4.1 Studying Atom. Early evidence used to develop models of atoms.
|
|
|
- Lizbeth Shelton
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4.1 Studying Atom Early evidence used to develop models of atoms.
2 Democritus said that all matter consisted of extremely small particles that could NOT be divided called these particles atoms from the Greek word atomos, which means uncut or indivisible.
3 Aristotle thought that all substances were made of only four elements earth, air, fire, and water. Aristotle s views on the structure of matter were accepted for many centuries. By the 1800s, scientists had enough experimental data to support an atomic model.
4 Dalton s Atomic Theory Dalton proposed the theory that all matter is made up of individual particles called atoms, which cannot be divided.
5 Dalton s Theory All elements are composed of atoms. All atoms of the same element have the same mass, and atoms of different elements have different masses.
6 Dalton s Theory Compounds contain atoms of more than one element. In a particular compound, atoms of different elements always combine in the same way.
7 Thomson s Model of the Atom Thomson s experiments provided the first evidence that atoms are made of even smaller particles (subatomic particles).
8 Thomson s Model Thomson revised Dalton s model to account for these subatomic particles. The atom has neither a positive nor a negative charge, but there must always be some positive charge in the atom. The atom is filled with a positively charged mass of matter that has negative charges evenly scattered throughout it.
9 Rutherford s Atomic Theory According to Rutherford s model, all of an atom s positive charge is concentrated in its nucleus.
10 Rutherford s Model Rutherford proposed a new model. The positive charge of an atom is not evenly spread throughout the atom. Positive charge is concentrated in a very small, central area. The nucleus of the atom is a dense, positively charged mass located in the center of the atom.
11 4.3: Modern Atomic Theory
12 Bohr s Model of the Atom Focuses on electrons and their arrangement. Bohr stated that electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, like planets around a sun. Bohr correctly assigned energy levels to electrons, but electrons do not move in fixed orbits around the nucleus.
13 What are Energy Levels? The possible energies that electrons in an atom can have are called energy levels. When an atom gains or loses energy, the energy of an electron can change. An electron in an atom can move from one energy level to another when the atom gains or loses energy. An electron cannot exist between energy levels.
14 Bohr s Model of the Atom Electron Nucleus
15 Electron Cloud Model The electron cloud model replaced Bohr's vision of electrons moving in predictable paths. An electron cloud is a visual model of the most likely locations for electrons in an atom. probability of finding an electron is higher in the denser regions of the cloud.
16 Electron Cloud Model An electron cloud is a good approximation of how electrons behave in their orbitals. An orbital is a region of space around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found. The electron cloud represents all the orbitals in an atom.
17 Electron Cloud Model
18 Electron Cloud Model The level in which an electron has the least energy the lowest energy level has only one orbital. Higher energy levels have more than one orbital.
19 Electron Configuration An electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom. The most stable electron configuration is the one in which the electrons are in orbitals with the lowest possible energies.
20 We will draw Bohr Models to illustrate the number of electrons for an element.
21 Before drawing a Bohr Model Horizontal rows on the Periodic Table are called periods. The row number tells you how many energy levels, or rings, the element has. Elements in the same row have the same number of rings. The number of rings increases as you move DOWN the Periodic Table. Example: Sodium (Na) and Magnesium (Mg) are in the third row so they both will have three rings in their Bohr Model.
22 Horizontal Rows=Period=Number of Rings 1 2 Will not draw Bohr Models for Transition Metals
23 Before drawing a Bohr Model Vertical columns on the Periodic Table are called groups. Group numbers tell you how many valence electrons each element in that column has. Valence electrons are electrons that are located on the LAST energy level. The number of valence electrons increases as you move ACROSS the Periodic Table. Example: Sodium and Potassium are both in the 1 st column, so they both will have one valence electron in their last energy level. If the group number is higher than nine, so 10-18, drop the one to determine the number of valence electrons.
24 Vertical Columns=Groups=Number of Valence Electrons ,8 Will not draw Bohr Models for Transition Metals
25 Drawing Bohr Models 1. Determine the number of rings, or energy levels. (Look at the period, or row, number.) 2. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3. Determine the number of valence electrons. (Look at the group, or column, number.) 4. Draw the correct number of rings. 5. Draw the correct number of electrons on each ring, or energy level. (Use Energy Levels, Orbitals, and Electrons table.)
Bohr s Model of the Atom
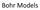 Bohr Models Bohr s Model of the Atom Focuses on electrons and their arrangement. Bohr stated that electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, like planets around a sun. Bohr
Bohr Models Bohr s Model of the Atom Focuses on electrons and their arrangement. Bohr stated that electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, like planets around a sun. Bohr
ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE CHAPTER 3 PHYSICAL SCIENCE
 ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE CHAPTER 3 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 3 Vocabulary Words (27 words) Nucleus Atomic number Proton Mass number Neutron Isotopes Electron Atomic mass unit (amu) Energy level Average
ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE CHAPTER 3 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 3 Vocabulary Words (27 words) Nucleus Atomic number Proton Mass number Neutron Isotopes Electron Atomic mass unit (amu) Energy level Average
9/13/2013. However, Dalton thought that an atom was just a tiny sphere with no internal parts. This is sometimes referred to as the cannonball model.
 John Dalton was an English scientist who lived in the early 1800s. Dalton s atomic theory served as a model for how matter worked. The principles of Dalton s atomic theory are: 1. Elements are made of
John Dalton was an English scientist who lived in the early 1800s. Dalton s atomic theory served as a model for how matter worked. The principles of Dalton s atomic theory are: 1. Elements are made of
ATOMS A T O M S, I S O T O P E S, A N D I O N S. The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 120, Page 1 of 39)
 ATOMS A T O M S, I S O T O P E S, A N D I O N S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 120, Page 1 of 39) THE ATOM All elements listed on the periodic table are made up of atoms.
ATOMS A T O M S, I S O T O P E S, A N D I O N S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 120, Page 1 of 39) THE ATOM All elements listed on the periodic table are made up of atoms.
History of the Atom & Atomic Theory
 Chapter 5 History of the Atom & Atomic Theory You re invited to a Thinking Inside the Box Conference Each group should nominate a: o Leader o Writer o Presenter You have 5 minutes to come up with observations
Chapter 5 History of the Atom & Atomic Theory You re invited to a Thinking Inside the Box Conference Each group should nominate a: o Leader o Writer o Presenter You have 5 minutes to come up with observations
Atomic Theory Part 1
 Atomic Theory Part 1 Reading: Ch 2 sections 1 6, 8 Homework: Chapter 2: 39, 47, 43, 49, 51*, 53, 55, 57, 71, 73, 77, 99, 103 (optional) * = important homework question The Atomic Theory (John Dalton, 1803)
Atomic Theory Part 1 Reading: Ch 2 sections 1 6, 8 Homework: Chapter 2: 39, 47, 43, 49, 51*, 53, 55, 57, 71, 73, 77, 99, 103 (optional) * = important homework question The Atomic Theory (John Dalton, 1803)
Untitled Document. 1. Which of the following best describes an atom? 4. Which statement best describes the density of an atom s nucleus?
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following best describes an atom? A. protons and electrons grouped together in a random pattern B. protons and electrons grouped together in an alternating pattern C. a core
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following best describes an atom? A. protons and electrons grouped together in a random pattern B. protons and electrons grouped together in an alternating pattern C. a core
Chemistry CP Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Electron Configuration. Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 2 will assess the following:)
 Chemistry CP Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Electron Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 2 will assess the following:) 2. Atomic Structure and Electron 2-1. Give the one main contribution to the
Chemistry CP Unit 2 Atomic Structure and Electron Learning Targets (Your exam at the end of Unit 2 will assess the following:) 2. Atomic Structure and Electron 2-1. Give the one main contribution to the
7.4. Using the Bohr Theory KNOW? Using the Bohr Theory to Describe Atoms and Ions
 7.4 Using the Bohr Theory LEARNING TIP Models such as Figures 1 to 4, on pages 218 and 219, help you visualize scientific explanations. As you examine Figures 1 to 4, look back and forth between the diagrams
7.4 Using the Bohr Theory LEARNING TIP Models such as Figures 1 to 4, on pages 218 and 219, help you visualize scientific explanations. As you examine Figures 1 to 4, look back and forth between the diagrams
Development of the Atomic Theory
 Development of the Atomic Theory Atom The smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same substance. Element A pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances
Development of the Atomic Theory Atom The smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same substance. Element A pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances
2 The Structure of Atoms
 CHAPTER 4 2 The Structure of Atoms SECTION Atoms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What do atoms of the same element have in common? What are isotopes? How is an element
CHAPTER 4 2 The Structure of Atoms SECTION Atoms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What do atoms of the same element have in common? What are isotopes? How is an element
NOTES ON The Structure of the Atom
 NOTES ON The Structure of the Atom Chemistry is the study of matter and its properties. Those properties can be explained by examining the atoms that compose the matter. An atom is the smallest particle
NOTES ON The Structure of the Atom Chemistry is the study of matter and its properties. Those properties can be explained by examining the atoms that compose the matter. An atom is the smallest particle
Chapter Five: Atomic Theory and Structure
 Chapter Five: Atomic Theory and Structure Evolution of Atomic Theory The ancient Greek scientist Democritus is often credited with developing the idea of the atom Democritus proposed that matter was, on
Chapter Five: Atomic Theory and Structure Evolution of Atomic Theory The ancient Greek scientist Democritus is often credited with developing the idea of the atom Democritus proposed that matter was, on
Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table Chapter 13 & 14 Assignment & Problem Set
 Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table 2 Study Guide: Things You
Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Electrons in Atoms & Periodic Table 2 Study Guide: Things You
Atomic Calculations. 2.1 Composition of the Atom. number of protons + number of neutrons = mass number
 2.1 Composition of the Atom Atomic Calculations number of protons + number of neutrons = mass number number of neutrons = mass number - number of protons number of protons = number of electrons IF positive
2.1 Composition of the Atom Atomic Calculations number of protons + number of neutrons = mass number number of neutrons = mass number - number of protons number of protons = number of electrons IF positive
Electrons In Atoms Mr. O Brien (SFHS) Chapter 5 Standard 1D
 Electrons In Atoms Mr. O Brien (SFHS) Chapter 5 Standard 1D Electrons in Atoms (std.1d) What are Bohr Models? planetary model in which the negatively-charged electrons orbit a small, positively-charged
Electrons In Atoms Mr. O Brien (SFHS) Chapter 5 Standard 1D Electrons in Atoms (std.1d) What are Bohr Models? planetary model in which the negatively-charged electrons orbit a small, positively-charged
Periodic Table, Valency and Formula
 Periodic Table, Valency and Formula Origins of the Periodic Table Mendelѐѐv in 1869 proposed that a relationship existed between the chemical properties of elements and their atomic masses. He noticed
Periodic Table, Valency and Formula Origins of the Periodic Table Mendelѐѐv in 1869 proposed that a relationship existed between the chemical properties of elements and their atomic masses. He noticed
ATOMS: ATOMIC STRUCTURE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 ATOMS: ATOMIC STRUCTURE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS QUESTION ONE: MODELS OF THE ATOM (2011;1) At different times scientists have proposed various descriptions or models of the atom to match experimental evidence
ATOMS: ATOMIC STRUCTURE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS QUESTION ONE: MODELS OF THE ATOM (2011;1) At different times scientists have proposed various descriptions or models of the atom to match experimental evidence
Elements, Atoms & Ions
 Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation FOURTH EDITION by Steven S. Zumdahl University of Illinois Elements, Atoms & Ions Chapter 4 1 2 Elements Aims: To learn about the relative abundances of the elements,
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation FOURTH EDITION by Steven S. Zumdahl University of Illinois Elements, Atoms & Ions Chapter 4 1 2 Elements Aims: To learn about the relative abundances of the elements,
******* KEY ******* Atomic Structure & Periodic Table Test Study Guide
 Atomic Structure & Periodic Table Test Study Guide VOCABULARY: Write a brief definition of each term in the space provided. 1. Atoms: smallest unit of an element that has all of the properties of that
Atomic Structure & Periodic Table Test Study Guide VOCABULARY: Write a brief definition of each term in the space provided. 1. Atoms: smallest unit of an element that has all of the properties of that
List the 3 main types of subatomic particles and indicate the mass and electrical charge of each.
 Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Basic Chemistry Why do we study chemistry in a biology course? All living organisms are composed of chemicals. To understand life, we must understand the structure, function, and properties of the chemicals
Objectives. PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics. Constituents of Atoms. Atoms. Atoms. Atoms. Basic Atomic Theory
 PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics Basic Atomic Theory Objectives Introduce and Molecules The periodic Table Electronic Energy Levels Atomic excitation & de-excitation Ionisation Molecules Constituents
PAM1014 Introduction to Radiation Physics Basic Atomic Theory Objectives Introduce and Molecules The periodic Table Electronic Energy Levels Atomic excitation & de-excitation Ionisation Molecules Constituents
P. Table & E Configuration Practice TEST
 P. Table & E Configuration Practice TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A line spectrum is produced when an electron moves from one energy
P. Table & E Configuration Practice TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A line spectrum is produced when an electron moves from one energy
6.7: Explaining the Periodic Table pg. 234
 Unit C: Atoms, elements, and Compounds 6.7: Explaining the Periodic Table pg. 234 Key Concepts: 3. Elements are organized according to their atomic number and electron arrangement on the periodic table.
Unit C: Atoms, elements, and Compounds 6.7: Explaining the Periodic Table pg. 234 Key Concepts: 3. Elements are organized according to their atomic number and electron arrangement on the periodic table.
The Models of the Atom
 The Models of the Atom All life, whether in the form of trees, whales, mushrooms, bacteria or amoebas, consists of cells. Similarly, all matter, whether in the form of aspirin, gold, vitamins, air or minerals,
The Models of the Atom All life, whether in the form of trees, whales, mushrooms, bacteria or amoebas, consists of cells. Similarly, all matter, whether in the form of aspirin, gold, vitamins, air or minerals,
Atomic Structure OBJECTIVES SCHEDULE PREPARATION VOCABULARY MATERIALS. For each team of four. The students. For the class.
 activity 4 Atomic Structure OBJECTIVES Students are introduced to the structure of the atom and the nature of subatomic particles. The students are introduced to the properties of protons, neutrons, and
activity 4 Atomic Structure OBJECTIVES Students are introduced to the structure of the atom and the nature of subatomic particles. The students are introduced to the properties of protons, neutrons, and
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner
 APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner Grade Level/Subject Chemistry Stage 1: Desired Results Enduring Understanding Topic 1: Elements and the Periodic Table: The placement of elements on the periodic table
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner Grade Level/Subject Chemistry Stage 1: Desired Results Enduring Understanding Topic 1: Elements and the Periodic Table: The placement of elements on the periodic table
47374_04_p25-32.qxd 2/9/07 7:50 AM Page 25. 4 Atoms and Elements
 47374_04_p25-32.qxd 2/9/07 7:50 AM Page 25 4 Atoms and Elements 4.1 a. Cu b. Si c. K d. N e. Fe f. Ba g. Pb h. Sr 4.2 a. O b. Li c. S d. Al e. H f. Ne g. Sn h. Au 4.3 a. carbon b. chlorine c. iodine d.
47374_04_p25-32.qxd 2/9/07 7:50 AM Page 25 4 Atoms and Elements 4.1 a. Cu b. Si c. K d. N e. Fe f. Ba g. Pb h. Sr 4.2 a. O b. Li c. S d. Al e. H f. Ne g. Sn h. Au 4.3 a. carbon b. chlorine c. iodine d.
2. John Dalton did his research work in which of the following countries? a. France b. Greece c. Russia d. England
 CHAPTER 3 1. Which combination of individual and contribution is not correct? a. Antoine Lavoisier - clarified confusion over cause of burning b. John Dalton - proposed atomic theory c. Marie Curie - discovered
CHAPTER 3 1. Which combination of individual and contribution is not correct? a. Antoine Lavoisier - clarified confusion over cause of burning b. John Dalton - proposed atomic theory c. Marie Curie - discovered
Level 3 Achievement Scale
 Unit 1: Atoms Level 3 Achievement Scale Can state the key results of the experiments associated with Dalton, Rutherford, Thomson, Chadwick, and Bohr and what this lead each to conclude. Can explain that
Unit 1: Atoms Level 3 Achievement Scale Can state the key results of the experiments associated with Dalton, Rutherford, Thomson, Chadwick, and Bohr and what this lead each to conclude. Can explain that
Chemistry - Elements Electron Configurations The Periodic Table. Ron Robertson
 Chemistry - Elements Electron Configurations The Periodic Table Ron Robertson History of Chemistry Before 16 th Century Alchemy Attempts (scientific or otherwise) to change cheap metals into gold no real
Chemistry - Elements Electron Configurations The Periodic Table Ron Robertson History of Chemistry Before 16 th Century Alchemy Attempts (scientific or otherwise) to change cheap metals into gold no real
( + and - ) ( - and - ) ( + and + ) Atoms are mostly empty space. = the # of protons in the nucleus. = the # of protons in the nucleus
 Atoms are mostly empty space Atomic Structure Two regions of every atom: Nucleus - is made of protons and neutrons - is small and dense Electron cloud -is a region where you might find an electron -is
Atoms are mostly empty space Atomic Structure Two regions of every atom: Nucleus - is made of protons and neutrons - is small and dense Electron cloud -is a region where you might find an electron -is
2014 Spring CHEM101 Ch1-2 Review Worksheet Modified by Dr. Cheng-Yu Lai,
 Ch1 1) Which of the following underlined items is not an intensive property? A) A chemical reaction requires 3.00 g of oxygen. B) The density of helium at 25 C is 1.64 10-4 g/cm3. C) The melting point
Ch1 1) Which of the following underlined items is not an intensive property? A) A chemical reaction requires 3.00 g of oxygen. B) The density of helium at 25 C is 1.64 10-4 g/cm3. C) The melting point
5.1 Evolution of the Atomic Model
 5.1 Evolution of the Atomic Model Studying the atom has been a fascination of scientists for hundreds of years. Even Greek philosophers, over 2500 years ago, discussed the idea of there being a smallest
5.1 Evolution of the Atomic Model Studying the atom has been a fascination of scientists for hundreds of years. Even Greek philosophers, over 2500 years ago, discussed the idea of there being a smallest
Electron Configurations, Isoelectronic Elements, & Ionization Reactions. Chemistry 11
 Electron Configurations, Isoelectronic Elements, & Ionization Reactions Chemistry 11 Note: Of the 3 subatomic particles, the electron plays the greatest role in determining the physical and chemical properties
Electron Configurations, Isoelectronic Elements, & Ionization Reactions Chemistry 11 Note: Of the 3 subatomic particles, the electron plays the greatest role in determining the physical and chemical properties
Unit 3 Study Guide: Electron Configuration & The Periodic Table
 Name: Teacher s Name: Class: Block: Date: Unit 3 Study Guide: Electron Configuration & The Periodic Table 1. For each of the following elements, state whether the element is radioactive, synthetic or both.
Name: Teacher s Name: Class: Block: Date: Unit 3 Study Guide: Electron Configuration & The Periodic Table 1. For each of the following elements, state whether the element is radioactive, synthetic or both.
PROTONS AND ELECTRONS
 reflect Imagine that you have a bowl of oranges, bananas, pineapples, berries, pears, and watermelon. How do you identify each piece of fruit? Most likely, you are familiar with the characteristics of
reflect Imagine that you have a bowl of oranges, bananas, pineapples, berries, pears, and watermelon. How do you identify each piece of fruit? Most likely, you are familiar with the characteristics of
3 CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS: ELEMENTS, ATOMS AND IONS
 3 CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS: ELEMENTS, ATOMS AND IONS All matter is built up from chemical combinations of elements. As of 2003, there are 114 known elements, of which 88 are naturally occurring; the remaining
3 CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS: ELEMENTS, ATOMS AND IONS All matter is built up from chemical combinations of elements. As of 2003, there are 114 known elements, of which 88 are naturally occurring; the remaining
Atomic Structure Chapter 5 Assignment & Problem Set
 Atomic Structure Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Atomic Structure 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know Vocabulary (know the definition
Atomic Structure Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Atomic Structure 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know Vocabulary (know the definition
Chapter 3, Elements, Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
 1. Which two scientists in 1869 arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic masses to form a precursor of the modern periodic table of elements? Ans. Mendeleev and Meyer 2. Who stated that the
1. Which two scientists in 1869 arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic masses to form a precursor of the modern periodic table of elements? Ans. Mendeleev and Meyer 2. Who stated that the
Chapter 18: The Structure of the Atom
 Chapter 18: The Structure of the Atom 1. For most elements, an atom has A. no neutrons in the nucleus. B. more protons than electrons. C. less neutrons than electrons. D. just as many electrons as protons.
Chapter 18: The Structure of the Atom 1. For most elements, an atom has A. no neutrons in the nucleus. B. more protons than electrons. C. less neutrons than electrons. D. just as many electrons as protons.
For convenience, we may consider an atom in two parts: the nucleus and the electrons.
 Atomic structure A. Introduction: In 1808, an English scientist called John Dalton proposed an atomic theory based on experimental findings. (1) Elements are made of extremely small particles called atoms.
Atomic structure A. Introduction: In 1808, an English scientist called John Dalton proposed an atomic theory based on experimental findings. (1) Elements are made of extremely small particles called atoms.
UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
 UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 2.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into simpler substances. Each element is represented by an abbreviation called
UNIT (2) ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 2.1 Elements An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into simpler substances. Each element is represented by an abbreviation called
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
 Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1. Methane and ethane are both made up of carbon and hydrogen. In methane, there are 12.0 g of carbon for every 4.00 g of hydrogen, a ration of 3:1 by mass. In ethane,
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1. Methane and ethane are both made up of carbon and hydrogen. In methane, there are 12.0 g of carbon for every 4.00 g of hydrogen, a ration of 3:1 by mass. In ethane,
Test Bank - Chapter 4 Multiple Choice
 Test Bank - Chapter 4 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 4. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Test Bank - Chapter 4 The questions in the test bank cover the concepts from the lessons in Chapter 4. Select questions from any of the categories that match the content you covered with students. The
Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table 2.1 (a) neutron; (b) law of conservation of mass; (c) proton; (d) main-group element; (e) relative atomic mass; (f) mass number; (g) isotope; (h) cation; (i)
Chapter 2 Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table 2.1 (a) neutron; (b) law of conservation of mass; (c) proton; (d) main-group element; (e) relative atomic mass; (f) mass number; (g) isotope; (h) cation; (i)
SCH 3UI Unit 2 Outline Up to Quiz #1 Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table
 Lesson Topics Covered SCH 3UI Unit 2 Outline Up to Quiz #1 Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table 1 Note: History of Atomic Theory progression of understanding of composition of matter; ancient Greeks and
Lesson Topics Covered SCH 3UI Unit 2 Outline Up to Quiz #1 Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table 1 Note: History of Atomic Theory progression of understanding of composition of matter; ancient Greeks and
Atoms and Molecules. Preparation. Objectives. Standards. Materials. Grade Level: 5-8 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 60 90 Minutes Presenters: 2-4
 Atoms and Molecules Preparation Grade Level: 5-8 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 60 90 Minutes Presenters: 2-4 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Describe how atoms are the building blocks of matter
Atoms and Molecules Preparation Grade Level: 5-8 Group Size: 20-30 Time: 60 90 Minutes Presenters: 2-4 Objectives This lesson will enable students to: Describe how atoms are the building blocks of matter
The Atom and the Periodic Table. Electron Cloud Structure Energy Levels Rows on the Periodic Table Bohr Models Electron Dot Diagrams
 The Atom and the Periodic Table Electron Cloud Structure Energy Levels Rows on the Periodic Table Bohr Models Electron Dot Diagrams Review The vertical columns in the periodic table are called groups.
The Atom and the Periodic Table Electron Cloud Structure Energy Levels Rows on the Periodic Table Bohr Models Electron Dot Diagrams Review The vertical columns in the periodic table are called groups.
Chapter 5 TEST: The Periodic Table name
 Chapter 5 TEST: The Periodic Table name HPS # date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The order of elements in the periodic table is based
Chapter 5 TEST: The Periodic Table name HPS # date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The order of elements in the periodic table is based
Atoms and Elements [6th grade]
![Atoms and Elements [6th grade] Atoms and Elements [6th grade]](/thumbs/40/21183873.jpg) Trinity University Digital Commons @ Trinity Understanding by Design: Complete Collection Understanding by Design Summer 6-11-2015 Atoms and Elements [6th grade] Jennifer J. Wray Trinity University, [email protected]
Trinity University Digital Commons @ Trinity Understanding by Design: Complete Collection Understanding by Design Summer 6-11-2015 Atoms and Elements [6th grade] Jennifer J. Wray Trinity University, [email protected]
Structure and Properties of Atoms
 PS-2.1 Compare the subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) of an atom with regard to mass, location, and charge, and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity,
PS-2.1 Compare the subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) of an atom with regard to mass, location, and charge, and explain how these particles affect the properties of an atom (including identity,
Chemical Building Blocks: Chapter 3: Elements and Periodic Table
 Name: Class: Date: Chemical Building Blocks: Chapter 3: Elements and Periodic Table Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Name: Class: Date: Chemical Building Blocks: Chapter 3: Elements and Periodic Table Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
 CHAPTER 10 MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Wavelength is defined as the distance between consecutive peaks in a wave. It is generally symbolized by the Greek
CHAPTER 10 MODERN ATOMIC THEORY AND THE PERIODIC TABLE SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Wavelength is defined as the distance between consecutive peaks in a wave. It is generally symbolized by the Greek
Part I: Principal Energy Levels and Sublevels
 Part I: Principal Energy Levels and Sublevels As you already know, all atoms are made of subatomic particles, including protons, neutrons, and electrons. Positive protons and neutral neutrons are found
Part I: Principal Energy Levels and Sublevels As you already know, all atoms are made of subatomic particles, including protons, neutrons, and electrons. Positive protons and neutral neutrons are found
Semester Exam Practice Questions
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Semester Exam Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not a material? a. air
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Semester Exam Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is not a material? a. air
Name Date Class ELECTRONS IN ATOMS. Standard Curriculum Core content Extension topics
 13 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Conceptual Curriculum Concrete concepts More abstract concepts or math/problem-solving Standard Curriculum Core content Extension topics Honors Curriculum Core honors content Options
13 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Conceptual Curriculum Concrete concepts More abstract concepts or math/problem-solving Standard Curriculum Core content Extension topics Honors Curriculum Core honors content Options
PERIODIC TABLE. reflect
 reflect Suppose you wanted to organize your locker at school. How could you separate and arrange everything in an organized way? You could place the books, notebooks, and folders on a shelf that is separate
reflect Suppose you wanted to organize your locker at school. How could you separate and arrange everything in an organized way? You could place the books, notebooks, and folders on a shelf that is separate
Atomic Structure: Chapter Problems
 Atomic Structure: Chapter Problems Bohr Model Class Work 1. Describe the nuclear model of the atom. 2. Explain the problems with the nuclear model of the atom. 3. According to Niels Bohr, what does n stand
Atomic Structure: Chapter Problems Bohr Model Class Work 1. Describe the nuclear model of the atom. 2. Explain the problems with the nuclear model of the atom. 3. According to Niels Bohr, what does n stand
Chapter Test. Teacher Notes and Answers 5 The Periodic Law TEST A 1. b 2. d 3. b 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. b 8. b 9. b 10. a 11. c 12. a.
 Assessment Chapter Test A Teacher Notes and Answers 5 The Periodic Law TEST A 1. b 2. d 3. b 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. b 8. b 9. b 10. a 11. c 12. a 13. c 14. d 15. c 16. b 17. d 18. a 19. d 20. c 21. d 22. a
Assessment Chapter Test A Teacher Notes and Answers 5 The Periodic Law TEST A 1. b 2. d 3. b 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. b 8. b 9. b 10. a 11. c 12. a 13. c 14. d 15. c 16. b 17. d 18. a 19. d 20. c 21. d 22. a
Unit 2 Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding
 Unit 2 Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding 6.1 Organizing the Elements I. The Periodic Law A. The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers B. Elements
Unit 2 Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding 6.1 Organizing the Elements I. The Periodic Law A. The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers B. Elements
Matter. Atomic weight, Molecular weight and Mole
 Matter Atomic weight, Molecular weight and Mole Atomic Mass Unit Chemists of the nineteenth century realized that, in order to measure the mass of an atomic particle, it was useless to use the standard
Matter Atomic weight, Molecular weight and Mole Atomic Mass Unit Chemists of the nineteenth century realized that, in order to measure the mass of an atomic particle, it was useless to use the standard
CHAPTER 4: ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
 CHAPTER 4: ATOMS AND ELEMENTS Problems: 1-70 then after Chapter 9, complete 71-94, 103-104, 107-108, 113-114 4.1 Experiencing Atoms at Tiburon atom: smallest identifiable unit of an element All matter
CHAPTER 4: ATOMS AND ELEMENTS Problems: 1-70 then after Chapter 9, complete 71-94, 103-104, 107-108, 113-114 4.1 Experiencing Atoms at Tiburon atom: smallest identifiable unit of an element All matter
Tro's "Introductory Chemistry", Chapter 4
 1 Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Atoms and Elements Opening figure showing a shore scene with molecules of O 2, N 2, triethyl amine (CH 3 CH 2 ) 3 N, and rocks made of silicates containing
1 Introductory Chemistry, 3 rd Edition Nivaldo Tro Atoms and Elements Opening figure showing a shore scene with molecules of O 2, N 2, triethyl amine (CH 3 CH 2 ) 3 N, and rocks made of silicates containing
Molecular Models in Biology
 Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
Atoms, Ions and Molecules The Building Blocks of Matter
 Atoms, Ions and Molecules The Building Blocks of Matter Chapter 2 1 Chapter Outline 2.1 The Rutherford Model of Atomic Structure 2.2 Nuclides and Their Symbols 2.3 Navigating the Periodic Table 2.4 The
Atoms, Ions and Molecules The Building Blocks of Matter Chapter 2 1 Chapter Outline 2.1 The Rutherford Model of Atomic Structure 2.2 Nuclides and Their Symbols 2.3 Navigating the Periodic Table 2.4 The
The Periodic Table: Periodic trends
 Unit 1 The Periodic Table: Periodic trends There are over one hundred different chemical elements. Some of these elements are familiar to you such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. Each one has
Unit 1 The Periodic Table: Periodic trends There are over one hundred different chemical elements. Some of these elements are familiar to you such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. Each one has
2 ATOMIC SYSTEMATICS AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE
 2 ATOMIC SYSTEMATICS AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE In this chapter the principles and systematics of atomic and nuclear physics are summarised briefly, in order to introduce the existence and characteristics of
2 ATOMIC SYSTEMATICS AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE In this chapter the principles and systematics of atomic and nuclear physics are summarised briefly, in order to introduce the existence and characteristics of
Elements in the periodic table are indicated by SYMBOLS. To the left of the symbol we find the atomic mass (A) at the upper corner, and the atomic num
 . ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
. ATOMIC STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS LEARNING OBJECTIVES To review the basics concepts of atomic structure that have direct relevance to the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry. This material is essential
EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements
 EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements INTRODUCTION Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 different elements known today. The elements
EXPERIMENT 4 The Periodic Table - Atoms and Elements INTRODUCTION Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 different elements known today. The elements
CHEMSITRY NOTES Chapter 13. Electrons in Atoms
 CHEMSITRY NOTES Chapter 13 Electrons in Atoms Goals : To gain an understanding of : 1. Atoms and their structure. 2. The development of the atomic theory. 3. The quantum mechanical model of the atom. 4.
CHEMSITRY NOTES Chapter 13 Electrons in Atoms Goals : To gain an understanding of : 1. Atoms and their structure. 2. The development of the atomic theory. 3. The quantum mechanical model of the atom. 4.
THE PERIODIC TABLE O F T H E E L E M E N T S. The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 117, Page 1 of 27)
 THE PERIODIC TABLE O F T H E E L E M E N T S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 117, Page 1 of 27) THE PERIODIC TABLE In 1872, Dmitri Mendeleev created the periodic table arranged
THE PERIODIC TABLE O F T H E E L E M E N T S The Academic Support Center @ Daytona State College (Science 117, Page 1 of 27) THE PERIODIC TABLE In 1872, Dmitri Mendeleev created the periodic table arranged
ANSWER KEY : BUILD AN ATOM PART I: ATOM SCREEN Build an Atom simulation ( http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build an atom )
 ANSWER KEY : PART I: ATOM SCREEN Build an Atom simulation ( http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build an atom ) 1. Explore the Build an Atom simulation with your group. As you explore, talk about what
ANSWER KEY : PART I: ATOM SCREEN Build an Atom simulation ( http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/build an atom ) 1. Explore the Build an Atom simulation with your group. As you explore, talk about what
19.1 Bonding and Molecules
 Most of the matter around you and inside of you is in the form of compounds. For example, your body is about 80 percent water. You learned in the last unit that water, H 2 O, is made up of hydrogen and
Most of the matter around you and inside of you is in the form of compounds. For example, your body is about 80 percent water. You learned in the last unit that water, H 2 O, is made up of hydrogen and
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table (Chapter 2)
 Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table (Chapter 2) Atomic Structure 1. Historical View - Dalton's Atomic Theory Based on empirical observations, formulated as Laws of: Conservation of Mass Definite Proportions
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table (Chapter 2) Atomic Structure 1. Historical View - Dalton's Atomic Theory Based on empirical observations, formulated as Laws of: Conservation of Mass Definite Proportions
Copyrighted by Gabriel Tang B.Ed., B.Sc.
 Chapter 8: The Periodic Table 8.1: Development of the Periodic Table Johann Dobereiner: - first to discover a pattern of a group of elements like Cl, Br, and I (called triads). John Newland: - suggested
Chapter 8: The Periodic Table 8.1: Development of the Periodic Table Johann Dobereiner: - first to discover a pattern of a group of elements like Cl, Br, and I (called triads). John Newland: - suggested
Chapter 3. Elements, Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
 Chapter 3. Elements, Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table In the early 1800's many elements had been discovered and found to have different properties. In 1817 Döbreiner's
Chapter 3. Elements, Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table In the early 1800's many elements had been discovered and found to have different properties. In 1817 Döbreiner's
Atomic Structure Ron Robertson
 Atomic Structure Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\atomicstructuretrans.doc I. What is Light? Debate in 1600's: Since waves or particles can transfer energy, what is
Atomic Structure Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\atomicstructuretrans.doc I. What is Light? Debate in 1600's: Since waves or particles can transfer energy, what is
ATOMS AND BONDS. Bonds
 ATOMS AND BONDS Atoms of elements are the simplest units of organization in the natural world. Atoms consist of protons (positive charge), neutrons (neutral charge) and electrons (negative charge). The
ATOMS AND BONDS Atoms of elements are the simplest units of organization in the natural world. Atoms consist of protons (positive charge), neutrons (neutral charge) and electrons (negative charge). The
Answers to Review Questions for Atomic Theory Quiz #1
 Answers to Review Questions for Atomic Theory Quiz #1 Multiple Choice Questions: 1. c 7. a 13. c 19. a 25. b 31. b 37. a 43. d 2. d 8. c 14. c 20. c 26. d 32. c 38. d 44. b 3. b 9. a 15. b 21. c 27. b
Answers to Review Questions for Atomic Theory Quiz #1 Multiple Choice Questions: 1. c 7. a 13. c 19. a 25. b 31. b 37. a 43. d 2. d 8. c 14. c 20. c 26. d 32. c 38. d 44. b 3. b 9. a 15. b 21. c 27. b
Chemistry. The student will be able to identify and apply basic safety procedures and identify basic equipment.
 Chemistry UNIT I: Introduction to Chemistry The student will be able to describe what chemistry is and its scope. a. Define chemistry. b. Explain that chemistry overlaps many other areas of science. The
Chemistry UNIT I: Introduction to Chemistry The student will be able to describe what chemistry is and its scope. a. Define chemistry. b. Explain that chemistry overlaps many other areas of science. The
Atoms, Ions and Molecules The Building Blocks of Matter
 Atoms, Ions and Molecules The Building Blocks of Matter Chapter 2 1 Chapter Outline 2.1 The Rutherford Model of Atomic Structure 2.2 Nuclides and Their Symbols 2.3 Navigating the Periodic Table 2.4 The
Atoms, Ions and Molecules The Building Blocks of Matter Chapter 2 1 Chapter Outline 2.1 The Rutherford Model of Atomic Structure 2.2 Nuclides and Their Symbols 2.3 Navigating the Periodic Table 2.4 The
WAVES AND ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION
 WAVES AND ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION All waves are characterized by their wavelength, frequency and speed. Wavelength (lambda, ): the distance between any 2 successive crests or troughs. Frequency (nu,):
WAVES AND ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION All waves are characterized by their wavelength, frequency and speed. Wavelength (lambda, ): the distance between any 2 successive crests or troughs. Frequency (nu,):
(1) e.g. H hydrogen that has lost 1 electron c. anion - negatively charged atoms that gain electrons 16-2. (1) e.g. HCO 3 bicarbonate anion
 GS106 Chemical Bonds and Chemistry of Water c:wou:gs106:sp2002:chem.wpd I. Introduction A. Hierarchy of chemical substances 1. atoms of elements - smallest particles of matter with unique physical and
GS106 Chemical Bonds and Chemistry of Water c:wou:gs106:sp2002:chem.wpd I. Introduction A. Hierarchy of chemical substances 1. atoms of elements - smallest particles of matter with unique physical and
Multi-electron atoms
 Multi-electron atoms Today: Using hydrogen as a model. The Periodic Table HWK 13 available online. Please fill out the online participation survey. Worth 10points on HWK 13. Final Exam is Monday, Dec.
Multi-electron atoms Today: Using hydrogen as a model. The Periodic Table HWK 13 available online. Please fill out the online participation survey. Worth 10points on HWK 13. Final Exam is Monday, Dec.
The Structure of the Atom
 The Structure of the Atom Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Section 4. Early Ideas About Matter pages 02 05 Section 4. Assessment page 05. Contrast the methods
The Structure of the Atom Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Section 4. Early Ideas About Matter pages 02 05 Section 4. Assessment page 05. Contrast the methods
Trends of the Periodic Table Diary
 Trends of the Periodic Table Diary Trends are patterns of behaviors that atoms on the periodic table of elements follow. Trends hold true most of the time, but there are exceptions, or blips, where the
Trends of the Periodic Table Diary Trends are patterns of behaviors that atoms on the periodic table of elements follow. Trends hold true most of the time, but there are exceptions, or blips, where the
Periodic Table Questions
 Periodic Table Questions 1. The elements characterized as nonmetals are located in the periodic table at the (1) far left; (2) bottom; (3) center; (4) top right. 2. An element that is a liquid at STP is
Periodic Table Questions 1. The elements characterized as nonmetals are located in the periodic table at the (1) far left; (2) bottom; (3) center; (4) top right. 2. An element that is a liquid at STP is
Unit 1 Practice Test. Matching
 Unit 1 Practice Test Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. proton d. electron b. nucleus e. neutron c. atom 1. the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of
Unit 1 Practice Test Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. proton d. electron b. nucleus e. neutron c. atom 1. the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of
Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes
 Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes Standards Connections Connections to NSTA Standards for Science Teacher Preparation C.3.a.1 Fundamental structures of atoms and molecules. C.3.b.27 Applications
Instructors Guide: Atoms and Their Isotopes Standards Connections Connections to NSTA Standards for Science Teacher Preparation C.3.a.1 Fundamental structures of atoms and molecules. C.3.b.27 Applications
Ernest Rutherford Atomic Model 1911. Plum Pudding Model J.J. Thomson 1897
 1 The arrangement of electrons in an atom determine most of the chemical properties of that atom. Electrons are what actually do the reacting. Plum Pudding Model J.J. Thomson 1897 Ernest Rutherford Atomic
1 The arrangement of electrons in an atom determine most of the chemical properties of that atom. Electrons are what actually do the reacting. Plum Pudding Model J.J. Thomson 1897 Ernest Rutherford Atomic
CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework Answers
 1 CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework Answers 1. Which statement regarding the gold foil experiment is false? (a) It was performed by Rutherford and his research group early in the 20 th century. (b) Most of
1 CHEM 1411 Chapter 5 Homework Answers 1. Which statement regarding the gold foil experiment is false? (a) It was performed by Rutherford and his research group early in the 20 th century. (b) Most of
Department of Physics and Geology The Elements and the Periodic Table
 Department of Physics and Geology The Elements and the Periodic Table Physical Science 1422 Equipment Needed Qty Periodic Table 1 Part 1: Background In 1869 a Russian chemistry professor named Dmitri Mendeleev
Department of Physics and Geology The Elements and the Periodic Table Physical Science 1422 Equipment Needed Qty Periodic Table 1 Part 1: Background In 1869 a Russian chemistry professor named Dmitri Mendeleev
Atomic Theory: History of the Atom
 Atomic Theory: History of the Atom Atomic Theory: experimental observations that led scientists to postulate the existence of the atom (smallest bit of an element). 1. Law of Conservation of Mass -During
Atomic Theory: History of the Atom Atomic Theory: experimental observations that led scientists to postulate the existence of the atom (smallest bit of an element). 1. Law of Conservation of Mass -During
Chapter 7. Electron Structure of the Atom. Chapter 7 Topics
 Chapter 7 Electron Structure of the Atom Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Chapter 7 Topics 1. Electromagnetic radiation 2. The Bohr model of
Chapter 7 Electron Structure of the Atom Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Chapter 7 Topics 1. Electromagnetic radiation 2. The Bohr model of
PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes.
 1 PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes. Metal Nonmetal Scheme (based on physical properties) Metals - most elements are metals - elements on left
1 PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes. Metal Nonmetal Scheme (based on physical properties) Metals - most elements are metals - elements on left
Ch. 9 - Electron Organization. The Bohr Model [9.4] Orbitals [9.5, 9.6] Counting Electrons, configurations [9.7]
![Ch. 9 - Electron Organization. The Bohr Model [9.4] Orbitals [9.5, 9.6] Counting Electrons, configurations [9.7] Ch. 9 - Electron Organization. The Bohr Model [9.4] Orbitals [9.5, 9.6] Counting Electrons, configurations [9.7]](/thumbs/27/11797291.jpg) Ch. 9 - Electron Organization The Bohr Model [9.4] Orbitals [9.5, 9.6] Counting Electrons, configurations [9.7] Predicting ion charges from electron configurations. CHEM 100 F07 1 Organization of Electrons
Ch. 9 - Electron Organization The Bohr Model [9.4] Orbitals [9.5, 9.6] Counting Electrons, configurations [9.7] Predicting ion charges from electron configurations. CHEM 100 F07 1 Organization of Electrons
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Introduction to Chemistry Exam 2 Practice Problems 1 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1.Atoms consist principally of what three
Introduction to Chemistry Exam 2 Practice Problems 1 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1.Atoms consist principally of what three
IONISATION ENERGY CONTENTS
 IONISATION ENERGY IONISATION ENERGY CONTENTS What is Ionisation Energy? Definition of t Ionisation Energy What affects Ionisation Energy? General variation across periods Variation down groups Variation
IONISATION ENERGY IONISATION ENERGY CONTENTS What is Ionisation Energy? Definition of t Ionisation Energy What affects Ionisation Energy? General variation across periods Variation down groups Variation
neutrons are present?
 AP Chem Summer Assignment Worksheet #1 Atomic Structure 1. a) For the ion 39 K +, state how many electrons, how many protons, and how many 19 neutrons are present? b) Which of these particles has the smallest
AP Chem Summer Assignment Worksheet #1 Atomic Structure 1. a) For the ion 39 K +, state how many electrons, how many protons, and how many 19 neutrons are present? b) Which of these particles has the smallest
