Hair Loss (Alopecia) Alopecia. Anatomy and Physiology of Hair. The Active Follicle
|
|
|
- Sabina York
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dr. Sahni BS DHMS Hons, PGRT (BOM), FF Hom Deputy Chief Medical Officer (H), ONGC Hospital Panvel , Navi Mumbai, INDIA Hair Loss (Alopecia) Website: Alopecia Alopecia partial or complete loss of hair that results from aging, hormone defects, drug allergy, anticancer treatment, or skin disease. Anatomy and Physiology of Hair Hair grows from follicle, which are stocking like in pushing of the superficial epithelium, each of which encloses at its base, a small stud of dermis known as the dermal papilla. The cylinder of hair may be regarded as a holocrine secretion arising by division of cells surrounding the papilla, in a region known as the bulb. The follicles are slanted in the dermis, and the longer ones extent into the adipose layer. An oblique muscle, the arrector pilli, runs from the point in the mid region in the follicle wall to the dermo epidermal junction. Above the muscle one or more sebaceous glands, and in some regions of the body an aprocrine gland open into the follicle. The Active Follicle The bulk of any hair is formed by a thick cortex made up of elongated keratinized cells cemented together, which in pigmented hairs contains granules of melanin. The cortex is surrounded by a cuticle and may have a continuous or discontinuous core or medulla. Although the cuticle is formed as a single layer, the cells become progressively imbricated as they move peripherally. The outer cells overlap, their free edges directed towards the tip, and they interlock with the cuticle of the surrounding inner root sheath. The inner root sheath consists, in addition to its cuticle of Henle s and Huxley s layers; it is formed in pace with the hair and its keratinized cells are ultimately desquamated. Investing it is the outer root sheath, which is continuous with the superficial epithelial and this is itself enclosed in a non-cellular partition known as the vitreous or glassy membrane. The entire follicle is surrounded by a connective-tissue sheath formed of collagenous fibers, a new elastic fibers and fibroblasts. (See Fig 1 below)
2 Figure 1: The Human hair cycle (a) an active follicle, (b) early catagen, (c) late catagen, showing ascent of the presumptive club, (d) tellogen, (e) early anagem Hormonal Influences It is important to make a clear distinction between the effects of a range of hormones on the follicular cycle, in evolutionary terms related to the adaptive function of moulting, and the particular role of androgens in the induction of sexual and other adult hair which is an adaptation for delaying until puberty the associated socio sexual signals. Most dermatological problems center around androgen dependent hair. Knowledge of other hormonal mechanisms is however relevant not only to understand the control of the moult cycle but also to the problems of human hair loss in thyroid disorder and following pregnancy. Human hair is profoundly affected by thyroid hormones. In a study carried out by Sheffield, 16 out of 150 women who complaint of hair loss were diagnosed as hypothyroid on the basis of serum protein bound iodine level confirmed by radio iodine tracer studies.
3 The phenomena of post partum hair loss also appear to result from a hormonally mediated change in the cycles of scalp follicles. A loss of hairs at about 2 to 3 times the normal rate gives rise to transit alopecia about 4 to 6 months after parturition. Changes with Age At puberty, terminal hair gradually replaces vellus, starting in the pubic regions. In both boys and girls, the first pubic hair is sparse, long, downy, slightly pigmented and almost straight. It later become s darker, coarser, and more curled and extends in area to form an inverse triangle. The boys have the first recognizable pubic hair at an average age of 13.4 years and the full adult female pattern at 14.2 years, about 3 ½ year after the start of development of the genetalia. The corresponding mean ages for girls were considerably earlier, mainly 11.7 years and 13.5 years. In about 80% of men and 10% of women, the pubic hair continues spreading until the mid 20 s or later; there is no absolute distinction between male and female pattern. Axillary hair first appears about 2 years after the start of pubic hair growth. The amount as measured by the fully-grown mass; continuous to increase until late 20 s in males as well as in females, in whom, however it is less at any age. The mean amounts grown per day increase from late puberty until the mid 20 s and thereafter decrease steadily. Facial hair in boys first appear at about the same time as the axillary hair, starting at the corner of the upper lip, and spreading medially to complete the mustache and then the cheeks and beard. Terminal hair development is continued in regular sequence on the legs, thighs, forearms, abdomen, buttocks, back, arms and shoulders. The extent of terminal hair tends to increase throughout the ears of sexual maturity, but most patterns occur over a vide age range. The adult pattern is not achieved until the forth decayed; when the androgen level is already somewhat lower than the early adult life. Moreover, aural hairs do not appear until late middle age. Certain follicles of the scalp may regress with age to produce only fine, short vellus hair. The condition of patterned baldness is inherited and requires male hormone; it is prevented by castration before puberty, though not substantially reversed by castration in maturity.
4 Androgenetic Alopecia (Common Baldness, Male Pattern Alopecia) Hair Patterns: Hamilton produced the first useful grading scale after examining 312 white males and 214 white females aged years (See Figure 2). This classification was modified by Norwood, who added grades III a, III vertex, IV a and V a to the Hamilton scale. Hamilton described the natural progression of the normal pre pubertal scalp pattern (Type I) in both sexes to type II in 96% of men and 79% of women after puberty. He also observed patterns type V to VIII (See Figure 3) in 58% of men aged over 50 years with the extent of baldness tending to increase to the 70. About 25% of women developed type IV scalps by the age of 50, after which there were no further increase in balding. Indeed, after 50, some women who have developed type II at puberty revert to type I. Types V to VIII were not found in any women. Although, as these figure shows, androgenetic alopecia occurs in females with some frequency androgenetic alopecia in women more often assumes a diffused form (See Figure 4 & 5) Fig 2: Hamilton Classification of Androgenetic Alopecia (Type II to IV overlapped) Fig 3: Grade VIII in a normal man. Fig 4: Androgenetic Alopecia Ludvig Grades, most typically seen in women. Fig 5: Ludvig Grade III in a normal postmenopausal woman.
5 Inheritance: The very high frequency of common baldness has complicated the many attempts to establish its mode of inheritance. Moreover, it is by no means clear that common baldness is genetically homogenous and some authorities differentiate between early on set (before the age of 30 in men) and the same pattern 20 years latter. Some think that baldness is determined by a single pair of sex-influenced factors. Both gene frequency studies and families history support this hypothesis. There is no association between baldness and dense hair patterns on the trunk and limbs; nor there is an association between hair loss and increased fertility. Pathology: The earliest histological change is focal perivascular basophilic degeneration in the lower third of the connective tissue sheath of otherwise normal anagen follicles. This is followed by a perifollicular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate at the level of the sebaceous duct. The basophilic sclerotic remains of the connective tissue sheath can be seen in the process as 'streamers'. The destruction of the connective tissue sheath may account for the irreversibility of hair loss. In about a third of biopsies, multinucleate giant cells are seen surrounding fragments of hair. The erector pili muscle decreases in size more slowly than the follicle. In the scalp, which appears totally bald, most of the follicles are short and small, with some quiescent terminal follicles. As the balding scalp loses its protective covering of hair, so solar degenerative changes may be seen. The reduction of blood supply has been confirmed by modern methods, but whether it follows or precedes baldness is unknown. The development of baldness is associated with shortening of the anagen phase of the hair cycle and consequently with an increase in the proportion of telogen hairs, which may be, detected m trichograms of the frontovertical region before baldness is evident. The reduction in the size of the affected follicles, which is the essential histological feature of ordinary baldness necessarily results in a reduction in the diameter of the hairs they, produce. This reduction is said to be greater in women than in men. Clinical Features: The essential clinical feature of androgenetic alopecia in both sexes is the replacement of terminal hairs by progressively finer hairs, which are eventually short and virtually un-pigmented. This process may begin at any age after puberty and may become clinically apparent by the age of 17 in the normal male and by in the endocrinologically normal female. The reduction in the size of the follicles is accompanied by shortening of anagen and by increased shedding of telogen hairs. Males: The replacement of terminal by smaller hairs occurs characteristically in a distinctive pattern, which spares the posterior and lateral scalp margins, even in the most advanced cases, and even in old age.
6 The sequence of patterns in the male has been described by Hamilton (Figures 2 & 3). Bitemporal recession is followed by balding of the vertex. Variations in the pattern are governed at least in part by genetic factors. The rate of progression is probably determined by heredity. Females: The use of the term 'male pattern alopecia' must be held partly responsible for the frequent failure to appreciate that in its earlier stages androgenetic alopecia in women need not conform to the 'male pattern' (See Figures 4 & 5 above). As in the male, increased shedding of telogen hairs accompanies the reduction of shaft diameter, but the follicles first affected are more widely distributed over the frontovertical region. As a result, many secondary vellus hairs are interspersed with hairs, which are still normal, and others only slightly reduced in diameter. Partial baldness is sometimes first apparent on the vertex, but the most frequent presentation of androgenetic alopecia in women is as a diffuse alopecia. Ludwig has classified the succession of patterns, which occur in women to produce the distinctive clinical features of 'female pattern alopecia'. However, Venning and Dawber have shown that all women display a change of scalp hair pattern after puberty. The rate of change of patterning is very slow but accelerates during and after the menopause. These workers also showed that hair patterns of the classical 'male type' shown by Hamilton (See Figures 2 & 3) occur with increasing frequency after the menopause. The occurrence of Ludwig pattern III or Hamilton pattern V or greater in a pre-menopausal woman is unlikely. Androgens also stimulate sebaceous gland activity. A full medical history and examination are essential, and in many cases endocrinological investigation is desirable in all women with androgenetic alopecia of rapid onset, even if it be an isolated abnormality, and in women with baldness of gradual onset but accompanied by menstrual disturbance, hirsutism or recrudescence of acne. Hair loss of Hamilton type IV may occur in women without hirsutism but extensive baldness (types VI-VII) is always accompanied by hirsutism. Homoeopathic Repertory: Hair Falling In Handfuls: Phosphorous From forehead: Heper Sulph, Merc Sol, Nat Mur, Phos From Sides: Graphites From Occipit: Carbo Veg., Chellidonium, Petroleum From Temples: Kali Carb, Nat Mur From Vertex: Lycopodium, Bryta Carb, Sulphur, Zinc Met From Grief: Ignatia, Staphisgaria, Acid Phos From Shock: Ignatia, Rescue Remedy (Bach Flower Remedy) During Pregnancy: Lachesis After Delivery: Cal Carb, Carbo Veg, Cantharis, Lycopodium, Nat Mur, Nitric Acid, Sepia, Sulphur Young Age: Acid Phos, Phosphorous, Kali Phos, Bryta Carb, Silicea
7 Old Age Male: Lycopodium, Selenium Old Age Female: Sepia, Sulphur Thyroid Disorders: Thyrodinum, Thallium,Jaborandi, Sepia, Silicea, Sulphur Due to Anemia: Ferrum Phos, Cal Phos, Nat Mur Tension: Kali Phos, Calming*, Tension* * Vibronic Remedies References Text Book of Dermatology Vol. 4 Fifth Edt. By R H Champion, J.L Burton & F.J.G Ebling Materia Medica, Murphy Materia Medica, Kent
Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot
 Chapter 1 All you need to know about hair almost Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot Typically
Chapter 1 All you need to know about hair almost Before you know about your future see your past before improving your future hair see what has been and is the state of your hair now Ravi Bhanot Typically
Hair Chemistry. Chapter 1. Hair Relaxers Science, Design, and Application www.alluredbooks.com
 Hair Relaxers Science, Design, and Application www.alluredbooks.com Chapter 1 Hair Chemistry We all know that the hair on our head is dead, but underneath the scalp, within the hair follicle, is a surprisingly
Hair Relaxers Science, Design, and Application www.alluredbooks.com Chapter 1 Hair Chemistry We all know that the hair on our head is dead, but underneath the scalp, within the hair follicle, is a surprisingly
What is androgenetic alopecia?
 What is androgenetic alopecia? Androgenetic alopecia is also called male pattern alopecia. It refers to a symptom that develops after puberty, influenced by the androgen, where thinning and/or loss of
What is androgenetic alopecia? Androgenetic alopecia is also called male pattern alopecia. It refers to a symptom that develops after puberty, influenced by the androgen, where thinning and/or loss of
PROPERTIES OF THE HAIR AND SCALP
 PROPERTIES OF THE HAIR AND SCALP 1. The scientific study of hair, its diseases and care is called: a. dermatology c. biology b. trichology d. cosmetology 2. The two parts of a mature hair strand are the
PROPERTIES OF THE HAIR AND SCALP 1. The scientific study of hair, its diseases and care is called: a. dermatology c. biology b. trichology d. cosmetology 2. The two parts of a mature hair strand are the
Notes on Hair Analysis
 Notes on Hair Analysis I have found local veterinarians very uncooperative when trying to get samples of dog and cat fur. I have found neighbors, friends and relatives a much better source of fur. There
Notes on Hair Analysis I have found local veterinarians very uncooperative when trying to get samples of dog and cat fur. I have found neighbors, friends and relatives a much better source of fur. There
X-Plain Alopecia Reference Summary
 X-Plain Alopecia Reference Summary Introduction Hair loss is very common in both men and women. You or someone you love may be experiencing hair loss. Hair follicle Learning about normal hair growth is
X-Plain Alopecia Reference Summary Introduction Hair loss is very common in both men and women. You or someone you love may be experiencing hair loss. Hair follicle Learning about normal hair growth is
STOP HAIR LOSS DR JOYCE LIM DERMATOLOGIST PARAGON MEDICAL CENTRE #11-16/20
 STOP HAIR LOSS DR JOYCE LIM DERMATOLOGIST PARAGON MEDICAL CENTRE #11-16/20 HAIR LOSS Types of Hair loss What causes them What are the solutions HAIR LOSS PATCHY HAIR LOSS PATCHY HAIR LOSS Single/ Multiple
STOP HAIR LOSS DR JOYCE LIM DERMATOLOGIST PARAGON MEDICAL CENTRE #11-16/20 HAIR LOSS Types of Hair loss What causes them What are the solutions HAIR LOSS PATCHY HAIR LOSS PATCHY HAIR LOSS Single/ Multiple
Chapter 3 The Study of Hair By the end of the chapter you will be able to:
 Chapter 3 The Study of Hair By the end of the chapter you will be able to: identify the various parts of a hair describe variations in the structure of the medulla, cortex, and cuticle distinguish between
Chapter 3 The Study of Hair By the end of the chapter you will be able to: identify the various parts of a hair describe variations in the structure of the medulla, cortex, and cuticle distinguish between
 no!no! Thermicon: A Novel, Home-based Hair Removal Device Dr. Mira Barki Yavne, Israel Introduction Lasers and intense pulsed light sources have become a popular method for long-term removal of unwanted
no!no! Thermicon: A Novel, Home-based Hair Removal Device Dr. Mira Barki Yavne, Israel Introduction Lasers and intense pulsed light sources have become a popular method for long-term removal of unwanted
www.healthoracle.org 1
 How does hair grow and should it recycle? A single hair follicle grows its hair strand over a period of four to six years (the anagen phase). It then rests for two to four months (the telogen phase), after
How does hair grow and should it recycle? A single hair follicle grows its hair strand over a period of four to six years (the anagen phase). It then rests for two to four months (the telogen phase), after
There are a wide range of factors that can impact on the health of the hair and hair growth.
 Welcome to Viviscal Viviscal, one of the best selling hair growth supplement in the US, is now available with TVSN. The Viviscal brand of hair care products is enjoying rapid and substantial growth in
Welcome to Viviscal Viviscal, one of the best selling hair growth supplement in the US, is now available with TVSN. The Viviscal brand of hair care products is enjoying rapid and substantial growth in
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
Hair loss? I ve got a grip on it! Brochure for women on hair loss and its treatment. Dependably effective against hair loss
 Hair loss? I ve got a grip on it! Brochure for women on hair loss and its treatment Dependably effective against hair loss Hair is part of a woman s natural beauty. Hair loss is more than a medical problem
Hair loss? I ve got a grip on it! Brochure for women on hair loss and its treatment Dependably effective against hair loss Hair is part of a woman s natural beauty. Hair loss is more than a medical problem
All About Human Hair and Hair Loss. 1. Story
 All About Human Hair and Hair Loss 1. Story Hair has always been an important sign of beauty. This is especially true for women. Next to the face, hair is one of the main qualities people look for when
All About Human Hair and Hair Loss 1. Story Hair has always been an important sign of beauty. This is especially true for women. Next to the face, hair is one of the main qualities people look for when
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Getting to the Root of Hair Loss
 26 March 2012 MP3 at voaspecialenglish.com Getting to the Root of Hair Loss Reuters An example of male pattern baldness SHIRLEY GRIFFITH: This is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS in VOA Special English. I'm Shirley
26 March 2012 MP3 at voaspecialenglish.com Getting to the Root of Hair Loss Reuters An example of male pattern baldness SHIRLEY GRIFFITH: This is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS in VOA Special English. I'm Shirley
CHAPTER 6: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
Hair. *credit to Anthony and Patti Bertino for image. Dec 2 8:10 PM
 Hair *credit to Anthony and Patti Bertino for image Dec 2 8:10 PM 1 Essential Question: How can hair be used to solve a crime? Dec 2 8:12 PM 2 History of hair evidence criminal evidence in 1800's 1883
Hair *credit to Anthony and Patti Bertino for image Dec 2 8:10 PM 1 Essential Question: How can hair be used to solve a crime? Dec 2 8:12 PM 2 History of hair evidence criminal evidence in 1800's 1883
HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN. by DAVID SALINGER. www.hair-loss-centre.com.au
 HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN by DAVID SALINGER HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN Loss of hair does worry people and when you realise that so many factors can be responsible for hair loss, you can appreciate that it is important
HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN by DAVID SALINGER HAIR LOSS IN WOMEN Loss of hair does worry people and when you realise that so many factors can be responsible for hair loss, you can appreciate that it is important
Smoothbeam Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris. Emerging Applications
 Smoothbeam Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris Emerging Applications About Acne Vulgaris Very common - Affects 80% of population Almost every person experiences acne Most common reason to visit dermatologist
Smoothbeam Laser Treatment of Acne Vulgaris Emerging Applications About Acne Vulgaris Very common - Affects 80% of population Almost every person experiences acne Most common reason to visit dermatologist
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Lecture Outline Integument Composition 1. Cutaneous membrane A. Epidermis B. Dermis 2. Accessory organs A. Hair B. Exocrine glands C. Nails Functions 1. Protection 2.
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System. What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system?
 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system? 1 Size of the Integument The integument is the largest system of the body: 16% of body weight 1.5
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System What are the structures and functions of the integumentary system? 1 Size of the Integument The integument is the largest system of the body: 16% of body weight 1.5
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial. Cutaneous Mucous Serous
 Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
Two main classes: Epithelial Connective (synovial) Epithelial Cutaneous Mucous Serous Epithelial Membranes = sheet of epithelia + connective tissue base 1. Cutaneous membrane: outer skin layer (stratified
CHEM 107. Hair handout. Basic Structure of Hair. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05
 CHEM 107 Hair handout. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05 Basic Structure of Hair A hair can be defined as a slender, thread-like outgrowth from a follicle in the skin of mammals. Composed mainly of keratin, it has three
CHEM 107 Hair handout. 3-22-05 and 3-24-05 Basic Structure of Hair A hair can be defined as a slender, thread-like outgrowth from a follicle in the skin of mammals. Composed mainly of keratin, it has three
HIRSUTISM. What are the aims of this leaflet?
 HIRSUTISM What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about hirsutism. It tells you what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it, and provides
HIRSUTISM What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about hirsutism. It tells you what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it, and provides
Approved for use September 2015 August 2016 (VERSION 2 ISSUED 16 OCTOBER 2015) Guidance
 Assignment brief Qualification Unit code/title AM20530 VTCT Level 2 Certificate in Hairdressing and Beauty Therapy (VRQ) UV21582 Hair and beauty science Approved for use September 2015 August 2016 (VERSION
Assignment brief Qualification Unit code/title AM20530 VTCT Level 2 Certificate in Hairdressing and Beauty Therapy (VRQ) UV21582 Hair and beauty science Approved for use September 2015 August 2016 (VERSION
Influence of the skin mechanical and microbial properties on hair growth
 Call for Interdisciplinary Projects Sevres 2014 A General Information Project title Influence of the skin mechanical and microbial properties on hair growth Acronym TADDEI: The Ambiguous Dupond and Dupont
Call for Interdisciplinary Projects Sevres 2014 A General Information Project title Influence of the skin mechanical and microbial properties on hair growth Acronym TADDEI: The Ambiguous Dupond and Dupont
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Hair & Fiber. (Unit 5)
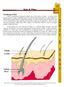 37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
37 Hair & Fiber (Unit 5) Morphology of Hair Hair is encountered as physical evidence in a wide variety of crimes. A review of the forensic aspects of hair examination must start with the observation that
ENDOMETRIOSIS He who knows endometriosis knows gynecology." Sir William Osler
 ENDOMETRIOSIS He who knows endometriosis knows gynecology." Sir William Osler Dr. Sahni BS DHMS Hons, PGRT (BOM), FF Hom Deputy Chief Medical Officer (H), ONGC Hospital Panvel-410221, Navi Mumbai, INDIA
ENDOMETRIOSIS He who knows endometriosis knows gynecology." Sir William Osler Dr. Sahni BS DHMS Hons, PGRT (BOM), FF Hom Deputy Chief Medical Officer (H), ONGC Hospital Panvel-410221, Navi Mumbai, INDIA
MENOPAUSE WOMAN'S TEST (Assessment of hormone balance)
 ATTACHMENT: Useful remarks for patient and doctor, to be associated to the analytical results. Your doctor should interpret this report. Cod. ID: 123456 CCV: 6bf Date: 01/01/2013 Patient: Rossi Mario Rapport
ATTACHMENT: Useful remarks for patient and doctor, to be associated to the analytical results. Your doctor should interpret this report. Cod. ID: 123456 CCV: 6bf Date: 01/01/2013 Patient: Rossi Mario Rapport
Integumentary System CHAPTER. Overview CHAPTER SUMMARY
 CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Overview CHAPTER SUMMARY Skin, the largest organ in the body, forms the integumentary system in conjunction with its accessory structures. The skin consists of two layers:
CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Overview CHAPTER SUMMARY Skin, the largest organ in the body, forms the integumentary system in conjunction with its accessory structures. The skin consists of two layers:
Testosterone. Testosterone For Women
 Testosterone Testosterone is a steroid hormone. Popular use of the term steroid leads people to believe that it signifies a drug that s illegal and abused by some body builders and other athletes. While
Testosterone Testosterone is a steroid hormone. Popular use of the term steroid leads people to believe that it signifies a drug that s illegal and abused by some body builders and other athletes. While
Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Protective Functions. Functions in Sensation. Functions in Excretion. Functions in Temperature Regulation
 Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
Functions INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part of this publication can be used for any commercial
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is a complex disease thought to be caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is a complex disease thought to be caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary
 X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
X-Plain Low Testosterone Reference Summary Introduction Testosterone is the most important male sex hormone. It helps the body produce and maintain adult male features. Low levels of testosterone affect
The Integumentary System
 5 The Integumentary System FOCUS: The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, nails, and a variety of glands. The epidermis of the skin provides protection against abrasion, ultraviolet light,
5 The Integumentary System FOCUS: The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, nails, and a variety of glands. The epidermis of the skin provides protection against abrasion, ultraviolet light,
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Additional information >>> HERE <<< Best Way to Get Cheapest natural remedies hair loss after pregnancy ebook
 Additional information >>> HERE
Additional information >>> HERE
Oxford University Hospitals. NHS Trust. Dermatology Department Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia. Information for patients
 Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Dermatology Department Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Information for patients What is Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA)? FFA is a condition which causes hair loss, mainly
Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust Dermatology Department Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Information for patients What is Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA)? FFA is a condition which causes hair loss, mainly
LASER HAIR REMOVAL: SCIENTIFIC PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICAL ASPECTS
 LASER HAIR REMOVAL: SCIENTIFIC PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICAL ASPECTS ABSTRACT Christine C. Dierickx, M.D. Visiting Research Scientist Wellman Laboratories of Photomedicine Harvard Medical School The use of
LASER HAIR REMOVAL: SCIENTIFIC PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICAL ASPECTS ABSTRACT Christine C. Dierickx, M.D. Visiting Research Scientist Wellman Laboratories of Photomedicine Harvard Medical School The use of
where hair grows Hair Restoration NO SCARS NO PAIN NO STRIPS It s your Hair - 100% Natural Results
 where hair grows Hair Restoration NO SCARS NO PAIN NO STRIPS It s your Hair - 100% Natural Results GOING BALD? HAIR LOSS? THINNING? NO MORE! - HAIR RESTORATION FROM FUECLINICS Hair transplantation involves
where hair grows Hair Restoration NO SCARS NO PAIN NO STRIPS It s your Hair - 100% Natural Results GOING BALD? HAIR LOSS? THINNING? NO MORE! - HAIR RESTORATION FROM FUECLINICS Hair transplantation involves
Please visit your examination provider s website for the most current bulletin prior to testing. IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS
 NATIONAL BARBER THEORY EXAMINATION CANDIDATE INFORMATION BULLETIN Please visit your examination provider s website for the most current bulletin prior to testing. The National Barber Theory Examination
NATIONAL BARBER THEORY EXAMINATION CANDIDATE INFORMATION BULLETIN Please visit your examination provider s website for the most current bulletin prior to testing. The National Barber Theory Examination
Breast Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1. Bonnie A. Barnes, BA, R.T.,(R)(M)(CT)(f) Xuan Ho, Ph.D., R.T.(R)
 Breast Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Bonnie A. Barnes, BA, R.T.,(R)(M)(CT)(f) Xuan Ho, Ph.D., R.T.(R) Key to Quality Mammograms Knowing the anatomy How to position Applying adequate compression Breast
Breast Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Bonnie A. Barnes, BA, R.T.,(R)(M)(CT)(f) Xuan Ho, Ph.D., R.T.(R) Key to Quality Mammograms Knowing the anatomy How to position Applying adequate compression Breast
Hair Analysis 2005, 2004, 2003, 2001, 1999 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved.
 Hair Analysis 2005, 2004, 2003, 2001, 1999 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Hair can be important physical evidence at a crime scene. Hair normally falls from the body over the course of a day. It
Hair Analysis 2005, 2004, 2003, 2001, 1999 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Hair can be important physical evidence at a crime scene. Hair normally falls from the body over the course of a day. It
Client Information for Informed Consent TESTOSTERONE FOR TRANSGENDER PATIENTS
 Client Information for Informed Consent TESTOSTERONE FOR TRANSGENDER PATIENTS You want to take testosterone to masculinize your body. Before taking it, there are several things you need to know about.
Client Information for Informed Consent TESTOSTERONE FOR TRANSGENDER PATIENTS You want to take testosterone to masculinize your body. Before taking it, there are several things you need to know about.
There are four areas where you can expect changes to occur as your hormone therapy progresses.
 You are considering taking testosterone, so you should learn about some of the risks, expectations, long term considerations, and medications associated with medical transition. If is very important to
You are considering taking testosterone, so you should learn about some of the risks, expectations, long term considerations, and medications associated with medical transition. If is very important to
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Thomas T. Jeneby, M.D. 7272 Wurzbach Suite 801 San Antonio, TX. 78240 210-782-8269/210 270 8595
 Laser hair removal is one of the most popular cosmetic procedures performed. Unwanted hair grows on various regions of the body. Often, individuals find the presence of hair in certain regions of the body
Laser hair removal is one of the most popular cosmetic procedures performed. Unwanted hair grows on various regions of the body. Often, individuals find the presence of hair in certain regions of the body
It works. Hair loss prevention and hair regeneration study
 Hair loss prevention and hair regeneration study Report of the findings of the clinical trial to evaluate the effectiveness of VR6 hair treatment Study conducted by: Centro de Tecnología Capilar, SL Report
Hair loss prevention and hair regeneration study Report of the findings of the clinical trial to evaluate the effectiveness of VR6 hair treatment Study conducted by: Centro de Tecnología Capilar, SL Report
A Free Guide to different Hair Removal Treatments
 A Free Guide to different Hair Removal Treatments 2 Introduction From peach-fuzz to long, dark, or coarse growth, both men and women have been doing battle with excess hair -and hair removal - for centuries.
A Free Guide to different Hair Removal Treatments 2 Introduction From peach-fuzz to long, dark, or coarse growth, both men and women have been doing battle with excess hair -and hair removal - for centuries.
HEALTH UPDATE. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
 HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Acne. Sofia Chaudhry M.D. Histology of an inflamed comedo. Bolognia, 2008.
 Acne Sofia Chaudhry M.D. Histology of an inflamed comedo. Bolognia, 2008. Acne Vulgaris (Common Acne) Multifactorial disorder of pilosebaceous unit Affects 40-50 million individuals annually in U.S. alone
Acne Sofia Chaudhry M.D. Histology of an inflamed comedo. Bolognia, 2008. Acne Vulgaris (Common Acne) Multifactorial disorder of pilosebaceous unit Affects 40-50 million individuals annually in U.S. alone
Lesions, and Masses, and Tumors Oh My!!
 Lesions, and Masses, and Tumors Oh My!! Presented by: Susan Ward, CPC, CPC-H, CPC-I, CPCD, CEMC, CPRC 1 1 CPT GUIDELINES Agenda CPT DEFINITIONS OP REPORT CASES 2 Definitions Cyst - a closed sac having
Lesions, and Masses, and Tumors Oh My!! Presented by: Susan Ward, CPC, CPC-H, CPC-I, CPCD, CEMC, CPRC 1 1 CPT GUIDELINES Agenda CPT DEFINITIONS OP REPORT CASES 2 Definitions Cyst - a closed sac having
Pseudohypoparathyroidism: A Variation on the Theme of Hypoparathyroidism
 Pseudohypoparathyroidism: A Variation on the Theme of Hypoparathyroidism Amanda Tencza MS IV 1 and Michael A. Levine, MD 2 1 Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University
Pseudohypoparathyroidism: A Variation on the Theme of Hypoparathyroidism Amanda Tencza MS IV 1 and Michael A. Levine, MD 2 1 Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine of Case Western Reserve University
Secrets of Your. Skin & Hair. sweat gland. hair. dermis epidermis. muscle subdermis. by Michael Bono. www.bonoelectrolysis.com
 Secrets of Your Skin & Hair hair sweat gland dermis epidermis muscle subdermis by Michael Bono 1 2 Preface... I ve been in the business of hair removal (electrolysis) since 1975 and have seen countless
Secrets of Your Skin & Hair hair sweat gland dermis epidermis muscle subdermis by Michael Bono 1 2 Preface... I ve been in the business of hair removal (electrolysis) since 1975 and have seen countless
Hair Loss: An Insider Guide to Hair Restoration and Replacement
 Hair Loss: An Insider Guide to Hair Restoration and Replacement November 2013 Why you may want more hair. Typically, people don t realize their hair is thinning until they ve lost 50% of it. By age 35,
Hair Loss: An Insider Guide to Hair Restoration and Replacement November 2013 Why you may want more hair. Typically, people don t realize their hair is thinning until they ve lost 50% of it. By age 35,
Integumentary System (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Integumentary System (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Integument = covering ~16% of body mass: ~2 meter 2 Primary Sources for figures
Integumentary System (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Integument = covering ~16% of body mass: ~2 meter 2 Primary Sources for figures
Acne (Acne Vulgaris) A common type of bacteria that lives on the skin, known as Propionibacterium acnes, sometimes
 Acne (Acne Vulgaris) Acne, clinically known as acne vulgaris, is the most common skin disease. It affects 85% of teenagers, some as young as 12, and often continues into adulthood. It is also called pimples,
Acne (Acne Vulgaris) Acne, clinically known as acne vulgaris, is the most common skin disease. It affects 85% of teenagers, some as young as 12, and often continues into adulthood. It is also called pimples,
Hair Analysis Notes. Hair s Anatomy
 Hair Analysis Notes Human hair is one of the most frequently found pieces of physical evidence located at the scene of a violent crime and can provide a substantive link between the criminal and their
Hair Analysis Notes Human hair is one of the most frequently found pieces of physical evidence located at the scene of a violent crime and can provide a substantive link between the criminal and their
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
BRCA Genes and Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer. Patient information leaflet
 BRCA Genes and Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer Patient information leaflet This booklet has been written for people who have a personal or family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer that could
BRCA Genes and Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer Patient information leaflet This booklet has been written for people who have a personal or family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer that could
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF BioBeam TM Acne
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF BioBeam TM Acne BioBeam ACNE is a Class 2A phototherapeutic medical device and complies with Annex VI of the Medical Device Directive 93/42/EEC and is CE certified (CE 0473). BioBeam
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF BioBeam TM Acne BioBeam ACNE is a Class 2A phototherapeutic medical device and complies with Annex VI of the Medical Device Directive 93/42/EEC and is CE certified (CE 0473). BioBeam
The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
Breast Cancer. Sometimes cells keep dividing and growing without normal controls, causing an abnormal growth called a tumor.
 Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Breast Cancer Introduction Cancer of the breast is the most common form of cancer that affects women but is no longer the leading cause of cancer deaths. About 1 out of 8 women are diagnosed with breast
Not Your Father s Hair Restoration: The Latest Clinical Advancements from Lasers to Robots in Treating in Men and Women
 Not Your Father s Hair Restoration: The Latest Clinical Advancements from Lasers to Robots in Treating in Men and Women Robert T. Leonard, Jr., DO, FAACS, FISHRS Founder and Chief Surgeon Leonard Hair
Not Your Father s Hair Restoration: The Latest Clinical Advancements from Lasers to Robots in Treating in Men and Women Robert T. Leonard, Jr., DO, FAACS, FISHRS Founder and Chief Surgeon Leonard Hair
Countless medications, nutrients, herbs, and chemicals have
 9Drugs That Grow Hair Countless medications, nutrients, herbs, and chemicals have been claimed to stop or reverse hair loss, however when tested scientifically in well controlled, double-blind clinical
9Drugs That Grow Hair Countless medications, nutrients, herbs, and chemicals have been claimed to stop or reverse hair loss, however when tested scientifically in well controlled, double-blind clinical
The Patient s Guide to Hair Restoration
 The Patient s Guide to Hair Restoration William R. Rassman, M.D. Robert M. Bernstein, M.D. Contributions by Robert McClellan, M.D., Roy Jones, M.D., Marc Pomerantz, M.D., and Richard C. Shiell, M.D. www.newhair.com
The Patient s Guide to Hair Restoration William R. Rassman, M.D. Robert M. Bernstein, M.D. Contributions by Robert McClellan, M.D., Roy Jones, M.D., Marc Pomerantz, M.D., and Richard C. Shiell, M.D. www.newhair.com
Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer: Questions and Answers
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Adjuvant Therapy for Breast
X-Plain Acne Reference Summary
 X-Plain Acne Reference Summary Introduction Nearly 17 million people in the United States have acne, making it one of the most common skin diseases in the USA. Although acne is not a serious health threat,
X-Plain Acne Reference Summary Introduction Nearly 17 million people in the United States have acne, making it one of the most common skin diseases in the USA. Although acne is not a serious health threat,
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Human Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory The Circulation (Two Weeks) 1 This lab involves two weeks work studying the vasculature of the human body. Both weeks involve the exercise in the lab manual entitled
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam #2
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court. A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and
 Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN
 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN The skin is an amazing structure; it is the largest organ of the body containing many structures such as capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, glands and
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE SKIN The skin is an amazing structure; it is the largest organ of the body containing many structures such as capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, glands and
Introduction to puberty
 Introduction to puberty Objective: Structure: Time: Materials: Participants will describe some of the common external changes associated with puberty. Presentation by educator with large group discussion.
Introduction to puberty Objective: Structure: Time: Materials: Participants will describe some of the common external changes associated with puberty. Presentation by educator with large group discussion.
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES
 DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
DIAGNOSING CHILDHOOD MUSCULAR DYSTROPHIES Extracts from a review article by KN North and KJ Jones: Recent advances in diagnosis of the childhood muscular dystrophies Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
Chapter 12: Physical and Cognitive Development in Adolescence
 Chapter 12: Physical and Cognitive Development in Adolescence McGraw-Hill 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. The Nature of Adolescence What physical changes occur in adolescence?
Chapter 12: Physical and Cognitive Development in Adolescence McGraw-Hill 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. The Nature of Adolescence What physical changes occur in adolescence?
Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too.
 Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Male Breast Cancer Introduction Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the cells of the breast. Breast cancer happens mainly in women. But men can get it too. Many people do not know that men can get breast
Development of Teeth
 Development of Teeth Dr. Khaldoun Darwich Specialist in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery Hamburg University PhD Hamburg University Academic Teacher - Department of OMF Surgery in Damascus University Instructor
Development of Teeth Dr. Khaldoun Darwich Specialist in Oral and Maxillo-Facial Surgery Hamburg University PhD Hamburg University Academic Teacher - Department of OMF Surgery in Damascus University Instructor
Baby Lab. Class Copy. Introduction
 Class Copy Baby Lab Introduction The traits on the following pages are believed to be inherited in the explained manner. Most of the traits, however, in this activity were created to illustrate how human
Class Copy Baby Lab Introduction The traits on the following pages are believed to be inherited in the explained manner. Most of the traits, however, in this activity were created to illustrate how human
The Journal of Integrated Health Sciences
 JIHS Available online at www.jihs.in The Journal of Integrated Health Sciences A study of endocrine profile in premenopausal women with hirsutism Lakhani Som J 1*, Lakhani Om J 2, Raval RC 3 1 Assistant
JIHS Available online at www.jihs.in The Journal of Integrated Health Sciences A study of endocrine profile in premenopausal women with hirsutism Lakhani Som J 1*, Lakhani Om J 2, Raval RC 3 1 Assistant
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components
 Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Sex for the purposes of this class refers to 4 components Gonadal sex Gonads or where gametes are produced by meiosis Somatic sex Somatic cells are cells that undergo mitosis. They can be divided into
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
 POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles. Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully
 Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully Multiple alleles: three or more alleles for a trait are found in the
Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully Multiple alleles: three or more alleles for a trait are found in the
Informed Consent Form for Testosterone Therapy
 Student Health Services Oregon State University, 201 Plageman Building, Corvallis, Oregon 97331-8567 Tel 541-737-9355 General Fax 541-737-4530 Medical Fax 541-737-9665 http://studenthealth.oregonstate.edu/
Student Health Services Oregon State University, 201 Plageman Building, Corvallis, Oregon 97331-8567 Tel 541-737-9355 General Fax 541-737-4530 Medical Fax 541-737-9665 http://studenthealth.oregonstate.edu/
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure
 Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Biology 2401 - Anatomy and Physiology I Exam 1 notes - Introduction, Cell and Tissue Structure Two major principles in study of animal bodies: (humans, like other living organisms are product of evolutionary
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen
 I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
About The Causes of Hearing Loss
 About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
About 1 in 500 infants is born with or develops hearing loss during early childhood. Hearing loss has many causes: some are genetic (that is, caused by a baby s genes) or non-genetic (such as certain infections
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
 Centre for Diabetes and Endocrinology - Patient information Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) Approximately 1 in 5 women have polycystic ovaries. This describes the appearance of the ovaries when they are
Centre for Diabetes and Endocrinology - Patient information Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) Approximately 1 in 5 women have polycystic ovaries. This describes the appearance of the ovaries when they are
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA
 CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
CHROMOSOMES Dr. Fern Tsien, Dept. of Genetics, LSUHSC, NO, LA Cytogenetics is the study of chromosomes and their structure, inheritance, and abnormalities. Chromosome abnormalities occur in approximately:
Information About Hormonal Treatment for
 Information About Hormonal Treatment for Trans Men Leighton J Seal PhD FRCP Consultant Endocrinologist, Gender Identity Clinic, West London Mental Health NHS Trust (Charing Cross) Leighton J Seal 1 Patient
Information About Hormonal Treatment for Trans Men Leighton J Seal PhD FRCP Consultant Endocrinologist, Gender Identity Clinic, West London Mental Health NHS Trust (Charing Cross) Leighton J Seal 1 Patient
The Background for the Diabetes Detection Model
 The Background for the Diabetes Detection Model James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 23, 2014 Outline The Background for
The Background for the Diabetes Detection Model James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 23, 2014 Outline The Background for
What is DCIS? Contents. The breasts
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding ductal carinoma in situ (DCIS). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 6. Contents The breasts What is
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding ductal carinoma in situ (DCIS). You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 6. Contents The breasts What is
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
