Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
|
|
|
- Samantha Hines
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS AND THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, the learner should be able to: Explain the importance of understanding the male and female reproductive systems Define the ovarian cycle, the menstrual (uterine) cycle and menstruation, the female reproductive cycle, and hormones Describe the anatomy and physiology of female and male reproductive systems Describe the phases of the menstrual cycle and what occurs in each phase Explain how fertilization and implantation occur and when during the menstrual cycle a woman can become pregnant. Teaching Resources in this Unit Handouts External Female Reproductive Anatomy 42 Internal Female Reproductive Anatomy 42 Male Reproductive Anatomy 43 Unit Assessment Quiz Questions 44 Quiz Questions Answer Key 48 37
2 Unit 3: Reproductive Systems and the Menstrual Cycle Key Points Understanding the female reproductive cycle is essential for understanding how pregnancy occurs and how family planning methods work to prevent it. The female reproductive cycle involves both the development of an egg in the ovaries (oogenesis) and the preparation of the uterus to receive a fertilized ovum. Sperm can usually live up to 48 hours in the woman s body. A woman is most likely to become pregnant if she has unprotected sex from 2 days before ovulation to the day after ovulation. 3.1 Importance of Understanding Human Reproductive Systems It is essential that family planning providers understand the female and male reproductive systems and female reproductive cycles in order to provide high quality family planning services. To be able to help their clients make informed decisions about family planning methods, instruct clients about how to use their chosen methods, and advise clients about managing side effects, service providers need to understand how pregnancy occurs, when a woman can become pregnant (her fertile time), and how contraceptive methods work. Another benefit of understanding the reproductive cycles is a greater understanding of their roles in female fertility problems and bleeding disorders. 3.2 Overview and Definitions (Note: This section was adapted from Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 7 th edition, by Gerard J Tortora and Sandra Reynolds Grabowski. Copyright 1993, HarperCollins College. Reprinted with permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.) During their reproductive years, non-pregnant females normally experience a cyclical series of changes in the ovaries and uterus. Each cycle takes about a month and involves both oogenesis (development of an ovum) and preparation of the uterus to receive a fertilized ovum. Hormones control the events in these cycles. The ovarian cycle is a series of events that are involved in the maturation of an ovum, or egg. The menstrual (uterine) cycle is a series of changes in the endometrium (lining) of the uterus. Each month, the endometrium is prepared for the potential arrival of a fertilized ovum that will develop in the uterus. If an ovum is not fertilized, the outer portion of the endometrium sheds off. Menstruation is the shedding of the endometrium accompanied by bleeding. Menstruation starts during puberty (at menarche) and stops permanently at menopause. It is also known as monthly bleeding, a period, and menses. The term female reproductive cycle refers to the ovarian and uterine cycles, the hormonal changes that regulate them, and cyclical changes in the breasts and cervix. 38 Preservice Education Family Planning Reference Guide
3 Male and female reproductive systems include all of the structures and organs involved in fertilization and implantation. Hormones are chemicals produced by glands and structures in the body. Hormones act as chemical messengers to another body structure or gland. Hormones control the events in the menstrual and ovarian cycles. This unit focuses on the phases of the menstrual cycle, and includes events in the ovarian cycle in the menstrual (uterine) cycle description. 3.3 The Female Reproductive System (Note: To save space, illustrations of female and male anatomy are not included here but are reprinted in the Handouts section at the end of this unit.) External female reproductive anatomy Structures of external female reproductive anatomy include: Pubic hair: Surrounds the female reproductive organs Clitoris: Sensitive ball of tissue creating sexual pleasure Labia majora (outer lips): Two folds of skin, 1 on either side of the vaginal opening, that protect the female organs Labia minora (inner lips): Two folds of skin, inside the labia majora, that extend from the clitoris Urethra: Opening where urine leaves the body Vaginal opening: Where a man s penis is inserted during sex, and where blood flows out during menstruation Anus: Where solid waste leaves the body. Internal female reproductive anatomy Primary structures and organs include: Uterus (womb): Reproductive organ where a fertilized ovum, or egg, grows and develops into a foetus Fallopian tube: Each of the two tubes that link the ovaries to the uterus. An ovum travels along one of these tubes once a month. Fertilization occurs in this tube. Ovary: Two reproductive glands where ova (eggs) develop and 1 is released each month Ovarian follicle: A hollow ball of cells that contains an immature ovum. Located in each ovary Endrometrium: The lining of the uterus, which gradually thickens and then is shed during menstruation Cervix: Lower portion of the uterus that extends into the upper vagina. It produces mucus. Vagina: Joins the outer sexual organs with the uterus. 3.4 The Male Reproductive System The primary structures and organs of the male reproductive system include: Penis: Male sex organ made of spongy tissue Unit 3: Reproductive Systems and the Menstrual Cycle 39
4 Urethra: Tube through which semen is released from the body. Urine is released through the same tube. Seminal vesicles: Where sperm is mixed with semen Foreskin: Hood of skin covering the end of the penis Prostate: Organ that produces some of the fluid in semen Testicles: Organs that produce sperm Scrotum: Sack of thin, loose skin containing the testicles Vas deferens: Each of the 2 thin tubes that carry sperm from the testicles to the seminal vesicles. 3.5 Phases of the Menstrual and Ovarian Cycles By definition, the menstrual (or uterine) cycle begins with the first day of bleeding, which is counted as day 1. The cycle ends just before the next menstrual period. Menstrual cycles normally range from about 25 to 36 days. The description of the phases of the menstrual cycle below assumes a cycle length of 28 days. However, only 10% to 15% of women have cycles that are exactly 28 days. The menstrual and ovarian cycles each have 3 phases: Menstrual cycle Days 1-5: Menstrual phase This phase is from first day of the menses to last day of bleeding (usually lasts from 3 5 days, up to 7 days). Bleeding occurs when there is no fertilization. Low levels of both progesterone and oestrogen make the blood vessels of the endometrium constrict, cutting off blood flow to the uterine lining. The cells of the uterine lining start to die, and the lining sloughs off and causes bleeding. Two-thirds of the endometrial lining sheds during menses. During this time the ovaries are beginning the follicular stage (see below). Days 6-14: Proliferative phase This phase is from cessation of menses to ovulation. Endometrial lining thickens in preparation for implantation of a fertilized ovum. Its thickness doubles to about 4 6 mm. Uterine secreting glands increase in size and produce mucus. Uterine blood vessels begin to grow. Ovulation occurs in the ovaries at the end of this stage, usually around day 14, triggered by a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland. Days 15-28: Secretory phase This phase is from ovulation to the start of the next menses. Endometrial glands secrete mucus, which prepares the uterus to receive a fertilized ovum. The corpus luteum produces oestrogen, while the cells of the ovaries produce progesterone. 40 Preservice Education Family Planning Reference Guide
5 Endometrium continues to thicken. Ovarian cycle: While the uterus is proceeding through the 3 phases above, the ovaries pass through the following phases: Follicular phase: (about 14 days): Between 3-30 follicles, each containing 1 ovum (egg), begin to grow, with usually 1 reaching maturity while the others break down. Ovulatory phase (about hours): The ovum is released from the follicle and enters the Fallopian tube. Luteal phase (about 14 days): The ruptured follicle forms a structure called the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum produces progesterone, which helps prepare the endometrium for a fertilized egg. 3.6 Fertilization and Implantation Once the egg is released from the ovary (ovulation), it can live for about 24 hours. Once sperm move up the female reproductive tract (through the cervix and into the uterus) after ejaculation, they can usually live for about 48 hours. Fertilization, when the egg joins with the sperm and forms the oocyte, usually happens within 24 hours of intercourse. The fertilized oocyte then implants into the endometrium by 5-7 days after fertilization. Following implantation: The developing placental tissues secrete chorionic gonadotropine, a hormone that helps maintain pregnancy, which maintains the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum of pregnancy, as this is now called, produces the oestrogens and progesterone required to maintain the pregnancy until the placenta takes over this function. If the ovum is not fertilized by a sperm, the corpus luteum regresses, levels of oestrogens and progesterone drop off, the endometrium begins to slough off and pass through the vagina, and menstruation begins the reproductive cycle again. 3.7 Fertile Days of the Menstrual Cycle A woman's fertile days depend on ovulation as well as the life span of the egg and the sperm. The egg and sperm are most likely to join, and pregnancy is most likely to occur, when unprotected sexual intercourse takes place during the 2 days before ovulation or on the day of ovulation. It is also possible a day or 2 after ovulation although this is less likely. Most women ovulate between 11 and 18 days after the first day of their last period. This is the time when women are most fertile and most likely to get pregnant. But the time of ovulation can be different from month to month and different between different women. Therefore, a woman could potentially become pregnant if she has unprotected sex on most days of her menstrual cycle. Unit 3: Reproductive Systems and the Menstrual Cycle 41
6 Handouts Reproductive Systems Teaching Resources External Female Reproductive Anatomy Internal Female Reproductive Anatomy 42 Preservice Education Family Planning Reference Guide
7 Male Reproductive Anatomy Unit 3: Reproductive Systems and the Menstrual Cycle 43
8 Reproductive Systems Quiz Questions Questions 1 9 : Indicate whether the following statements about the reproductive systems are true or false by writing a T for true or an F for false in the space provided before each statement. 1. Proteins control the changes in the ovaries and uterus associated with the reproductive cycle. 2. The urethra is a tube through which semen is released from the body. 3. The vas deferens are 2 thin tubes that carry sperm from the seminal vesicles to the testicles. 4. Fertilization occurs in the uterus. 5. The menstrual cycle begins with the first day of bleeding. 6. The majority of women have menstrual cycles that last 28 days. 7. Blood pools in the uterus during the month and is released during the menstrual phase of the menstrual cycle. 8. During the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle, endometrial glands secrete mucus, which prepares the uterus to receive a fertilized ovum. 9. Fertilization is most likely to occur when unprotected sexual intercourse happens during the 2 days before ovulation or on the day of ovulation. Questions : Please fill in the blank spaces to complete the following sentences. 10. After ovulation, the ovum normally lives for (length of time) in the reproductive tract. 11. After ejaculation, sperm normally survive (length of time) in the female reproductive tract. 12. If an ovum is fertilized, it continues to travel down the toward the. 13. A fertilized ovum implants into the about days after fertilization. 14. At the end of the proliferative phase, occurs in the ovaries. 15. The phases of the menstrual cycle, in the order in which they occur, are,, and. 44 Preservice Education Family Planning Reference Guide
9 External Female Reproductive Anatomy Assessment Label the major structures in this illustration: Unit 3: Reproductive Systems and the Menstrual Cycle 45
10 Internal Female Reproductive Anatomy Assessment Label the major organs and structures in this illustration: Preservice Education Family Planning Reference Guide
11 Male Reproductive Anatomy Assessment Label all the major reproductive structures and organs in this illustration: Unit 3: Reproductive Systems and the Menstrual Cycle 47
12 Reproductive Systems Quiz Questions Answer Key F 1. Proteins control the changes in the ovaries and uterus associated with the reproductive cycle. T 2. The urethra is a tube through which semen is released from the body. F 3. The vas deferens are 2 thin tubes that carry sperm from the seminal vesicles to the testicles. F 4. Fertilization occurs in the uterus. T 5. The menstrual cycle begins with the first day of bleeding. F 6. The majority of women have menstrual cycles that last 28 days. F 7. Blood pools in the uterus during the month and is released during the menstrual phase of the menstrual cycle. F 8. During the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle, endometrial glands secrete mucus, which prepares the uterus to receive a fertilized ovum. T 9. Fertilization is most likely to occur when unprotected sexual intercourse happens during the 2 days before ovulation or on the day of ovulation. 10. After ovulation, the ovum normally lives for 24 hours (length of time) in the reproductive tract. 11. After ejaculation, sperm normally survive 2 days (length of time) in the female reproductive tract. 12. If an ovum is fertilized, it continues to travel down the Fallopian tube toward the uterus_. 13. A fertilized ovum implants into the endometrium about 5-7 days after fertilization. 14. At the end of the proliferative phase, ovulation occurs in the ovaries. 15. The phases of the menstrual cycle, in the order in which they occur, are _menstrual phase_, _proliferative phase, and secretory phase. 48 Preservice Education Family Planning Reference Guide
13 Anatomy Assessment Answer Key External female reproductive anatomy 1. clitoris 2. labia majora (outer lips) 3. urethra 4. vagina 5. labia minora (inner lips) 6. anus Internal female reproductive anatomy 1. Fallopian tube 2. ovary 3. endometrium 4. uterus 5. ovarian follicle 6. cervix 7. vagina Male reproductive anatomy 1. urethra 2. penis 3. foreskin 4. seminal vesicles 5. prostate 6. vas deferens 7. testicles 8. scrotum Unit 3: Reproductive Systems and the Menstrual Cycle 49
14 References Ministry of Health Malawi national reproductive health service delivery guidelines. Lilongwe, Malawi: Ministry of Health. Marieb, Elaine N Essentials of human anatomy and physiology. 6th ed. San Francisco, CA: Benjamin/Cummings. Tortora, Gerard J. and Sandra Reynolds Grabowski Principles of anatomy and physiology. 7th ed. New York, NY: HarperCollins College. World Health Organization/Department of Reproductive Health and Research (WHO/RHR) and Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health/Center for Communications Programs (CCP), Knowledge for Health Project. Family Planning: A global handbook for providers (2008 update). Baltimore and Geneva: CCP and WHO/RHR Preservice Education Family Planning Reference Guide
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions
 Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
Reproduction Multiple Choice questions 1. In mammals that are seasonal breeders, females are receptive only once a year. This is called A) a follicular cycle B) an estrous cycle C) a menstrual cycle D)
2. What muscle pulls the testis down into the scrotum during development?
 Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
Anatomy & Physiology Reproductive System Worksheet Male 1. Put the following structures in order from testis to urethra: ductus deferens, rete testis, epididymus, seminiferous tubules 1) 2) 3) 4) 2. What
The Menstrual Cycle. Model 1: Ovarian Cycle follicular cells
 The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
The Menstrual Cycle REVIEW questions to complete before starting this POGIL activity 1. Gonads produce both gametes and sex steroid hormones. For the female, name the: A. gonads ovaries B. gametes oocyte/ovum/egg
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control
 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Page 1 Reproduction and its Hormonal Control Different mammals have different patterns of reproduction Eg mammals, rats and mice can breed all year round, whereas
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface) sperm producing organs testes ducts that
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment
 The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
The Menstrual Cycle, Hormones and Fertility Treatment How many of us understand how our monthly cycle works? Every 28 days (or thereabouts), between the ages of around 13 and 51, a woman will release a
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
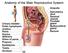 Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System External genitalia (can be seen on the body surface) penis scrotum Internal genitalia (can t be seen on the body surface)
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Reproduction. Module 10a
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Understanding Fertility
 Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Understanding Fertility 6 Introduction The word fertile means the ability to become pregnant or to cause pregnancy. Basic knowledge of both the male and female reproductive systems is important for understanding
Page 1. 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems
 1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
1. The production of monoploid cells by spermatogenesis occurs in (1) zygotes (3) ovaries (2) testes (4) meristems Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on the diagram below of the female reproductive
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Function: producing offspring Reproductive System propagation of the species in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously only activated
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I
 Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
Lesson Plan Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I TOPIC: Sexual & Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Part I SUBJECT: Life Skills TARGET AGE RANGE: 9 15 TIME: 45 minutes IDEAL NUMBER OF LEARNERS:
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS. Eva M. Zamudio Zamudio
 STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
STUDENT S WORKSHEETS January April 2009 HUMAN LIFE CYCLE HANDOUT 1 1. Write the name of each stage in the right order: retirement adolescence babyhood adulthood - childhood 2. What stage does it belong
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks bodyworks bodywor bodyworks yworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks odyworks body
 Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Bodyworks Your guide to understanding reproduction orksody odyworks body bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks dyworks ork bodywor odyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodyworks bodywork
Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system.
 Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Ovarian Cysts Introduction Ovarian cysts are a very common female condition. An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac on an ovary in the female reproductive system. Most women have ovarian cysts sometime
Timing is everything. Ovulation Tracking. Patient Information Booklet
 Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Timing is everything Ovulation Tracking Patient Information Booklet Contents Getting pregnant naturally 3 Getting pregnant the basics 3 What is ovulation? 3 Menstrual cycle 4 When does ovulation take place?
Female Reproductive System. Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued
 Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System Unit 8 Lesson 2 Continued Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Female produce ovum or egg cells. The egg (ovum) cell is the female sex cell. Female Reproductive
Glossary. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty.
 Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
Glossary amenorrhea - absence or cessation of menstrual periods. amenorrhea, primary - from the beginning and lifelong; menstruation never begins at puberty. A amenorrhea, secondary - due to some physical
1. AMOUNT OF FSH PRESENT
 The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
The Menstrual Cycle Name Date Period PRE-LAB 1. Write down three facts you know about the menstrual cycle. A. B. C. FOLLICULAR PHASE Within the ovaries are located many egg cells. Each egg is enclosed
Ovarian Cyst. Homoeopathy Clinic. Introduction. Types of Ovarian Cysts. Contents. Case Reports. 21 August 2002
 Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
Case Reports 21 August 2002 Ovarian Cyst Homoeopathy Clinic Check Yourself If you have any of the following symptoms call your doctor. Sense of fullness or pressure or a dull ache in the abdomen Pain during
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 4 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 4 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of the
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know
 Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
Sterilisation for women and men: what you need to know Published January 2004 by the RCOG Contents Page number Key points 1 About this information 2 What are tubal occlusion and vasectomy? 2 What do I
OVARIAN CYSTS. Types of Ovarian Cysts There are many types of ovarian cysts and these can be categorized into functional and nonfunctional
 OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
OVARIAN CYSTS Follicular Cyst Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form within or on the ovary. The majority of these cysts are functional meaning they usually form during a normal menstrual cycle.
NATURE TAKES ITS COURSE
 Alabama Department of Public Health Mother s Milk Education Activity Package for Grades K-12 Level: 5 Adapted from New York Department of Health LEARNING OBJECTIVE FOR LEVEL 5 NATURE TAKES ITS COURSE Students
Alabama Department of Public Health Mother s Milk Education Activity Package for Grades K-12 Level: 5 Adapted from New York Department of Health LEARNING OBJECTIVE FOR LEVEL 5 NATURE TAKES ITS COURSE Students
Sexual reproduction in humans
 Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
Sexual reproduction in humans Name: WHY DO HUMANS NEED TO REPRODUCE? The reason humans reproduce is to have children so that our species can continue to exist. Humans reproduce sexually, which means like
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Ovarian Cysts
 Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Ovarian Cysts WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The ovaries are two small organs located on either side of a woman s uterus. An ovarian cyst is a sac or pouch filled with fluid
Unit #5 Human Growth and Development 6 th Grade - Chapter 7, 8 7 th Grade - Chapter 12 8 th Grade - Chapter 16, 17
 8 th Grade HGD Chapter 16 Summary Your Body Systems Lesson 1 Your Skeletal System 1. Skeletal system is a body system: a. Bones b. Joints c. Connective tissue 2. Marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center
8 th Grade HGD Chapter 16 Summary Your Body Systems Lesson 1 Your Skeletal System 1. Skeletal system is a body system: a. Bones b. Joints c. Connective tissue 2. Marrow, which is a soft tissue in the center
GLOSSARY. A Abstinence: having no vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It is the only method that is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy and STI s.
 WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
WOMEN S HEALTH GLOSSARY We encourage you to learn the meanings behind these words for your personal health and to fully understand the words being used during your appointments at the Falcon Health Center.
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels. Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College
 From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
From Menses to Menopause: How Hormones Can Affect Blood Glucose Levels Christine Day, RN, MS, CNS-BC Lake Superior College Overview Will review hormonal changes over the female lifespan Discuss the effects
Birth Control Options
 1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
1 of 5 6/2/2014 9:46 AM Return to Web version Birth Control Options What is contraception? Contraception means preventing pregnancy, also called birth control. Most people know about options such as birth
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System
 Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Anatomy of Male Reproductive System A. Reproductive Systems 1. Gonads: primary sex organs a. Produce gametes b. Produce hormones c. Male Gonads: testes d. Female Gonads: ovaries 2. Gametes: sex cells a.
Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3
 Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems,
Reproductive System Grades 9 and 10, Lesson #3 Time Needed One class period Student Learning Objectives To be able to 1. Locate and spell at least 75% of the parts of the male and female reproductive systems,
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Final Exam Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Final Exam Name: Instructions This exam consists of 40 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation (men-stray-shuhn) is a woman's monthly bleeding. When you menstruate, your body sheds the lining of the uterus (womb). Menstrual
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Abnormal uterine bleeding is one of the most common reasons women see their doctors. It can occur at any age and has
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court. A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and
 Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
Hormonal Oral Contraceptives: An Overview By Kelsie Court A variety of methods of contraception are currently available, giving men and women plenty of options in choosing a method suitable to his or her
For The Providers of Youth Friendly Services
 For The Providers of Youth Friendly Services FAMILY PLANNING AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH In July 2011, FHI became FHI 360. FHI 360 is a nonprofit human development organization dedicated to improving lives
For The Providers of Youth Friendly Services FAMILY PLANNING AND REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH In July 2011, FHI became FHI 360. FHI 360 is a nonprofit human development organization dedicated to improving lives
How Your Fertility Works
 How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
How Your Fertility Works These pages give a simple explanation of how male and female fertility work and complement each other, enabling couples to plan, space and limit family size, without using any
Artificial insemination
 Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
Artificial insemination What is involved? Artificial insemination is an assisted reproduction technique that consists of inserting laboratory-treated spermatozoa into the woman s uterus or cervical canal.
LEARNER OUTCOME 1 W-6.3:
 GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
GRADE 6 FETAL DEVELOPMENT LESSON 2 FETAL DEVELOPMENT Lesson 2 GRADE 6 LEARNER OUTCOME W-6.3: Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth.
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida. Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 10; Lecture 1; Monday Stuart Sumida Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cycles OVARY Location : near kidneys, anchored by fallopian tubes to
About the Uterus. Hysterectomy may be done to treat conditions that affect the uterus. Some reasons a hysterectomy may be needed include:
 Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
Hysterectomy removal of the uterus is a way of treating problems that affect the uterus. Many conditions can be cured with hysterectomy. Because it is major surgery, your doctor may suggest trying other
How do fertility drugs work?
 How do fertility drugs work? Under normal circumstances, ovulation occurs once a month when a ripened egg which is ready to be fertilised is released from the ovaries. For couples who are trying to conceive,
How do fertility drugs work? Under normal circumstances, ovulation occurs once a month when a ripened egg which is ready to be fertilised is released from the ovaries. For couples who are trying to conceive,
Reproductive System. from the Human Body System Series. catalog # 3322. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle
 Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Menstruation and the Menstrual Cycle Q: What is menstruation? A: Menstruation is a woman s monthly bleeding, also called a period. When you menstruate, your body is shedding the lining of the uterus (womb).
Agenda: 1. Help students learn about health and major body systems. 2. Introduce the reproductive system
 FOURTH GRADE BODY SYSTEMS LESSON PLAN STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student will learn: That health has three parts: physical, mental and social About major body systems including an introduction to
FOURTH GRADE BODY SYSTEMS LESSON PLAN STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student will learn: That health has three parts: physical, mental and social About major body systems including an introduction to
Reproduction in Mammals
 Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Reproduction in Mammals A. Introduction 1. The organs of the male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of the species. 2. They do this by producing gametes and by providing a method
Artificial insemination with donor sperm
 Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
Artificial insemination with donor sperm Ref. 123 / 2009 Reproductive Medicine Unit Servicio de Medicina de la Reproducción Gran Vía Carlos III 71-75 08028 Barcelona Tel. (+34) 93 227 47 00 Fax. (+34)
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Birth Control Pills
 Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
Birth Control Pills WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Birth control pills (also called oral contraceptives or "the pill") are used by millions of women in the United States to
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet
 Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding FAQ Sheet What is abnormal uterine bleeding? Under normal circumstances, a woman's uterus sheds a limited amount of blood during each menstrual period. Bleeding that occurs between
Saint Mary s Hospital. Ovarian Cysts. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
Saint Mary s Hospital Ovarian Cysts Information For Patients 2 Contents Welcome 4 What are ovarian cysts? 4 How common are ovarian cysts? 6 Ovarian cysts and fertility 6 What are the symptoms of ovarian
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook
 In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
In - Vitro Fertilization Handbook William F. Ziegler, D.O. Medical Director Scott Kratka, ELD, TS Embryology Laboratory Director Lauren F. Lucas, P.A.-C, M.S. Physician Assistant Frances Cerniak, R.N.
Chapter 28: Reproductive System
 I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
I. Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System A. Scrotum 1. What does the scrotum contain? 2. An incomplete connective tissue septum divides the scrotum into 3. Externally the scrotum has an irregular ridge
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
patient education Fact Sheet PFS003: Hormone Therapy APRIL 2015 Hormone Therapy Menopause is the time in a woman s life when she naturally stops having menstrual periods. Menopause marks the end of the
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Menstruation
 Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Menstruation WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Menstruation is a normal and healthy part of growing up. The discharge of blood and tissue from the lining of your uterus each
Reproductive System. Anatomy of Male Reproductive System. Major Organs. Function: producing offspring. External Reproductive Organs
 Reproductive System Function: producing offspring propagation of the species!in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously! only activated
Reproductive System Function: producing offspring propagation of the species!in terms of evolution the only reason all the other systems exist only major system that doesn t work continuously! only activated
FERTILITY AND AGE. Introduction. Fertility in the later 30's and 40's. Am I fertile?
 FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
FERTILITY AND AGE Introduction Delaying pregnancy is a common choice for women in today's society. The number of women in their late 30s and 40s attempting pregnancy and having babies has increased in
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
THE WELL. Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices WOMAN CENTRE
 THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
THE WELL WOMAN CENTRE Intrauterine Contraceptive Devices INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES How does the Mirena work? How effective is the Mirena? What are the advantages of the Mirena? What are the disadvantages
Endocrinology of the Female Reproductive Axis
 Endocrinology of the Female Reproductive Axis girlontheriver.com Geralyn Lambert-Messerlian, PhD, FACB Professor Women and Infants Hospital Alpert Medical School at Brown University Women & Infants BROWN
Endocrinology of the Female Reproductive Axis girlontheriver.com Geralyn Lambert-Messerlian, PhD, FACB Professor Women and Infants Hospital Alpert Medical School at Brown University Women & Infants BROWN
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME
 POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME Information Leaflet Your Health. Our Priority. Page 2 of 6 What is polycystic ovary syndrome? (PCOS) Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder in women
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE UTERINE FIBROIDS A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Endometriosis
 Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Endometriosis WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. Sometimes, endometrial tissue grows elsewhere in the body. When this happens
Growing up what s it all about?
 4YOU Growing up what s it all about? GROWING UP... WHAT S HAPPENING? You may have noticed things about yourself and your friends that are starting to change. Changing bodies, changing feelings, changing
4YOU Growing up what s it all about? GROWING UP... WHAT S HAPPENING? You may have noticed things about yourself and your friends that are starting to change. Changing bodies, changing feelings, changing
The IUI procedure Who should consider an IUI IUI success rates IUI cost What to consider if IUI is unsuccessful. The IUI procedure:
 A Complete Guide to understanding IUI (intrauterine insemination) and artificial insemination (Eric Daiter, MD Board Certified in Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility) The IUI procedure Who should
A Complete Guide to understanding IUI (intrauterine insemination) and artificial insemination (Eric Daiter, MD Board Certified in Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility) The IUI procedure Who should
Explore and Discover... Human growth. You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Teacher information
 You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
You have been asked to write a short leaflet for young people about growing up and puberty. Explore and Discover... Teacher information Gallery visited Human Biology Suitable for Key Stage 3 (ages 11 to
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
HEALTH UPDATE. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
 HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
HEALTH UPDATE PO Box 800760 Charlottesville, VA 22908 Gynecology: (434) 924-2773 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) What is it? An endocrine (hormonal) disorder. Because there is such variability in how
Birth Control Methods
 page 1 Birth Control Methods Q: What is the best method of birth control (or contraception)? A: There is no best method of birth control. Each method has its pros and cons. All women and men can have control
page 1 Birth Control Methods Q: What is the best method of birth control (or contraception)? A: There is no best method of birth control. Each method has its pros and cons. All women and men can have control
The Endocrine System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Slides 9.1 9.48 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Endocrine System Second messenger
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Slides 9.1 9.48 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Endocrine System Second messenger
LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The only system not essential for life, but ensures continued human existence. However all living organisms must reproduce in order to continue their species.
LECTURE 10: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The only system not essential for life, but ensures continued human existence. However all living organisms must reproduce in order to continue their species.
Revised Spring 2006 1
 It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
It is important that you know the anatomy and the histology BEFORE the physiology can be covered in lecture. Study the anatomy of the reproductive system using this handout in conjunction with Text Chapter
vasectomy your questions answered
 vasectomy your questions answered About Marie Stopes International Marie Stopes International is one of the UK s most respected names in sexual health. Each year, our nine centres across the UK help over
vasectomy your questions answered About Marie Stopes International Marie Stopes International is one of the UK s most respected names in sexual health. Each year, our nine centres across the UK help over
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
 Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome What is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome? Polycystic ovary syndrome (or PCOS) is a common condition affecting 3 to 5% of women of reproductive age. It is linked with hormonal imbalances,
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500. Hormone Therapy
 Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Hormone Therapy WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 At menopause, a woman's body makes less estrogen and she stops having menstrual periods. This is a natural stage in a woman's
Puberty is the name given to the physical changes that happen between childhood and adulthood
 LENScience 09-501-A3 Growing Up! A resource for Science Classes Growing Up! As a human you are going to spend a life time growing and changing. It all started at the time of fertilisation, or conception,
LENScience 09-501-A3 Growing Up! A resource for Science Classes Growing Up! As a human you are going to spend a life time growing and changing. It all started at the time of fertilisation, or conception,
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Male Infertility. Penis. Epididymis
 Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
Male Infertility Introduction Infertility is a term used when a man is unable to get a woman pregnant. But the term is only used after at least one year of trying. Infertility is a common problem. About
A Guide to Hysteroscopy. Patient Education
 A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
A Guide to Hysteroscopy Patient Education QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ABOUT HYSTEROSCOPY Your doctor has recommended that you have a procedure called a hysteroscopy. Naturally, you may have questions about
Here we will talk about:
 Here we will talk about: What is puberty? When changes happen to boys? What are the sex organs? What are erections and why do they happen? For more information you can visit: What s Happening? What is
Here we will talk about: What is puberty? When changes happen to boys? What are the sex organs? What are erections and why do they happen? For more information you can visit: What s Happening? What is
Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO
 9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
9339 Genesee Avenue, Suite 220 San Diego, CA 92121 858 455 7520 Assisted Reproductive Technologies at IGO Although IGO no longer operates an IVF laboratory or program as such, we work closely with area
All methods of birth control are MUCH SAFER than being pregnant! If 100 women use each method for a year, how many of them get pregnant?
 The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
The Correct Use of Birth Control: In order for any method of birth control to be effective, it must be used correctly ALL THE TIME. This means: One condom every time you have sex One pill every day One
Ovarian Cystectomy / Oophorectomy
 Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Cystectomy and Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are sacs filled with fluids or pockets located on or in an ovary. In some cases, these cysts need to be removed surgically. Types of Cysts Ovarian cysts are quite
Infertility: An Overview
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
BARRIER METHODS (MALE AND FEMALE CONDOMS)
 Unit 17 BARRIER METHODS (MALE AND FEMALE CONDOMS) Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, learners will be able to: Describe condoms Explain the effectiveness of condoms and how they work List the
Unit 17 BARRIER METHODS (MALE AND FEMALE CONDOMS) Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, learners will be able to: Describe condoms Explain the effectiveness of condoms and how they work List the
What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up. (for boys and girls)
 What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up (for boys and girls) introduction Changes as you get older This is a booklet about growing up. As you get older you ll notice that your body changes and you develop
What s GoinG on? your guide to growing up (for boys and girls) introduction Changes as you get older This is a booklet about growing up. As you get older you ll notice that your body changes and you develop
Intrauterine Device (IUD) THE FACTS
 Intrauterine Device (IUD) Quick Facts Effectiveness in Preventing Pregnancy: Use: Of 100 women using IUDs for a year, about one may become pregnant. IUDs are better at preventing pregnancy than condoms,
Intrauterine Device (IUD) Quick Facts Effectiveness in Preventing Pregnancy: Use: Of 100 women using IUDs for a year, about one may become pregnant. IUDs are better at preventing pregnancy than condoms,
In Vitro Fertilization
 Patient Education In Vitro Fertilization What to expect This handout describes how to prepare for and what to expect when you have in vitro fertilization. It provides written information about this process,
Patient Education In Vitro Fertilization What to expect This handout describes how to prepare for and what to expect when you have in vitro fertilization. It provides written information about this process,
FERTILITY AWARENESS METHODS
 Unit 16 FERTILITY AWARENESS METHODS Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, learners should be able to: Define fertility awareness methods of contraception Describe the 2 categories of fertility awareness
Unit 16 FERTILITY AWARENESS METHODS Learning Objectives By the end of this unit, learners should be able to: Define fertility awareness methods of contraception Describe the 2 categories of fertility awareness
Medications for Inducing Ovulation
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Medications for Inducing Ovulation A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Medications for Inducing Ovulation A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction
Patient Information: Endometriosis Disease Process and Treatment
 1 William N. Burns, M. D. Associate Professor Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine Marshall University Huntington, West Virginia, USA Patient Information: Endometriosis
1 William N. Burns, M. D. Associate Professor Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine Marshall University Huntington, West Virginia, USA Patient Information: Endometriosis
Medications for Inducing Ovulation
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Medications for Inducing Ovulation A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Medications for Inducing Ovulation A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction
Ectopic Pregnancy. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Ectopic Pregnancy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Ectopic Pregnancy A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications
Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion.
 Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion. After the abortion I started re-thinking my birth control method. I am looking
Effective long-lasting strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy. The intrauterine system for contraception after abortion. After the abortion I started re-thinking my birth control method. I am looking
Summa Health System. A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy
 Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
Summa Health System A Woman s Guide to Hysterectomy Hysterectomy A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a woman s uterus (womb). The uterus is the organ which shelters and nourishes a baby during
