The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
|
|
|
- Olivia Hoover
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg C. sex steroid hormones estrogen & progesterone The menstrual cycle includes cycles observed in the ovary, in plasma levels of reproductive hormones, and in the uterus. This activity looks at each of these cycles and the relationships among them. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells oocytes 2. How many days are shown for this typical ovarian cycle? An ovarian follicle is an oocyte (developing egg) and its supporting or follicular cells in any stage of development, from immature to mature. Label the oocyte and the follicular cells in Model The ovarian cycle is subdivided into three phases. Complete the table below with information from Model 1. Ovarian Phase Name Days of Cycle Ovarian Events Follicular phase 1-13 Ovarian follicle develops Ovulation 14 Oocyte is released Luteal phase Corpus luteum forms then breaks down 5. When ovulation occurs, where does the oocyte go? Into the uterine tube
2 6. The corpus luteum is made from transformed cells. Where do these cells come from? Follicular cells remaining in the ovary after the mature follicle ruptures and releases the oocyte. 7. What happens to the corpus luteum near the end of the cycle? Predict the effect this has on its function. Corpus luteum regresses near the end of the cycle. It has a finite lifespan of days unless stimulated by HCG. As a result of the corpus luteum regressing, its function declines. Model 2: Ovarian Cycle + Plasma Levels of Sex Steroid Hormones 8. Name the two sex steroid hormones in Model 2. estrogen & progesterone 9. Name the ovarian phase(s) during which each hormone is secreted: Estrogen follicular & luteal phases Progesterone luteal phase 10. Predict the specific source(s) of each hormone: Estrogen follicular cells & corpus luteum Progesterone corpus luteum 11. Name the ovarian phase during which each hormone reaches its peak: Estrogen near the end of the follicular phase
3 Progesterone mid luteal phase 12. Plasma levels of both sex steroid hormones decrease near the end of the cycle. Predict the cause of this. Regression of the corpus luteum Model 3: Ovarian Cycle + Plasma Levels of Gonadotropins and Sex Steroid Hormones 13. The anterior pituitary secretes two gonadotropins. Name them, including both the abbreviated and long versions of their names. FSH = Follicle Stimulating Hormone LH = Luteinizing Hormone
4 14. What is the target tissue of these gonadotropins? ovaries 15. Plasma levels of gonadotropins peak on day 13. What ovarian event immediately follows the surge in LH? ovulation 16. Using your knowledge of the endocrine system and male hormones, complete this flow chart showing the relationship among female hormones, their sources, and their effects. Possible terms include: corpus luteum, estrogen, follicle cells, FSH, gametes/oocytes/ova, GnRH, LH, progesterone. GnRH FSH LH estrogen gametes corpus luteum 17. Progesterone exerts a negative feedback on LH and FSH release. A. In the flow chart above, draw in the arrow/line showing this negative feedback. B. Explain the meaning of negative feedback. Response lessens the stimulus 18. Estrogen is special in that it exerts both a negative and positive feedback on LH. The type of feedback depends on the concentration of estrogen. A. Explain the difference between negative feedback and positive feedback. Negative - response lessens the stimulus; important in homeostasis because it maintains variables within physiological ranges Positive response adds to the stimulus; used less often in homeostasis but is important in the menstrual cycle to stimulate ovulation.
5 B. Examine Model 3 to determine the feedback and circle the correct responses below. A small rise in estrogen levels (inhibits/stimulates) LH release; this shows (negative/positive) feedback on the anterior pituitary. High estrogen levels (inhibit/stimulate) LH release; this shows (negative/positive) feedback on the anterior pituitary. Model 4: Ovarian Cycle + Plasma Levels of Gonadotropins and Sex Steroid Hormones + Uterine Cycle
6 19. What part of the uterus is shown in Model 4? Which layer of the uterine wall is this? Endometrium the uterine lining 20. What event signals the start of the uterine cycle? Why do you think this event was chosen as the starting time? Onset of menstruation; it s the one event that is quite obvious and easily detected 21. The uterine cycle is subdivided into three phases. Fill in the information about these phases in the table below. Uterine Phase Name Days of Cycle Endometrial Events Menstruation 1-5 Shedding of the endometrium Proliferative phase 6-14 Rebuilding of the endometrium Secretory phase Endometrial glands and vasculature develop so that the lining becomes thicker 22. Each phase of the uterine cycle is associated with a phase of the ovarian cycle. Fillin the table below showing these associations. Days of Menstrual Ovarian Cycle Phase Uterine Cycle Phase Cycle 1-5 Follicular phase Menstruation 6-13 Follicular phase Proliferative phase 14 Ovulation Proliferative phase Luteal phase Secretory phase 23. Is the uterine cycle more directly influenced by gonadotropin or sex steroid levels? Explain. Sex steroids directly target the endometrium and affect is growth and development. 24. Describe the relationship between the elevated levels of progesterone during the luteal phase and the thickness of the endometrium days High levels of progesterone stimulate increased vasculature and glandular growth so the endometrium becomes thick, and ready for implantation. 25. What causes the decreased thickness of the endometrium near the end of the cycle? Regression of the corpus luteum decreased levels of estrogen & progesterone endometrium is no longer maintained menstruation will start soon.
7 Applications Questions: 26. What is menarche? What causes menarche? Menarche = first menstrual period. Changes in the hypothalamus occur increased GnRH increased gonadotropins secreted stimulation of the ovary beginning of a menstrual cycle. 27. What is menopause? What causes menopause? Menopause = no menstrual period for one year. The ovaries become refractory to the gonadotropins decreased secretion of estrogen and progesterone the endometrium no longer goes through the uterine cycle. 28. Why is it important for the endometrium to increase in thickness and vascularity during the menstrual cycle? Provides environment needed for implantation. 29. List three possible sources of reproductive failure (infertility) in females. Abnormal levels or cycling of gonadotropins and/or sex steroids Abnormal response of ovaries and/or endometrium to hormones Blockage of the uterine tubes 30. Predict changes that would occur in the uterine cycle if fertilization and implantation occur. (What are fertilization and implantation?) Fertilization = union of sperm and egg (secondary oocyte) Implantation = blastocyst settles into and interacts with endometrium; soon a placenta begins to develop. If fertilization and implantation occur, HCG is secreted corpus luteum is stimulated and does not regress estrogen & progesterone levels increase endometrium is maintained/grows thicker and menstruation does not occur. 31. If a woman has one ovary surgically removed, can she still become pregnant? Explain. She can still become pregnant because she has everything needed. 32. Considering Model 4, explain possible mechanisms of hormonal birth control methods. Combination pill contains estrogen & a progestin. If these steroid levels are maintained at a constant level, estrogen does not exert a positive feedback the LH surge does not occur ovulation does not occur (and follicles probably do not develop normally). Depo Provera is a progestin which exerts negative feedback and blocks typical ovarian cycles. 33. Do hormonal forms of birth control reduce one s chances of getting a STI/STD during sexual activity? Explain. No, they do not provide any mechanical barrier between the male and female genitals.
1. AMOUNT OF FSH PRESENT
 The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control
 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment
 The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels. Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College
 From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
Timing is everything. Ovulation Tracking. Patient Information Booklet
 Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Endocrinology of the Female Reproductive Axis
 Endocrinology of the Female Reproductive Axis girlontheriver.com Geralyn Lambert-Messerlian, PhD, FACB Professor Women and Infants Hospital Alpert Medical School at Brown University Women & Infants BROWN
Endocrinology of the Female Reproductive Axis girlontheriver.com Geralyn Lambert-Messerlian, PhD, FACB Professor Women and Infants Hospital Alpert Medical School at Brown University Women & Infants BROWN
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
The Endocrine System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Slides 9.1 9.48 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Endocrine System Second messenger
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Slides 9.1 9.48 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Endocrine System Second messenger
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
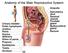 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
FERTILITY AND AGE. Introduction. Fertility in the later 30's and 40's. Am I fertile?
 FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court. A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and
 Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
SYNCHRONIZATION OF CATTLE
 UNDER ESTRUS SYNCHRONIZATION OF CATTLE FS921C Robin Salverson, Extension Livestock Educator, Harding County, and George Perry, Extension Beef Reproduction and Management Specialist Reproductive failure
UNDER ESTRUS SYNCHRONIZATION OF CATTLE FS921C Robin Salverson, Extension Livestock Educator, Harding County, and George Perry, Extension Beef Reproduction and Management Specialist Reproductive failure
HEALTH UPDATE. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
 HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Medications for Inducing Ovulation
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Medications for Inducing Ovulation A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Medications for Inducing Ovulation A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
 POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
How do fertility drugs work?
 How do fertility drugs work? Under normal circumstances, ovulation occurs once a month when a ripened egg which is ready to be fertilised is released from the ovaries. For couples who are trying to conceive,
How do fertility drugs work? Under normal circumstances, ovulation occurs once a month when a ripened egg which is ready to be fertilised is released from the ovaries. For couples who are trying to conceive,
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproduction: Control of Ovarian Function
 2 Female Reproduction: Control of Ovarian Function F E Robinson and R A Renema Alberta Poultry Research Centre, University of Alberta Edmonton, AB, Canada T6G 2P5 Introduction The control of the release
2 Female Reproduction: Control of Ovarian Function F E Robinson and R A Renema Alberta Poultry Research Centre, University of Alberta Edmonton, AB, Canada T6G 2P5 Introduction The control of the release
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida. Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Ovarian Cysts in Dairy Cattle
 AS-451-W Reviewed 2001 Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service West Lafayette, IN 47907 Ovarian Cysts in Dairy Cattle R. D. Allrich, Department of Animal Sciences Purdue University, West Lafayette,
AS-451-W Reviewed 2001 Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service West Lafayette, IN 47907 Ovarian Cysts in Dairy Cattle R. D. Allrich, Department of Animal Sciences Purdue University, West Lafayette,
Artificial insemination
 Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Welcome. Thank you for purchasing the OvaCue Fertility Monitor!
 Owners Manual Welcome Thank you for purchasing the OvaCue Fertility Monitor! Recommended by fertility specialists, this convenient, easy to use fertility monitor provides up to seven days advance notice
Owners Manual Welcome Thank you for purchasing the OvaCue Fertility Monitor! Recommended by fertility specialists, this convenient, easy to use fertility monitor provides up to seven days advance notice
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
AB N O R M A LUT E R I N E BL E E D I N G
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE AB N O R M A LUT E R I N E BL E E D I N G A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE AB N O R M A LUT E R I N E BL E E D I N G A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
Patient Information: Endometriosis Disease Process and Treatment
 1 William N. Burns, M. D. Associate Professor Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine Marshall University Huntington, West Virginia, USA Patient Information: Endometriosis
1 William N. Burns, M. D. Associate Professor Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine Marshall University Huntington, West Virginia, USA Patient Information: Endometriosis
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects as many as 5 10% of women. PCOS has three key features: 1) high levels of hormones called androgens; 2) irregular menstrual
Endocrine System Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Endocrine System Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Endocrine System Review Consists of discrete individual
Endocrine System Review Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Endocrine System Review Consists of discrete individual
Outline Fertilization Gametes Germ Cells Meiosis Male Reproductive Tract Spermatogenesis Female Reproductive Tract Oogenesis Menstrual Cycle Hormones
 Outline Fertilization Gametes Germ Cells Meiosis Male Reproductive Tract Spermatogenesis Female Reproductive Tract Oogenesis Menstrual Cycle Hormones Fertilization Gametes Oocyte, Sperm Acrosomal reaction
Outline Fertilization Gametes Germ Cells Meiosis Male Reproductive Tract Spermatogenesis Female Reproductive Tract Oogenesis Menstrual Cycle Hormones Fertilization Gametes Oocyte, Sperm Acrosomal reaction
Understanding Blood Tests - Pregnancy/Fertility Monitoring by Beth Anne Ary M.D
 Understanding Blood Tests - Pregnancy/Fertility Monitoring by Beth Anne Ary M.D Blood tests are the most common and most important method of monitoring pregnancy-- both assisted pregnancies, and unassisted.
Understanding Blood Tests - Pregnancy/Fertility Monitoring by Beth Anne Ary M.D Blood tests are the most common and most important method of monitoring pregnancy-- both assisted pregnancies, and unassisted.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Signs, symptoms, and treatments What is PCOS? Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects up to 1 in 10 women of reproductive
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Signs, symptoms, and treatments What is PCOS? Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects up to 1 in 10 women of reproductive
Welcome to chapter 8. The following chapter is called "Monitoring IVF Cycle & Oocyte Retrieval". The author is Professor Jie Qiao.
 Welcome to chapter 8. The following chapter is called "Monitoring IVF Cycle & Oocyte Retrieval". The author is Professor Jie Qiao. The learning objectives of this chapter are 2 fold. The first section
Welcome to chapter 8. The following chapter is called "Monitoring IVF Cycle & Oocyte Retrieval". The author is Professor Jie Qiao. The learning objectives of this chapter are 2 fold. The first section
Infertility: An Overview
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook
 In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
regulation of ECF composition and volume regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon
 Hormonal Effects regulation of ECF composition and volume ADH, aldosterone, ANF regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon regulation of muscle contraction
Hormonal Effects regulation of ECF composition and volume ADH, aldosterone, ANF regulation of metabolism thyroid hormones, epinephrine, growth hormone, insulin and glucagon regulation of muscle contraction
Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO
 9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
HOW IS OVARIAN RESERVE ASSESSED?
 HOW IS OVARIAN RESERVE ASSESSED? The majority of indicators we have to assess OR assess egg quantity rather than egg quality and these two do not always go hand in hand. No individual test is a perfect
HOW IS OVARIAN RESERVE ASSESSED? The majority of indicators we have to assess OR assess egg quantity rather than egg quality and these two do not always go hand in hand. No individual test is a perfect
Medications for Inducing Ovulation
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Medications for Inducing Ovulation A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Medications for Inducing Ovulation A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Symposium on RECENT ADVANCES IN ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY
 Symposium on RECENT ADVANCES IN ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY Dr Niel Senewirathne Senior Consultant of Obstetrician & Gynaecologist De zoyza Maternity Hospita 1 ART - IVF & ICSI 2 Infertility No pregnancy
Symposium on RECENT ADVANCES IN ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY Dr Niel Senewirathne Senior Consultant of Obstetrician & Gynaecologist De zoyza Maternity Hospita 1 ART - IVF & ICSI 2 Infertility No pregnancy
Preventive Powers of Ovulation and Progesterone
 Preventive Powers of Ovulation and Progesterone Detection of Ovulation by Dr. Jerilynn C. Prior, Scientific Director, Centre for Menstrual Cycle and Ovulation Research. I believe that ovulation with a
Preventive Powers of Ovulation and Progesterone Detection of Ovulation by Dr. Jerilynn C. Prior, Scientific Director, Centre for Menstrual Cycle and Ovulation Research. I believe that ovulation with a
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
PUBERTY. Dr. Valérie M. Schwitzgebel. Division of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology Hôpital des Enfants HUG Genève Valerie.Schwitzgebel@hcuge.
 PUBERTY Dr. Valérie M. Schwitzgebel Division of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology Hôpital des Enfants HUG Genève [email protected] V. Schwitzgebel 2004 PHYSIOLOGY of PUBERTY DEFINITION
PUBERTY Dr. Valérie M. Schwitzgebel Division of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology Hôpital des Enfants HUG Genève [email protected] V. Schwitzgebel 2004 PHYSIOLOGY of PUBERTY DEFINITION
COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF ILLINOIS, INC. COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF MISSOURI, INC. Medical Management Policy and Procedure PROPRIETARY
 COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF ILLINOIS, INC. COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF MISSOURI, INC. Medical Management Policy and Procedure PROPRIETARY Policy: Infertility Evaluation and Treatment Number: MM 1306 Date Effective:
COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF ILLINOIS, INC. COVENTRY HEALTH CARE OF MISSOURI, INC. Medical Management Policy and Procedure PROPRIETARY Policy: Infertility Evaluation and Treatment Number: MM 1306 Date Effective:
Ectopic Pregnancy. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Ectopic Pregnancy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Ectopic Pregnancy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
For The Providers of Youth Friendly Services
 For The Providers of Youth Friendly Services FAMILY PLANNING AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH In July 2011, FHI became FHI 360. FHI 360 is a nonprofit human development organization dedicated to improving lives
For The Providers of Youth Friendly Services FAMILY PLANNING AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH In July 2011, FHI became FHI 360. FHI 360 is a nonprofit human development organization dedicated to improving lives
AGE & FERTILITY: Effective Evaluation & Treatment I. LANE WONG, MD, FACOG. www.hopefertilitycenter.com www.hopeivf.com
 Page 1 of 6 AGE & FERTILITY: Effective Evaluation & Treatment I. LANE WONG, MD, FACOG. www.hopefertilitycenter.com www.hopeivf.com Age has a profound effect on female fertility. This is common knowledge,
Page 1 of 6 AGE & FERTILITY: Effective Evaluation & Treatment I. LANE WONG, MD, FACOG. www.hopefertilitycenter.com www.hopeivf.com Age has a profound effect on female fertility. This is common knowledge,
Guidelines for Ordering Serum Levels of Gonadotropins (FSH, LH) and Prolactin CLP 021 Revised June, 2008 (Replaces October 2000 version)
 Guidelines for Ordering Serum Levels of Gonadotropins (FSH, LH) and Prolactin CLP 021 Revised June, 2008 (Replaces October 2000 version) 1. Scope This laboratory Guideline is intended to assist community
Guidelines for Ordering Serum Levels of Gonadotropins (FSH, LH) and Prolactin CLP 021 Revised June, 2008 (Replaces October 2000 version) 1. Scope This laboratory Guideline is intended to assist community
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility
 Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
Getting Pregnant: The Natural Approach Revealing the Secrets to Increase Your Fertility Page 1 Contents Introduction 3 Part I Understanding Fertility and Infertility Chapter 1: What is Fertility? 4 - Signs
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
The IUI procedure Who should consider an IUI IUI success rates IUI cost What to consider if IUI is unsuccessful. The IUI procedure:
 A Complete Guide to understanding IUI (intrauterine insemination) and artificial insemination (Eric Daiter, MD Board Certified in Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility) The IUI procedure Who should
A Complete Guide to understanding IUI (intrauterine insemination) and artificial insemination (Eric Daiter, MD Board Certified in Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility) The IUI procedure Who should
Connecting the Dots: Basal Body Temperature Charting BBT charting: A useful tool to identify your body composition and monitor your progress
 Connecting the Dots: Basal Body Temperature Charting BBT charting: A useful tool to identify your body composition and monitor your progress By Michelle Buchanan, Certified Acupuncturist The History of
Connecting the Dots: Basal Body Temperature Charting BBT charting: A useful tool to identify your body composition and monitor your progress By Michelle Buchanan, Certified Acupuncturist The History of
Hirsutism and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Hirsutism and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Hirsutism and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under
The relevant NICE Clinical Guidance 156, Fertility can be accessed here: http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg156
 City and Hackney CCG Fertility policy Approved January 2015 Introduction City and Hackney CCG is responsible for commissioning a range of health services including hospital, mental health and community
City and Hackney CCG Fertility policy Approved January 2015 Introduction City and Hackney CCG is responsible for commissioning a range of health services including hospital, mental health and community
Fertility Preservation in Women with Cancer. Objectives. Patient #1 10/24/2011. The audience will understand: How cancer therapy affects fertility.
 Fertility Preservation in Women with Cancer Leslie R. DeMars Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Objectives The audience will understand: How cancer therapy affects fertility. Who should be considered for
Fertility Preservation in Women with Cancer Leslie R. DeMars Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Objectives The audience will understand: How cancer therapy affects fertility. Who should be considered for
GLOSSARY. A Abstinence: having no vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It is the only method that is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and STI s.
 WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
MINISTRY OF HEALTH Quality and Service Administration. Fe r t i l i z at i o n. to I n - V i t r o. G u i d e. i n I s r a e l
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH Quality and Service Administration G u i d e to I n - V i t r o Fe r t i l i z at i o n i n I s r a e l Contents Introduction 3 The Natural Fertilization Process 4 In Vitro Fertilization
MINISTRY OF HEALTH Quality and Service Administration G u i d e to I n - V i t r o Fe r t i l i z at i o n i n I s r a e l Contents Introduction 3 The Natural Fertilization Process 4 In Vitro Fertilization
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma)
 Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Uterine fibroids (Leiomyoma) What are uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids are fairly common benign (not cancer) growths in the uterus. They occur in about 25 50% of all women. Many women who have fibroids
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE and ITS RELATION TO CONTRACEPTIVE METHODS. A Reference for Reproductive Health Trainers
 THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE and ITS RELATION TO CONTRACEPTIVE METHODS A Reference for Reproductive Health Trainers Grace Mtawali Manuel Pina Marcia Angle Catherine Murphy This publication was produced by INTRAH
THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE and ITS RELATION TO CONTRACEPTIVE METHODS A Reference for Reproductive Health Trainers Grace Mtawali Manuel Pina Marcia Angle Catherine Murphy This publication was produced by INTRAH
Reproductive Technology. Chapter 21
 Reproductive Technology Chapter 21 Assisted Reproduction When a couple is sub-fertile or infertile they may need Assisted Reproduction to become pregnant: Replace source of gametes Sperm, oocyte or zygote
Reproductive Technology Chapter 21 Assisted Reproduction When a couple is sub-fertile or infertile they may need Assisted Reproduction to become pregnant: Replace source of gametes Sperm, oocyte or zygote
Tower Hamlets CCG Fertility policy
 Tower Hamlets CCG Fertility policy Approved December 2014 Introduction Tower Hamlets CCG is responsible for commissioning a range of health services including hospital, mental health and community services
Tower Hamlets CCG Fertility policy Approved December 2014 Introduction Tower Hamlets CCG is responsible for commissioning a range of health services including hospital, mental health and community services
Reproduction in Mammals
 Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Chapter 45: Hormones and the Endocrine System
 Name Period Overview 1. What is a hormone? 2. Why does a hormone elicit a response only with target cells? 3. The body has two long-distance regulating systems. Which involves chemical signals by hormones?
Name Period Overview 1. What is a hormone? 2. Why does a hormone elicit a response only with target cells? 3. The body has two long-distance regulating systems. Which involves chemical signals by hormones?
THE CENTER FOR ADVANCED REPRODUCTIVE SERVICES (CARS) (The Center) CONSENT FOR IN VITRO FERTILIZATION AND EMBRYO TRANSFER
 THE CENTER FOR ADVANCED REPRODUCTIVE SERVICES (CARS) (The Center) CONSENT FOR IN VITRO FERTILIZATION AND EMBRYO TRANSFER Partner #1 Last Name (Surname): Partner #1 First Name: Partner #1 Last 5 Digits
THE CENTER FOR ADVANCED REPRODUCTIVE SERVICES (CARS) (The Center) CONSENT FOR IN VITRO FERTILIZATION AND EMBRYO TRANSFER Partner #1 Last Name (Surname): Partner #1 First Name: Partner #1 Last 5 Digits
LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The only system not essential for life, but ensures continued human existence. However all living organisms must reproduce in order to continue their species.
LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The only system not essential for life, but ensures continued human existence. However all living organisms must reproduce in order to continue their species.
Shira Miller, M.D. Los Angeles, CA 310-734-8864 www.shiramillermd.com. The Compounding Pharmacy of Beverly Hills Beverly Hills Public Library
 Shira Miller, M.D. Los Angeles, CA 310-734-8864 The Compounding Pharmacy of Beverly Hills Beverly Hills Public Library 2 Outline What is hormone therapy? Why would healthy men and women need to think about
Shira Miller, M.D. Los Angeles, CA 310-734-8864 The Compounding Pharmacy of Beverly Hills Beverly Hills Public Library 2 Outline What is hormone therapy? Why would healthy men and women need to think about
Chapter 28: Reproductive System
 I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
Lakeview Endocrinology and Diabetes Consultants. 2719 N Halsted St C-1. Chicago IL 60614 P: 773 388 5685 F: 773 388 5687. www.lakeviewendocrinolgy.
 Lakeview Endocrinology and Diabetes Consultants 2719 N Halsted St C-1 Chicago IL 60614 P: 773 388 5685 F: 773 388 5687 www.lakeviewendocrinolgy.com Patient information: Early menopause (premature ovarian
Lakeview Endocrinology and Diabetes Consultants 2719 N Halsted St C-1 Chicago IL 60614 P: 773 388 5685 F: 773 388 5687 www.lakeviewendocrinolgy.com Patient information: Early menopause (premature ovarian
Smoking and Age of Menopause. Women who smoke experience menopause an average of 2 years earlier than women who do not smoke.
 Menopause Menopause Feared event To many, it indicates old age - a sign of life coming to a close. Many expect a difficult psychological adjustment to menopause (bad press, bad jokes). Menopause Effect
Menopause Menopause Feared event To many, it indicates old age - a sign of life coming to a close. Many expect a difficult psychological adjustment to menopause (bad press, bad jokes). Menopause Effect
Director, IVF Program, Division of Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility
 Director, IVF Program, Division of Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility Date: January 17, 2006 To: From: RE: All IVF candidates Chief, Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility Criteria for IVF program
Director, IVF Program, Division of Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility Date: January 17, 2006 To: From: RE: All IVF candidates Chief, Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility Criteria for IVF program
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
INSULIN RESISTANCE, POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME
 1 University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR INSULIN RESISTANCE, POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN
1 University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR INSULIN RESISTANCE, POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Fertility and Women With Cancer
 Fertility and Women With Cancer Although not everyone ends up having children, most people want to at least have the option. Cancer and treatment for cancer can sometimes make this harder or even take
Fertility and Women With Cancer Although not everyone ends up having children, most people want to at least have the option. Cancer and treatment for cancer can sometimes make this harder or even take
BOER GOAT EMBRYO TRANSFER
 BOER GOAT EMBRYO TRANSFER Good management No shortcuts PLAN AHEAD AVOID STRESS Some examples of how stress is induced are: Mixing groups or individual animals together that have not previously been together.
BOER GOAT EMBRYO TRANSFER Good management No shortcuts PLAN AHEAD AVOID STRESS Some examples of how stress is induced are: Mixing groups or individual animals together that have not previously been together.
Saint Mary s Hospital. Ovarian Cysts. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
The following chapter is called "Follow-ups with a Positive or a Negative Pregnancy Test".
 Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 7. The following chapter is called "Follow-ups with a Positive or a Negative Pregnancy Test". The author is Professor Pasquale Patrizio. Slide 2 This chapter has the following
Slide 1 Welcome to chapter 7. The following chapter is called "Follow-ups with a Positive or a Negative Pregnancy Test". The author is Professor Pasquale Patrizio. Slide 2 This chapter has the following
Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013
 Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013 Topics Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines Pap smears Colposcopy Contraception Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Can I get pregnant? Miscarriage Abnormal Uterine
Abigail R. Proffer, M.D. October 4, 2013 Topics Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccines Pap smears Colposcopy Contraception Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Can I get pregnant? Miscarriage Abnormal Uterine
