X-Ray Peak Profile Analysis of Nanostructured Hydroxyapatite and Fluorapatite
|
|
|
- Edwin Simon
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics, Vol. 2, No. 6, November 20 X-Ray Peak Profile Analysis of Nanostructured Hydroxyapatite and Fluorapatite K. Venkateswarlu, D. Sreekanth, M. Sandhyarani, V. Muthupandi, A. C. Bose, and N. Rameshbabu (F) incorporation within apatite lattice on the biological, mechanical and physicochemical properties of HA such as, thermal stability [2], solubility [], stem cell growth-colonisation [4], hardness, crystallinity and corrosion resistance [5]-[7]. Thus most of the existed studies focussed on qualitative description of the variations in the properties shown by HA and F-HA. But a certain gap exists in the literatures to quantify the microstructural parameters for better understanding of the observed differences in physicochemical properties of FA compared to HA. Nanocrystalline HA is expected to have homogeneous resorption and better bioactivity than coarser crystals [8]. Further, the properties shown by nanomaterials are crystallite size dependant. Thus, for complete understanding of nanoscale material properties, the crystallite size and other related microstructural quantities such as dislocation density need to be calculated correctly. Keeping in mind the need and importance of analytical methods such as X-ray peak profile analysis (XPPA) to estimate the microstructural quantities and to correlate them to the observed material properties, the present work aims at estimating the crystallite size, lattice strain, lattice stress and lattice strain energy density of HA and FA, based on conventional W-H plot by using W-H-ISM, W-H-ASM and W-H-EDM models, thereby correlating them to the differences in the literature reported and presently observed physicochemical properties of nanocrystalline HA and FA. Abstract In present study, X-ray peak profile analysis (XPPA) by modified Williamson-Hall (W-H) models, namely W-H-isotropic strain model (W-H-ISM), W-H-anisotropic strain model (W-H-ASM) and W-H-energy density model (W-H-EDM), was employed to estimate the microstructural parameters such as, crystallite size, lattice strain, lattice deformation stress and deformation energy density from the powder diffraction data obtained for the microwave synthesized hydroxyapatite (HA) and fluorapatite (FA) nanoparticles prepared under identical processing conditions of mixing and aging. The as-prepared powder particles were also characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) method. The average crystallite size values estimated for HA and FA by XPPA were correlated to their respective transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis results. In addition, the estimated values of HA and FA were correlated to their in-vitro dissolution characteristics studied by ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid (EDTA) titrimetric method. It is found that the average crystallite size estimated by W-H models is in good agreement with TEM results. The controlled in-vitro dissolution behavior of FA was found to be resulted out of its higher crystallite size, lower lattice strain and lower dislocation density compared to that of HA. Index Terms Hydroxyapatite, fluorapatite, applications, defects, X-ray peak profile analysis. biomedical I. INTRODUCTION Synthetic hydroxyapatite [HA; Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2] has been extensively used as an implant material, because of its similarity with human bone composition and thereby its ability to form a strong bond to the human hard tissue. However, synthetic HA presents poor thermal stability. On the other hand, fluorapatite [FA; Ca10(PO4)6F2)] exhibits lower dissolution rate and high thermal stability by retaining its phase purity up to a temperature of 1400 C. Further, FA is found to form as an outer layer in tooth enamel [1]. Hence, FA is desirable as an outer layer in tooth enamel, because it is less soluble in acidic solutions (like those produced by oral bacteria or by Diet Coke) than the HA. Many researchers have addressed the influence of fluorine II. MATERIALS AND METHODS A. Synthesis and Characterization of HA and FA Nanoparticles The precursors used and the detailed procedure for the synthesis of HA [9] and FA [10] particles was reported in one of the authors previous study. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques were employed to study the phase composition, the size and the morphology of as-prepared HA and FA powders. The isolated and preferred high intensity diffraction peaks namely, (002), (102), (202), (11), (222), (21) and (004) were chosen to estimate the microstructural parameters by various models based on W-H plot. Manuscript received July 24, 20; revised October 2, 20. K. Venkateswarlu is with the Department of Physics and Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli, , Tamil Nadu, India ( kotharu.venkat@ gmail.com). A. C. Bose is with the Department of Physics, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli, , Tamil Nadu, India ( [email protected]) D. Sreekanth, M. Sandhya Rani, V. Muthupandi, and N. Rameshbabu are with the Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli, , Tamil Nadu, India ( [email protected], [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]). B. In-Vitro Dissolution Study The dissolution behaviour of the as-prepared HA and FA powder particles was studied by determining the amount of calcium released from each of the samples into the host ambience (4.5 ph medium) by EDTA titrimetric method. 89
2 International Journal of Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics, Vol. 2, No. 6, November 20 cylindrical glass bottle with 4.5 ph solution and maintained at temperature 7 C for 72 h. The ph was maintained throughout 72 h by adding variable quantity of N HNO. After 72 h the supernatant liquid was collected by micro pipette and centrifuged at 500 rpm for 15 minutes. 1 ml of 1 N NaOH was added to 10 ml of sample taken in a conical flask. A pinch of ammonium purpurate powder followed by NaOH solution was added to the above solution which ends up the solution with pink colour. This solution in the conical flask was titrated against 0.02 N EDTA solution taken in the burette and the titration reaction was carried out till the colour of the solution changes from pink to purple. The volume of EDTA consumed was noted. The amount of calcium released was determined by the following formulae [11]. Amount of calcium (P) present in the given sample in terms of CaCo P B. Determination of Crystallite Size of HA and FA by Scherrer Analysis The instrumental corrected broadening βhkl [] corresponding to the diffraction peaks of HA and FA was estimated using the equation hkl hkl measured hkl instrumental (1) Here the crystallite size value is calculated by using Scherrer s formula to compare with the values obtained from the W-H models and TEM analysis results. The crystallite sizes of HA and FA were estimated from the Scherrer s equation as given below: hkl cos hkl (2) where is the volume weighted crystallite size (nm); k is the shape factor (k = 0.9); λ is the wave length of the X-rays (λ = nm for Cu Kα1 radiation); θhkl is Bragg diffraction angle ( ) and βhkl is the broadening of the hkl diffraction peak measured at half of its maximum intensity (in radians). volume of EDTA 1000 volume of sample taken Calcium present in the sample (mg/l) = P Molecular weight of calcium Molecular weight of calcium carbonate III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION A. XRD Analysis of HA and FA Nanoparticles The XRD patterns of HA and FA samples are shown in Fig. 1(a) and 1(b) respectively. C. Estimation of Lattice Strain (ε) and Crystallite Size () by W-H-ISM The XPPA by W-H models is a simplified method which clearly differentiates between size induced and strain induced peak broadening by considering the peak width as a function of 2θ [1]. Fig. 1. XRD patterns of as-prepared nanosized HA (a) and FA (b). The XRD patterns of HA and FA are similar and exhibit several diffraction peaks which can be assigned to hexagonal crystal structure with space group P6/m. In addition, the diffraction peaks are markedly broader suggesting that the prepared powder particles were in nanosize. As compared to the broad X-ray diffraction peaks of HA particles in [Fig. 1 (a)], the diffraction peaks of FA particles [Fig. 1 (b)] are narrow and well separated. It confirms that FA sample is of improved crystallinity and increased crystallite size. The calculated percentage crystallinity of HA and FA are 22 and 50. The improved crystallinity of FA may come from the driving force provided by the high affinity F- groups (compared to OH- groups in the precursor solution) for the apatite crystal growth during precipitation [10]. Fig. 2. W-H-ISM plots of as-prepared nanosized HA (a) and FA (b). The strain induced line broadening s is given by the relation s 4 tan hkl. Now the total peak broadening is represented by the sum of the contributions of crystallite size and strain present in the material. 90
3 International Journal of Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics, Vol. 2, No. 6, November 20 TABLE I: THE ESTIMATED MICROSTRUCTURAL PARAMETERS OF AS-PREPARED NANOSIZED HA AND FA. Analysis Estimated values HA FA σ (MPa) u (kjm-) ± ±6 Model Scherrer analysis W-H-ISM W-H analysis W-H-ASM W-H-EDM TEM analysis Parameter (unit) Assuming that the strain present in HA and FA crystals is isotropic, the W-H equation [] for the total peak broadening is given by 4 sin hkl intersection of the HA and FA linear fits made to their respective 4sin hkl E hkl vs. hkl cos hkl plots. The estimated values of the lattice stress and the crystallite size values for HA and FA are shown in Table I. () E. Estimation of Deformation Energy Density and Crystallite Size () by W-H-EDM In equation, it is considered the homogeneous isotropic nature of the HA and FA crystals which, in many cases, is not fulfilled. Moreover, all the constants of proportionality associated with the stress-strain relation are no longer independent when the lattice strain energy density u is considered. According to Hook s law u 2Ehkl 2 and therefore, the modified W-H-ASM equations for HA and FA can be expressed as A plot is drawn for HA and FA by taking 4 sin hkl along X-axis and hkl cos hkl along Y-axis as shown in Fig. 2 (a) and (b), respectively. In W-H-ISM model, the lattice strain values and the crystallite size values of HA and FA are respectively extracted from the slopes and the intercepts of the respective linear fits made to their experimental data. The estimated values of the lattice strain and the crystallite size for HA and FA are shown in Table I. D. Estimation of Lattice Deformation Stress (σ) and Crystallite Size () by W-H-ASM According to Hook s law, the relation between stress and strain is given by σ = Eε, where E is the modulus of elasticity or Young s modulus. Assuming a small strain to be present in HA and FA particles, Hook s law can be applied to estimate the lattice deformation stress to a reasonable approximation. Hence by assuming that the lattice deformation stress is uniform in all crystallographic directions, the strain factor in second term of the equation () is replaced by E hkl and 4 sin hkl E hkl 4 sin hkl 2 E hkl u (6) The lattice deformation energy density u and the crystallite size values are separately extracted for HA and FA from the slope and the intersection of the linear fits made to 4sin hkl 2 Ehkl their respective hkl cos hkl vs. plots. The estimated crystallite size and lattice deformation energy density for HA and FA were shown in Table I. F. Estimation of Dislocation Density (ρ) Dislocation density is defined as the length of dislocation line per unit volume of the crystal. The dislocation density is calculated for HA and FA using the following relation [16]. the modified equation is given by (4) Here Ehkl is Young s modulus in the direction normal to the set of (hkl) crystal lattice planes. The crystallographic direction dependent Young s modulus in hexagonal crystals [14] of HA and FA is given by the following equation (5) nc F e 2 (7) b where n, the number of dislocations on each face of the particle, C is the constant depending on the strain distribution, F is an interaction parameter, <e2>1/2 is the root mean squared (RMS) strain, b is the burgers vector and is the crystallite size. For Cauchy strain profiles the value of C is about 25, whereas for Gaussian strain profiles it is nearly 4. In the absence of extensive polygonization, dislocation density can be calculated from the above equation (4), by assuming n F, b=d, the interplanar spacing and C=4. Now the equation (4) reduces to 2 2 h 2k 2 a 2 1 h c Ehk h 2k s a1 2s s h 2 h 2k a1 2 s11 h c c (5) Here s11, s, s44 and s1 are the elastic compliances which are common for HA and FA and their standard hand book values are , , , , respectively [15]. The lattice deformation stress and crystallite size were respectively extracted from the slope and 91 e2 d (8)
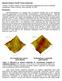
4 International Journal of Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics, Vol. 2, No. 6, November 20 The estimated values of the dislocation density are and lines/m2 respectively for HA and FA. with more accuracy. The incorporation of F in the crystal lattice of HA results in higher crystallinity, crystallite size and reduced lattice strain, lattice stress, lattice strain energy density and dissolution rate of FA. G. In-Vitro Dissolution Study of HA and FA Particles The content of Ca released out of HA and FA into the test medium, as determined by EDTA titrimetric method, is mg/l and 8 mg/l respectively for HA and FA. It can be observed that the released Ca content is higher for HA compared to that of FA. This is due to the lower crystallinity, higher internal lattice strain and lower chemical stability of HA. Thus the higher solubility of HA can be attributed to its higher dislocation density compared to that of FA. Higher the dislocation density more is the dissolution rate. The effect of dislocation density on the dissolution behaviour of HA was explained in detail by [17]. Hence, it can be concluded that the HA with a higher dislocation density is more likely to be attacked by the acids on the surface, compared to that of FA. This results in the higher dissolution rate for HA compared to that of FA. Fig.. TEM micrographs of as-prepared nanosized (a) HA and (b) FA. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The authors would like to acknowledge the grants from Department of Biotechnology, New Delhi (BT/PR-1171/ MED/2/99/2008, dated ) and the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi (SR/NM/NS-27/2008, dated ). H. TEM Analysis of HA and FA Particles The bright field transmission electron microscopic images of HA and FA nanoparticles in as-prepared condition were shown in Fig. (a) and (b), respectively. The HA particles were of ellipsoid like morphology and were a bit shorter with more irregular and less clear contour. On the other hand, FA particles were a bit longer than HA particles with rod like morphology and with clear contours and less agglomeration. The sizes of HA and FA nanoparticles were estimated from TEM images by image analysis done with a freely available IMAGE J software. The HA particles exhibited a length of about 45 nm and a width of about 11 nm corresponding to an aspect ratio of about 4. On the other hand the FA particles exhibited a length of about 65 nm and a width of about 1 nm corresponding to an aspect ratio of about 5. However, to correlate the results obtained from various analyses, the sizes of HA and FA obtained from TEM analysis were expressed as (length + width)/2 and were given as 28±5 nm and 9±6 nm (mean ±SD) for HA and FA respectively. REFERENCES [1] [2] [] [4] [5] [6] [7] IV. CONCLUSION XPPA was successfully employed to estimate the microstructural parameters of HA and FA powder particles. There is a good agreement between the crystallite size values obtained by W-H analysis and that obtained by TEM analysis for HA and FA powder particles. Hence, W-H analysis results are more accurate for the estimation of crystallite size, when compared to Scherrer analysis. Therefore it is suggested that the contribution from instrumental effects and lattice strain effect to the X-ray peak broadening need to be considered while calculating the crystallite size value of nanomaterials. Within the materials elastic limit, the W-H models can be applied to estimate other microstructural parameters such as lattice strain, lattice deformation stress and lattice deformation energy density in a reasonable approximation. The crystallite size and the lattice strain values obtained from the W-H-ISM model for HA and FA can be further extended to estimate the dislocation densities present in the materials [8] [9] [10] [11] [] [1] [14] [15] 92 F. Brudevold, D. E. Gardner, and F. A. Smith, The distribution of fluoride in human enamel, J. Dent. Res., vol. 5, pp , A. Bianco, I. Cacciotti, M. Lombardi, L. Montanaro, E. Bemporad, and M. Sebastiani, F-substituted hydroxyapatite nanopowders: Thermal stability, sintering behaviour and mechanical properties, Ceram. Int., vol. 6, pp. 1-22, M. Okazaki, Y. Miake, H. Tohda, T. Yanagisawa, T. Matsumoto, and J. Takahashi, Functionally graded fluoridated apatites, Biomaterials, vol. 20, pp , J. Harrison, A. J. Melville, J. S. Forsythe, B. C. Muddle, A. O. Trounson, K. A. Gross, and R. Mollard, Sintered hydroxyfluorapatites-iv: The effect of fluoride substitutions upon colonisation of hydroxyapatites by mouse embryonic stem cells, Biomaterials, vol. 25, pp , H. Qu and M. Wei, The effect of fluoride contents in fluoridated hydroxyapatite, Acta Biomater., vol. 2, pp , Y. Chen and X. Miao, Effect of fluorine addition on the corrosion resistance of hydroxyapatite ceramics, Ceram. Int., vol. 0, pp , S. J. Kim, H. G. Bang, J. H. Song, and S. Y. Park, Effect of fluoride additive on the mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite/alumina composites, Ceram. Int., vol. 5, pp , T. J. Webster, C. Ergun, R. H. Doremus, R. W. Siegel, and R. Bizios, Enhanced osteoclast-like cell functions on nanophase ceramics, Biomaterials, vol. 22, pp , N. Rameshbabu, K. Prasad Rao, and T. S. S. Kumar, Accelerated microwave synthesis of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite, J. Mater. Sci., vol. 40, pp , N. Rameshbabu, T. S. S. Kumar, and K. P. Rao, Synthesis of nanocrystalline fluoridated hydroxyapatite by microwave processing and its in vitro dissolution study, Bull. Mater. Sci., vol. 29, pp , S. K. Garg, Environmental engineering, Water Supply Engineering, Khanna Publishing, vol. 1, K. Venkateswarlu, A. C. Bose, and N. Rameshbabu, X-ray peak broadening studies of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite by Williamson-Hall analysis, Physica B, vol. 405, pp , C. Suryanarayana and M. G. Norton, X-ray diffraction: A practical approach, New York: Plenum Press Publishing, R. Yogamalar, R. Srinivasan, A. Vinu, K. Ariga, and A. C. Bose, X-ray peak broadening analysis in ZnO nanoparticles, Solid State Commun., vol. 149, pp , D. E. Gray, American institute of physics handbook, New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1972.
5 International Journal of Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics, Vol. 2, No. 6, November 20 [16] T. Mahalingam, V. S. John, and L. S. Hsu, Microstructural analysis of electrodeposited zinc oxide thin films, J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst., vol. 10, pp. 9-14, [17] H. M. Burt and A. G. Mitchell, Crystal defects and dissolution, Int. J. Pharm., vol. 9, pp , V. Muthupandi is a doctorate from Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, India. His research interests are structure property correlation, plasma electrolytic oxidation and corrosion engineering. K. Venkateswarlu obtained his M.Tech. degree (2009) from the Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering and presently is pursuing Ph.D. degree in the Department of Physics, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India. His research interests are surface modification and characterization of biomaterials. A. Chandra Bose is currently working as associate professor in the Department of Physics, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli, India. His current research interests are in the field of oxide nanomaterials and microplasma for MEMS applications. D. Sreekanth obtained his M.Tech. degree in 2005 and presently pursuing Ph.D. degree in the Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India. His research interest is surface modification of biodegradable implant materials. N. Ramesh Babu is currently working as assistant professor in the Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli, India. His research interests are in the field of advanced bioceramics, surface modification of metallic implants, nanostructured processing of materials. M. Sandhyarani obtained her M.Tech. degree in 2009 and presently pursuing Ph.D. degree in the Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India. Her research interests are plasma electrolytic oxidation treatment and corrosion study of biomedical implant materials. 9
BIOACTIVE COATINGS ON 316L STAINLESS STEEL IMPLANTS
 Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs. Vol. 17(2) pp 43-47 (2004) http//www.sbaoi.org BIOACTIVE COATINGS ON 316L STAINLESS STEEL IMPLANTS N. Ramesh Babu*,+, Sushant Manwatkar*, K. Prasada Rao* and T. S. Sampath
Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs. Vol. 17(2) pp 43-47 (2004) http//www.sbaoi.org BIOACTIVE COATINGS ON 316L STAINLESS STEEL IMPLANTS N. Ramesh Babu*,+, Sushant Manwatkar*, K. Prasada Rao* and T. S. Sampath
Phase Characterization of TiO 2 Powder by XRD and TEM
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 357-361 (28) Phase Characterization of TiO 2 Powder by XRD and TEM Kheamrutai Thamaphat 1 *, Pichet Limsuwan 1 and Boonlaer Ngotawornchai 2 ABSTRACT In this study, the commercial
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 357-361 (28) Phase Characterization of TiO 2 Powder by XRD and TEM Kheamrutai Thamaphat 1 *, Pichet Limsuwan 1 and Boonlaer Ngotawornchai 2 ABSTRACT In this study, the commercial
Effect of surface area, pore volume and particle size of P25 titania on the phase transformation of anatase to rutile
 Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 48A, October 2009, pp. 1378-1382 Notes Effect of surface area, pore volume and particle size of P25 titania on the phase transformation of anatase to rutile K Joseph Antony
Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 48A, October 2009, pp. 1378-1382 Notes Effect of surface area, pore volume and particle size of P25 titania on the phase transformation of anatase to rutile K Joseph Antony
Crystal Structure of High Temperature Superconductors. Marie Nelson East Orange Campus High School NJIT Professor: Trevor Tyson
 Crystal Structure of High Temperature Superconductors Marie Nelson East Orange Campus High School NJIT Professor: Trevor Tyson Introduction History of Superconductors Superconductors are material which
Crystal Structure of High Temperature Superconductors Marie Nelson East Orange Campus High School NJIT Professor: Trevor Tyson Introduction History of Superconductors Superconductors are material which
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2009
 Supporting Information Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Controlled Synthesis of Co 3 O 4 Nanopolyhedrons and Nanosheets at Low Temperature Hongying Liang a, Joan M. Raitano a, Lihua
Supporting Information Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Controlled Synthesis of Co 3 O 4 Nanopolyhedrons and Nanosheets at Low Temperature Hongying Liang a, Joan M. Raitano a, Lihua
X-Ray Diffraction HOW IT WORKS WHAT IT CAN AND WHAT IT CANNOT TELL US. Hanno zur Loye
 X-Ray Diffraction HOW IT WORKS WHAT IT CAN AND WHAT IT CANNOT TELL US Hanno zur Loye X-rays are electromagnetic radiation of wavelength about 1 Å (10-10 m), which is about the same size as an atom. The
X-Ray Diffraction HOW IT WORKS WHAT IT CAN AND WHAT IT CANNOT TELL US Hanno zur Loye X-rays are electromagnetic radiation of wavelength about 1 Å (10-10 m), which is about the same size as an atom. The
Introduction to X-Ray Powder Diffraction Data Analysis
 Introduction to X-Ray Powder Diffraction Data Analysis Center for Materials Science and Engineering at MIT http://prism.mit.edu/xray An X-ray diffraction pattern is a plot of the intensity of X-rays scattered
Introduction to X-Ray Powder Diffraction Data Analysis Center for Materials Science and Engineering at MIT http://prism.mit.edu/xray An X-ray diffraction pattern is a plot of the intensity of X-rays scattered
Preparation of ZnS and SnS Nanopowders by Modified SILAR Technique
 Journal of Physical Sciences, Vol. 13, 009, 9-34 ISSN: 097-8791 : www.vidyasagar.ac.in/journal Preparation of ZnS and SnS Nanopowders by Modified SILAR Technique Department of Physics The University of
Journal of Physical Sciences, Vol. 13, 009, 9-34 ISSN: 097-8791 : www.vidyasagar.ac.in/journal Preparation of ZnS and SnS Nanopowders by Modified SILAR Technique Department of Physics The University of
Production of ferrite nanopowders in radiofrequency thermal plasma
 Production of ferrite nanopowders in radiofrequency thermal plasma PhD Theses Loránd Gál Budapest, 2008 HAS Chemical Research Center Institute of Materials and Environmental Chemistry Department of Plasma
Production of ferrite nanopowders in radiofrequency thermal plasma PhD Theses Loránd Gál Budapest, 2008 HAS Chemical Research Center Institute of Materials and Environmental Chemistry Department of Plasma
This is an author-deposited version published in: http://sam.ensam.eu Handle ID:.http://hdl.handle.net/10985/10324
 Science Arts & Métiers (SAM) is an open access repository that collects the work of Arts et Métiers ParisTech researchers and makes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
Science Arts & Métiers (SAM) is an open access repository that collects the work of Arts et Métiers ParisTech researchers and makes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
In vitro examination of human teeth using ultrasound and X-ray diffraction
 Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 6, No. 1, 2004 In vitro examination of human teeth using ultrasound and X-ray diffraction HELENA GAWDA, LESZEK SĘKOWSKI, HANNA TRĘBACZ Department of Biophysics,
Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 6, No. 1, 2004 In vitro examination of human teeth using ultrasound and X-ray diffraction HELENA GAWDA, LESZEK SĘKOWSKI, HANNA TRĘBACZ Department of Biophysics,
DURABILITY OF MORTAR LININGS IN DUCTILE IRON PIPES Durability of mortar linings
 DURABILITY OF MORTAR LININGS IN DUCTILE IRON PIPES Durability of mortar linings I. S. MELAND SINTEF Civil and Environmental Engineering, Cement and Concrete, Trondheim, Norway Durability of Building Materials
DURABILITY OF MORTAR LININGS IN DUCTILE IRON PIPES Durability of mortar linings I. S. MELAND SINTEF Civil and Environmental Engineering, Cement and Concrete, Trondheim, Norway Durability of Building Materials
RAPIDLY SOLIDIFIED COPPER ALLOYS RIBBONS
 Association of Metallurgical Engineers of Serbia AMES Scientific paper UDC:669.35-153.881-412.2=20 RAPIDLY SOLIDIFIED COPPER ALLOYS RIBBONS M. ŠULER 1, L. KOSEC 1, A. C. KNEISSL 2, M. BIZJAK 1, K. RAIĆ
Association of Metallurgical Engineers of Serbia AMES Scientific paper UDC:669.35-153.881-412.2=20 RAPIDLY SOLIDIFIED COPPER ALLOYS RIBBONS M. ŠULER 1, L. KOSEC 1, A. C. KNEISSL 2, M. BIZJAK 1, K. RAIĆ
Mechanical Properties of Metals Mechanical Properties refers to the behavior of material when external forces are applied
 Mechanical Properties of Metals Mechanical Properties refers to the behavior of material when external forces are applied Stress and strain fracture or engineering point of view: allows to predict the
Mechanical Properties of Metals Mechanical Properties refers to the behavior of material when external forces are applied Stress and strain fracture or engineering point of view: allows to predict the
Lösungen Übung Verformung
 Lösungen Übung Verformung 1. (a) What is the meaning of T G? (b) To which materials does it apply? (c) What effect does it have on the toughness and on the stress- strain diagram? 2. Name the four main
Lösungen Übung Verformung 1. (a) What is the meaning of T G? (b) To which materials does it apply? (c) What effect does it have on the toughness and on the stress- strain diagram? 2. Name the four main
Asian Journal on Energy and Environment
 As. J. Energy Env. 2005, 6(04), 193-201 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Synthesis,Characterization and Application of Single and
As. J. Energy Env. 2005, 6(04), 193-201 Asian Journal on Energy and Environment ISSN 1513-4121 Available online at www.asian-energy-journal.info Synthesis,Characterization and Application of Single and
Experiment: Crystal Structure Analysis in Engineering Materials
 Experiment: Crystal Structure Analysis in Engineering Materials Objective The purpose of this experiment is to introduce students to the use of X-ray diffraction techniques for investigating various types
Experiment: Crystal Structure Analysis in Engineering Materials Objective The purpose of this experiment is to introduce students to the use of X-ray diffraction techniques for investigating various types
The atomic packing factor is defined as the ratio of sphere volume to the total unit cell volume, or APF = V S V C. = 2(sphere volume) = 2 = V C = 4R
 3.5 Show that the atomic packing factor for BCC is 0.68. The atomic packing factor is defined as the ratio of sphere volume to the total unit cell volume, or APF = V S V C Since there are two spheres associated
3.5 Show that the atomic packing factor for BCC is 0.68. The atomic packing factor is defined as the ratio of sphere volume to the total unit cell volume, or APF = V S V C Since there are two spheres associated
Structure Factors 59-553 78
 78 Structure Factors Until now, we have only typically considered reflections arising from planes in a hypothetical lattice containing one atom in the asymmetric unit. In practice we will generally deal
78 Structure Factors Until now, we have only typically considered reflections arising from planes in a hypothetical lattice containing one atom in the asymmetric unit. In practice we will generally deal
Size effects. Lecture 6 OUTLINE
 Size effects 1 MTX9100 Nanomaterials Lecture 6 OUTLINE -Why does size influence the material s properties? -How does size influence the material s performance? -Why are properties of nanoscale objects
Size effects 1 MTX9100 Nanomaterials Lecture 6 OUTLINE -Why does size influence the material s properties? -How does size influence the material s performance? -Why are properties of nanoscale objects
Crystal Structure Determination I
 Crystal Structure Determination I Dr. Falak Sher Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences National Workshop on Crystal Structure Determination using Powder XRD, organized by the Khwarzimic
Crystal Structure Determination I Dr. Falak Sher Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences National Workshop on Crystal Structure Determination using Powder XRD, organized by the Khwarzimic
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF STRUCTURAL ZONE MODEL FOR COMPOSITE THIN FILMS IN MAGNETIC RECORDING MEDIA APPLICATION
 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF STRUCTURAL ZONE MODEL FOR COMPOSITE THIN FILMS IN MAGNETIC RECORDING MEDIA APPLICATION Hua Yuan and David E. Laughlin Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Carnegie Mellon
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF STRUCTURAL ZONE MODEL FOR COMPOSITE THIN FILMS IN MAGNETIC RECORDING MEDIA APPLICATION Hua Yuan and David E. Laughlin Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Carnegie Mellon
Estimation of Hardness of Water by EDTA Method
 Estimation of Hardness of Water by EDTA Method 1 EXPERIMENT 1 Estimation of Hardness of Water by EDTA Method INTRODUCTION Water hardness is the traditional measure of the capacity of water to precipitate
Estimation of Hardness of Water by EDTA Method 1 EXPERIMENT 1 Estimation of Hardness of Water by EDTA Method INTRODUCTION Water hardness is the traditional measure of the capacity of water to precipitate
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope
 Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
Numerical Analysis of Independent Wire Strand Core (IWSC) Wire Rope Rakesh Sidharthan 1 Gnanavel B K 2 Assistant professor Mechanical, Department Professor, Mechanical Department, Gojan engineering college,
MISCIBILITY AND INTERACTIONS IN CHITOSAN AND POLYACRYLAMIDE MIXTURES
 MISCIBILITY AND INTERACTIONS IN CHITOSAN AND POLYACRYLAMIDE MIXTURES Katarzyna Lewandowska Faculty of Chemistry Nicolaus Copernicus University, ul. Gagarina 7, 87-100 Toruń, Poland e-mail: [email protected]
MISCIBILITY AND INTERACTIONS IN CHITOSAN AND POLYACRYLAMIDE MIXTURES Katarzyna Lewandowska Faculty of Chemistry Nicolaus Copernicus University, ul. Gagarina 7, 87-100 Toruń, Poland e-mail: [email protected]
Sputtered AlN Thin Films on Si and Electrodes for MEMS Resonators: Relationship Between Surface Quality Microstructure and Film Properties
 Sputtered AlN Thin Films on and Electrodes for MEMS Resonators: Relationship Between Surface Quality Microstructure and Film Properties S. Mishin, D. R. Marx and B. Sylvia, Advanced Modular Sputtering,
Sputtered AlN Thin Films on and Electrodes for MEMS Resonators: Relationship Between Surface Quality Microstructure and Film Properties S. Mishin, D. R. Marx and B. Sylvia, Advanced Modular Sputtering,
Preparation and characterization of nanostructured powders of hydroxyapatite
 Preparation and characterization of nanostructured powders of hydroxyapatite Martínez-Castañón G. A. *, Loyola-Rodríguez J. P., Zavala-Alonso N. V. Maestría en Ciencias Odontológicas, Facultad de Estomatología,
Preparation and characterization of nanostructured powders of hydroxyapatite Martínez-Castañón G. A. *, Loyola-Rodríguez J. P., Zavala-Alonso N. V. Maestría en Ciencias Odontológicas, Facultad de Estomatología,
Defects Introduction. Bonding + Structure + Defects. Properties
 Defects Introduction Bonding + Structure + Defects Properties The processing determines the defects Composition Bonding type Structure of Crystalline Processing factors Defects Microstructure Types of
Defects Introduction Bonding + Structure + Defects Properties The processing determines the defects Composition Bonding type Structure of Crystalline Processing factors Defects Microstructure Types of
ORIENTATION CHARACTERISTICS OF THE MICROSTRUCTURE OF MATERIALS
 ORIENTATION CHARACTERISTICS OF THE MICROSTRUCTURE OF MATERIALS K. Sztwiertnia Polish Academy of Sciences, Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science, 25 Reymonta St., 30-059 Krakow, Poland MMN 2009
ORIENTATION CHARACTERISTICS OF THE MICROSTRUCTURE OF MATERIALS K. Sztwiertnia Polish Academy of Sciences, Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science, 25 Reymonta St., 30-059 Krakow, Poland MMN 2009
MSE 528 - PRECIPITATION HARDENING IN 7075 ALUMINUM ALLOY
 MSE 528 - PRECIPITATION HARDENING IN 7075 ALUMINUM ALLOY Objective To study the time and temperature variations in the hardness and electrical conductivity of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu high strength alloy on isothermal
MSE 528 - PRECIPITATION HARDENING IN 7075 ALUMINUM ALLOY Objective To study the time and temperature variations in the hardness and electrical conductivity of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu high strength alloy on isothermal
Effects of aging on the kinetics of nanocrystalline anatase crystallite growth
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 95 (2006) 275 279 Effects of aging on the kinetics of nanocrystalline anatase crystallite growth Hsing-I Hsiang, Shih-Chung Lin Department of Resources Engineering, National
Materials Chemistry and Physics 95 (2006) 275 279 Effects of aging on the kinetics of nanocrystalline anatase crystallite growth Hsing-I Hsiang, Shih-Chung Lin Department of Resources Engineering, National
The study of structural and optical properties of TiO 2 :Tb thin films
 Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXVII, No. 4, 2007 The study of structural and optical properties of TiO 2 :Tb thin films AGNIESZKA BORKOWSKA, JAROSLAW DOMARADZKI, DANUTA KACZMAREK, DAMIAN WOJCIESZAK Faculty of
Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXVII, No. 4, 2007 The study of structural and optical properties of TiO 2 :Tb thin films AGNIESZKA BORKOWSKA, JAROSLAW DOMARADZKI, DANUTA KACZMAREK, DAMIAN WOJCIESZAK Faculty of
EFFECT OF SEVERE PLASTIC DEFORMATION ON STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF AUSTENITIC AISI 316 GRADE STEEL
 EFFECT OF SEVERE PLASTIC DEFORMATION ON STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF AUSTENITIC AISI 316 GRADE STEEL Ladislav KANDER a, Miroslav GREGER b a MATERIÁLOVÝ A METALURGICKÝ VÝZKUM, s.r.o., Ostrava, Czech Republic,
EFFECT OF SEVERE PLASTIC DEFORMATION ON STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF AUSTENITIC AISI 316 GRADE STEEL Ladislav KANDER a, Miroslav GREGER b a MATERIÁLOVÝ A METALURGICKÝ VÝZKUM, s.r.o., Ostrava, Czech Republic,
Laser sintering of greens compacts of MoSi 2
 Laser sintering of greens compacts of MoSi 2 G. de Vasconcelos 1, R. Cesar Maia 2, C.A.A.Cairo 3, R. Riva 2, N.A.S.Rodrigues 2, F.C.L.Mello 3 Instituto de Estudos Avançados 1, Instituto Tecnológico de
Laser sintering of greens compacts of MoSi 2 G. de Vasconcelos 1, R. Cesar Maia 2, C.A.A.Cairo 3, R. Riva 2, N.A.S.Rodrigues 2, F.C.L.Mello 3 Instituto de Estudos Avançados 1, Instituto Tecnológico de
X-ray Diffraction and EBSD
 X-ray Diffraction and EBSD Jonathan Cowen Swagelok Center for the Surface Analysis of Materials Case School of Engineering Case Western Reserve University October 27, 2014 Outline X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
X-ray Diffraction and EBSD Jonathan Cowen Swagelok Center for the Surface Analysis of Materials Case School of Engineering Case Western Reserve University October 27, 2014 Outline X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
X-ray diffraction techniques for thin films
 X-ray diffraction techniques for thin films Rigaku Corporation Application Laboratory Takayuki Konya 1 Today s contents (PM) Introduction X-ray diffraction method Out-of-Plane In-Plane Pole figure Reciprocal
X-ray diffraction techniques for thin films Rigaku Corporation Application Laboratory Takayuki Konya 1 Today s contents (PM) Introduction X-ray diffraction method Out-of-Plane In-Plane Pole figure Reciprocal
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2005 69451 Weinheim, Germany Magnetic Nanoparticle-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanorod-Based Stimuli-Responsive Controlled Release Delivery System** Supratim Giri, Brian G.
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2005 69451 Weinheim, Germany Magnetic Nanoparticle-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanorod-Based Stimuli-Responsive Controlled Release Delivery System** Supratim Giri, Brian G.
CONSOLIDATION AND HIGH STRAIN RATE MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF NANOCRYSTALLINE TANTALUM POWDER
 CONSOLIDATION AND HIGH STRAIN RATE MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF NANOCRYSTALLINE TANTALUM POWDER Sang H. Yoo, T.S. Sudarshan, Krupa Sethuram Materials Modification Inc, 2929-P1 Eskridge Rd, Fairfax, VA, 22031
CONSOLIDATION AND HIGH STRAIN RATE MECHANICAL BEHAVIOR OF NANOCRYSTALLINE TANTALUM POWDER Sang H. Yoo, T.S. Sudarshan, Krupa Sethuram Materials Modification Inc, 2929-P1 Eskridge Rd, Fairfax, VA, 22031
Chapter Outline. Mechanical Properties of Metals How do metals respond to external loads?
 Mechanical Properties of Metals How do metals respond to external loads? Stress and Strain Tension Compression Shear Torsion Elastic deformation Plastic Deformation Yield Strength Tensile Strength Ductility
Mechanical Properties of Metals How do metals respond to external loads? Stress and Strain Tension Compression Shear Torsion Elastic deformation Plastic Deformation Yield Strength Tensile Strength Ductility
Enhancement of Breakdown Strength and Energy Density in
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Enhancement of Breakdown Strength and Energy Density in
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Enhancement of Breakdown Strength and Energy Density in
CHEMICAL PRECIPITATION: WATER SOFTENING
 CHEMICAL PRECIPITATION: WATER SOFTENING Submitted to: Dr. Hashsham Research Complex Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Michigan State University East Lansing, MI 4884 Authors
CHEMICAL PRECIPITATION: WATER SOFTENING Submitted to: Dr. Hashsham Research Complex Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Michigan State University East Lansing, MI 4884 Authors
Physical & Chemical Properties. Properties
 Physical & Chemical Properties Properties Carbon black can be broadly defined as very fine particulate aggregates of carbon possessing an amorphous quasi-graphitic molecular structure. The most significant
Physical & Chemical Properties Properties Carbon black can be broadly defined as very fine particulate aggregates of carbon possessing an amorphous quasi-graphitic molecular structure. The most significant
Chemical Engineering - CHEN
 Auburn University 1 Chemical Engineering - CHEN Courses CHEN 2100 PRINCIPLES OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING (4) LEC. 3. LAB. 3. Pr. (CHEM 1110 or CHEM 1117 or CHEM 1030) and (MATH 1610 or MATH 1613 or MATH 1617
Auburn University 1 Chemical Engineering - CHEN Courses CHEN 2100 PRINCIPLES OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING (4) LEC. 3. LAB. 3. Pr. (CHEM 1110 or CHEM 1117 or CHEM 1030) and (MATH 1610 or MATH 1613 or MATH 1617
Pulsed laser deposition of organic materials
 Pulsed laser deposition of organic materials PhD theses Gabriella Kecskeméti Department of Optics and Quantum Electronics University of Szeged Supervisor: Dr. Béla Hopp senior research fellow Department
Pulsed laser deposition of organic materials PhD theses Gabriella Kecskeméti Department of Optics and Quantum Electronics University of Szeged Supervisor: Dr. Béla Hopp senior research fellow Department
5.0 EXPERIMENT ON DETERMINATION OF TOTAL HARDNESS
 5.0 EXPERIMENT ON DETERMINATION OF TOTAL HARDNESS Sl. No. Contents Preamble 5.1 Aim 5.2 Introduction 5.2.1 Environmental Significance 5.3 Principle 5.4 Materials Required 5.4.1 Apparatus Required 5.4.2
5.0 EXPERIMENT ON DETERMINATION OF TOTAL HARDNESS Sl. No. Contents Preamble 5.1 Aim 5.2 Introduction 5.2.1 Environmental Significance 5.3 Principle 5.4 Materials Required 5.4.1 Apparatus Required 5.4.2
WEEKLY COURSE SCHEDULE : PRIMARY EDUCATION
 WEEKLY COURSE SCHEDULE : PRIMARY EDUCATION Semester 1 Week 1 ( 19.09.2011-23.09.2011 ) Introduction to sol-gel processes Properties of X-Rays General Explanations on Process Planning Introduction Semester
WEEKLY COURSE SCHEDULE : PRIMARY EDUCATION Semester 1 Week 1 ( 19.09.2011-23.09.2011 ) Introduction to sol-gel processes Properties of X-Rays General Explanations on Process Planning Introduction Semester
Module #17. Work/Strain Hardening. READING LIST DIETER: Ch. 4, pp. 138-143; Ch. 6 in Dieter
 Module #17 Work/Strain Hardening READING LIST DIETER: Ch. 4, pp. 138-143; Ch. 6 in Dieter D. Kuhlmann-Wilsdorf, Trans. AIME, v. 224 (1962) pp. 1047-1061 Work Hardening RECALL: During plastic deformation,
Module #17 Work/Strain Hardening READING LIST DIETER: Ch. 4, pp. 138-143; Ch. 6 in Dieter D. Kuhlmann-Wilsdorf, Trans. AIME, v. 224 (1962) pp. 1047-1061 Work Hardening RECALL: During plastic deformation,
LECTURE SUMMARY September 30th 2009
 LECTURE SUMMARY September 30 th 2009 Key Lecture Topics Crystal Structures in Relation to Slip Systems Resolved Shear Stress Using a Stereographic Projection to Determine the Active Slip System Slip Planes
LECTURE SUMMARY September 30 th 2009 Key Lecture Topics Crystal Structures in Relation to Slip Systems Resolved Shear Stress Using a Stereographic Projection to Determine the Active Slip System Slip Planes
1. Fluids Mechanics and Fluid Properties. 1.1 Objectives of this section. 1.2 Fluids
 1. Fluids Mechanics and Fluid Properties What is fluid mechanics? As its name suggests it is the branch of applied mechanics concerned with the statics and dynamics of fluids - both liquids and gases.
1. Fluids Mechanics and Fluid Properties What is fluid mechanics? As its name suggests it is the branch of applied mechanics concerned with the statics and dynamics of fluids - both liquids and gases.
Departments and Specializations
 Departments and Specializations Department Post Specialization Areas Aerospace Engineering: Only candidates with a clear focus on one or more of the specified areas will be considered Experimental Structural
Departments and Specializations Department Post Specialization Areas Aerospace Engineering: Only candidates with a clear focus on one or more of the specified areas will be considered Experimental Structural
Modern Construction Materials Prof. Ravindra Gettu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Modern Construction Materials Prof. Ravindra Gettu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 2 Lecture - 2 Part 2 of 2 Review of Atomic Bonding II We will continue
Modern Construction Materials Prof. Ravindra Gettu Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 2 Lecture - 2 Part 2 of 2 Review of Atomic Bonding II We will continue
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Simple and Rapid Synthesis of Ultrathin Gold Nanowires, Their Self-Assembly and Application in Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Huajun Feng, a Yanmei Yang, a Yumeng You, b Gongping
Supporting Information Simple and Rapid Synthesis of Ultrathin Gold Nanowires, Their Self-Assembly and Application in Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Huajun Feng, a Yanmei Yang, a Yumeng You, b Gongping
Microscopy and Nanoindentation. Combining Orientation Imaging. to investigate localized. deformation behaviour. Felix Reinauer
 Combining Orientation Imaging Microscopy and Nanoindentation to investigate localized deformation behaviour Felix Reinauer René de Kloe Matt Nowell Introduction Anisotropy in crystalline materials Presentation
Combining Orientation Imaging Microscopy and Nanoindentation to investigate localized deformation behaviour Felix Reinauer René de Kloe Matt Nowell Introduction Anisotropy in crystalline materials Presentation
DIEGO TONINI MORPHOLOGY OF NIOBIUM FILMS SPUTTERED AT DIFFERENT TARGET SUBSTRATE ANGLE
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA SCIENCE FACULTY MATERIAL SCIENCE DEGREE INFN LABORATORI NAZIONALI DI LEGNARO DIEGO TONINI MORPHOLOGY OF NIOBIUM FILMS SPUTTERED AT DIFFERENT TARGET SUBSTRATE ANGLE 2 QUESTIONS
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA SCIENCE FACULTY MATERIAL SCIENCE DEGREE INFN LABORATORI NAZIONALI DI LEGNARO DIEGO TONINI MORPHOLOGY OF NIOBIUM FILMS SPUTTERED AT DIFFERENT TARGET SUBSTRATE ANGLE 2 QUESTIONS
Effect of Consolidation Process on Tensile Properties of Fe Cu P/M Alloy from Rapidly Solidified Powder
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 44, No. 7 (2003) pp. 1311 to 1315 Special Issue on Growth of Ecomaterials as a Key to Eco-Society #2003 The Japan Institute of Metals Effect of Consolidation Process on Tensile
Materials Transactions, Vol. 44, No. 7 (2003) pp. 1311 to 1315 Special Issue on Growth of Ecomaterials as a Key to Eco-Society #2003 The Japan Institute of Metals Effect of Consolidation Process on Tensile
Chemistry 119: Experiment 7. Potentiometric Titration of Ascorbic Acid in Vitamin C Tablets
 Chemistry 119: Experiment 7 Potentiometric Titration of Ascorbic Acid in Vitamin C Tablets Vitamin C is another name for ascorbic acid (C 6 H 8 O 6, see below ), a weak acid that can be determined by titration
Chemistry 119: Experiment 7 Potentiometric Titration of Ascorbic Acid in Vitamin C Tablets Vitamin C is another name for ascorbic acid (C 6 H 8 O 6, see below ), a weak acid that can be determined by titration
Optical Properties of Sputtered Tantalum Nitride Films Determined by Spectroscopic Ellipsometry
 Optical Properties of Sputtered Tantalum Nitride Films Determined by Spectroscopic Ellipsometry Thomas Waechtler a, Bernd Gruska b, Sven Zimmermann a, Stefan E. Schulz a, Thomas Gessner a a Chemnitz University
Optical Properties of Sputtered Tantalum Nitride Films Determined by Spectroscopic Ellipsometry Thomas Waechtler a, Bernd Gruska b, Sven Zimmermann a, Stefan E. Schulz a, Thomas Gessner a a Chemnitz University
Lecture 18 Strain Hardening And Recrystallization
 -138- Lecture 18 Strain Hardening And Recrystallization Strain Hardening We have previously seen that the flow stress (the stress necessary to produce a certain plastic strain rate) increases with increasing
-138- Lecture 18 Strain Hardening And Recrystallization Strain Hardening We have previously seen that the flow stress (the stress necessary to produce a certain plastic strain rate) increases with increasing
THE EFFECT OF HIGH ENERGY MILLING ON THE MICROSTRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF A Ti-13Nb-13Zr ALLOY PRODUCED BY POWDER METALLURGY
 THE EFFECT OF HIGH ENERGY MILLING ON THE MICROSTRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF A Ti-13Nb-13Zr ALLOY PRODUCED BY POWDER METALLURGY J. H. Duvaizem¹, S. C. Silva¹, A. H. Bressiani¹, R. N. de Faria¹,
THE EFFECT OF HIGH ENERGY MILLING ON THE MICROSTRUCTURE AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF A Ti-13Nb-13Zr ALLOY PRODUCED BY POWDER METALLURGY J. H. Duvaizem¹, S. C. Silva¹, A. H. Bressiani¹, R. N. de Faria¹,
Objectives. Experimentally determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and modules of elasticity and ductility of given materials.
 Lab 3 Tension Test Objectives Concepts Background Experimental Procedure Report Requirements Discussion Objectives Experimentally determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and modules of elasticity
Lab 3 Tension Test Objectives Concepts Background Experimental Procedure Report Requirements Discussion Objectives Experimentally determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and modules of elasticity
Spectroscopic Ellipsometry:
 Spectroscopic : What it is, what it will do, and what it won t do by Harland G. Tompkins Introduction Fundamentals Anatomy of an ellipsometric spectrum Analysis of an ellipsometric spectrum What you can
Spectroscopic : What it is, what it will do, and what it won t do by Harland G. Tompkins Introduction Fundamentals Anatomy of an ellipsometric spectrum Analysis of an ellipsometric spectrum What you can
USING MATLAB FOR MATERIALS DESIGN: DESCRIBING GRAIN ORIENTATIONS IN METALS Claes Olsson, PhD - Docent / Sandvik Materials Technology
 USING MATLAB FOR MATERIALS DESIGN: DESCRIBING GRAIN ORIENTATIONS IN METALS Claes Olsson, PhD - Docent / Sandvik Materials Technology THE SANDVIK GROUP MACHINING SOLUTIONS MINING AND CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS
USING MATLAB FOR MATERIALS DESIGN: DESCRIBING GRAIN ORIENTATIONS IN METALS Claes Olsson, PhD - Docent / Sandvik Materials Technology THE SANDVIK GROUP MACHINING SOLUTIONS MINING AND CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS
Formation of solids from solutions and melts
 Formation of solids from solutions and melts Solids from a liquid phase. 1. The liquid has the same composition as the solid. Formed from the melt without any chemical transformation. Crystallization and
Formation of solids from solutions and melts Solids from a liquid phase. 1. The liquid has the same composition as the solid. Formed from the melt without any chemical transformation. Crystallization and
HYDROGEN STORAGE AND MICROSTRUCTURE INVESTIGATIONS OF La 0.7- Av. Prof. Lineu Prestes, 2242, ZIP 05508-000, São Paulo, Brazil.
 HYDROGEN STORAGE AND MICROSTRUCTURE INVESTIGATIONS OF La 0.7- x Pr x ALLOYS G. S. Galdino 1,a, J. C. S. Casini 1, E. A. Ferreira 1, R. N. Faria 1, H. Takiishi 1 a [email protected] 1 Department of Metallurgy,
HYDROGEN STORAGE AND MICROSTRUCTURE INVESTIGATIONS OF La 0.7- x Pr x ALLOYS G. S. Galdino 1,a, J. C. S. Casini 1, E. A. Ferreira 1, R. N. Faria 1, H. Takiishi 1 a [email protected] 1 Department of Metallurgy,
Multi-walled Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Aluminum Nanocomposites by Cold Kinetic Spraying
 Multi-walled Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Aluminum Nanocomposites by Cold Kinetic Spraying SRINIVASA R BAKSHI 1, and ARVIND AGARWAL 2 1,2 Florida International University, Miami, FL 33174, USA. E-mail: [email protected]
Multi-walled Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Aluminum Nanocomposites by Cold Kinetic Spraying SRINIVASA R BAKSHI 1, and ARVIND AGARWAL 2 1,2 Florida International University, Miami, FL 33174, USA. E-mail: [email protected]
Chapter 7: Basics of X-ray Diffraction
 Providing Solutions To Your Diffraction Needs. Chapter 7: Basics of X-ray Diffraction Scintag has prepared this section for use by customers and authorized personnel. The information contained herein is
Providing Solutions To Your Diffraction Needs. Chapter 7: Basics of X-ray Diffraction Scintag has prepared this section for use by customers and authorized personnel. The information contained herein is
Heterogeneous Catalysis and Catalytic Processes Prof. K. K. Pant Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Heterogeneous Catalysis and Catalytic Processes Prof. K. K. Pant Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module - 03 Lecture 10 Good morning. In my last lecture, I was
Heterogeneous Catalysis and Catalytic Processes Prof. K. K. Pant Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module - 03 Lecture 10 Good morning. In my last lecture, I was
HW 10. = 3.3 GPa (483,000 psi)
 HW 10 Problem 15.1 Elastic modulus and tensile strength of poly(methyl methacrylate) at room temperature [20 C (68 F)]. Compare these with the corresponding values in Table 15.1. Figure 15.3 is accurate;
HW 10 Problem 15.1 Elastic modulus and tensile strength of poly(methyl methacrylate) at room temperature [20 C (68 F)]. Compare these with the corresponding values in Table 15.1. Figure 15.3 is accurate;
PIEZOELECTRIC FILMS TECHNICAL INFORMATION
 PIEZOELECTRIC FILMS TECHNICAL INFORMATION 1 Table of Contents 1. PIEZOELECTRIC AND PYROELECTRIC EFFECTS 3 2. PIEZOELECTRIC FILMS 3 3. CHARACTERISTICS PROPERTIES OF PIEZOELECTRIC FILMS 3 4. PROPERTIES OF
PIEZOELECTRIC FILMS TECHNICAL INFORMATION 1 Table of Contents 1. PIEZOELECTRIC AND PYROELECTRIC EFFECTS 3 2. PIEZOELECTRIC FILMS 3 3. CHARACTERISTICS PROPERTIES OF PIEZOELECTRIC FILMS 3 4. PROPERTIES OF
/ DSM / IRAMIS / LLB)
 RESIDUAL STRESSES ANF Métallurgie Fondamentale Vincent Klosek (CEA / DSM / IRAMIS / LLB) 23/10/2012 8 NOVEMBRE 2012 CEA 23 OCTOBRE 2012 PAGE 1 INTRODUCTION Residual Stresses? Static multiaxial stresses
RESIDUAL STRESSES ANF Métallurgie Fondamentale Vincent Klosek (CEA / DSM / IRAMIS / LLB) 23/10/2012 8 NOVEMBRE 2012 CEA 23 OCTOBRE 2012 PAGE 1 INTRODUCTION Residual Stresses? Static multiaxial stresses
Syllabus OC18 Use litmus or a universal indicator to test a variety of solutions, and classify these as acidic, basic or neutral
 Chemistry: 9. Acids and Bases Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OC18 Use litmus or a universal indicator to test a variety
Chemistry: 9. Acids and Bases Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OC18 Use litmus or a universal indicator to test a variety
Master's Programs. Applied Chemisty. Subject
 Master's Programs Applied Chemisty Optional Advanced Seminar in Materials Science and Engineering I Advanced Seminar in Materials Science and Engineering II Special Project in Materials Science and Engineering
Master's Programs Applied Chemisty Optional Advanced Seminar in Materials Science and Engineering I Advanced Seminar in Materials Science and Engineering II Special Project in Materials Science and Engineering
TIE-31: Mechanical and thermal properties of optical glass
 PAGE 1/10 1 Density The density of optical glass varies from 239 for N-BK10 to 603 for SF66 In most cases glasses with higher densities also have higher refractive indices (eg SF type glasses) The density
PAGE 1/10 1 Density The density of optical glass varies from 239 for N-BK10 to 603 for SF66 In most cases glasses with higher densities also have higher refractive indices (eg SF type glasses) The density
Diffraction Course Series 2015
 Diffraction Course Series 2015 Mark Wainwright Analytical Centre Kensington Campus, Chemical Sciences Building F10, Room G37 The Mark Wainwright Analytical Centre is offering a new series of courses covering
Diffraction Course Series 2015 Mark Wainwright Analytical Centre Kensington Campus, Chemical Sciences Building F10, Room G37 The Mark Wainwright Analytical Centre is offering a new series of courses covering
Indiana's Academic Standards 2010 ICP Indiana's Academic Standards 2016 ICP. map) that describe the relationship acceleration, velocity and distance.
 .1.1 Measure the motion of objects to understand.1.1 Develop graphical, the relationships among distance, velocity and mathematical, and pictorial acceleration. Develop deeper understanding through representations
.1.1 Measure the motion of objects to understand.1.1 Develop graphical, the relationships among distance, velocity and mathematical, and pictorial acceleration. Develop deeper understanding through representations
J H Liao 1, Jianshe Tang 2,b, Ching Hwa Weng 2, Wei Lu 2, Han Wen Chen 2, John TC Lee 2
 Solid State Phenomena Vol. 134 (2008) pp 359-362 Online available since 2007/Nov/20 at www.scientific.net (2008) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.134.359 Metal Hard
Solid State Phenomena Vol. 134 (2008) pp 359-362 Online available since 2007/Nov/20 at www.scientific.net (2008) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.134.359 Metal Hard
Chapter 3. 1. 3 types of materials- amorphous, crystalline, and polycrystalline. 5. Same as #3 for the ceramic and diamond crystal structures.
 Chapter Highlights: Notes: 1. types of materials- amorphous, crystalline, and polycrystalline.. Understand the meaning of crystallinity, which refers to a regular lattice based on a repeating unit cell..
Chapter Highlights: Notes: 1. types of materials- amorphous, crystalline, and polycrystalline.. Understand the meaning of crystallinity, which refers to a regular lattice based on a repeating unit cell..
MANUFACTURE OF CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY DEVICE OF POLYCAPROLACTONE BY SELECTIVE LASER SINTERING ABSTRACT
 MANUFACTURE OF CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY DEVICE OF POLYCAPROLACTONE BY SELECTIVE LASER SINTERING P. Klauss 1*, G. V. Salmoria 1, M. Souza 1, L. A. Kanis 2 1* Laboratory CIMJECT, Federal University of Santa
MANUFACTURE OF CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY DEVICE OF POLYCAPROLACTONE BY SELECTIVE LASER SINTERING P. Klauss 1*, G. V. Salmoria 1, M. Souza 1, L. A. Kanis 2 1* Laboratory CIMJECT, Federal University of Santa
Oil absorption in mesoporous silica particles
 Processing and Application of Ceramics 4 [4] (2010) 265 269 Oil absorption in mesoporous silica particles Radislav Filipović 1,2,*, Dragica Lazić 1, Mitar Perušić 1, Ivan Stijepović 3 1 Faculty of Technology,
Processing and Application of Ceramics 4 [4] (2010) 265 269 Oil absorption in mesoporous silica particles Radislav Filipović 1,2,*, Dragica Lazić 1, Mitar Perušić 1, Ivan Stijepović 3 1 Faculty of Technology,
Effect of Hydrogenation Pressure on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-13Nb-13Zr Alloy Produced by Powder Metallurgy
 Materials Science Forum Vols. 660-661 (2010) pp 176-181 Online available since 2010/Oct/25 at www.scientific.net (2010) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.660-661.176
Materials Science Forum Vols. 660-661 (2010) pp 176-181 Online available since 2010/Oct/25 at www.scientific.net (2010) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.660-661.176
Determination of the amount of sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide in a mixture by titration.
 Module 9 : Experiments in Chemistry Lecture 38 : Titrations : Acid-Base, Redox and Complexometric Objectives In this lecture you will learn the techniques to do following Determination of the amount of
Module 9 : Experiments in Chemistry Lecture 38 : Titrations : Acid-Base, Redox and Complexometric Objectives In this lecture you will learn the techniques to do following Determination of the amount of
Phosphate Recovery from Municipal Wastewater through Crystallization of Calcium Phosphate
 Phosphate Recovery from Municipal Wastewater through Crystallization of Calcium Phosphate A. Alamdari, Ph.D. * and S. Rohani, M.Sc. * Department of Chemical Engineering, School of Engineering, Shiraz University,
Phosphate Recovery from Municipal Wastewater through Crystallization of Calcium Phosphate A. Alamdari, Ph.D. * and S. Rohani, M.Sc. * Department of Chemical Engineering, School of Engineering, Shiraz University,
Silver-zinc oxide electrical contact materials by mechanochemical synthesis route
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 45, January 2007, pp. 9-15 Silver-zinc oxide electrical contact materials by mechanochemical synthesis route P B Joshi 1, V J Rao 1, B R Rehani 1 & Arun Pratap
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 45, January 2007, pp. 9-15 Silver-zinc oxide electrical contact materials by mechanochemical synthesis route P B Joshi 1, V J Rao 1, B R Rehani 1 & Arun Pratap
Using the PDF for material identification using elemental data. from XRF and SEM EDS.
 XRF and SEM EDS Using the PDF for material identification using elemental data from XRF and SEM EDS. XRF and SEM EDS What? The Powder Diffraction File contains data on pure solid state compounds of well
XRF and SEM EDS Using the PDF for material identification using elemental data from XRF and SEM EDS. XRF and SEM EDS What? The Powder Diffraction File contains data on pure solid state compounds of well
Photocatalytic and photoelectric properties of cubic Ag 3 PO 4 sub-microcrystals with sharp corners and edges
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Supporting Information for Photocatalytic and photoelectric properties of cubic Ag 3 PO 4 sub-microcrystals with sharp corners and edges
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Supporting Information for Photocatalytic and photoelectric properties of cubic Ag 3 PO 4 sub-microcrystals with sharp corners and edges
The interaction of Cu(100)-Fe surfaces with oxygen studied with photoelectron spectroscopy. I
 5 The interaction of Cu(100)-Fe surfaces with oxygen studied with photoelectron spectroscopy. I Mg Kα excited photoemission. Abstract The oxidation of Cu(100)-Fe surfaces was studied using XPS. Surfaces
5 The interaction of Cu(100)-Fe surfaces with oxygen studied with photoelectron spectroscopy. I Mg Kα excited photoemission. Abstract The oxidation of Cu(100)-Fe surfaces was studied using XPS. Surfaces
Science Standard Articulated by Grade Level Strand 5: Physical Science
 Concept 1: Properties of Objects and Materials Classify objects and materials by their observable properties. Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 PO 1. Identify the following observable properties
Concept 1: Properties of Objects and Materials Classify objects and materials by their observable properties. Kindergarten Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 PO 1. Identify the following observable properties
Heat Transfer Prof. Dr. Aloke Kumar Ghosal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Heat Transfer Prof. Dr. Aloke Kumar Ghosal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module No. # 02 One Dimensional Steady State Heat Transfer Lecture No. # 05 Extended
Heat Transfer Prof. Dr. Aloke Kumar Ghosal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module No. # 02 One Dimensional Steady State Heat Transfer Lecture No. # 05 Extended
Thomas J. Webster, Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering and School of Materials Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907
 Nanotechnology to Benefit Tissue Engineering Thomas J. Webster, Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering and School of Materials Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907 Introduction Nanobiotechnology
Nanotechnology to Benefit Tissue Engineering Thomas J. Webster, Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering and School of Materials Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907 Introduction Nanobiotechnology
VALIDATION OF ANALYTICAL PROCEDURES: TEXT AND METHODOLOGY Q2(R1)
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE VALIDATION OF ANALYTICAL PROCEDURES: TEXT AND METHODOLOGY
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE VALIDATION OF ANALYTICAL PROCEDURES: TEXT AND METHODOLOGY
Mehmet Burak KAYNAR Physics Engineer. Outline. Personal Information
 Mehmet Burak KAYNAR Physics Engineer Hacettepe Uni. Physic Engineering Dept. SNTG Lab. Beytepe, Ankara Turkey Tel: +90 536 251 1158 Fax: +90 312 299 20 37 e-mail: [email protected] Web: http://yunus.hacettepe.edu.tr/~bkaynar/
Mehmet Burak KAYNAR Physics Engineer Hacettepe Uni. Physic Engineering Dept. SNTG Lab. Beytepe, Ankara Turkey Tel: +90 536 251 1158 Fax: +90 312 299 20 37 e-mail: [email protected] Web: http://yunus.hacettepe.edu.tr/~bkaynar/
How to prepare standard solutions
 World Bank & Government of The Netherlands funded Training module # WQ -04 How to prepare standard solutions New Delhi, May 1999 CSMRS Building, 4th Floor, Olof Palme Marg, Hauz Khas, New Delhi 11 00 16
World Bank & Government of The Netherlands funded Training module # WQ -04 How to prepare standard solutions New Delhi, May 1999 CSMRS Building, 4th Floor, Olof Palme Marg, Hauz Khas, New Delhi 11 00 16
Fundamentals of grain boundaries and grain boundary migration
 1. Fundamentals of grain boundaries and grain boundary migration 1.1. Introduction The properties of crystalline metallic materials are determined by their deviation from a perfect crystal lattice, which
1. Fundamentals of grain boundaries and grain boundary migration 1.1. Introduction The properties of crystalline metallic materials are determined by their deviation from a perfect crystal lattice, which
QUALANOD SPECIFICATIONS UPDATE SHEET Nº 9 Edition 01.07.2010 22.11.11 page 1/5 COLD SEALING PROCESS
 page 1/5 COLD SEALING PROCESS Proposal QUALITAL QUALANOD resolution: Meeting in June 2010, October 2011 Date of application: 1 January 2012 Parts of the Specifications concerned: Section 3.3.6 furthermore
page 1/5 COLD SEALING PROCESS Proposal QUALITAL QUALANOD resolution: Meeting in June 2010, October 2011 Date of application: 1 January 2012 Parts of the Specifications concerned: Section 3.3.6 furthermore
X-ray thin-film measurement techniques
 Technical articles X-ray thin-film measurement techniques II. Out-of-plane diffraction measurements Toru Mitsunaga* 1. Introduction A thin-film sample is two-dimensionally formed on the surface of a substrate,
Technical articles X-ray thin-film measurement techniques II. Out-of-plane diffraction measurements Toru Mitsunaga* 1. Introduction A thin-film sample is two-dimensionally formed on the surface of a substrate,
