MATH ajajoo/math2433
|
|
|
- Morris Gary Webb
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MATH Aarti Jajoo Office : PGH 606 Lecture : MoWeFre 10-11am in SR 116 Office hours : MW 11:30-12:30pm and BY APPOINTMENT ajajoo/math2433 A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
2 Parametrized Surfaces; Surface Area A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
3 We can parametrized a surface S in space by a vector function r = r(u, v), where (u, v) ranges over some region Ω of the uv-plane. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
4 The fundamental vector product Let the surface S be parametrized by a differentiable vector function We denote r = r(u, v) = x(u, v)i + y(u, v)j + z(u, v)k. r u = x u i + y u j + z u k, r v = x v i + y v j + z v k. Definition The cross product N = r u r v is called the fundamental vector product of the surface. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
5 The fundamental vector product The vector N(u, v) = r u(u, v) r v (u, v) is perpendicular to the surface S at the tip of r(u, v). A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
6 Example Find the fundamental vector product for r(u, v) = u cos(v)i + u sin(v)j + vk. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
7 How to evaluate the area of S Let S be a surface parametrized by a continuously differentiable function r = r(u, v), (u, v) Ω. Definition If Ω is a basic region in the uv-plane and r is one-to-one on the interior of Ω, we call S a smooth surface. If N(u, v) is never zero on the interior of Ω, then we have area(s) = N(u, v) dudv. Ω A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
8 How to evaluate the area of S (particular case) If S is the graph of z = f (x, y) for (x, y) Ω, we can parametrize it like this: S : r(x, y) = xi + yj + f (x, y)k, (x, y) Ω. Then, we have area(s) = Ω [f x (x, y)] 2 + [f y (x, y)] dxdy. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
9 Example Find the area of the surface z = y 2, for 0 x y, 0 y 1. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
10 (continue) Find the area of the surface z = y 2, for 0 x y, 0 y 1. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
11 Surface Integrals A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
12 Surface integrals Let H = H(x, y, z) be a scalar field continuous over S : r = r(u, v), with (u, v) Ω. The surface integral of H over S is: S H(x, y, z) dσ = Ω H(x(u, v), y(u, v), z(u, v)) N(u, v) dudv Notice that if H(x, y, z) = 1, we have dσ = S Ω N(u, v) dudv = area(s). A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
13 Example Evaluate S 2y dσ where S is the surface S : z = 1 2 y 2, 0 x 2, 0 y 1. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
14 (continue) Evaluate S 2y dσ where S is the surface S : z = 1 2 y 2, 0 x 2, 0 y 1. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
15 Example Evaluate S 2xy dσ where S is the surface x + 2y + 2z = 4 in the first octant. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
16 (continue) Evaluate S 2xy dσ where S is the surface x + 2y + 2z = 4 in the first octant. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
17
18 The Vector Differential Operator A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
19 Formal definition The vector differential operator is formally defined by = x i + y j + z k. So far, we have seen applied to a differentiable scalar field, e.g. f, but it can also be applied to vector fields. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
20 Divergence and curl Consider vector field v = v 1 (x, y, z)i + v 2 (x, y, z)j + v 3 (x, y, z)k. Divergence v = v 1 x + v 2 y + v 3 z. Curl v = Det i j k x y z v 1 v 2 v 3 A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
21 The curl of a gradient is zero. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
22 Example Given v(x, y) = calculate v and v. ( ) ( ) 1 1 x 2 + y 2 i + x 2 + y 2 j, A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
23 (continue) Given v(x, y) = calculate v and v. ( ) ( ) 1 1 x 2 + y 2 i + x 2 + y 2 j, A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
24 Example Given calculate v and v. v(x, y, z) = (3yz) i + (4xz) j + (3xy)k, A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
25 (continue) Given calculate v and v. v(x, y, z) = (3yz) i + (4xz) j + (3xy)k, A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
26 The Divergence Theorem Section 17.9 A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
27 Divergence theorem Set v = Qi Pj. Green s theorem can be written as: ( v)dxdy = (v )ds, where is the outer unit normal for Ω. In 3D, we have: Divergence theorem Ω Let T be a solid bounded by a closed oriented surface S which is piecewise smooth. If the vector field v = v(x, y, z) is continuously differentiable throughout T, then ( v)dxdydz = (v )dσ. where is the outer unit normal. T C S A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
28 Flux Definition The quantity is called flux of v out of S. S (v )dσ The divergence theorem tells you that you can evaluate the flux of v out of S through a triple integral on T, which is the solid bounded by S flux of v out of S = ( v)dxdydz. T A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
29 Example Use the divergence theorem to find the total flux out of the solid x 2 + y 2 4, 0 z 1, given v(x, y, z) = xi + 3y 2 j + 2z 2 k. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
30 (continue) Use the divergence theorem to find the total flux out of the solid x 2 + y 2 4, 0 z 1, given v(x, y, z) = xi + 3y 2 j + 2z 2 k. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
31 Example Use the divergence theorem to find the total flux out of the solid 0 x 1, 0 y 1 x, 0 z 1 x y, given v(x, y, z) = 2x 2 i + 4xyj 4xzk. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
32 (continue) Use the divergence theorem to find the total flux out of the solid 0 x 1, 0 y 1 x, 0 z 1 x y, given v(x, y, z) = 2x 2 i + 4xyj 4xzk. A. Jajoo, UH MATH / 31
AB2.5: Surfaces and Surface Integrals. Divergence Theorem of Gauss
 AB2.5: urfaces and urface Integrals. Divergence heorem of Gauss epresentations of surfaces or epresentation of a surface as projections on the xy- and xz-planes, etc. are For example, z = f(x, y), x =
AB2.5: urfaces and urface Integrals. Divergence heorem of Gauss epresentations of surfaces or epresentation of a surface as projections on the xy- and xz-planes, etc. are For example, z = f(x, y), x =
4.2. LINE INTEGRALS 1. 2 2 ; z = t. ; y = sin
 4.2. LINE INTEGRALS 1 4.2 Line Integrals MATH 294 FALL 1982 FINAL # 7 294FA82FQ7.tex 4.2.1 Consider the curve given parametrically by x = cos t t ; y = sin 2 2 ; z = t a) Determine the work done by the
4.2. LINE INTEGRALS 1 4.2 Line Integrals MATH 294 FALL 1982 FINAL # 7 294FA82FQ7.tex 4.2.1 Consider the curve given parametrically by x = cos t t ; y = sin 2 2 ; z = t a) Determine the work done by the
Solutions - Homework sections 17.7-17.9
 olutions - Homework sections 7.7-7.9 7.7 6. valuate xy d, where is the triangle with vertices (,, ), (,, ), and (,, ). The three points - and therefore the triangle between them - are on the plane x +
olutions - Homework sections 7.7-7.9 7.7 6. valuate xy d, where is the triangle with vertices (,, ), (,, ), and (,, ). The three points - and therefore the triangle between them - are on the plane x +
vector calculus 2 Learning outcomes
 29 ontents vector calculus 2 1. Line integrals involving vectors 2. Surface and volume integrals 3. Integral vector theorems Learning outcomes In this Workbook you will learn how to integrate functions
29 ontents vector calculus 2 1. Line integrals involving vectors 2. Surface and volume integrals 3. Integral vector theorems Learning outcomes In this Workbook you will learn how to integrate functions
Chapter 17. Review. 1. Vector Fields (Section 17.1)
 hapter 17 Review 1. Vector Fields (Section 17.1) There isn t much I can say in this section. Most of the material has to do with sketching vector fields. Please provide some explanation to support your
hapter 17 Review 1. Vector Fields (Section 17.1) There isn t much I can say in this section. Most of the material has to do with sketching vector fields. Please provide some explanation to support your
FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS Math 21a, Spring 03
 INAL EXAM SOLUIONS Math 21a, Spring 3 Name: Start by printing your name in the above box and check your section in the box to the left. MW1 Ken Chung MW1 Weiyang Qiu MW11 Oliver Knill h1 Mark Lucianovic
INAL EXAM SOLUIONS Math 21a, Spring 3 Name: Start by printing your name in the above box and check your section in the box to the left. MW1 Ken Chung MW1 Weiyang Qiu MW11 Oliver Knill h1 Mark Lucianovic
Fundamental Theorems of Vector Calculus
 Fundamental Theorems of Vector Calculus We have studied the techniques for evaluating integrals over curves and surfaces. In the case of integrating over an interval on the real line, we were able to use
Fundamental Theorems of Vector Calculus We have studied the techniques for evaluating integrals over curves and surfaces. In the case of integrating over an interval on the real line, we were able to use
F = 0. x ψ = y + z (1) y ψ = x + z (2) z ψ = x + y (3)
 MATH 255 FINAL NAME: Instructions: You must include all the steps in your derivations/answers. Reduce answers as much as possible, but use exact arithmetic. Write neatly, please, and show all steps. Scientists
MATH 255 FINAL NAME: Instructions: You must include all the steps in your derivations/answers. Reduce answers as much as possible, but use exact arithmetic. Write neatly, please, and show all steps. Scientists
Section 12.6: Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 Section 26: Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Recall that if f is a differentiable function of x and y and z = f(x, y), then the partial derivatives f x (x, y) and f y (x, y) give the rate
Section 26: Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector Recall that if f is a differentiable function of x and y and z = f(x, y), then the partial derivatives f x (x, y) and f y (x, y) give the rate
If Σ is an oriented surface bounded by a curve C, then the orientation of Σ induces an orientation for C, based on the Right-Hand-Rule.
 Oriented Surfaces and Flux Integrals Let be a surface that has a tangent plane at each of its nonboundary points. At such a point on the surface two unit normal vectors exist, and they have opposite directions.
Oriented Surfaces and Flux Integrals Let be a surface that has a tangent plane at each of its nonboundary points. At such a point on the surface two unit normal vectors exist, and they have opposite directions.
This makes sense. t 2 1 + 1/t 2 dt = 1. t t 2 + 1dt = 2 du = 1 3 u3/2 u=5
 1. (Line integrals Using parametrization. Two types and the flux integral) Formulas: ds = x (t) dt, d x = x (t)dt and d x = T ds since T = x (t)/ x (t). Another one is Nds = T ds ẑ = (dx, dy) ẑ = (dy,
1. (Line integrals Using parametrization. Two types and the flux integral) Formulas: ds = x (t) dt, d x = x (t)dt and d x = T ds since T = x (t)/ x (t). Another one is Nds = T ds ẑ = (dx, dy) ẑ = (dy,
A QUICK GUIDE TO THE FORMULAS OF MULTIVARIABLE CALCULUS
 A QUIK GUIDE TO THE FOMULAS OF MULTIVAIABLE ALULUS ontents 1. Analytic Geometry 2 1.1. Definition of a Vector 2 1.2. Scalar Product 2 1.3. Properties of the Scalar Product 2 1.4. Length and Unit Vectors
A QUIK GUIDE TO THE FOMULAS OF MULTIVAIABLE ALULUS ontents 1. Analytic Geometry 2 1.1. Definition of a Vector 2 1.2. Scalar Product 2 1.3. Properties of the Scalar Product 2 1.4. Length and Unit Vectors
The Vector or Cross Product
 The Vector or ross Product 1 ppendix The Vector or ross Product We saw in ppendix that the dot product of two vectors is a scalar quantity that is a maximum when the two vectors are parallel and is zero
The Vector or ross Product 1 ppendix The Vector or ross Product We saw in ppendix that the dot product of two vectors is a scalar quantity that is a maximum when the two vectors are parallel and is zero
Solutions for Review Problems
 olutions for Review Problems 1. Let be the triangle with vertices A (,, ), B (4,, 1) and C (,, 1). (a) Find the cosine of the angle BAC at vertex A. (b) Find the area of the triangle ABC. (c) Find a vector
olutions for Review Problems 1. Let be the triangle with vertices A (,, ), B (4,, 1) and C (,, 1). (a) Find the cosine of the angle BAC at vertex A. (b) Find the area of the triangle ABC. (c) Find a vector
Math 21a Curl and Divergence Spring, 2009. 1 Define the operator (pronounced del ) by. = i
 Math 21a url and ivergence Spring, 29 1 efine the operator (pronounced del by = i j y k z Notice that the gradient f (or also grad f is just applied to f (a We define the divergence of a vector field F,
Math 21a url and ivergence Spring, 29 1 efine the operator (pronounced del by = i j y k z Notice that the gradient f (or also grad f is just applied to f (a We define the divergence of a vector field F,
Scalar Valued Functions of Several Variables; the Gradient Vector
 Scalar Valued Functions of Several Variables; the Gradient Vector Scalar Valued Functions vector valued function of n variables: Let us consider a scalar (i.e., numerical, rather than y = φ(x = φ(x 1,
Scalar Valued Functions of Several Variables; the Gradient Vector Scalar Valued Functions vector valued function of n variables: Let us consider a scalar (i.e., numerical, rather than y = φ(x = φ(x 1,
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 8.5. VECTORS 5 (Vector equations of straight lines) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 8.5 VECTORS 5 (Vector equations of straight lines) by A.J.Hobson 8.5.1 Introduction 8.5. The straight line passing through a given point and parallel to a given vector 8.5.3
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 8.5 VECTORS 5 (Vector equations of straight lines) by A.J.Hobson 8.5.1 Introduction 8.5. The straight line passing through a given point and parallel to a given vector 8.5.3
Math 241, Exam 1 Information.
 Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 9/24/12, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.1-14.3. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241fa12/241.html)
Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 9/24/12, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.1-14.3. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241fa12/241.html)
Class Meeting # 1: Introduction to PDEs
 MATH 18.152 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 1 18.152 Introduction to PDEs, Fall 2011 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeting # 1: Introduction to PDEs 1. What is a PDE? We will be studying functions u = u(x
MATH 18.152 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 1 18.152 Introduction to PDEs, Fall 2011 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeting # 1: Introduction to PDEs 1. What is a PDE? We will be studying functions u = u(x
Solutions to Practice Problems for Test 4
 olutions to Practice Problems for Test 4 1. Let be the line segmentfrom the point (, 1, 1) to the point (,, 3). Evaluate the line integral y ds. Answer: First, we parametrize the line segment from (, 1,
olutions to Practice Problems for Test 4 1. Let be the line segmentfrom the point (, 1, 1) to the point (,, 3). Evaluate the line integral y ds. Answer: First, we parametrize the line segment from (, 1,
PHY 301: Mathematical Methods I Curvilinear Coordinate System (10-12 Lectures)
 PHY 301: Mathematical Methods I Curvilinear Coordinate System (10-12 Lectures) Dr. Alok Kumar Department of Physical Sciences IISER, Bhopal Abstract The Curvilinear co-ordinates are the common name of
PHY 301: Mathematical Methods I Curvilinear Coordinate System (10-12 Lectures) Dr. Alok Kumar Department of Physical Sciences IISER, Bhopal Abstract The Curvilinear co-ordinates are the common name of
MULTIPLE INTEGRALS. h 2 (y) are continuous functions on [c, d] and let f(x, y) be a function defined on R. Then
![MULTIPLE INTEGRALS. h 2 (y) are continuous functions on [c, d] and let f(x, y) be a function defined on R. Then MULTIPLE INTEGRALS. h 2 (y) are continuous functions on [c, d] and let f(x, y) be a function defined on R. Then](/thumbs/40/21201569.jpg) MULTIPLE INTEGALS 1. ouble Integrals Let be a simple region defined by a x b and g 1 (x) y g 2 (x), where g 1 (x) and g 2 (x) are continuous functions on [a, b] and let f(x, y) be a function defined on.
MULTIPLE INTEGALS 1. ouble Integrals Let be a simple region defined by a x b and g 1 (x) y g 2 (x), where g 1 (x) and g 2 (x) are continuous functions on [a, b] and let f(x, y) be a function defined on.
Review of Vector Analysis in Cartesian Coordinates
 R. evicky, CBE 6333 Review of Vector Analysis in Cartesian Coordinates Scalar: A quantity that has magnitude, but no direction. Examples are mass, temperature, pressure, time, distance, and real numbers.
R. evicky, CBE 6333 Review of Vector Analysis in Cartesian Coordinates Scalar: A quantity that has magnitude, but no direction. Examples are mass, temperature, pressure, time, distance, and real numbers.
M PROOF OF THE DIVERGENCE THEOREM AND STOKES THEOREM
 68 Theor Supplement Section M M POOF OF THE DIEGENE THEOEM ND STOKES THEOEM In this section we give proofs of the Divergence Theorem Stokes Theorem using the definitions in artesian coordinates. Proof
68 Theor Supplement Section M M POOF OF THE DIEGENE THEOEM ND STOKES THEOEM In this section we give proofs of the Divergence Theorem Stokes Theorem using the definitions in artesian coordinates. Proof
Surface Normals and Tangent Planes
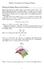 Surface Normals and Tangent Planes Normal and Tangent Planes to Level Surfaces Because the equation of a plane requires a point and a normal vector to the plane, nding the equation of a tangent plane to
Surface Normals and Tangent Planes Normal and Tangent Planes to Level Surfaces Because the equation of a plane requires a point and a normal vector to the plane, nding the equation of a tangent plane to
L 2 : x = s + 1, y = s, z = 4s + 4. 3. Suppose that C has coordinates (x, y, z). Then from the vector equality AC = BD, one has
 The line L through the points A and B is parallel to the vector AB = 3, 2, and has parametric equations x = 3t + 2, y = 2t +, z = t Therefore, the intersection point of the line with the plane should satisfy:
The line L through the points A and B is parallel to the vector AB = 3, 2, and has parametric equations x = 3t + 2, y = 2t +, z = t Therefore, the intersection point of the line with the plane should satisfy:
Fluid Dynamics and the Navier-Stokes Equation
 Fluid Dynamics and the Navier-Stokes Equation CMSC498A: Spring 12 Semester By: Steven Dobek 5/17/2012 Introduction I began this project through a desire to simulate smoke and fire through the use of programming
Fluid Dynamics and the Navier-Stokes Equation CMSC498A: Spring 12 Semester By: Steven Dobek 5/17/2012 Introduction I began this project through a desire to simulate smoke and fire through the use of programming
THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
 Chapter 8 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY 8.1 Introduction In this chapter we present a vector algebra approach to three dimensional geometry. The aim is to present standard properties of lines and planes,
Chapter 8 THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY 8.1 Introduction In this chapter we present a vector algebra approach to three dimensional geometry. The aim is to present standard properties of lines and planes,
Differentiation of vectors
 Chapter 4 Differentiation of vectors 4.1 Vector-valued functions In the previous chapters we have considered real functions of several (usually two) variables f : D R, where D is a subset of R n, where
Chapter 4 Differentiation of vectors 4.1 Vector-valued functions In the previous chapters we have considered real functions of several (usually two) variables f : D R, where D is a subset of R n, where
Gradient, Divergence and Curl in Curvilinear Coordinates
 Gradient, Divergence and Curl in Curvilinear Coordinates Although cartesian orthogonal coordinates are very intuitive and easy to use, it is often found more convenient to work with other coordinate systems.
Gradient, Divergence and Curl in Curvilinear Coordinates Although cartesian orthogonal coordinates are very intuitive and easy to use, it is often found more convenient to work with other coordinate systems.
= y y 0. = z z 0. (a) Find a parametric vector equation for L. (b) Find parametric (scalar) equations for L.
 Math 21a Lines and lanes Spring, 2009 Lines in Space How can we express the equation(s) of a line through a point (x 0 ; y 0 ; z 0 ) and parallel to the vector u ha; b; ci? Many ways: as parametric (scalar)
Math 21a Lines and lanes Spring, 2009 Lines in Space How can we express the equation(s) of a line through a point (x 0 ; y 0 ; z 0 ) and parallel to the vector u ha; b; ci? Many ways: as parametric (scalar)
Elasticity Theory Basics
 G22.3033-002: Topics in Computer Graphics: Lecture #7 Geometric Modeling New York University Elasticity Theory Basics Lecture #7: 20 October 2003 Lecturer: Denis Zorin Scribe: Adrian Secord, Yotam Gingold
G22.3033-002: Topics in Computer Graphics: Lecture #7 Geometric Modeling New York University Elasticity Theory Basics Lecture #7: 20 October 2003 Lecturer: Denis Zorin Scribe: Adrian Secord, Yotam Gingold
Vector Calculus Solutions to Sample Final Examination #1
 Vector alculus s to Sample Final Examination #1 1. Let f(x, y) e xy sin(x + y). (a) In what direction, starting at (,π/), is f changing the fastest? (b) In what directions starting at (,π/) is f changing
Vector alculus s to Sample Final Examination #1 1. Let f(x, y) e xy sin(x + y). (a) In what direction, starting at (,π/), is f changing the fastest? (b) In what directions starting at (,π/) is f changing
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 9: Subspaces of vector spaces (continued). Span. Spanning set.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 9: Subspaces of vector spaces (continued). Span. Spanning set. Vector space A vector space is a set V equipped with two operations, addition V V (x,y) x + y V and scalar
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 9: Subspaces of vector spaces (continued). Span. Spanning set. Vector space A vector space is a set V equipped with two operations, addition V V (x,y) x + y V and scalar
RARITAN VALLEY COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC COURSE OUTLINE MATH 251 CALCULUS III
 RARITAN VALLEY COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC COURSE OUTLINE MATH 251 CALCULUS III I. Basic Course Information A. Course Number and Title: MATH 251 Calculus III B. New or Modified Course: Modified Course C.
RARITAN VALLEY COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC COURSE OUTLINE MATH 251 CALCULUS III I. Basic Course Information A. Course Number and Title: MATH 251 Calculus III B. New or Modified Course: Modified Course C.
MATH2420 Multiple Integrals and Vector Calculus
 MATH2420 Multiple Integrals and Vector Calculus Prof. F.W. Nijhoff Semester 1, 2007-8. Course Notes and General Information Vector calculus is the normal language used in applied mathematics for solving
MATH2420 Multiple Integrals and Vector Calculus Prof. F.W. Nijhoff Semester 1, 2007-8. Course Notes and General Information Vector calculus is the normal language used in applied mathematics for solving
Unified Lecture # 4 Vectors
 Fall 2005 Unified Lecture # 4 Vectors These notes were written by J. Peraire as a review of vectors for Dynamics 16.07. They have been adapted for Unified Engineering by R. Radovitzky. References [1] Feynmann,
Fall 2005 Unified Lecture # 4 Vectors These notes were written by J. Peraire as a review of vectors for Dynamics 16.07. They have been adapted for Unified Engineering by R. Radovitzky. References [1] Feynmann,
CONSERVATION LAWS. See Figures 2 and 1.
 CONSERVATION LAWS 1. Multivariable calculus 1.1. Divergence theorem (of Gauss). This states that the volume integral in of the divergence of the vector-valued function F is equal to the total flux of F
CONSERVATION LAWS 1. Multivariable calculus 1.1. Divergence theorem (of Gauss). This states that the volume integral in of the divergence of the vector-valued function F is equal to the total flux of F
MATH 275: Calculus III. Lecture Notes by Angel V. Kumchev
 MATH 275: Calculus III Lecture Notes by Angel V. Kumchev Contents Preface.............................................. iii Lecture 1. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems..................... 1 Lecture
MATH 275: Calculus III Lecture Notes by Angel V. Kumchev Contents Preface.............................................. iii Lecture 1. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems..................... 1 Lecture
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4, MATH 253
 SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4, MATH 253 1. Prove that the following differential equations are satisfied by the given functions: (a) 2 u + 2 u 2 y + 2 u 2 z =0,whereu 2 =(x2 + y 2 + z 2 ) 1/2. (b)
SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #4, MATH 253 1. Prove that the following differential equations are satisfied by the given functions: (a) 2 u + 2 u 2 y + 2 u 2 z =0,whereu 2 =(x2 + y 2 + z 2 ) 1/2. (b)
MTH 277 01 (seated)/277 V01 (online): Vector Calculus, Fall 2015
 Blue Ridge Community College MTH 277 01 (seated)/277 V01 (online): Vector Calculus, Fall 2015 Lynne Ryan Course Meets: MW 1:30 3:10 in ( 01 section) My : T 123 Hours: See block schedule at end Email: [email protected]
Blue Ridge Community College MTH 277 01 (seated)/277 V01 (online): Vector Calculus, Fall 2015 Lynne Ryan Course Meets: MW 1:30 3:10 in ( 01 section) My : T 123 Hours: See block schedule at end Email: [email protected]
DERIVATIVES AS MATRICES; CHAIN RULE
 DERIVATIVES AS MATRICES; CHAIN RULE 1. Derivatives of Real-valued Functions Let s first consider functions f : R 2 R. Recall that if the partial derivatives of f exist at the point (x 0, y 0 ), then we
DERIVATIVES AS MATRICES; CHAIN RULE 1. Derivatives of Real-valued Functions Let s first consider functions f : R 2 R. Recall that if the partial derivatives of f exist at the point (x 0, y 0 ), then we
Chapter 28 Fluid Dynamics
 Chapter 28 Fluid Dynamics 28.1 Ideal Fluids... 1 28.2 Velocity Vector Field... 1 28.3 Mass Continuity Equation... 3 28.4 Bernoulli s Principle... 4 28.5 Worked Examples: Bernoulli s Equation... 7 Example
Chapter 28 Fluid Dynamics 28.1 Ideal Fluids... 1 28.2 Velocity Vector Field... 1 28.3 Mass Continuity Equation... 3 28.4 Bernoulli s Principle... 4 28.5 Worked Examples: Bernoulli s Equation... 7 Example
Practice Final Math 122 Spring 12 Instructor: Jeff Lang
 Practice Final Math Spring Instructor: Jeff Lang. Find the limit of the sequence a n = ln (n 5) ln (3n + 8). A) ln ( ) 3 B) ln C) ln ( ) 3 D) does not exist. Find the limit of the sequence a n = (ln n)6
Practice Final Math Spring Instructor: Jeff Lang. Find the limit of the sequence a n = ln (n 5) ln (3n + 8). A) ln ( ) 3 B) ln C) ln ( ) 3 D) does not exist. Find the limit of the sequence a n = (ln n)6
HEARTLAND COMMUNITY COLLEGE MATH 163 Calculus III Syllabus Spring 2013
 HEARTLAND COMMUNITY COLLEGE MATH 163 Calculus III Syllabus Spring 2013 Class: MTWR: 2:00 3:50 pm Office Hours:10:30 noon Wednesday and Thursday; 5 6 pm Tuesday and Thursday Instructor s Name: Dr. Kim McHale
HEARTLAND COMMUNITY COLLEGE MATH 163 Calculus III Syllabus Spring 2013 Class: MTWR: 2:00 3:50 pm Office Hours:10:30 noon Wednesday and Thursday; 5 6 pm Tuesday and Thursday Instructor s Name: Dr. Kim McHale
Reference: Introduction to Partial Differential Equations by G. Folland, 1995, Chap. 3.
 5 Potential Theory Reference: Introduction to Partial Differential Equations by G. Folland, 995, Chap. 3. 5. Problems of Interest. In what follows, we consider Ω an open, bounded subset of R n with C 2
5 Potential Theory Reference: Introduction to Partial Differential Equations by G. Folland, 995, Chap. 3. 5. Problems of Interest. In what follows, we consider Ω an open, bounded subset of R n with C 2
Equations Involving Lines and Planes Standard equations for lines in space
 Equations Involving Lines and Planes In this section we will collect various important formulas regarding equations of lines and planes in three dimensional space Reminder regarding notation: any quantity
Equations Involving Lines and Planes In this section we will collect various important formulas regarding equations of lines and planes in three dimensional space Reminder regarding notation: any quantity
88 CHAPTER 2. VECTOR FUNCTIONS. . First, we need to compute T (s). a By definition, r (s) T (s) = 1 a sin s a. sin s a, cos s a
 88 CHAPTER. VECTOR FUNCTIONS.4 Curvature.4.1 Definitions and Examples The notion of curvature measures how sharply a curve bends. We would expect the curvature to be 0 for a straight line, to be very small
88 CHAPTER. VECTOR FUNCTIONS.4 Curvature.4.1 Definitions and Examples The notion of curvature measures how sharply a curve bends. We would expect the curvature to be 0 for a straight line, to be very small
Vectors VECTOR PRODUCT. Graham S McDonald. A Tutorial Module for learning about the vector product of two vectors. Table of contents Begin Tutorial
 Vectors VECTOR PRODUCT Graham S McDonald A Tutorial Module for learning about the vector product of two vectors Table of contents Begin Tutorial c 2004 [email protected] 1. Theory 2. Exercises
Vectors VECTOR PRODUCT Graham S McDonald A Tutorial Module for learning about the vector product of two vectors Table of contents Begin Tutorial c 2004 [email protected] 1. Theory 2. Exercises
LECTURE 1: DIFFERENTIAL FORMS. 1. 1-forms on R n
 LECTURE 1: DIFFERENTIAL FORMS 1. 1-forms on R n In calculus, you may have seen the differential or exterior derivative df of a function f(x, y, z) defined to be df = f f f dx + dy + x y z dz. The expression
LECTURE 1: DIFFERENTIAL FORMS 1. 1-forms on R n In calculus, you may have seen the differential or exterior derivative df of a function f(x, y, z) defined to be df = f f f dx + dy + x y z dz. The expression
14.11. Geodesic Lines, Local Gauss-Bonnet Theorem
 14.11. Geodesic Lines, Local Gauss-Bonnet Theorem Geodesics play a very important role in surface theory and in dynamics. One of the main reasons why geodesics are so important is that they generalize
14.11. Geodesic Lines, Local Gauss-Bonnet Theorem Geodesics play a very important role in surface theory and in dynamics. One of the main reasons why geodesics are so important is that they generalize
RAJALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE MA 2161 UNIT I - ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS PART A
 RAJALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE MA 26 UNIT I - ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS. Solve (D 2 + D 2)y = 0. 2. Solve (D 2 + 6D + 9)y = 0. PART A 3. Solve (D 4 + 4)x = 0 where D = d dt 4. Find Particular Integral:
RAJALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE MA 26 UNIT I - ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS. Solve (D 2 + D 2)y = 0. 2. Solve (D 2 + 6D + 9)y = 0. PART A 3. Solve (D 4 + 4)x = 0 where D = d dt 4. Find Particular Integral:
(a) We have x = 3 + 2t, y = 2 t, z = 6 so solving for t we get the symmetric equations. x 3 2. = 2 y, z = 6. t 2 2t + 1 = 0,
 Name: Solutions to Practice Final. Consider the line r(t) = 3 + t, t, 6. (a) Find symmetric equations for this line. (b) Find the point where the first line r(t) intersects the surface z = x + y. (a) We
Name: Solutions to Practice Final. Consider the line r(t) = 3 + t, t, 6. (a) Find symmetric equations for this line. (b) Find the point where the first line r(t) intersects the surface z = x + y. (a) We
Electrostatic Fields: Coulomb s Law & the Electric Field Intensity
 Electrostatic Fields: Coulomb s Law & the Electric Field Intensity EE 141 Lecture Notes Topic 1 Professor K. E. Oughstun School of Engineering College of Engineering & Mathematical Sciences University
Electrostatic Fields: Coulomb s Law & the Electric Field Intensity EE 141 Lecture Notes Topic 1 Professor K. E. Oughstun School of Engineering College of Engineering & Mathematical Sciences University
Figure 1.1 Vector A and Vector F
 CHAPTER I VECTOR QUANTITIES Quantities are anything which can be measured, and stated with number. Quantities in physics are divided into two types; scalar and vector quantities. Scalar quantities have
CHAPTER I VECTOR QUANTITIES Quantities are anything which can be measured, and stated with number. Quantities in physics are divided into two types; scalar and vector quantities. Scalar quantities have
MATH 425, PRACTICE FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS.
 MATH 45, PRACTICE FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS. Exercise. a Is the operator L defined on smooth functions of x, y by L u := u xx + cosu linear? b Does the answer change if we replace the operator L by the operator
MATH 45, PRACTICE FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS. Exercise. a Is the operator L defined on smooth functions of x, y by L u := u xx + cosu linear? b Does the answer change if we replace the operator L by the operator
Edmund Li. Where is defined as the mutual inductance between and and has the SI units of Henries (H).
 INDUCTANCE MUTUAL INDUCTANCE If we consider two neighbouring closed loops and with bounding surfaces respectively then a current through will create a magnetic field which will link with as the flux passes
INDUCTANCE MUTUAL INDUCTANCE If we consider two neighbouring closed loops and with bounding surfaces respectively then a current through will create a magnetic field which will link with as the flux passes
6 J - vector electric current density (A/m2 )
 Determination of Antenna Radiation Fields Using Potential Functions Sources of Antenna Radiation Fields 6 J - vector electric current density (A/m2 ) M - vector magnetic current density (V/m 2 ) Some problems
Determination of Antenna Radiation Fields Using Potential Functions Sources of Antenna Radiation Fields 6 J - vector electric current density (A/m2 ) M - vector magnetic current density (V/m 2 ) Some problems
Scalars, Vectors and Tensors
 Scalars, Vectors and Tensors A scalar is a physical quantity that it represented by a dimensional number at a particular point in space and time. Examples are hydrostatic pressure and temperature. A vector
Scalars, Vectors and Tensors A scalar is a physical quantity that it represented by a dimensional number at a particular point in space and time. Examples are hydrostatic pressure and temperature. A vector
Adding vectors We can do arithmetic with vectors. We ll start with vector addition and related operations. Suppose you have two vectors
 1 Chapter 13. VECTORS IN THREE DIMENSIONAL SPACE Let s begin with some names and notation for things: R is the set (collection) of real numbers. We write x R to mean that x is a real number. A real number
1 Chapter 13. VECTORS IN THREE DIMENSIONAL SPACE Let s begin with some names and notation for things: R is the set (collection) of real numbers. We write x R to mean that x is a real number. A real number
Høgskolen i Narvik Sivilingeniørutdanningen STE6237 ELEMENTMETODER. Oppgaver
 Høgskolen i Narvik Sivilingeniørutdanningen STE637 ELEMENTMETODER Oppgaver Klasse: 4.ID, 4.IT Ekstern Professor: Gregory A. Chechkin e-mail: [email protected] Narvik 6 PART I Task. Consider two-point
Høgskolen i Narvik Sivilingeniørutdanningen STE637 ELEMENTMETODER Oppgaver Klasse: 4.ID, 4.IT Ekstern Professor: Gregory A. Chechkin e-mail: [email protected] Narvik 6 PART I Task. Consider two-point
Example SECTION 13-1. X-AXIS - the horizontal number line. Y-AXIS - the vertical number line ORIGIN - the point where the x-axis and y-axis cross
 CHAPTER 13 SECTION 13-1 Geometry and Algebra The Distance Formula COORDINATE PLANE consists of two perpendicular number lines, dividing the plane into four regions called quadrants X-AXIS - the horizontal
CHAPTER 13 SECTION 13-1 Geometry and Algebra The Distance Formula COORDINATE PLANE consists of two perpendicular number lines, dividing the plane into four regions called quadrants X-AXIS - the horizontal
Rolle s Theorem. q( x) = 1
 Lecture 1 :The Mean Value Theorem We know that constant functions have derivative zero. Is it possible for a more complicated function to have derivative zero? In this section we will answer this question
Lecture 1 :The Mean Value Theorem We know that constant functions have derivative zero. Is it possible for a more complicated function to have derivative zero? In this section we will answer this question
Section 2.4: Equations of Lines and Planes
 Section.4: Equations of Lines and Planes An equation of three variable F (x, y, z) 0 is called an equation of a surface S if For instance, (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) S if and only if F (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) 0. x + y
Section.4: Equations of Lines and Planes An equation of three variable F (x, y, z) 0 is called an equation of a surface S if For instance, (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) S if and only if F (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) 0. x + y
The Heat Equation. Lectures INF2320 p. 1/88
 The Heat Equation Lectures INF232 p. 1/88 Lectures INF232 p. 2/88 The Heat Equation We study the heat equation: u t = u xx for x (,1), t >, (1) u(,t) = u(1,t) = for t >, (2) u(x,) = f(x) for x (,1), (3)
The Heat Equation Lectures INF232 p. 1/88 Lectures INF232 p. 2/88 The Heat Equation We study the heat equation: u t = u xx for x (,1), t >, (1) u(,t) = u(1,t) = for t >, (2) u(x,) = f(x) for x (,1), (3)
Line and surface integrals: Solutions
 hapter 5 Line and surface integrals: olutions Example 5.1 Find the work done by the force F(x, y) x 2 i xyj in moving a particle along the curve which runs from (1, ) to (, 1) along the unit circle and
hapter 5 Line and surface integrals: olutions Example 5.1 Find the work done by the force F(x, y) x 2 i xyj in moving a particle along the curve which runs from (1, ) to (, 1) along the unit circle and
9 Multiplication of Vectors: The Scalar or Dot Product
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 9 Multiplication of Vectors: The Scalar or Dot Product Up to this point we have defined what vectors are and discussed basic notation
Arkansas Tech University MATH 934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 9 Multiplication of Vectors: The Scalar or Dot Product Up to this point we have defined what vectors are and discussed basic notation
Electromagnetism - Lecture 2. Electric Fields
 Electromagnetism - Lecture 2 Electric Fields Review of Vector Calculus Differential form of Gauss s Law Poisson s and Laplace s Equations Solutions of Poisson s Equation Methods of Calculating Electric
Electromagnetism - Lecture 2 Electric Fields Review of Vector Calculus Differential form of Gauss s Law Poisson s and Laplace s Equations Solutions of Poisson s Equation Methods of Calculating Electric
11.1. Objectives. Component Form of a Vector. Component Form of a Vector. Component Form of a Vector. Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 11 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 11.1 Vectors in the Plane Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives! Write the component form of
11 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 11.1 Vectors in the Plane Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives! Write the component form of
Dot product and vector projections (Sect. 12.3) There are two main ways to introduce the dot product
 Dot product and vector projections (Sect. 12.3) Two definitions for the dot product. Geometric definition of dot product. Orthogonal vectors. Dot product and orthogonal projections. Properties of the dot
Dot product and vector projections (Sect. 12.3) Two definitions for the dot product. Geometric definition of dot product. Orthogonal vectors. Dot product and orthogonal projections. Properties of the dot
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: Inner product spaces. Orthogonal sets.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: Inner product spaces. Orthogonal sets. Norm The notion of norm generalizes the notion of length of a vector in R n. Definition. Let V be a vector space. A function α
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 20: Inner product spaces. Orthogonal sets. Norm The notion of norm generalizes the notion of length of a vector in R n. Definition. Let V be a vector space. A function α
Lecture 3 Fluid Dynamics and Balance Equa6ons for Reac6ng Flows
 Lecture 3 Fluid Dynamics and Balance Equa6ons for Reac6ng Flows 3.- 1 Basics: equations of continuum mechanics - balance equations for mass and momentum - balance equations for the energy and the chemical
Lecture 3 Fluid Dynamics and Balance Equa6ons for Reac6ng Flows 3.- 1 Basics: equations of continuum mechanics - balance equations for mass and momentum - balance equations for the energy and the chemical
α = u v. In other words, Orthogonal Projection
 Orthogonal Projection Given any nonzero vector v, it is possible to decompose an arbitrary vector u into a component that points in the direction of v and one that points in a direction orthogonal to v
Orthogonal Projection Given any nonzero vector v, it is possible to decompose an arbitrary vector u into a component that points in the direction of v and one that points in a direction orthogonal to v
Review Sheet for Test 1
 Review Sheet for Test 1 Math 261-00 2 6 2004 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And
Review Sheet for Test 1 Math 261-00 2 6 2004 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And
The degree of a polynomial function is equal to the highest exponent found on the independent variables.
 DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to [email protected]. Thank you! PLEASE NOTE
DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CONCEPTS - POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Prepared by Ingrid Stewart, Ph.D., College of Southern Nevada Please Send Questions and Comments to [email protected]. Thank you! PLEASE NOTE
Vector Algebra CHAPTER 13. Ü13.1. Basic Concepts
 CHAPTER 13 ector Algebra Ü13.1. Basic Concepts A vector in the plane or in space is an arrow: it is determined by its length, denoted and its direction. Two arrows represent the same vector if they have
CHAPTER 13 ector Algebra Ü13.1. Basic Concepts A vector in the plane or in space is an arrow: it is determined by its length, denoted and its direction. Two arrows represent the same vector if they have
Truman College-Mathematics Department Math 209-ABC: Calculus and Analytic Geometry III Course Syllabus Spring 2012
 Truman College-Mathematics Department Math 209-ABC: Calculus and Analytic Geometry III Course Syllabus Spring 2012 Instructor: Dr. Abdallah Shuaibi Office #: 3816 Email: [email protected] URL: http://faculty.ccc.edu/ashuaibi/
Truman College-Mathematics Department Math 209-ABC: Calculus and Analytic Geometry III Course Syllabus Spring 2012 Instructor: Dr. Abdallah Shuaibi Office #: 3816 Email: [email protected] URL: http://faculty.ccc.edu/ashuaibi/
THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF ALGEBRA VIA PROPER MAPS
 THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF ALGEBRA VIA PROPER MAPS KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra says every nonconstant polynomial with complex coefficients can be factored into linear
THE FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF ALGEBRA VIA PROPER MAPS KEITH CONRAD 1. Introduction The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra says every nonconstant polynomial with complex coefficients can be factored into linear
v 1 v 3 u v = (( 1)4 (3)2, [1(4) ( 2)2], 1(3) ( 2)( 1)) = ( 10, 8, 1) (d) u (v w) = (u w)v (u v)w (Relationship between dot and cross product)
![v 1 v 3 u v = (( 1)4 (3)2, [1(4) ( 2)2], 1(3) ( 2)( 1)) = ( 10, 8, 1) (d) u (v w) = (u w)v (u v)w (Relationship between dot and cross product) v 1 v 3 u v = (( 1)4 (3)2, [1(4) ( 2)2], 1(3) ( 2)( 1)) = ( 10, 8, 1) (d) u (v w) = (u w)v (u v)w (Relationship between dot and cross product)](/thumbs/40/20880945.jpg) 0.1 Cross Product The dot product of two vectors is a scalar, a number in R. Next we will define the cross product of two vectors in 3-space. This time the outcome will be a vector in 3-space. Definition
0.1 Cross Product The dot product of two vectors is a scalar, a number in R. Next we will define the cross product of two vectors in 3-space. This time the outcome will be a vector in 3-space. Definition
Summary: Transformations. Lecture 14 Parameter Estimation Readings T&V Sec 5.1-5.3. Parameter Estimation: Fitting Geometric Models
 Summary: Transformations Lecture 14 Parameter Estimation eadings T&V Sec 5.1-5.3 Euclidean similarity affine projective Parameter Estimation We will talk about estimating parameters of 1) Geometric models
Summary: Transformations Lecture 14 Parameter Estimation eadings T&V Sec 5.1-5.3 Euclidean similarity affine projective Parameter Estimation We will talk about estimating parameters of 1) Geometric models
1 of 79 Erik Eberhardt UBC Geological Engineering EOSC 433
 Stress & Strain: A review xx yz zz zx zy xy xz yx yy xx yy zz 1 of 79 Erik Eberhardt UBC Geological Engineering EOSC 433 Disclaimer before beginning your problem assignment: Pick up and compare any set
Stress & Strain: A review xx yz zz zx zy xy xz yx yy xx yy zz 1 of 79 Erik Eberhardt UBC Geological Engineering EOSC 433 Disclaimer before beginning your problem assignment: Pick up and compare any set
13.4 THE CROSS PRODUCT
 710 Chapter Thirteen A FUNDAMENTAL TOOL: VECTORS 62. Use the following steps and the results of Problems 59 60 to show (without trigonometry) that the geometric and algebraic definitions of the dot product
710 Chapter Thirteen A FUNDAMENTAL TOOL: VECTORS 62. Use the following steps and the results of Problems 59 60 to show (without trigonometry) that the geometric and algebraic definitions of the dot product
AP CALCULUS AB 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP CALCULUS AB 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 Let R be the region bounded by the graphs of y = sin( π x) and y = x 4 x, as shown in the figure above. (a) Find the area of R. (b) The horizontal line
AP CALCULUS AB 2008 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1 Let R be the region bounded by the graphs of y = sin( π x) and y = x 4 x, as shown in the figure above. (a) Find the area of R. (b) The horizontal line
December 4, 2013 MATH 171 BASIC LINEAR ALGEBRA B. KITCHENS
 December 4, 2013 MATH 171 BASIC LINEAR ALGEBRA B KITCHENS The equation 1 Lines in two-dimensional space (1) 2x y = 3 describes a line in two-dimensional space The coefficients of x and y in the equation
December 4, 2013 MATH 171 BASIC LINEAR ALGEBRA B KITCHENS The equation 1 Lines in two-dimensional space (1) 2x y = 3 describes a line in two-dimensional space The coefficients of x and y in the equation
Two vectors are equal if they have the same length and direction. They do not
 Vectors define vectors Some physical quantities, such as temperature, length, and mass, can be specified by a single number called a scalar. Other physical quantities, such as force and velocity, must
Vectors define vectors Some physical quantities, such as temperature, length, and mass, can be specified by a single number called a scalar. Other physical quantities, such as force and velocity, must
KELLOGG COMMUNITY COLLEGE MATH 241 Calculus III Fall 2013 Course Syllabus. Refund Date: 8 September 2013 Withdraw: 1 December 2013
 KELLOGG COMMUNITY COLLEGE MATH 241 Calculus III Fall 2013 Course Syllabus Refund Date: 8 September 2013 Withdraw: 1 December 2013 COURSE NUMBER/TITLE/CREDITS: MATH 241-01 Calculus III - 4 Credit Hours
KELLOGG COMMUNITY COLLEGE MATH 241 Calculus III Fall 2013 Course Syllabus Refund Date: 8 September 2013 Withdraw: 1 December 2013 COURSE NUMBER/TITLE/CREDITS: MATH 241-01 Calculus III - 4 Credit Hours
LINES AND PLANES CHRIS JOHNSON
 LINES AND PLANES CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract. In this lecture we derive the equations for lines and planes living in 3-space, as well as define the angle between two non-parallel planes, and determine the distance
LINES AND PLANES CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract. In this lecture we derive the equations for lines and planes living in 3-space, as well as define the angle between two non-parallel planes, and determine the distance
Section 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes
 Section 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Generalizing Linear Equations One of the main aspects of single variable calculus was approximating graphs of functions by lines - specifically, tangent lines.
Section 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Generalizing Linear Equations One of the main aspects of single variable calculus was approximating graphs of functions by lines - specifically, tangent lines.
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 25 Notes
 Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 009-10 Lecture 5 Notes These notes correspond to Section 10.5 in the text. Equations of Lines A line can be viewed, conceptually, as the set of all points in space that
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 009-10 Lecture 5 Notes These notes correspond to Section 10.5 in the text. Equations of Lines A line can be viewed, conceptually, as the set of all points in space that
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 18: Rank and nullity of a matrix.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 18: Rank and nullity of a matrix. Nullspace Let A = (a ij ) be an m n matrix. Definition. The nullspace of the matrix A, denoted N(A), is the set of all n-dimensional column
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 18: Rank and nullity of a matrix. Nullspace Let A = (a ij ) be an m n matrix. Definition. The nullspace of the matrix A, denoted N(A), is the set of all n-dimensional column
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics. 8.02 Spring 2013 Conflict Exam Two Solutions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 802 Spring 2013 Conflict Exam Two Solutions Problem 1 (25 points): answers without work shown will not be given any credit A uniformly charged
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 802 Spring 2013 Conflict Exam Two Solutions Problem 1 (25 points): answers without work shown will not be given any credit A uniformly charged
Vectors 2. The METRIC Project, Imperial College. Imperial College of Science Technology and Medicine, 1996.
 Vectors 2 The METRIC Project, Imperial College. Imperial College of Science Technology and Medicine, 1996. Launch Mathematica. Type
Vectors 2 The METRIC Project, Imperial College. Imperial College of Science Technology and Medicine, 1996. Launch Mathematica. Type
Section 1.4. Lines, Planes, and Hyperplanes. The Calculus of Functions of Several Variables
 The Calculus of Functions of Several Variables Section 1.4 Lines, Planes, Hyperplanes In this section we will add to our basic geometric understing of R n by studying lines planes. If we do this carefully,
The Calculus of Functions of Several Variables Section 1.4 Lines, Planes, Hyperplanes In this section we will add to our basic geometric understing of R n by studying lines planes. If we do this carefully,
Vector Math Computer Graphics Scott D. Anderson
 Vector Math Computer Graphics Scott D. Anderson 1 Dot Product The notation v w means the dot product or scalar product or inner product of two vectors, v and w. In abstract mathematics, we can talk about
Vector Math Computer Graphics Scott D. Anderson 1 Dot Product The notation v w means the dot product or scalar product or inner product of two vectors, v and w. In abstract mathematics, we can talk about
Math 265 (Butler) Practice Midterm II B (Solutions)
 Math 265 (Butler) Practice Midterm II B (Solutions) 1. Find (x 0, y 0 ) so that the plane tangent to the surface z f(x, y) x 2 + 3xy y 2 at ( x 0, y 0, f(x 0, y 0 ) ) is parallel to the plane 16x 2y 2z
Math 265 (Butler) Practice Midterm II B (Solutions) 1. Find (x 0, y 0 ) so that the plane tangent to the surface z f(x, y) x 2 + 3xy y 2 at ( x 0, y 0, f(x 0, y 0 ) ) is parallel to the plane 16x 2y 2z
LINES AND PLANES IN R 3
 LINES AND PLANES IN R 3 In this handout we will summarize the properties of the dot product and cross product and use them to present arious descriptions of lines and planes in three dimensional space.
LINES AND PLANES IN R 3 In this handout we will summarize the properties of the dot product and cross product and use them to present arious descriptions of lines and planes in three dimensional space.
The Tangent Bundle. Jimmie Lawson Department of Mathematics Louisiana State University. Spring, 2006
 The Tangent Bundle Jimmie Lawson Department of Mathematics Louisiana State University Spring, 2006 1 The Tangent Bundle on R n The tangent bundle gives a manifold structure to the set of tangent vectors
The Tangent Bundle Jimmie Lawson Department of Mathematics Louisiana State University Spring, 2006 1 The Tangent Bundle on R n The tangent bundle gives a manifold structure to the set of tangent vectors
MAT 1341: REVIEW II SANGHOON BAEK
 MAT 1341: REVIEW II SANGHOON BAEK 1. Projections and Cross Product 1.1. Projections. Definition 1.1. Given a vector u, the rectangular (or perpendicular or orthogonal) components are two vectors u 1 and
MAT 1341: REVIEW II SANGHOON BAEK 1. Projections and Cross Product 1.1. Projections. Definition 1.1. Given a vector u, the rectangular (or perpendicular or orthogonal) components are two vectors u 1 and

