
Micro-Measurements Strain Gages and Instruments Errors Due to Shared Leadwires in Parallel Strain Gage Circuits TN-516 1. Introduction The usual, and preferred, practice with multiple quarterbridge strain
1 Introduction. 2 Two Phases. J.L. Kirtley Jr.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.061 Introduction to Power Systems Class otes Chapter 3 Polyphase etworks J.L. Kirtley Jr. 1 Introduction
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.061 Introduction to Power Systems Class otes Chapter 3 Polyphase etworks J.L. Kirtley Jr. 1 Introduction
