How to perform BOLD-MRI in body tumours: feasibility study
|
|
|
- Calvin Stafford
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How to perform BOLD-MRI in body tumours: feasibility study Poster No.: C-2435 Congress: ECR 205 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Alcala-Mata, A. Luna, J. Broncano, J. Sánchez-González, T Martin-Noguerol ; Jaen/ES, Córdoba/ES, Madrid/ES Keywords: Oncology, MR physics, Molecular imaging, MR-Functional imaging, Chemotherapy, Radiation therapy / Oncology, Metastases, Neoplasia DOI: 0.594/ecr205/C-2435 Any information contained in this pdf file is automatically generated from digital material submitted to EPOS by third parties in the form of scientific presentations. References to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are provided solely as a convenience to you and do not in any way constitute or imply ECR's endorsement, sponsorship or recommendation of the third party, information, product or service. ECR is not responsible for the content of these pages and does not make any representations regarding the content or accuracy of material in this file. As per copyright regulations, any unauthorised use of the material or parts thereof as well as commercial reproduction or multiple distribution by any traditional or electronically based reproduction/publication method ist strictly prohibited. You agree to defend, indemnify, and hold ECR harmless from and against any and all claims, damages, costs, and expenses, including attorneys' fees, arising from or related to your use of these pages. Please note: Links to movies, ppt slideshows and any other multimedia files are not available in the pdf version of presentations. Page of 23
2 Aims and objectives AIMS. 2. Describe the physical basis and how to perform Blood Oxygen Level Dependent (BOLD) MRI with hyperoxia in the body Highlight how BOLD-MRI can be performed for the analysis of tissue oxygenation and angiogenesis of different body tumors Background Tumor hypoxia is one of the main cancer hallmarks, as it promotes cell division, invasion, angiogenesis and metastatic risk. Interestingly, it has been related to increase resistance to several treatment types as radiation, chemotherapy, thermal ablation and photodynamic therapies. Different efforts have been spent in order to measure tissue oxygenation of cancer, as it predicts the radiation response and regional tumor control. Different approaches with PET and MRI have been tested for noninvasinve quantification of oxygenation. Dynamic contrast enhanced MRRI (DCE-MRI) has shown to provide indirect estimates of hypoxia but with not clear relationship to tumor hypoxia. Interestingly, BOLD-imaging has demonstrated interesting results in the evaluation of tissue hypoxia with different approaches. Changes in concentration of paramagnetic molecules (e.g.: deoxyhemoglobin) in and around vessels create local variations in the image phase, which are identified as a decay of signal on T2* sequences. The concentration of deoxyhemoglobin within the vessel increases with rising oxygen consumption, leading to a decreasing T2* relaxation time of surrounding tissue. The rate of spin dephasing (R2*=/T2*) is an index of the oxygenation of tissue. Native relaxometry with BOLD (calculation of native tissue R2*) is easy to perform but show clear limitations in specificity. Most commonly, T2*measurements have been performed, as short values of the reversible transverse relaxation time T2* are related to low blood oxygenation, due to the paramagnetic nature of deoxygenated blood. In the body, this approach has been used to demonstrate differences in R2* between solid and cystic renal lesions. However, T2* is not only related to blood oxygen saturation but also Page 2 of 23
3 to tissue T2, local magnetic field variations, hematocrit level, and vessel microstructure. Therefore, if the blood flow is high and the hemoglobin saturation rate is low, then R2* only reflects the blood flow of the studied tissue More promising are BOLD approaches using physiologic and pharmacologic challenges such as hyperoxia (inhalation of oxygen at high concentrations), hypoxia (breath-holding) or hypercapnia (inhalation of Carbogen: 95% O2/5% CO2). Relative changes in R2* (#R2*) in response to these challenges are a better biomarker of po2 than the absolute value of R2*. An increase of R2*in an area of tissue compared to other part of the same organ under the same pathological circumstances, has been related to the existence of hypoxia. Oxygen-enhanced R2* measurements is a promising technique to interrogate tumor oxygen delivery and hypoxia, although little clinical experience with this technique has been accumulated by the moment. It requires of the delivery of oxygen-enriched air to patients, and provides a qualitative assessment of tumor hypoxia, although does not require any dedicated hardware of postprocessing software. This approach measures #R2*- and R2-weighted signal intensities in response to oxygen breathing scales compared with baseline [deoxyhemoglobin: deoxyhb]. BOLD measurements with hyperoxia have shown a good correlation with tissue changes in po2, as it measures the hypoxia secondary to the fall of perfusion or the acute hypoxia secondary to the functional and structural abnormalities of tumor neoangiogenesis. Reported limitations of this technique are limited specificity for high so2, low blood volume or in cases of oxygensteal. In addition, the underlying hemodynamic and oxygenation-related mechanisms are far from being fully understood. However, it lacks of potential complications as the use of carbogen, which may cause respiratory distress. DCE-MRI may provide an indirect estimation of tumor hypoxia, as it gives information of the total vascular volume of the tumor; whereas BOLD MRI is sensitive only to vessels where gaseous interchange occurs. It is well known that in tumors, not all neovessels show effective blood cell transport due to vascular occlusions. Therefore, hypoxic tumors with high blood volume will show a greater #R2* to physiological challenges, and are theoretically candidates for radiosensitisation. In the body, preliminary data has shown promising results for cervical and prostate cancers. However, BOLD-MRI is still in the preclinical phase due to lack of standardization of technique, multiple approaches and different outcomes chosen for comparison Basis of BOLD imaging Page 3 of 23
4 BOLD imaging is based on the effect that paramagnetic molecules of the blood (e.g.: deoxyhb) produce on local fields. They create local variations in the image phase, which are identified as a variation (decay) of signal on T2* sequences. If pure O2 is administered, there is an increase pass of O2 from blood to the tissue. The concentration of deoxyhb increases with rising oxygen consumption, leading to a decreasing T2* relaxation time of the surrounding tissue ( Fig. on page 4 ). The connection between changes in BOLD sequences and tissue oxygenation can be explained through the relationship between oxygen and Hb in the blood. DeoxyHb has an iron atom that directly influences the magnetic fields producing a local signal drop BOLD imaging measures the hypoxia secondary to the fall of perfusion or the acute hypoxia secondary to the functional and structural abnormalities of tumor neoangiogenesis. The rate of spin dephasing, R2*, is an index of the oxygenation of tissue (/T2*). If the blood flow is high and the Hb saturation rate is low, then R2* only reflects the blood flow of the studied tissue. An increase of R2* (drop of T2* and positive #R2*) in an area of tissue compared to other part of the same organ under the same pathological circumstances, is due to the existence of hypoxia Images for this section: Page 4 of 23
5 Fig. : If pure O2 is administered, there is an increase pass of O2 from blood to the tissue. The concentration of deoxyhb increases with rising oxygen consumption, leading to a decreasing T2* relaxation time of the surrounding tissue. Page 5 of 23
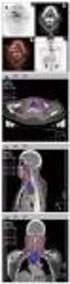
6 Methods and materials BOLD-MRI with hyperoxia was performed in 4 patients with confirmed body malignancies (Table ) and submitted to MRI for locoregional and/or distant staging. Our institutional review board approved our study and informed consent was obtained from all patients Table. Study population Tumor type Number of patients Age (years) Sex Prostate adenocarcinoma 62 Male Rectal adenocarcinoma 2 48/69 Male/ Female Endometrial carcinoma 50 Female Cervical uterine carcinoma 53 Female Ovarian carcinoma 47 Female Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma 69 Female Retroperitoneal liposarcoma 69 Male Pancreatic adenocarcinoma 83 Male Clear cell Renal carcinoma (RCC) 54 Male Hepatocellular carcinoma 62 Male Liver metastasis (neuroendocrine tumor) 52 Male Liver metastasis (colorectal carcinoma) 50 Male Non Small Cell Lung cancer (NSCLC) 50 Male Page 6 of 23
7 MRI study All studies were performed in a 3T magnet (Achieva. Philips. Best. Netherlands) using a phased-array body coil of 6 elements. BOLD-MRI was included as part of the MRI protocol for staging. MRI protocols varied accordingly to tumor type and location BOLD MRI Fig. 2 on page 8 represents the 3 steps of our BOLD acquisition: Step. Acquisition of multiecho Fast Field Sequence A multiecho FFE T2* sequence ( Fig. 3 on page 0 ) was performed. Two different of acquisitions strategies were used, each of one in 7 patiens. Protocol included a multiecho FFE acquisitions in basal conditions and 5, 0 and 5minutes after the inhalation of pure O2 (5 l/mn). Protocol 2 included multiecho FFE acquisitions in basal conditions and 2, 5, 7 and 0 minutes after the inhalation of pure O2 (5 l/mn). A final acquisiton 3 minutes after cesation of O2 administration was also performed. Table 2. Patiens submitted to different BOLD-MRI protocols Protocol Protocol 2 Prostate adenocarcinoma Endometrial carcinoma Rectal adenocarcinoma (2) Cervical uterine carcinoma Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Ovarian carcinoma Retroperitoneal liposarcoma Pancreatic adenocarcinoma Hepatocellular carcinoma Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) Non Small Cell Lung cancer (NSCLC) Liver metastasis (neuroendocrine tumor) Liver metastasis (colorectal carcinoma) BOLD sequence design: 3 different echo od times from 2.3 to 30 ms Echo spacing: 2.3 ms to avoid fat contamination on the T2* estunatuob Page 7 of 23
8 Flip angle relatively high (#=25) to obtain T-weighting in the first echo image and evalaute T changes due to oxygen variations Step 2. T2* estimation Signal intensity of all echoes were fitted to a mono-exponential decay model to estimate the T2* values of every pixel ( Fig. 4 on page 3 ). T2* was estimated for each acquisition and R2* was also calculated. Step 3. Fusion of T2* mapping and anatomical image and #R2* curves T2* maps of each acquisition were fused with TSE T2-weighted image in order to obtain a fusion image, that permitted a visual evaluation of the changes produced in the tumor with the hyperoxia ( Fig. 5 on page ). Fig. 6 on page 2 explains how these maps can be read. In addition, a ROI in the solid component of the tumor was drawn in the original T2* map, and then the ROI was copied and pasted in the rest of acquisitions, in order to monitoring #R2* during the different acquisitions using a graphic representation ( Fig. 7 on page 9 ). Hypoxic tumors with high blood volume show greater #R2* to oxygen challenge. Therefore, an ascending or flat curve of #R2* during O2 administration was considered as a sign of radioresistance and a descending curve of #R2* related to radiosensitivity. Images for this section: Page 8 of 23
9 Fig. 2: Diagram shows the three steps of each BOLD acquisition:. Performance of a multiecho Fast Field Sequence with 3 different echo times from 2.3 to 30 ms. Echo spacing 2.3 ms to avoid fat contamination on the T2* estimation. Flip Angle relatively high (a=25) to obtain T weighting in the first echo image and evaluate T changes due to oxygen variations. 2. T2* estimation: signal intensity of all echoes are fitted to a monoexponential decay model to estimate the T2* values of every pixel. 3. Fusion on T2 TSE sequence and T2* mapping to obtain a color parametric map Page 9 of 23
10 Fig. 7: DiagraM represents the different time of acquistions of our BOLD approach with hyperoxia: basal acquisition, acquisition after 95% O2 breathing at 5, 7 and 0 mn and finally an acquisition without O2 Page 0 of 23
11 Fig. 3 Page of 23
12 Fig. 5 Page 2 of 23
13 Fig. 6 Page 3 of 23
14 Fig. 4 Page 4 of 23
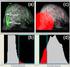
15 Results All studies were perfectly tolerated and could be performed satisfactorily. There was no complications during any of the procedures. malignancies (78,6%) showed a descending curve during the first 5 to 7 mn of O2 administration ( Fig. 8 on page 6 and Fig. 9 on page 6 )related to radiosensitivity 2 tumors (4,2%) demonstrated an ascending curve during the first 5 to 7 mn of O2 administration ( Fig. 0 on page 7 and Fig. on page 8 ) cancer (7,2%) showed a flat curve ( Fig. 2 on page 9 ) Ascending and flat curves were related to radiosensistance In the comparison between the 2 different groups of protocols. In 5 of 7 cases (7,4%) using protocol, an increase in #R2* after 5 to 0 mn of O2 administration ( Fig. 8 on page 6 ) was demonstrated, probably due to saturation of gaseous interchange between vessel and tumor. This delay ascent was detected in 5 of 6 cases (83,3%) showing a descendent curve, except in the case of prostate adenocarcinoma ( Fig. 9 on page 6 ). In all the tumors submitted to protocol 2, between 5 to 0 minutes after O2 administration the curve of #R2* changed its morphology to return in the delayed acuisition without O2 to similar levels of oxygenation that in basal conditions. This effect was appreciated either in cases showing an ascendent curve ( Fig. 0 on page 7 ), or a descendent one ( Fig. 3 on page 20 ). This is, the initial and final oxygenation during BOLD imaging of all tumors submitted to protocols 2 were very similar. Table 3. Curve type in tumors submitted to protocol Protocol Curve type Prostate adenocarcinoma Descendent Rectal adenocarcinoma (2) Descendent (2) Non-Hodgkin lymphoma Descendent Retroperitoneal liposarcoma Flat Hepatocellular carcinoma Descendent Non Small Cell Lung cancer (NSCLC) Descendent Table 4. Curve type in tumors submitted to protocol 2 Page 5 of 23
16 Protocol 2 Curve type Endometrial carcinoma Descendent Cervical uterine carcinoma Descendent Ovarian carcinoma Descendent Pancreatic adenocarcinoma Ascendent Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) Ascendent Liver metastasis (neuroendocrine tumor) Descendent Liver metastasis (colorectal carcinoma) Descendent Images for this section: Fig. 8: HCC using protocol shows an initial descent in R2* during the first 5 minutes of O2 admimistration and a delay ascent of R2* Page 6 of 23
17 Fig. 9: Prostate adenocarcinoma. BOLD imaging using protocol demonstrated a descent in R2* signal during all point time of O2 administration Page 7 of 23
18 Fig. 0: Pancreatic carcinoma submitted to protocol 2 which shows an ascendent curve of R2* during the first 5 minutes of O2 administration and delayed descent of R2*. Page 8 of 23
19 Fig. : Clear cell renal carcinoma. BOLD imaging was obtained using protocol 2. This tumor showed increase values of R2* during of O2 administration with a decrease in R2* after O2 cessation. Page 9 of 23
20 Fig. 2: Retroperitoneal liposarcoma which shows a small peripheral solid nodule (arrow) submitted to BOLD imaging using protocol and demostrating a flat curv (absence of gaseous interchange in solid component) Page 20 of 23
21 Fig. 3: Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma submitted to BOLD imaging using protocol 2 demonstrates a descent curve during the first 5 minutes after O2 administration with a delay ascent of R2* values in the rest of acquisitions Page 2 of 23
22 Conclusion BOLD-MRI with hyperoxia is feasible in different body regions in a clinical setting, allowing the assessment of tumor neoangiogenesis and hypoxia. According to this short series, BOLD-MRI with hyperoxia at 3T has the potential to estimate tumor hypoxia which may be of interest for treatment selection and therapy monitoring This preliminary data suggests that BOLD-MRI with hyperoxia can be performed as part of the MRI assessment of body malignancies in different organs and systems After 5 to 0 minutes of O2 administration a saturation effect in gaseous interchange occurs, which can be better estimated with a protocol that limits O2 administration to 0 mn and a final acquisition without O2 Further research is needed to validate these short series and to further establish the clinical usefulness of this technique Personal information References Barrett T, Brechbiel M, Bernardo M, Choyke PL. MRI of tumor angiogenesis. J Magn Reson Imaging 2007; 26: Kuperman VY, et al. Changes in T2*-weighted images during hyperoxia differentiate tumors from normal tissue. Magn Reson Med. 995;33: Rodrigues LM, et al. Tumor R2* is a prognostic indicator of acute radiotherapeutic response in rodent tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2004;9: Notohamiprodjo M, Reiser MF, Sourbron SP. Diffusion and perfusion of the kidney. Eur J Radiol 200;76: Padhani A, Krohn K, Lewis J et al. Imaging oxygenation of human tumours. Eur Radiol 2007; 7: Hallac RR, Ding Y, Yuan Q, et al. Oxygenation in cervical cancer and normal uterine cervix assessed using blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) MRI at 3T. NMR Biomed 202; 25(2): Remmele S, Mason RP, O Connor PB. MRI Hypoxia Measurements. In: Luna A et al. Functional imaging in Oncology volume ; 204: Springer-Verlag. Berlin. Page 22 of 23
23 8. Baudelet C, Gallez B. How does blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) contrast correlate with oxygen partial pressure (po2) inside tumors? Magn Reson Med. 2002;48: Müller A. Intracranial tumor response to respiratory challenges at 3.0 T: impact of different methods to quantify changes in the MR relaxation rate R2*.J Magn Reson Med. 200;32: Remmele S, et al. Quantification of the magnetic resonance signal response to dynamic (C)O(2)-enhanced imaging in the brain at 3 T: R(2)* BOLD vs. balanced SSFP. J Magn Reson Imaging. 200;3: Hallac RR, et al. Oxygenation in cervical cancer and normal uterine cervix assessed using blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) MRI at 3T. NMR Biomed. 202;25: Karczmar GS, et al. Magnetic resonance measurement of response to hyperoxia differentiates tumors from normal tissue and may be sensitive to oxygen consumption. Invest Radiol. 994;29(2):6-3. Page 23 of 23
Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging
 Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging Poster No.: C-0276 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: P. P. Arcuri,
Diffuse infiltration in multiple myeloma treatment response assessment with "total-spine" contrast enhanced MR imaging Poster No.: C-0276 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: P. P. Arcuri,
Patterns of nodal spread in thoracic malignancies
 Patterns of nodal spread in thoracic malignancies Poster No.: C-0977 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: R. dos Santos, M. Duarte, J. Alpendre, J. Castaño, Z. Seabra, Â.
Patterns of nodal spread in thoracic malignancies Poster No.: C-0977 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: R. dos Santos, M. Duarte, J. Alpendre, J. Castaño, Z. Seabra, Â.
CT findings in Differential Diagnosis between Tuberculous Pleurisy and Malignant Effusion
 CT findings in Differential Diagnosis between Tuberculous Pleurisy and Malignant Effusion Poster No.: E-0084 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. S. Shim, Y. Kim; Seoul/KR Keywords:
CT findings in Differential Diagnosis between Tuberculous Pleurisy and Malignant Effusion Poster No.: E-0084 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. S. Shim, Y. Kim; Seoul/KR Keywords:
Comparison of radiation dose from X-ray, CT, and PET/ CT in paediatric patients with neuroblastoma using a dose monitoring program
 Comparison of radiation dose from X-ray, CT, and PET/ CT in paediatric patients with neuroblastoma using a dose monitoring program Poster No.: C-0591 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Comparison of radiation dose from X-ray, CT, and PET/ CT in paediatric patients with neuroblastoma using a dose monitoring program Poster No.: C-0591 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
An Image Based Semiautomatic Online Cancer Staging Program for Common Female Pelvic Malignancies
 An Image Based Semiautomatic Online Cancer Staging Program for Common Female Pelvic Malignancies Poster No.: C-1050 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Talanow; Lexington, KY/US Keywords:
An Image Based Semiautomatic Online Cancer Staging Program for Common Female Pelvic Malignancies Poster No.: C-1050 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Talanow; Lexington, KY/US Keywords:
Preoperative evaluation of future remnant liver function by the contrast enhance ratio in hepatocellular image.
 Preoperative evaluation of future remnant liver function by the contrast enhance ratio in hepatocellular image. Poster No.: C-0564 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Matsushima, Y.
Preoperative evaluation of future remnant liver function by the contrast enhance ratio in hepatocellular image. Poster No.: C-0564 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Matsushima, Y.
Utilization management for successful process optimization in radiology
 Utilization management for successful process optimization in radiology Poster No.: C-0737 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: H.-P. Busch 1, W. Frewer 1, A. van Est 2 ; 1 Trier/DE, 2 Eindhoven/NL
Utilization management for successful process optimization in radiology Poster No.: C-0737 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: H.-P. Busch 1, W. Frewer 1, A. van Est 2 ; 1 Trier/DE, 2 Eindhoven/NL
OA related pain medication intake in subjects from the OAI incidence cohort - association with focal knee lesions and cartilage T2 measurements
 OA related pain medication intake in subjects from the OAI incidence cohort - association with focal knee lesions and cartilage T2 measurements Poster No.: C-0007 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
OA related pain medication intake in subjects from the OAI incidence cohort - association with focal knee lesions and cartilage T2 measurements Poster No.: C-0007 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Pancreatic masses: What is there besides cancer
 Pancreatic masses: What is there besides cancer Poster No.: C-0201 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid Organs) Authors: M. A. Portilha, C. Ruivo, I. Santiago, M.
Pancreatic masses: What is there besides cancer Poster No.: C-0201 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid Organs) Authors: M. A. Portilha, C. Ruivo, I. Santiago, M.
Determination of bone age using MRI of hand/wrist: a pilot study
 Determination of bone age using MRI of hand/wrist: a pilot study Poster No.: C-0963 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Tomei, M. Marini, A. Stagnitti, A. sartori, L. bertana, N. Al
Determination of bone age using MRI of hand/wrist: a pilot study Poster No.: C-0963 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Tomei, M. Marini, A. Stagnitti, A. sartori, L. bertana, N. Al
Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging
 Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Differential diagnosis of vertebral compression fracture using in-phase/opposed-phase and Short TI inversion recovery imaging Poster No.: C-0795 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
MRI scanning of the claustrophobic patients
 MRI scanning of the claustrophobic patients Poster No.: C-0549 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. minov, A. Doreski, M. Popovska, G. Markoski, S. 1 2 3 2 2 1 2 2 3 Jovanoska, I. miladinovski
MRI scanning of the claustrophobic patients Poster No.: C-0549 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. minov, A. Doreski, M. Popovska, G. Markoski, S. 1 2 3 2 2 1 2 2 3 Jovanoska, I. miladinovski
Development and implementation of a help desk system in a radiology department in a high complexity hospital: a South American experience
 Development and implementation of a help desk system in a radiology department in a high complexity hospital: a South American experience Poster No.: C-2409 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords:
Development and implementation of a help desk system in a radiology department in a high complexity hospital: a South American experience Poster No.: C-2409 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords:
Needle crystal detector technology in mammography further dose reduction and clinical image quality with
 Needle crystal detector technology in mammography further dose reduction and clinical image quality with different beam qualities (W/Rh vs. Mo/Rh) Poster No.: C-1461 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific
Needle crystal detector technology in mammography further dose reduction and clinical image quality with different beam qualities (W/Rh vs. Mo/Rh) Poster No.: C-1461 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific
Comparison between photoacoustic mammography images of breasts cancers and histological staining patterns of CD31 and carbonic anhydrase IX
 Comparison between photoacoustic mammography images of breasts cancers and histological staining patterns of CD31 and carbonic anhydrase IX Poster No.: C-1893 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Comparison between photoacoustic mammography images of breasts cancers and histological staining patterns of CD31 and carbonic anhydrase IX Poster No.: C-1893 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Normal vascular variants of the upper extremity
 Normal vascular variants of the upper extremity Poster No.: C-1039 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Paixao, A. P. Gomes, M. S. C. Sousa, I. Santiago, A. S. C. C. Germano; Amadora/PT
Normal vascular variants of the upper extremity Poster No.: C-1039 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Paixao, A. P. Gomes, M. S. C. Sousa, I. Santiago, A. S. C. C. Germano; Amadora/PT
Metastatic malignant melanoma revisited
 Metastatic malignant melanoma revisited Poster No.: C-2446 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Paulino, B. Gonçalves, P. Marques, M. Gonçalo, F. CaseiroAlves;
Metastatic malignant melanoma revisited Poster No.: C-2446 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: C. Paulino, B. Gonçalves, P. Marques, M. Gonçalo, F. CaseiroAlves;
Acute abdominal pain in the elderly patient: Impact of early MDCT examination on diagnosis and management
 Acute abdominal pain in the elderly patient: Impact of early MDCT examination on diagnosis and management Poster No.: C-1464 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit GI Tract Authors: A. Pinto,
Acute abdominal pain in the elderly patient: Impact of early MDCT examination on diagnosis and management Poster No.: C-1464 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit GI Tract Authors: A. Pinto,
Eye lens dose measurements in Interventional Cardiology
 Eye lens dose measurements in Interventional Cardiology Poster No.: 479 Congress: ESCR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: N. Kollaros 1, E. Carinou 2, C. Plemmenos 1, I. Stathopoulos 1, V. Keywords:
Eye lens dose measurements in Interventional Cardiology Poster No.: 479 Congress: ESCR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: N. Kollaros 1, E. Carinou 2, C. Plemmenos 1, I. Stathopoulos 1, V. Keywords:
Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine
 Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine Poster No.: C-1399 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Martel,
Diagnostic performance of MRI in differentiating metastatic from acute osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine Poster No.: C-1399 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Martel,
DICOM metadata-mining in PACS for computed radiography X-Ray exposure analysis: a mammography multisite study
 DICOM metadata-mining in PACS for computed radiography X-Ray exposure analysis: a mammography multisite study Poster No.: B-0276 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper M. R.
DICOM metadata-mining in PACS for computed radiography X-Ray exposure analysis: a mammography multisite study Poster No.: B-0276 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper M. R.
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD
 Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Characterization of small renal lesions: Problem solving with MRI Gary Israel, MD With the widespread use of cross-sectional imaging, many renal masses are incidentally found. These need to be accurately
Angio-CT preoperative planning of inferior limb free flaps in plastic surgery
 Angio-CT preoperative planning of inferior limb free flaps in plastic surgery Poster No.: C-3046 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Vascular Authors: L. Saba, M. Atzeni, D. Ribuffo, G.
Angio-CT preoperative planning of inferior limb free flaps in plastic surgery Poster No.: C-3046 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Vascular Authors: L. Saba, M. Atzeni, D. Ribuffo, G.
What is Cancer? Cancer is a genetic disease: Cancer typically involves a change in gene expression/function:
 Cancer is a genetic disease: Inherited cancer Sporadic cancer What is Cancer? Cancer typically involves a change in gene expression/function: Qualitative change Quantitative change Any cancer causing genetic
Cancer is a genetic disease: Inherited cancer Sporadic cancer What is Cancer? Cancer typically involves a change in gene expression/function: Qualitative change Quantitative change Any cancer causing genetic
Respiratory dynamic MRI for determining aortic invasion of thoracic neoplasms
 Respiratory dynamic MRI for determining aortic invasion of thoracic neoplasms Poster No.: C-0760 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. J. Hong, J. Hur, H.-J. Lee, Y. J. Kim, B. W. Choi;
Respiratory dynamic MRI for determining aortic invasion of thoracic neoplasms Poster No.: C-0760 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. J. Hong, J. Hur, H.-J. Lee, Y. J. Kim, B. W. Choi;
Role of 3D volumetry CT in the correlation between postoperative gastric volume and weight loss in obese patients undergoing gastric sleeve surgery.
 Role of 3D volumetry CT in the correlation between postoperative gastric volume and weight loss in obese patients undergoing gastric sleeve surgery. Poster No.: C-2145 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific
Role of 3D volumetry CT in the correlation between postoperative gastric volume and weight loss in obese patients undergoing gastric sleeve surgery. Poster No.: C-2145 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific
Abdominal CT Perfusion: Effects of Breath Control Technique
 Abdominal CT Perfusion: Effects of Breath Control Technique Poster No.: C-0068 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Yoshikawa, T. Kanda, Y. Ohno, Y. Fujisawa, N. Negi, M. 1 1 2 1 1 1
Abdominal CT Perfusion: Effects of Breath Control Technique Poster No.: C-0068 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Yoshikawa, T. Kanda, Y. Ohno, Y. Fujisawa, N. Negi, M. 1 1 2 1 1 1
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW
 Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
Kidney Cancer OVERVIEW Kidney cancer is the third most common genitourinary cancer in adults. There are approximately 54,000 new cancer cases each year in the United States, and the incidence of kidney
NEOPLASMS C00 D49. Presented by Jan Halloran CCS
 NEOPLASMS C00 D49 Presented by Jan Halloran CCS 1 INTRODUCTION A neoplasm is a new or abnormal growth. In the ICD-10-CM classification system, neoplastic disease is classified in categories C00 through
NEOPLASMS C00 D49 Presented by Jan Halloran CCS 1 INTRODUCTION A neoplasm is a new or abnormal growth. In the ICD-10-CM classification system, neoplastic disease is classified in categories C00 through
Second look ultrasound examination for breast lesions: MRI and pathologic correlation
 Second look ultrasound examination for breast lesions: MRI and pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-0559 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Serrano Tamayo, E. López Soriano, M. Muñoz
Second look ultrasound examination for breast lesions: MRI and pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-0559 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Serrano Tamayo, E. López Soriano, M. Muñoz
PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience
 20 th April 2013, Barcelona, Sp PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience Philippe Appenzeller, MD Staff Radiologist and Nuclear Medicine Physician Department Medical Imaging, University Hospital Zurich PET/CT-MR
20 th April 2013, Barcelona, Sp PET/CT-MRI First clinical experience Philippe Appenzeller, MD Staff Radiologist and Nuclear Medicine Physician Department Medical Imaging, University Hospital Zurich PET/CT-MR
Your Certified Professional Cancer Coach. An Integrative Answer to Cancer Exclusive Professional Program for Patients with Cancer
 Your Certified Professional Cancer Coach An Integrative Answer to Cancer Exclusive Professional Program for Patients with Cancer The CPCC Patient Program Nutrition & Lifestyle Oncology A Cancer Diagnosis
Your Certified Professional Cancer Coach An Integrative Answer to Cancer Exclusive Professional Program for Patients with Cancer The CPCC Patient Program Nutrition & Lifestyle Oncology A Cancer Diagnosis
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT
 Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
Case Report: Whole-body Oncologic Imaging with syngo TimCT Eric Hatfield, M.D. 1 ; Agus Priatna, Ph.D. 2 ; John Kotyk, Ph.D. 1 ; Benjamin Tan, M.D. 1 ; Alto Stemmer 3 ; Stephan Kannengiesser, Ph.D. 3 ;
CHAPTER 2. Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014. 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc.
 Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Neoplasms (C00-D49) March 2014 2014 MVP Health Care, Inc. CHAPTER SPECIFIC CATEGORY CODE BLOCKS C00-C14 Malignant neoplasms of lip, oral cavity and pharynx C15-C26 Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs
Functional MRI (DCE-MRI) in the follow-up of prostate cancer after beam radiotherapy (EBRT)
 Functional MRI (DCE-MRI) in the follow-up of prostate cancer after beam radiotherapy (EBRT) Poster No.: C-0748 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. E. Méndez Escalante, D. Hernandez,
Functional MRI (DCE-MRI) in the follow-up of prostate cancer after beam radiotherapy (EBRT) Poster No.: C-0748 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. E. Méndez Escalante, D. Hernandez,
Paul S Tofts. Institute of Neurology (Queen Square), University College London, WC1N 3BG, UK
 What can quantitative DCE T -weighted MR imaging tell us? Paul S Tofts Institute of Neurology (Queen Square), University College London, WCN 3BG, UK http://www.ion.ucl.ac.uk/nmrphysics/paultofts/ p.tofts@ion.ucl.ac.uk
What can quantitative DCE T -weighted MR imaging tell us? Paul S Tofts Institute of Neurology (Queen Square), University College London, WCN 3BG, UK http://www.ion.ucl.ac.uk/nmrphysics/paultofts/ p.tofts@ion.ucl.ac.uk
Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical
 Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
Summary. 111 Detection and staging of recurrent prostate cancer is still one of the important clinical problems in prostate cancer. A rise in PSA or biochemical recurrence (BCR) is the first sign of recurrent
MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA
 MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA Poster No.: C-0019 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid
MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA Poster No.: C-0019 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid
Case Number: RT2009-124(M) Potential Audiences: Intent Doctor, Oncology Special Nurse, Resident Doctor
 Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Left Kidney Post Radical Surgery with pt4 Classification with Multiple Lung and Single Brain Metastases: the Role and Treatment Consideration of Radiotherapy Case Number: RT2009-124(M)
Renal Cell Carcinoma of the Left Kidney Post Radical Surgery with pt4 Classification with Multiple Lung and Single Brain Metastases: the Role and Treatment Consideration of Radiotherapy Case Number: RT2009-124(M)
The following information is only meant for people who have been diagnosed with advanced non-small cell
 Important information for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer The following information is only meant for people who have been diagnosed with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). NSCLC
Important information for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer The following information is only meant for people who have been diagnosed with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). NSCLC
The effect of the introduction of ICD-10 on cancer mortality trends in England and Wales
 The effect of the introduction of ICD-10 on cancer mortality trends in Anita Brock, Clare Griffiths and Cleo Rooney, Offi ce for INTRODUCTION From January 2001 deaths in have been coded to the Tenth Revision
The effect of the introduction of ICD-10 on cancer mortality trends in Anita Brock, Clare Griffiths and Cleo Rooney, Offi ce for INTRODUCTION From January 2001 deaths in have been coded to the Tenth Revision
Physiological Basis of the BOLD Signal. Kerstin Preuschoff Social and Neural systems Lab University of Zurich
 Physiological Basis of the BOLD Signal Kerstin Preuschoff Social and Neural systems Lab University of Zurich Source: Arthurs & Boniface, 2002 From Stimulus to Bold Overview Physics of BOLD signal - Magnetic
Physiological Basis of the BOLD Signal Kerstin Preuschoff Social and Neural systems Lab University of Zurich Source: Arthurs & Boniface, 2002 From Stimulus to Bold Overview Physics of BOLD signal - Magnetic
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO ABLATION THERAPY THE DIVISION OF VASCULAR/INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY THE ROBERT WOOD JOHNSON UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Treatment options for patients with cancer continue to expand, providing
Cancer is the leading cause of death for Canadians aged 35 to 64 and is also the leading cause of critical illness claims in Canada.
 Underwriting cancer In this issue of the Decision, we provide an overview of Canadian cancer statistics and the information we use to make an underwriting decision. The next few issues will deal with specific
Underwriting cancer In this issue of the Decision, we provide an overview of Canadian cancer statistics and the information we use to make an underwriting decision. The next few issues will deal with specific
Advanced Radiation Therapy of Cancer by Proton Beam
 March 20th, 2014 Advanced Radiation Therapy of Cancer by Proton Beam Fukui Prefectural Hospital Proton Therapy Center Yamamoto, Kazutaka Wave (electromagnetic wave) IR (Ionizing) Radiation 700 400 350~100
March 20th, 2014 Advanced Radiation Therapy of Cancer by Proton Beam Fukui Prefectural Hospital Proton Therapy Center Yamamoto, Kazutaka Wave (electromagnetic wave) IR (Ionizing) Radiation 700 400 350~100
Are children more sensitive to radiation than adults?
 Are children more sensitive to radiation than adults? By Madan M. Rehani Director of Radiation Protection, European Society of Radiology There is a commonly held belief that children may be two to three
Are children more sensitive to radiation than adults? By Madan M. Rehani Director of Radiation Protection, European Society of Radiology There is a commonly held belief that children may be two to three
Current Status and Future Direction of Proton Beam Therapy
 Current Status and Future Direction of Proton Beam Therapy National Cancer Center Hospital East Division of Radiation Oncology and Particle Therapy Tetsuo Akimoto Comparison of status of particle therapy
Current Status and Future Direction of Proton Beam Therapy National Cancer Center Hospital East Division of Radiation Oncology and Particle Therapy Tetsuo Akimoto Comparison of status of particle therapy
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
In Practice Whole Body MR for Visualizing Metastatic Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. 1 Great strides have
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
 Abhishek Vadalia Introduction Chemoembolization is being used with increasing frequency in the treatment of solid hepatic tumors such as Hepatocellular Carinoma (HCC) & rare Cholangiocellular Carcinoma
Abhishek Vadalia Introduction Chemoembolization is being used with increasing frequency in the treatment of solid hepatic tumors such as Hepatocellular Carinoma (HCC) & rare Cholangiocellular Carcinoma
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing
 Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Us TOO University Presents: Understanding Diagnostic Testing for Prostate Cancer Patients Today s speaker is Manish Bhandari, MD Program moderator is Pam Barrett, Us TOO International Made possible by
Avastin: Glossary of key terms
 Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Avastin: Glossary of key terms Adenocarcinoma Adenoma Adjuvant therapy Angiogenesis Anti-angiogenics Antibody Antigen Avastin (bevacizumab) Benign A form of carcinoma that originates in glandular tissue.
Future Directions in Cancer Research What does is mean for medical physicists and AAPM?
 Future Directions in Cancer Research What does is mean for medical physicists and AAPM? John D. Hazle, Ph.D., FAAPM, FACR President-elect American Association of Physicists in Medicine Professor and Chairman
Future Directions in Cancer Research What does is mean for medical physicists and AAPM? John D. Hazle, Ph.D., FAAPM, FACR President-elect American Association of Physicists in Medicine Professor and Chairman
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy
 Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Metastatic Cervical Cancer s/p Radiation Therapy, Radical Hysterectomy and Attempted Modified Internal Hemipelvectomy Sarah Hutto,, MSIV Marc Underhill, M.D. January 27, 2009 Past History 45 yo female
Level 1. Nutrition & Lifestyle Oncology Certificate
 Level 1 Nutrition & Lifestyle Oncology Certificate ONE MODULE 1 A Cancer Diagnosis Learn what cancer is; how/why it develops; diagnostic tests; inflammatory/ hormonal connections; 5 most important steps
Level 1 Nutrition & Lifestyle Oncology Certificate ONE MODULE 1 A Cancer Diagnosis Learn what cancer is; how/why it develops; diagnostic tests; inflammatory/ hormonal connections; 5 most important steps
The Lewin Group undertook the following steps to identify the guidelines relevant to the 11 targeted procedures:
 Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
Guidelines The following is a list of proposed medical specialty guidelines that have been found for the 11 targeted procedures to be included in the Medicare Imaging Demonstration. The list includes only
False positive PET in lymphoma
 False positive PET in lymphoma Thomas Krause Introduction and conclusion 2 3 Introduction 4 FDG-PET in staging of lymphoma 34 studies with 2227 Patients CT FDG-PET Sensitivity 63 % 89 % (58%-100%) (63%-100%)
False positive PET in lymphoma Thomas Krause Introduction and conclusion 2 3 Introduction 4 FDG-PET in staging of lymphoma 34 studies with 2227 Patients CT FDG-PET Sensitivity 63 % 89 % (58%-100%) (63%-100%)
Come valutare la risposta o la progressione nei pazienti in trattamento con terapie biologiche
 Come valutare la risposta o la progressione nei pazienti in trattamento con terapie biologiche Andrea Busolo U.O. di Radiologia Rocco De Vivo U.O. di Oncologia Medica ULSS 6 - Vicenza Activity and efficacy
Come valutare la risposta o la progressione nei pazienti in trattamento con terapie biologiche Andrea Busolo U.O. di Radiologia Rocco De Vivo U.O. di Oncologia Medica ULSS 6 - Vicenza Activity and efficacy
EMRI ERASMUS COURSE ON MAGNETIC RESONANCE. MRI Abdominal Module
 EMRI ERASMUS COURSE ON MAGNETIC RESONANCE MRI Abdominal Module September, 23-26, 2015 Coimbra, Portugal LOCAL ORGANIZERS F Caseiro-Alves L Curvo-Semedo Dear Colleagues: It is our pleasure to receive you
EMRI ERASMUS COURSE ON MAGNETIC RESONANCE MRI Abdominal Module September, 23-26, 2015 Coimbra, Portugal LOCAL ORGANIZERS F Caseiro-Alves L Curvo-Semedo Dear Colleagues: It is our pleasure to receive you
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data
 The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
The File-Card-Browser View for Breast DCE-MRI Data Sylvia Glaßer 1, Kathrin Scheil 1, Uta Preim 2, Bernhard Preim 1 1 Department of Simulation and Graphics, University of Magdeburg 2 Department of Radiology,
Role of taxanes in the treatment of advanced NHL patients: A randomized study of 87 cases
 Role of taxanes in the treatment of advanced NHL patients: A randomized study of 87 cases R. Shraddha, P.N. Pandit Radium Institute, Patna Medical College and Hospital, Patna, India Abstract NHL is a highly
Role of taxanes in the treatment of advanced NHL patients: A randomized study of 87 cases R. Shraddha, P.N. Pandit Radium Institute, Patna Medical College and Hospital, Patna, India Abstract NHL is a highly
Our Facility. Advanced clinical center with the newest and highly exact technology for treatment of patients with cancer pencil beam
 PTC Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently comes closest to this
PTC Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently comes closest to this
PET. Can we afford PET-CT. Positron annihilation. PET-CT scanner. PET detection
 PET-CT Can we afford PET-CT John Buscombe New technology Combines functional information-pet anatomical information-ct Machine able to perform both studies in single imaging episode PET imaging depends
PET-CT Can we afford PET-CT John Buscombe New technology Combines functional information-pet anatomical information-ct Machine able to perform both studies in single imaging episode PET imaging depends
Co-pay assistance organizations offering assistance
 Acromegaly Acute Exacerbations of Multiple Sclerosis Acute Porphyrias Advanced Idiopathic Parkinson' s Disease Age-Related Macular Degeneration www.theassistancefund.org Alcohol Dependence Alpha-1 Antitrypsin
Acromegaly Acute Exacerbations of Multiple Sclerosis Acute Porphyrias Advanced Idiopathic Parkinson' s Disease Age-Related Macular Degeneration www.theassistancefund.org Alcohol Dependence Alpha-1 Antitrypsin
Functional neuroimaging. Imaging brain function in real time (not just the structure of the brain).
 Functional neuroimaging Imaging brain function in real time (not just the structure of the brain). The brain is bloody & electric Blood increase in neuronal activity increase in metabolic demand for glucose
Functional neuroimaging Imaging brain function in real time (not just the structure of the brain). The brain is bloody & electric Blood increase in neuronal activity increase in metabolic demand for glucose
OBJECTIVES By the end of this segment, the community participant will be able to:
 Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Cancer 101: Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Linda U. Krebs, RN, PhD, AOCN, FAAN OCEAN Native Navigators and the Cancer Continuum (NNACC) (NCMHD R24MD002811) Cancer 101: Diagnosis & Staging (Watanabe-Galloway
Medullary Renal Cell Carcinoma Case Report
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 4, December 2005 Medullary Renal Cell Carcinoma Case Report Mohammed Abdulla Al-Tantawi MBBCH, CABS* Abdul Amir Issa MBBCH, CABS*** Mohammed Abdulla MBBCH, CABS**
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 4, December 2005 Medullary Renal Cell Carcinoma Case Report Mohammed Abdulla Al-Tantawi MBBCH, CABS* Abdul Amir Issa MBBCH, CABS*** Mohammed Abdulla MBBCH, CABS**
Cancer of the Cervix
 Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer of the Cervix WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 A woman's cervix (the opening of the uterus) is lined with cells. Cancer of the cervix occurs when those cells change,
Cancer: DNA Synthesis, Mitosis, and Meiosis
 Chapter 5 Cancer: DNA Synthesis, Mitosis, and Meiosis Copyright 2007 Pearson Copyright Prentice Hall, 2007 Inc. Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. 1 What Is Cancer? Benign tumors do not invade surrounding tissue
Chapter 5 Cancer: DNA Synthesis, Mitosis, and Meiosis Copyright 2007 Pearson Copyright Prentice Hall, 2007 Inc. Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. 1 What Is Cancer? Benign tumors do not invade surrounding tissue
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS
 LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS LIVER CANCER AND TUMOURS Healthy Liver Cirrhotic Liver Tumour What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood
Future Oncology: Technology, Products, Market and Service Opportunities
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/296370/ Future Oncology: Technology, Products, Market and Service Opportunities Description: Future Oncology is an analytical newsletter
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/296370/ Future Oncology: Technology, Products, Market and Service Opportunities Description: Future Oncology is an analytical newsletter
PRINIPLES OF RADIATION THERAPY Adarsh Kumar. The basis of radiation therapy revolve around the principle that ionizing radiations kill cells
 PRINIPLES OF RADIATION THERAPY Adarsh Kumar The basis of radiation therapy revolve around the principle that ionizing radiations kill cells Radiotherapy terminology: a. Radiosensitivity: refers to susceptibility
PRINIPLES OF RADIATION THERAPY Adarsh Kumar The basis of radiation therapy revolve around the principle that ionizing radiations kill cells Radiotherapy terminology: a. Radiosensitivity: refers to susceptibility
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases.
 Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Staging and Prognosis of Three Separate Cases. Abstract This paper describes the staging, imaging, treatment, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma. Three case studies
Cryosurgery in Cancer Treatment: Questions and Answers. Key Points
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Cryosurgery in Cancer
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Cryosurgery in Cancer
Diagnosis of Recurrent Prostate Tumor at Multiparametric Prostate MRI: Pearls and Pitfalls
 Diagnosis of Recurrent Prostate Tumor at Multiparametric Prostate MRI: Pearls and Pitfalls Mark Notley, MD; Jinxing Yu, MD; Ann S. Fulcher, MD; Mary A. Turner, MD; Don Nguyen, MD Virginia Commonwealth
Diagnosis of Recurrent Prostate Tumor at Multiparametric Prostate MRI: Pearls and Pitfalls Mark Notley, MD; Jinxing Yu, MD; Ann S. Fulcher, MD; Mary A. Turner, MD; Don Nguyen, MD Virginia Commonwealth
PET/CT: Basic Principles, Applications in Oncology
 PET/CT: Basic Principles, Applications in Oncology Mabel Djang, HMS III Overview PET Basics and Limitations PET/CT - Advantages and Limitations Applications of PET/CT in oncology Summary 2 Principles of
PET/CT: Basic Principles, Applications in Oncology Mabel Djang, HMS III Overview PET Basics and Limitations PET/CT - Advantages and Limitations Applications of PET/CT in oncology Summary 2 Principles of
Proton Therapy Center Czech
 Proton Therapy Center Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently
Proton Therapy Center Czech The main goal of radiotherapy is to irreversibly damage tumor cells, whereas the cells of healthy tissue are damaged only reversibly or not at all. Proton therapy currently
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF LUNG CANCER BY Ali Shamseddine, MD (Coordinator); as04@aub.edu.lb Fady Geara, MD Bassem Shabb, MD Ghassan Jamaleddine, MD CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR THE TREATMENT
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microwave_tumor_ablation 12/2011 11/2015 11/2016 11/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Microwave ablation
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microwave_tumor_ablation 12/2011 11/2015 11/2016 11/2015 Description of Procedure or Service Microwave ablation
PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY
 PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY INTRODUCTION The RITA project is aimed at estimating the burden of rare malignant tumours in Italy using the population based cancer registries (CRs) data. One of
PROTOCOL OF THE RITA DATA QUALITY STUDY INTRODUCTION The RITA project is aimed at estimating the burden of rare malignant tumours in Italy using the population based cancer registries (CRs) data. One of
Biochemistry of Cancer Cell
 Biochemistry of Cancer Cell Prof. Taha Kumosani Prof. Taha Kumosani http://biochemistry4all.com/taha/5.htm Cancer: an Overview Paleopathologists Dinosaur bones Egyptians Papyrus Autopsis Hippocrates Carcinoma
Biochemistry of Cancer Cell Prof. Taha Kumosani Prof. Taha Kumosani http://biochemistry4all.com/taha/5.htm Cancer: an Overview Paleopathologists Dinosaur bones Egyptians Papyrus Autopsis Hippocrates Carcinoma
New strategies in anticancer therapy
 癌 症 診 療 指 引 簡 介 及 臨 床 應 用 New strategies in anticancer therapy 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 腫 瘤 內 科 蔡 明 宏 醫 師 2014/3/29 Anti-Cancer Therapy Surgical Treatment Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Target Therapy Supportive
癌 症 診 療 指 引 簡 介 及 臨 床 應 用 New strategies in anticancer therapy 中 山 醫 學 大 學 附 設 醫 院 腫 瘤 內 科 蔡 明 宏 醫 師 2014/3/29 Anti-Cancer Therapy Surgical Treatment Radiotherapy Chemotherapy Target Therapy Supportive
Title: Immunohistochemical staining of radixin and moesin in prostatic adenocarcinoma
 Author's response to reviews Title: Immunohistochemical staining of radixin and moesin in prostatic adenocarcinoma Authors: Tanner L Bartholow (bartholow.tanner@medstudent.pitt.edu) Uma R Chandran (chandranur@msx.upmc.edu)
Author's response to reviews Title: Immunohistochemical staining of radixin and moesin in prostatic adenocarcinoma Authors: Tanner L Bartholow (bartholow.tanner@medstudent.pitt.edu) Uma R Chandran (chandranur@msx.upmc.edu)
HADRON THERAPY FOR CANCER TREATMENT
 HADRON THERAPY FOR CANCER TREATMENT Seminar presented by Arlene Lennox at Fermilab on Nov 21, 2003 CANCER STAGES LOCAL TUMOR REGIONAL METASTASIS SYSTEMIC DISEASE CANCER TREATMENT SURGERY RADIATION THERAPY
HADRON THERAPY FOR CANCER TREATMENT Seminar presented by Arlene Lennox at Fermilab on Nov 21, 2003 CANCER STAGES LOCAL TUMOR REGIONAL METASTASIS SYSTEMIC DISEASE CANCER TREATMENT SURGERY RADIATION THERAPY
BNC105 PHASE II RENAL CANCER TRIAL RESULTS
 ABN 53 075 582 740 ASX ANNOUNCEMENT 19 March 2014 BNC105 PHASE II RENAL CANCER TRIAL RESULTS Results show BNC105 utility in patients with advanced disease Identified biomarkers which correlate with patient
ABN 53 075 582 740 ASX ANNOUNCEMENT 19 March 2014 BNC105 PHASE II RENAL CANCER TRIAL RESULTS Results show BNC105 utility in patients with advanced disease Identified biomarkers which correlate with patient
Saturation Biopsy vs. 3D Spatial Biopsy vs. Free Hand Ultrasound biopsy for Targeted Prostate Cancer Therapies
 Saturation Biopsy vs. 3D Spatial Biopsy vs. Free Hand Ultrasound biopsy for Targeted Prostate Cancer Therapies John F. Ward, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Ablation
Saturation Biopsy vs. 3D Spatial Biopsy vs. Free Hand Ultrasound biopsy for Targeted Prostate Cancer Therapies John F. Ward, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Ablation
NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER
 Media Release April 7, 2009 For Immediate Release NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER London, Ontario Improved hybrid imaging techniques developed
Media Release April 7, 2009 For Immediate Release NEW HYBRID IMAGING TECHNOLOGY MAY HAVE BIG POTENTIAL FOR IMPROVING DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATE CANCER London, Ontario Improved hybrid imaging techniques developed
Robert Bristow MD PhD FRCPC
 Robert Bristow MD PhD FRCPC Clinician-Scientist and Professor, Radiation Oncology and Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto and Ontario Cancer Institute/ (UHN) Head, PMH-CFCRI Prostate Cancer Research
Robert Bristow MD PhD FRCPC Clinician-Scientist and Professor, Radiation Oncology and Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto and Ontario Cancer Institute/ (UHN) Head, PMH-CFCRI Prostate Cancer Research
Influenza (Flu) Influenza is a viral infection that may affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are three types of flu virus:
 Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
DWI Case Study - QIBA PDF- MRI Technical Committee. What is IMI?
 DWI Case Study - QIBA PDF- MRI Technical Committee QIBA Annual Meeting May 21, 2014 What is IMI? The Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) is the world s largest biomedical /healthcare public-private initiative
DWI Case Study - QIBA PDF- MRI Technical Committee QIBA Annual Meeting May 21, 2014 What is IMI? The Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) is the world s largest biomedical /healthcare public-private initiative
Immunohistochemical differentiation of metastatic tumours
 Immunohistochemical differentiation of metastatic tumours Dr Abi Wheal ST1. TERA 3/2/14 Key points from a review article written by Daisuke Nonaka Intro Metastatic disease is the initial presentation in
Immunohistochemical differentiation of metastatic tumours Dr Abi Wheal ST1. TERA 3/2/14 Key points from a review article written by Daisuke Nonaka Intro Metastatic disease is the initial presentation in
LCFA/IASLC LORI MONROE SCHOLARSHIP IN TRANSLATIONAL LUNG CANCER RESEARCH
 LCFA/IASLC LORI MONROE SCHOLARSHIP IN TRANSLATIONAL LUNG CANCER RESEARCH FUNDING OPPORTUNITY DESCRIPTION 2016 REQUEST FOR APPLICATION (RFA) Lung Cancer Foundation of America (LCFA) and the International
LCFA/IASLC LORI MONROE SCHOLARSHIP IN TRANSLATIONAL LUNG CANCER RESEARCH FUNDING OPPORTUNITY DESCRIPTION 2016 REQUEST FOR APPLICATION (RFA) Lung Cancer Foundation of America (LCFA) and the International
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS. Diagnosis/Initial evaluation. Treatment and Prognosis
 LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
LYMPHOMA IN DOGS Lymphoma is a relatively common cancer in dogs. It is a cancer of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and lymphoid tissues. Lymphoid tissue is normally present in many places in the
Metastatic Prostate Cancer Causing Complete Obstruction of the IVC
 Department of Radiology Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan Metastatic Prostate Cancer Causing Complete Obstruction of the IVC Jennifer Johnston MSIII, Wayne State Medical School Stage 4 Metastatic
Department of Radiology Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan Metastatic Prostate Cancer Causing Complete Obstruction of the IVC Jennifer Johnston MSIII, Wayne State Medical School Stage 4 Metastatic
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma
 A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
A912: Kidney, Renal cell carcinoma General facts of kidney cancer Renal cell carcinoma, a form of kidney cancer that involves cancerous changes in the cells of the renal tubule, is the most common type
GE Medical Systems Training in Partnership. Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time
 Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time IQ : Acquisition Time Objectives...Describe types of data acquisition modes....compute acquisition times for 2D and 3D scans. 2D Acquisitions The 2D mode acquires and reconstructs
Module 8: IQ: Acquisition Time IQ : Acquisition Time Objectives...Describe types of data acquisition modes....compute acquisition times for 2D and 3D scans. 2D Acquisitions The 2D mode acquires and reconstructs
Luis D. Carcorze Soto, MD PGY-3
 Luis D. Carcorze Soto, MD PGY-3 Peritoneal Surface Malignancies Peritoneum Patient Selection Operative Technique HIPEC EPIC Primary: Primary Peritoneal Carcinoma Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Metastatic:
Luis D. Carcorze Soto, MD PGY-3 Peritoneal Surface Malignancies Peritoneum Patient Selection Operative Technique HIPEC EPIC Primary: Primary Peritoneal Carcinoma Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Metastatic:
3/30/2013. Disclosure. Advanced Neuro MRI: Imaging Techniques and Protocol Optimization. MRI, 35 year ago. MRI Today. Outlines
 http://www.magnet.fsu.edu Disclosure Advanced Neuro MRI: Imaging Techniques and Protocol Optimization Research funding provided by Siemens Healthcare. Chen Lin, PhD DABR Indiana University School of Medicine
http://www.magnet.fsu.edu Disclosure Advanced Neuro MRI: Imaging Techniques and Protocol Optimization Research funding provided by Siemens Healthcare. Chen Lin, PhD DABR Indiana University School of Medicine
Smoking and misuse of certain pain medicines can affect the risk of developing renal cell cancer.
 Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
Renal cell cancer Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which
NICE Pathways bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic.
 bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
bring together all NICE guidance, quality standards and other NICE information on a specific topic. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published.
