Exploring Number System
|
|
|
- Charleen Hall
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exploring Number System Mun Chou, Fong QED Education Scientific Malaysia LEVEL High schools after students have been introduced to concepts of number systems. OBJECTIVES To explore converting between binary, octal, decimal and hexadecimal number systems by hand and also by using the Base-N mode. OVERVIEW Alternative to the decimal number system such as the binary has proven to be vitally important in computer sciences. We explore this binary system together with the octal (base-8) number system and the hexadecimal number system (base-16) as they are natural conversions from binary and are just as important in computer sciences. The decimal system is the widely used number system and as such we shall explore a lot on the relation between the three aforementioned systems with the decimal system. EXPLORATORY ACTIVITIES [Note] (a) Unless otherwise specified, we choose MthIO mode in the SETUP menu by tapping (b) The system each number represented will be described with a subscript of 2, 8, and 16 for binary, octal and hexadecimal respectively; except for number in base-10, which will be written just as it is. Binary, Octal and Hexadecimal Systems The decimal number system (base-10) is a position-value system which uses the numeral symbols of 0, 1, 2 9. In similar fashion, the binary uses only 1 s and 0 s for representation of number. For example the number 55 in decimal system will be represented as and can be easily illustrated using the binary table as follow: 2005 CASIO Computer Co., LTD. All Right Reserved. Page A
2 In power Of Input in 1 and So based on the table above, if we are to convert into decimal, the calculation is = = 55. On the calculator this can be done fairly easy in the Base-N mode. Each time you enter Base-N the calculator by default is in the Dec, or decimal system. Switch to the Bin, or binary system Enter the number Register into the calculator Switch to Dec to convert The calculator displays 55 verifying our hand calculation. How about expressing in octal (base-8) or hexadecimal (base-16)? Switch to Oct for conversion Or switch to Hex for base-16 Both these outputs of 67 8 and can be easily illustrated with the base tables. For example the octal representation of or 55: In power Of Input from 0 till = = And to explain the hexadecimal representation of or 55: In power Of = = Input from 0 till Hexadecimal in Focus Let s explore further on the hexadecimal (base-16) system. We begin by entering 10 in the Dec mode CASIO Computer Co., LTD. All Right Reserved. Page A
3 Enter Base-N/Dec mode Input 10 and register it Now tap once on to switch to the base-16 mode. Do you notice the output is A? The reason of this is for avoiding confusion when using the base-16 system. Since we use 0 till 15 in hexadecimal for representation, we may get confused over and 10, therefore 10 is represented as A in hexadecimal. How about the representation for 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15? Key these numbers into Dec mode and then switch to Hex mode to find out. The actual representation is as below. The digit In Hexadecimal A B C D E F Conversion from Base-10 to the Other 3 Systems As shown above if we want to do a conversion from the other three systems to decimal we can use the base table. Converting from decimal to the other systems is slightly more challenging. Suppose we are to express 13 in binary, an effective method is the repeated-division technique: 13 2 = 6 remainder is = 3 remainder is = 1 remainder is 1 The division stops when the quotient is < 2, then we read the binary conversion following the curved arrows, i.e. 13 = Similarly, conversion from decimal to octal or hexadecimal is along the same line too. For example to express 742 in hexadecimal: = 46 remainder is = 2 remainder is 14 We stop when the quotient is < 16; in this case it is 2. Reading in direction of the curved arrows, 742 is expressed as 2(14)6 16, but recalling the table just now, 14 is written as E in hexadecimal, therefore we have 742 = 2E6 16. The repeated-division algorithm could take a while if we convert a larger number such as 175. The calculator can be used to process the conversion CASIO Computer Co., LTD. All Right Reserved. Page A
4 While in Dec mode, input 742 Then switch to Hex mode And the result of the conversion is displayed immediately. Conversion between the 3 Systems Conversion between the binary, octal and hexadecimal is much easier as the octal or the hexadecimal system is naturally closer to the binary than decimal. Consider the number Since the octal system has power index of 3 (2 3 = 8) as relative to the binary system, conversion can be performed as follow: Partitions into bits of 3 starting from right: / 010 / Then convert each part to its decimal equivalent: In decimal equivalent Reading the numbers in the direction of the shaded arrow, we have = To convert into hexadecimal, we partition the binary number to bits of 4 from the right, as hexadecimal system has power index of 4 (2 4 = 16) relative to the binary system: In decimal equivalent 13 5 Therefore = (13)5 16 or more appropriately, D5 16. Use the calculator to verify your conversion for all the above. Switch to Bin mode Now input the binary number Now switch to Hex or Oct mode It seems that the calculator outputs verify the manual calculation. Conversion from octal or hexadecimal into binary is the reverse of the above algorithm. Consider the number 1A5D 16. Again using the partition technique: Split all the digits in 1A5D 16 into 4 parts (because it has 4 digits): 1A5D A D CASIO Computer Co., LTD. All Right Reserved. Page A
5 Then convert each digit to its 4-bit binary equivalent: 1 16 A D 16 In 4-bit binary equivalent And in the direction of the shaded arrow, we have 1A5D 2 = or more appropriately, 1A5D 2 = , excluding the zeroes at front. Again use the calculator to verify the conversion for all the above. Switch to Hex mode, input 1A5D 16 Switch to Bin mode for result The output verifies that 1A5D 2 is equivalent to EXERCISES These exercises should enhance your understanding on the subject matter of number systems while using the calculator to explore further on conversion between different number systems. Calculate each one manually before verifying the solution with 991-ES. Exercise 1 Use the base table to express each of the following in decimal, then verify with the Base-N mode. (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) E3AC 16 Exercise 2 Express 167 in (i) binary, (ii) Octal, and finally (iii) Hexadecimal form. Exercise 3 Express in base-8 and base-16 using the 3-bit and 4 bit conversions. Exercise 4 Express (i) 37A 16 and (ii) in binary. Exercise 5 The number system of base-5 should observe all the techniques and properties we discussed in the exploration also. Referring to the number system of base-5: (i) Express 389 in base-5; (ii) Convert into decimal and binary. Hint: You might not able to use the calculator for verification. SOLUTIONS to Exercises Exercise 1 (i) 45 (ii) 175 (iii) 41 (iv) CASIO Computer Co., LTD. All Right Reserved. Page A
6 Exercise 2 (i) (ii) (iii) A7 16 Exercise 3 174D 16 and Exercise 4 (i) (ii) Exercise 5 (i) 389 = (ii) 1482 and CASIO Computer Co., LTD. All Right Reserved. Page A
Sequence of Numbers. Mun Chou, Fong QED Education Scientific Malaysia
 Sequence of Numbers Mun Chou, Fong QED Education Scientific Malaysia LEVEL High school after students have learned sequence. OBJECTIVES To review sequences and generate sequences using scientific calculator.
Sequence of Numbers Mun Chou, Fong QED Education Scientific Malaysia LEVEL High school after students have learned sequence. OBJECTIVES To review sequences and generate sequences using scientific calculator.
Useful Number Systems
 Useful Number Systems Decimal Base = 10 Digit Set = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} Binary Base = 2 Digit Set = {0, 1} Octal Base = 8 = 2 3 Digit Set = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} Hexadecimal Base = 16 = 2
Useful Number Systems Decimal Base = 10 Digit Set = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} Binary Base = 2 Digit Set = {0, 1} Octal Base = 8 = 2 3 Digit Set = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} Hexadecimal Base = 16 = 2
CSI 333 Lecture 1 Number Systems
 CSI 333 Lecture 1 Number Systems 1 1 / 23 Basics of Number Systems Ref: Appendix C of Deitel & Deitel. Weighted Positional Notation: 192 = 2 10 0 + 9 10 1 + 1 10 2 General: Digit sequence : d n 1 d n 2...
CSI 333 Lecture 1 Number Systems 1 1 / 23 Basics of Number Systems Ref: Appendix C of Deitel & Deitel. Weighted Positional Notation: 192 = 2 10 0 + 9 10 1 + 1 10 2 General: Digit sequence : d n 1 d n 2...
Oct: 50 8 = 6 (r = 2) 6 8 = 0 (r = 6) Writing the remainders in reverse order we get: (50) 10 = (62) 8
 ECE Department Summer LECTURE #5: Number Systems EEL : Digital Logic and Computer Systems Based on lecture notes by Dr. Eric M. Schwartz Decimal Number System: -Our standard number system is base, also
ECE Department Summer LECTURE #5: Number Systems EEL : Digital Logic and Computer Systems Based on lecture notes by Dr. Eric M. Schwartz Decimal Number System: -Our standard number system is base, also
Chapter Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations
 Chapter 5 Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations This calculator is capable of performing the following operations involving different number systems. Number system conversion Arithmetic
Chapter 5 Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations This calculator is capable of performing the following operations involving different number systems. Number system conversion Arithmetic
Binary Numbers. Binary Octal Hexadecimal
 Binary Numbers Binary Octal Hexadecimal Binary Numbers COUNTING SYSTEMS UNLIMITED... Since you have been using the 10 different digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 all your life, you may wonder how
Binary Numbers Binary Octal Hexadecimal Binary Numbers COUNTING SYSTEMS UNLIMITED... Since you have been using the 10 different digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 all your life, you may wonder how
Positional Numbering System
 APPENDIX B Positional Numbering System A positional numbering system uses a set of symbols. The value that each symbol represents, however, depends on its face value and its place value, the value associated
APPENDIX B Positional Numbering System A positional numbering system uses a set of symbols. The value that each symbol represents, however, depends on its face value and its place value, the value associated
Computer Science 281 Binary and Hexadecimal Review
 Computer Science 281 Binary and Hexadecimal Review 1 The Binary Number System Computers store everything, both instructions and data, by using many, many transistors, each of which can be in one of two
Computer Science 281 Binary and Hexadecimal Review 1 The Binary Number System Computers store everything, both instructions and data, by using many, many transistors, each of which can be in one of two
Base Conversion written by Cathy Saxton
 Base Conversion written by Cathy Saxton 1. Base 10 In base 10, the digits, from right to left, specify the 1 s, 10 s, 100 s, 1000 s, etc. These are powers of 10 (10 x ): 10 0 = 1, 10 1 = 10, 10 2 = 100,
Base Conversion written by Cathy Saxton 1. Base 10 In base 10, the digits, from right to left, specify the 1 s, 10 s, 100 s, 1000 s, etc. These are powers of 10 (10 x ): 10 0 = 1, 10 1 = 10, 10 2 = 100,
Everything you wanted to know about using Hexadecimal and Octal Numbers in Visual Basic 6
 Everything you wanted to know about using Hexadecimal and Octal Numbers in Visual Basic 6 Number Systems No course on programming would be complete without a discussion of the Hexadecimal (Hex) number
Everything you wanted to know about using Hexadecimal and Octal Numbers in Visual Basic 6 Number Systems No course on programming would be complete without a discussion of the Hexadecimal (Hex) number
2 Number Systems. Source: Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning. Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to:
 2 Number Systems 2.1 Source: Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Understand the concept of number systems. Distinguish
2 Number Systems 2.1 Source: Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: Understand the concept of number systems. Distinguish
Section 1.4 Place Value Systems of Numeration in Other Bases
 Section.4 Place Value Systems of Numeration in Other Bases Other Bases The Hindu-Arabic system that is used in most of the world today is a positional value system with a base of ten. The simplest reason
Section.4 Place Value Systems of Numeration in Other Bases Other Bases The Hindu-Arabic system that is used in most of the world today is a positional value system with a base of ten. The simplest reason
Machine Architecture and Number Systems. Major Computer Components. Schematic Diagram of a Computer. The CPU. The Bus. Main Memory.
 1 Topics Machine Architecture and Number Systems Major Computer Components Bits, Bytes, and Words The Decimal Number System The Binary Number System Converting from Decimal to Binary Major Computer Components
1 Topics Machine Architecture and Number Systems Major Computer Components Bits, Bytes, and Words The Decimal Number System The Binary Number System Converting from Decimal to Binary Major Computer Components
Number Conversions Dr. Sarita Agarwal (Acharya Narendra Dev College,University of Delhi)
 Conversions Dr. Sarita Agarwal (Acharya Narendra Dev College,University of Delhi) INTRODUCTION System- A number system defines a set of values to represent quantity. We talk about the number of people
Conversions Dr. Sarita Agarwal (Acharya Narendra Dev College,University of Delhi) INTRODUCTION System- A number system defines a set of values to represent quantity. We talk about the number of people
Binary Number System. 16. Binary Numbers. Base 10 digits: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9. Base 2 digits: 0 1
 Binary Number System 1 Base 10 digits: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Base 2 digits: 0 1 Recall that in base 10, the digits of a number are just coefficients of powers of the base (10): 417 = 4 * 10 2 + 1 * 10 1
Binary Number System 1 Base 10 digits: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Base 2 digits: 0 1 Recall that in base 10, the digits of a number are just coefficients of powers of the base (10): 417 = 4 * 10 2 + 1 * 10 1
Chapter 7 Lab - Decimal, Binary, Octal, Hexadecimal Numbering Systems
 Chapter 7 Lab - Decimal, Binary, Octal, Hexadecimal Numbering Systems This assignment is designed to familiarize you with different numbering systems, specifically: binary, octal, hexadecimal (and decimal)
Chapter 7 Lab - Decimal, Binary, Octal, Hexadecimal Numbering Systems This assignment is designed to familiarize you with different numbering systems, specifically: binary, octal, hexadecimal (and decimal)
3. Convert a number from one number system to another
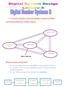 3. Convert a number from one number system to another Conversion between number bases: Hexa (16) Decimal (10) Binary (2) Octal (8) More Interest Way we need conversion? We need decimal system for real
3. Convert a number from one number system to another Conversion between number bases: Hexa (16) Decimal (10) Binary (2) Octal (8) More Interest Way we need conversion? We need decimal system for real
NUMBER SYSTEMS. 1.1 Introduction
 NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.1 Introduction There are several number systems which we normally use, such as decimal, binary, octal, hexadecimal, etc. Amongst them we are most familiar with the decimal number system.
NUMBER SYSTEMS 1.1 Introduction There are several number systems which we normally use, such as decimal, binary, octal, hexadecimal, etc. Amongst them we are most familiar with the decimal number system.
COMP 250 Fall 2012 lecture 2 binary representations Sept. 11, 2012
 Binary numbers The reason humans represent numbers using decimal (the ten digits from 0,1,... 9) is that we have ten fingers. There is no other reason than that. There is nothing special otherwise about
Binary numbers The reason humans represent numbers using decimal (the ten digits from 0,1,... 9) is that we have ten fingers. There is no other reason than that. There is nothing special otherwise about
CDA 3200 Digital Systems. Instructor: Dr. Janusz Zalewski Developed by: Dr. Dahai Guo Spring 2012
 CDA 3200 Digital Systems Instructor: Dr. Janusz Zalewski Developed by: Dr. Dahai Guo Spring 2012 Outline Data Representation Binary Codes Why 6-3-1-1 and Excess-3? Data Representation (1/2) Each numbering
CDA 3200 Digital Systems Instructor: Dr. Janusz Zalewski Developed by: Dr. Dahai Guo Spring 2012 Outline Data Representation Binary Codes Why 6-3-1-1 and Excess-3? Data Representation (1/2) Each numbering
Decimal to Binary Conversion
 Decimal to Binary Conversion A tool that makes the conversion of decimal values to binary values simple is the following table. The first row is created by counting right to left from one to eight, for
Decimal to Binary Conversion A tool that makes the conversion of decimal values to binary values simple is the following table. The first row is created by counting right to left from one to eight, for
Lecture 11: Number Systems
 Lecture 11: Number Systems Numeric Data Fixed point Integers (12, 345, 20567 etc) Real fractions (23.45, 23., 0.145 etc.) Floating point such as 23. 45 e 12 Basically an exponent representation Any number
Lecture 11: Number Systems Numeric Data Fixed point Integers (12, 345, 20567 etc) Real fractions (23.45, 23., 0.145 etc.) Floating point such as 23. 45 e 12 Basically an exponent representation Any number
Goals. Unary Numbers. Decimal Numbers. 3,148 is. 1000 s 100 s 10 s 1 s. Number Bases 1/12/2009. COMP370 Intro to Computer Architecture 1
 Number Bases //9 Goals Numbers Understand binary and hexadecimal numbers Be able to convert between number bases Understand binary fractions COMP37 Introduction to Computer Architecture Unary Numbers Decimal
Number Bases //9 Goals Numbers Understand binary and hexadecimal numbers Be able to convert between number bases Understand binary fractions COMP37 Introduction to Computer Architecture Unary Numbers Decimal
NUMBER SYSTEMS. William Stallings
 NUMBER SYSTEMS William Stallings The Decimal System... The Binary System...3 Converting between Binary and Decimal...3 Integers...4 Fractions...5 Hexadecimal Notation...6 This document available at WilliamStallings.com/StudentSupport.html
NUMBER SYSTEMS William Stallings The Decimal System... The Binary System...3 Converting between Binary and Decimal...3 Integers...4 Fractions...5 Hexadecimal Notation...6 This document available at WilliamStallings.com/StudentSupport.html
CS101 Lecture 11: Number Systems and Binary Numbers. Aaron Stevens 14 February 2011
 CS101 Lecture 11: Number Systems and Binary Numbers Aaron Stevens 14 February 2011 1 2 1 3!!! MATH WARNING!!! TODAY S LECTURE CONTAINS TRACE AMOUNTS OF ARITHMETIC AND ALGEBRA PLEASE BE ADVISED THAT CALCULTORS
CS101 Lecture 11: Number Systems and Binary Numbers Aaron Stevens 14 February 2011 1 2 1 3!!! MATH WARNING!!! TODAY S LECTURE CONTAINS TRACE AMOUNTS OF ARITHMETIC AND ALGEBRA PLEASE BE ADVISED THAT CALCULTORS
2011, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 3.1 Decimal System The radix or base of a number system determines the total number of different symbols or digits used by that system. The decimal system has a base of 10 with the digits 0 through
Chapter 3 3.1 Decimal System The radix or base of a number system determines the total number of different symbols or digits used by that system. The decimal system has a base of 10 with the digits 0 through
Numbering Systems. InThisAppendix...
 G InThisAppendix... Introduction Binary Numbering System Hexadecimal Numbering System Octal Numbering System Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) Numbering System Real (Floating Point) Numbering System BCD/Binary/Decimal/Hex/Octal
G InThisAppendix... Introduction Binary Numbering System Hexadecimal Numbering System Octal Numbering System Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) Numbering System Real (Floating Point) Numbering System BCD/Binary/Decimal/Hex/Octal
Unsigned Conversions from Decimal or to Decimal and other Number Systems
 Page 1 of 5 Unsigned Conversions from Decimal or to Decimal and other Number Systems In all digital design, analysis, troubleshooting, and repair you will be working with binary numbers (or base 2). It
Page 1 of 5 Unsigned Conversions from Decimal or to Decimal and other Number Systems In all digital design, analysis, troubleshooting, and repair you will be working with binary numbers (or base 2). It
Chapter 2. Binary Values and Number Systems
 Chapter 2 Binary Values and Number Systems Numbers Natural numbers, a.k.a. positive integers Zero and any number obtained by repeatedly adding one to it. Examples: 100, 0, 45645, 32 Negative numbers A
Chapter 2 Binary Values and Number Systems Numbers Natural numbers, a.k.a. positive integers Zero and any number obtained by repeatedly adding one to it. Examples: 100, 0, 45645, 32 Negative numbers A
6 3 4 9 = 6 10 + 3 10 + 4 10 + 9 10
 Lesson The Binary Number System. Why Binary? The number system that you are familiar with, that you use every day, is the decimal number system, also commonly referred to as the base- system. When you
Lesson The Binary Number System. Why Binary? The number system that you are familiar with, that you use every day, is the decimal number system, also commonly referred to as the base- system. When you
Number Systems. Introduction / Number Systems
 Number Systems Introduction / Number Systems Data Representation Data representation can be Digital or Analog In Analog representation values are represented over a continuous range In Digital representation
Number Systems Introduction / Number Systems Data Representation Data representation can be Digital or Analog In Analog representation values are represented over a continuous range In Digital representation
Memory Management Simulation Interactive Lab
 Memory Management Simulation Interactive Lab The purpose of this lab is to help you to understand deadlock. We will use a MOSS simulator for this. The instructions for this lab are for a computer running
Memory Management Simulation Interactive Lab The purpose of this lab is to help you to understand deadlock. We will use a MOSS simulator for this. The instructions for this lab are for a computer running
Binary, Hexadecimal, Octal, and BCD Numbers
 23CH_PHCalter_TMSETE_949118 23/2/2007 1:37 PM Page 1 Binary, Hexadecimal, Octal, and BCD Numbers OBJECTIVES When you have completed this chapter, you should be able to: Convert between binary and decimal
23CH_PHCalter_TMSETE_949118 23/2/2007 1:37 PM Page 1 Binary, Hexadecimal, Octal, and BCD Numbers OBJECTIVES When you have completed this chapter, you should be able to: Convert between binary and decimal
Digital System Design Prof. D Roychoudhry Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Digital System Design Prof. D Roychoudhry Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 04 Digital Logic II May, I before starting the today s lecture
Digital System Design Prof. D Roychoudhry Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 04 Digital Logic II May, I before starting the today s lecture
Cyber Security Workshop Encryption Reference Manual
 Cyber Security Workshop Encryption Reference Manual May 2015 Basic Concepts in Encoding and Encryption Binary Encoding Examples Encryption Cipher Examples 1 P a g e Encoding Concepts Binary Encoding Basics
Cyber Security Workshop Encryption Reference Manual May 2015 Basic Concepts in Encoding and Encryption Binary Encoding Examples Encryption Cipher Examples 1 P a g e Encoding Concepts Binary Encoding Basics
Chapter 4: Computer Codes
 Slide 1/30 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer data Computer codes: representation of data in binary Most commonly used computer codes Collating sequence 36 Slide 2/30 Data
Slide 1/30 Learning Objectives In this chapter you will learn about: Computer data Computer codes: representation of data in binary Most commonly used computer codes Collating sequence 36 Slide 2/30 Data
Lecture 2. Binary and Hexadecimal Numbers
 Lecture 2 Binary and Hexadecimal Numbers Purpose: Review binary and hexadecimal number representations Convert directly from one base to another base Review addition and subtraction in binary representations
Lecture 2 Binary and Hexadecimal Numbers Purpose: Review binary and hexadecimal number representations Convert directly from one base to another base Review addition and subtraction in binary representations
4.3 TABLE 3 TABLE 4. 1342 five 1 125 3 25 4 5 2 1 125 75 20 2 222.
 .3 Conversion Between Number Bases 169.3 Conversion Between Number Bases Although the numeration systems discussed in the opening section were all base ten, other bases have occurred historically. For
.3 Conversion Between Number Bases 169.3 Conversion Between Number Bases Although the numeration systems discussed in the opening section were all base ten, other bases have occurred historically. For
THE BINARY NUMBER SYSTEM
 THE BINARY NUMBER SYSTEM Dr. Robert P. Webber, Longwood University Our civilization uses the base 10 or decimal place value system. Each digit in a number represents a power of 10. For example, 365.42
THE BINARY NUMBER SYSTEM Dr. Robert P. Webber, Longwood University Our civilization uses the base 10 or decimal place value system. Each digit in a number represents a power of 10. For example, 365.42
CPEN 214 - Digital Logic Design Binary Systems
 CPEN 4 - Digital Logic Design Binary Systems C. Gerousis Digital Design 3 rd Ed., Mano Prentice Hall Digital vs. Analog An analog system has continuous range of values A mercury thermometer Vinyl records
CPEN 4 - Digital Logic Design Binary Systems C. Gerousis Digital Design 3 rd Ed., Mano Prentice Hall Digital vs. Analog An analog system has continuous range of values A mercury thermometer Vinyl records
EE 261 Introduction to Logic Circuits. Module #2 Number Systems
 EE 261 Introduction to Logic Circuits Module #2 Number Systems Topics A. Number System Formation B. Base Conversions C. Binary Arithmetic D. Signed Numbers E. Signed Arithmetic F. Binary Codes Textbook
EE 261 Introduction to Logic Circuits Module #2 Number Systems Topics A. Number System Formation B. Base Conversions C. Binary Arithmetic D. Signed Numbers E. Signed Arithmetic F. Binary Codes Textbook
1. Give the 16 bit signed (twos complement) representation of the following decimal numbers, and convert to hexadecimal:
 Exercises 1 - number representations Questions 1. Give the 16 bit signed (twos complement) representation of the following decimal numbers, and convert to hexadecimal: (a) 3012 (b) - 435 2. For each of
Exercises 1 - number representations Questions 1. Give the 16 bit signed (twos complement) representation of the following decimal numbers, and convert to hexadecimal: (a) 3012 (b) - 435 2. For each of
BINARY CODED DECIMAL: B.C.D.
 BINARY CODED DECIMAL: B.C.D. ANOTHER METHOD TO REPRESENT DECIMAL NUMBERS USEFUL BECAUSE MANY DIGITAL DEVICES PROCESS + DISPLAY NUMBERS IN TENS IN BCD EACH NUMBER IS DEFINED BY A BINARY CODE OF 4 BITS.
BINARY CODED DECIMAL: B.C.D. ANOTHER METHOD TO REPRESENT DECIMAL NUMBERS USEFUL BECAUSE MANY DIGITAL DEVICES PROCESS + DISPLAY NUMBERS IN TENS IN BCD EACH NUMBER IS DEFINED BY A BINARY CODE OF 4 BITS.
for ECM Titanium) This guide contains a complete explanation of the Driver Maker plug-in, an add-on developed for
 Driver Maker User Guide (Plug-in for ECM Titanium) Introduction This guide contains a complete explanation of the Driver Maker plug-in, an add-on developed for ECM Titanium, the chip-tuning software produced
Driver Maker User Guide (Plug-in for ECM Titanium) Introduction This guide contains a complete explanation of the Driver Maker plug-in, an add-on developed for ECM Titanium, the chip-tuning software produced
COMPSCI 210. Binary Fractions. Agenda & Reading
 COMPSCI 21 Binary Fractions Agenda & Reading Topics: Fractions Binary Octal Hexadecimal Binary -> Octal, Hex Octal -> Binary, Hex Decimal -> Octal, Hex Hex -> Binary, Octal Animation: BinFrac.htm Example
COMPSCI 21 Binary Fractions Agenda & Reading Topics: Fractions Binary Octal Hexadecimal Binary -> Octal, Hex Octal -> Binary, Hex Decimal -> Octal, Hex Hex -> Binary, Octal Animation: BinFrac.htm Example
2010/9/19. Binary number system. Binary numbers. Outline. Binary to decimal
 2/9/9 Binary number system Computer (electronic) systems prefer binary numbers Binary number: represent a number in base-2 Binary numbers 2 3 + 7 + 5 Some terminology Bit: a binary digit ( or ) Hexadecimal
2/9/9 Binary number system Computer (electronic) systems prefer binary numbers Binary number: represent a number in base-2 Binary numbers 2 3 + 7 + 5 Some terminology Bit: a binary digit ( or ) Hexadecimal
Number of bits needed to address hosts 8
 Advanced Subnetting Example 1: Your ISP has assigned you a Class C network address of 198.47.212.0. You have 3 networks in your company with the largest containing 134 hosts. You need to figure out if
Advanced Subnetting Example 1: Your ISP has assigned you a Class C network address of 198.47.212.0. You have 3 networks in your company with the largest containing 134 hosts. You need to figure out if
CS321. Introduction to Numerical Methods
 CS3 Introduction to Numerical Methods Lecture Number Representations and Errors Professor Jun Zhang Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506-0633 August 7, 05 Number in
CS3 Introduction to Numerical Methods Lecture Number Representations and Errors Professor Jun Zhang Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506-0633 August 7, 05 Number in
PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS Unit code: A/601/1625 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 TUTORIAL OUTCOME 2 Part 1
 UNIT 22: PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS Unit code: A/601/1625 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 TUTORIAL OUTCOME 2 Part 1 This work covers part of outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module. The material is
UNIT 22: PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS Unit code: A/601/1625 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 TUTORIAL OUTCOME 2 Part 1 This work covers part of outcome 2 of the Edexcel standard module. The material is
http://computernetworkingnotes.com/ccna-study-guide/basic-of-network-addressing.html
 Subnetting is a process of dividing large network into the smaller networks based on layer 3 IP address. Every computer on network has an IP address that represent its location on network. Two version
Subnetting is a process of dividing large network into the smaller networks based on layer 3 IP address. Every computer on network has an IP address that represent its location on network. Two version
A Step towards an Easy Interconversion of Various Number Systems
 A towards an Easy Interconversion of Various Number Systems Shahid Latif, Rahat Ullah, Hamid Jan Department of Computer Science and Information Technology Sarhad University of Science and Information Technology
A towards an Easy Interconversion of Various Number Systems Shahid Latif, Rahat Ullah, Hamid Jan Department of Computer Science and Information Technology Sarhad University of Science and Information Technology
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture
 Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 2: Number Systems and Arithmetic Number Systems - Base The number system that we use is base : 734 = + 7 + 3 + 4 = x + 7x + 3x + 4x = x 3 + 7x
Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture 2: Number Systems and Arithmetic Number Systems - Base The number system that we use is base : 734 = + 7 + 3 + 4 = x + 7x + 3x + 4x = x 3 + 7x
Binary Representation
 Binary Representation The basis of all digital data is binary representation. Binary - means two 1, 0 True, False Hot, Cold On, Off We must tbe able to handle more than just values for real world problems
Binary Representation The basis of all digital data is binary representation. Binary - means two 1, 0 True, False Hot, Cold On, Off We must tbe able to handle more than just values for real world problems
Chapter 5. Binary, octal and hexadecimal numbers
 Chapter 5. Binary, octal and hexadecimal numbers A place to look for some of this material is the Wikipedia page http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/binary_numeral_system#counting_in_binary Another place that
Chapter 5. Binary, octal and hexadecimal numbers A place to look for some of this material is the Wikipedia page http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/binary_numeral_system#counting_in_binary Another place that
User Manual. DG LINK Application Program 071-0056-50. www.tektronix.com. This document applies to firmware version 2.00 and above.
 User Manual DG LINK Application Program 071-0056-50 This document applies to firmware version 2.00 and above. www.tektronix.com Copyright Tektronix Japan, Ltd. All rights reserved. Copyright Tektronix,
User Manual DG LINK Application Program 071-0056-50 This document applies to firmware version 2.00 and above. www.tektronix.com Copyright Tektronix Japan, Ltd. All rights reserved. Copyright Tektronix,
LSN 2 Number Systems. ECT 224 Digital Computer Fundamentals. Department of Engineering Technology
 LSN 2 Number Systems Department of Engineering Technology LSN 2 Decimal Number System Decimal number system has 10 digits (0-9) Base 10 weighting system... 10 5 10 4 10 3 10 2 10 1 10 0. 10-1 10-2 10-3
LSN 2 Number Systems Department of Engineering Technology LSN 2 Decimal Number System Decimal number system has 10 digits (0-9) Base 10 weighting system... 10 5 10 4 10 3 10 2 10 1 10 0. 10-1 10-2 10-3
Keystation Pro 88 Advanced Guide. Contents: 1 Getting Started. 2 Terminology. 3 Performance Operations of the Keystation Pro 88
 Keystation Pro 88 Advanced Guide Contents: 1 Getting Started 2 Terminology 3 Performance Operations of the Keystation Pro 88 Sending Program Changes During Performance Sending Bank Changes During Performance
Keystation Pro 88 Advanced Guide Contents: 1 Getting Started 2 Terminology 3 Performance Operations of the Keystation Pro 88 Sending Program Changes During Performance Sending Bank Changes During Performance
5.4 Solving Percent Problems Using the Percent Equation
 5. Solving Percent Problems Using the Percent Equation In this section we will develop and use a more algebraic equation approach to solving percent equations. Recall the percent proportion from the last
5. Solving Percent Problems Using the Percent Equation In this section we will develop and use a more algebraic equation approach to solving percent equations. Recall the percent proportion from the last
Jianjian Song LogicWorks 4 Tutorials (5/15/03) Page 1 of 14
 LogicWorks 4 Tutorials Jianjian Song Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology March 23 Table of Contents LogicWorks 4 Installation and update...2 2 Tutorial
LogicWorks 4 Tutorials Jianjian Song Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology March 23 Table of Contents LogicWorks 4 Installation and update...2 2 Tutorial
You can probably work with decimal. binary numbers needed by the. Working with binary numbers is time- consuming & error-prone.
 IP Addressing & Subnetting Made Easy Working with IP Addresses Introduction You can probably work with decimal numbers much easier than with the binary numbers needed by the computer. Working with binary
IP Addressing & Subnetting Made Easy Working with IP Addresses Introduction You can probably work with decimal numbers much easier than with the binary numbers needed by the computer. Working with binary
Number Systems and Radix Conversion
 Number Systems and Radix Conversion Sanjay Rajopadhye, Colorado State University 1 Introduction These notes for CS 270 describe polynomial number systems. The material is not in the textbook, but will
Number Systems and Radix Conversion Sanjay Rajopadhye, Colorado State University 1 Introduction These notes for CS 270 describe polynomial number systems. The material is not in the textbook, but will
Comp 255Q - 1M: Computer Organization Lab #3 - Machine Language Programs for the PDP-8
 Comp 255Q - 1M: Computer Organization Lab #3 - Machine Language Programs for the PDP-8 January 22, 2013 Name: Grade /10 Introduction: In this lab you will write, test, and execute a number of simple PDP-8
Comp 255Q - 1M: Computer Organization Lab #3 - Machine Language Programs for the PDP-8 January 22, 2013 Name: Grade /10 Introduction: In this lab you will write, test, and execute a number of simple PDP-8
Numeration systems. Resources and methods for learning about these subjects (list a few here, in preparation for your research):
 Numeration systems This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Numeration systems This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Lab 1: Full Adder 0.0
 Lab 1: Full Adder 0.0 Introduction In this lab you will design a simple digital circuit called a full adder. You will then use logic gates to draw a schematic for the circuit. Finally, you will verify
Lab 1: Full Adder 0.0 Introduction In this lab you will design a simple digital circuit called a full adder. You will then use logic gates to draw a schematic for the circuit. Finally, you will verify
The Hexadecimal Number System and Memory Addressing
 APPENDIX C The Hexadecimal Number System and Memory Addressing U nderstanding the number system and the coding system that computers use to store data and communicate with each other is fundamental to
APPENDIX C The Hexadecimal Number System and Memory Addressing U nderstanding the number system and the coding system that computers use to store data and communicate with each other is fundamental to
Numeral Systems. The number twenty-five can be represented in many ways: Decimal system (base 10): 25 Roman numerals:
 Numeral Systems Which number is larger? 25 8 We need to distinguish between numbers and the symbols that represent them, called numerals. The number 25 is larger than 8, but the numeral 8 above is larger
Numeral Systems Which number is larger? 25 8 We need to distinguish between numbers and the symbols that represent them, called numerals. The number 25 is larger than 8, but the numeral 8 above is larger
NUMBER SYSTEMS APPENDIX D. You will learn about the following in this appendix:
 APPENDIX D NUMBER SYSTEMS You will learn about the following in this appendix: The four important number systems in computing binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal. A number system converter program
APPENDIX D NUMBER SYSTEMS You will learn about the following in this appendix: The four important number systems in computing binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal. A number system converter program
IBM Emulation Mode Printer Commands
 IBM Emulation Mode Printer Commands Section 3 This section provides a detailed description of IBM emulation mode commands you can use with your printer. Control Codes Control codes are one-character printer
IBM Emulation Mode Printer Commands Section 3 This section provides a detailed description of IBM emulation mode commands you can use with your printer. Control Codes Control codes are one-character printer
Binary Representation. Number Systems. Base 10, Base 2, Base 16. Positional Notation. Conversion of Any Base to Decimal.
 Binary Representation The basis of all digital data is binary representation. Binary - means two 1, 0 True, False Hot, Cold On, Off We must be able to handle more than just values for real world problems
Binary Representation The basis of all digital data is binary representation. Binary - means two 1, 0 True, False Hot, Cold On, Off We must be able to handle more than just values for real world problems
Activity 1: Using base ten blocks to model operations on decimals
 Rational Numbers 9: Decimal Form of Rational Numbers Objectives To use base ten blocks to model operations on decimal numbers To review the algorithms for addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
Rational Numbers 9: Decimal Form of Rational Numbers Objectives To use base ten blocks to model operations on decimal numbers To review the algorithms for addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
Preliminary Mathematics
 Preliminary Mathematics The purpose of this document is to provide you with a refresher over some topics that will be essential for what we do in this class. We will begin with fractions, decimals, and
Preliminary Mathematics The purpose of this document is to provide you with a refresher over some topics that will be essential for what we do in this class. We will begin with fractions, decimals, and
20 Saving Device Data Backup
 20 Saving Device Data Backup 20.1 Try to Save Device Data Backup...20-2 20.2 Setting Guide...20-6 20-1 Try to Save Device Data Backup 20.1 Try to Save Device Data Backup The device data in Device/PLC can
20 Saving Device Data Backup 20.1 Try to Save Device Data Backup...20-2 20.2 Setting Guide...20-6 20-1 Try to Save Device Data Backup 20.1 Try to Save Device Data Backup The device data in Device/PLC can
NAND Flash Memories. Using Linux MTD compatible mode. on ELNEC Universal Device Programmers. (Quick Guide)
 NAND Flash Memories Using Linux MTD compatible mode on ELNEC Universal Device Programmers (Quick Guide) Application Note April 2012 an_elnec_linux_mtd, version 1.04 Version 1.04/04.2012 Page 1 of 16 As
NAND Flash Memories Using Linux MTD compatible mode on ELNEC Universal Device Programmers (Quick Guide) Application Note April 2012 an_elnec_linux_mtd, version 1.04 Version 1.04/04.2012 Page 1 of 16 As
plc numbers - 13.1 Encoded values; BCD and ASCII Error detection; parity, gray code and checksums
 plc numbers - 3. Topics: Number bases; binary, octal, decimal, hexadecimal Binary calculations; s compliments, addition, subtraction and Boolean operations Encoded values; BCD and ASCII Error detection;
plc numbers - 3. Topics: Number bases; binary, octal, decimal, hexadecimal Binary calculations; s compliments, addition, subtraction and Boolean operations Encoded values; BCD and ASCII Error detection;
Table 1 below is a complete list of MPTH commands with descriptions. Table 1 : MPTH Commands. Command Name Code Setting Value Description
 MPTH: Commands Table 1 below is a complete list of MPTH commands with descriptions. Note: Commands are three bytes long, Command Start Byte (default is 128), Command Code, Setting value. Table 1 : MPTH
MPTH: Commands Table 1 below is a complete list of MPTH commands with descriptions. Note: Commands are three bytes long, Command Start Byte (default is 128), Command Code, Setting value. Table 1 : MPTH
Teaching Pre-Algebra in PowerPoint
 Key Vocabulary: Numerator, Denominator, Ratio Title Key Skills: Convert Fractions to Decimals Long Division Convert Decimals to Percents Rounding Percents Slide #1: Start the lesson in Presentation Mode
Key Vocabulary: Numerator, Denominator, Ratio Title Key Skills: Convert Fractions to Decimals Long Division Convert Decimals to Percents Rounding Percents Slide #1: Start the lesson in Presentation Mode
Decimal Notations for Fractions Number and Operations Fractions /4.NF
 Decimal Notations for Fractions Number and Operations Fractions /4.NF Domain: Cluster: Standard: 4.NF Number and Operations Fractions Understand decimal notation for fractions, and compare decimal fractions.
Decimal Notations for Fractions Number and Operations Fractions /4.NF Domain: Cluster: Standard: 4.NF Number and Operations Fractions Understand decimal notation for fractions, and compare decimal fractions.
Software Tool for Implementing RSA Algorithm
 Software Tool for Implementing RSA Algorithm Adriana Borodzhieva, Plamen Manoilov Rousse University Angel Kanchev, Rousse, Bulgaria Abstract: RSA is one of the most-common used algorithms for public-key
Software Tool for Implementing RSA Algorithm Adriana Borodzhieva, Plamen Manoilov Rousse University Angel Kanchev, Rousse, Bulgaria Abstract: RSA is one of the most-common used algorithms for public-key
Q&As: Microsoft Excel 2013: Chapter 2
 Q&As: Microsoft Excel 2013: Chapter 2 In Step 5, why did the date that was entered change from 4/5/10 to 4/5/2010? When Excel recognizes that you entered a date in mm/dd/yy format, it automatically formats
Q&As: Microsoft Excel 2013: Chapter 2 In Step 5, why did the date that was entered change from 4/5/10 to 4/5/2010? When Excel recognizes that you entered a date in mm/dd/yy format, it automatically formats
The Answer to the 14 Most Frequently Asked Modbus Questions
 Modbus Frequently Asked Questions WP-34-REV0-0609-1/7 The Answer to the 14 Most Frequently Asked Modbus Questions Exactly what is Modbus? Modbus is an open serial communications protocol widely used in
Modbus Frequently Asked Questions WP-34-REV0-0609-1/7 The Answer to the 14 Most Frequently Asked Modbus Questions Exactly what is Modbus? Modbus is an open serial communications protocol widely used in
COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS
 COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/combinational_circuits.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Combinational circuit is a circuit in which we combine the different
COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_logical_organization/combinational_circuits.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Combinational circuit is a circuit in which we combine the different
Subnetting Examples. There are three types of subnetting examples I will show in this document:
 Subnetting Examples There are three types of subnetting examples I will show in this document: 1) Subnetting when given a required number of networks 2) Subnetting when given a required number of clients
Subnetting Examples There are three types of subnetting examples I will show in this document: 1) Subnetting when given a required number of networks 2) Subnetting when given a required number of clients
Dr Brian Beaudrie pg. 1
 Multiplication of Decimals Name: Multiplication of a decimal by a whole number can be represented by the repeated addition model. For example, 3 0.14 means add 0.14 three times, regroup, and simplify,
Multiplication of Decimals Name: Multiplication of a decimal by a whole number can be represented by the repeated addition model. For example, 3 0.14 means add 0.14 three times, regroup, and simplify,
Logarithmic and Exponential Equations
 11.5 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations 11.5 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve a logarithmic equation 2. Solve an exponential equation 3. Solve an application involving an exponential equation Much of the importance
11.5 Logarithmic and Exponential Equations 11.5 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve a logarithmic equation 2. Solve an exponential equation 3. Solve an application involving an exponential equation Much of the importance
Today s topics. Digital Computers. More on binary. Binary Digits (Bits)
 Today s topics! Binary Numbers! Brookshear.-.! Slides from Prof. Marti Hearst of UC Berkeley SIMS! Upcoming! Networks Interactive Introduction to Graph Theory http://www.utm.edu/cgi-bin/caldwell/tutor/departments/math/graph/intro
Today s topics! Binary Numbers! Brookshear.-.! Slides from Prof. Marti Hearst of UC Berkeley SIMS! Upcoming! Networks Interactive Introduction to Graph Theory http://www.utm.edu/cgi-bin/caldwell/tutor/departments/math/graph/intro
CS201: Architecture and Assembly Language
 CS201: Architecture and Assembly Language Lecture Three Brendan Burns CS201: Lecture Three p.1/27 Arithmetic for computers Previously we saw how we could represent unsigned numbers in binary and how binary
CS201: Architecture and Assembly Language Lecture Three Brendan Burns CS201: Lecture Three p.1/27 Arithmetic for computers Previously we saw how we could represent unsigned numbers in binary and how binary
Setup CMS 1500 (02/12) Claim Form
 Setup CMS-1500 (02/12) Claim Form Setup CMS 1500 (02/12) Claim Form The CMS 1500 (02/12) Form was added in Helper 8.1. Clients who upgrade from a version prior to 8.1 have two options; update an existing
Setup CMS-1500 (02/12) Claim Form Setup CMS 1500 (02/12) Claim Form The CMS 1500 (02/12) Form was added in Helper 8.1. Clients who upgrade from a version prior to 8.1 have two options; update an existing
The string of digits 101101 in the binary number system represents the quantity
 Data Representation Section 3.1 Data Types Registers contain either data or control information Control information is a bit or group of bits used to specify the sequence of command signals needed for
Data Representation Section 3.1 Data Types Registers contain either data or control information Control information is a bit or group of bits used to specify the sequence of command signals needed for
Prerequisite knowledge Students should have a good understanding of how our decimal number system works as well as understand place value.
 CSP Number Systems Mrs., GA Lesson Overview Learning Objectives and Evidence Statements 2.1.2 Explain how binary sequences are used to represent digital data. [P5] Prerequisite knowledge Students should
CSP Number Systems Mrs., GA Lesson Overview Learning Objectives and Evidence Statements 2.1.2 Explain how binary sequences are used to represent digital data. [P5] Prerequisite knowledge Students should
Lesson Plan. Course Title: Computer Maintenance Session Title: Numbering Systems
 Lesson Plan Course Title: Computer Maintenance Session Title: Numbering Systems Lesson Duration: Lesson length is subjective and will vary from instructor to instructor Performance Objective: Upon completion
Lesson Plan Course Title: Computer Maintenance Session Title: Numbering Systems Lesson Duration: Lesson length is subjective and will vary from instructor to instructor Performance Objective: Upon completion
Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders
 Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders In this set of slides, we present the two basic types of adders: 1. Half adders, and 2. Full adders. Each type of adder functions to add two binary bits. In order
Binary Adders: Half Adders and Full Adders In this set of slides, we present the two basic types of adders: 1. Half adders, and 2. Full adders. Each type of adder functions to add two binary bits. In order
Chapter 5 Instructor's Manual
 The Essentials of Computer Organization and Architecture Linda Null and Julia Lobur Jones and Bartlett Publishers, 2003 Chapter 5 Instructor's Manual Chapter Objectives Chapter 5, A Closer Look at Instruction
The Essentials of Computer Organization and Architecture Linda Null and Julia Lobur Jones and Bartlett Publishers, 2003 Chapter 5 Instructor's Manual Chapter Objectives Chapter 5, A Closer Look at Instruction
Chapter Table & Graph
 Chapter Table & Graph The Table & Graph menu makes it possible to generate numeric tables from functions stored in memory. You can also use multiple functions to generate tables. Since Table & Graph uses
Chapter Table & Graph The Table & Graph menu makes it possible to generate numeric tables from functions stored in memory. You can also use multiple functions to generate tables. Since Table & Graph uses
Irrational Numbers. A. Rational Numbers 1. Before we discuss irrational numbers, it would probably be a good idea to define rational numbers.
 Irrational Numbers A. Rational Numbers 1. Before we discuss irrational numbers, it would probably be a good idea to define rational numbers. Definition: Rational Number A rational number is a number that
Irrational Numbers A. Rational Numbers 1. Before we discuss irrational numbers, it would probably be a good idea to define rational numbers. Definition: Rational Number A rational number is a number that
Cluster APIs. Cluster APIs
 Cluster APIs Cluster APIs Cluster APIs include: Cluster Control APIs Cluster Resource Group APIs Cluster Resource Group Exit Program Topics covered here are: Cluster APIs Cluster Resource Services Characteristics
Cluster APIs Cluster APIs Cluster APIs include: Cluster Control APIs Cluster Resource Group APIs Cluster Resource Group Exit Program Topics covered here are: Cluster APIs Cluster Resource Services Characteristics
1. How many unique network IDs are there in class A addresses? # of unique hosts?
 CS445: IPv4 Addresses In-class activity Names: Part 1: Address Classes Original three classes of IPv4 addresses: A: 0 network (7 bits) host (24 bits) B: 10 network (14 bits) host (16 bits) C: 110 network
CS445: IPv4 Addresses In-class activity Names: Part 1: Address Classes Original three classes of IPv4 addresses: A: 0 network (7 bits) host (24 bits) B: 10 network (14 bits) host (16 bits) C: 110 network
COMBINATIONAL and SEQUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design
 PH-315 COMINATIONAL and SEUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design A La Rosa I PURPOSE: To familiarize with combinational and sequential logic circuits Combinational circuits
PH-315 COMINATIONAL and SEUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design A La Rosa I PURPOSE: To familiarize with combinational and sequential logic circuits Combinational circuits
isppac-powr1220at8 I 2 C Hardware Verification Utility User s Guide
 November 2005 Introduction Application Note AN6067 The isppac -POWR1220AT8 device from Lattice is a full-featured second-generation Power Manager chip. As part of its feature set, this device supports
November 2005 Introduction Application Note AN6067 The isppac -POWR1220AT8 device from Lattice is a full-featured second-generation Power Manager chip. As part of its feature set, this device supports
Levent EREN levent.eren@ieu.edu.tr A-306 Office Phone:488-9882 INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL LOGIC
 Levent EREN levent.eren@ieu.edu.tr A-306 Office Phone:488-9882 1 Number Systems Representation Positive radix, positional number systems A number with radix r is represented by a string of digits: A n
Levent EREN levent.eren@ieu.edu.tr A-306 Office Phone:488-9882 1 Number Systems Representation Positive radix, positional number systems A number with radix r is represented by a string of digits: A n
This is great when speed is important and relatively few words are necessary, but Max would be a terrible language for writing a text editor.
 Dealing With ASCII ASCII, of course, is the numeric representation of letters used in most computers. In ASCII, there is a number for each character in a message. Max does not use ACSII very much. In the
Dealing With ASCII ASCII, of course, is the numeric representation of letters used in most computers. In ASCII, there is a number for each character in a message. Max does not use ACSII very much. In the
