Dendritic Cells: A Basic Review *last updated May 2003
|
|
|
- Jonathan Leslie Clark
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 *last updated May 2003 Prepared by: Eric Wieder, PhD MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX USA What is a dendritic cell? Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells (APCs) which play a critical role in the regulation of the adaptive immune response. Dendritic cells (DCs) are unique APCs and have been referred to as professional APCs, since the principal function of DCs is to present antigens, and because only DCs have the ability to induce a primary immune response in resting naïve T lymphocytes. To perform this function, DCs are capable of capturing antigens, processing them, and presenting them on the cell surface along with appropriate costimulation molecules. DCs also play a role in the maintenance of B cell function and recall responses. Thus, DCs are critical in the establishment of immunological memory. Background: DCs were first described by Ralph Steinman nearly thirty years ago. He found a population of striking dendritic-shaped cells in the spleen. Shortly thereafter it became clear that DCs existed in all lymphoid and most non-lymphoid tissues. During the 1970s, most immunologists considered macrophages to be the principal APC in the immune system. Compared to DCs, macrophages were more abundant, were uniformly distributed throughout the body, and were known to have antigen presenting capablilities. Since DCs are so rare, initial studies were difficult and it was not until the 1980s that it became widely accepted that DCs were professional APCs. While the rarity of DCs was a hindrance to studying them, in the 1990 s researchers learned how to generate large numbers of DCs from CD34+ bone marrow precursors or from CD14+ monocytes in vitro. The ability to expand functional DCs in vitro has increased researchers ability to study DCs to understand mechanisms of DC interactions with the immune system and to begin to test DC therapy regiments in the clinic. How is a dendritic cell detected? Mature DCs are defined by key morphological features and by the presence or absence of various molecules on the cell surface. The key morphological characteristic of DCs is the presence of numerous membrane processes that extend out from the main cell body (similar to dendrites on neurons). An additional morphological feature of DCs is that they contain abundant intracellular structures relating to antigen processing including endosomes, lysosomes, and Birbeck granules of Langerhans cells of the epidermis.
2 An obstacle to the detection of DCs is that a single cell surface marker exclusively expressed on DCs has not yet been identified. Therefore, a combination of the presence and absence of various surface markers has been used to identify DCs. These include the presence of large amounts of class II MHC antigens and the absence of various lineage markers such as CD3 (T cell), CD14 (monocyte), CD19 (B cell), CD56 (natural killer cell) and CD66b (granulocyte). DCs also express a variety of adhesion molecules including CD11a (LFA-1), CD11c, CD50 (ICAM-2), CD54 (ICAM-1), CD58 (LFA-3), and CD102 (ICAM-3). DCs also express costimulatory molecules including CD80 (B7.1), and CD86 (B7.2), which are upregulated during DC activation. CD86 tends to be a marker of early DC maturation, while CD80 only appears in mature DC. Two additional markers of mature DC in humans are CD83 and CMRF-44. CD83 also stains activated B cells, and CMRF-44 will also stain macrophages and monocytes. With such a variety of surface markers available for identifying DCs, yet none which specifically stain DCs only, the neophyte to detecting DCs may become bewildered at the prospect of where to start when attempting to identify DCs. In practice, however, the identification of DCs by surface phenotyping may be accomplished by simply demonstrating a high level of MHC class II or a costimulatory molecule such as CD80 and the absence of lineage markers. Thus, a two-color analysis by flow cytometry using a cocktail of lineage markers in one color and a positive marker for DC in the other can be sufficient to identify DCs. Of course, depending on the purpose of identification, the use of additional markers/colors may be required as well. Recently, subsets of DC were recognized based on their function in immune responses. DC1 cells, also called myeloid DCs, express different Toll-like receptors (TLR)-2, -3, -4, and -7. After encountering different natural ligands or pathogens for these TLRs in the blood, DC1 cells become activated and mature into antigen-presenting cells (APC) that can secrete Th-1 or Th-2 cytokines and prime naive T cells for a proper immune response. DC2 cells, also called plasmacytoid DC, only express TLR7 and TLR9 receptors and are the principle producers of interferon-alpha after encountering invading viruses. These two types of DCs play important role on linking the innate and adaptive immunity through their unique expression patterns of TLRs and cytokine production. What is the function of dendritic cells? The function of DCs falls broadly into three categories, each of which involve antigen presentation. The first category of DCs function is antigen presentation and activation of T cells. The second category of DC function is not as well established, but it has been suggested that a different class of DCs exist with the function of inducing and maintaining immune tolerance. The third category of DCs, known as follicular DCs, appear to work to maintain immune memory in tandem with B cells. Page 2
3 T cell activation: DCs process and present antigen to activate both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. This appears to be the most prominent role for DCs, since only DCs are capable of activating naïve T cells. Immature DCs originate in the bone marrow and migrate throughout the body. Once there, the immature DCs lay dormant waiting to interact with invading pathogens or other foreign bodies. At this point, the primary function of the immature DC is to capture antigens. In the case of a wound accompanied by inflammation, DCs are attracted to the area of inflammation and stimulated to capture and internally process antigens. So, the function of an immature DC is to find and capture foreign bodies and antigens. Once captured, the antigen is processed either by an exogenous or endosomal pathway, or by endogenous or proteosomal pathway. For MHC class I presentation to stimulate CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, the antigen or protein is taken up by phagocytosis or receptor mediated endocytosis into the cytosol. The antigens are further degraded in the cytosol via proteosome and enter the endoplasmic reticulum where peptides bind to newly synthesized MHC class I molecules for presentation on the cell surface. For MHC class II presentation to stimulate CD4+ T helper cells, antigen is taken up by phagocytosis or receptor-mediated endocytosis to endosomes where some proteolysis occurs. The peptides enter a vesicle containing MHC class II where they bind and are transported to the cell surface. A key component on DCs in addition to antigen capture, processing and presentation is the presence of costimulatory molecules. DCs maintain on their cell surface costimulatory molecules including members of the B7 family, TNF family and intracellular adhesion molecules which are critical to the activation of T cells and for the proper homing of DCs before and after antigen capture. Immune tolerance: Tolerance is the inability of the immune system to respond to specific antigens. Central tolerance occurs in the thymus for T cells and the bone marrow for B cells. The primary mechanism for central tolerance in T cells is the induction of T cell death. DCs are found in abundance in the thymus, where newly produced T cells are educated to become functional CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells and undergo selection to eliminate immunity against self. Low affinity reactive T cells are positively selected and allowed to survive and reach the periphery. This does not involve DC function. T cells that respond to DCs carrying self-peptides are destroyed in the thymus by negative selection. This process involves T cells which recognize MHC/peptides with high avidity. DCs contribute to this negative selection process along with thymic epithelial cells. The mechanisms of peripheral tolerance include T cell death, anergy, and active supression by T regulatory cells. DCs could contribute by inducing apoptosis in T cells and by producing IL- 10, a cytokine that stimulates T cells and induces T regulatory cells. DCs might also contribute to tolerance by inducing anergy in responder T cells. Page 3
4 B cell stimulation/function: DCs can contribute to the stimulation of B cells, both in the lymph node T cell areas and in germinal centers. DCs produce a number of cytokines and factors which are critical to the activation and differentiation of B cells. The follicular DCs (FDCs), which are found in germinal centers of lymph nodes, appear to be important in the maintenance of B cell memory. FDCs are not involved in the initial antibody response to foreign antigens. However, after the initial antibody response begins, the FDCs form numerous complexes of antigen and antibody. FDCs are believed to serve as both a reservoir for antibody and as a source of continued stimulation for B cells. The B cells can in turn take up the antigen from FDCs and present it to T cells. The reservoir of antigen and antibody complexes on FDCs is believed to be able to last a very long time, perhaps up to months or years. Origins and nomenclature: There is little argument that DCs are derived from hematopoietic stem cells; however, DCs can originate from both lymphoid and myeloid lineages. In humans, myeloid lineage DCs are considered the classical DC. These cells originate from myeloid commited CD34+ progenitor cells, and monocytes can be driven to become DCs in the presence of GM-CSF and TNFα ± IL- 4. When this type of DC matures, it is known as an interstitial DC. In addition to being able to activate naïve CD4 and CD8 T cells, interstitial DCs can induce differentiation of naïve B cells to antibody secreting plasma cells. Interstitial DCs are assumed to migrate to the lymphoid follicles and become follicular DCs. Myeloid committed CD34+ cells which are CD14 negative can mature to what is called a Langerhans DC, in the presence of TGF-β. Langerhans DC are also capable of activating naïve T cells, but not B cells. Langerhans DC are those that capture antigen, migrate to lymphoid tissues and present antigen to T cells. The lymphoid DCs -- the DC subset that originates from CD34+ cells committed to the lymphoid lineage, are CD11c- and are driven to become DCs by IL-3. These DCs are referred to as Plasmacytoid DCs, and they have the capacity to produce IFN-α and reside in the T cell compartment of lymphoid tissues. Dendritric cell generation: DCs can be generated by culturing CD34+ cells in the presence of various cytokines. One approach which has been taken involves depleting the CD34+ cells of differentiated precursors and then culturing the cells in the presence of GM-CSF and IL-4 ± TNF-α. CD34+ cells can be obtained from bone marrow, cord blood or G-CSF mobilized peripheral blood. Another approach is to generate DC-like cells by culturing CD14+ monocyte-enriched PBMC. In the presence of GM-CSF and IL-4, these cultures give rise to large numbers of DC like cells. Page 4
5 These monocyte-derived DCs need additional conditioning in vitro with either TNF-α or monocyte-conditioned media to be able to fully function as a DC capable of priming antigenspecific T cell responses. Additional information of the generation of DCs and the cytokines involved is presented in a review article by Syme and Gluck. A novel approach to expand DCs in vivo is presented in a review by Fong and Engleman. They saw an increase in circulating DCs by fold in a clinical protocol using Flt3-ligand. These cells could be harvested with a leukapheresis procedure and used for later immunotherapy. Other molecules may also prove useful for the in vivo expansion and mobilization of DCs. Dendritic cell immunotherapy: There is a great deal of interest in how DCs might be exploited as a form of immunotherapy. DCs are being studied as adjuvants for vaccines or as a direct therapy to induce immunity against cancer. That DCs may prove useful in cancer has been most often studied in animal models. DCs loaded with tumor lysates, tumor antigen-derived peptides, MHC class I restricted peptides, or whole protein have all been shown to generate anti-cancer immune responses and activity, including in some cases the ability to induce complete regression of existing tumor. Thus, there is a great desire to test these strategies and use tumor-antigen bearing DCs as a vaccine in humans. Human clinical trials are ongoing in several institutions to use DCs to induce immunity to antigens against breast cancer, lung cancer, melanoma, prostate and renal cell cancers. While efforts to isolate DCs, expand them in vitro, coat them with antigens, and infuse them into patients are ongoing, it is going to be important to understand which antigens or peptides are going to be the most useful to use on the DCs for immunotherapy. Therefore, research to determine which antigens are most immunogenic and useful in the immune system s fight against cancer needs to continue. Since each cancer is heterogeneous, it is likely that immunity against multiple antigens may be required for complete, effective immunity against cancer. In the future, it may be possible to screen each cancer and determine which cocktail of antigens is required to induce immunity in that particular patient. How the antigen is loaded onto the DCs also needs to be optimized. It may be useful for the DCs to be transfected with RNA or DNA to produce the appropriate antigen and to present it on the surface. Finally, it may be that DC immunotherapy will work better when administered in combination with cytokines or other molecules which activate DCs. In summary, DCs are being actively pursued as a means to induce immunity in human patients. Since DCs are potent regulators of the immune system, much research is being done to try to understand how DCs can be harnessed to induce immunity. While our understanding of DCs has evolved tremendously in the 30 years since they were first described, the use of DCs as a form of immunotherapy is in it s infancy. We are poised to learn whether and how DCs will be useful as a tool in our arsenal to exploit human immunity against disease. Page 5
6 Further reading: The source of much of the material contained in this educational note and additional information can be found in the following reviews: Lipscomb M.F., Masten B.J., Dendritic cells: Immune regulators in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 82:97-130, Fong L., Engleman E.G., Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 18: , Syme R., Gluck S. Generation of dendritic cells: role of cytokines and potential clinical applications. Transfusion and Apheresis Science 24: , ISCT Head Office Phone: Fax: Page 6
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6)
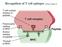 Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
The Immune System: A Tutorial
 The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
2) Macrophages function to engulf and present antigen to other immune cells.
 Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity
 B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES JASON CYSTER SECTION 13
 SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
Name (print) Name (signature) Period. (Total 30 points)
 AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation
 T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
T Cell Maturation,Activation and Differentiation Positive Selection- In thymus, permits survival of only those T cells whose TCRs recognize self- MHC molecules (self-mhc restriction) Negative Selection-
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation. B cell maturation
 B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
B Cell Generation, Activation & Differentiation Naïve B cells- have not encountered Ag. Have IgM and IgD on cell surface : have same binding VDJ regions but different constant region leaves bone marrow
Activation and effector functions of HMI
 Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Immunity. Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity
 Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
The immune system. Bone marrow. Thymus. Spleen. Bone marrow. NK cell. B-cell. T-cell. Basophil Neutrophil. Eosinophil. Myeloid progenitor
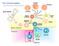 The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
The immune system Basophil Neutrophil Bone marrow Eosinophil Myeloid progenitor Dendritic cell Pluripotent Stem cell Lymphoid progenitor Platelets Bone marrow Thymus NK cell T-cell B-cell Spleen Cancer
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
How do plasma cells survive
 How do plasma cells survive Claudia Berek Deutsches Rheuma Forschungs Zentrum, Berlin Institut der Leibniz Gemeinschaft Immune response Naive B cell Peripheral lymphoid organs Memory B cell Germinal T
How do plasma cells survive Claudia Berek Deutsches Rheuma Forschungs Zentrum, Berlin Institut der Leibniz Gemeinschaft Immune response Naive B cell Peripheral lymphoid organs Memory B cell Germinal T
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
MHC (MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX)
 MHC (MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX) MHC complex is group of genes on a single chromosome that codes the MHC antigens. Major as well as minor histocompatibility antigens (also called transplantation
MHC (MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX) MHC complex is group of genes on a single chromosome that codes the MHC antigens. Major as well as minor histocompatibility antigens (also called transplantation
ΔΕΝΤΡΙΤΙΚΑ ΚΥΤΤΑΡΑ ΚΑΙ ΕΜΒΟΛΙΑ ΓΙΑ ΤΟΝ ΚΑΡΚΙΝΟ DENDRITIC CELLS AND CANCER VACCINES
 ΔΕΝΤΡΙΤΙΚΑ ΚΥΤΤΑΡΑ ΚΑΙ ΕΜΒΟΛΙΑ ΓΙΑ ΤΟΝ ΚΑΡΚΙΝΟ DENDRITIC CELLS AND CANCER VACCINES David Hunt. Cell Systems Initiative, U. of Washington. Βαίος Καρανίκας EU Marie Curie Fellow Μοναδα Ανοσολογίας Καρκίνου
ΔΕΝΤΡΙΤΙΚΑ ΚΥΤΤΑΡΑ ΚΑΙ ΕΜΒΟΛΙΑ ΓΙΑ ΤΟΝ ΚΑΡΚΙΝΟ DENDRITIC CELLS AND CANCER VACCINES David Hunt. Cell Systems Initiative, U. of Washington. Βαίος Καρανίκας EU Marie Curie Fellow Μοναδα Ανοσολογίας Καρκίνου
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: adoptive_immunotherapy 11/1993 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description of Procedure or Service The spontaneous regression
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: adoptive_immunotherapy 11/1993 3/2016 3/2017 3/2016 Description of Procedure or Service The spontaneous regression
The Immune System. 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms. Lines of Defense. Line of Defense. Lines of Defense
 The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
BioResearch. Hematopoietic and Immune Cell Products Essential Tools for Hematopoietic Research
 BioResearch Hematopoietic and Immune Cell Products Essential Tools for Hematopoietic Research BioResearch Hematopoietic and Immune Cell Products Essential Tools for Hematopoietic Research Working with
BioResearch Hematopoietic and Immune Cell Products Essential Tools for Hematopoietic Research BioResearch Hematopoietic and Immune Cell Products Essential Tools for Hematopoietic Research Working with
Overview. Transcriptional cascades. Amazing aspects of lineage plasticity. Conventional (B2) B cell development
 Overview B cell development Transcriptional cascades Amazing aspects of lineage plasticity Conventional (B2) B cell development What happens to an autoreactive B cell? B1 vs B2 cells Key anatomical sites
Overview B cell development Transcriptional cascades Amazing aspects of lineage plasticity Conventional (B2) B cell development What happens to an autoreactive B cell? B1 vs B2 cells Key anatomical sites
The Four Pillars of Cancer Therapy
 Improving the Overall Understanding of Immunotherapy in Multiple Myeloma Webinar 2, August 19, 2015 Myeloma Vaccines: A New Use of a Time-Tested Treatment The Four Pillars of Cancer Therapy Surgery Radiation
Improving the Overall Understanding of Immunotherapy in Multiple Myeloma Webinar 2, August 19, 2015 Myeloma Vaccines: A New Use of a Time-Tested Treatment The Four Pillars of Cancer Therapy Surgery Radiation
Hapten - a small molecule that is antigenic but not (by itself) immunogenic.
 Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center
 Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center Bodnar s Law Simple Things are Important Very Simple Things are Very Important
Cancer Immunotherapy: Can Your Immune System Cure Cancer? Steve Emerson, MD, PhD Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center Bodnar s Law Simple Things are Important Very Simple Things are Very Important
Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer
 Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer What you need to know ONCHQ14NP07519 Introduction: Immuno-oncology represents an innovative approach to cancer research that seeks to harness the body s own
Immuno-Oncology Therapies to Treat Lung Cancer What you need to know ONCHQ14NP07519 Introduction: Immuno-oncology represents an innovative approach to cancer research that seeks to harness the body s own
ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES. Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
Lymph capillaries, Lymphatic collecting vessels, Valves, Lymph Duct, Lymph node, Vein
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
Immunotherapy for Multiple Myeloma. Sarah Holstein, MD, PhD April 2, 2015 MIR-508
 Immunotherapy for Multiple Myeloma Sarah Holstein, MD, PhD April 2, 2015 MIR-508 Outline Myeloma overview IMiDs Monoclonal antibodies Anti-CS1 Vaccines Dendritic cell/myeloma fusion Multiple Myeloma Monoclonal
Immunotherapy for Multiple Myeloma Sarah Holstein, MD, PhD April 2, 2015 MIR-508 Outline Myeloma overview IMiDs Monoclonal antibodies Anti-CS1 Vaccines Dendritic cell/myeloma fusion Multiple Myeloma Monoclonal
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education. Su et al.
 Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Uses of Flow Cytometry
 Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types:
 Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis. Bonita S. Libman, M.D.
 The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis Bonita S. Libman, M.D. Disclosures Two googled comics The Normal Immune System Network of cells and proteins that work together Goal: protect against
The Most Common Autoimmune Disease: Rheumatoid Arthritis Bonita S. Libman, M.D. Disclosures Two googled comics The Normal Immune System Network of cells and proteins that work together Goal: protect against
Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual
 Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0067.02 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human CD4+T Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human CD4+T cells are shipped on dry ice and should be stored in liquid nitrogen
Human CD4+T Cell Care Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZBM0067.02 SHIPPING CONDITIONS Human CD4+T Cells, cryopreserved Cryopreserved human CD4+T cells are shipped on dry ice and should be stored in liquid nitrogen
Drug Development Services
 Drug Development Services USING BLOOD AND BONE MARROW PRIMARY CELL SYSTEMS Clinically Relevant In Vitro Assays Broad Spectrum of Drug Classes Multi-Species Platforms Enhancing Drug Development through
Drug Development Services USING BLOOD AND BONE MARROW PRIMARY CELL SYSTEMS Clinically Relevant In Vitro Assays Broad Spectrum of Drug Classes Multi-Species Platforms Enhancing Drug Development through
Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells. Effector T cells. After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells
 After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells After activation, T cells remain in lymph nodes for 5-6 days Effector T cells
After activation, naïve T cells differentiate into effector and memory T cells Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTLs) and NK Cells After activation, T cells remain in lymph nodes for 5-6 days Effector T cells
This presentation may contain forward-looking statements, which reflect Trillium's current expectation regarding future events. These forward-looking
 Q1/2016 This presentation may contain forward-looking statements, which reflect Trillium's current expectation regarding future events. These forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties
Q1/2016 This presentation may contain forward-looking statements, which reflect Trillium's current expectation regarding future events. These forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties
CONTENT. Chapter 1 Review of Literature. List of figures. List of tables
 Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Disclosures Outline Starting with the Immune System The Innate Immune System The Adaptive Immune System
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
The Body s Defenses CHAPTER 24
 CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity
 Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses. COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015
 The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY A TOLEROGENIC VACCINATION A USING sirna MODIFIED DENDRITIC CELLS.
 TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY A TOLEROGENIC VACCINATION A USING sirna MODIFIED DENDRITIC CELLS. B.Sai Mrudula*, N.K. Durga Devi, B.Radha Madhavi,M.Madhu Babu,V.L.Annapurna ABSTRACT: KVSR Siddhartha
TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY A TOLEROGENIC VACCINATION A USING sirna MODIFIED DENDRITIC CELLS. B.Sai Mrudula*, N.K. Durga Devi, B.Radha Madhavi,M.Madhu Babu,V.L.Annapurna ABSTRACT: KVSR Siddhartha
A disease and antibody biology approach to antibody drug discovery
 A disease and antibody biology approach to antibody drug discovery Björn Frendéus, PhD VP, Preclinical research Presenter: Björn Frendéus Date: 2011-11-08 1 Antibodies have revolutionized Cancer Treatment!
A disease and antibody biology approach to antibody drug discovery Björn Frendéus, PhD VP, Preclinical research Presenter: Björn Frendéus Date: 2011-11-08 1 Antibodies have revolutionized Cancer Treatment!
Immunology. B lymphocytes & Antibodies. 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, [email protected]
 Immunology B lymphocytes & Antibodies 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, [email protected] What is an antibody? An antibody is a glycoprotein, which specifically binds to a substance,
Immunology B lymphocytes & Antibodies 20.10.2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, [email protected] What is an antibody? An antibody is a glycoprotein, which specifically binds to a substance,
Enhancing Anti-Tumor Activity of Checkpoint Inhibition
 Enhancing Anti-Tumor Activity of Checkpoint Inhibition Jeffrey Schlom, Ph.D. Laboratory of Tumor Immunology and Biology (LTIB) Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute, NIH Laboratory of Tumor
Enhancing Anti-Tumor Activity of Checkpoint Inhibition Jeffrey Schlom, Ph.D. Laboratory of Tumor Immunology and Biology (LTIB) Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute, NIH Laboratory of Tumor
LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
10. T and B cells are types of a. endocrine cells. c. lymphocytes. b. platelets. d. complement cells.
 Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Natalia Taborda Vanegas. Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia
 Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
LYMPHOMA. BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons
 LYMPHOMA BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons Normal development of lymphocytes Lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation:
LYMPHOMA BACHIR ALOBEID, M.D. HEMATOPATHOLOGY DIVISION PATHOLOGY DEPARTMENT Columbia University/ College of Physicians & Surgeons Normal development of lymphocytes Lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation:
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy
 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy Yi Lin, MD, PhD Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN Alliance Spring Group Meeting - May 13, 2016 Presentation Objectives l Scientific overview of chimeric antigen receptor
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy Yi Lin, MD, PhD Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN Alliance Spring Group Meeting - May 13, 2016 Presentation Objectives l Scientific overview of chimeric antigen receptor
NEW CLINICAL RESEARCH OPTIONS IN PANCREATIC CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY. Alan Melcher Professor of Clinical Oncology and Biotherapy Leeds
 NEW CLINICAL RESEARCH OPTIONS IN PANCREATIC CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY Alan Melcher Professor of Clinical Oncology and Biotherapy Leeds CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY - Breakthrough of the Year in Science magazine 2013.
NEW CLINICAL RESEARCH OPTIONS IN PANCREATIC CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY Alan Melcher Professor of Clinical Oncology and Biotherapy Leeds CANCER IMMUNOTHERAPY - Breakthrough of the Year in Science magazine 2013.
Report series: General cancer information
 Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Fighting cancer with information Report series: General cancer information Eastern Cancer Registration and Information Centre ECRIC report series: General cancer information Cancer is a general term for
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
Bottle-neck Problems of Current Human Cancer Therapy
 International Conference on Human Cell, Tissue-based Products and Tissue Banks, Oct. 13-14,Taipei, Taiwan Autologous Dendritic Cell-based Immunotherapy of Glioblastoma Multiforme: Post-Phase-I Clinical
International Conference on Human Cell, Tissue-based Products and Tissue Banks, Oct. 13-14,Taipei, Taiwan Autologous Dendritic Cell-based Immunotherapy of Glioblastoma Multiforme: Post-Phase-I Clinical
The Adaptive Immune System
 Chapter 25 The Adaptive Immune ystem 25 Our adaptive immune system saves us from certain death by infection. An infant born with a severely defective adaptive immune system will soon die unless extraordinary
Chapter 25 The Adaptive Immune ystem 25 Our adaptive immune system saves us from certain death by infection. An infant born with a severely defective adaptive immune system will soon die unless extraordinary
Immune System Memory Game
 Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy
 What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy Lung.org/immunotherapy What is immunotherapy? Immunotherapy for cancer, sometimes called immune-oncology, is a type of medicine that treats cancer
What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy Lung.org/immunotherapy What is immunotherapy? Immunotherapy for cancer, sometimes called immune-oncology, is a type of medicine that treats cancer
Bio 20 Chapter 11 Workbook Blood and the Immune System Ms. Nyboer
 Bio 20 Chapter 11 Workbook Blood and the Immune System Ms. Nyboer Name: Part A: Components of Blood 1. List the 3 plasma proteins and describe the function of each Albumins osmotic balance Globulins antibodies,
Bio 20 Chapter 11 Workbook Blood and the Immune System Ms. Nyboer Name: Part A: Components of Blood 1. List the 3 plasma proteins and describe the function of each Albumins osmotic balance Globulins antibodies,
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 10 October 2007 Doc. Ref. COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON POTENCY TESTING OF CELL BASED IMMUNOTHERAPY
European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 10 October 2007 Doc. Ref. COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON POTENCY TESTING OF CELL BASED IMMUNOTHERAPY
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
Additional file 1. Progress of phase II clinical trials of Panagen
 Additional file 1. Progress of phase II clinical trials of Panagen Documentation Phase II clinical trial of preparation Panagen was performed in compliance with the following documentation: Approval of
Additional file 1. Progress of phase II clinical trials of Panagen Documentation Phase II clinical trial of preparation Panagen was performed in compliance with the following documentation: Approval of
HemaCare Corporation Company Overview. Comprehensive Product and Service Solutions for BioResearch and Cellular Therapy
 HemaCare Corporation Company Overview Comprehensive Product and Service Solutions for BioResearch and Cellular Therapy 2015 HemaCare Corporation Leading provider of apheresis products, human blood cells,
HemaCare Corporation Company Overview Comprehensive Product and Service Solutions for BioResearch and Cellular Therapy 2015 HemaCare Corporation Leading provider of apheresis products, human blood cells,
Immunology and immunotherapy in allergic disease
 Immunology and immunotherapy in allergic disease Jing Shen, MD Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation February 2005
Immunology and immunotherapy in allergic disease Jing Shen, MD Faculty Advisor: Matthew Ryan, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation February 2005
Expression of CD163 on Bovine Alveolar Macrophages and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
 Expression of CD163 on Bovine Alveolar Macrophages and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Mary E. Kopechek Honor s Research Thesis May 17, 2007 Research Advisor: Dr. Jeff Lakritz, DVM, PhD The Ohio State
Expression of CD163 on Bovine Alveolar Macrophages and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Mary E. Kopechek Honor s Research Thesis May 17, 2007 Research Advisor: Dr. Jeff Lakritz, DVM, PhD The Ohio State
Final Review. Aptamers. Making Aptamers: SELEX 6/3/2011. sirna and mirna. Central Dogma. RNAi: A translation regulation mechanism.
 Central Dogma Final Review Section Week 10 DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA replication DNA RNA transcription RNA Protein translation **RNA DNA reverse transcription http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html
Central Dogma Final Review Section Week 10 DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA replication DNA RNA transcription RNA Protein translation **RNA DNA reverse transcription http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture20/lecture1_1.html
1 The Immune System. j 5. 1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Host Defence Against Infection
 j 5 1 The Immune System 1.1 Introduction All living things animals, plants and even bacteria can act as hosts for infectious organisms and thus have evolved mechanisms to defend themselves against infection.
j 5 1 The Immune System 1.1 Introduction All living things animals, plants and even bacteria can act as hosts for infectious organisms and thus have evolved mechanisms to defend themselves against infection.
BLOOD-Chp. Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? What is the composition of blood? 3 major types of plasma proteins
 6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA Advances in Clinical Trials
 LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA Advances in Clinical Trials OUR FOCUS ABOUT emerging treatments Presentation for: Judith E. Karp, MD Advancements for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Supported by an unrestricted educational
LEUKEMIA LYMPHOMA MYELOMA Advances in Clinical Trials OUR FOCUS ABOUT emerging treatments Presentation for: Judith E. Karp, MD Advancements for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Supported by an unrestricted educational
Oncos Therapeutics: ONCOS THERAPEUTICS Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy. March 2015. Antti Vuolanto, COO and co-founder
 Oncos Therapeutics: Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy ONCOS THERAPEUTICS Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy March 2015 Antti Vuolanto, COO and co-founder 1 History of Oncos Therapeutics 2002 2007 2009 Research
Oncos Therapeutics: Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy ONCOS THERAPEUTICS Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy March 2015 Antti Vuolanto, COO and co-founder 1 History of Oncos Therapeutics 2002 2007 2009 Research
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes
 Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Immunotherapy Concept Turned Reality
 Authored by: Jennifer Dolan Fox, PhD VirtualScopics Inc. [email protected] +1 585 249 6231 Immunotherapy Concept Turned Reality Introduction While using the body s own immune system as a
Authored by: Jennifer Dolan Fox, PhD VirtualScopics Inc. [email protected] +1 585 249 6231 Immunotherapy Concept Turned Reality Introduction While using the body s own immune system as a
Multiple Myeloma and Colorectal Cancer
 Multiple Myeloma and Colorectal Cancer From Systems Immunology to Single Cells Leo Hansmann Mark M. Davis Lab Department of Microbiology&Immunology Stanford University Multiple Myeloma Monoclonal disease
Multiple Myeloma and Colorectal Cancer From Systems Immunology to Single Cells Leo Hansmann Mark M. Davis Lab Department of Microbiology&Immunology Stanford University Multiple Myeloma Monoclonal disease
Medigene Corporate Presentation
 Medigene Corporate Presentation This presentation contains forward-looking statements - that is, statements related to future, not past, events. These statements may be identified either orally or in writing
Medigene Corporate Presentation This presentation contains forward-looking statements - that is, statements related to future, not past, events. These statements may be identified either orally or in writing
Chapter 3. Immunity and how vaccines work
 Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
INFORMATION ON STEM CELLS/BONE MARROW AND REINFUSION/TRANSPLANTATION SUR703.002
 INFORMATION ON STEM CELLS/BONE MARROW AND REINFUSION/TRANSPLANTATION SUR703.002 COVERAGE: SPECIAL COMMENT ON POLICY REVIEW: Due to the complexity of the Peripheral and Bone Marrow Stem Cell Transplantation
INFORMATION ON STEM CELLS/BONE MARROW AND REINFUSION/TRANSPLANTATION SUR703.002 COVERAGE: SPECIAL COMMENT ON POLICY REVIEW: Due to the complexity of the Peripheral and Bone Marrow Stem Cell Transplantation
One of the most important recent developments in cancer treatment has been the ability to harvest stem
 BIOTECHNOLOGY A Patient-Friendly Approach to Human Cell Transplantation One of the most important recent developments in cancer treatment has been the ability to harvest stem cells from bone marrow or
BIOTECHNOLOGY A Patient-Friendly Approach to Human Cell Transplantation One of the most important recent developments in cancer treatment has been the ability to harvest stem cells from bone marrow or
MULTIPLE MYELOMA. Dr Malkit S Riyat. MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist
 MULTIPLE MYELOMA Dr Malkit S Riyat MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist Multiple myeloma is an incurable malignancy that arises from postgerminal centre, somatically hypermutated B cells.
MULTIPLE MYELOMA Dr Malkit S Riyat MBChB, FRCPath(UK) Consultant Haematologist Multiple myeloma is an incurable malignancy that arises from postgerminal centre, somatically hypermutated B cells.
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
2006 7.012 Problem Set 6 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on WEDNESDAY, November 22, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You create an artificial
The Human Immune System
 The Human Immune System What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles The First Line of Defense Skin The dead, outer layer
The Human Immune System What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles The First Line of Defense Skin The dead, outer layer
Modelling and analysis of T-cell epitope screening data.
 Modelling and analysis of T-cell epitope screening data. Tim Beißbarth 2, Jason A. Tye-Din 1, Gordon K. Smyth 1, Robert P. Anderson 1 and Terence P. Speed 1 1 WEHI, 1G Royal Parade, Parkville, VIC 3050,
Modelling and analysis of T-cell epitope screening data. Tim Beißbarth 2, Jason A. Tye-Din 1, Gordon K. Smyth 1, Robert P. Anderson 1 and Terence P. Speed 1 1 WEHI, 1G Royal Parade, Parkville, VIC 3050,
Mechanical barriers are a crucial first line of defence. It would be impossible to provide an exhaustive list. Two examples are:
 Back to Index 1. The immune response to infection 1. Non-specific immunity The immune system has evolved to deal with infectious pathogens. There are several lines of host defence. When evaluating the
Back to Index 1. The immune response to infection 1. Non-specific immunity The immune system has evolved to deal with infectious pathogens. There are several lines of host defence. When evaluating the
MACS cell separation - the faster way to ultrapure, Dr. Katharina Winnemoeller [email protected]
 MACS cell separation - the faster way to ultrapure, viable cells + Dr. Katharina Winnemoeller [email protected] About us Germany's largest independent, privately owned biotech company 1300
MACS cell separation - the faster way to ultrapure, viable cells + Dr. Katharina Winnemoeller [email protected] About us Germany's largest independent, privately owned biotech company 1300
Processing & Utilization of Cord Blood for Transplant
 Processing & Utilization of Cord Blood for Transplant 2010-Jan Jan-15 Nicole L. Prokopishyn, PhD HPC Processing Laboratory Director Calgary Laboratory Services Overview Cord Blood Processing Pre-Freeze
Processing & Utilization of Cord Blood for Transplant 2010-Jan Jan-15 Nicole L. Prokopishyn, PhD HPC Processing Laboratory Director Calgary Laboratory Services Overview Cord Blood Processing Pre-Freeze
ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES
 ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION OF GRANT MECHANISM The Alliance for Lupus Research (ALR) is an independent,
ALLIANCE FOR LUPUS RESEARCH AND PFIZER S CENTERS FOR THERAPEUTIC INNOVATION CHALLENGE GRANT PROGRAM PROGRAM GUIDELINES DESCRIPTION OF GRANT MECHANISM The Alliance for Lupus Research (ALR) is an independent,
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary. Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide
 Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Identification of CD4+ T cell epitopes specific for the breast cancer associated antigen NY-BR-1
 9/8/2015 Identification of CD4+ T cell epitopes specific for the breast cancer associated antigen NY-BR-1 Stefan Eichmüller, PhD GMP & T Cell Therapy Unit, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany
9/8/2015 Identification of CD4+ T cell epitopes specific for the breast cancer associated antigen NY-BR-1 Stefan Eichmüller, PhD GMP & T Cell Therapy Unit, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany
Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work
 Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work This is a promising and hopeful time in the field of multiple sclerosis (MS). Many new and different therapies are nearing the final stages of
Understanding How Existing and Emerging MS Therapies Work This is a promising and hopeful time in the field of multiple sclerosis (MS). Many new and different therapies are nearing the final stages of
T Cell Immunotherapy for Cancer
 T Cell Immunotherapy for Cancer Chimeric Antigen Receptors Targeting Tag-72 Glycoprotein for Colorectal Cancer Mitchell H. Finer Ph.D Genetix Pharmaceuticals Inc Work Completed at Cell Genesys Inc T Cell
T Cell Immunotherapy for Cancer Chimeric Antigen Receptors Targeting Tag-72 Glycoprotein for Colorectal Cancer Mitchell H. Finer Ph.D Genetix Pharmaceuticals Inc Work Completed at Cell Genesys Inc T Cell
Immunotherapy of Uveal Melanoma
 Eye Am Not Alone (EANA) Patient Retreat Saturday Session - March 3, 2012 Immunotherapy of Uveal Melanoma Do not distribute or copy without the express permission of the Ocular Melanoma Foundation (OMF).
Eye Am Not Alone (EANA) Patient Retreat Saturday Session - March 3, 2012 Immunotherapy of Uveal Melanoma Do not distribute or copy without the express permission of the Ocular Melanoma Foundation (OMF).
 Blood Sticky, opaque fluid with a metallic taste (Fe 2+ ) Varies from scarlet (P O2 = 100) to dark red (P O2 = 40) ph is between 7.35 and 7.45 Average volume in an adult is 5 L (7% of body weight) 2 L
Blood Sticky, opaque fluid with a metallic taste (Fe 2+ ) Varies from scarlet (P O2 = 100) to dark red (P O2 = 40) ph is between 7.35 and 7.45 Average volume in an adult is 5 L (7% of body weight) 2 L
