Exome sequencing e targeted sequencing in diagnostica e ricerca applicata: pro e contro
|
|
|
- Clarissa Hubbard
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exome sequencing e targeted sequencing in diagnostica e ricerca applicata: pro e contro P. Gasparini University of Trieste IRCCS-Burlo Garofolo Children Hospital SIGU Sorrento 22/11/2012
2 Our NGS facility NGS core facility is located at: 1)CBM scrl Basovizza,TS, Italy 2)IRCCS-Burlo Garofolo, TS, Italy NGS systems available: 1) HiScanSQ - Illumina 2) Solid4 System- LifeTecnologies 3) Ion Torrent LifeTechnologies
3 Our experience 274 whole genome sequencing data from isolated populations 110 whole exome sequencing data from families with inherited diseases Several targeted sequencing data for diagnostic purposes
4 The pipeline Data production Mapping Quality control Filtering Final data analysis Variants prioritization Sanger confirmation
5 Whole genome sequencing in isolated populations Italy Qatar Genetically, cultural, social and environmental factors homogeneous Silk Road Geographic and/or linguistic barrier Founder effect or a bottleneck Endogamy rate very high
6 Protocol Whole genome genotyping Whole genome sequencing Imputation Phenotype To identify rare variants underlying qualitative and quantitative traits
7 What we have learned: Useful approach to accurately impute rare variants Outsourcing for data production is a good option!! Need for fully dedicated people for data analysis
8 Whole exome sequencing (WES) Exome = Protein coding sequences exons 50 megabases Includes canonical splice sites, mirnas 5 &3 untranslated regions
9 WES example 1 mental retardation
10 Project Dissecting the molecular bases of mental retardation (without other signs and symptoms) 1. SNP array in RM 2. Patients selection 3. Exome sequencing 4. Variants selection 5. Validations 6. Future plan 250 cases MR array 216 neg for causative CNVs 10 probands with parents 34 pos for causative CNVs Inclusion criteria
11 Study criteria Inclusion s criteria Moderate to severe Mental Retardation Healthy parents No familial aggregation Negative SNP array data Negative test for fragile-x syndrome Exclusion s criteria Pre/perinatal infections Malformations brain abdominal cardiac Hearing loss Micro/macrocefaly Skeletal abnormalities Genital abnormalities Epilepsy
12 Material and methods Sample preparation: Illumina TruSeq DNA Sample Preparation (LT) Kit Enrichment: Illumina TruSeq kit approximately 62 Mb of genome sequencing was targeted Exome sequencing: Illumina HiScanSQ platform Production Time: Enrichment+Library 4 days. Ilumina 8 days Filtering of data: 1. Coverage at least 20x in probands and 4x in parents. 2. db SNPs 3. Internal database 4. Selection of de novo variants 5. Type of mutations
13 0
14 Prioritarization of the variants According to: a) Literature b) Gene function and pathways (if known) c) Gene expression d) in silico evaluation of the variant using different software/algorithms e) Possible clinical relationships
15 Filtering (pattern of inheritance): 1 de novo, 2 X-linked, 3 recessive
16 Summary of results (de novo) Family de novo selected Sanger True de novo TOTAL /130 confirmed (false positive) 3/29 true de novo (false negative)
17 Filtering - de novo JARID1B/KDM5B: Histone demethylase interacts with FOXG1 JARID1C already found to be involved in mental retardation Am J Hum Genet Feb;76(2): CIC : Granular cell development in CNS. A recent NGS study showed a de novo mutation in a MR case Nat Genet Dec;42(12): KIAA2022 : highly expressed in fetal and adult brain. Known to be associated with MR Gene Expr Patterns Sep;9(6):423-9.
18 Filtering X-linked Secreted semaphorins control spine distribution and morphogenesis in the postnatal CNS Nature Dec 24;462(7276): Epub 2009 Dec 13
19 Filtering recessive (homozigosity)
20 What we have learned: A high number of false positive and false negative cases A lot of Sanger sequencing to be carried out Some MR cases clearly explained through this approach A useful combination of filtering according different patterns of inheritance
21 WES example 2 Hearing loss
22 HEARING LOSS 70% GENETIC CAUSES Hereditary Hearing loss (HHL) Complex disease Dominant loci genes lacking Recessive loci genes lacking X-linked loci 5 3 genes lacking Age-Related Hearing loss HHL genes ion homeostasis: e.g GJB2, ion channels (KCNQ4, SLC26A4) hair bundle morphogenesis: e.g motor proteins (MYO15A), adhesion protein: CDH23) extracellular matrix proteins: ion homeostasis proteins (COCH, TECTA) poorly understood function
23 HHL: The Italian and Qatari picture GJB2 gene accounts for approx 1/3 of all cases and 35delG represents approx 70% of all GJB2 alleles GJB2 mutations are present in only a minority (<10%) of Qatari patients affected with non-syndromic hearing loss Mitochondrial A1555G mutation is present in 1/1000 in the general population Many families have been collected over several decades; they are not large enough to be included in linkage studies but can be used for NGS studies GJB6 deletion (D13S1830) was never detected Mitochondrial mutation MT-RNR1 (1555G>A) was never detected There is a strong need to search for the causative Qatari gene/s
24 What we have learned: Two new genes have been identified A high number of false positive and false negative cases A lot of Sanger sequencing to be carried out Bioinformatics analysis and the databases searches (i.e. expression, mutation, prediction, etc.) play a key role
25 WES example 3 Alagille syndrome
26 Alagille syndrome autosomal dominant, multi-system disorder with highly variability. Population prevalence = 1: Two genes have been described: -JAG1 (99% of cases) -NOTCH2 (1% of cases). Our family III-1 -> Neonatal jaundice; retinal hemorrhage; high levels of hepatic enzymes values and thoracic aorta hypoplasia. ALGS was suspected > liver biopsy > paucity of intrahepatic bile ducts. II-1 -> Coarctation of aorta; normal liver functionality. II-3 -> No clinical symptoms. I-2 -> Unspecified renal failure. III-1-> coding region of JAG1 and NOTCH-2 analyzed by dhplc and MLPA no mutation!
27 Exome sequencing was performed on 3 family members (III-1, II-1 and II-3) -SureSelect Human All Exon 38Mb Target Enrichment System (Agilent Technologies) -SOLiD 4 (Life Technologies) A new missense mutation (-> c.1308c>g, p.c436w, NM_00124) was identified in JAG1 gene confirmed by Sanger Sequencing and segregating with the disease PolyPhen-2, Mutation Taster, Condel: predict mutation as pathogenic.
28 What we have learned: There is a need to revise all the molecular diagnostic work done so far and hopefully lead to remarkable improvements of counseling and of diagnostic algorithms
29 WES example 4 Usher syndrome
30 Whole Exome Sequencing and focused analysis: Usher syndrome Retinitis + hearing loss Autosomal recessive inheritance 3 Clinical types (I, II and III) 13 loci mapped 10 genes identified Digenic inheritance demonstrated (CDH23/PCDH15)
31 Whole Exome sequencing 9 cases negative for the presence of mutations within the Asper chip
32 What we have learned: In the best scenario we can explain 7 cases with known genes, but not the remaining two (homozigosity might help) In most cases we do not have idea about the pathogenetic role of the variants detected!!...how can we prepare a diagnostic report? The enrichment step dramatically affects the coverage of each gene (probes are not equally distributed and some exons/genes are lacking). For this reason we have decided, both for HHL and Usher, to design custom targeted resequencing protocols based on Ion Torrent platform There is a huge need to functionally validate variants
33 Targeted resequencing Diagnostic
34 Usher Genes Long PCR NGS of Long PCR to detect unknown mutations. 1) 2 Sample with single different identified causal heterozygote mutation. 2) 1 Sample from patient clinically identified without molecular characterization. 3) 1 Healthy sample. Long PCR DNA Whole Genomic region : 2.5M bp ooptimization of: ofocus on coding regions. oaverage amplicons length. ogc content. After optimization: 0.7M bp GAII GAII Single Sample per line 2x75bp reads. 4 Sample Multiplexing 2x100bp reads. 454 FX 4-Region Plate: 4 Sample Multiplexing. Titanium reads
35 Long PCR On-Exon) -4,3% -4,5% -10% -17,4% Long PCR covers % of exons in the selected genes even for high (>40X) coverage. Agilent SureSelect shows a lower percentage of covered exons and a further dropping for high (>40X) coverage.
36 Step 1. Targeted re-sequencing by multiplex long PCR A positive control, a heterozygous, one patient with unknown allelles, and a negative control. All patients (3) are characterized by known genes, some differences have been detected among platforms.
37 Additional examples Ion Torrent technology 1)Small size: CFTR gene analysis 2)Medium size: Chronic Lymphocytic leukemia (9 genes) and Usher syndrome (10 genes) 3)Large size: hearing loss chip (100 genes)
38 An example of RDB/Sanger sequencing vs NGS Ion Torrent The CFTR gene (AmpliSeq design CDS+UTR) Besides these causing mutations we were able to detect 3 known polymorphisms in all samples
39 What we have learned: Targeted resequecing is reliable, accurate and affordable in few words it works!!!
40 Acknowledgements Medical Genetics, DSM, University of Trieste, IRCCS-Burlo Garofolo Trieste, Italy Danilo Licastro Diego Vozzi Flavio Faletra Giorgia Girotto Emmanouil Athanasakis Laura Esposito Angela D eustacchio Savina Dipresa Marcello Morgutti SUN and Tigem, Naples, Italy Sandro Banfi Vincenzo Nigro Funds from Telethon Foundation (Italy), QNRF (Qatar)
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics
 G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
G. Shashidhar Pai, MD MUSC Children s Hospital Department of Pediatrics Division of Genetics One of every 500 newborns has bilateral permanent sensorineural hearing loss 40 db which makes it the most common
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_hereditary_hearing_loss 10/2013 8/2015 8/2016
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_hereditary_hearing_loss 10/2013 8/2015 8/2016
Automated DNA sequencing 20/12/2009. Next Generation Sequencing
 DNA sequencing the beginnings Ghent University (Fiers et al) pioneers sequencing first complete gene (1972) first complete genome (1976) Next Generation Sequencing Fred Sanger develops dideoxy sequencing
DNA sequencing the beginnings Ghent University (Fiers et al) pioneers sequencing first complete gene (1972) first complete genome (1976) Next Generation Sequencing Fred Sanger develops dideoxy sequencing
Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics
 Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Session # : 46 Day/Time: Friday, May 1, 2015, 1:00 4:00 pm Title: Genetics and Hearing Loss: Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Presenter: Kathleen S. Arnos, PhD, Gallaudet University This presentation
Disease gene identification with exome sequencing
 Disease gene identification with exome sequencing Christian Gilissen Dept. of Human Genetics Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre c.gilissen@antrg.umcn.nl Contents Infrastructure Exome sequencing
Disease gene identification with exome sequencing Christian Gilissen Dept. of Human Genetics Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre c.gilissen@antrg.umcn.nl Contents Infrastructure Exome sequencing
Overview of Next Generation Sequencing platform technologies
 Overview of Next Generation Sequencing platform technologies Dr. Bernd Timmermann Next Generation Sequencing Core Facility Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics Berlin, Germany Outline 1. Technologies
Overview of Next Generation Sequencing platform technologies Dr. Bernd Timmermann Next Generation Sequencing Core Facility Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics Berlin, Germany Outline 1. Technologies
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects:
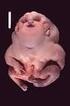 Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Genetic Mutations Cause Many Birth Defects: What We Learned from the FORGE Canada Project Jan M. Friedman, MD, PhD University it of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada I have no conflicts of interest related
Targeted. sequencing solutions. Accurate, scalable, fast TARGETED
 Targeted TARGETED Sequencing sequencing solutions Accurate, scalable, fast Sequencing for every lab, every budget, every application Ion Torrent semiconductor sequencing Ion Torrent technology has pioneered
Targeted TARGETED Sequencing sequencing solutions Accurate, scalable, fast Sequencing for every lab, every budget, every application Ion Torrent semiconductor sequencing Ion Torrent technology has pioneered
Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss
 MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss Number 12.04.87 Effective
MEDICAL POLICY POLICY RELATED POLICIES POLICY GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION SCOPE BENEFIT APPLICATION RATIONALE REFERENCES CODING APPENDIX HISTORY Genetic Testing for Hereditary Hearing Loss Number 12.04.87 Effective
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation. 5 y.o. boy with severe SNHL
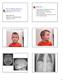 Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Objectives Role of Medical Genetics in Hearing Loss Evaluation Millan Patel, MD UBC Dept. of Medical Genetics October 22, 2010 Case presentation to illustrate importance of defining syndromic hearing loss
Next Generation Sequencing. mapping mutations in congenital heart disease
 Next Generation Sequencing mapping mutations in congenital heart disease AV Postma PhD Academic Medical Center Amsterdam, the Netherlands Overview talk Congenital heart disease and genetics Next generation
Next Generation Sequencing mapping mutations in congenital heart disease AV Postma PhD Academic Medical Center Amsterdam, the Netherlands Overview talk Congenital heart disease and genetics Next generation
G E N OM I C S S E RV I C ES
 GENOMICS SERVICES THE NEW YORK GENOME CENTER NYGC is an independent non-profit implementing advanced genomic research to improve diagnosis and treatment of serious diseases. capabilities. N E X T- G E
GENOMICS SERVICES THE NEW YORK GENOME CENTER NYGC is an independent non-profit implementing advanced genomic research to improve diagnosis and treatment of serious diseases. capabilities. N E X T- G E
Patient Information. for Childhood
 Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Patient Information Genetic Testing for Childhood Hearing Loss Introduction This document describes the most common genetic cause of childhood hearing loss and explains the role of genetic testing. Childhood
Genetic diagnostics the gateway to personalized medicine
 Micronova 20.11.2012 Genetic diagnostics the gateway to personalized medicine Kristiina Assoc. professor, Director of Genetic Department HUSLAB, Helsinki University Central Hospital The Human Genome Packed
Micronova 20.11.2012 Genetic diagnostics the gateway to personalized medicine Kristiina Assoc. professor, Director of Genetic Department HUSLAB, Helsinki University Central Hospital The Human Genome Packed
Delivering the power of the world s most successful genomics platform
 Delivering the power of the world s most successful genomics platform NextCODE Health is bringing the full power of the world s largest and most successful genomics platform to everyday clinical care NextCODE
Delivering the power of the world s most successful genomics platform NextCODE Health is bringing the full power of the world s largest and most successful genomics platform to everyday clinical care NextCODE
Nouvelles méthodes de diagnostic génétique des maladies mitochondriales
 Nouvelles méthodes de diagnostic génétique des maladies mitochondriales Mitochondrial disorders 1/8000 live birth Primary mitochondrial disorders Mutations in 80 nuclear genes Mutations in 13 mitochondrial
Nouvelles méthodes de diagnostic génétique des maladies mitochondriales Mitochondrial disorders 1/8000 live birth Primary mitochondrial disorders Mutations in 80 nuclear genes Mutations in 13 mitochondrial
Data Analysis for Ion Torrent Sequencing
 IFU022 v140202 Research Use Only Instructions For Use Part III Data Analysis for Ion Torrent Sequencing MANUFACTURER: Multiplicom N.V. Galileilaan 18 2845 Niel Belgium Revision date: August 21, 2014 Page
IFU022 v140202 Research Use Only Instructions For Use Part III Data Analysis for Ion Torrent Sequencing MANUFACTURER: Multiplicom N.V. Galileilaan 18 2845 Niel Belgium Revision date: August 21, 2014 Page
The future role of genetic screening to detect newborns at risk of childhood-onset hearing loss
 International Journal of Audiology 2013; 52: 124 133 Discussion Article The future role of genetic screening to detect newborns at risk of childhood-onset hearing loss Luan Linden Phillips *, Maria Bitner-Glindzicz,
International Journal of Audiology 2013; 52: 124 133 Discussion Article The future role of genetic screening to detect newborns at risk of childhood-onset hearing loss Luan Linden Phillips *, Maria Bitner-Glindzicz,
Focusing on results not data comprehensive data analysis for targeted next generation sequencing
 Focusing on results not data comprehensive data analysis for targeted next generation sequencing Daniel Swan, Jolyon Holdstock, Angela Matchan, Richard Stark, John Shovelton, Duarte Mohla and Simon Hughes
Focusing on results not data comprehensive data analysis for targeted next generation sequencing Daniel Swan, Jolyon Holdstock, Angela Matchan, Richard Stark, John Shovelton, Duarte Mohla and Simon Hughes
Single Gene and NextGen Panels
 Molecular Testing for Hearing Loss: Single Gene and NextGen Panels Honey V Reddi, PhD, FACMG Clinical Molecular Geneticist Prevention Genetics, Marshfield, WI www.preventiongenetics.com Outline of Presentation
Molecular Testing for Hearing Loss: Single Gene and NextGen Panels Honey V Reddi, PhD, FACMG Clinical Molecular Geneticist Prevention Genetics, Marshfield, WI www.preventiongenetics.com Outline of Presentation
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) and Childhood Diagnostic Evaluation
 IG O Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) and Childhood Diagnostic Evaluation KD Carsten Bergmann carsten.bergmann@bioscientia.de carsten.bergmann@uniklinik-freiburg.de Controversies Conference on ADPKD
IG O Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) and Childhood Diagnostic Evaluation KD Carsten Bergmann carsten.bergmann@bioscientia.de carsten.bergmann@uniklinik-freiburg.de Controversies Conference on ADPKD
Information leaflet. Centrum voor Medische Genetica. Version 1/20150504 Design by Ben Caljon, UZ Brussel. Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel
 Information on genome-wide genetic testing Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (array CGH) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism array (SNP array) Massive Parallel Sequencing (MPS) Version 120150504 Design
Information on genome-wide genetic testing Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization (array CGH) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism array (SNP array) Massive Parallel Sequencing (MPS) Version 120150504 Design
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida
 Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
Jennifer A. Defant, M.S., C.G.C. Certified Genetic Counselor Division of Genetics and Metabolism University of Florida 60% of childhood hearing loss is genetic Syndromic Nonsyndromic 40% of childhood hearing
Advances in RainDance Sequence Enrichment Technology and Applications in Cancer Research. March 17, 2011 Rendez-Vous Séquençage
 Advances in RainDance Sequence Enrichment Technology and Applications in Cancer Research March 17, 2011 Rendez-Vous Séquençage Presentation Overview Core Technology Review Sequence Enrichment Application
Advances in RainDance Sequence Enrichment Technology and Applications in Cancer Research March 17, 2011 Rendez-Vous Séquençage Presentation Overview Core Technology Review Sequence Enrichment Application
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Additional Markers 13 core STR loci Obtain further information from additional markers: Y STRs Separating male samples Mitochondrial DNA Working with extremely degraded
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Additional Markers 13 core STR loci Obtain further information from additional markers: Y STRs Separating male samples Mitochondrial DNA Working with extremely degraded
Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program
 Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program Introduction: Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited chronic disease that affects the lungs and
Cystic Fibrosis Webquest Sarah Follenweider, The English High School 2009 Summer Research Internship Program Introduction: Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited chronic disease that affects the lungs and
Next Generation Sequencing: Technology, Mapping, and Analysis
 Next Generation Sequencing: Technology, Mapping, and Analysis Gary Benson Computer Science, Biology, Bioinformatics Boston University gbenson@bu.edu http://tandem.bu.edu/ The Human Genome Project took
Next Generation Sequencing: Technology, Mapping, and Analysis Gary Benson Computer Science, Biology, Bioinformatics Boston University gbenson@bu.edu http://tandem.bu.edu/ The Human Genome Project took
Next Generation Mendelian Genetics by Exome Sequencing. Jay Shendure, MD, PhD Dept. of Genome Sciences University of Washington
 Next Generation Mendelian Genetics by Exome Sequencing Jay Shendure, MD, PhD Dept. of Genome Sciences University of Washington Second generation sequencing 10,000-fold drop in the cost of DNA sequencing
Next Generation Mendelian Genetics by Exome Sequencing Jay Shendure, MD, PhD Dept. of Genome Sciences University of Washington Second generation sequencing 10,000-fold drop in the cost of DNA sequencing
Becker Muscular Dystrophy
 Muscular Dystrophy A Case Study of Positional Cloning Described by Benjamin Duchenne (1868) X-linked recessive disease causing severe muscular degeneration. 100 % penetrance X d Y affected male Frequency
Muscular Dystrophy A Case Study of Positional Cloning Described by Benjamin Duchenne (1868) X-linked recessive disease causing severe muscular degeneration. 100 % penetrance X d Y affected male Frequency
IMMEDIATE HOT LINE: Effective March 2, 2015
 MEDICARE COVERAGE OF LABORATORY TESTING Please remember when ordering laboratory tests that are billed to Medicare/Medicaid or other federally funded programs, the following requirements apply: 1. Only
MEDICARE COVERAGE OF LABORATORY TESTING Please remember when ordering laboratory tests that are billed to Medicare/Medicaid or other federally funded programs, the following requirements apply: 1. Only
Services. Updated 05/31/2016
 Updated 05/31/2016 Services 1. Whole exome sequencing... 2 2. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)... 3 3. 16S rrna sequencing... 4 4. Customized gene panels... 5 5. RNA-Seq... 6 6. qpcr... 7 7. HLA typing...
Updated 05/31/2016 Services 1. Whole exome sequencing... 2 2. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)... 3 3. 16S rrna sequencing... 4 4. Customized gene panels... 5 5. RNA-Seq... 6 6. qpcr... 7 7. HLA typing...
Molecular Genetic Testing in Public Health and Clinical Settings
 Molecular Genetic Testing in Public Health and Clinical Settings Ira M. Lubin, PhD, FACMG Division of Laboratory Systems NCPDCID, CCID Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Atlanta, Georgia Disclaimers
Molecular Genetic Testing in Public Health and Clinical Settings Ira M. Lubin, PhD, FACMG Division of Laboratory Systems NCPDCID, CCID Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Atlanta, Georgia Disclaimers
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
 Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
Lecture 6: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs) Single nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs (pronounced "snips") are DNA sequence variations that occur
SEQUENCING. From Sample to Sequence-Ready
 SEQUENCING From Sample to Sequence-Ready ACCESS ARRAY SYSTEM HIGH-QUALITY LIBRARIES, NOT ONCE, BUT EVERY TIME The highest-quality amplicons more sensitive, accurate, and specific Full support for all major
SEQUENCING From Sample to Sequence-Ready ACCESS ARRAY SYSTEM HIGH-QUALITY LIBRARIES, NOT ONCE, BUT EVERY TIME The highest-quality amplicons more sensitive, accurate, and specific Full support for all major
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
 DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15
 Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
Gene mutation and molecular medicine Chapter 15 Lecture Objectives What Are Mutations? How Are DNA Molecules and Mutations Analyzed? How Do Defective Proteins Lead to Diseases? What DNA Changes Lead to
This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive.
 11111 This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive. In summary Genes contain the instructions for
11111 This fact sheet describes how genes affect our health when they follow a well understood pattern of genetic inheritance known as autosomal recessive. In summary Genes contain the instructions for
About The Causes of Hearing Loss
 About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing in Your Hands On the Path towards Diagnostics
 The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing in Your Hands On the Path towards Diagnostics The GS Junior System The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing on Your Benchtop Proven technology: Uses the same long
The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing in Your Hands On the Path towards Diagnostics The GS Junior System The Power of Next-Generation Sequencing on Your Benchtop Proven technology: Uses the same long
Lecture 3: Mutations
 Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Lecture 3: Mutations Recall that the flow of information within a cell involves the transcription of DNA to mrna and the translation of mrna to protein. Recall also, that the flow of information between
Nazneen Aziz, PhD. Director, Molecular Medicine Transformation Program Office
 2013 Laboratory Accreditation Program Audioconferences and Webinars Implementing Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) as a Clinical Tool in the Laboratory Nazneen Aziz, PhD Director, Molecular Medicine Transformation
2013 Laboratory Accreditation Program Audioconferences and Webinars Implementing Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) as a Clinical Tool in the Laboratory Nazneen Aziz, PhD Director, Molecular Medicine Transformation
AGILENT S BIOINFORMATICS ANALYSIS SOFTWARE
 ACCELERATING PROGRESS IS IN OUR GENES AGILENT S BIOINFORMATICS ANALYSIS SOFTWARE GENESPRING GENE EXPRESSION (GX) MASS PROFILER PROFESSIONAL (MPP) PATHWAY ARCHITECT (PA) See Deeper. Reach Further. BIOINFORMATICS
ACCELERATING PROGRESS IS IN OUR GENES AGILENT S BIOINFORMATICS ANALYSIS SOFTWARE GENESPRING GENE EXPRESSION (GX) MASS PROFILER PROFESSIONAL (MPP) PATHWAY ARCHITECT (PA) See Deeper. Reach Further. BIOINFORMATICS
Core Facility Genomics
 Core Facility Genomics versatile genome or transcriptome analyses based on quantifiable highthroughput data ascertainment 1 Topics Collaboration with Harald Binder and Clemens Kreutz Project: Microarray
Core Facility Genomics versatile genome or transcriptome analyses based on quantifiable highthroughput data ascertainment 1 Topics Collaboration with Harald Binder and Clemens Kreutz Project: Microarray
Development of two Novel DNA Analysis methods to Improve Workflow Efficiency for Challenging Forensic Samples
 Development of two Novel DNA Analysis methods to Improve Workflow Efficiency for Challenging Forensic Samples Sudhir K. Sinha, Ph.D.*, Anne H. Montgomery, M.S., Gina Pineda, M.S., and Hiromi Brown, Ph.D.
Development of two Novel DNA Analysis methods to Improve Workflow Efficiency for Challenging Forensic Samples Sudhir K. Sinha, Ph.D.*, Anne H. Montgomery, M.S., Gina Pineda, M.S., and Hiromi Brown, Ph.D.
Wissenschaftliche Highlights der GSF 2007
 H Forschungszentrum für Umwelt und Gesundheit GmbH in der Helmholtzgemeinschaft Wissenschaftlich-Technische Abteilung Wissenschaftliche Highlights der GSF 2007 Abfrage Oktober 2007 Institut / Selbst. Abteilung
H Forschungszentrum für Umwelt und Gesundheit GmbH in der Helmholtzgemeinschaft Wissenschaftlich-Technische Abteilung Wissenschaftliche Highlights der GSF 2007 Abfrage Oktober 2007 Institut / Selbst. Abteilung
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 12; 02-12-2012
 SALSA MLPA probemix P083-C1 CDH1 Lot C1-0211. As compared to previous B1 version, new in version C1: two CDH1 probes and several reference probes have been replaced/added. In addition, the 88 and 96nt
SALSA MLPA probemix P083-C1 CDH1 Lot C1-0211. As compared to previous B1 version, new in version C1: two CDH1 probes and several reference probes have been replaced/added. In addition, the 88 and 96nt
Introduction To Epigenetic Regulation: How Can The Epigenomics Core Services Help Your Research? Maria (Ken) Figueroa, M.D. Core Scientific Director
 Introduction To Epigenetic Regulation: How Can The Epigenomics Core Services Help Your Research? Maria (Ken) Figueroa, M.D. Core Scientific Director Gene expression depends upon multiple factors Gene Transcription
Introduction To Epigenetic Regulation: How Can The Epigenomics Core Services Help Your Research? Maria (Ken) Figueroa, M.D. Core Scientific Director Gene expression depends upon multiple factors Gene Transcription
Next generation DNA sequencing technologies. theory & prac-ce
 Next generation DNA sequencing technologies theory & prac-ce Outline Next- Genera-on sequencing (NGS) technologies overview NGS applica-ons NGS workflow: data collec-on and processing the exome sequencing
Next generation DNA sequencing technologies theory & prac-ce Outline Next- Genera-on sequencing (NGS) technologies overview NGS applica-ons NGS workflow: data collec-on and processing the exome sequencing
Population Genetics and Multifactorial Inheritance 2002
 Population Genetics and Multifactorial Inheritance 2002 Consanguinity Genetic drift Founder effect Selection Mutation rate Polymorphism Balanced polymorphism Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Population Genetics and Multifactorial Inheritance 2002 Consanguinity Genetic drift Founder effect Selection Mutation rate Polymorphism Balanced polymorphism Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
School of Nursing. Presented by Yvette Conley, PhD
 Presented by Yvette Conley, PhD What we will cover during this webcast: Briefly discuss the approaches introduced in the paper: Genome Sequencing Genome Wide Association Studies Epigenomics Gene Expression
Presented by Yvette Conley, PhD What we will cover during this webcast: Briefly discuss the approaches introduced in the paper: Genome Sequencing Genome Wide Association Studies Epigenomics Gene Expression
Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation
 PN 100-9879 A1 TECHNICAL NOTE Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation Introduction Cancer is a dynamic evolutionary process of which intratumor genetic and phenotypic
PN 100-9879 A1 TECHNICAL NOTE Single-Cell Whole Genome Sequencing on the C1 System: a Performance Evaluation Introduction Cancer is a dynamic evolutionary process of which intratumor genetic and phenotypic
Chapter 4 Pedigree Analysis in Human Genetics. Chapter 4 Human Heredity by Michael Cummings 2006 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning
 Chapter 4 Pedigree Analysis in Human Genetics Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Pigmentation Gene and Albinism Fig. 3.14 Two Genes Fig. 3.15 The Inheritance of Human Traits Difficulties Long generation time
Chapter 4 Pedigree Analysis in Human Genetics Mendelian Inheritance in Humans Pigmentation Gene and Albinism Fig. 3.14 Two Genes Fig. 3.15 The Inheritance of Human Traits Difficulties Long generation time
Breast cancer and the role of low penetrance alleles: a focus on ATM gene
 Modena 18-19 novembre 2010 Breast cancer and the role of low penetrance alleles: a focus on ATM gene Dr. Laura La Paglia Breast Cancer genetic Other BC susceptibility genes TP53 PTEN STK11 CHEK2 BRCA1
Modena 18-19 novembre 2010 Breast cancer and the role of low penetrance alleles: a focus on ATM gene Dr. Laura La Paglia Breast Cancer genetic Other BC susceptibility genes TP53 PTEN STK11 CHEK2 BRCA1
Diagnostic Scoring System for LQTS
 Medical Coverage Policy Genetic Testing: Congenital Long QT Syndrome Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 2/15/2011 Policy Last Updated: 2/21/2012 Prospective review is recommended/required.
Medical Coverage Policy Genetic Testing: Congenital Long QT Syndrome Device/Equipment Drug Medical Surgery Test Other Effective Date: 2/15/2011 Policy Last Updated: 2/21/2012 Prospective review is recommended/required.
BRCA1 / 2 testing by massive sequencing highlights, shadows or pitfalls?
 BRCA1 / 2 testing by massive sequencing highlights, shadows or pitfalls? Giovanni Luca Scaglione, PhD ------------------------ Laboratory of Clinical Molecular Diagnostics and Personalized Medicine, Institute
BRCA1 / 2 testing by massive sequencing highlights, shadows or pitfalls? Giovanni Luca Scaglione, PhD ------------------------ Laboratory of Clinical Molecular Diagnostics and Personalized Medicine, Institute
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection
 Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Fanconi Anemia
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Fanconi Anemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_fanconi_anemia 03/2015 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Fanconi Anemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_fanconi_anemia 03/2015 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description
GENOMICS: REINVIGORATING THE FIELD OF PSYCHIATRIC RESEARCH
 Office of Communications www.broadinstitute.org T 617-714-7151 communications@broadinstitute.org 7 Cambridge Center, Cambridge, MA 02142 GENOMICS: REINVIGORATING THE FIELD OF PSYCHIATRIC RESEARCH For decades,
Office of Communications www.broadinstitute.org T 617-714-7151 communications@broadinstitute.org 7 Cambridge Center, Cambridge, MA 02142 GENOMICS: REINVIGORATING THE FIELD OF PSYCHIATRIC RESEARCH For decades,
Clinical Policy Title: Genomic tests in sensorineural hearing loss
 Clinical Policy Title: Genomic tests in sensorineural hearing loss Clinical Policy Number: 02.01.18 Effective Date: January 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: September 16, 2015 Most Recent Review Date: September
Clinical Policy Title: Genomic tests in sensorineural hearing loss Clinical Policy Number: 02.01.18 Effective Date: January 1, 2016 Initial Review Date: September 16, 2015 Most Recent Review Date: September
NGS and complex genetics
 NGS and complex genetics Robert Kraaij Genetic Laboratory Department of Internal Medicine r.kraaij@erasmusmc.nl Gene Hunting Rotterdam Study and GWAS Next Generation Sequencing Gene Hunting Mendelian gene
NGS and complex genetics Robert Kraaij Genetic Laboratory Department of Internal Medicine r.kraaij@erasmusmc.nl Gene Hunting Rotterdam Study and GWAS Next Generation Sequencing Gene Hunting Mendelian gene
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3
 Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
BRCA in Men. Mary B. Daly,M.D.,Ph.D. June 25, 2010
 BRCA in Men Mary B. Daly,M.D.,Ph.D. June 25, 2010 BRCA in Men Inheritance patterns of BRCA1/2 Cancer Risks for men with BRCA1/2 mutations Risk management recommendations for men with BRCA1/2 mutations
BRCA in Men Mary B. Daly,M.D.,Ph.D. June 25, 2010 BRCA in Men Inheritance patterns of BRCA1/2 Cancer Risks for men with BRCA1/2 mutations Risk management recommendations for men with BRCA1/2 mutations
Influence of Sex on Genetics. Chapter Six
 Influence of Sex on Genetics Chapter Six Humans 23 Autosomes Chromosomal abnormalities very severe Often fatal All have at least one X Deletion of X chromosome is fatal Males = heterogametic sex XY Females
Influence of Sex on Genetics Chapter Six Humans 23 Autosomes Chromosomal abnormalities very severe Often fatal All have at least one X Deletion of X chromosome is fatal Males = heterogametic sex XY Females
Validation and Replication
 Validation and Replication Overview Definitions of validation and replication Difficulties and limitations Working examples from our group and others Why? False positive results still occur. even after
Validation and Replication Overview Definitions of validation and replication Difficulties and limitations Working examples from our group and others Why? False positive results still occur. even after
Human Genome Organization: An Update. Genome Organization: An Update
 Human Genome Organization: An Update Genome Organization: An Update Highlights of Human Genome Project Timetable Proposed in 1990 as 3 billion dollar joint venture between DOE and NIH with 15 year completion
Human Genome Organization: An Update Genome Organization: An Update Highlights of Human Genome Project Timetable Proposed in 1990 as 3 billion dollar joint venture between DOE and NIH with 15 year completion
Mendelian inheritance and the
 Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
Mendelian inheritance and the most common genetic diseases Cornelia Schubert, MD, University of Goettingen, Dept. Human Genetics EUPRIM-Net course Genetics, Immunology and Breeding Mangement German Primate
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES. Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD
 LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
LEUKODYSTROPHY GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE OPTIONS FOR AFFECTED FAMILIES Leila Jamal, ScM Kennedy Krieger Institute, Baltimore MD 2 Outline Genetics 101: Basic Concepts and Myth Busting Inheritance Patterns
Validation parameters: An introduction to measures of
 Validation parameters: An introduction to measures of test accuracy Types of tests All tests are fundamentally quantitative Sometimes we use the quantitative result directly However, it is often necessary
Validation parameters: An introduction to measures of test accuracy Types of tests All tests are fundamentally quantitative Sometimes we use the quantitative result directly However, it is often necessary
Tools for human molecular diagnosis. Joris Vermeesch
 Tools for human molecular diagnosis Joris Vermeesch Chromosome > DNA Genetic Code Effect of point mutations/polymorphisms Effect of deletions/insertions Effect of splicing mutations IVS2-2A>G Normal splice
Tools for human molecular diagnosis Joris Vermeesch Chromosome > DNA Genetic Code Effect of point mutations/polymorphisms Effect of deletions/insertions Effect of splicing mutations IVS2-2A>G Normal splice
MRC-Holland MLPA. Related SALSA MLPA probemix P091 CFTR: contains probes for the CFTR gene, related to chronic pancreatitis.
 SALSA MLPA probemix P242-B3 Pancreatitis Lot B3-0215. As compared to version B2 (lot B2-1212), one flanking probe has been removed and four reference probes have been replaced. Hereditary Pancreatitis
SALSA MLPA probemix P242-B3 Pancreatitis Lot B3-0215. As compared to version B2 (lot B2-1212), one flanking probe has been removed and four reference probes have been replaced. Hereditary Pancreatitis
Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
Oncology Insights Enabled by Knowledge Base-Guided Panel Design and the Seamless Workflow of the GeneReader NGS System
 White Paper Oncology Insights Enabled by Knowledge Base-Guided Panel Design and the Seamless Workflow of the GeneReader NGS System Abstract: This paper describes QIAGEN s philosophy and process for developing
White Paper Oncology Insights Enabled by Knowledge Base-Guided Panel Design and the Seamless Workflow of the GeneReader NGS System Abstract: This paper describes QIAGEN s philosophy and process for developing
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing?
 Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing? Simon Hughes, Richard Capper, Sandra Lam and Nicole Sparkes Introduction The human genome is comprised of more than
Sequencing and microarrays for genome analysis: complementary rather than competing? Simon Hughes, Richard Capper, Sandra Lam and Nicole Sparkes Introduction The human genome is comprised of more than
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger
 The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
The Developing Person Through the Life Span 8e by Kathleen Stassen Berger Chapter 3 Heredity and Environment PowerPoint Slides developed by Martin Wolfger and Michael James Ivy Tech Community College-Bloomington
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_alpha_1_antitrypsin_deficiency 5/2012
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_alpha_1_antitrypsin_deficiency 5/2012
TITLE: Next Generation DNA Sequencing: A Review of the Cost Effectiveness and Guidelines
 TITLE: Next Generation DNA Sequencing: A Review of the Cost Effectiveness and Guidelines DATE: 06 February 2014 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES The use of genetic methodologies in health-care is not a novel
TITLE: Next Generation DNA Sequencing: A Review of the Cost Effectiveness and Guidelines DATE: 06 February 2014 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES The use of genetic methodologies in health-care is not a novel
DNA Sequencing and Personalised Medicine
 DNA Sequencing and Personalised Medicine Mick Watson Director of ARK-Genomics The Roslin Institute PERSONALISED MEDICINE What is personalised medicine? Personalized Medicine refers to the tailoring of
DNA Sequencing and Personalised Medicine Mick Watson Director of ARK-Genomics The Roslin Institute PERSONALISED MEDICINE What is personalised medicine? Personalized Medicine refers to the tailoring of
Leading Genomics. Diagnostic. Discove. Collab. harma. Shanghai Cambridge, MA Reykjavik
 Leading Genomics Diagnostic harma Discove Collab Shanghai Cambridge, MA Reykjavik Global leadership for using the genome to create better medicine WuXi NextCODE provides a uniquely proven and integrated
Leading Genomics Diagnostic harma Discove Collab Shanghai Cambridge, MA Reykjavik Global leadership for using the genome to create better medicine WuXi NextCODE provides a uniquely proven and integrated
Typing in the NGS era: The way forward!
 Typing in the NGS era: The way forward! Valeria Michelacci NGS course, June 2015 Typing from sequence data NGS-derived conventional Multi Locus Sequence Typing (University of Warwick, 7 housekeeping genes)
Typing in the NGS era: The way forward! Valeria Michelacci NGS course, June 2015 Typing from sequence data NGS-derived conventional Multi Locus Sequence Typing (University of Warwick, 7 housekeeping genes)
Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare
 We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research & Healthcare We Innovate Healthcare Genetic Testing in Research and Healthcare Human genetic testing is a growing science. It is used to study genes
The Genetics of Hearing Loss. Heidi L. Rehm, Ph.D. Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
 The Genetics of Hearing Loss Heidi L. Rehm, Ph.D. Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Faculty Disclosure Information In the past 12 months, I have not had a significant financial interest or other relationship
The Genetics of Hearing Loss Heidi L. Rehm, Ph.D. Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Faculty Disclosure Information In the past 12 months, I have not had a significant financial interest or other relationship
Test Information Sheet
 Test Information Sheet GeneDx 207 Perry Parkway Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Phone: 888-729-1206 Fax: 301-710-6594 E-mail: wecare@genedx.com www.genedx.com/oncology OncoGene Dx: High/Moderate Risk Panel Sequence
Test Information Sheet GeneDx 207 Perry Parkway Gaithersburg, MD 20877 Phone: 888-729-1206 Fax: 301-710-6594 E-mail: wecare@genedx.com www.genedx.com/oncology OncoGene Dx: High/Moderate Risk Panel Sequence
1 Mutation and Genetic Change
 CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
CHAPTER 14 1 Mutation and Genetic Change SECTION Genes in Action KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is the origin of genetic differences among organisms? What kinds
How many of you have checked out the web site on protein-dna interactions?
 How many of you have checked out the web site on protein-dna interactions? Example of an approximately 40,000 probe spotted oligo microarray with enlarged inset to show detail. Find and be ready to discuss
How many of you have checked out the web site on protein-dna interactions? Example of an approximately 40,000 probe spotted oligo microarray with enlarged inset to show detail. Find and be ready to discuss
OpenMedicine Foundation (OMF)
 Scientific Advisory Board Director Ronald Davis, Ph.D. Genome Technology Center Paul Berg, PhD Molecular Genetics Mario Capecchi, Ph.D Genetics & Immunology University of Utah Mark Davis, Ph.D. Immunology
Scientific Advisory Board Director Ronald Davis, Ph.D. Genome Technology Center Paul Berg, PhD Molecular Genetics Mario Capecchi, Ph.D Genetics & Immunology University of Utah Mark Davis, Ph.D. Immunology
Forensic DNA Testing Terminology
 Forensic DNA Testing Terminology ABI 310 Genetic Analyzer a capillary electrophoresis instrument used by forensic DNA laboratories to separate short tandem repeat (STR) loci on the basis of their size.
Forensic DNA Testing Terminology ABI 310 Genetic Analyzer a capillary electrophoresis instrument used by forensic DNA laboratories to separate short tandem repeat (STR) loci on the basis of their size.
UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities
 Unit 13 Genetic Abnormailities 1 UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities Originally developed by: Hildur Helgedottir RN, MN Revised (2000) by: Marlene Reimer RN, PhD, CCN (C) Associate Professor Faculty
Unit 13 Genetic Abnormailities 1 UNIT 13 (OPTION) Genetic Abnormalities Originally developed by: Hildur Helgedottir RN, MN Revised (2000) by: Marlene Reimer RN, PhD, CCN (C) Associate Professor Faculty
Common Cancers & Hereditary Syndromes
 Common Cancers & Hereditary Syndromes Elizabeth Hoodfar, MS, LCGC Regional Cancer Genetics Coordinator Kaiser Permanente Northern California Detect clinical characteristics of hereditary cancer syndromes.
Common Cancers & Hereditary Syndromes Elizabeth Hoodfar, MS, LCGC Regional Cancer Genetics Coordinator Kaiser Permanente Northern California Detect clinical characteristics of hereditary cancer syndromes.
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005. Lectures 1 2
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Commonly Used STR Markers
 Commonly Used STR Markers Repeats Satellites 100 to 1000 bases repeated Minisatellites VNTR variable number tandem repeat 10 to 100 bases repeated Microsatellites STR short tandem repeat 2 to 6 bases repeated
Commonly Used STR Markers Repeats Satellites 100 to 1000 bases repeated Minisatellites VNTR variable number tandem repeat 10 to 100 bases repeated Microsatellites STR short tandem repeat 2 to 6 bases repeated
The correct answer is c A. Answer a is incorrect. The white-eye gene must be recessive since heterozygous females have red eyes.
 1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE
 AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
July 7th 2009 DNA sequencing
 July 7th 2009 DNA sequencing Overview Sequencing technologies Sequencing strategies Sample preparation Sequencing instruments at MPI EVA 2 x 5 x ABI 3730/3730xl 454 FLX Titanium Illumina Genome Analyzer
July 7th 2009 DNA sequencing Overview Sequencing technologies Sequencing strategies Sample preparation Sequencing instruments at MPI EVA 2 x 5 x ABI 3730/3730xl 454 FLX Titanium Illumina Genome Analyzer
Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening
 Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Integrating Genetics into Your Practice Webinar Series Overview of Genetic Testing and Screening Genetic testing is an important tool in the screening and diagnosis of many conditions. New technology is
Simplifying Data Interpretation with Nexus Copy Number
 Simplifying Data Interpretation with Nexus Copy Number A WHITE PAPER FROM BIODISCOVERY, INC. Rapid technological advancements, such as high-density acgh and SNP arrays as well as next-generation sequencing
Simplifying Data Interpretation with Nexus Copy Number A WHITE PAPER FROM BIODISCOVERY, INC. Rapid technological advancements, such as high-density acgh and SNP arrays as well as next-generation sequencing
Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis Markey Lecture Series
 Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis Markey Lecture Series Al Kim akim@dom.wustl.edu 2012.09.06 Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Autoimmune disease primarily targeting the synovium
Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis Markey Lecture Series Al Kim akim@dom.wustl.edu 2012.09.06 Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Autoimmune disease primarily targeting the synovium
Bioruptor NGS: Unbiased DNA shearing for Next-Generation Sequencing
 STGAAC STGAACT GTGCACT GTGAACT STGAAC STGAACT GTGCACT GTGAACT STGAAC STGAAC GTGCAC GTGAAC Wouter Coppieters Head of the genomics core facility GIGA center, University of Liège Bioruptor NGS: Unbiased DNA
STGAAC STGAACT GTGCACT GTGAACT STGAAC STGAACT GTGCACT GTGAACT STGAAC STGAAC GTGCAC GTGAAC Wouter Coppieters Head of the genomics core facility GIGA center, University of Liège Bioruptor NGS: Unbiased DNA
