IMMUNE SYSTEM I Keri Smith, PhD Reading: Gartner & Hiatt, Chapter 9; Sheedlo Chapter 12, p109
|
|
|
- Muriel Warren
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IMMUNE SYSTEM I Keri Smith, PhD Reading: Gartner & Hiatt, Chapter 9; Sheedlo Chapter 12, p109 Learning Objectives: Identify the organs and tissues that comprise the lymphoid system. Know the functions of the lymphatic system. Describe the histologic organization of the thymus. Describe the histologic organization of the lymph node. Key Words: Lymphocytes, Lymphatic Circulation, Cortex, Medulla, Thymus, Hassall's Corpuscles, Lymph Node, High Endothelial Venule (HEV) Lymphoid System (G&H, p. 175)
2 I. BASIC INFORMATION A. Lymphatic and lymphoid -- tissues or organs in which lymphocytes form the major cellular component. B. Includes: 1. Thymus 2. Lymph nodes 3. Spleen 4. Lymphoid nodules: tonsils, appendix, Peyer's patches in ileum, as well as small collections of lymphoid tissue throughout the GI, respiratory, and urinary tracts (termed Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue or MALT). C. All lymphoid organs originate from mesoderm, EXCEPT the thymus that originates from mesoderm and endoderm. D. Function is surveillance and defense ( immunity ) II. LYMPHOID TISSUE AND THE IMMUNE RESPONSE A. Specialized form of connective tissue containing large numbers of lymphocytes. Reticular cells and reticular fibers make up the supporting network B. Types of lymphocytes 1. T-lymphocytes or T-cells. Mediate cellular immunity (protect against microorganisms, tumor cells, and viruses). 2. B-lymphocytes or B-cells. Mediate humoral immunity through production of antibodies (or immunoglobulins). C. Both T- and B-lymphocytes originate from stem cells in the bone marrow. 1. Maturation site for T-cells is the thymus. 2. Maturation site for B-cells is uncertain. In birds, the B-cell maturation site is the bursa of Fabricius. The bursa equivalent in man may be the bone marrow or gut-related lymphoid tissue. 3. All lymphocytes express glycoproteins on their surface membranes. These surface markers are named according to an international classification: CD (Cluster Designation or Cluster of Differentiation) system.
3 Lymphocyte Differentiation (G&H, p. 175) D. B-lymphocytes 1. When come into contact with antigen, proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells. Plasma cells secrete immunoglobulins. 2. A small percentage of activated B-cells transform into memory B cells that are preprogrammed to respond rapidly to a subsequent exposure with the same antigen. B Lymphocytes (G&H, p. 177)
4 E. T-lymphocytes 1. When come into contact with antigen, transform into activated T-cells. Two primary subpopulations of T-lymphocytes: a. T-Helper cells: Secrete a variety of cytokines that coordinate cell-mediated as well as humoral immunity. These cells are CD4+ b. T-Suppressor/Cytotoxic cells: Function in the killing of some malignant cells, foreign cells, and virus-infected cells. Also suppress the activity of B-cells, thereby curbing the response to foreign antigens and one's own (self) antigens. These cells are CD8+. F. Natural killer (NK) lymphocytes % of circulating lymphocytes. Main function is to kill virus-infected cells and cancer cells. G. Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) 1. Responsible for processing antigen and "presenting" it to lymphocytes. Derived from the bone marrow and belong to the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS). 2. Include macrophages, Kupffer cells (liver), Langerhans cells (skin), dendritic cells present in lymphoid organs, and epithelial cells of the thymus. III. LYMPHATIC CIRCULATION A. Composed of vessels that remove excess extracellular fluid (lymph) from spaces between tissues and return it to the cardiovascular system. Most numerous under the skin and in mucous membranes. Are not present in the central nervous system, eye, ear, cartilage or bone. 1. Begin as blind-ended vessels in tissues. Walls of these vessels are more permeable than walls of capillaries, so cells and foreign substances pass readily into the "lymph." 2. Lymphatic vessels empty into the thoracic duct which joins the venous system at the junction of the internal jugular and subclavian veins. Lymphocytes that were in the lymph fluid now become components of blood. B. Lymph passes through various lymphoid organs (primarily lymph nodes) where antigens are concentrated and presented to lymphocytes, ultimately leading to an immune response. 1. Lymph enters lymph node through afferent lymphatics and leaves via efferent lymphatics. Some lymphocytes will remain in the B-dependent or T-dependent areas of the lymph node. 2. Lymphocytes regain entry into the lymphatic system via postcapillary venules (also called high endothelial venules or HEVs) in the lymph nodes. 3. This recirculation of lymphocytes involves all lymphatic tissue except the thymus and bone marrow.
5 IV. THYMUS A. Bilobed lymphoid organ in the mediastinum. Progressively atrophies from puberty to old age and is partially replaced by fat and connective tissue. Is a T-cell dependent organ. B. Has a thin loose connective tissue capsule that penetrates into the parenchyma, dividing the organ into lobules. Each lobule has a cortex and medulla. 1. Connective tissue contains blood vessels, efferent lymphatic vessels (NO afferent lymphatics), and nerves. C. Cortex 1. Composed of many closely packed, small pre-t-lymphocytes, epithelial reticular cells, and macrophages. There are NO lymphoid nodules or follicles. 2. Epithelial reticular cells are connected to each other via desmosomes at the end of long cytoplasmic processes. 3. Immature T-lymphocytes (thymocytes) are produced and accumulate in the cortex. Most will die here; the surviving cells will migrate to the medulla where they acquire their CD markers, enter the bloodstream through venules, and migrate to the T-dependent areas of other lymphoid organs (paracortical area of lymph nodes, PALS of the spleen, some parts of Peyer s patches) where they complete the maturation process. D. Medulla 1. Contains a large number of epithelial reticular cells, some large immature T-lymphocytes, and macrophages. 2. Contains Hassall's corpuscles. Composed of flattened epithelial reticular cells which have degenerated; they may show some keratinization. Arranged in a concentric formation and vary in size. Function is unknown.
6 Thymus (G&H, p. 189) E. Thymic function 1. Essential for the development of T-lymphocytes. Produces several growth factors (thymosin, thymotaxin, thymopoietin, serum thymic factor) that stimulate proliferation and differentiation of T-lymphocytes. 2. Most of the growth factors are thought to be produced by the epithelial reticular cells. 3. Blood-Thymus Barrier continuous, non-fenestrated endothelial cells with tight junctions + basal lamina + epithelial reticular cells. Found in cortex only. Prevents exposure of thymocytes to antigens. V. LYMPH NODES A. Lymphoid organs distributed throughout body along the lymphatic vessel system. 1. All lymph passes through at least one node before it enters the circulatory system. 2. Afferent lymphatic vessels enter the LN along the convex surface of the capsule. Efferent lymphatic vessels leave the LN at the hilum. Arteries enter and veins leave the node via the hilum. 3. Dense connective tissue capsule that sends connective tissue septae or trabeculae into the node. Reticular cells and reticular fibers form a supporting meshwork that extends throughout the parenchyma. 4. The parenchyma consists of diffuse and nodular lymphoid tissue and is separated into an inner and outer cortex and a medulla. B. Lymph Flow 1. Afferent lymphatic vessels subcapsular sinus cortical (intermediate) sinuses medullary sinuses efferent lymphatic vessels. 2. Lymphatic vessels contain one-way valves to assure flow of lymph in the proper direction.
7 C. Cortex 1. Subcapsular sinus located immediately beneath the capsule. Empties into the medullary sinuses via the cortical (also called paratrabecular or intermediate) sinuses that run alongside the connective tissue trabeculae. 2. Outer cortex is meshwork of diffuse lymphoid tissue with macrophages, T-lymphocytes, plasma cells, and reticular cells. Contains lymphoid nodules (follicles) composed of B- lymphocytes. 3. Inner (or deep) cortex is continuation of the outer cortex and contains diffusely arranged T- lymphocytes. Also called the paracortex or paracortical zone. Few, if any, lymphoid nodules are found. a. Contains specialized vessels called high endothelial venules (HEVs). Are lined with cuboidal endothelial cells with large nuclei, and serve as the point of entry for lymphocytes from peripheral blood into LN parenchyma. D. Follicles 1. Primary follicles contain small B-lymphocytes. 2. Secondary follicle has a pale central area, the germinal center. Germinal center contains activated B-cells that will give rise to plasma cells. Germinal center is surrounded by a cuff of small B-lymphocytes called the mantle zone. The presence of germinal centers indicates the lymph node is antigenically-stimulated. Germinal Center Mantle Zone Primary Follicle Secondary Follicle
8 3. Germinal center contains Dendritic Reticulum Cells (DRCs) which trap antigens and present them to B-cells. Are long-lived and difficult to see by light microscopy. 4. B-cells in the germinal center are large with vesicular nuclei. These are proliferating cells; mitotic figures are not uncommon. 5. Tingible body macrophages can be found. Are large cells whose cytoplasm contains phagocytized debris. Cytoplasm is not conspicuous, so appear as "clear areas" in the tissue. Lymph Node (G&H, p. 183, 185) E. Medulla 1. Composed of medullary cords separated by medullary sinuses that contain lymph, lymphocytes, and macrophages. 2. Medullary cords contain primarily B-lymphocytes, macrophages, plasma cells, and reticular cells. Major site of phagocytosis and immunoglobulin synthesis. F. Lymph node function 1. Main function is to filter lymph before it returns to the circulatory system. Phagocytic cells within the lymph node will remove foreign particles and bacteria. Foreign antigens become trapped on the surface of the APCs and then presented to memory B-cells. 2. B-cells may recognize the antigen with or without the assistance of T-cells. Activated B-cells migrate to the germinal center of the follicles and begin multiple mitotic divisions that eventually give rise to immature lymphoblasts. 3. Lymphoblasts give rise to plasma cells and memory B-cells. Plasma cells migrate to medullary cords where they begin synthesizing antibodies. Memory B-cells circulate to various areas of the body and set up housekeeping, waiting for the antigen to reappear. 4. T lymphocytes can become activated with eventual dissemination of cytotoxic T-cells throughout the body. 5. Lymph nodes that contain cells responding to an antigenic load typically become enlarged due to formation of germinal centers and proliferation of B-lymphocytes.
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
= Lymphatic systems =
 = Lymphatic systems = Why do we need it? Lymph node Lymphatic vessel Lymphatic vessel Vein Capillary Artery tissues blood Capillaries Speaker: 許 書 豪 解 剖 學 科 助 理 教 授 1 Lymphatic tissue and organ Lymphatic
= Lymphatic systems = Why do we need it? Lymph node Lymphatic vessel Lymphatic vessel Vein Capillary Artery tissues blood Capillaries Speaker: 許 書 豪 解 剖 學 科 助 理 教 授 1 Lymphatic tissue and organ Lymphatic
Lymph capillaries, Lymphatic collecting vessels, Valves, Lymph Duct, Lymph node, Vein
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
The Immune System: A Tutorial
 The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System
 The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system runs though the body and is made up of organs and lymphatic tissue, this includes organs like the spleen and thymus and also lymphatic
The Structure and Function of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system runs though the body and is made up of organs and lymphatic tissue, this includes organs like the spleen and thymus and also lymphatic
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237)
 Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Unit Four. Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 16 Lymphatic System URLs http://www.howstuffworks.com/immune-system.htm http://www.thebody.com/step/immune.html http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookIMMUN.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 16 Lymphatic System URLs http://www.howstuffworks.com/immune-system.htm http://www.thebody.com/step/immune.html http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookIMMUN.html
The Immune System. 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms. Lines of Defense. Line of Defense. Lines of Defense
 The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
Name (print) Name (signature) Period. (Total 30 points)
 AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
Immunity. Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity
 Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Biology 2402 CHAPTER 22 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Pathogens are disease-producing organisms. Survival and good health depends on
Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Biology 2402 CHAPTER 22 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Pathogens are disease-producing organisms. Survival and good health depends on
2) Macrophages function to engulf and present antigen to other immune cells.
 Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
10. T and B cells are types of a. endocrine cells. c. lymphocytes. b. platelets. d. complement cells.
 Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
LYMPHOMA. BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons
 LYMPHOMA BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons Normal development of lymphocytes Lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation:
LYMPHOMA BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons Normal development of lymphocytes Lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation:
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education. Su et al.
 Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
The Tissue Level of Organization Tissues A groups of similar cells, usually having similar embryonic origin and specialized function Histology: the study of tissues Four general types Epithelial Muscle
Immune System Memory Game
 Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity
 Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
The Immune System. How your immune system works. Organs of the Immune System
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION The Immune System How your immune system works The immune system is a network of special cells, tissues, and organs that defend the body against attacks from foreign invaders,
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION The Immune System How your immune system works The immune system is a network of special cells, tissues, and organs that defend the body against attacks from foreign invaders,
The lymphatic system and the immune system
 Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk The lymphatic system and the immune system Lymphoma is a cancer that usually grows in the body s lymphatic system. The
Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphomas.org.uk www.lymphomas.org.uk The lymphatic system and the immune system Lymphoma is a cancer that usually grows in the body s lymphatic system. The
White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes
 Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types:
 Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Adaptive Immune System
 Chapter 25 The Adaptive Immune ystem 25 Our adaptive immune system saves us from certain death by infection. An infant born with a severely defective adaptive immune system will soon die unless extraordinary
Chapter 25 The Adaptive Immune ystem 25 Our adaptive immune system saves us from certain death by infection. An infant born with a severely defective adaptive immune system will soon die unless extraordinary
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation
 Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Activation and effector functions of HMI
 Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6)
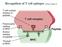 Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
Lab Exercise 4. Epithelial Tissues. Connective Tissue Proper. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
Lab Exercise 4 Epithelial Tissues Connective Tissue Proper Textbook Reference: See Chapter 4 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to identify each type
The Body s Defenses CHAPTER 24
 CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Ground substance is the component of connective tissue between the cells and the fibers
 Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
Connective Tissues Directions: Insert and install your Interactions: Foundations CD. a. Click the "Contents" button. b. Open the Tissue Level of Organization file. c. Click on Anatomy Overviews. d. Work
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I.
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
Vertebrate Body Organization
 Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
Vertebrate Body Organization Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom
ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES. Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer
 Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer What you need to know ONCHQ14NP07519 Introduction: Immuno-oncology represents an innovative approach to cancer research that seeks to harness the body s own
Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer What you need to know ONCHQ14NP07519 Introduction: Immuno-oncology represents an innovative approach to cancer research that seeks to harness the body s own
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity
 B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 3. Immunity and how vaccines work
 Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Immune and Lymphatic Systems
 1. All of the following organs actively FIGHT pathogens EXCEPT: a. Cervical lymph nodes b. Tonsils c. Spleen d. Thymus e. Axillary lymph nodes 2. T lymphocytes gain immunocompetence within the: a. Bone
1. All of the following organs actively FIGHT pathogens EXCEPT: a. Cervical lymph nodes b. Tonsils c. Spleen d. Thymus e. Axillary lymph nodes 2. T lymphocytes gain immunocompetence within the: a. Bone
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
 About B Cell Lymphomas Groupmeeting Klipp/Spang, December 09 2002 Dennis Kostka Max-Planck-Institute for Molecular Genetics Computational Molecular Biology Berlin 1 Overview Short History of Lymphoma Classification
About B Cell Lymphomas Groupmeeting Klipp/Spang, December 09 2002 Dennis Kostka Max-Planck-Institute for Molecular Genetics Computational Molecular Biology Berlin 1 Overview Short History of Lymphoma Classification
The Human Immune System
 The Human Immune System What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles The First Line of Defense Skin The dead, outer layer
The Human Immune System What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles The First Line of Defense Skin The dead, outer layer
Thought for the Day. Courage is not simply one of the virtues, but the form of every virtue at the testing point. ~ C. S. Lewis
 Thought for the Day Courage is not simply one of the virtues, but the form of every virtue at the testing point. ~ C. S. Lewis Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Section 2 Lecture
Thought for the Day Courage is not simply one of the virtues, but the form of every virtue at the testing point. ~ C. S. Lewis Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Section 2 Lecture
Dendritic Cells: A Basic Review *last updated May 2003
 *last updated May 2003 Prepared by: Eric Wieder, PhD MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX USA What is a dendritic cell? Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells (APCs) which play a critical role in
*last updated May 2003 Prepared by: Eric Wieder, PhD MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX USA What is a dendritic cell? Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells (APCs) which play a critical role in
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56
 Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
Structure of the Kidney Laboratory Exercise 56 Background The two kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. They are located in the upper quadrants of the abdominal cavity, against the posterior
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
CELLS AND ORGANS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM
 CELLS AND ORGANS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Specific as well as non-specific immunity is maintained in the body the lymphoreticular system that is a complex organization of cells of diverse morphology and distributed
CELLS AND ORGANS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Specific as well as non-specific immunity is maintained in the body the lymphoreticular system that is a complex organization of cells of diverse morphology and distributed
Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer
 Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer Normal blood contains circulating white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets 700 red cells (oxygen) 1 white cell Neutrophils (60%) bacterial infection Lymphocytes
Leukemias and Lymphomas: A primer Normal blood contains circulating white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets 700 red cells (oxygen) 1 white cell Neutrophils (60%) bacterial infection Lymphocytes
Tissue Types. 1. Epithelial Tissue (or epithelium) is the lining, covering, and glandular tissue of the body
 Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Tissue Types A. Tissues 1. Tissues: groups of cells similar in structure and function 2. Four Types of Tissues: a. Epithelium: for covering b. Connective Tissue: for support c. Muscle: for movement d.
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary. Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide
 Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES JASON CYSTER SECTION 13
 SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
Bio 20 Chapter 11 Workbook Blood and the Immune System Ms. Nyboer
 Bio 20 Chapter 11 Workbook Blood and the Immune System Ms. Nyboer Name: Part A: Components of Blood 1. List the 3 plasma proteins and describe the function of each Albumins osmotic balance Globulins antibodies,
Bio 20 Chapter 11 Workbook Blood and the Immune System Ms. Nyboer Name: Part A: Components of Blood 1. List the 3 plasma proteins and describe the function of each Albumins osmotic balance Globulins antibodies,
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation. B cell maturation
 B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
How do plasma cells survive
 How do plasma cells survive Claudia Berek Deutsches Rheuma Forschungs Zentrum, Berlin Institut der Leibniz Gemeinschaft Immune response Naive B cell Peripheral lymphoid organs Memory B cell Germinal T
How do plasma cells survive Claudia Berek Deutsches Rheuma Forschungs Zentrum, Berlin Institut der Leibniz Gemeinschaft Immune response Naive B cell Peripheral lymphoid organs Memory B cell Germinal T
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes
 Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes a. Cells tissues organs body systems Division of labour occurs in multicellular organisms (rather than each cell carrying out every function) Most cells become
Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow
 13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
13.01.2015 Nervous Tissue Dr. Archana Rani Associate Professor Department of Anatomy KGMU UP, Lucknow Introduction Property of irritability and conductivity Respond to various types of stimuli Distributed
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
P a g e 52 A & P II SWARTZ NOTES Page 52
 P a g e 52 A & P II SWARTZ NOTES Page 52 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY The lymphatic system consists of a fluid called lymph, vessels that convey lymph called lymphatics, and a number of structures
P a g e 52 A & P II SWARTZ NOTES Page 52 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY The lymphatic system consists of a fluid called lymph, vessels that convey lymph called lymphatics, and a number of structures
Cardiovascular System. Blood Components
 Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Cardiovascular System Blood Components 1 Components of Blood Formed elements: erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets Plasma: water, proteins, other solutes The components of blood can be divided into two
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
33.1 The Circulatory System
 33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
3. The Circulatory System
 3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
The Integumentary System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi The Skin The integument system consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane) and its accessory organs. The skin is composed of three layers of tissue: the outer
IMMUNE SYSTEM. The body s defense against:
 The body s defense against: IMMUNE SYSTEM disease causing organisms or infectious agents malfunctioning cells or abnormal body cells as cancer foreign cells or particles Basic Immunity Depends on the ability
The body s defense against: IMMUNE SYSTEM disease causing organisms or infectious agents malfunctioning cells or abnormal body cells as cancer foreign cells or particles Basic Immunity Depends on the ability
Inflammation and Healing. Review of Normal Defenses. Review of Normal Capillary Exchange. BIO 375 Pathophysiology
 Inflammation and Healing BIO 375 Pathophysiology Review of Normal Defenses Review of Normal Capillary Exchange 1 Inflammation Inflammation is a biochemical and cellular process that occurs in vascularized
Inflammation and Healing BIO 375 Pathophysiology Review of Normal Defenses Review of Normal Capillary Exchange 1 Inflammation Inflammation is a biochemical and cellular process that occurs in vascularized
Role of bursa Fabricius in Chicken s Immunocompetence. Dr. Vilmos Palya Director of Scientific Support and Investigation Ceva-Phylaxia, Budapest
 Role of bursa Fabricius in Chicken s Immunocompetence Dr. Vilmos Palya Director of Scientific Support and Investigation Ceva-Phylaxia, Budapest PRIMARY LYMPHOID ORGANS: The stucture of chicken s immune
Role of bursa Fabricius in Chicken s Immunocompetence Dr. Vilmos Palya Director of Scientific Support and Investigation Ceva-Phylaxia, Budapest PRIMARY LYMPHOID ORGANS: The stucture of chicken s immune
Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14
 Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14 Functions: Fluid balance by returning excess tissue fluid to the blood; returning solutes (especially plasma proteins) to the blood; filter body
Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14 Functions: Fluid balance by returning excess tissue fluid to the blood; returning solutes (especially plasma proteins) to the blood; filter body
Blood. Functions of Blood. Components of Blood. Transporting. Distributing body heat. A type of connective tissue. Formed elements.
 Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
RAD 223. Radiography physiology. Lecture Notes. First lecture: Cell and Tissue
 RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
RAD 223 Radiography physiology Lecture Notes First lecture: Cell and Tissue Physiology: the word physiology derived from a Greek word for study of nature. It is the study of how the body and its part work
Joint projects of Transition Technologies and Emerson Process Management.
 Polish-American cooperation in the field of modern coal-fired boilers optimization techniques (artificial immune systems). Joint projects of Transition Technologies and Emerson Process Management. PROF.
Polish-American cooperation in the field of modern coal-fired boilers optimization techniques (artificial immune systems). Joint projects of Transition Technologies and Emerson Process Management. PROF.
MISSION DEBRIEFING: Teacher Guide
 Activity on the IMMUNE SYSTEM: The Body Fights Back In this activity, the students will use a hands-on approach to learn about the immune system and how it fights off pathogens that invade the body. They
Activity on the IMMUNE SYSTEM: The Body Fights Back In this activity, the students will use a hands-on approach to learn about the immune system and how it fights off pathogens that invade the body. They
Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture
 I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
I. Histology the study of tissues A. 4 basic tissue types epithelial connective muscle nervous Tissues (Histology) Ch. 3 Human Anatomy lecture B. Usually found in combinations to form organs. C. As you
STEM CELL FELLOWSHIP
 Module I: The Basic Principles of Stem Cells 1. Basics of Stem Cells a. Understanding the development of embryonic stem cells i. Embryonic stem cells ii. Embryonic germ cells iii. Differentiated stem cell
Module I: The Basic Principles of Stem Cells 1. Basics of Stem Cells a. Understanding the development of embryonic stem cells i. Embryonic stem cells ii. Embryonic germ cells iii. Differentiated stem cell
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
R-16: Chronic nonspecific cervisit
 R-16: Chronic nonspecific cervisit Ectoservikal squamous epithelium Endoservical columnar epithelium Dilated cystic endoservical glands lymphoplasmocytes R18:Squamous cell carcinoma insitu Neoplastic epithelium
R-16: Chronic nonspecific cervisit Ectoservikal squamous epithelium Endoservical columnar epithelium Dilated cystic endoservical glands lymphoplasmocytes R18:Squamous cell carcinoma insitu Neoplastic epithelium
SQA CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 4: Immunology and Public Health
 SCHOLAR Study Guide SQA CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 4: Immunology and Public Health Authored by: Eoin McIntyre Reviewed by: Sheena Haddow Previously authored by: Mike Cheung Eileen Humphrey Eoin McIntyre
SCHOLAR Study Guide SQA CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 4: Immunology and Public Health Authored by: Eoin McIntyre Reviewed by: Sheena Haddow Previously authored by: Mike Cheung Eileen Humphrey Eoin McIntyre
Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org
 Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this booklet This booklet provides information on selective IgA deficiency (sigad). It has been produced by the PID UK
Selective IgA deficiency (slgad) hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this booklet This booklet provides information on selective IgA deficiency (sigad). It has been produced by the PID UK
Granulocytes vs. Agranulocytes
 Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
CHAPTER 6: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
OBJECTIVES: 1. Explain why the skin is called the cutaneous membrane. 2. Name the layers of the skin, describe the structure (tissues) of each, and name a general function of each. 3. Discuss the four
