Multi-beam laser Doppler vibrometry for acoustic landmine detection using airborne and mechanically-coupled vibration
|
|
|
- Hector Watson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Multi-beam laser Doppler vibrometry for acoustic landmine detection using airborne and mechanically-coupled vibration Vyacheslav Aranchuk *a,james M. Sabatier b, Amit K. Lal a, Cecil F. Hess a, Richard. D. Burgett c, and Michael O Neill d a MetroLaser, Inc., 57 White Road, Irvine, CA 964 b National Center for Physical Acoustics, University of Mississippi, University, MS 8677 c Planning Systems Inc., d LD Consulting, LLC ABSTRACT Acoustic-to-seismic coupling-based technology using a multi-beam laser Doppler vibrometer (LDV) as a vibration sensor has proved itself as a potential confirmatory sensor for buried landmine detection. The multi-beam LDV simultaneously measures the vibration of the ground at 6 points spread over a -meter line. The multi-beam LDV was used in two modes of operation: stop-and-stare, and continuously scanning beams. The noise floor of measurements in the continuously scanning mode increased with increasing scanning speed. This increase in the velocity noise floor is caused by dynamic speckles. The influence of amplitude and phase fluctuations of the Doppler signal due to dynamic speckles on the phase locked loop (PLL) demodulated output is discussed in the paper. Either airborne sound or mechanical shakers can be used as a source to excite vibration of the ground. A specially-designed loudspeaker array and mechanical shakers were used in the frequency range from 85- Hz to excite vibrations in the ground and elicit resonances in the mine. The efficiency of these two methods of excitation has been investigated and is discussed in the paper. This research is supported by the U. S. Army Research, Development, and Engineering Command, Night, Vision and Electronic Sensors Directorate under Contract DAAB5--C-4. Keywords: land mine detection, laser-acoustic sensing, laser Doppler vibrometer, LDV. INTRODUCTION Acoustic landmine detection using a multi-beam laser Doppler vibrometer (MB-LDV) as a vibration sensor has demonstrated promising results in laboratory and field experiments,. The technique uses airborne sound or mechanical shakers to excite vibration in the ground and a scanning LDV is then used to measure the ground vibration at multiple points. The presence of a buried landmine can be detected by studying the spatial distribution of the ground velocity spectra. A critical issue in landmine detection is operational speed. Use of a multi-beam LDV developed by MetroLaser significantly reduces the time of the measurements. This vibrometer illuminates the ground with a linear array of 6 beams, and simultaneously measures the ground velocity at all 6 points. The 6 beams are spread uniformly across a -meter line, and the velocity sensitivity of each beam is approximately micrometer/second. The vibrometer can work in a continuously scanning mode when all 6 beams move in the transverse direction across the interrogated area. A two-dimensional velocity map of the ground over one square meter can be obtained in a time less then seconds. A continuous scanning beam introduces additional noise to the measurements due to dynamic speckles, which increase the velocity noise floor of the vibrometer. In this paper an experimental investigation of the velocity noise floor of the LDV with a PLL demodulator caused by dynamic speckles is presented. The MB-LDV working in continuously scanning mode was tested in the field at an Army eastern temperate site. Two methods of excitation, loudspeakers and mechanical shakers, were used. The efficiency of these two methods of excitation has been investigated and is discussed in the paper. Some results of field experiments are presented and discussed.. VIBRATION MEASUREMENTS WITH MULTI-BEAM LDV A schematic of the multi-beam LDV and its principles of operation were described in detail in references,4. The principle of measurement is based on detection of the Doppler shift of laser light scattered from a vibrating object. The multi-beam LDV is a multi-channel laser heterodyne interferometer. The laser beam is split into 6 object * aranchuk@metrolaserinc.com; Phone: ; Web:
2 beams and 6 reference beams. The reference beams are frequency shifted by khz. The 6 object beams are focused onto a target along a line. The light backscattered from the target is optically mixed with the reference beams, producing 6 frequency modulated signals having a khz carrier frequency. The frequency deviation (Doppler shift) of each signal is proportional to the velocity of the target in the point of measurement. The functional layout of the system is shown in Figure. The output signals of the multi-beam LDV are demodulated by means of a 6 channel PLL. The PLL output is proportional to the velocity of the target. Each PLL output signal is then digitized with a 6 channel A-D card in a computer, and the target velocity spectrum of each beam is calculated in software. MB LDV PLL Laser Beams Scanning Direction PC/Signal Processor Object Figure. Layout of the vibration measurement system with scanning multi-beam LDV. All of the beams can be moved in the direction perpendicular to the line formed by the beams by using a rotating mirror. The vibrometer can work in two modes: stop-and-stare mode, and continuously scanning mode. In the stop-and-stare mode the beams are moved a specified angle, stopped, the data are collected, and the beams are moved to the next location. In the continuously scanning mode, the beams can be continuously scanned across the target at variable speeds. In order to produce a velocity image, the time domain data for each beam is divided into time segments, typically of length from.sec to second. Over each time segment, the velocity vs. time is Fourier analyzed to generate the velocity vs. frequency data over each time segment. When the velocity spectra over each time segment and each beam has been computed, a velocity image over the entire scanned area can be generated at any selected frequency band. In the stop-and-stare mode, each time segment corresponds to a specific location of beams, while each time segment in the continuous scanning method is an average over a finite length. Figure (see the color image on the last page) shows an example of the segmented velocity image over a buried landmine.. NOISE INDUCED BY DYNAMIC SPECKLES Scanning a laser beam across a target introduces noise at the vibrometer output due to dynamic speckles 5. Coherent light scattering from an optically rough surface creates a speckle field. Figure shows an example of a speckle pattern. The statistical characteristics of laser speckles are well studied 6. The phase of speckles is uniformly distributed in the range from π to π, and the intensity of speckles has a negative exponential probability distribution. When the laser beam moves across the target, the intensity and phase of speckles change in a random way. This results in random fluctuations of the amplitude and phase of the Doppler signal. The Doppler signal at the output of a photodetector can be written: i d [ π ( f + f ) + Φ] = I t cos () R D
3 .5 carrier signal vibration Figure. Speckle pattern. Figure 4. Doppler signal and demodulated vibration velocity for a stationary beam. f and f are the where I is the amplitude of the Doppler signal, Φ is the phase of the Doppler signal, R D frequency shift of the reference radiation and the Doppler shift of the object radiation respectively. Since the Doppler signal results from coherent addition of the reference beam and the speckles, the amplitude I and the phase Φ of the Doppler signal are random quantities. For a laser beam stationary relative to the target, the amplitude and phase of the Doppler signal do not change with time. Figure 4 shows a khz carrier Doppler signal and a demodulated velocity signal when the laser beam is stationary. When a beam moves across the target the speckles at the photodetector vary, resulting in random variation of the Doppler signal amplitude and phase. The amplitude of the Doppler signal varies randomly, and can occasionally drop down to a very small value below the photodetector noise level. In that case, because of insufficient signal, the PLL can lose lock, which results in a spike in the PLL output. When the Doppler signal reappears the PLL locks in again. Figure 5 shows the khz carrier Doppler signal and a demodulated velocity signal when the laser beam scans the target. The demodulated velocity signal (PLL output) contains spikes caused by Doppler signal drop-outs. The spikes in the demodulated signal have a broadband spectrum and increase the velocity noise floor of the vibrometer. Figure 5(b) shows an expanded view of the spike near.76 seconds, and the corresponding drop in the carrier signal amplitude..5 carrier signal carrier signal vibration - vibration (a) (b) Figure 5. (a) Doppler signal and demodulated vibration velocity for a moving beam. (b) Expanded view of the data between.7 and.8 seconds, showing the velocity spike and the drop in carrier signal amplitude.
4 The phase fluctuation of the Doppler signal due to the motion of the laser beam is another effect that increases the velocity noise floor. The frequency f C of the carrier Doppler signal at the LDV output is given by the time derivative of the argument in the cosine function in expression (): f C = f R + When the laser beam is stationary, the speckles on the photodetector do not change with time and dφ/dt = making the frequency of the carrier Doppler signal equal to: f = f + f () C When the beam moves across the target, the noise corresponding to the frequency content of dφ/dt appears in the signal 5. Figure 6 shows the dependence of the velocity noise floor of the PLL demodulated signal on the speed of the scanning beam. The velocity noise floor increases with the increase in the speed of the moving beam. As said above, two effects are responsible for the increase in the velocity noise floor: signal dropouts causing spikes in the PLL output and signal phase fluctuations. The velocity noise floor for the data points in Figure 6 was calculated by averaging the noise floor over all the time segments of. seconds of the demodulated signal. f D R + π D dφ dt () t () Velocity (microns/sec) Beam Speed (cm/sec) Figure 6. Velocity noise floor versus scanning speed of the beam. Figure 7 again shows the average noise floor vs. beam speed (dashed line), and also shows the average noise floor over time segments without spikes (solid line). The dashed line in Figure 7 is caused by both spikes in the PLL output due to the carrier signal dropout, as well as the phase fluctuations due to dynamic speckles. The solid line shows the part of the noise floor caused by the phase fluctuations of dynamic speckles. There were no time segments of length. seconds without spikes at beam speeds higher than 6 cm/second in our experiments. Velocity (microns/sec) Beam Speed (cm/sec) Figure 7. The dashed line is the average noise floor over all time segments of length. seconds. The solid line is the average noise floor over time segments of. seconds without spikes.
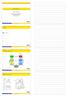
5 4. FIELD EXPERIMENTS The layout of the experimental setup is shown in Figure 8. The MB-LDV was mounted on a forklift at a height of. meters above the ground. The ground vibration was excited by using loudspeakers or mechanical shakers. Pseudo-random noise was used as an excitation signal. The beams were oriented in the down-track direction, and were scanned in the across-track direction. The speed of beams on the ground could be set from cm/second to cm/second. The data were taken during the time when the beams scan the ground. The PLL output signals were digitized with a 6 channel A-D card in a computer, and the data file was stored in the computer memory. A photograph of the multi-beam system mounted on the forklift is shown in Figure 9. A specially designed loudspeaker array and a mechanical shaker array were used in the frequency range from 85- Hz to excite vibration in the ground. Due to the different nature of the vibration excitation of the ground the frequency response of the ground to shakers and loudspeakers is different. Figure shows the acceleration produced by the shakers and the loudspeakers on the ground and on the vibrometer platform. The shakers have limited frequency bandwidth; they produce high excitation at low frequencies but exhibit a high frequency roll-off. The loudspeakers excite vibration of the ground over a wide bandwidth up to Hz. The shakers have an advantage over the speakers in lower excitation of the vibrometer platform. Since shakers radiate less sound in the air, they create db lower vibration of the LDV platform when they are used as an excitation source. 4 Laser beams 6 5 Scanning direction Figure 8. Schematic of experimental setup. - scanning multi-beam LDV, - loudspeaker, -signal generator, 4 - shakers, 5 - landmine, 6 PC/signal processor. Figure 9. Multi-beam LDV mounted on the forklift. ) MB-LDV, ) loudspeaker array, ) shakers. Data was obtained with the MB-LDV in continuous scanning mode on different landmines buried at depths from flush to 5 cm, and on different types of soil. Both loudspeakers and mechanical shakers were used for excitation. The pseudo-random noise was used as an excitation signal. Mines were scanned at different scanning rates from 5 cm/second to cm/second. The time of scanning a one-meter by one -meter spot was from second to seconds. A velocity image of a mine can be obtained at any of these speeds. Figures and show velocity images of mines obtained at different scanning speed. However, an increase in scanning speed increases the velocity noise floor due to dynamic speckles. A higher excitation level is required to resolve the difference in velocity over the target and off the target due to the higher velocity noise floor. Figure shows velocity images of a buried landmine obtained at a scanning speed of 5 cm/second at different excitation levels. The image in Figure a was obtained with a low excitation level while the image in Figure b was obtained with the excitation db higher. One can see that an increase in excitation level allows one to overcome the limitations imposed by the higher velocity noise floor, and improve the on target/off target contrast of the velocity image.
6 - -4 Releative level (db) Frequency (Hz) Figure. Acceleration produced by shakers and a loudspeaker on the ground and on the vibrometer. acceleration produced by shakers, - acceleration produced by a loudspeaker, - acceleration of the vibrometer produced by a speaker, 4- acceleration of the vibrometer produced by shakers. 5. CONCLUSIONS Field experiments show that buried landmines can be detected within one square meter in several seconds using a multi-beam laser Doppler vibrometer in a continuously scanning mode, with loudspeakers or shakers as the excitation source. Experiments show that shakers have better performance at low frequencies, but exhibit a high frequency roll-off. The speakers excite vibration of the ground over a wide bandwidth up to Hz. The shakers have an advantage over the speakers in lower excitation of the vibrometer platform. Increasing the scanning speed increases the velocity noise floor due to dynamic speckles. This increase in the velocity noise floor is caused by Doppler signal dropouts resulting in spikes in the PLL output, and phase fluctuation of speckles. Operation at higher scanning speeds require a higher excitation level to overcome the limitations imposed by the increasing velocity noise floor. Development of a new demodulation technique that can provide a lower noise floor in continuously scanning mode is a high-priority task of the future work. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work is sponsored by U.S. Army Research, Development, and Engineering Command, Night Vision Electronic Sensors Directorate, under Contract DAAB5--C-4. The content of the information does not necessarily reflect the position or the policy of the Government and no official endorsement should be inferred. REFERENCES. Sabatier, J.M., and Xiang, N., Laser-Doppler Based Acoustic-to-Seismic Detection of Buried Mines, Proceedings of the SPIE, Vol. 7, p. 5, Orlando, March Xiang, N. and Sabatier, J.M., Land Mine Detection Measurements using Acoustic-to-Seismic Coupling, Proceedings of the SPIE, Vol. 48, p. 645, Orlando, April.. Lal, A.K., Zhang, H., Aranchuk, V., Hurtado, E., Hess, C.F., Burgett, R.D, Sabatier, J.M., Multi-beam LDV system for buried landmine detection, Proceedings of the SPIE, Vol. 589, p. 579, Orlando, April. 4. Lal, A.K., Hess, C.F., Zhang, H., Hurtado, E., Aranchuk, V., Markov, V.B., and Mayo, W.T., Whole-field laser vibrometer for buried landmine detection, Proceedings of the SPIE, Vol. 474, p. 64, Orlando, April. 5. Rothberg S. G., Barker J.F. and Halliwell N.A., Laser vibrometry: pseudo-vibrations, Journal of Sound and Vibration, 5 (), p J.W.Goodman, Statistical Properties of Laser Speckle patterns, Laser Speckle and Related Phenomena, J.C. Dainty, pp. 9-75, 975.
7 Figure. Segmented velocity image above a buried antitank mine. a). second time segment, b).5 second time segment. The scan rate was 5cm/second. Figure. Antitank mine VS. buried 5 cm deep at different scanning speeds. a) cm/second; b) cm/second; c) 5cm/second; d) cm/second. Figure. Antitank mine M5 buried 5 cm deep at different scanning speeds. a) cm/second; b) cm/second; c) cm/second; d) 5cm/second. Figure. Image of an antitank mine VS.6 buried cm deep at different levels of excitation. a) low excitation, b) db higher excitation.
Self-Mixing Laser Diode Vibrometer with Wide Dynamic Range
 Self-Mixing Laser Diode Vibrometer with Wide Dynamic Range G. Giuliani,, S. Donati, L. Monti -, Italy Outline Conventional Laser vibrometry (LDV) Self-mixing interferometry Self-mixing vibrometer Principle:
Self-Mixing Laser Diode Vibrometer with Wide Dynamic Range G. Giuliani,, S. Donati, L. Monti -, Italy Outline Conventional Laser vibrometry (LDV) Self-mixing interferometry Self-mixing vibrometer Principle:
Self-Mixing Differential Laser Vibrometer
 Self-Mixing Differential Laser Vibrometer Michele Norgia e Informazione, Politecnico di Milano, Italy Guido Giuliani,, Silvano Donati -,, Italy guido.giuliani@unipv.it Outline Conventional Laser Doppler
Self-Mixing Differential Laser Vibrometer Michele Norgia e Informazione, Politecnico di Milano, Italy Guido Giuliani,, Silvano Donati -,, Italy guido.giuliani@unipv.it Outline Conventional Laser Doppler
MEASURING THE 3D PROPAGATION OF SOUND WAVES USING SCANNING LASER VIBROMETRY
 MEASURING THE 3D PROPAGATION OF SOUND WAVES USING SCANNING LASER VIBROMETRY Andreas Dittmar, IAV GmbH Kauffahrtei 45, 09120 Chemnitz, Germany Reinhard Behrendt Polytec GmbH, Büro Berlin, Schwarzschildstraße
MEASURING THE 3D PROPAGATION OF SOUND WAVES USING SCANNING LASER VIBROMETRY Andreas Dittmar, IAV GmbH Kauffahrtei 45, 09120 Chemnitz, Germany Reinhard Behrendt Polytec GmbH, Büro Berlin, Schwarzschildstraße
Non-Contact Vibration Measurement of Micro-Structures
 Non-Contact Vibration Measurement of Micro-Structures Using Laser Doppler Vibrometry (LDV) and Planar Motion Analysis (PMA) to examine and assess the vibration characteristics of micro- and macro-structures.
Non-Contact Vibration Measurement of Micro-Structures Using Laser Doppler Vibrometry (LDV) and Planar Motion Analysis (PMA) to examine and assess the vibration characteristics of micro- and macro-structures.
E190Q Lecture 5 Autonomous Robot Navigation
 E190Q Lecture 5 Autonomous Robot Navigation Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Spring 2014 1 Figures courtesy of Siegwart & Nourbakhsh Control Structures Planning Based Control Prior Knowledge Operator
E190Q Lecture 5 Autonomous Robot Navigation Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Spring 2014 1 Figures courtesy of Siegwart & Nourbakhsh Control Structures Planning Based Control Prior Knowledge Operator
Robot Perception Continued
 Robot Perception Continued 1 Visual Perception Visual Odometry Reconstruction Recognition CS 685 11 Range Sensing strategies Active range sensors Ultrasound Laser range sensor Slides adopted from Siegwart
Robot Perception Continued 1 Visual Perception Visual Odometry Reconstruction Recognition CS 685 11 Range Sensing strategies Active range sensors Ultrasound Laser range sensor Slides adopted from Siegwart
Building Design for Advanced Technology Instruments Sensitive to Acoustical Noise
 Building Design for Advanced Technology Instruments Sensitive to Acoustic Noise Michael Gendreau Colin Gordon & Associates Presentation Outline! High technology research and manufacturing instruments respond
Building Design for Advanced Technology Instruments Sensitive to Acoustic Noise Michael Gendreau Colin Gordon & Associates Presentation Outline! High technology research and manufacturing instruments respond
Linear Parameter Measurement (LPM)
 (LPM) Module of the R&D SYSTEM FEATURES Identifies linear transducer model Measures suspension creep LS-fitting in impedance LS-fitting in displacement (optional) Single-step measurement with laser sensor
(LPM) Module of the R&D SYSTEM FEATURES Identifies linear transducer model Measures suspension creep LS-fitting in impedance LS-fitting in displacement (optional) Single-step measurement with laser sensor
Module 13 : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems
 Module 13 : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Lecture : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Attenuation (Loss)
Module 13 : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Lecture : Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Measurements on Fiber Optic Systems Attenuation (Loss)
Lab 9: The Acousto-Optic Effect
 Lab 9: The Acousto-Optic Effect Incoming Laser Beam Travelling Acoustic Wave (longitudinal wave) O A 1st order diffracted laser beam A 1 Introduction qb d O 2qb rarefractions compressions Refer to Appendix
Lab 9: The Acousto-Optic Effect Incoming Laser Beam Travelling Acoustic Wave (longitudinal wave) O A 1st order diffracted laser beam A 1 Introduction qb d O 2qb rarefractions compressions Refer to Appendix
Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment
 Fluid Structure Interaction VI 3 Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment J. Hengstler & J. Dual Department of Mechanical and Process
Fluid Structure Interaction VI 3 Fluid structure interaction of a vibrating circular plate in a bounded fluid volume: simulation and experiment J. Hengstler & J. Dual Department of Mechanical and Process
Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications
 Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications Saulius Marcinkevičius Optics, ICT, KTH 1 Outline Optical near field. Principle of scanning near field optical microscope
Scanning Near Field Optical Microscopy: Principle, Instrumentation and Applications Saulius Marcinkevičius Optics, ICT, KTH 1 Outline Optical near field. Principle of scanning near field optical microscope
Development of Optical Wave Microphone Measuring Sound Waves with No Diaphragm
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium Proceedings, Taipei, March 5 8, 3 359 Development of Optical Wave Microphone Measuring Sound Waves with No Diaphragm Yoshito Sonoda, Takashi Samatsu, and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium Proceedings, Taipei, March 5 8, 3 359 Development of Optical Wave Microphone Measuring Sound Waves with No Diaphragm Yoshito Sonoda, Takashi Samatsu, and
Comparison of the Response of a Simple Structure to Single Axis and Multiple Axis Random Vibration Inputs
 Comparison of the Response of a Simple Structure to Single Axis and Multiple Axis Random Vibration Inputs Dan Gregory Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque NM 87185 (505) 844-9743 Fernando Bitsie Sandia
Comparison of the Response of a Simple Structure to Single Axis and Multiple Axis Random Vibration Inputs Dan Gregory Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque NM 87185 (505) 844-9743 Fernando Bitsie Sandia
Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Spindle
 UCRL-CONF-206108 Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Spindle D. J. Hopkins, P. Geraghty August 18, 2004 American Society of Precision Engineering Annual Conference Orlando, FL, United States
UCRL-CONF-206108 Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Spindle D. J. Hopkins, P. Geraghty August 18, 2004 American Society of Precision Engineering Annual Conference Orlando, FL, United States
Projects. Objective To gain hands-on design and measurement experience with real-world applications. Contents
 Projects Contents 9-1 INTRODUCTION...................... 43 9-2 PROJECTS......................... 43 9-2.1 Alarm Radar Sensor................ 43 9-2.2 Microwave FM Communication Link....... 46 9-2.3 Optical
Projects Contents 9-1 INTRODUCTION...................... 43 9-2 PROJECTS......................... 43 9-2.1 Alarm Radar Sensor................ 43 9-2.2 Microwave FM Communication Link....... 46 9-2.3 Optical
ANALYZER BASICS WHAT IS AN FFT SPECTRUM ANALYZER? 2-1
 WHAT IS AN FFT SPECTRUM ANALYZER? ANALYZER BASICS The SR760 FFT Spectrum Analyzer takes a time varying input signal, like you would see on an oscilloscope trace, and computes its frequency spectrum. Fourier's
WHAT IS AN FFT SPECTRUM ANALYZER? ANALYZER BASICS The SR760 FFT Spectrum Analyzer takes a time varying input signal, like you would see on an oscilloscope trace, and computes its frequency spectrum. Fourier's
Digital demodulator unit of laser vibrometer standard for in situ measurement
 ACTA IMEKO December 13, Volume, Number, 61 66 www.imeko.org Digital demodulator unit of laser vibrometer standard for in situ measurement Akihiro Oota 1, Hideaki Nozato 1, Wataru Kokuyama 1, Yoshinori
ACTA IMEKO December 13, Volume, Number, 61 66 www.imeko.org Digital demodulator unit of laser vibrometer standard for in situ measurement Akihiro Oota 1, Hideaki Nozato 1, Wataru Kokuyama 1, Yoshinori
INTERFERENCE OF SOUND WAVES
 1/2016 Sound 1/8 INTERFERENCE OF SOUND WAVES PURPOSE: To measure the wavelength, frequency, and propagation speed of ultrasonic sound waves and to observe interference phenomena with ultrasonic sound waves.
1/2016 Sound 1/8 INTERFERENCE OF SOUND WAVES PURPOSE: To measure the wavelength, frequency, and propagation speed of ultrasonic sound waves and to observe interference phenomena with ultrasonic sound waves.
Doppler. Doppler. Doppler shift. Doppler Frequency. Doppler shift. Doppler shift. Chapter 19
 Doppler Doppler Chapter 19 A moving train with a trumpet player holding the same tone for a very long time travels from your left to your right. The tone changes relative the motion of you (receiver) and
Doppler Doppler Chapter 19 A moving train with a trumpet player holding the same tone for a very long time travels from your left to your right. The tone changes relative the motion of you (receiver) and
Active noise control in practice: transformer station
 Active noise control in practice: transformer station Edwin Buikema 1 ; Fokke D. van der Ploeg 2 ; Jan H. Granneman 3 1, 2, 3 Peutz bv, Netherlands ABSTRACT Based on literature and extensive measurements
Active noise control in practice: transformer station Edwin Buikema 1 ; Fokke D. van der Ploeg 2 ; Jan H. Granneman 3 1, 2, 3 Peutz bv, Netherlands ABSTRACT Based on literature and extensive measurements
inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE
 Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 2.1 WHISTLING PHENOMENA
Copyright SFA - InterNoise 2000 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 2.1 WHISTLING PHENOMENA
Synthetic Sensing: Proximity / Distance Sensors
 Synthetic Sensing: Proximity / Distance Sensors MediaRobotics Lab, February 2010 Proximity detection is dependent on the object of interest. One size does not fit all For non-contact distance measurement,
Synthetic Sensing: Proximity / Distance Sensors MediaRobotics Lab, February 2010 Proximity detection is dependent on the object of interest. One size does not fit all For non-contact distance measurement,
Analysis of free reed attack transients
 Analysis of free reed attack transients James Cottingham Physics Department, Coe College, Cedar Rapids, Iowa, United States Summary Attack transients of harmonium-type free reeds from American reed organs
Analysis of free reed attack transients James Cottingham Physics Department, Coe College, Cedar Rapids, Iowa, United States Summary Attack transients of harmonium-type free reeds from American reed organs
Experiment 5. Lasers and laser mode structure
 Northeastern University, PHYS5318 Spring 2014, 1 1. Introduction Experiment 5. Lasers and laser mode structure The laser is a very important optical tool that has found widespread use in science and industry,
Northeastern University, PHYS5318 Spring 2014, 1 1. Introduction Experiment 5. Lasers and laser mode structure The laser is a very important optical tool that has found widespread use in science and industry,
Acceleration levels of dropped objects
 Acceleration levels of dropped objects cmyk Acceleration levels of dropped objects Introduction his paper is intended to provide an overview of drop shock testing, which is defined as the acceleration
Acceleration levels of dropped objects cmyk Acceleration levels of dropped objects Introduction his paper is intended to provide an overview of drop shock testing, which is defined as the acceleration
Lock-in amplifiers. A short tutorial by R. Scholten
 Lock-in amplifiers A short tutorial by R. cholten Measuring something Common task: measure light intensity, e.g. absorption spectrum Need very low intensity to reduce broadening Noise becomes a problem
Lock-in amplifiers A short tutorial by R. cholten Measuring something Common task: measure light intensity, e.g. absorption spectrum Need very low intensity to reduce broadening Noise becomes a problem
Numerical simulation of speckle noise in laser vibrometry
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Numerical simulation of speckle noise in laser vibrometry This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author.
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Numerical simulation of speckle noise in laser vibrometry This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author.
Email: tjohn@mail.nplindia.ernet.in
 USE OF VIRTUAL INSTRUMENTS IN RADIO AND ATMOSPHERIC EXPERIMENTS P.N. VIJAYAKUMAR, THOMAS JOHN AND S.C. GARG RADIO AND ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE DIVISION, NATIONAL PHYSICAL LABORATORY, NEW DELHI 110012, INDIA
USE OF VIRTUAL INSTRUMENTS IN RADIO AND ATMOSPHERIC EXPERIMENTS P.N. VIJAYAKUMAR, THOMAS JOHN AND S.C. GARG RADIO AND ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE DIVISION, NATIONAL PHYSICAL LABORATORY, NEW DELHI 110012, INDIA
Outer Diameter 23 φ mm Face side Dimension 20.1 φ mm. Baffle Opening. Normal 0.5 Watts Maximum 1.0 Watts Sine Wave.
 1. MODEL: 23CR08FH-50ND 2 Dimension & Weight Outer Diameter 23 φ mm Face side Dimension 20.1 φ mm Baffle Opening 20.1 φ mm Height Refer to drawing Weight 4.0Grams 3 Magnet Materials Rare Earth Size φ 9.5
1. MODEL: 23CR08FH-50ND 2 Dimension & Weight Outer Diameter 23 φ mm Face side Dimension 20.1 φ mm Baffle Opening 20.1 φ mm Height Refer to drawing Weight 4.0Grams 3 Magnet Materials Rare Earth Size φ 9.5
FTIR Instrumentation
 FTIR Instrumentation Adopted from the FTIR lab instruction by H.-N. Hsieh, New Jersey Institute of Technology: http://www-ec.njit.edu/~hsieh/ene669/ftir.html 1. IR Instrumentation Two types of instrumentation
FTIR Instrumentation Adopted from the FTIR lab instruction by H.-N. Hsieh, New Jersey Institute of Technology: http://www-ec.njit.edu/~hsieh/ene669/ftir.html 1. IR Instrumentation Two types of instrumentation
Vibrometry. Laser Vibrometers Optical Measurement Solutions for Vibration Product Brochure
 Vibrometry Laser Vibrometers Optical Measurement Solutions for Vibration Product Brochure Vibrometry Laser Doppler Vibrometry Polytec manufactures a range of laser vibrometers that have become the accepted
Vibrometry Laser Vibrometers Optical Measurement Solutions for Vibration Product Brochure Vibrometry Laser Doppler Vibrometry Polytec manufactures a range of laser vibrometers that have become the accepted
Index-Velocity Rating Development for Rapidly Changing Flows in an Irrigation Canal Using Broadband StreamPro ADCP and ChannelMaster H-ADCP
 Index-Velocity Rating Development for Rapidly Changing Flows in an Irrigation Canal Using Broadband StreamPro ADCP and ChannelMaster H-ADCP HENING HUANG, RD Instruments, 9855 Businesspark Avenue, San Diego,
Index-Velocity Rating Development for Rapidly Changing Flows in an Irrigation Canal Using Broadband StreamPro ADCP and ChannelMaster H-ADCP HENING HUANG, RD Instruments, 9855 Businesspark Avenue, San Diego,
Optical Measurement Techniques for Dynamic Characterization of MEMS Devices
 Technical Paper Optical Measurement Techniques for Dynamic Characterization of MEMS Devices Eric Lawrence, Polytec, Inc. March 2012 Polytec GmbH Polytec-Platz 1-7 D-76337 Waldbronn Germany Tel. + 49 (0)
Technical Paper Optical Measurement Techniques for Dynamic Characterization of MEMS Devices Eric Lawrence, Polytec, Inc. March 2012 Polytec GmbH Polytec-Platz 1-7 D-76337 Waldbronn Germany Tel. + 49 (0)
Optical Fibres. Introduction. Safety precautions. For your safety. For the safety of the apparatus
 Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Introduction Optical fibres are widely used for transmitting data at high speeds. In this experiment,
Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Introduction Optical fibres are widely used for transmitting data at high speeds. In this experiment,
The Calculation of G rms
 The Calculation of G rms QualMark Corp. Neill Doertenbach The metric of G rms is typically used to specify and compare the energy in repetitive shock vibration systems. However, the method of arriving
The Calculation of G rms QualMark Corp. Neill Doertenbach The metric of G rms is typically used to specify and compare the energy in repetitive shock vibration systems. However, the method of arriving
Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water
 Experiment (8) Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water The aim of work: The goals of this experiment are to confirm the relationship between angular frequency and wave vector
Experiment (8) Using light scattering method to find The surface tension of water The aim of work: The goals of this experiment are to confirm the relationship between angular frequency and wave vector
Room Acoustic Reproduction by Spatial Room Response
 Room Acoustic Reproduction by Spatial Room Response Rendering Hoda Nasereddin 1, Mohammad Asgari 2 and Ayoub Banoushi 3 Audio Engineer, Broadcast engineering department, IRIB university, Tehran, Iran,
Room Acoustic Reproduction by Spatial Room Response Rendering Hoda Nasereddin 1, Mohammad Asgari 2 and Ayoub Banoushi 3 Audio Engineer, Broadcast engineering department, IRIB university, Tehran, Iran,
Timing Errors and Jitter
 Timing Errors and Jitter Background Mike Story In a sampled (digital) system, samples have to be accurate in level and time. The digital system uses the two bits of information the signal was this big
Timing Errors and Jitter Background Mike Story In a sampled (digital) system, samples have to be accurate in level and time. The digital system uses the two bits of information the signal was this big
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB NO. 0704-0188 The public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB NO. 0704-0188 The public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
Improved Fault Detection by Appropriate Control of Signal
 Improved Fault Detection by Appropriate Control of Signal Bandwidth of the TSA Eric Bechhoefer 1, and Xinghui Zhang 2 1 GPMS Inc., President, Cornwall, VT, 05753, USA eric@gpms-vt.com 2 Mechanical Engineering
Improved Fault Detection by Appropriate Control of Signal Bandwidth of the TSA Eric Bechhoefer 1, and Xinghui Zhang 2 1 GPMS Inc., President, Cornwall, VT, 05753, USA eric@gpms-vt.com 2 Mechanical Engineering
Nano Meter Stepping Drive of Surface Acoustic Wave Motor
 Proc. of 1st IEEE Conf. on Nanotechnology, Oct. 28-3, pp. 495-5, (21) Maui, Hawaii Nano Meter Stepping Drive of Surface Acoustic Wave Motor Takashi Shigematsu*, Minoru Kuribayashi Kurosawa*, and Katsuhiko
Proc. of 1st IEEE Conf. on Nanotechnology, Oct. 28-3, pp. 495-5, (21) Maui, Hawaii Nano Meter Stepping Drive of Surface Acoustic Wave Motor Takashi Shigematsu*, Minoru Kuribayashi Kurosawa*, and Katsuhiko
Acousto-optic modulator
 1 of 3 Acousto-optic modulator F An acousto-optic modulator (AOM), also called a Bragg cell, uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves (usually at radio-frequency).
1 of 3 Acousto-optic modulator F An acousto-optic modulator (AOM), also called a Bragg cell, uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves (usually at radio-frequency).
SOFTWARE FOR GENERATION OF SPECTRUM COMPATIBLE TIME HISTORY
 3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 24 Paper No. 296 SOFTWARE FOR GENERATION OF SPECTRUM COMPATIBLE TIME HISTORY ASHOK KUMAR SUMMARY One of the important
3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 24 Paper No. 296 SOFTWARE FOR GENERATION OF SPECTRUM COMPATIBLE TIME HISTORY ASHOK KUMAR SUMMARY One of the important
AP1 Waves. (A) frequency (B) wavelength (C) speed (D) intensity. Answer: (A) and (D) frequency and intensity.
 1. A fire truck is moving at a fairly high speed, with its siren emitting sound at a specific pitch. As the fire truck recedes from you which of the following characteristics of the sound wave from the
1. A fire truck is moving at a fairly high speed, with its siren emitting sound at a specific pitch. As the fire truck recedes from you which of the following characteristics of the sound wave from the
Environmental Effects On Phase Coherent Underwater Acoustic Communications: A Perspective From Several Experimental Measurements
 Environmental Effects On Phase Coherent Underwater Acoustic Communications: A Perspective From Several Experimental Measurements T. C. Yang, Naval Research Lab., Washington DC 20375 Abstract. This paper
Environmental Effects On Phase Coherent Underwater Acoustic Communications: A Perspective From Several Experimental Measurements T. C. Yang, Naval Research Lab., Washington DC 20375 Abstract. This paper
Acoustic Processor of the MCM Sonar
 AUTOMATYKA/ AUTOMATICS 2013 Vol. 17 No. 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.7494/automat.2013.17.1.73 Mariusz Rudnicki*, Jan Schmidt*, Aleksander Schmidt*, Wojciech Leœniak* Acoustic Processor of the MCM Sonar 1. Introduction
AUTOMATYKA/ AUTOMATICS 2013 Vol. 17 No. 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.7494/automat.2013.17.1.73 Mariusz Rudnicki*, Jan Schmidt*, Aleksander Schmidt*, Wojciech Leœniak* Acoustic Processor of the MCM Sonar 1. Introduction
Time Domain and Frequency Domain Techniques For Multi Shaker Time Waveform Replication
 Time Domain and Frequency Domain Techniques For Multi Shaker Time Waveform Replication Thomas Reilly Data Physics Corporation 1741 Technology Drive, Suite 260 San Jose, CA 95110 (408) 216-8440 This paper
Time Domain and Frequency Domain Techniques For Multi Shaker Time Waveform Replication Thomas Reilly Data Physics Corporation 1741 Technology Drive, Suite 260 San Jose, CA 95110 (408) 216-8440 This paper
An octave bandwidth dipole antenna
 An octave bandwidth dipole antenna Abstract: Achieving wideband performance from resonant structures is challenging because their radiation properties and impedance characteristics are usually sensitive
An octave bandwidth dipole antenna Abstract: Achieving wideband performance from resonant structures is challenging because their radiation properties and impedance characteristics are usually sensitive
Fibre Bragg Grating Sensors An Introduction to Bragg gratings and interrogation techniques
 Fibre Bragg Grating Sensors An ntroduction to Bragg gratings and interrogation techniques Dr Crispin Doyle Senior Applications Engineer, Smart Fibres Ltd. 2003 1) The Fibre Bragg Grating (FBG) There are
Fibre Bragg Grating Sensors An ntroduction to Bragg gratings and interrogation techniques Dr Crispin Doyle Senior Applications Engineer, Smart Fibres Ltd. 2003 1) The Fibre Bragg Grating (FBG) There are
Polarization of Light
 Polarization of Light References Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics, Chapter 33, 7 th ed. Wiley 005 PASCO EX997A and EX999 guide sheets (written by Ann Hanks) weight Exercises and weights
Polarization of Light References Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics, Chapter 33, 7 th ed. Wiley 005 PASCO EX997A and EX999 guide sheets (written by Ann Hanks) weight Exercises and weights
Bandwidth-dependent transformation of noise data from frequency into time domain and vice versa
 Topic Bandwidth-dependent transformation of noise data from frequency into time domain and vice versa Authors Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany),
Topic Bandwidth-dependent transformation of noise data from frequency into time domain and vice versa Authors Peter Bormann (formerly GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam, Telegrafenberg, D-14473 Potsdam, Germany),
EECC694 - Shaaban. Transmission Channel
 The Physical Layer: Data Transmission Basics Encode data as energy at the data (information) source and transmit the encoded energy using transmitter hardware: Possible Energy Forms: Electrical, light,
The Physical Layer: Data Transmission Basics Encode data as energy at the data (information) source and transmit the encoded energy using transmitter hardware: Possible Energy Forms: Electrical, light,
Part IV. Conclusions
 Part IV Conclusions 189 Chapter 9 Conclusions and Future Work CFD studies of premixed laminar and turbulent combustion dynamics have been conducted. These studies were aimed at explaining physical phenomena
Part IV Conclusions 189 Chapter 9 Conclusions and Future Work CFD studies of premixed laminar and turbulent combustion dynamics have been conducted. These studies were aimed at explaining physical phenomena
Acoustic Terms, Definitions and General Information
 Acoustic Terms, Definitions and General Information Authored by: Daniel Ziobroski Acoustic Engineer Environmental and Acoustic Engineering GE Energy Charles Powers Program Manager Environmental and Acoustic
Acoustic Terms, Definitions and General Information Authored by: Daniel Ziobroski Acoustic Engineer Environmental and Acoustic Engineering GE Energy Charles Powers Program Manager Environmental and Acoustic
Lecture 14. Point Spread Function (PSF)
 Lecture 14 Point Spread Function (PSF), Modulation Transfer Function (MTF), Signal-to-noise Ratio (SNR), Contrast-to-noise Ratio (CNR), and Receiver Operating Curves (ROC) Point Spread Function (PSF) Recollect
Lecture 14 Point Spread Function (PSF), Modulation Transfer Function (MTF), Signal-to-noise Ratio (SNR), Contrast-to-noise Ratio (CNR), and Receiver Operating Curves (ROC) Point Spread Function (PSF) Recollect
A comparison of radio direction-finding technologies. Paul Denisowski, Applications Engineer Rohde & Schwarz
 A comparison of radio direction-finding technologies Paul Denisowski, Applications Engineer Rohde & Schwarz Topics General introduction to radiolocation Manual DF techniques Doppler DF Time difference
A comparison of radio direction-finding technologies Paul Denisowski, Applications Engineer Rohde & Schwarz Topics General introduction to radiolocation Manual DF techniques Doppler DF Time difference
Optical Metrology. Third Edition. Kjell J. Gasvik Spectra Vision AS, Trondheim, Norway JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD
 2008 AGI-Information Management Consultants May be used for personal purporses only or by libraries associated to dandelon.com network. Optical Metrology Third Edition Kjell J. Gasvik Spectra Vision AS,
2008 AGI-Information Management Consultants May be used for personal purporses only or by libraries associated to dandelon.com network. Optical Metrology Third Edition Kjell J. Gasvik Spectra Vision AS,
SIGNAL GENERATORS and OSCILLOSCOPE CALIBRATION
 1 SIGNAL GENERATORS and OSCILLOSCOPE CALIBRATION By Lannes S. Purnell FLUKE CORPORATION 2 This paper shows how standard signal generators can be used as leveled sine wave sources for calibrating oscilloscopes.
1 SIGNAL GENERATORS and OSCILLOSCOPE CALIBRATION By Lannes S. Purnell FLUKE CORPORATION 2 This paper shows how standard signal generators can be used as leveled sine wave sources for calibrating oscilloscopes.
RF Network Analyzer Basics
 RF Network Analyzer Basics A tutorial, information and overview about the basics of the RF Network Analyzer. What is a Network Analyzer and how to use them, to include the Scalar Network Analyzer (SNA),
RF Network Analyzer Basics A tutorial, information and overview about the basics of the RF Network Analyzer. What is a Network Analyzer and how to use them, to include the Scalar Network Analyzer (SNA),
MATRIX TECHNICAL NOTES
 200 WOOD AVENUE, MIDDLESEX, NJ 08846 PHONE (732) 469-9510 FAX (732) 469-0418 MATRIX TECHNICAL NOTES MTN-107 TEST SETUP FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF X-MOD, CTB, AND CSO USING A MEAN SQUARE CIRCUIT AS A DETECTOR
200 WOOD AVENUE, MIDDLESEX, NJ 08846 PHONE (732) 469-9510 FAX (732) 469-0418 MATRIX TECHNICAL NOTES MTN-107 TEST SETUP FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF X-MOD, CTB, AND CSO USING A MEAN SQUARE CIRCUIT AS A DETECTOR
Sensori ottici e laser nelle applicazioni industriali
 Sensori ottici e laser nelle applicazioni industriali Guido GIULIANI Pavia giuliani@julight.it 1 Outline Optical sensors in industry: why? Types of optical sensors optical barriers distance measurement
Sensori ottici e laser nelle applicazioni industriali Guido GIULIANI Pavia giuliani@julight.it 1 Outline Optical sensors in industry: why? Types of optical sensors optical barriers distance measurement
AN-837 APPLICATION NOTE
 APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 916 Norwood, MA 262-916, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.47 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com DDS-Based Clock Jitter Performance vs. DAC Reconstruction Filter Performance
APPLICATION NOTE One Technology Way P.O. Box 916 Norwood, MA 262-916, U.S.A. Tel: 781.329.47 Fax: 781.461.3113 www.analog.com DDS-Based Clock Jitter Performance vs. DAC Reconstruction Filter Performance
INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA
 COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/6/2014 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/6/2014 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
FRAUNHOFER INSTITUTE FOR INTEg RATEd CIRCUITS IIS. drm TesT equipment
 FRAUNHOFER INSTITUTE FOR INTEg RATEd CIRCUITS IIS drm TesT equipment dt230 playback of drm signals recording of drm signals channel simulation receiver performance analysis real-time modulation Architecture
FRAUNHOFER INSTITUTE FOR INTEg RATEd CIRCUITS IIS drm TesT equipment dt230 playback of drm signals recording of drm signals channel simulation receiver performance analysis real-time modulation Architecture
The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking
 The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking EQUIPMENT Pasco sonometers (pick up 5 from teaching lab) and 5 kits to go with them BK Precision function generators and Tenma oscilloscopes
The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking EQUIPMENT Pasco sonometers (pick up 5 from teaching lab) and 5 kits to go with them BK Precision function generators and Tenma oscilloscopes
CHAPTER 3 MODAL ANALYSIS OF A PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD
 45 CHAPTER 3 MODAL ANALYSIS OF A PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD 3.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the methodology for performing the modal analysis of a printed circuit board used in a hand held electronic
45 CHAPTER 3 MODAL ANALYSIS OF A PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD 3.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the methodology for performing the modal analysis of a printed circuit board used in a hand held electronic
Doppler Effect Plug-in in Music Production and Engineering
 , pp.287-292 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2014.9.8.26 Doppler Effect Plug-in in Music Production and Engineering Yoemun Yun Department of Applied Music, Chungwoon University San 29, Namjang-ri, Hongseong,
, pp.287-292 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2014.9.8.26 Doppler Effect Plug-in in Music Production and Engineering Yoemun Yun Department of Applied Music, Chungwoon University San 29, Namjang-ri, Hongseong,
RANDOM VIBRATION AN OVERVIEW by Barry Controls, Hopkinton, MA
 RANDOM VIBRATION AN OVERVIEW by Barry Controls, Hopkinton, MA ABSTRACT Random vibration is becoming increasingly recognized as the most realistic method of simulating the dynamic environment of military
RANDOM VIBRATION AN OVERVIEW by Barry Controls, Hopkinton, MA ABSTRACT Random vibration is becoming increasingly recognized as the most realistic method of simulating the dynamic environment of military
Robot Sensors. Outline. The Robot Structure. Robots and Sensors. Henrik I Christensen
 Robot Sensors Henrik I Christensen Robotics & Intelligent Machines @ GT Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA 30332-0760 hic@cc.gatech.edu Henrik I Christensen (RIM@GT) Sensors 1 / 38 Outline 1
Robot Sensors Henrik I Christensen Robotics & Intelligent Machines @ GT Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA 30332-0760 hic@cc.gatech.edu Henrik I Christensen (RIM@GT) Sensors 1 / 38 Outline 1
Dispersion diagrams of a water-loaded cylindrical shell obtained from the structural and acoustic responses of the sensor array along the shell
 Dispersion diagrams of a water-loaded cylindrical shell obtained from the structural and acoustic responses of the sensor array along the shell B.K. Jung ; J. Ryue ; C.S. Hong 3 ; W.B. Jeong ; K.K. Shin
Dispersion diagrams of a water-loaded cylindrical shell obtained from the structural and acoustic responses of the sensor array along the shell B.K. Jung ; J. Ryue ; C.S. Hong 3 ; W.B. Jeong ; K.K. Shin
The Phase Modulator In NBFM Voice Communication Systems
 The Phase Modulator In NBFM Voice Communication Systems Virgil Leenerts 8 March 5 The phase modulator has been a point of discussion as to why it is used and not a frequency modulator in what are called
The Phase Modulator In NBFM Voice Communication Systems Virgil Leenerts 8 March 5 The phase modulator has been a point of discussion as to why it is used and not a frequency modulator in what are called
High-Concentration Submicron Particle Size Distribution by Dynamic Light Scattering
 High-Concentration Submicron Particle Size Distribution by Dynamic Light Scattering Power spectrum development with heterodyne technology advances biotechnology and nanotechnology measurements. M. N. Trainer
High-Concentration Submicron Particle Size Distribution by Dynamic Light Scattering Power spectrum development with heterodyne technology advances biotechnology and nanotechnology measurements. M. N. Trainer
Non-Data Aided Carrier Offset Compensation for SDR Implementation
 Non-Data Aided Carrier Offset Compensation for SDR Implementation Anders Riis Jensen 1, Niels Terp Kjeldgaard Jørgensen 1 Kim Laugesen 1, Yannick Le Moullec 1,2 1 Department of Electronic Systems, 2 Center
Non-Data Aided Carrier Offset Compensation for SDR Implementation Anders Riis Jensen 1, Niels Terp Kjeldgaard Jørgensen 1 Kim Laugesen 1, Yannick Le Moullec 1,2 1 Department of Electronic Systems, 2 Center
4.3.5: High Temperature Test 3
 temperature and 800 degrees Celsius is made by matching the optical path lengths of the measurement and sensing arms at both temperatures. By marking the relative distance between the GRIN lens and mirror
temperature and 800 degrees Celsius is made by matching the optical path lengths of the measurement and sensing arms at both temperatures. By marking the relative distance between the GRIN lens and mirror
ISC Dual Frequency WFS RFPD Test Procedure:
 LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY LIGO Laboratory / LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO 08 January 2013 ISC Dual Frequency WFS RFPD Test Procedure: Richard Abbott Distribution of this
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY LIGO Laboratory / LIGO Scientific Collaboration LIGO 08 January 2013 ISC Dual Frequency WFS RFPD Test Procedure: Richard Abbott Distribution of this
MSAN-001 X-Band Microwave Motion Sensor Module Application Note
 1. Introduction HB Series of microwave motion sensor module are X-Band Mono-static DRO Doppler transceiver front-end module. These modules are designed for movement detection, like intruder alarms, occupancy
1. Introduction HB Series of microwave motion sensor module are X-Band Mono-static DRO Doppler transceiver front-end module. These modules are designed for movement detection, like intruder alarms, occupancy
RF-thermal-structural-RF coupled analysis on the travelling wave disk-loaded accelerating structure
 RF-thermal-structural-RF coupled analysis on the travelling wave disk-loaded accelerating structure PEI Shi-Lun( 裴 士 伦 ) 1) CHI Yun-Long( 池 云 龙 ) ZHANG Jing-Ru( 张 敬 如 ) HOU Mi( 侯 汨 ) LI Xiao-Ping( 李 小
RF-thermal-structural-RF coupled analysis on the travelling wave disk-loaded accelerating structure PEI Shi-Lun( 裴 士 伦 ) 1) CHI Yun-Long( 池 云 龙 ) ZHANG Jing-Ru( 张 敬 如 ) HOU Mi( 侯 汨 ) LI Xiao-Ping( 李 小
Waves - Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
 Waves - Transverse and Longitudinal Waves wave may be defined as a periodic disturbance in a medium that carries energy from one point to another. ll waves require a source and a medium of propagation.
Waves - Transverse and Longitudinal Waves wave may be defined as a periodic disturbance in a medium that carries energy from one point to another. ll waves require a source and a medium of propagation.
Optiffuser. High-performance, high bandwidth lightweight 1D diffuser.
 Optiffuser High-performance, high bandwidth lightweight 1D diffuser. General product information The Optiffuser comes in packs of four panels. Two positives and two negatives (see page 5) per package.
Optiffuser High-performance, high bandwidth lightweight 1D diffuser. General product information The Optiffuser comes in packs of four panels. Two positives and two negatives (see page 5) per package.
Frequency Response of Filters
 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 2 Frequency Response of Filters 1 Introduction Objectives To
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:224 Principles of Electrical Engineering II Laboratory Experiment 2 Frequency Response of Filters 1 Introduction Objectives To
Measurement of RF Emissions from a Final Coat Electronics Corrosion Module
 Engineering Test Report No. 37802-02 Rev. A Measurement of RF Emissions from a Final Coat Electronics Corrosion Module For : Canadian Auto Preservation, Inc. 390 Bradwick Drive Concord, Ontario CANADA
Engineering Test Report No. 37802-02 Rev. A Measurement of RF Emissions from a Final Coat Electronics Corrosion Module For : Canadian Auto Preservation, Inc. 390 Bradwick Drive Concord, Ontario CANADA
Direct and Reflected: Understanding the Truth with Y-S 3
 Direct and Reflected: Understanding the Truth with Y-S 3 -Speaker System Design Guide- December 2008 2008 Yamaha Corporation 1 Introduction Y-S 3 is a speaker system design software application. It is
Direct and Reflected: Understanding the Truth with Y-S 3 -Speaker System Design Guide- December 2008 2008 Yamaha Corporation 1 Introduction Y-S 3 is a speaker system design software application. It is
arxiv:astro-ph/0509450 v1 15 Sep 2005
 arxiv:astro-ph/0509450 v1 15 Sep 2005 TESTING THERMO-ACOUSTIC SOUND GENERATION IN WATER WITH PROTON AND LASER BEAMS K. GRAF, G. ANTON, J. HÖSSL, A. KAPPES, T. KARG, U. KATZ, R. LAHMANN, C. NAUMANN, K.
arxiv:astro-ph/0509450 v1 15 Sep 2005 TESTING THERMO-ACOUSTIC SOUND GENERATION IN WATER WITH PROTON AND LASER BEAMS K. GRAF, G. ANTON, J. HÖSSL, A. KAPPES, T. KARG, U. KATZ, R. LAHMANN, C. NAUMANN, K.
Electromagnetic (EM) waves. Electric and Magnetic Fields. L 30 Electricity and Magnetism [7] James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879)
![Electromagnetic (EM) waves. Electric and Magnetic Fields. L 30 Electricity and Magnetism [7] James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Electromagnetic (EM) waves. Electric and Magnetic Fields. L 30 Electricity and Magnetism [7] James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879)](/thumbs/40/20813653.jpg) L 30 Electricity and Magnetism [7] ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Faraday laid the groundwork with his discovery of electromagnetic induction Maxwell added the last piece of the puzzle Heinrich Hertz made the experimental
L 30 Electricity and Magnetism [7] ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Faraday laid the groundwork with his discovery of electromagnetic induction Maxwell added the last piece of the puzzle Heinrich Hertz made the experimental
FFT Spectrum Analyzers
 FFT Spectrum Analyzers SR760 and SR770 100 khz single-channel FFT spectrum analyzers SR760 & SR770 FFT Spectrum Analyzers DC to 100 khz bandwidth 90 db dynamic range Low-distortion source (SR770) Harmonic,
FFT Spectrum Analyzers SR760 and SR770 100 khz single-channel FFT spectrum analyzers SR760 & SR770 FFT Spectrum Analyzers DC to 100 khz bandwidth 90 db dynamic range Low-distortion source (SR770) Harmonic,
Two primary advantages of radars: all-weather and day /night imaging
 Lecture 0 Principles of active remote sensing: Radars. Objectives: 1. Radar basics. Main types of radars.. Basic antenna parameters. Required reading: G: 8.1, p.401-40 dditional/advanced reading: Online
Lecture 0 Principles of active remote sensing: Radars. Objectives: 1. Radar basics. Main types of radars.. Basic antenna parameters. Required reading: G: 8.1, p.401-40 dditional/advanced reading: Online
v = fλ PROGRESSIVE WAVES 1 Candidates should be able to :
 PROGRESSIVE WAVES 1 Candidates should be able to : Describe and distinguish between progressive longitudinal and transverse waves. With the exception of electromagnetic waves, which do not need a material
PROGRESSIVE WAVES 1 Candidates should be able to : Describe and distinguish between progressive longitudinal and transverse waves. With the exception of electromagnetic waves, which do not need a material
Design of Bidirectional Coupling Circuit for Broadband Power-Line Communications
 Journal of Electromagnetic Analysis and Applications, 2012, 4, 162-166 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jemaa.2012.44021 Published Online April 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) Design of Bidirectional
Journal of Electromagnetic Analysis and Applications, 2012, 4, 162-166 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jemaa.2012.44021 Published Online April 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) Design of Bidirectional
Christine E. Hatch University of Nevada, Reno
 Christine E. Hatch University of Nevada, Reno Roadmap What is DTS? How Does it Work? What Can DTS Measure? Applications What is Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS)? Temperature measurement using only
Christine E. Hatch University of Nevada, Reno Roadmap What is DTS? How Does it Work? What Can DTS Measure? Applications What is Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS)? Temperature measurement using only
CHAPTER 6. Precision Approach Systems
 ELEC4504 Avionics Systems 77 CHAPTER 6. Precision Approach Systems 6.1. Introduction The word approach is used to describe the phase of flight which immediately precedes the landing. While the approach
ELEC4504 Avionics Systems 77 CHAPTER 6. Precision Approach Systems 6.1. Introduction The word approach is used to describe the phase of flight which immediately precedes the landing. While the approach
A Sound Analysis and Synthesis System for Generating an Instrumental Piri Song
 , pp.347-354 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2014.9.8.32 A Sound Analysis and Synthesis System for Generating an Instrumental Piri Song Myeongsu Kang and Jong-Myon Kim School of Electrical Engineering,
, pp.347-354 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2014.9.8.32 A Sound Analysis and Synthesis System for Generating an Instrumental Piri Song Myeongsu Kang and Jong-Myon Kim School of Electrical Engineering,
Study of the Human Eye Working Principle: An impressive high angular resolution system with simple array detectors
 Study of the Human Eye Working Principle: An impressive high angular resolution system with simple array detectors Diego Betancourt and Carlos del Río Antenna Group, Public University of Navarra, Campus
Study of the Human Eye Working Principle: An impressive high angular resolution system with simple array detectors Diego Betancourt and Carlos del Río Antenna Group, Public University of Navarra, Campus
This presentation reports on the progress made during the first year of the Mapping the Underworld project. As multiple Universities and Departments
 This presentation reports on the progress made during the first year of the Mapping the Underworld project. As multiple Universities and Departments are involved with the project, a single speaker will
This presentation reports on the progress made during the first year of the Mapping the Underworld project. As multiple Universities and Departments are involved with the project, a single speaker will
Marine broadband seismic: Is the earth response helping the resolution revolution? N. Woodburn*, A. Hardwick, and R. Herring, TGS
 Marine broadband seismic: Is the earth response helping the resolution revolution? N. Woodburn*, A. Hardwick, and R. Herring, TGS Summary Broadband seismic aims to provide a greater richness of both (a),
Marine broadband seismic: Is the earth response helping the resolution revolution? N. Woodburn*, A. Hardwick, and R. Herring, TGS Summary Broadband seismic aims to provide a greater richness of both (a),
Pump-probe experiments with ultra-short temporal resolution
 Pump-probe experiments with ultra-short temporal resolution PhD candidate: Ferrante Carino Advisor:Tullio Scopigno Università di Roma ƒla Sapienza 22 February 2012 1 Pump-probe experiments: generalities
Pump-probe experiments with ultra-short temporal resolution PhD candidate: Ferrante Carino Advisor:Tullio Scopigno Università di Roma ƒla Sapienza 22 February 2012 1 Pump-probe experiments: generalities
Atomic Force Microscope
 Atomic Force Microscope (Veeco Nanoman) User Manual Basic Operation 4 th Edition Aug 2012 NR System Startup If the system is currently ON To start the NanoScope software, double-click the NanoScope startup
Atomic Force Microscope (Veeco Nanoman) User Manual Basic Operation 4 th Edition Aug 2012 NR System Startup If the system is currently ON To start the NanoScope software, double-click the NanoScope startup
Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies
 Soonwook Hong, Ph. D. Michael Zuercher Martinson Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies 1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the
Soonwook Hong, Ph. D. Michael Zuercher Martinson Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the Mitigation Strategies 1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the
Radar images Università di Pavia Fabio Dell Acqua Gruppo di Telerilevamento
 Radar images Radar images radar image DNs linked to backscattered field Backscattered field depends on wave-target interaction, with different factors relevant to it: within-pixel coherent combination
Radar images Radar images radar image DNs linked to backscattered field Backscattered field depends on wave-target interaction, with different factors relevant to it: within-pixel coherent combination
Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect
 Objectives: PS-7.1 Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect Illustrate ways that the energy of waves is transferred by interaction with
Objectives: PS-7.1 Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect Illustrate ways that the energy of waves is transferred by interaction with
