TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT. What do we need our TMJ for? (Function?)
|
|
|
- Stephanie Morrison
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT What do we need our TMJ for? (Function?)
2 Clarification of Terminology TMJ = Temporomandibular Joint TMJD = Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction The vast majority of people have a TMJ Not everyone has TMJD Lippert, p197
3 Osteology Bones of the Skull and Face: Frontal Parietal Occipital Temporal Sphenoid Zygomatic Mandible Maxilla Nasal Lippert, p198
4 Osteology of the TMJ The TMJ is located to the ear The TMJ is an articulation between the articular fossa of the bone of the skull & the condyle of the mandible Lippert, p197
5 Osteology continued The skull has 2 parts: The bones of the large cranium cavity, which encase the brain The bones of the face The TMJ is an articulation between one facial bone (the mandible) and one cranial bone (the temporal bone) Lippert, p198
6 Osteology continued The Mandible: Shaped kind-of like a horseshoe Often referred to as the jaw Articulates with the temporal bone on each side of the face forming TWO IDENTICAL joints on either side of the face Lippert, p198
7
8 Osteology continued The Temporal Bone: Where is it? Articular fossa Mastoid process Articular Tubercle External auditory meatus Styloid process Zygomatic process Articular Tubercle Lippert, p199
9 Osteology continued The Hyoid Bone: Horseshoe shaped bone Lies just superior to the thyroid cartilage at the level of C3 It has NO BONY ARTICULATION!!! It is suspended from the styloid process of the temporal bone by the stylohyoid ligament Main Function: attachment site for tongue muscles and muscles that open/close the jaw Lippert, p201
10 Osteology continued Thyroid Cartilage: The largest of the 9 cartilages of the larynx Commonly called the Adam s apple More prominent in males Lies just inferior to the hyoid bone at the level of C3 C4 Lippert, p201
11 TMJ Structure Synovial Joint with a Hinge-like shape (not a pure hinge joint because it allows some gliding motion) Consists of: 2 bones A disk that divides the joint into 2 spaces A joint capsule 4 ligaments 4 main muscles that create 5 motions Lippert, p197
12 TMJ Movement Osteokinematics: Depression Elevation Lateral deviation Protrusion Retrusion Lippert, p198
13 TMJ Movement continued Arthrokinematics: Depression: involves two motions. First, the mandibular condyle rotates anteriorly on the disk. Second, the condyle and the disk both glide anteriorly and inferiorly over the articular tubercle of the temporal bone Elevation: the reverse action of depression Protrusion and Retrusion: no rotation occurs, the mandible moves either anteriorly or posteriorly in the transverse plane. The mandibular condyle and disk move as one unit against the articular fossa of the temporal bone Lateral deviation: occurs in the transverse plane. To move the mandible to the left, the left condyle rotates around a vertical axis and the right condyle glides anteriorly. The opposite occurs to deviate to the right. Lippert, p202
14 Disc Condyle During opening of the mouth, the condyles of the mandible move forward along the articular disc. This is a smooth movement unless the opening is excessive. Repeated excessive opening can cause trauma to the area and potential disc injury. Lippert, p202
15 The condyle of the mandible is seated in the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone. The lips are closed and the teeth are several millimeters apart. Lippert, p198
16 This would be maintained by low levels of activity of the temporalis muscles You should be able to open your mouth enough to fit 2-3 finger widths between the front upper and lower teeth. Lippert, p198 What motion is she performing with her mandible?
17 TMJ Supporting Structures Articular Disk Joint Capsule Four ligaments The Lateral Ligament (aka temporomandibular ligament) Sphenomandibular Ligament Stylomandibular Ligament Stylohyoid Ligament Lippert, p201
18 TMJ Myology The four PRIME MOVERS of the TMJ are (all of which are innervated by the Trigeminal Nerve, CN 5): Temporalis Masseter Medial Pterygoid Lateral Pterygoid Unless otherwise stated, the action of these muscles is considered to be BILATERAL and occurs at each joint (right and left) simultaneously. Lippert, p203
19 Please identify the following muscle: Temporalis Location Action Origin: Temporal Fossa Insertion: Coronoid Process and ramus of mandible Bilateral: elevation of the mandible (closing the mouth), retrusion of the mandible Unilateral: ipsilateral lateral deviation Innervation Trigmeninal nerve (Cranial n. V) Palpate it on yourself! Lippert, p204
20 Please identify the following muscle: Masseter Location Action Between the zygomatic arch of the temporal bone and the mandible Bilateral: elevation of the mandible (closing the mouth) Unilateral: ipsilateral lateral deviation Innervation Trigmeninal nerve (Cranial n. V) Palpate it on yourself! Lippert, p204
21 Please identify the following muscles: Medial Pterygoids (the p is silent) Location Action Internal angle of ramus of mandible Bilateral: elevation of the mandible (closing the mouth) & protrusion of the mandible Unilateral: contralateral lateral deviation Innervation Trigmeninal nerve (Cranial n. V) Lippert, p204
22 Please identify the following muscles: Lateral Pterygoids Location Action Inside the mouth near the condyle of the mandible Bilateral: depression of the mandible (opening the mouth) & Protrusion of the mandible Unilateral: contralateral lateral deviation Innervation Trigmeninal nerve (Cranial n. V) Lippert, p205
23 TMJ Myology continued The muscles that ASSIST with TMJ movement are: Suprahyoid Muscles Infrahyoid Muscles Mylohyoid Sternohyoid Geniohyoid Sternothyroid Stylohyoid Thyrohyoid Digastric Omohyoid Lippert, p
24 Common Pathology Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction (TMJD)
25 References Lippert, L.S. (2011). Clinical Kinesiology and Anatomy, 5 th ed. Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis.
TMJ Dysfunction & Pain
 TMJ Dysfunction & Pain The temporomandibular joints (TMJs) are two of the most functionally important and frequently used joints in the body. It is with these joints that important processes such as chewing,
TMJ Dysfunction & Pain The temporomandibular joints (TMJs) are two of the most functionally important and frequently used joints in the body. It is with these joints that important processes such as chewing,
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions
 The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions
 Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions I. Exercise Generalizations: A. Patients with post-traumatic TMJ problems or with recent-onset dysfunction that is largely posture-related will generally
Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions I. Exercise Generalizations: A. Patients with post-traumatic TMJ problems or with recent-onset dysfunction that is largely posture-related will generally
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S?
 Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Elbow & Forearm H O W V I T A L I S T H E E L B O W T O O U R D A I L Y L I V E S? Clarification of Terms The elbow includes: 3 bones (humerus, radius, and ulna) 2 joints (humeroulnar and humeroradial)
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
TMJ Exercises Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Specialist Surgery TMJ Exercises Information for patients What is the Temporomandibular Joint? The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is located in front of the ear where
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Specialist Surgery TMJ Exercises Information for patients What is the Temporomandibular Joint? The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is located in front of the ear where
Lateral pterygoid muscle Medial pterygoid muscle
 PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Trismus Normal Jaw Function The jaw is a pair of bones that form the framework of the mouth and teeth. The upper jaw is called the maxilla. The lower jaw is called the mandible.
PATIENT INFORMATION BOOKLET Trismus Normal Jaw Function The jaw is a pair of bones that form the framework of the mouth and teeth. The upper jaw is called the maxilla. The lower jaw is called the mandible.
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
NEUROSTRUCTURAL INTEGRATION TECHNIQUE
 NEUROSTRUCTURAL INTEGRATION TECHNIQUE IMPACT OF TMJ ON BODY FUNCTION Presented by Ron Phelan NST Practitioner and Instructor Remedial Massage Therapist Assessment and treatment guide for soft tissue therapists:
NEUROSTRUCTURAL INTEGRATION TECHNIQUE IMPACT OF TMJ ON BODY FUNCTION Presented by Ron Phelan NST Practitioner and Instructor Remedial Massage Therapist Assessment and treatment guide for soft tissue therapists:
its lifetime. The skeletal system is divided into: 1. Axial Division: bones of the body s axis (skulll, ribs, vertebrae)
 The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Level IA: Submental Group
 IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Fig. 1 The level system is used for describing the location of lymph nodes in the neck: Level I, submental and submandibular group; Level II, upper jugular
IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Fig. 1 The level system is used for describing the location of lymph nodes in the neck: Level I, submental and submandibular group; Level II, upper jugular
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10
 Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Clinical examination of the temporomandibular joint
 Clinical examination of the temporomandibular joint CHAPTER CONTENTS Pain............................ e202 Pain referred from the temporomandibular joint......................... e202 Pain referred to
Clinical examination of the temporomandibular joint CHAPTER CONTENTS Pain............................ e202 Pain referred from the temporomandibular joint......................... e202 Pain referred to
The Axial Skeleton. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Skeletal System The skeleton forms the framework for the body Provides support: Attachment
7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Skeletal System The skeleton forms the framework for the body Provides support: Attachment
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
24, 2006 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN:
 TITLE: Regional Anesthesia in Head and Neck Surgery SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: May 24, 2006 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Jacques Peltier, MD FACULTY ADVISOR: Francis
TITLE: Regional Anesthesia in Head and Neck Surgery SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: May 24, 2006 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Jacques Peltier, MD FACULTY ADVISOR: Francis
II. Axial Skeleton (Skull, Thoracic Cage, and Vertebral Column)
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Lab Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Recognize bones and bone markings for the axial and appendicular skeleton 2. Recognize bones disarticulated and/or articulated 3. Identify
6/26/2014 MUSCLE TENSION DYSPHONIA: TREATMENT WHAT IS MTD?
 MUSCLE TENSION DYSPHONIA: TREATMENT Lisa Valasek, MS CCC-SLP WHAT IS MTD? Hypercontraction of the extrinsic muscles of the larynx Incoordination of muscle activity controlling adduction, abduction, and
MUSCLE TENSION DYSPHONIA: TREATMENT Lisa Valasek, MS CCC-SLP WHAT IS MTD? Hypercontraction of the extrinsic muscles of the larynx Incoordination of muscle activity controlling adduction, abduction, and
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Deeper: geniohyoid, cricothyroid
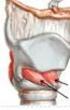 VitalStim Therapy ELECTRODE PLACEMENT WITH NECK MUSCLES Electrode Placements Placement 1 - All electrodes aligned vertically along midline - First electrode is placed well above hyoid bone - Second electrode
VitalStim Therapy ELECTRODE PLACEMENT WITH NECK MUSCLES Electrode Placements Placement 1 - All electrodes aligned vertically along midline - First electrode is placed well above hyoid bone - Second electrode
DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE
 2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
Chapter 5. The Shoulder Joint. The Shoulder Joint. Bones. Bones. Bones
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. Chapter 5 The Shoulder Joint Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Structural Kinesiology The Shoulder Joint 5-1 The Shoulder
The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle
 The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle The shoulder complex 4 articulations involving The sternum The clavicle The ribs The scapula and The humerus Bony Landmarks provide attachment points for muscles
The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle The shoulder complex 4 articulations involving The sternum The clavicle The ribs The scapula and The humerus Bony Landmarks provide attachment points for muscles
Classification of Malocclusion
 Classification of Malocclusion What s going on here? How would you describe this? Dr. Robert Gallois REFERENCE: Where Do We Begin? ESSENTIALS FOR ORTHODONTIC PRACTICE By Riolo and Avery Chapter 6 pages
Classification of Malocclusion What s going on here? How would you describe this? Dr. Robert Gallois REFERENCE: Where Do We Begin? ESSENTIALS FOR ORTHODONTIC PRACTICE By Riolo and Avery Chapter 6 pages
by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin
 by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin body mechanics palpation of the anterior neck ESOUCES For more information go to www.medlineplus.gov and search under anterior neck. The anterior
by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin body mechanics palpation of the anterior neck ESOUCES For more information go to www.medlineplus.gov and search under anterior neck. The anterior
Structure and Function of the Hip
 Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
Structure and Function of the Hip Objectives Identify the bones and bony landmarks of the hip and pelvis Identify and describe the supporting structures of the hip joint Describe the kinematics of the
The Skeleton. The word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up THE AXIAL SKELETON THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 PART 1 THE AXIAL SKELETON The Skull (pp. 200 216) The Skeleton The Vertebral Column (pp. 216 223) The Thoracic Cage (pp. 223 225) PART 2 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle (pp. 225
PART 1 THE AXIAL SKELETON The Skull (pp. 200 216) The Skeleton The Vertebral Column (pp. 216 223) The Thoracic Cage (pp. 223 225) PART 2 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle (pp. 225
Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle
 Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
Chapter 4 The Shoulder Girdle Key Manubrium Clavicle Coracoidprocess Acromionprocess bony landmarks Glenoid fossa Bones Lateral Inferior Medial border angle McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
10/15/2012. The Hand. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Hand (Bones) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related
 The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
The Hand http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=idxuwerttj A&feature=related Clarification of Terms The hand is made up of the thumb, metacarpals, and phalanges The digits are numbered (with the thumb being #1
Anatomy of Bones and Joints
 C HAPTER 7 Learning Outcomes AFTER YOU COMPLETE THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Anatomy of Bones and Joints 7.1 General Considerations of Bones 150 1. Define the general anatomical terms for various
C HAPTER 7 Learning Outcomes AFTER YOU COMPLETE THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Anatomy of Bones and Joints 7.1 General Considerations of Bones 150 1. Define the general anatomical terms for various
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Human, Male, White. Bone Clones Osteological Evaluation Report. Product Number: 1 intact mandible. General observations:
 Human, Male, White Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-107 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations: In general, the molding process has preserved
Human, Male, White Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: BC-107 Bone Clones replica 1 intact cranium 1 intact mandible General observations: In general, the molding process has preserved
Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
 Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Sean M. Healy, D.D.S. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Francis B. Quinn, M.D., FACS Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery The University of Texas
Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Sean M. Healy, D.D.S. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Francis B. Quinn, M.D., FACS Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery The University of Texas
X-Plain Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Reference Summary
 X-Plain Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Reference Summary Introduction Temporomandibular joint disorders, or TMJ disorders, are a group of medical problems related to the jaw joint. TMJ disorders can
X-Plain Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Reference Summary Introduction Temporomandibular joint disorders, or TMJ disorders, are a group of medical problems related to the jaw joint. TMJ disorders can
Structure & Function of the Knee. One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity.
 Structure & Function of the Knee One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity. Osteology of the Knee Distal femur (ADDuctor tubercle) Right Femur
Structure & Function of the Knee One of the most complex simple structures in the human body. The middle child of the lower extremity. Osteology of the Knee Distal femur (ADDuctor tubercle) Right Femur
Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy
 Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy Kris Cummings, M.D. Axial CT Unlabeled Labeled Deep s/lymph Node Chains s/lymph Nodes Temporalis Muscle Occipitalis Muscle s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph
Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy Kris Cummings, M.D. Axial CT Unlabeled Labeled Deep s/lymph Node Chains s/lymph Nodes Temporalis Muscle Occipitalis Muscle s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names
 Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
Muscle Movements, Types, and Names A. Gross Skeletal Muscle Activity 1. With a few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint it crossed
The Trigeminal and Facial Nerves The Facial and Blink
 The Trigeminal and Facial Nerves The Facial and Blink Introduction We commonly perform nerve conduction studies on three cranial nerves. Two of these, the trigeminal nerve (CN V) and the facial nerve (CN
The Trigeminal and Facial Nerves The Facial and Blink Introduction We commonly perform nerve conduction studies on three cranial nerves. Two of these, the trigeminal nerve (CN V) and the facial nerve (CN
Diagnosis of TMD and Associated Head Pain. Cortex Thalamus C 1 C 2 C 3. A Peer-Reviewed Publication Written by Steven R.
 Cortex Thalamus Earn 3 CE credits This course was written for dentists, dental hygienists, and assistants. C 1 C 2 C 3 Diagnosis of TMD and Associated Head Pain A Peer-Reviewed Publication Written by Steven
Cortex Thalamus Earn 3 CE credits This course was written for dentists, dental hygienists, and assistants. C 1 C 2 C 3 Diagnosis of TMD and Associated Head Pain A Peer-Reviewed Publication Written by Steven
Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Removable appliances II. Functional jaw orthopedics
 Removable appliances II. Functional jaw orthopedics Melinda Madléna DMD, PhD Associate professor Department of Pedodontics and Orthodontics Faculty of Dentistry Semmelweis University Budapest Classification
Removable appliances II. Functional jaw orthopedics Melinda Madléna DMD, PhD Associate professor Department of Pedodontics and Orthodontics Faculty of Dentistry Semmelweis University Budapest Classification
Headache: Is it a migraine? Think again
 Techniques in Regional Anesthesia and Pain Management (2005) 9, 68-72 : Is it a migraine? Think again Andrea Trescot, MD, FIPP From The Pain Center, Orange Park, Florida. KEYWORDS: Migraine; ; Cephalgia;
Techniques in Regional Anesthesia and Pain Management (2005) 9, 68-72 : Is it a migraine? Think again Andrea Trescot, MD, FIPP From The Pain Center, Orange Park, Florida. KEYWORDS: Migraine; ; Cephalgia;
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI
 Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE
 ZOO 4377L - VERTEBRATE MORPHOLOGY LAB LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE Name: Name: SSN: SSN: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZOO 4377L - VERTEBRATE MORPHOLOGY LAB LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE Name: Name: SSN: SSN: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
How to Tell If Your Headache Patients Have a Dental Problem
 How to Tell when Chronic Headaches have a Dental Cause: Functional occlusion in patients with chronic headaches: Interview with Jeri Coffey, DDS Jeri Coffey, DDS, Ross A. Hauser, MD, Nicole M. Baird, CHFP,
How to Tell when Chronic Headaches have a Dental Cause: Functional occlusion in patients with chronic headaches: Interview with Jeri Coffey, DDS Jeri Coffey, DDS, Ross A. Hauser, MD, Nicole M. Baird, CHFP,
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics
 Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
Knee Kinematics and Kinetics Definitions: Kinematics is the study of movement without reference to forces http://www.cogsci.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/webwn2.0?stage=1&word=kinematics Kinetics is the study
TMJ DISEASE TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISEASE
 TMJ DISEASE TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISEASE The temporomandibular joint is the point at which the mandible (lower jaw) hinges on the skull. Frequently, the pain experienced is ear pain, s o patients are
TMJ DISEASE TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT DISEASE The temporomandibular joint is the point at which the mandible (lower jaw) hinges on the skull. Frequently, the pain experienced is ear pain, s o patients are
The Interpositional Dermis Fat Graft in the Management of Temporomandibular Joint Ankylosis: A Case Report
 Case Report The Interpositional Dermis Fat Graft in the Management of Temporomandibular Joint Ankylosis: A Case Report Pavan Prabhakar Vairagar 1, Shehzad Shafi Sheikh 1, Chandrashekhar Shriram Pingal
Case Report The Interpositional Dermis Fat Graft in the Management of Temporomandibular Joint Ankylosis: A Case Report Pavan Prabhakar Vairagar 1, Shehzad Shafi Sheikh 1, Chandrashekhar Shriram Pingal
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS. The Bones & Joints
 THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. Facial Esthetics. Dental Esthetics
 ABSTRACT The FACE philosophy is characterized by clearly defined treatment goals. This increases diagnostic ability and improves the quality and stability of the end result. The objective is to establish
ABSTRACT The FACE philosophy is characterized by clearly defined treatment goals. This increases diagnostic ability and improves the quality and stability of the end result. The objective is to establish
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column
 Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Vertebral Abdominal 24 31 most column complex some intricate & complex articulating vertebrae do pairs
Chapter 12 The Trunk and Spinal Column Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Vertebral Abdominal 24 31 most column complex some intricate & complex articulating vertebrae do pairs
Temporomandibular Joint Pain and Dysfunction
 Temporomandibular Joint Pain and Dysfunction Kathleen Herb, DMD, MD, Sung Cho, DMD, and Marlind Alan Stiles, DMD Corresponding author Marlind Alan Stiles, DMD Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,
Temporomandibular Joint Pain and Dysfunction Kathleen Herb, DMD, MD, Sung Cho, DMD, and Marlind Alan Stiles, DMD Corresponding author Marlind Alan Stiles, DMD Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
HEADACHES AND THE THIRD OCCIPITAL NERVE
 HEADACHES AND THE THIRD OCCIPITAL NERVE Edward Babigumira M.D. FAAPMR. Interventional Pain Management, Lincoln. B. Pain Clinic, Ltd. Diplomate ABPMR. Board Certified Pain Medicine No disclosures Disclosure
HEADACHES AND THE THIRD OCCIPITAL NERVE Edward Babigumira M.D. FAAPMR. Interventional Pain Management, Lincoln. B. Pain Clinic, Ltd. Diplomate ABPMR. Board Certified Pain Medicine No disclosures Disclosure
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination
 Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine. Bones of the Spine (Vertebrae)
 Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Unilateral Nasal Polyps
 Unilateral Nasal Polyps This tutorial follows on from the rhinosinusitis tutorial but only concerns itself with the unilateral nasal polyp. The majority of unilateral nasal polyps form in the same way
Unilateral Nasal Polyps This tutorial follows on from the rhinosinusitis tutorial but only concerns itself with the unilateral nasal polyp. The majority of unilateral nasal polyps form in the same way
Regional Anesthesia Blocks in Head and Face
 Regional Anesthesia Blocks in Head and Face Resident Physician: Leon Martinez, MD Faculty Mentor: Paul Brindley, MD, FACS The University of Texas Medical Branch UTMB Health Department of Otolaryngology
Regional Anesthesia Blocks in Head and Face Resident Physician: Leon Martinez, MD Faculty Mentor: Paul Brindley, MD, FACS The University of Texas Medical Branch UTMB Health Department of Otolaryngology
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord.
 Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Headgear Appliances. Dentofacial Orthopedics and Orthodontics. A Common Misconception. What is Headgear? Ideal Orthodontic Treatment Sequence
 Ideal Orthodontic Treatment Sequence Headgear Appliances Natalie A. Capan, D.M.D. 580 Sylvan Avenue, Suite 1M Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 (201)569-9055 www.capanorthodontics.com CapanOrtho@nj.rr.com
Ideal Orthodontic Treatment Sequence Headgear Appliances Natalie A. Capan, D.M.D. 580 Sylvan Avenue, Suite 1M Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632 (201)569-9055 www.capanorthodontics.com CapanOrtho@nj.rr.com
A Look at Two Syndromes:
 TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT & CERVICOCRANIAL DYSFUNCTION IN THE EDS PATIENT John Mitakides D.D.S., FAACP A Look at Two Syndromes: How TMJ and CCD impact the EDS patient as they occur separately or together
TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT & CERVICOCRANIAL DYSFUNCTION IN THE EDS PATIENT John Mitakides D.D.S., FAACP A Look at Two Syndromes: How TMJ and CCD impact the EDS patient as they occur separately or together
Biometry of Mandible in Tiger (Panthera tigris)
 Annual Review & Research in Biology 1(1): 14-21, 2011 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Biometry of Mandible in Tiger (Panthera tigris) Y. Tiwari 1*, J. S.Taluja 1 and R. Vaish 1 1 Department
Annual Review & Research in Biology 1(1): 14-21, 2011 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org Biometry of Mandible in Tiger (Panthera tigris) Y. Tiwari 1*, J. S.Taluja 1 and R. Vaish 1 1 Department
The Knee Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) The Knee. The Knee Anatomy of the anteromedial aspect. The Knee
 Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
Orthopedics and Neurology James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, FACO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Internal derangement of the knee (IDK) This a common provisional diagnosis for any patient with
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Ear, Nose, Throat, Teeth and the Jaw
 Many people suffer from ear related problems, such as ear pain, a feeling of pressure or fullness of the ear, or ringing of the ear. If you suffer from any of these symptoms, it may surprise you to learn
Many people suffer from ear related problems, such as ear pain, a feeling of pressure or fullness of the ear, or ringing of the ear. If you suffer from any of these symptoms, it may surprise you to learn
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
Developmental Cysts. Non-odontogenic Cysts. Nasopalatine duct cyst. Palatal and gingival cysts of newborns
 Non-odontogenic Cysts Dr. Ioannis G. Koutlas Division of Oral Pathology Developmental Cysts a.k.a. fissural cysts Exact pathogenesis of some of them uncertain Generally, slow increase May be identified
Non-odontogenic Cysts Dr. Ioannis G. Koutlas Division of Oral Pathology Developmental Cysts a.k.a. fissural cysts Exact pathogenesis of some of them uncertain Generally, slow increase May be identified
The Muscular System Interactions of Skeletal Muscles in the Body (p. 321)
 The Muscular System Interactions of Skeletal Muscles in the Body (p. 321) Naming Skeletal Muscles (pp. 321 322) Muscle Mechanics: Importance of Fascicle Arrangement and Leverage (pp. 322 324) Arrangement
The Muscular System Interactions of Skeletal Muscles in the Body (p. 321) Naming Skeletal Muscles (pp. 321 322) Muscle Mechanics: Importance of Fascicle Arrangement and Leverage (pp. 322 324) Arrangement
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS. Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain. Assessment & Treatment of. Low Back Pain. Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D.
 THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
THE BENJAMIN INSTITUTE PRESENTS Excerpt from Listen To Your Pain Assessment & Treatment of Low Back Pain A B E N J A M I N I N S T I T U T E E B O O K Ben E. Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 THERAPIST/CLIENT MANUAL The
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
The Human Skeleton. Bone and Bone Growth
 The Human Skeleton Bone and Bone Growth Bone is living tissue, and, as such, can grow and remodel during a person s lifetime. The three types of bone cells are the osteoblasts, which are responsible for
The Human Skeleton Bone and Bone Growth Bone is living tissue, and, as such, can grow and remodel during a person s lifetime. The three types of bone cells are the osteoblasts, which are responsible for
Maxillary Sinus. (Antrum of Higmore)
 Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Dr. Brendan Stack Orthodontist, DDS, MS Washington, DC
 Dr. Brendan Stack Orthodontist, DDS, MS Washington, DC Dr. Stack is a University trained orthodontist (Georgetown University) who, since 1965, has limited his practice in Northern Virginia (Washington,
Dr. Brendan Stack Orthodontist, DDS, MS Washington, DC Dr. Stack is a University trained orthodontist (Georgetown University) who, since 1965, has limited his practice in Northern Virginia (Washington,
CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. 4. Name the three types of fibrous joints and give an example of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
How effective is chiropractic for patients with jaw pain?
 How effective is chiropractic for patients with jaw pain? How much improved are chronic jaw pain patients after a short course of chiropractic care? 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% Data taken from:
How effective is chiropractic for patients with jaw pain? How much improved are chronic jaw pain patients after a short course of chiropractic care? 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% Data taken from:
Eastman Dental Hospital. Temporomandibular disorder. Facial Pain Team
 Eastman Dental Hospital Temporomandibular disorder Facial Pain Team If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of an interpreter contact us on 020 3456
Eastman Dental Hospital Temporomandibular disorder Facial Pain Team If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of an interpreter contact us on 020 3456
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
REHAB 544 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY & LOWER EXTREMITY
 REHAB 544 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY & LOWER EXTREMITY Mark Guthrie, PhD Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington REHAB 544: Musculoskeletal Anatomy of the Upper & Lower Extremities,
REHAB 544 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY & LOWER EXTREMITY Mark Guthrie, PhD Rehabilitation Medicine University of Washington REHAB 544: Musculoskeletal Anatomy of the Upper & Lower Extremities,
Chapter 11 The Muscular System. Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin and Insertion
 Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
MOLLOY COLLEGE DIVISION OF NURSING NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAMS. Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam
 DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
