Page 1 of 17 TABLE OF CONTENTS. Section
|
|
|
- Edmund Nelson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 of 17 ACTIVITY: Drosophila TABLE OF CONTENTS Section i. Overview ii. Learning Ojectives iii. Prior Knowledge Needed iv. Expected Learning Outcomes v. Estimated Time vi. Alignment to Standards 1. Introduction 2. Teacher Registration and Workspace Guide 3. Activity Entry Page 4. Starting the Activity 5. Ordering Flies 6. Mating Flies 7. Using the Microscope 8. Analyzing Data 9. Entering a Numerical Hypothesis 9a. Chi-square Test 10. Recording into the Noteook 11. Composing a Report 12. Taking the Quiz 13. Assessment Results 14. Suggested Assignments 15. Appendix i. Overview Students learn and apply the principles of Mendelian inheritance y experimentation with the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Students make hypotheses for monohyrid, dihyrid and sex-linked traits and test their hypotheses y selecting fruit flies with different visile mutations, mating them, and analyzing the phenotypic ratios of the offspring. Students record their oservations into an online noteook and write an online la report. ii. Learning Ojectives 1. Formulate hypotheses 2. Design experiments 3. Analyze and interpret data iii. Prior knowledge needed Basic terminology and principles of Mendelian genetics, including recessive, dominant, and sex-linked inheritance Formation of gametes y meiosis The laws of segregation and independent assortment Predicting the results of monohyrid and dihyrid crosses y constructing a Punnett square How genetic mutations can produce changes in phenotype Chi-square statistical analysis
2 Page 2 of 17 iv. Expected Learning Outcomes Demonstrate the meaning of dominant and recessive traits and the genetic principles of segregation and independent assortment. Demonstrate the implications of sex-linked traits for heredity (optional). Demonstrate genetic linkage and recomination (optional). Demonstrate a chi-square analysis. Reach conclusions regarding the principles of genetic inheritance v. Estimated Time Teacher Preparation 15 minutes Previewing the activity 10 minutes Registering a Teacher Account and setting up a class 20 minutes Editing and activating the report guide and ruric 40 minutes Online assessment (grading the report) Class Time (if students have Internet access outside the classroom, they can work on their own time) 30 minutes Minimum amount of time to ecome familiar with the activity minutes Working on experiments and composing report 30 minutes Online assessment quiz vi. Alignment to Standards National Science Education Standards A Science as Inquiry (Grades 9-12) Ailities necessary to do scientific inquiry: Identify questions and concepts that guide scientific investigations Design and conduct scientific investigations Use technology and mathematics to improve investigations and communications Formulate and revise scientific explanations and models using logic and evidence Recognize and analyze alternative explanations and models Communicate and defend a scientific argument C2 Life Science Molecular asis of heredity State Standards Access the alignment of this activity to your state s standards y selecting your state at:
3 Page 3 of Introduction Drosophila is an interactive simulation activity that enhances the traditional fruit fly laoratory experience. The experience takes place in a virtual environment where students have an unlimited aility to design experiments and analyze patterns of genetic inheritance to discover the principles of genetics. The Drosophila application presents students with a virtual la ench where they can order fruit fly mutants from a we merchant, mate the flies in an incuator, anesthetize flies for oservation, examine flies under a microscope, and analyze the data from offspring to determine patterns of inheritance. This application allows students to learn principles of genetic inheritance (e.g. dominant versus recessive traits, sex-linkage, etc.) y designing, conducting, and analyzing the results from their own experiments or y repeating classic experiments y pioneers in genetic research. As students work through the assignments, they can capture and save data and figures into their online noteook, and will e ale to write their own notes online in their virtual laoratory noteook. Students also learn to organize results into a scientific report that can e graded on-line y their teachers. The activities include an online assessment quiz that consists of randomized interactive questions. The students answers are graded automatically and stored in a dataase server hosted y our institution, and a printale Certificate of Completion is issued for each student. The instructor has the option of editing the templates for the grading ruric and guiding questions for the laoratory report. The instructor has access to individual student and class results. A learning ojectives report allows the instructor to quickly gauge how well the key concepts were understood. 2. Teacher Registration and Workspace Guide See the Teacher Registration and Workspace Guide for setting up and using a Teacher Account availale on the VCISE homepage at: Includes directions on adding classes, editing the templates for the Report and Ruric, reviewing student performance with the online assessment tools, and accessing the Teacher Manual for the any of the VCISE activities.
4 Page 4 of Activity Entry Page The entry page for Drosophila is found directly at: In the User Homepage ta (red), the student user creates a new account y clicking on the Create New Account utton. The student enters the Class Code (generated when a teacher registers and sets up a class account), their name, username, and password to create their student account. Once a Username is created, the activity is accessed y entering the information in the Registered Users section. The Background Information ta (orange) provides a rief overview on what the student should expect in the activity. The Tour ta (lue) provides an animated demonstration of the whole activity. This Teacher Manual for the activity is ased on that demo. Preview the Tour yourself, and encourage your students to take to the Tour efore doing the activity. The Education Standards ta (green) provides links to this activity s alignment to state and National Science Content Standards.
5 Page 5 of Starting the Activity Once a student logs in as a registered user, the La Bench ecomes the starting screen of the Drosophila activity. The tas on the top menu ar indicate different parts of the activity package: The Activity ta shows the La Bench screen. Images and tales from the activity can e added into the Noteook. The Noteook ta gives students access to their la notes. Once the Report is activated, the Report ta guides the student in writing an online la report on his or her experiments. Once the Quiz is activated, students can use this ta to take an interactive and randomized assessment quiz. In the Options ta, the sounds, transitions, or the on screen directions can e turned off or on. The transitions can e turned off to save time after the students understand what occurs in etween two steps of the simulation. The On Screen Directions are step-y-step directions highlighted in yellow oxes that can also e closed on individual pages. 5. Ordering Flies In general, the student: (1) selects a and fe fly with specific traits, (2) mates these two parent flies, (3) oserves and records the characteristics that are passed onto their offspring, and (4) analyzes the results and provides a hypothesis ased on the outcome of the experiments. The computer in the virtual la ench allows the student to custom order flies or to analyze the data that is collected. The icon for ordering flies leads to the store front page where flies can e customized for a particular experiment.
6 Page 6 of 17 On the Fly s Supplies Order Screen, the fly eing customized is in the view on the left half of the screen along with a listing of its characteristics. Up to three traits may e selected in this application. The tas on the far right of the screen have possile choices for gender and the wild-type or 29 mutant traits in nine different categories listed as: Bristles, Body Color, Antennae, Eye Color, Eye Shape, Wing Size, Wing Shape, Wing Vein, and Wing Angle. To promote inquiry-ased learning, students do not have access to the detailed information on these mutations shown in Tale 1 of the Appendix. Therefore, the areviations for the mutations in this activity are capitalized to hide any clue as to its dominance or recessiveness. Special emphasis should e made so that students understand that it is not the traditional genetic areviation, ut rather just an areviation of the phenotype. At the most asic level, students choose one mutation and cross it with a fly having the wild-type version. For example, a fe with vestigial wings and a wild-type are ordered and added to the Shopping Cart. At Checkout, these images of these flies can e recorded directly into the online noteook when the alert ox appears. 6. Mating Flies The flies are shipped to the la ench, unpacked, added to a mating jar, and placed in the incuator to start mating. The first generation (F1) of offspring develop. An animation shows that the offspring are anesthetized y ether in preparation for viewing under the microscope.
7 Page 7 of Using the Microscope The flies are automatically sorted ased on their appearance, that is, their phenotype. In the Microscope View, the data listed on the upper right of the screen includes the gender, count, and phenotype of each pile. Rolling over a pile with the mouse cursor reveals the same information. This data can e sent to the computer y clicking on Send Data to Computer. This is how students save their experimental results for analysis later. Clicking on a pile zooms the view on one of the flies in a pile. In the zoomed-in view of one fly, several options are availale: Add to Noteook saves the image and phenotype of the fly into the online noteook. Use in New Mating uses this particular fly in another mating. Offspring from this mating, or a new fly from the store can e used for the next mating. Zoom Out returns to the microscope view with the sorted piles. In this example, oth and fe offspring showing a wild-type phenotype are used in a new mating, Cross #2. The mating jar appears when Return to La is clicked, and the development process produces the next generation of offspring (F2 generation). Returning to the microscope view, the F2 generation is now sorted into four piles and the data (gender, count, and phenotype) are listed in the upper right section. Clicking Send Data to Computer transfers the data from the microscope view into the analysis view of the computer screen.
8 Page 8 of Analyzing Data The purpose of the data analysis view is for the student to determine the pattern of inheritance ased on the experimental results. In analyzing the empirical data generated, the student will apply principles of genetic inheritance to make a hypothesis of the resulting offspring ratios. Data sets from multiple crosses are numered and can e accessed from the pull down menu on top of the tale. The gender, phenotype, numer of flies, and the proportion of the total population are listed in a taular format. Checking the Ignore Sex ox will comine the s and fes of one phenotype together. This can simplify the analysis of matings in which the mutations are autosomal, and thus, gender has no effect on the inheritance pattern. For advanced classes studying sexlinked traits, see Appendix. Clicking the Add to Noteook will enter the tale of results into the la notes. 9. Entering a Numerical Hypothesis The Chi Square Analysis utton prompts the student to enter a numerical hypothesis for the offspring ratios that resulted from a mating. These ratios are usually derived y performing a Punnett square analysis of the parents genotypes. Students enter a hypothesized ratio (positive integers). Clicking on Test This Hypothesis checks if the ratio fits using a chi square analysis of the data.
9 Page 9 of 17 The chi square test statistic, the degrees of freedom, and the level of significance are automatically calculated. Based on these results, the student needs to determine their hypothesis is acceptale. A level of significance equal to or less than 0.05 suggests that the hypothesis is unlikely. The student may enter a new hypothesis y clicking on Enter New Hypothesis. Clicking Add to Noteook records the analysis into the student s la notes. 9a. Chi-square Test A chi-square analysis is a statistical test that measures how well a suggested numerical hypothesis compares to the oserved results. In other words, do the oserved results reflect acceptale differences from the expected values? The actual offspring numers that result from the mating are compared to expected values ased on the student s hypotheses for the ratios among the different types of offspring. For example, ased on some genetic mechanism that you are proposing, you elieve that there should e a 4 to 1 ratio of wild type flies to flies with paisley eyes. Of course, the ratio won't e exactly 4 to 1; one has to allow for random error. The question is: do the results differ "significantly" from a 4 to 1 ratio? To put it differently, if the 4 to 1 ratio is true, what is the proaility that you would get deviations from a 4 to 1 ratio that are as large (or larger) than the deviations which you oserve in the data? Statisticians call this proaility the "level of significance." So how do you calculate the level of significance? Statisticians have derived a test statistic called "chisquare" that can e used compute the level of significance. The chi-square test statistic measures the deviations of the oserved values from the "expected values" that you would get if your hypothesis is true. The formula for calculating the chi-square (χ 2 ) test statistic is: χ 2 = Σ (O i - E i ) 2 E i In this formula, you take oserved numer for each phenotype, O i, sutract the expected numer, E i, square the difference, and divide the squared difference y the expected numer. You sum the chisquared terms for all of the phenotypes to otain your test statistic. If the squared deviations etween the oserved and expected values are small (i.e., the oserved and expected values are similar), the test statistic will e small. Thus, the data support the hypothesis. On the other hand, if the squared deviations etween the oserved and expected values are large, the test statistic will e large and, thus, there is a smaller proaility that the hypothesis is true. This will lead to small values for the level of significance, and a hypothesis that should e rejected. The test statistic can e compared with a theoretical proaility distriution to otain the level of significance. This proaility distriution depends on the "degrees of freedom" which equals numer of phenotypic groups used in the calculation minus one. The Drosophila program automatically calculates the level of significance. If the level of significance is large, there is a good chance (high proaility) that the deviations from your hypothesis are simply due to random error. In other words, there is no evidence to reject your hypothesis. The hypothesis fits the data. On the other hand if the level of significance is small (less than 0.05), it is unlikely (low proaility) that the deviations from your hypothesis are due to random error alone. Therefore, your hypothesis is proaly wrong. In other words, if there is a less than a 5% chance that the deviations from your hypothesis are due to random error, then you should reject your hypothesis. Your hypothesis is inconsistent with the data. A new ratio ased on a different genetic hypothesis should e entered.
10 Page 10 of Recording into the Noteook An online noteook is availale. The student records images and data from experiments throughout the activity. In the Fly s Supplies ordering screen, there is a check ox in an alert panel that has Also add flies to the noteook as the default during the order confirmation process. Additionally, there are Add to Noteook uttons in the microscope and Analyze Results views. These data are added into the Noteook section of the activity as separate folders in the view on the left panel. The data are fully displayed in the section on the right. Each folder can e expanded y left clicking on the arrow. Right clicking allows file management. Additional notes for each piece of data can e typed in the text area elow the images or tales. The students will use the information recorded in their noteooks to compose the la report. 11. Composing a Report From the Report ta in the activity, students use the questions in the right panel to guide them on how they designed, performed, and analyzed their experiment. The evidence should have een collected during the activity and recorded into their noteook, which is now shown on the left panel. By using the pull down menu on top of the left panel, students are ale to toggle to a view of the ruric the teacher has activated. In addition to the guiding questions in the report, the ruric will assist the students in composing their la report. The ojectives in the ruric can e edited y the teacher. However, this must e completed prior to activating it for your students from the Teacher Workspace. If more fields for entering results are needed in the report, students can click Add New Results. Only what is typed or inserted into the lank fields is what will appear in the report, which should e saved into the activity s server dataase for editing at a later time or for grading y the teacher. Each student s noteook and report can e accessed in the Assessment ta of the Teacher Workspace section. The text in the pink area of the Report guide in the right panel can e edited y the teacher. However, this must e completed prior to activating it for your students from the Teacher Workspace. The text in the Report guide will not e included in the Student Report file. Only what is typed or inserted into the lank fields y the student is what will appear in the student s printed and/or saved report.
11 Page 11 of Taking the Quiz Once the Quiz is activated from the Teacher Workspace, it will e accessile to your students in that particular class. For the Drosophila activity, there are two possile quizzes: one that includes 12 asic questions on monohyrid and dihyrid crosses, and another that has six additional questions related to sex-linkage. Select the appropriate one for your particular class in your Teacher Account page. Once a student starts the quiz, the noteook, report, and activity will not e accessile until the quiz is completed. Questions are located at the ottom of the screen. They are randomized and unique each time the quiz is taken. The graphical set up of the prolem is viewed aove the question and takes familiar elements of the activity. The arrow controls at the ottom of the page allows the student to go forward to the next question or reverse to review a previous question. All the answers are sumitted into the server dataase only at the end of quiz. An alert panel reminds the student that the answers can not e changed after clicking on the Yes utton to finish the quiz. When the student confirms his or her completion of the quiz, it is automatically scored and a tale compares the student answers with the correct answers. The student may go ack to review the quiz questions, ut will not e ale to change his or her answers. Moreover, since the quiz is randomized with multiple cominations of possiilities, this is the only time that the student would e ale to review his or her particular set of quiz questions. The percentage score and each individual response y the student are recorded into the Assessment tool in the Teacher Account pages. Finally, a personalized Certificate of Completion is availale to the student after the quiz has een completed. The certificate can e printed y clicking the Print utton or saved y right clicking on the certificate image (PC).
12 Page 12 of Assessment Results See the Teacher Registration and Workspace Guide for reviewing student performance with the online assessment tools availale on the VCISE homepage at: Suggested Assignments Basic Level Assignment 1: Study the inheritance patterns of mutations from the list of autosomal mutations (excludes sex-linked and lethal mutations). (a) Students should try reciprocal crosses (fe mutant vs. wild type and fe wild type vs. mutant). () Students should try a test cross for recessive traits. Mate an F1 wild type to a homozygous recessive mutant from the store. (c) Students should cross an F1 x F1 to get an F2 generation. This should demonstrate a 3:1 Mendelian ratio. (d) Optional: Students can test the 3:1 ratio y using a chi-square analysis. Autosomal Mutation Standard Notation VCISE Notation Dominant / Recessive Apterous ap AP recessive Black ody BL recessive Brown eyes w BW recessive Curved wings c C recessive Dumpy wings DP recessive Eony ody e E recessive Eyeless eyes ey EY recessive Loe eyes L L dominant Purple eyes pr PR recessive Radius incompletus ri RI recessive Sepia eyes se SE recessive Spineless ristles ss SS recessive Shaven ristles sv SV recessive Vestigial wings vg VG recessive Assignment 2: Select any two traits on two different chromosomes and study their inheritance patterns (excludes sex-linked and lethal mutations). (a) Students should try reciprocal crosses: i. fe with mutant A vs. with mutant B ii. fe with mutant B vs. mutant A () Students should cross an F1 offspring with another F1 offspring to generate an F2 generation. This should demonstrate a 9:3:3:1 Mendelian ratio.
13 Page 13 of 17 (c) Optional: Students can test the 9:3:3:1 ratio y using a chi-square analysis. Chromosome II III IV Autosomal Mutation Standard Notation VCISE Notation Dominant / Recessive Dumpy Wings DP recessive Black Body BL recessive Purple Eyes pr PR recessive Apterous ap AP recessive Vestigial Wings vg VG recessive Loe Eyes L L dominant Curved Wings c C recessive Brown Eyes w BW recessive Sepia Eyes se SE recessive Radius Incompletus ri RI recessive Spineless Bristles ss SS recessive Eony Body e E recessive Eyeless ey EY recessive Shaven Bristles sv SV recessive Advanced Level: For classes studying linkage, sex-linkage, and lethal traits Assignment 3: From the tale in Assignment 2, select two traits on the same chromosome and study their inheritance patterns (excludes sex-linked and lethal mutations). Also see the Appendix in Section 15 for a pictorial genetic distance map. (a) Students should cross a doule mutant with a wild type. Best examples from which to choose are traits that are less than 20 map units apart. For example: F1 cross X If crossing over does not occur in the F1 generation (also known as a nonrecominant event), an F2 mating produces a traditional Mendelian 3:1 ratio as demonstrated in the figure elow. nonrecominant events (non-crossing over) NCO However, if crossing over (CO) occurs in the F1 generation, then an F2 mating will produce an offspring ratio different than that of the traditional Mendelian ratio as demonstrated in the figure elow. Crossing Over (in Drosophila, occurs only in fes) fe fe F2 cross X X
14 Page 14 of 17 F2 cross in a Punnett Square fe fe There is a 3:1 phenotypic ratio of the wild type to the mutant offspring. There is a 2:1:1 phenotypic ratio of the wild type to the mutant and to the mutant offspring. () Students should select and cross different mutations on different parents. For example: F1 cross X If crossing over does not occur in the F1 generation (also known as a nonrecominant event), an F2 mating produces a 2:1:1 offspring ratio as demonstrated in the figure elow. However, if crossing over (CO) occurs in the F1 generation, then an F2 mating produces a 3:1 offspring ratio as demonstrated in the figure elow. fe fe F2 cross X X fe fe F2 cross in a Punnett Square There is a 2:1:1 phenotypic ratio of the wild type to the mutant and to the mutant offspring. There is a 3:1 phenotypic ratio of the wild type to the mutant offspring. Take note: ecause of linkage of the genes on the same chromosome, the aove dihyrid crosses do not produce the typical 9:3:3:1 Mendelian ratio.
15 Page 15 of 17 (c) Estimate the map distance y test crossing an F1 fe to a doule homozygote recessive. X If crossing over does not occur, the offspring will have the parental phenotypes. If crossing over occurs, the offspring are considered as recominants. The frequency of recominants is equivalent to the map distance of the two genes. NCO fe CO fe Parental types Recominants Assignment 4: In addition to autosomes, genes are found on the sex chromosome (I-X). The pattern of inheritance in these cases is different. These traits are considered as sex-linked. The tale elow and in the Appendix of Section 15 lists the traits that are found on the sex chromosome. (a) Students should try reciprocal crosses (fe wild type vs. mutant and fe mutant vs. wild type). Sex Chromosome I-X Mutation Standard Notation VCISE Notation Dominant / Recessive Yellow Body y Y recessive White Eyes w W recessive Crossveinless cv CV recessive Singed Bristles sn SN recessive Tan Body t T recessive Miniature Wings m M recessive Sale Body s S recessive Scalloped Wings sd SD recessive Forked Bristles f F recessive Bar Eyes B B dominant Parental: X X x X w Y X w X w x X Y F1: X X w x X Y 100% (wild type) X X w x X w Y fes, s w F2: X X w X X w X fe X w w fe Y w Y w Phenotypic ratios 2 : 1 : 1 1 : 1 : 1 : 1 fe : : w fe : fe w : : w
16 Page 16 of 17 Assignment 5: Mate two flies from the store that oth have lethal mutations. i. Note that the wild type phenotype is otained. Therefore, the store flies must e heterozygous. ii. There is a 2:1 ratio of mutant to wild type ecause homozygous mutant flies die. Chromosome II III Lethal Mutation Standard Notation VCISE Notation Dominant / Recessive Star Eyes S SS dominant Curly Wings Cy CY dominant Dichaete Wings D D dominant Aristapedia Ar AR dominant Stule Bristles S SB dominant 15. Appendix The first column gives the name of the mutation followed y its standard genetic areviation. The next column gives the areviation used y this Drosophila application, which is capitalized to hide any clue as to its dominance or recessiveness. This nondescript, capitalized areviation is used throughout the online activity. Special emphasis should e made so that students understand that it is not the traditional genetic areviation, ut rather just an areviation of the phenotype. The next column gives the chromosome numer. Chromosome I-X is the sex chromosome. For advanced classes, the map distance is indicated in the next column and in the genetic map of mutations in the figure elow the tale. The last two columns indicate whether the mutation is dominant or recessive and whether or not it is lethal when homozygous (Biology Las On-Line, 2001). Mutation Standard VFL Chromo- Map Dominant / Notation Notation some No. Distance Recessive Lethal Apterous ap AP II 55.2 recessive no Aristapedia Ar AR III 47.5 dominant yes Bar eyes B B I-X 57.0 dominant no Black ody BL II 48.5 recessive no Brown eyes w BW II recessive no Curved wings c C II 75.5 recessive no Crossveinless wings cv CV I-X 13.7 recessive no Curly wings Cy CY II 6.1 dominant yes Dichaete wings D D III 41.0 dominant yes Dumpy wings DP II 13.0 recessive no Eony ody e E III 70.7 recessive no Eyeless eyes ey EY IV 2.0 recessive no Forked ristles f F I-X 56.7 recessive no Loe eyes L L II 72.0 dominant no Miniature wings m M I-X 36.1 recessive no Purple eyes pr PR II 54.5 recessive no Radius incompletus ri RI III 47.0 recessive no Sale ody s S I-X 43.0 recessive no Stule ristles S SB III 58.2 dominant yes Scalloped wings sd SD I-X 51.5 recessive no Sepia eyes se SE III 26.0 recessive no Singed ristles sn SN I-X 21.0 recessive no Spineless ristles ss SS III 58.5 recessive no Star Eyes S ST II 1.3 dominant yes Shaven ristles sv SV IV 3.0 recessive no Tan ody t T I-X 27.5 recessive no Vestigial wings vg VG II 67.0 recessive no White eyes w W I-X 1.5 recessive no Yellow ody y Y I-X 0.0 recessive no
17 Genetic map of the mutations in Drosophila. Page 17 of 17
Mendelian Genetics in Drosophila
 Mendelian Genetics in Drosophila Lab objectives: 1) To familiarize you with an important research model organism,! Drosophila melanogaster. 2) Introduce you to normal "wild type" and various mutant phenotypes.
Mendelian Genetics in Drosophila Lab objectives: 1) To familiarize you with an important research model organism,! Drosophila melanogaster. 2) Introduce you to normal "wild type" and various mutant phenotypes.
The Genetics of Drosophila melanogaster
 The Genetics of Drosophila melanogaster Thomas Hunt Morgan, a geneticist who worked in the early part of the twentieth century, pioneered the use of the common fruit fly as a model organism for genetic
The Genetics of Drosophila melanogaster Thomas Hunt Morgan, a geneticist who worked in the early part of the twentieth century, pioneered the use of the common fruit fly as a model organism for genetic
Mendelian and Non-Mendelian Heredity Grade Ten
 Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
AP: LAB 8: THE CHI-SQUARE TEST. Probability, Random Chance, and Genetics
 Ms. Foglia Date AP: LAB 8: THE CHI-SQUARE TEST Probability, Random Chance, and Genetics Why do we study random chance and probability at the beginning of a unit on genetics? Genetics is the study of inheritance,
Ms. Foglia Date AP: LAB 8: THE CHI-SQUARE TEST Probability, Random Chance, and Genetics Why do we study random chance and probability at the beginning of a unit on genetics? Genetics is the study of inheritance,
LAB 11 Drosophila Genetics
 LAB 11 Drosophila Genetics Introduction: Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is an excellent organism for genetics studies because it has simple food requirements, occupies little space, is hardy,
LAB 11 Drosophila Genetics Introduction: Drosophila melanogaster, the fruit fly, is an excellent organism for genetics studies because it has simple food requirements, occupies little space, is hardy,
CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 7 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A person who has a disorder caused
Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
Bio 100 Patterns of Inheritance 1 Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Modern genetics began with Gregor Mendel s quantitative experiments with pea plants History of Heredity Blending theory of heredity -
Lesson Plan: GENOTYPE AND PHENOTYPE
 Lesson Plan: GENOTYPE AND PHENOTYPE Pacing Two 45- minute class periods RATIONALE: According to the National Science Education Standards, (NSES, pg. 155-156), In the middle-school years, students should
Lesson Plan: GENOTYPE AND PHENOTYPE Pacing Two 45- minute class periods RATIONALE: According to the National Science Education Standards, (NSES, pg. 155-156), In the middle-school years, students should
Designing and Implementing Virtual Courseware to Promote Inquiry based Learning
 Designing and Implementing Virtual Courseware to Promote Inquiry based Learning Robert A. Desharnais Professor, Department of Biological Sciences and Director, Virtual Courseware Project California State
Designing and Implementing Virtual Courseware to Promote Inquiry based Learning Robert A. Desharnais Professor, Department of Biological Sciences and Director, Virtual Courseware Project California State
Heredity. Sarah crosses a homozygous white flower and a homozygous purple flower. The cross results in all purple flowers.
 Heredity 1. Sarah is doing an experiment on pea plants. She is studying the color of the pea plants. Sarah has noticed that many pea plants have purple flowers and many have white flowers. Sarah crosses
Heredity 1. Sarah is doing an experiment on pea plants. She is studying the color of the pea plants. Sarah has noticed that many pea plants have purple flowers and many have white flowers. Sarah crosses
LAB : THE CHI-SQUARE TEST. Probability, Random Chance, and Genetics
 Period Date LAB : THE CHI-SQUARE TEST Probability, Random Chance, and Genetics Why do we study random chance and probability at the beginning of a unit on genetics? Genetics is the study of inheritance,
Period Date LAB : THE CHI-SQUARE TEST Probability, Random Chance, and Genetics Why do we study random chance and probability at the beginning of a unit on genetics? Genetics is the study of inheritance,
LAB : PAPER PET GENETICS. male (hat) female (hair bow) Skin color green or orange Eyes round or square Nose triangle or oval Teeth pointed or square
 Period Date LAB : PAPER PET GENETICS 1. Given the list of characteristics below, you will create an imaginary pet and then breed it to review the concepts of genetics. Your pet will have the following
Period Date LAB : PAPER PET GENETICS 1. Given the list of characteristics below, you will create an imaginary pet and then breed it to review the concepts of genetics. Your pet will have the following
Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance
 Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance Genes and Alleles A. Genes 1. A sequence of nucleotides that codes for a special functional product a. Transfer RNA b. Enzyme c. Structural protein d. Pigments 2. Genes
Heredity - Patterns of Inheritance Genes and Alleles A. Genes 1. A sequence of nucleotides that codes for a special functional product a. Transfer RNA b. Enzyme c. Structural protein d. Pigments 2. Genes
CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE
 SECTION 12-1 REVIEW CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. sex chromosome, autosome 2. germ-cell mutation, somatic-cell
SECTION 12-1 REVIEW CHROMOSOMES AND INHERITANCE VOCABULARY REVIEW Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. sex chromosome, autosome 2. germ-cell mutation, somatic-cell
7A The Origin of Modern Genetics
 Life Science Chapter 7 Genetics of Organisms 7A The Origin of Modern Genetics Genetics the study of inheritance (the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles) Heredity: the
Life Science Chapter 7 Genetics of Organisms 7A The Origin of Modern Genetics Genetics the study of inheritance (the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles) Heredity: the
GENETIC CROSSES. Monohybrid Crosses
 GENETIC CROSSES Monohybrid Crosses Objectives Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype Explain the difference between homozygous and heterozygous Explain how probability is used to predict
GENETIC CROSSES Monohybrid Crosses Objectives Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype Explain the difference between homozygous and heterozygous Explain how probability is used to predict
PRACTICE PROBLEMS - PEDIGREES AND PROBABILITIES
 PRACTICE PROBLEMS - PEDIGREES AND PROBABILITIES 1. Margaret has just learned that she has adult polycystic kidney disease. Her mother also has the disease, as did her maternal grandfather and his younger
PRACTICE PROBLEMS - PEDIGREES AND PROBABILITIES 1. Margaret has just learned that she has adult polycystic kidney disease. Her mother also has the disease, as did her maternal grandfather and his younger
2 GENETIC DATA ANALYSIS
 2.1 Strategies for learning genetics 2 GENETIC DATA ANALYSIS We will begin this lecture by discussing some strategies for learning genetics. Genetics is different from most other biology courses you have
2.1 Strategies for learning genetics 2 GENETIC DATA ANALYSIS We will begin this lecture by discussing some strategies for learning genetics. Genetics is different from most other biology courses you have
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection
 Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis Inheritance Connection Carl Correns 1900 Chapter 13 First suggests central role for chromosomes Rediscovery of Mendel s work Walter Sutton 1902 Chromosomal theory
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Meiosis Quiz 1. (1 point) A kidney cell is an example of which type of cell? a. sex cell b. germ cell c. somatic cell d. haploid cell 2. (1 point) How many chromosomes are in a human
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Meiosis Quiz 1. (1 point) A kidney cell is an example of which type of cell? a. sex cell b. germ cell c. somatic cell d. haploid cell 2. (1 point) How many chromosomes are in a human
Genetics with a Smile
 Teacher Notes Materials Needed: Two coins (penny, poker chip, etc.) per student - One marked F for female and one marked M for male Copies of student worksheets - Genetics with a Smile, Smiley Face Traits,
Teacher Notes Materials Needed: Two coins (penny, poker chip, etc.) per student - One marked F for female and one marked M for male Copies of student worksheets - Genetics with a Smile, Smiley Face Traits,
Problems 1-6: In tomato fruit, red flesh color is dominant over yellow flesh color, Use R for the Red allele and r for the yellow allele.
 Genetics Problems Name ANSWER KEY Problems 1-6: In tomato fruit, red flesh color is dominant over yellow flesh color, Use R for the Red allele and r for the yellow allele. 1. What would be the genotype
Genetics Problems Name ANSWER KEY Problems 1-6: In tomato fruit, red flesh color is dominant over yellow flesh color, Use R for the Red allele and r for the yellow allele. 1. What would be the genotype
A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes.
 1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
1 Biology Chapter 10 Study Guide Trait A trait is a variation of a particular character (e.g. color, height). Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes. Genes Genes are located on chromosomes
Genetics 1. Defective enzyme that does not make melanin. Very pale skin and hair color (albino)
 Genetics 1 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents. Parents and their children tend to have similar appearance because children inherit genes from their parents and these genes influence
Genetics 1 We all know that children tend to resemble their parents. Parents and their children tend to have similar appearance because children inherit genes from their parents and these genes influence
Networking Guide. 2008 www.lexmark.com
 Networking Guide 2008 www.lexmark.com Contents Installing the printer on a wireless network...5 Wireless network compatiility...5 Information you will need to set up the printer on a wireless network...5
Networking Guide 2008 www.lexmark.com Contents Installing the printer on a wireless network...5 Wireless network compatiility...5 Information you will need to set up the printer on a wireless network...5
I. Genes found on the same chromosome = linked genes
 Genetic recombination in Eukaryotes: crossing over, part 1 I. Genes found on the same chromosome = linked genes II. III. Linkage and crossing over Crossing over & chromosome mapping I. Genes found on the
Genetic recombination in Eukaryotes: crossing over, part 1 I. Genes found on the same chromosome = linked genes II. III. Linkage and crossing over Crossing over & chromosome mapping I. Genes found on the
5 GENETIC LINKAGE AND MAPPING
 5 GENETIC LINKAGE AND MAPPING 5.1 Genetic Linkage So far, we have considered traits that are affected by one or two genes, and if there are two genes, we have assumed that they assort independently. However,
5 GENETIC LINKAGE AND MAPPING 5.1 Genetic Linkage So far, we have considered traits that are affected by one or two genes, and if there are two genes, we have assumed that they assort independently. However,
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Problems
 Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Problems 1. The frequency of two alleles in a gene pool is 0.19 (A) and 0.81(a). Assume that the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. (a) Calculate the percentage of
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Problems 1. The frequency of two alleles in a gene pool is 0.19 (A) and 0.81(a). Assume that the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. (a) Calculate the percentage of
A and B are not absolutely linked. They could be far enough apart on the chromosome that they assort independently.
 Name Section 7.014 Problem Set 5 Please print out this problem set and record your answers on the printed copy. Answers to this problem set are to be turned in to the box outside 68-120 by 5:00pm on Friday
Name Section 7.014 Problem Set 5 Please print out this problem set and record your answers on the printed copy. Answers to this problem set are to be turned in to the box outside 68-120 by 5:00pm on Friday
The correct answer is c A. Answer a is incorrect. The white-eye gene must be recessive since heterozygous females have red eyes.
 1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
1. Why is the white-eye phenotype always observed in males carrying the white-eye allele? a. Because the trait is dominant b. Because the trait is recessive c. Because the allele is located on the X chromosome
Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
 Name: Date: Period: Incomplete Dominance and Codominance 1. In Japanese four o'clock plants red (R) color is incompletely dominant over white (r) flowers, and the heterozygous condition (Rr) results in
Name: Date: Period: Incomplete Dominance and Codominance 1. In Japanese four o'clock plants red (R) color is incompletely dominant over white (r) flowers, and the heterozygous condition (Rr) results in
Two copies of each autosomal gene affect phenotype.
 SECTION 7.1 CHROMOSOMES AND PHENOTYPE Study Guide KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. VOCABULARY carrier sex-linked gene X chromosome inactivation
SECTION 7.1 CHROMOSOMES AND PHENOTYPE Study Guide KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. VOCABULARY carrier sex-linked gene X chromosome inactivation
Biology Final Exam Study Guide: Semester 2
 Biology Final Exam Study Guide: Semester 2 Questions 1. Scientific method: What does each of these entail? Investigation and Experimentation Problem Hypothesis Methods Results/Data Discussion/Conclusion
Biology Final Exam Study Guide: Semester 2 Questions 1. Scientific method: What does each of these entail? Investigation and Experimentation Problem Hypothesis Methods Results/Data Discussion/Conclusion
Ex) A tall green pea plant (TTGG) is crossed with a short white pea plant (ttgg). TT or Tt = tall tt = short GG or Gg = green gg = white
 Worksheet: Dihybrid Crosses U N I T 3 : G E N E T I C S STEP 1: Determine what kind of problem you are trying to solve. STEP 2: Determine letters you will use to specify traits. STEP 3: Determine parent
Worksheet: Dihybrid Crosses U N I T 3 : G E N E T I C S STEP 1: Determine what kind of problem you are trying to solve. STEP 2: Determine letters you will use to specify traits. STEP 3: Determine parent
DRAGON GENETICS LAB -- Principles of Mendelian Genetics
 DragonGeneticsProtocol Mendelian Genetics lab Student.doc DRAGON GENETICS LAB -- Principles of Mendelian Genetics Dr. Pamela Esprivalo Harrell, University of North Texas, developed an earlier version of
DragonGeneticsProtocol Mendelian Genetics lab Student.doc DRAGON GENETICS LAB -- Principles of Mendelian Genetics Dr. Pamela Esprivalo Harrell, University of North Texas, developed an earlier version of
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3
 Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
Genetics Module B, Anchor 3 Key Concepts: - An individual s characteristics are determines by factors that are passed from one parental generation to the next. - During gamete formation, the alleles for
Tic, Tie & Calculate Quick Start Guide. Quick Start Guide
 Quick Start Guide 1 Table of Contents Quick Start Guide... 3 Welcome to Tic, Tie & Calculate... 3 Features Overview... 3 Important Installation Notes... 3 Installation... 4 Step 1: Receive Account Creation
Quick Start Guide 1 Table of Contents Quick Start Guide... 3 Welcome to Tic, Tie & Calculate... 3 Features Overview... 3 Important Installation Notes... 3 Installation... 4 Step 1: Receive Account Creation
SEX DETERMINATION AND SEX CHROMOSOMES
 4 CHAPTER OUTLINE 4.1 Mechanisms of Sex Determination Among Various Species 4.2 Dosage Compensation and X Inactivation in Mammals 4.3 Properties of the X and Y Chromosome in Mammals 4.4 Transmission Patterns
4 CHAPTER OUTLINE 4.1 Mechanisms of Sex Determination Among Various Species 4.2 Dosage Compensation and X Inactivation in Mammals 4.3 Properties of the X and Y Chromosome in Mammals 4.4 Transmission Patterns
Course outline. Code: SCI212 Title: Genetics
 Course outline Code: SCI212 Title: Genetics Faculty of: Science, Health, Education and Engineering Teaching Session: Semester 2 Year: 2015 Course Coordinator: Wayne Knibb Tel: 5430 2831 Email: wknibb@usc.edu.au
Course outline Code: SCI212 Title: Genetics Faculty of: Science, Health, Education and Engineering Teaching Session: Semester 2 Year: 2015 Course Coordinator: Wayne Knibb Tel: 5430 2831 Email: wknibb@usc.edu.au
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005. Lectures 1 2
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
COMPLETING THE KEY STAGE 2 2016 DATA COLLECTION GUIDANCE
 COMPLETING THE KEY STAGE 2 2016 DATA COLLECTION GUIDANCE Please ensure you have completed the Import Routine for All Key Stages prior to starting the following processes Key Stage 2 2016 1 Contents PROCEDURE
COMPLETING THE KEY STAGE 2 2016 DATA COLLECTION GUIDANCE Please ensure you have completed the Import Routine for All Key Stages prior to starting the following processes Key Stage 2 2016 1 Contents PROCEDURE
Saffiyah Y. Manboard Biology Instructor Seagull Alternative High School Saffiyah.manboard@browardschools.com
 The Effect of Discovery Learning through Biotechnology on the Knowledge and Perception of Sickle Cell Anemia and It s Genetics on Lower Income Students Saffiyah Y. Manboard Biology Instructor Seagull Alternative
The Effect of Discovery Learning through Biotechnology on the Knowledge and Perception of Sickle Cell Anemia and It s Genetics on Lower Income Students Saffiyah Y. Manboard Biology Instructor Seagull Alternative
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
After you complete the survey, compare what you saw on the survey to the actual questions listed below:
 Creating a Basic Survey Using Qualtrics Clayton State University has purchased a campus license to Qualtrics. Both faculty and students can use Qualtrics to create surveys that contain many different types
Creating a Basic Survey Using Qualtrics Clayton State University has purchased a campus license to Qualtrics. Both faculty and students can use Qualtrics to create surveys that contain many different types
eschoolplus Users Guide Teacher Access Center 2.1
 eschoolplus Users Guide Teacher Access Center 2.1. i Table of Contents Introduction to Teacher Access Center... 1 Logging in to Teacher Access Center (TAC)...1 Your My Home Page... 2 My Classes...3 News...4
eschoolplus Users Guide Teacher Access Center 2.1. i Table of Contents Introduction to Teacher Access Center... 1 Logging in to Teacher Access Center (TAC)...1 Your My Home Page... 2 My Classes...3 News...4
Reading Management Software. Software Manual. Motivate Your Students to Read More and Better Books!
 Reading Management Software Software Manual Motivate Your Students to Read More and Better Books! Renaissance Learning P. O. Box 8036 Wisconsin Rapids, WI 54495-8036 Phone: (866) 846-7323* Fax: (715) 424-4242
Reading Management Software Software Manual Motivate Your Students to Read More and Better Books! Renaissance Learning P. O. Box 8036 Wisconsin Rapids, WI 54495-8036 Phone: (866) 846-7323* Fax: (715) 424-4242
Name: 4. A typical phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross is a) 9:1 b) 3:4 c) 9:3:3:1 d) 1:2:1:2:1 e) 6:3:3:6
 Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
Name: Multiple-choice section Choose the answer which best completes each of the following statements or answers the following questions and so make your tutor happy! 1. Which of the following conclusions
Genetics and Evolution: An ios Application to Supplement Introductory Courses in. Transmission and Evolutionary Genetics
 G3: Genes Genomes Genetics Early Online, published on April 11, 2014 as doi:10.1534/g3.114.010215 Genetics and Evolution: An ios Application to Supplement Introductory Courses in Transmission and Evolutionary
G3: Genes Genomes Genetics Early Online, published on April 11, 2014 as doi:10.1534/g3.114.010215 Genetics and Evolution: An ios Application to Supplement Introductory Courses in Transmission and Evolutionary
Genetics for the Novice
 Genetics for the Novice by Carol Barbee Wait! Don't leave yet. I know that for many breeders any article with the word genetics in the title causes an immediate negative reaction. Either they quickly turn
Genetics for the Novice by Carol Barbee Wait! Don't leave yet. I know that for many breeders any article with the word genetics in the title causes an immediate negative reaction. Either they quickly turn
Creating an Event Registration Web Page with Special Features using regonline Page 1
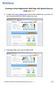 Creating an Event Registration Web Page with Special Features using regonline 1. To begin, enter www.regonline.com in your browser s address bar. A red arrow on each screen shot shows you where to place
Creating an Event Registration Web Page with Special Features using regonline 1. To begin, enter www.regonline.com in your browser s address bar. A red arrow on each screen shot shows you where to place
MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009
 MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 7 pages including this page. You will have 50 minutes for
MCB41: Second Midterm Spring 2009 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 7 pages including this page. You will have 50 minutes for
The Making of the Fittest: Natural Selection in Humans
 OVERVIEW MENDELIN GENETIC, PROBBILITY, PEDIGREE, ND CHI-QURE TTITIC This classroom lesson uses the information presented in the short film The Making of the Fittest: Natural election in Humans (http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/making-fittest-natural-selection-humans)
OVERVIEW MENDELIN GENETIC, PROBBILITY, PEDIGREE, ND CHI-QURE TTITIC This classroom lesson uses the information presented in the short film The Making of the Fittest: Natural election in Humans (http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/making-fittest-natural-selection-humans)
Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles. Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully
 Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully Multiple alleles: three or more alleles for a trait are found in the
Human Blood Types: Codominance and Multiple Alleles Codominance: both alleles in the heterozygous genotype express themselves fully Multiple alleles: three or more alleles for a trait are found in the
Step-by-Step Guide to Bi-Parental Linkage Mapping WHITE PAPER
 Step-by-Step Guide to Bi-Parental Linkage Mapping WHITE PAPER JMP Genomics Step-by-Step Guide to Bi-Parental Linkage Mapping Introduction JMP Genomics offers several tools for the creation of linkage maps
Step-by-Step Guide to Bi-Parental Linkage Mapping WHITE PAPER JMP Genomics Step-by-Step Guide to Bi-Parental Linkage Mapping Introduction JMP Genomics offers several tools for the creation of linkage maps
DATA COLLECTION GUIDANCE
 COMPLETING THE EARLY YEARS FOUNDATION STAGE PROFILE 2016 DATA COLLECTION GUIDANCE Please ensure you have completed the Import Routine for all Key Stages prior to starting the following processes 1 2 CONTENTS
COMPLETING THE EARLY YEARS FOUNDATION STAGE PROFILE 2016 DATA COLLECTION GUIDANCE Please ensure you have completed the Import Routine for all Key Stages prior to starting the following processes 1 2 CONTENTS
Basics of Marker Assisted Selection
 asics of Marker ssisted Selection Chapter 15 asics of Marker ssisted Selection Julius van der Werf, Department of nimal Science rian Kinghorn, Twynam Chair of nimal reeding Technologies University of New
asics of Marker ssisted Selection Chapter 15 asics of Marker ssisted Selection Julius van der Werf, Department of nimal Science rian Kinghorn, Twynam Chair of nimal reeding Technologies University of New
Reporting Student Progress and Achievement
 Reporting Student Progress and Achievement CompassLearning Odyssey Manager takes pride in the quality of its product content. However, technical inaccuracies, typographical errors, and editorial omissions
Reporting Student Progress and Achievement CompassLearning Odyssey Manager takes pride in the quality of its product content. However, technical inaccuracies, typographical errors, and editorial omissions
Drosophila Genetics by Michael Socolich May, 2003
 Drosophila Genetics by Michael Socolich May, 2003 I. General Information and Fly Husbandry II. Nomenclature III. Genetic Tools Available to the Fly Geneticists IV. Example Crosses V. P-element Transformation
Drosophila Genetics by Michael Socolich May, 2003 I. General Information and Fly Husbandry II. Nomenclature III. Genetic Tools Available to the Fly Geneticists IV. Example Crosses V. P-element Transformation
Virtual Ems User Guide
 Virtual Ems User Guide Welcome to the Virtual EMS User Guide! This guide will assist you in requesting space using the Virtual EMS online reservation system. Please read the selections below to assit you
Virtual Ems User Guide Welcome to the Virtual EMS User Guide! This guide will assist you in requesting space using the Virtual EMS online reservation system. Please read the selections below to assit you
This Skill Builder demonstrates how to define and place sketched symbols in drawings.
 Sketched Symbols This Skill Builder demonstrates how to define and place sketched symbols in drawings. A sketched symbol is a user-defined symbol. You create sketched symbols in the sketch environment
Sketched Symbols This Skill Builder demonstrates how to define and place sketched symbols in drawings. A sketched symbol is a user-defined symbol. You create sketched symbols in the sketch environment
Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 Handout
 Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 Handout PowerPoint is a presentation software program that is part of the Microsoft Office package. This program helps you to enhance your oral presentation and keep the audience
Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 Handout PowerPoint is a presentation software program that is part of the Microsoft Office package. This program helps you to enhance your oral presentation and keep the audience
SMART NOTEBOOK 10. Instructional Technology Enhancing ACHievement
 SMART NOTEBOOK 10 Instructional Technology Enhancing ACHievement TABLE OF CONTENTS SMART Notebook 10 Themes... 3 Page Groups... 4 Magic Pen... 5 Shape Pen... 6 Tables... 7 Object Animation... 8 Aligning
SMART NOTEBOOK 10 Instructional Technology Enhancing ACHievement TABLE OF CONTENTS SMART Notebook 10 Themes... 3 Page Groups... 4 Magic Pen... 5 Shape Pen... 6 Tables... 7 Object Animation... 8 Aligning
Development Office for Information Technology (DOIT) Mapúa Institute of Technology Moodle 2.3 Managers Quick Guide. January 2013.
 Development Office for Information Technology (DOIT) Mapúa Institute of Technology Moodle 2.3 Managers Quick Guide January 2013 Page 1 Part I. Accessing the Website LOGIN AND LOGOUT 1. Open an internet
Development Office for Information Technology (DOIT) Mapúa Institute of Technology Moodle 2.3 Managers Quick Guide January 2013 Page 1 Part I. Accessing the Website LOGIN AND LOGOUT 1. Open an internet
Bio 102 Practice Problems Genetic Code and Mutation
 Bio 102 Practice Problems Genetic Code and Mutation Multiple choice: Unless otherwise directed, circle the one best answer: 1. Beadle and Tatum mutagenized Neurospora to find strains that required arginine
Bio 102 Practice Problems Genetic Code and Mutation Multiple choice: Unless otherwise directed, circle the one best answer: 1. Beadle and Tatum mutagenized Neurospora to find strains that required arginine
Helpful Links 8 Helpful Documents 8 Writing History 9 Pending Peer Reviews 9 Navigation Tabs 10 Changing Courses 10
 V7.30.15 2014 GETTING STARTED Table of Contents Welcome to WPP Online 3 WPP Online Welcome Page 3 Logging in to WPP Online 4 Changing your Password 5 Accessing your Courses 7 Selecting a Course 7 The Course
V7.30.15 2014 GETTING STARTED Table of Contents Welcome to WPP Online 3 WPP Online Welcome Page 3 Logging in to WPP Online 4 Changing your Password 5 Accessing your Courses 7 Selecting a Course 7 The Course
Introduction. Teacher s lesson notes The notes and examples are useful for new teachers and can form the basis of lesson plans.
 KS3 Mathematics Pack A: Level 4 Introduction Introduction The Key Stage 3 Mathematics series covers the new National Curriculum for Mathematics (SCAA: The National Curriculum Orders, DFE, January 1995,
KS3 Mathematics Pack A: Level 4 Introduction Introduction The Key Stage 3 Mathematics series covers the new National Curriculum for Mathematics (SCAA: The National Curriculum Orders, DFE, January 1995,
Baby Lab. Class Copy. Introduction
 Class Copy Baby Lab Introduction The traits on the following pages are believed to be inherited in the explained manner. Most of the traits, however, in this activity were created to illustrate how human
Class Copy Baby Lab Introduction The traits on the following pages are believed to be inherited in the explained manner. Most of the traits, however, in this activity were created to illustrate how human
SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE
 AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
AP Biology Date SICKLE CELL ANEMIA & THE HEMOGLOBIN GENE TEACHER S GUIDE LEARNING OBJECTIVES Students will gain an appreciation of the physical effects of sickle cell anemia, its prevalence in the population,
Phenotypes and Genotypes of Single Crosses
 GENETICS PROBLEM PACKET- Gifted NAME PER Phenotypes and Genotypes of Single Crosses Use these characteristics about plants to answer the following questions. Round seed is dominant over wrinkled seed Yellow
GENETICS PROBLEM PACKET- Gifted NAME PER Phenotypes and Genotypes of Single Crosses Use these characteristics about plants to answer the following questions. Round seed is dominant over wrinkled seed Yellow
Bio 102 Practice Problems Mendelian Genetics and Extensions
 Bio 102 Practice Problems Mendelian Genetics and Extensions Short answer (show your work or thinking to get partial credit): 1. In peas, tall is dominant over dwarf. If a plant homozygous for tall is crossed
Bio 102 Practice Problems Mendelian Genetics and Extensions Short answer (show your work or thinking to get partial credit): 1. In peas, tall is dominant over dwarf. If a plant homozygous for tall is crossed
SMART Notebook: Basics and Application
 SMART Notebook: Basics and Application Table of Contents TESS Connection... 3 Version Number... 3 Tour of the Window... 5 The Main Toolbar... 5 The Sidebar... 18 Page Sorter... 19 The Gallery... 23 Searching...
SMART Notebook: Basics and Application Table of Contents TESS Connection... 3 Version Number... 3 Tour of the Window... 5 The Main Toolbar... 5 The Sidebar... 18 Page Sorter... 19 The Gallery... 23 Searching...
Biology 1406 - Notes for exam 5 - Population genetics Ch 13, 14, 15
 Biology 1406 - Notes for exam 5 - Population genetics Ch 13, 14, 15 Species - group of individuals that are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring; genetically similar 13.7, 14.2 Population
Biology 1406 - Notes for exam 5 - Population genetics Ch 13, 14, 15 Species - group of individuals that are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring; genetically similar 13.7, 14.2 Population
Educator s Guide to Excel Graphing
 Educator s Guide to Excel Graphing Overview: Students will use Excel to enter data into a spreadsheet and make a graph. Grades and Subject Areas: Grade 3-6 Subject Math Objectives: Students will: make
Educator s Guide to Excel Graphing Overview: Students will use Excel to enter data into a spreadsheet and make a graph. Grades and Subject Areas: Grade 3-6 Subject Math Objectives: Students will: make
Probability Using Dice
 Using Dice One Page Overview By Robert B. Brown, The Ohio State University Topics: Levels:, Statistics Grades 5 8 Problem: What are the probabilities of rolling various sums with two dice? How can you
Using Dice One Page Overview By Robert B. Brown, The Ohio State University Topics: Levels:, Statistics Grades 5 8 Problem: What are the probabilities of rolling various sums with two dice? How can you
COURSE DESCRIPTION. Course Number: NM: 17994100 RISD: 13109A, 13109B. Successful completion of Forensics I (C or better)
 COURSE DESCRIPTION Date: February 2011 COURSE TITLE: STARS Course Title: Forensic Science II Life and Physical Sciences Course Number: NM: 17994100 RISD: 13109A, 13109B Open to Grades: 12 Prerequisites:
COURSE DESCRIPTION Date: February 2011 COURSE TITLE: STARS Course Title: Forensic Science II Life and Physical Sciences Course Number: NM: 17994100 RISD: 13109A, 13109B Open to Grades: 12 Prerequisites:
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9
 Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
Biology 1406 Exam 4 Notes Cell Division and Genetics Ch. 8, 9 Ch. 8 Cell Division Cells divide to produce new cells must pass genetic information to new cells - What process of DNA allows this? Two types
Trasposable elements: P elements
 Trasposable elements: P elements In 1938 Marcus Rhodes provided the first genetic description of an unstable mutation, an allele of a gene required for the production of pigment in maize. This instability
Trasposable elements: P elements In 1938 Marcus Rhodes provided the first genetic description of an unstable mutation, an allele of a gene required for the production of pigment in maize. This instability
How to Use the H-ITT Analyzer Version 2.4.4
 How to Use the H-ITT Analyzer Version 2.4.4 I. Preparing to Use Analyzer: Adding Your Class II. Introduction to the Analyzer Interface III. Sync Your Class Roster in Analyzer IV. Update Your Class Roster
How to Use the H-ITT Analyzer Version 2.4.4 I. Preparing to Use Analyzer: Adding Your Class II. Introduction to the Analyzer Interface III. Sync Your Class Roster in Analyzer IV. Update Your Class Roster
Student Orientation Guide CHIPOLA COLLEGE e-learning Desire2Learn (D2L)
 Student Orientation Guide CHIPOLA COLLEGE e-learning Desire2Learn (D2L) Chipola d2l Student Orientation Guide Page 1 Table of Contents What s in this Orientation?... 3 Chipola College e-learning with D2L...
Student Orientation Guide CHIPOLA COLLEGE e-learning Desire2Learn (D2L) Chipola d2l Student Orientation Guide Page 1 Table of Contents What s in this Orientation?... 3 Chipola College e-learning with D2L...
17. A testcross A.is used to determine if an organism that is displaying a recessive trait is heterozygous or homozygous for that trait. B.
 ch04 Student: 1. Which of the following does not inactivate an X chromosome? A. Mammals B. Drosophila C. C. elegans D. Humans 2. Who originally identified a highly condensed structure in the interphase
ch04 Student: 1. Which of the following does not inactivate an X chromosome? A. Mammals B. Drosophila C. C. elegans D. Humans 2. Who originally identified a highly condensed structure in the interphase
Scientific Graphing in Excel 2010
 Scientific Graphing in Excel 2010 When you start Excel, you will see the screen below. Various parts of the display are labelled in red, with arrows, to define the terms used in the remainder of this overview.
Scientific Graphing in Excel 2010 When you start Excel, you will see the screen below. Various parts of the display are labelled in red, with arrows, to define the terms used in the remainder of this overview.
AP Biology Essential Knowledge Student Diagnostic
 AP Biology Essential Knowledge Student Diagnostic Background The Essential Knowledge statements provided in the AP Biology Curriculum Framework are scientific claims describing phenomenon occurring in
AP Biology Essential Knowledge Student Diagnostic Background The Essential Knowledge statements provided in the AP Biology Curriculum Framework are scientific claims describing phenomenon occurring in
Outlook Web App McKinney ISD 5/27/2011
 Outlook Web App McKinney ISD 5/27/2011 Outlook Web App Tutorial Outlook Web Access allows you to gain access to your messages, calendars, contacts, tasks and public folders from any computer with internet
Outlook Web App McKinney ISD 5/27/2011 Outlook Web App Tutorial Outlook Web Access allows you to gain access to your messages, calendars, contacts, tasks and public folders from any computer with internet
Microsoft PowerPoint 2007
 Microsoft PowerPoint 2007 PowerPoint is currently the most common software used for making visual aids for presentations. It has been redesigned for the 2007 release with a much more user-friendly and
Microsoft PowerPoint 2007 PowerPoint is currently the most common software used for making visual aids for presentations. It has been redesigned for the 2007 release with a much more user-friendly and
Influence of Sex on Genetics. Chapter Six
 Influence of Sex on Genetics Chapter Six Humans 23 Autosomes Chromosomal abnormalities very severe Often fatal All have at least one X Deletion of X chromosome is fatal Males = heterogametic sex XY Females
Influence of Sex on Genetics Chapter Six Humans 23 Autosomes Chromosomal abnormalities very severe Often fatal All have at least one X Deletion of X chromosome is fatal Males = heterogametic sex XY Females
Manual. OIRE Escuela de Profesiones de la Salud. Power Point 2007
 Power Point 2007 Manual OIRE Escuela de Profesiones de la Salud Power Point 2007 2008 The New Power Point Interface PowerPoint is currently the most common software used for making visual aids for presentations.
Power Point 2007 Manual OIRE Escuela de Profesiones de la Salud Power Point 2007 2008 The New Power Point Interface PowerPoint is currently the most common software used for making visual aids for presentations.
Publisher 2010 Cheat Sheet
 April 20, 2012 Publisher 2010 Cheat Sheet Toolbar customize click on arrow and then check the ones you want a shortcut for File Tab (has new, open save, print, and shows recent documents, and has choices
April 20, 2012 Publisher 2010 Cheat Sheet Toolbar customize click on arrow and then check the ones you want a shortcut for File Tab (has new, open save, print, and shows recent documents, and has choices
NJCU WEBSITE TRAINING MANUAL
 NJCU WEBSITE TRAINING MANUAL Submit Support Requests to: http://web.njcu.edu/its/websupport/ (Login with your GothicNet Username and Password.) Table of Contents NJCU WEBSITE TRAINING: Content Contributors...
NJCU WEBSITE TRAINING MANUAL Submit Support Requests to: http://web.njcu.edu/its/websupport/ (Login with your GothicNet Username and Password.) Table of Contents NJCU WEBSITE TRAINING: Content Contributors...
Genetic Mutations. Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes.
 Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Genetic Mutations Indicator 4.8: Compare the consequences of mutations in body cells with those in gametes. Agenda Warm UP: What is a mutation? Body cell? Gamete? Notes on Mutations Karyotype Web Activity
Content Author's Reference and Cookbook
 Sitecore CMS 6.5 Content Author's Reference and Cookbook Rev. 110621 Sitecore CMS 6.5 Content Author's Reference and Cookbook A Conceptual Overview and Practical Guide to Using Sitecore Table of Contents
Sitecore CMS 6.5 Content Author's Reference and Cookbook Rev. 110621 Sitecore CMS 6.5 Content Author's Reference and Cookbook A Conceptual Overview and Practical Guide to Using Sitecore Table of Contents
Introduction to SharePoint For Team Site Owner/Administrators. Instructional Guide
 Instructional Guide Class Goals: 1. Understanding & Navigating the SP Team Site Structure 2. Using SP to create & maintain a collaborative site for your team: Planning & Design, Lists, Libraries, Web Parts
Instructional Guide Class Goals: 1. Understanding & Navigating the SP Team Site Structure 2. Using SP to create & maintain a collaborative site for your team: Planning & Design, Lists, Libraries, Web Parts
How QuizStar Works for Students. Use either link to enter as a student.
 How QuizStar Works for Students Contents I. Logging-on II. New user III. Registering for a class- IV. Taking a quiz V. Viewing your results VI. Help VII. Logging out Click either place to enter QuizStar
How QuizStar Works for Students Contents I. Logging-on II. New user III. Registering for a class- IV. Taking a quiz V. Viewing your results VI. Help VII. Logging out Click either place to enter QuizStar
Ringneck Doves. A Handbook of Care & Breeding
 Ringneck Doves A Handbook of Care & Breeding With over 100 Full Color Photos, Including Examples and Descriptions of 33 Different Colors and Varieties. K. Wade Oliver Table of Contents Introduction, 4
Ringneck Doves A Handbook of Care & Breeding With over 100 Full Color Photos, Including Examples and Descriptions of 33 Different Colors and Varieties. K. Wade Oliver Table of Contents Introduction, 4
Qualtrics Survey Tool
 Qualtrics Survey Tool This page left blank intentionally. Table of Contents Overview... 5 Uses for Qualtrics Surveys:... 5 Accessing Qualtrics... 5 My Surveys Tab... 5 Survey Controls... 5 Creating New
Qualtrics Survey Tool This page left blank intentionally. Table of Contents Overview... 5 Uses for Qualtrics Surveys:... 5 Accessing Qualtrics... 5 My Surveys Tab... 5 Survey Controls... 5 Creating New
Creating Online Surveys with Qualtrics Survey Tool
 Creating Online Surveys with Qualtrics Survey Tool Copyright 2015, Faculty and Staff Training, West Chester University. A member of the Pennsylvania State System of Higher Education. No portion of this
Creating Online Surveys with Qualtrics Survey Tool Copyright 2015, Faculty and Staff Training, West Chester University. A member of the Pennsylvania State System of Higher Education. No portion of this
Reebops. A model organism for teaching genetic concepts
 A model organism for teaching genetic concepts The activity helps to demonstrate how genetics is responsible both for similarities and variation among members of the same species. are imaginary organisms
A model organism for teaching genetic concepts The activity helps to demonstrate how genetics is responsible both for similarities and variation among members of the same species. are imaginary organisms
Terms: The following terms are presented in this lesson (shown in bold italics and on PowerPoint Slides 2 and 3):
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Unit B: Understanding Animal Reproduction Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Power Point 2003 Table of Contents
 Power Point 2003 Table of Contents Creating a Presentation... 2 Selecting Background and Format for Slide... 3 Creating the Title Slide... 4 Adding a New Slide... 5 Types of Text for a Slide: Taken from
Power Point 2003 Table of Contents Creating a Presentation... 2 Selecting Background and Format for Slide... 3 Creating the Title Slide... 4 Adding a New Slide... 5 Types of Text for a Slide: Taken from
EXCEL FINANCIAL USES
 EXCEL FINANCIAL USES Table of Contents Page LESSON 1: FINANCIAL DOCUMENTS...1 Worksheet Design...1 Selecting a Template...2 Adding Data to a Template...3 Modifying Templates...3 Saving a New Workbook as
EXCEL FINANCIAL USES Table of Contents Page LESSON 1: FINANCIAL DOCUMENTS...1 Worksheet Design...1 Selecting a Template...2 Adding Data to a Template...3 Modifying Templates...3 Saving a New Workbook as
Figure 3.5: Exporting SWF Files
 Li kewhatyou see? Buyt hebookat t hefocalbookst or e Fl ash + Af t eref f ect s Chr i sjackson ISBN 9780240810317 Flash Video (FLV) contains only rasterized images, not vector art. FLV files can be output
Li kewhatyou see? Buyt hebookat t hefocalbookst or e Fl ash + Af t eref f ect s Chr i sjackson ISBN 9780240810317 Flash Video (FLV) contains only rasterized images, not vector art. FLV files can be output
