HUMAN TORSOS WITH CD AND MUSCULAR FIGURES
|
|
|
- Juliet Dickerson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HUMAN TORSOS WITH CD AND MUSCULAR FIGURES MINI TORSO MINI TORSO - african TORSO UNI SEX * TORSO DUAL SEX* TORSO DUAL SEX OPENBACK* MUSCULAR TORSO DUAL SEX OPENBACK* MUSCULAR FIGURE Some of the detachable parts of human torsos ( ): HUMAN TORSOS *SUPPLIED WITH CD ROM GUIDE Size 0x15xh5 cm 0x15xh5 cm 30x33xh87 cm Removable structures, of s , include the following: - eye with optic nerve and extraocular muscles - half of the brain - trachea - descending thoracic aorta and esophagus - right and left lungs (two parts each)- liver with gallbladder - half of one kidney - two part heart - stomach dissected in two parts (not for 0005) - pancreas, duodenum and spleen - small and large intestines - male and female urogenital systems ( parts each), (on 0009 female system is in 3 parts and provided of detachable fetus) - thoracic vertebra (T1) with spinal cord ( 0008 and 0009 only)..1 kg.1 kg 9 kg kg Detachable parts of human muscular figure 0019: This CD-ROM Guide greatly extends the educational value of the anatomical torsos by identifying hundreds of structures that are not included on the printed key. High-resolution digital images of torso components show the finest anatomical details of all body systems from various angles. HEAD MUSCULATURE 0015 HEAD/NECK MUSCULATURE Size: 37x3x6 cm kg - 1 part - life size Superficial and deep musculature are well represented as are the pathways of the subclavian and carotid arteries 0015 MUSCLES: SHOULDER, ARM, LEG 00 SHOULDER MUSCLE Size: 3x19x11 cm - 35 g 1 part - Mounted on a base with stand 00 This model illustrates in great details the muscles, ligaments and bones of the shoulder. Through different muscles section it is possible to observe the deep musculature to the bone ARM MUSCLE Size: 7x0x1 cm kg - 7 parts 0017 This 7-part life size model shows, in great detail, the anatomical structure of the arm, complete with superficial and deeper muscles, vascular structures, nerves and ligaments. The hand and the shoulder are also well represented. The following parts are removable: - deltoid muscle - biceps muscle - triceps muscle - long palmar muscle with radial flexor muscle of wrist - brachioradial muscle - radial extensor muscle of wrist - palmar aponeurosis 0018 LEG MUSCLE Size: 110x19x1.5 cm kg 13 parts Mounted on a base with stand This 13-part model shows, in great detail, the anatomical structure of the leg, complete with superficial and deeper muscles, vascular structures, nerves and ligaments. The following parts are removable: - sartorius - long head of biceps - gluteus maximus - soleus - gastrocnemius - gluteus medius - gracilis - semitendinosus and semimembranous - rectus femoris - extensor digitorum longus - sole of foot - tensor fasciae latae
2 HEAD AND BRAIN 0010 HEAD DISSECTION - life size Size: 18x5x3 cm - 10 g - parts SENSE ORGANS: EYE AND EAR EAR SIZES 33x3x1 cm 33x3x1 cm These models show the external, middle and inner ear. The eardrum with malleus, incus and stapes are removable. Also cochlea and labyrinth with vestibular and cochlear nerves and bones sections (00 only) that define the middle and inner ear are removable. Kg x life size, the model shows a medial section of the nasal cavity. The nasal septum and part of the olfactory epithelium are removable to show deep internal structures NASAL CAVITY Size: 15x0x30 cm - 1 kg - 3 parts LIVER SECTION WITH GALLBLADDER Size: 8x7x1 cm g - 1 part - 1.5X Life size Can be divided into 9 parts showing the temporal and occipital lobes, the frontal and parietal lobes, the cerebellum, the brain stem and basilary artery 000 BRAIN WITH ARTERIES Size: x18x cm - 1 kg - 9 parts Disassembled DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS: LIVER, PANCREAS, STOMACH This model, 1.5x life size, shows the liver and gallbladder in open section with the complex network of vessels and bile ducts, displayed in different colours to clarity and ease of examination. Cornea, iris, lens and vitreous body can be removed. Accurate representation of the pancreas, spleen and duodenum. The pancreas is open to show the entire pancreatic duct. The duodenum is partially dissected to expose its internal structure Assembled A life size reproduction of the complete human respiratory system. It is composed of 7 parts showing the larynx (dissected along the sagittal plane), the lungs (dissected along the frontal plane) and a part -part heart RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Size: 6x0x1 cm parts life size 0086 PANCREAS, DUODENUM AND SPLEEN Size: x15x3 cm g - 1 part REGIONAL BRAIN Size: 0x17x15 cm parts Models show the eye ball with optic nerves and muscles in its natural position in the bony orbit EYE WITH ORBIT SIZES 15x17x7 cm x30x31 cm x30x31 cm RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: NASAL CAVITY, LARYNX Kg STOMACH Size: x1.5x5 cm - 35 g - parts - 1.5X X 5X 5X 0058 LARYNX Size: 18x11x8 cm - 50 g - 5 parts - X Can be opened to show the internal structure of the stomach, including the mucosa, the pylorus, and a section of the gastric wall. Superficial dissection exposes the longitudinal, circular and oblique muscle layers, with nerves and vascular structures Life size brain with distinct colour for: frontal lobe, pariental lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe, motor cortex, somatosensory cortex, limbic cortex, cerebellum, brain stem Longitudinally sectioned to reveal inner details of internal structure including hyoid bone, vessels, ligaments, cartilages, muscles, nerves and thyroid gland 0088
3 HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 0071 Life size in parts. The anterior heart wall can be removed to show the left and right ventricles and atria as well as the tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral and aortic valves. Show internal structures including the cardiac valves and the comparative morphology of the right and left ventricles. The right atrium is also removable. 007 A general view of the human circulation. It includes the heart ( parts), lungs, liver, spleen, kidneys and relevant connections with the pulmonary and systematic circulatory pathways. Assembled Disassembled Enlarged 000 times, 0077 this model shows the various types of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells (lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils) and blood platelets PELVIS - FEMALE AND MALE HEART - mounted on base GIANT HEART - mounted on base BLOOD CELLS - mounted on board CIRCULATORY SYSTEM - mounted on board This life size model, composed of parts, presents an open view through a median sagittal section of the pelvis. Internal structures of the male urogenital system are represented in fine detail. The removable parts include a half penis divided into medial and transverse sections, and half of the male reproductive system with an open dissection of a testis showing details of the internal structure. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Size cm 11x7x10 x5x8 58x38x7 90x3x11 URINARY SYSTEM: MALE BLADDER, KIDNEY 0090 MALE URINARY BLADDER WITH PROSTATE Size: 7x0x15 cm - 1, kg - parts - This model, enlarged 3 times, shows the male urinary bladder with the prostate gland surrounding the urethra. The model is dissected medially to expose both internal and external structures of the bladder and prostate, including the ureteric and urethral orifices, ductus deferens, seminal gland, ejaculatory duct KIDNEY WITH ADRENAL GLAND+RENAL CORPUSCLE Size: 0x15x8 cm - 1, kg - 1 part - This model shows a frontal section of the human kidney enlarged 3 times. The kidney is shown with the renal capsule. Additional structures include: the cortex, medulla, pyramids with papillae, partially dissected renal pelvis, renal calices, ureter, blood vessels, suprarenal gland with cortex and medulla. A schematic representation of the renal corpuscle with the system of collecting tubules is included kg PREGNANCY PELVIS This life size model depicts the female human pelvis in median section with a fetus in the 0th week of pregnancy. The fetus is in the normal position prior to birth, showing the anatomical relationship between various structures of the maternal pelvis and the fetus. Fetus is detachable for closer examination nif. 000X 0.5X 009 This life size model, composed of 3 parts, shows an open dissection through the median sagittal section of the pelvis. Internal structures of the female urogenital system are portrayed in great detail. Removable parts include half of the female reproductive system with the uterus opened to reveal medial and transverse sectional views. SKIN 0061 SKIN MODEL - 30X Size: 0x15x15.5 cm - 1. kg Mounted on base All the skin layers can be easily identified and the main structures such as hair follicle, sensitive corpuscles, sebaceous and sweat glands, are numbered and referred on the accompanying k-card PELVIS Sex Kg size cm 30x0x7 fem x0x7 male SKIN MODEL - 70X Size: 5x18x8 cm kg parts - 70X Mounted on base Anatomical structures are shown in details including the hair follicles, sebaceous, glands, sweat glands, erector muscles, Pacinian corpuscles, nerves and blood vessels. The different layers of the skin are clearly defined. A portion of a hair shaft can be removed to show internal details PREGNANCY PELVIS WITH MATURE FETUS Size: 0x6x3 cm part - 30
4 010 HUMAN ANATOMY - MODELS SKELETONS 015 VERTEBRAL COLUMNS MINI SKELETON Height: 80 cm : 1.5 kg. This 1/ life size model shows the anatomy of the human skeleton in high detail. The skull can be disassembled into 3 parts: skullcap, base of skull and mandible. All the main joints are articulated. Arms and legs can be removed easily. Mounted on a stand for hanging. 010 HUMAN SKELETON Height: 170 cm. : approx 10 kg. This model is a replica of a life size human skeleton and shows all the skeleton parts in high detail. It's hand-assembled to provide intricate details and long-lasting durability. The main joints are articulated; the upper and lower limbs can be removed easily. The following parts are detachable: Calvarium, Skull, Jaw, Arms, Legs. Supplied with 5-caster roller stand. 015 MUSCULAR HUMAN SKELETON Same as 010 but with the left side of the skeleton showing the point of origin (red) and the point of insertion (blue) of the muscles KNEE AND SHOULDER 010 SHOULDER JOINT Size: 9x1x1cm - 560g - 1 part - Mounted on stand. 015 KNEE JOINT Size: 1x1x31cm - 0g - 1 part - The life size model represents a functional model of knee joint with lateral ligaments, meniscus and patellar ligament. 010 SKELETAL SYSTEM Advanced osteoporosis model. Shows 3 vertebrae: one healthy vertebra, one vertebra with pathological changes at first stage, one vertebra with pathological changes at advanced stage FLEXIBLE VERTEBRAL COLUMNS Fully flexible life size vertebral columns consisting of the occipital plate, cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, complete pelvis with symphysis, removable femur heads (only 0130,31,3). All models also feature representation of the vertebral arteries, spinal nerve branches, and a prolapsed L3-L intervertebral disc. On 0131 the left side of the skeleton shows the points of origin (red) and the point of insertion (blue) of the muscles. On 0131 and 013 the sacral crest and coccyx are removable to show the sacral section of the spinal cord and associated nerve branches. On 0133 the various regions of the spinal column are colour d for easy identification FLEXIBLE VERTEBRAL COLUMNS VERTEBRAL COLUMN with femur heads VERTEBRAL COL with femur + muscle VERTEBRAL COL with femur + open sacrum SPINAL COL with colour d regions Size cm 95x0x0 95x0x0 95x0x0 98x3x3 nif. 970 g Cervical spinal column consists of 7 cervical vertebrae with intervertebral discs, occipital plate, cervical nerves, vertebral arteries, spinal cord and brain stem Thoracic spinal Lumbar spinal column consists of 1 thoracic vertebrae with intervertebral discs, thoracic nerves and spinal cord. SKELETAL SYSTEM CERVICAL SPINAL COLUMN THORACIC SPINAL COLUMN LUMBAR SPINAL COLUMN HERNIA PATHOLOGY ADVANCED OSTEOPOROSIS column with sacral and coccyx bones. It consists of 5 lumbar vertebrae with intervertebral discs, lumbar nerves and spinal cord. The sacral crest and coccyx are removable. Size cm 1x1x 1x1x0 1x1x36.5x1x6 1x1x15 3 lumbar vertebrae with hernia and prolapsed intervertebral disc. Shows 3 lumbar vertebrae with spinal nerves, dura mater and intervertebral discs affected by lateral and medial hernia. 350 g 600 g 800 g 300 g 00 g nif.
5 HUMAN SKULLS - 3 PARTS RANGE OF HUMAN SKULLS - 3 parts A detailed reproduction of a life size human skull with all structural details. The mandible is articulated and removable. The skullcap is removable to show internal details. All of the joints, sutures, fissure, foramina and processes are portrayed with utmost accuracy. Numbered skull (01) Significant structures are numerated Coloured skull (0) All the bones are depicted in different colours, making this model a useful tool to study the correct position and relationship of all the structures. Muscular skull (03) The left side of the skull shows the points of origin(red) and the point of insertion (blue) of the muscles. DENTAL MODELS 006 DECIDUOUS TEETH Size: 9x9x10 cm - weight: 85 g. This life size model shows the upper and lower jaw of a 5 year old child. The lower jaw is movable to reproduce the natural chew. The model exposes the arrangement of the young teeth. MINI SKULL (05) ½ adult natural size It depicts all structural details of the skull. It can be disassembled into skullcap and base of skull. Articulated mandible. HUMAN SKULLS (0155-6) - parts Life size human skull reproduction with all details, made in PVC. Removable skull cap and articulated mandible. HUMAN SKULLS Size cm g 0155 nif. 00 HUMAN SKULL x1x HUMAN SKULL - numerated x1x HUMAN SKULL - coloured 19.5x17x HUMAN SKULL - muscular 18x17x MINI SKULL 11x11x X 0155 HUMAN SKULL 19x13.5x HUMAN SKULL - numerated 19x13.5x PERMANENT TEETH Size: 11x11x1 cm - weight: 170 g. This life size model shows the upper and lower jaw of an adult. The lower jaw is movable to reproduce the natural chew. The model exposes the complete set of permanent teeth with roots and nerves fibres LOWER JAW Size: 35x18x31 cm - weight: 1130 g This life size model is divisible into 6 parts to show all the characteristics of an adult half mandible. A portion of the jaw can be removed to show the roots of the teeth and the internal structure of the bone. Canine and molar teeth can be removed and dissected longitudinally to observe the tooth roots, pulp and nerves. 01 DENTAL PATHOLOGY MODEL Size: 6x.5x11 cm - weight: approx. 100 g This X life size model shows the process of dental caries in its progressive stages. The tissues forming the tooth (enamel, dentine and pulp) are shown, along with the way in which they are affected by the caries process. 000 ORAL HYGIENE Size: 1xx cm - weight: 1 kg Mounted on base. A life size model useful to teach the correct way to brush teeth. A giant toothbrush is included. 013 SET 3 TEETH: INCISOR, CANINE, MOLAR Size: 33x33x11 cm - weight: 700 g 5-part model includes representations (10X life size) of human incisor, canine and molar teeth. The canine and molar can be divided into parts each, showing internal features (dentine, enamel, cement and pulp). 01 LOWER MOLAR WITH CARIES Size: 11x11x19.5 cm - weight: approx. 50 g This 1-piece model is approximately 10X life size; it shows the most important dental pathologies, including dental caries, pulpitis, gingivitis and periapical periodontitis. 011 DENTAL CARIES Size: 1x6x6 cm - weight: approx. 300 g This model, composed of 7 parts, is X life size. It consists of 3 teeth, seated in their sockets, showing the progressive deterioration of tooth structure by dental caries. The first tooth shows the caries in the enamel. In the second tooth, the caries spreads through the dentine. In the third tooth, the pathology affects the pulp, jeopardizing the vitality of the tooth. 3
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Glossary (continued)
 1. Maxillary bone 2. Maxillary teeth 3. Mandibular arch 4. Vomerine teeth 5. Lining of buccal (mouth) cavity 6. Inferior aspect of eyeball (floor of eye socket) 7. Tongue (with right half cut away) 8.
1. Maxillary bone 2. Maxillary teeth 3. Mandibular arch 4. Vomerine teeth 5. Lining of buccal (mouth) cavity 6. Inferior aspect of eyeball (floor of eye socket) 7. Tongue (with right half cut away) 8.
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Biology Dissection THE FROG
 Biology Dissection THE FROG Name Note: The organism you are cutting up today was once alive and vibrant, a living being. Dissection of a complex organism is not a right, but a privilege. Please be aware
Biology Dissection THE FROG Name Note: The organism you are cutting up today was once alive and vibrant, a living being. Dissection of a complex organism is not a right, but a privilege. Please be aware
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
ANATOMY 1 LEARNING TARGETS ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY 1. Define "anatomy" and "physiology." 2. Describe homeostasis. 3. Identify examples of homeostasis 4. Describe the organization of the body according
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
Learning Objectives for Anatomy & Physiology
 Learning Objectives for Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology by Visible Body contains 12 units. Below is a listing of each unit, the chapters within it, and the unit s associated learning objectives.
Learning Objectives for Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology by Visible Body contains 12 units. Below is a listing of each unit, the chapters within it, and the unit s associated learning objectives.
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Systems of the Human Body
 . s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
. s^^-^^. 0^^- B «*-^.^^^--"'- s»'"-^w.^*"' Systems of the Human Body The body is made up of an amazing group of systems. The systems of the body all work together and need each other to keep the body
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Placement: First Year Theory - Anatomy: 60 Physiology: 60 Course Description -The course is designed to assist students to acquire the knowledge of the normal Structure of human
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Organ Systems Overview
 E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
E x e r c i s e 2 Organ Systems Overview Time Allotment: 1½ hours (rat dissection: 1 hour; if performing reproductive system dissection, ½ hour each for male and female; dissectible human torso model:
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56
 Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE Unit 4 Anatomy and physiology for health and social care K/507/4368 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 Revised content March 2016 ocr.org.uk/healthandsocialcare
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE Unit 4 Anatomy and physiology for health and social care K/507/4368 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 Revised content March 2016 ocr.org.uk/healthandsocialcare
Urinary System Lab Guide
 Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
Urinary System Lab Guide I. Prelab Questions Name 1. Describe the location of the kidneys. 2. Describe the following structures: a. renal cortex b. renal pyramid c. renal column d. minor calyx e. renal
KIDNEY Locate the following structures on the sheep kidney and human kidney models:
 Laboratory Handouts 163 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1:
Laboratory Handouts 163 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1:
Range of Injury Scale Values
 Range of Injury Scale Values Civil Liability Regulations 2014 SCHEDULE 4 Range of Injury Scale Values (summary) Item Injury ISV Range Part 1-Central Nervous System and Head Injuries 1 Quadriplegia 75 100
Range of Injury Scale Values Civil Liability Regulations 2014 SCHEDULE 4 Range of Injury Scale Values (summary) Item Injury ISV Range Part 1-Central Nervous System and Head Injuries 1 Quadriplegia 75 100
Frog Dissection. Procedure
 Name Class Date Skills Practice Lab Frog Dissection Amphibians, such as frogs, are examples of animals that have structural adaptations for living in or near water and for living on land. As tadpoles,
Name Class Date Skills Practice Lab Frog Dissection Amphibians, such as frogs, are examples of animals that have structural adaptations for living in or near water and for living on land. As tadpoles,
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Comparative Anatomy of the Domestic Cat and Selected Organs of the Sheep, Cow, & Pig With Reference to the Human
 Comparative Anatomy of the Domestic Cat and Selected Organs of the Sheep, Cow, & Pig With Reference to the Human Karen McMahon Biological Science The University of Tulsa HAPS Institute - Using Cadavers
Comparative Anatomy of the Domestic Cat and Selected Organs of the Sheep, Cow, & Pig With Reference to the Human Karen McMahon Biological Science The University of Tulsa HAPS Institute - Using Cadavers
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 6: The Human Digestive System Welcome back. Today, we embark on Lesson 6 where we ll study the human digestive system. After completing this lesson, you should be able to define
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAT DISSECTION UNIT
 CAT DISSECTION UNIT INTRODUCTION To conclude our study of anatomy and physiology, we will dissect a cat in a day unit lesson. Through this dissection we will be able to observe all of the systems we have
CAT DISSECTION UNIT INTRODUCTION To conclude our study of anatomy and physiology, we will dissect a cat in a day unit lesson. Through this dissection we will be able to observe all of the systems we have
Part 1: Introduction Tell the name of your organ system and describe the major functions.
 Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Team Members: System: Your team s job is prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
Activity: Can You Identify the Age?
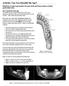 Activity: Can You Identify the Age? Skeletons are good age markers because teeth and bones mature at fairly predictable rates. How Teeth Reveal Age For toddler to age 21, teeth are the most accurate age
Activity: Can You Identify the Age? Skeletons are good age markers because teeth and bones mature at fairly predictable rates. How Teeth Reveal Age For toddler to age 21, teeth are the most accurate age
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan
 Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus
 LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus Course Number: DI 281 B Course Title: Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Course Credit: 3 units = 135
LINCOLN UNIVERSITY DI 281 B Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Summer 2015 Course Syllabus Course Number: DI 281 B Course Title: Practicum / Externship II in Sonography Course Credit: 3 units = 135
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
its lifetime. The skeletal system is divided into: 1. Axial Division: bones of the body s axis (skulll, ribs, vertebrae)
 The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
Anatomy and Physiology
 Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 2 ORGANIZATION OF THE BODY Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic parts, each with its own identity,
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE. BIOL 207 Human Anatomy
 STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE BIOL 207 Human Anatomy Prepared By: Ron Tavernier, PhD School of Science, Health and Criminal Justice Science Department
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE BIOL 207 Human Anatomy Prepared By: Ron Tavernier, PhD School of Science, Health and Criminal Justice Science Department
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements
 Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
Diagnostic MSK Case Submission Requirements Note: MSK Ultrasound-Guided Interventional Procedures (USGIP) is considered a separate specialty. Corresponds with 4/21/16 Accred Newsletter* From the main site:
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Reprinted by permission. The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Chapter 9 The Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, Ed.D, ATC, CSCS Hip joint
Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs
 Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY
 THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
THE SPINAL CORD AND THE INFLUENCE OF ITS DAMAGE ON THE HUMAN BODY THE SPINAL CORD. A part of the Central Nervous System The nervous system is a vast network of cells, which carry information in the form
Human Growth and Reproduction
 Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Human Growth and Reproduction Sperm reach ovum and cluster around it Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate egg When the sperm penetrates the egg, the egg immediately releases a chemical creating a hard
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord.
 Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Spine Anatomy and Spine General The purpose of the spine is to help us stand and sit straight, move, and provide protection to the spinal cord. Normal List Kyphosis The human spine has 7 Cervical vertebra
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Chapter 8. Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
Chapter 8 Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles of the Body INTRODUCTION This chapter continues our study of the muscular system by examining the distribution of muscles throughout the body. We learned in
BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more
 BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing
BIO 113 LAB 1. Anatomical Terminology, Positions, Planes, and Sections and more Objectives Describe the anatomical position verbally or by demonstrating it Demonstrate ability to use anatomical terms describing
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis. Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University
 Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
Anatomy and Pathomechanics of the Sacrum and Pelvis Charles R. Thompson Head Athletic Trainer Princeton University Simplify Everything There are actually only three bones: Two innominates, one sacrum.
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Student WORKSHEET. September, 2013 WORKSHEETS
 September, 2013 STUDENT WORKSHEETS 1 INSTRUCTIONS The following worksheets are mostly grouped according to the major systems of the body, just as the BODY WORLDS exhibition is. Complete these questions
September, 2013 STUDENT WORKSHEETS 1 INSTRUCTIONS The following worksheets are mostly grouped according to the major systems of the body, just as the BODY WORLDS exhibition is. Complete these questions
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
RAT DISSECTION GUIDE
 RAT DISSECTION GUIDE INTRODUCTION Rats are often used in dissection classes because they are readily available and they possess the typical mammalian body plan. Most of what you learn on the rat is applicable
RAT DISSECTION GUIDE INTRODUCTION Rats are often used in dissection classes because they are readily available and they possess the typical mammalian body plan. Most of what you learn on the rat is applicable
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014
 Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Biol 111 Comparative & Human Anatomy Lab 9: Circulatory System of the Cat Spring 2014 Philip J. Bergmann Lab Objectives 1. To learn how blood flows through a dual circuit circulation with lungs. 2. To
Alimentary canal (gastrointestinal or GI tract) continuous coiled hollow tube
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn external anatomy of the pig. 2. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. I. Introduction: Humans (Homo sapiens) and domestic pigs (Sus scrofa) are
The Digestive System Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn external anatomy of the pig. 2. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. I. Introduction: Humans (Homo sapiens) and domestic pigs (Sus scrofa) are
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding
CHAPTER 1: AN INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
 The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
The Anatomy of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) What is the Spinal Cord? The spinal cord is that part of your central nervous system that transmits messages between your brain and your body. The spinal cord has
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number APEH 3.0 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 50 minutes MOCK Level 3 Anatomy and
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter I Overview Chapter Contents
 Chapter I Overview Chapter Contents Table Number Contents I-1 Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths for 2005 I-2 53-Year Trends in US Cancer Death Rates I-3 Summary of Changes in Cancer Incidence and Mortality
Chapter I Overview Chapter Contents Table Number Contents I-1 Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths for 2005 I-2 53-Year Trends in US Cancer Death Rates I-3 Summary of Changes in Cancer Incidence and Mortality
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine. Bones of the Spine (Vertebrae)
 Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
