10/01/57. Overview. Goal. Conclusions. Immunity to infection. How to classify immunity by time?? (stages, cells involved in immune responses)
|
|
|
- Dwain Anthony
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Overview Immunity to infection Animal Immunology Vibuntita chankitisakul, D.V.M.,Ph.D. Immune system Bacteria infection Virus infection Fungus infection Goal How to classify immunity by time?? (stages, cells involved in immune responses) To understand basic principles of defense against infections induced by: Bacteria - extracellular - intracellular Virus Fungus Parasites What are the mechanisms of HMI and CMI?? Conclusions against_disease/index.htm 1
2 Make sure you understand these following words Innate immunity Physical barriers Chemical barriers Phagocyte Neutrophils Eosinophil Basophils Macrophage Monocytes Acquired immunity Cellular immunity Humoral immunity T, B lymphocytes Antibody NK cells Complements Cytokine Interferon Immunity response to microbial infection Microbes Site of infection microbiologists deal with four fundamental kinds of microbial infectious agents bacteria fungus viruses parasites helminthes (worms) protozoa (single-celled) (intracellular) 2
3 Site of infection Extracellular Intracellular Location of infectious agents in host tissue is of the essence for development and differentiation of immune responses Microbial type Extracellular Intracellular Bacterium E. coli, Salmonella Mycobacteria, Listeria Organisms Bacteria, protozoa, fungus, worms Viruses, bacteria, protozoa,fungus Fungus Candida Histoplasma Parasite Helminths (worms) Plasmodium Protective immunity Antibodies, Complement, Phagocytosis, Neutralization Cytotoxic T-cells, NK cells Virus None All Bacterial infection Bacterial infection 1. Extracellular bacteria are capable of replicating outside host cells Inflammation Toxins (endotoxin, extoxin) 2. Intracellular bacteria ability to survive and even to replicate within phagocytes Tuberculosis 1) Innate immunity Complement activation Activation of phagocytes and inflammation 2) Acquired immunity Humoral immunity is a major protective immune response Neutralization of toxins Complement activation Opsonization Phagocytes 3
4 Acquired immunity Acquired immunity ability to survive from antibodies Intracellular bac. Innate and adaptive immunity to intracellular bacteria 1. Innate immunity Phagocytes and NK cells Bacteria stimulate Macrophage to release Cytokines, then stimulate NK cells to release IFN to activate macrophage (activated macrophage) CD8 CD4 2) Adaptive immunity CMI Intracellular bac. Virus infection 4
5 Viruses Viruses do not have ribosomes and cannot make their own protein After the virus attaches to the host cell s membrane, it injects its genetic material which directs synthesis of viral proteins Virus infection Intracellular microorganisms Based on Harvard Medical School Family Health Guide Fungus infection Fungus infection extracellular and intracellular (phagocyte) fungi Innate immunity Neutrophils and macrophages Adaptive immunity CMI (same as intracellular bacteria) Antibody important for diagnosis only (not for eradication) 5
6 Complex eukaryotic organisms Complex life cycles protozoa (unicellular) intra- & extracellular agents helmints (multicellular worms) extracellular agents Innate immunity Mostly resistant complement and phagocytosis (protozoa) eosinophil and macrophages (worms) Adaptive immunity Protozoa (intracellular) CMI Immunity against worms (T H 2 response) Worms (extracellular) Antibody (IgE) + Eosinophil Immunity against helmints (function of eosinophils) 6
ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES. Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
AP BIOLOGY ANIMALS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #4 NAME DATE HOUR BODY DEFENSES NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES PHYSICAL BARRIERS PHAGOCYTES Animals Form & Function Activity #4 page 1 INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE ANTIMICROBIAL
specific B cells Humoral immunity lymphocytes antibodies B cells bone marrow Cell-mediated immunity: T cells antibodies proteins
 Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Adaptive Immunity Chapter 17: Adaptive (specific) Immunity Bio 139 Dr. Amy Rogers Host defenses that are specific to a particular infectious agent Can be innate or genetic for humans as a group: most microbes
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity
 Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
Chapter 16: Innate Immunity 1. Overview of Innate Immunity 2. Inflammation & Phagocytosis 3. Antimicrobial Substances 1. Overview of Innate Immunity The Body s Defenses The body has 2 types of defense
Name (print) Name (signature) Period. (Total 30 points)
 AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
AP Biology Worksheet Chapter 43 The Immune System Lambdin April 4, 2011 Due Date: Thurs. April 7, 2011 You may use the following: Text Notes Power point Internet One other person in class "On my honor,
Chapter 43: The Immune System
 Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Name Period Our students consider this chapter to be a particularly challenging and important one. Expect to work your way slowly through the first three concepts. Take particular care with Concepts 43.2
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity. Chapter 17 Specific Defenses of the Host: The Immune Response B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein
Course Descriptions. I. Professional Courses: MSEG 7216: Introduction to Infectious Diseases (Medical Students)
 Course Descriptions I. Professional Courses: MSEG 7216: Introduction to Infectious Diseases (Medical Students) This course is offered during the first semester of the second year of the MD Program. It
Course Descriptions I. Professional Courses: MSEG 7216: Introduction to Infectious Diseases (Medical Students) This course is offered during the first semester of the second year of the MD Program. It
The Immune System: A Tutorial
 The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
The Immune System: A Tutorial Modeling and Simulation of Biological Systems 21-366B Shlomo Ta asan Images taken from http://rex.nci.nih.gov/behindthenews/uis/uisframe.htm http://copewithcytokines.de/ The
Immunity Unit Test Z
 Immunity Unit Test Z Name MB Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the pathogens in Figure 31.1 cause disease by taking over healthy
Immunity Unit Test Z Name MB Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the pathogens in Figure 31.1 cause disease by taking over healthy
10. T and B cells are types of a. endocrine cells. c. lymphocytes. b. platelets. d. complement cells.
 Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes
 Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
Lec.5 Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Medical Physiology White Blood Cells (WBCs) or Leukocytes Although leukocytes are far less numerous than red blood cells, they are important to body defense against disease. On average,
The Immune System. 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms. Lines of Defense. Line of Defense. Lines of Defense
 The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
The Immune System 2 Types of Defense Mechanisms Immune System the system that fights infection by producing cells to inactivate foreign substances to avoid infection and disease. Immunity the body s ability
CHAPTER 35 HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM STANDARDS:SC.912.L.14.52 & SC.912.L.14.6
 CHAPTER 35 HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM STANDARDS:SC.912.L.14.52 & SC.912.L.14.6 SECTION 1 - Infectious Disease 1.Identify the causes of infectious disease. 2.Explain how infectious diseases are spread. Causes
CHAPTER 35 HUMAN IMMUNE SYSTEM STANDARDS:SC.912.L.14.52 & SC.912.L.14.6 SECTION 1 - Infectious Disease 1.Identify the causes of infectious disease. 2.Explain how infectious diseases are spread. Causes
CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS
 CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS See APPENDIX (1) THE PRECIPITIN CURVE; (2) LABELING OF ANTIBODIES The defining characteristic of HUMORAL immune responses (which distinguishes them from CELL-MEDIATED
CHAPTER 2 ANTIGEN/ANTIBODY INTERACTIONS See APPENDIX (1) THE PRECIPITIN CURVE; (2) LABELING OF ANTIBODIES The defining characteristic of HUMORAL immune responses (which distinguishes them from CELL-MEDIATED
One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types:
 Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
Immune system. One of the more complex systems we re looking at. An immune response (a response to a pathogen) can be of two types: (pathogen - disease causing organism) 1) Non specific. Anything foreign
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses. COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015
 The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
The role of IBV proteins in protection: cellular immune responses COST meeting WG2 + WG3 Budapest, Hungary, 2015 1 Presentation include: Laboratory results Literature summary Role of T cells in response
Core Topic 2. The immune system and how vaccines work
 Core Topic 2 The immune system and how vaccines work Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work in individuals and populations Learning objectives Explain
Core Topic 2 The immune system and how vaccines work Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work in individuals and populations Learning objectives Explain
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 14 The Lymphoid System and Immunity Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The lymphoid system is composed of A) lymphatic vessels. B) lymph nodes.
1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins that compete with animal A) Antibodies. B) Red blood cells. C) Transferrin. D) White blood cells. E) Receptors.
 Prof. Lester s BIOL 210 Practice Exam 4 (There is no answer key. Please do not email or ask me for answers.) Chapters 15, 16, 17, 19, HIV/AIDS, TB, Quorum Sensing 1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins
Prof. Lester s BIOL 210 Practice Exam 4 (There is no answer key. Please do not email or ask me for answers.) Chapters 15, 16, 17, 19, HIV/AIDS, TB, Quorum Sensing 1) Siderophores are bacterial proteins
Chapter 3. Immunity and how vaccines work
 Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Chapter 3 Immunity and how vaccines work 3.1 Objectives: To understand and describe the immune system and how vaccines produce immunity To understand the differences between Passive and Active immunity
Basics of Immunology
 Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Basics of Immunology 2 Basics of Immunology What is the immune system? Biological mechanism for identifying and destroying pathogens within a larger organism. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Bacteria,
Lymph capillaries, Lymphatic collecting vessels, Valves, Lymph Duct, Lymph node, Vein
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name Lymphatic System Practice 1. Figure 12-1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. First color code the following structures. Color code in Figure 12-1 Heart Veins Lymphatic vessels/lymph
1 The Immune System. j 5. 1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Host Defence Against Infection
 j 5 1 The Immune System 1.1 Introduction All living things animals, plants and even bacteria can act as hosts for infectious organisms and thus have evolved mechanisms to defend themselves against infection.
j 5 1 The Immune System 1.1 Introduction All living things animals, plants and even bacteria can act as hosts for infectious organisms and thus have evolved mechanisms to defend themselves against infection.
B Cells and Antibodies
 B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
B Cells and Antibodies Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture outline Functions of antibodies B cell activation; the role of helper T cells in antibody production
Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute
 Glossary Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute On behalf of the Faculty and Staff at the Child & Family Research Institute (CFRI), we would like to welcome you to CFRI s
Glossary Welcome to Mini Med School at the Child & Family Research Institute On behalf of the Faculty and Staff at the Child & Family Research Institute (CFRI), we would like to welcome you to CFRI s
Approaches to Infection Control
 Approaches to Infection Control Considerations for PTAs in the Clinic Objectives Describe the basic characteristics of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Discuss the locations, advantages, and disadvantages
Approaches to Infection Control Considerations for PTAs in the Clinic Objectives Describe the basic characteristics of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Discuss the locations, advantages, and disadvantages
7- Master s Degree in Public Health and Public Health Sciences (Majoring Microbiology)
 7- Master s Degree in Public Health and Public Health Sciences (Majoring Microbiology) Students should fulfill a total of 38 credit hours: 1- Basic requirements: 10 credit hours. 150701, 150702, 150703,
7- Master s Degree in Public Health and Public Health Sciences (Majoring Microbiology) Students should fulfill a total of 38 credit hours: 1- Basic requirements: 10 credit hours. 150701, 150702, 150703,
Granulocytes vs. Agranulocytes
 Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Leukocytes are white blood cells (AKA colorless (non-pigmented) blood cells). (Much) smaller in number than RBCs. Unlike RBCs, there are several different types of WBCs. All contain a visible nucleus.
Mechanical barriers are a crucial first line of defence. It would be impossible to provide an exhaustive list. Two examples are:
 Back to Index 1. The immune response to infection 1. Non-specific immunity The immune system has evolved to deal with infectious pathogens. There are several lines of host defence. When evaluating the
Back to Index 1. The immune response to infection 1. Non-specific immunity The immune system has evolved to deal with infectious pathogens. There are several lines of host defence. When evaluating the
2) Macrophages function to engulf and present antigen to other immune cells.
 Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Immunology The immune system has specificity and memory. It specifically recognizes different antigens and has memory for these same antigens the next time they are encountered. The Cellular Components
Mini-Medical School on Infectious Diseases. Session #1 - Basic Science
 Mini-Medical School on Infectious Diseases Session #1 - Basic Science The Microbial World Michael V. Norgard, Ph.D., Chairman Department of Microbiology U.T. Southwestern Medical Center The Microbial World
Mini-Medical School on Infectious Diseases Session #1 - Basic Science The Microbial World Michael V. Norgard, Ph.D., Chairman Department of Microbiology U.T. Southwestern Medical Center The Microbial World
Hapten - a small molecule that is antigenic but not (by itself) immunogenic.
 Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Chapter 3. Antigens Terminology: Antigen: Substances that can be recognized by the surface antibody (B cells) or by the TCR (T cells) when associated with MHC molecules Immunogenicity VS Antigenicity:
Kermodul : Angeborene Immunität Innate Immunity. Uwe Sonnewald Email usonne@biologie.uni-erlangen.de
 BC Kermodul : Angeborene Immunität Innate Immunity Pathogens Invasion strategies Pathogen Host Interactions Basal Defence Uwe Sonnewald Email usonne@biologie.uni-erlangen.de 1 BC Immunity (mammalian) Innate
BC Kermodul : Angeborene Immunität Innate Immunity Pathogens Invasion strategies Pathogen Host Interactions Basal Defence Uwe Sonnewald Email usonne@biologie.uni-erlangen.de 1 BC Immunity (mammalian) Innate
Immunity and how vaccines work
 1 Introduction Immunity is the ability of the human body to protect itself from infectious disease. The defence mechanisms of the body are complex and include innate (non-specific, non-adaptive) mechanisms
1 Introduction Immunity is the ability of the human body to protect itself from infectious disease. The defence mechanisms of the body are complex and include innate (non-specific, non-adaptive) mechanisms
Lecture Objectives: Why study microbiology? What is microbiology? Roots of microbiology
 1 Lecture Objectives: Why study microbiology? What is microbiology? Roots of microbiology Why study microbiology? ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICAL APPLIED SCIENCE BASIC SCIENCE The science of microbiology Microbiology
1 Lecture Objectives: Why study microbiology? What is microbiology? Roots of microbiology Why study microbiology? ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICAL APPLIED SCIENCE BASIC SCIENCE The science of microbiology Microbiology
Thought for the Day. Courage is not simply one of the virtues, but the form of every virtue at the testing point. ~ C. S. Lewis
 Thought for the Day Courage is not simply one of the virtues, but the form of every virtue at the testing point. ~ C. S. Lewis Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Section 2 Lecture
Thought for the Day Courage is not simply one of the virtues, but the form of every virtue at the testing point. ~ C. S. Lewis Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Section 2 Lecture
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education. Su et al.
 Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
Supplemental Material CBE Life Sciences Education Su et al. APPENDIX Human Body's Immune System Test This test consists of 31 questions, with only 1 answer to be selected for each question. Please select
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 4P03 / BIOLOGY 6P03 - Medical Microbiology
 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 4P03 / BIOLOGY 6P03 - Medical Microbiology Term II 2015-2016 Instructor: Guest Lecturers: Dr. Jianping Xu (Microbiologist) Dr. Marek Smieja (Medical Microbiologist, Infectious Diseases
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 4P03 / BIOLOGY 6P03 - Medical Microbiology Term II 2015-2016 Instructor: Guest Lecturers: Dr. Jianping Xu (Microbiologist) Dr. Marek Smieja (Medical Microbiologist, Infectious Diseases
Immunity. Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity
 Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
Immunity Humans have three types of immunity innate, adaptive, and passive: Innate Immunity Everyone is born with innate (or natural) immunity, a type of general protection. Many of the germs that affect
Viral Attack! Your Clean-Up Crew to the Rescue! A Gallery Demonstration at Arizona Science Center
 Viral Attack! Your Clean-Up Crew to the Rescue! A Gallery Demonstration at Arizona Science Center Table of Contents Background Information Links Background Information What is the immune system? Our body
Viral Attack! Your Clean-Up Crew to the Rescue! A Gallery Demonstration at Arizona Science Center Table of Contents Background Information Links Background Information What is the immune system? Our body
Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1
 Oregon State University BEEF043 Beef Cattle Library Beef Cattle Sciences Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1 Reinaldo F. Cooke 2 Introduction On average, the U.S. cattle industry loses more than $1
Oregon State University BEEF043 Beef Cattle Library Beef Cattle Sciences Overview of the Cattle Immune System 1 Reinaldo F. Cooke 2 Introduction On average, the U.S. cattle industry loses more than $1
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells
 Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
Laboratory 12 Blood Cells Objectives: Identify microscopically each of the following: erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs), the five types of leukocytes (white blood cells or WBCs), and thrombocytes
Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Disclosures Outline Starting with the Immune System The Innate Immune System The Adaptive Immune System
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Asthma (With a little SCID to start) Lauren Smith, MD CHKD Pediatric Allergy/Immunology Disclosures None Will be discussing some medications that are not yet FDA approved Outline SCID
VPM 152. INFLAMMATION: Chemical Mediators
 General Pathology VPM 152 INFLAMMATION: Chemical Mediators CHEMICAL MEDIATORS OF INFLAMMATION Definition: any messenger that acts on blood vessels, inflammatory cells or other cells to contribute to an
General Pathology VPM 152 INFLAMMATION: Chemical Mediators CHEMICAL MEDIATORS OF INFLAMMATION Definition: any messenger that acts on blood vessels, inflammatory cells or other cells to contribute to an
Focus on Preventing Disease. keeping an eye on a healthy bottom line. Cattle Industry
 Focus on Preventing Disease keeping an eye on a healthy bottom line Cattle Industry Multimin + VACCINES : University OF FLORIDA study data Study 1 Effect of injectable trace minerals on the humoral immune
Focus on Preventing Disease keeping an eye on a healthy bottom line Cattle Industry Multimin + VACCINES : University OF FLORIDA study data Study 1 Effect of injectable trace minerals on the humoral immune
The Immune System and Disease
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Kermodul : Angeborene Immunität Innate Immunity. Uwe Sonnewald Email usonne@biologie.uni-erlangen.de
 BC Kermodul : Angeborene Immunität Innate Immunity Pathogens Invasion strategies Pathogen Host Interactions Basal Defence Uwe Sonnewald Email usonne@biologie.uni-erlangen.de 1 Pathogens and diseases Viruses
BC Kermodul : Angeborene Immunität Innate Immunity Pathogens Invasion strategies Pathogen Host Interactions Basal Defence Uwe Sonnewald Email usonne@biologie.uni-erlangen.de 1 Pathogens and diseases Viruses
HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES JASON CYSTER SECTION 13
 SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
SECTION 13 HUMORAL IMMUNE RE- SPONSES: ACTIVATION OF B CELLS AND ANTIBODIES CONTACT INFORMATION Jason Cyster, PhD (Email) READING Basic Immunology: Functions and Disorders of the Immune System. Abbas,
Immune System Memory Game
 Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
Immune System Memory Game Recommended Age: 12 years old Time: 45 minutes Everyday our bodies come in contact with millions of tiny organisms and particles that could potentially make us sick. Despite this,
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 1 WHAT IS MICROBIOLOGY AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? WHO / TDR / Crump WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Microbiology is more relevant than ever in today s world. Infectious diseases are a leading health-related
CHAPTER 1 WHAT IS MICROBIOLOGY AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? WHO / TDR / Crump WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? Microbiology is more relevant than ever in today s world. Infectious diseases are a leading health-related
Why use passive immunity?
 Vaccines Active vs Passive Immunization Active is longer acting and makes memory and effector cells Passive is shorter acting, no memory and no effector cells Both can be obtained through natural processes:
Vaccines Active vs Passive Immunization Active is longer acting and makes memory and effector cells Passive is shorter acting, no memory and no effector cells Both can be obtained through natural processes:
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
Chapter 14: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Major function of the Lymphatic System o Network of vessels that collect and carry excess fluid from interstitial spaces back to blood circulation o Organs
Bacteria: The good, the bad, and the ugly. SEPA BioScience Montana Module 2
 Bacteria: The good, the bad, and the ugly. SEPA BioScience Montana Module 2 Introduction: The following reading will give you a basic introduction to bacteria and their role in illness. It will explore
Bacteria: The good, the bad, and the ugly. SEPA BioScience Montana Module 2 Introduction: The following reading will give you a basic introduction to bacteria and their role in illness. It will explore
LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 3: ANTIBODIES/BCR/B-CELL RESPONSES Today we will get to know: The antibodies How antibodies are produced, their classes and their maturation processes Antigen recognition
Candy Antigens and Antibodies
 LAB ACTIVITY: Candy Antigens and Antibodies TEACHER S EDITION Curricular Links: Biology 20, Science 30 Class Time: 1 period Suggested Answers: Question 1: What is the main function of red blood cells?
LAB ACTIVITY: Candy Antigens and Antibodies TEACHER S EDITION Curricular Links: Biology 20, Science 30 Class Time: 1 period Suggested Answers: Question 1: What is the main function of red blood cells?
Required Text: Tortora, Funke, and Case. Microbiology, An Introduction, 9 th ed. Benjamin Cummings, 2007.
 Department of Biology Introduction to Microbiology Biol 132 (3 credit hours) Dr. Kathryn Sutton, Assistant Professor of Biology Spring, 2007 M 9-9:50; CBH Room 203 General Information Office Location CBH
Department of Biology Introduction to Microbiology Biol 132 (3 credit hours) Dr. Kathryn Sutton, Assistant Professor of Biology Spring, 2007 M 9-9:50; CBH Room 203 General Information Office Location CBH
DISEASE CAUSES AND TRANSMISSION DISEASE - any condition that prevents an organism from functioning effectively in its surroundings INFECTIOUS DISEASES
 DISEASE CAUSES AND TRANSMISSION DISEASE - any condition that prevents an organism from functioning effectively in its surroundings INFECTIOUS DISEASES caused by pathogen (e.g. bacterium, fungus, protozoan,
DISEASE CAUSES AND TRANSMISSION DISEASE - any condition that prevents an organism from functioning effectively in its surroundings INFECTIOUS DISEASES caused by pathogen (e.g. bacterium, fungus, protozoan,
SQA CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 4: Immunology and Public Health
 SCHOLAR Study Guide SQA CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 4: Immunology and Public Health Authored by: Eoin McIntyre Reviewed by: Sheena Haddow Previously authored by: Mike Cheung Eileen Humphrey Eoin McIntyre
SCHOLAR Study Guide SQA CfE Higher Human Biology Unit 4: Immunology and Public Health Authored by: Eoin McIntyre Reviewed by: Sheena Haddow Previously authored by: Mike Cheung Eileen Humphrey Eoin McIntyre
Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 I M M U N I T Y Innate (inborn) Immunity does not distinguish one pathogen from another Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Our first line of defense includes physical and chemical barriers
I M M U N I T Y Innate (inborn) Immunity does not distinguish one pathogen from another Figure 14.2 Overview of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Our first line of defense includes physical and chemical barriers
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1. Immunity and Disease
 ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
ELISA BIO 110 Lab 1 Immunity and Disease Introduction The principal role of the mammalian immune response is to contain infectious disease agents. This response is mediated by several cellular and molecular
Medical Microbiology Culture Media :
 Lecture 3 Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology Culture Media : Culture media are used for recognition and identification (diagnosis) of microorganisms. The media are contained in plates (Petri dishes),
Lecture 3 Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology Culture Media : Culture media are used for recognition and identification (diagnosis) of microorganisms. The media are contained in plates (Petri dishes),
FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE
 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Naresuan University 171 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology The time is critical now for graduate education and research
Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Naresuan University 171 Doctor of Philosophy Program in Microbiology The time is critical now for graduate education and research
Chapter 20: Antimicrobial Drugs
 Chapter 20: Antimicrobial Drugs 1. Overview of Antimicrobial Drugs 2. Antibacterial Drugs 3. Antiviral Drugs 4. Drugs for Eukaryotic Pathogens 1. Overview of Antimicrobial Drugs Antibiotics An antibiotic
Chapter 20: Antimicrobial Drugs 1. Overview of Antimicrobial Drugs 2. Antibacterial Drugs 3. Antiviral Drugs 4. Drugs for Eukaryotic Pathogens 1. Overview of Antimicrobial Drugs Antibiotics An antibiotic
Natalia Taborda Vanegas. Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia
 Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Pathogenesis of Dengue Natalia Taborda Vanegas Doc. Sci. Student Immunovirology Group Universidad de Antioquia Infection process Epidermis keratinocytes Dermis Archives of Medical Research 36 (2005) 425
Immunology Ambassador Guide (updated 2014)
 Immunology Ambassador Guide (updated 2014) Immunity and Disease We will talk today about the immune system and how it protects us from disease. Also, we ll learn some unique ways that our immune system
Immunology Ambassador Guide (updated 2014) Immunity and Disease We will talk today about the immune system and how it protects us from disease. Also, we ll learn some unique ways that our immune system
Bacterial evasion of host immunity
 Bacterial evasion of host immunity Gunnar Lindahl Lund University, Sweden and Copenhagen University, Denmark A pathogen must evade attack by the immune system of the host innate immunity adaptive immunity
Bacterial evasion of host immunity Gunnar Lindahl Lund University, Sweden and Copenhagen University, Denmark A pathogen must evade attack by the immune system of the host innate immunity adaptive immunity
Masters of Science in Microbiology and Immunology 2013/2014
 Fall semester: Graduate Medical Microbiology (4 credits). This course is designed to introduce graduate students to bacterial, fungal and viral pathogens that are the etiological agents of the most significant
Fall semester: Graduate Medical Microbiology (4 credits). This course is designed to introduce graduate students to bacterial, fungal and viral pathogens that are the etiological agents of the most significant
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity
 B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
B cell activation and Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity is mediated by secreted antibodies and its physiological function is defense against extracellular microbes (including viruses) and microbial exotoxins.
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
IMMUNE SYSTEM. The body s defense against:
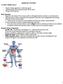 The body s defense against: IMMUNE SYSTEM disease causing organisms or infectious agents malfunctioning cells or abnormal body cells as cancer foreign cells or particles Basic Immunity Depends on the ability
The body s defense against: IMMUNE SYSTEM disease causing organisms or infectious agents malfunctioning cells or abnormal body cells as cancer foreign cells or particles Basic Immunity Depends on the ability
Effector Mechanisms of Humoral Immunity
 Immunologie II für Naturwissenschaftler Effector Mechanisms of Humoral Immunity Beda M. Stadler Institute of Immunology Inselspital Bern, Switzerland http://www.immunology.unibe.ch/teaching/imm2/immuno2.htm
Immunologie II für Naturwissenschaftler Effector Mechanisms of Humoral Immunity Beda M. Stadler Institute of Immunology Inselspital Bern, Switzerland http://www.immunology.unibe.ch/teaching/imm2/immuno2.htm
SYSTEM Teacher Pages THE IMMUNE. Your students will learn:
 Grade Level 3-5 Sergeant Cell s Immune System Defense Team Webquest Activity Summary Comparing immune cells with a police team, the webquest activity guides students to research the immune system online.
Grade Level 3-5 Sergeant Cell s Immune System Defense Team Webquest Activity Summary Comparing immune cells with a police team, the webquest activity guides students to research the immune system online.
An Overview of Cells and Cell Research
 An Overview of Cells and Cell Research 1 An Overview of Cells and Cell Research Chapter Outline Model Species and Cell types Cell components Tools of Cell Biology Model Species E. Coli: simplest organism
An Overview of Cells and Cell Research 1 An Overview of Cells and Cell Research Chapter Outline Model Species and Cell types Cell components Tools of Cell Biology Model Species E. Coli: simplest organism
Body Defenses & Immunity. Nonspecific Immunity
 Body Defenses & Immunity immunity = resistance to disease the immune system provides defense against all the microorganisms and toxic cells to which we are exposed! without it we would not survive till
Body Defenses & Immunity immunity = resistance to disease the immune system provides defense against all the microorganisms and toxic cells to which we are exposed! without it we would not survive till
(D) 181-183, 186-187, 190-193 TFYI 187 TPK 190
 NEVADA Life Science Content Standards for Grade 8 Life s Structure and Function A From Bacteria to Plants B Animal Diversity C Human Body Systems D OBJECTIVES Content Standard 6.0: Structure and Function
NEVADA Life Science Content Standards for Grade 8 Life s Structure and Function A From Bacteria to Plants B Animal Diversity C Human Body Systems D OBJECTIVES Content Standard 6.0: Structure and Function
Hepatitis C. Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C
 Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
Hepatitis C Laboratory Tests and Hepatitis C If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will use laboratory tests to check your health. This handout will help you understand what the major tests are and what
CONTENT. Chapter 1 Review of Literature. List of figures. List of tables
 Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Abstract Abbreviations List of figures CONTENT I-VI VII-VIII IX-XII List of tables XIII Chapter 1 Review of Literature 1. Vaccination against intracellular pathogens 1-34 1.1 Role of different immune responses
Autoimmunity and immunemediated. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
1 Autoimmunity and immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails Genetics of autoimmune diseases Therapeutic
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6)
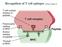 Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
Recognition of T cell epitopes (Abbas Chapter 6) Functions of different APCs (Abbas Chapter 6)!!! Directon Routes of antigen entry (Abbas Chapter 6) Flow of Information Barrier APCs LNs Sequence of Events
Understanding the Immune System
 Understanding the Immune System How It Works U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Cancer Institute Understanding
Understanding the Immune System How It Works U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases National Cancer Institute Understanding
The Body s Defenses CHAPTER 24
 CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
CHAPTER 24 The Body s Defenses PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
What Does My Bone Marrow Do?
 What Does My Bone Marrow Do? the myelodysplastic syndromes foundation, inc. Illustrations by Kirk Moldoff Published by The Myelodysplastic Syndromes Foundation, Inc. First Edition, 2009. 2012. Table of
What Does My Bone Marrow Do? the myelodysplastic syndromes foundation, inc. Illustrations by Kirk Moldoff Published by The Myelodysplastic Syndromes Foundation, Inc. First Edition, 2009. 2012. Table of
Course Outline and Syllabus for Students
 Course Outline and Syllabus for Students Name: Ian Crandall Course Number: PHM242H1 Course Title: Microbiology of Infectious Diseases Course Description: The course provides a brief introduction to the
Course Outline and Syllabus for Students Name: Ian Crandall Course Number: PHM242H1 Course Title: Microbiology of Infectious Diseases Course Description: The course provides a brief introduction to the
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary. Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide
 Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Blood & Marrow Transplant Glossary Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant Program Patient Guide Glossary Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) -- Also called "absolute granulocyte count" amount of white blood
Blood. Functions of Blood. Components of Blood. Transporting. Distributing body heat. A type of connective tissue. Formed elements.
 Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Blood Functions of Blood Transporting nutrients respiratory gases waste products Distributing body heat Components of Blood A type of connective tissue Formed elements Living blood cells Plasma Nonliving
Introduction to Medical Microbiology
 Introduction to Medical Microbiology Course Medical Microbiology Unit I Introduction to Microbiology Essential Question What is Medical Microbiology? TEKS 130.207(c) 2A, 3D Prior Student Learning n/a Estimated
Introduction to Medical Microbiology Course Medical Microbiology Unit I Introduction to Microbiology Essential Question What is Medical Microbiology? TEKS 130.207(c) 2A, 3D Prior Student Learning n/a Estimated
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
Given these characteristics of life, which of the following objects is considered a living organism? W. X. Y. Z.
 Cell Structure and Organization 1. All living things must possess certain characteristics. They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on to their offspring.
Cell Structure and Organization 1. All living things must possess certain characteristics. They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on to their offspring.
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Serology
 Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Serology The Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences / Clinical Microbiology, Immunology or
Course Curriculum for Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences/Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Serology The Master Degree in Medical Laboratory Sciences / Clinical Microbiology, Immunology or
Unit Four. Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 16 Lymphatic System URLs http://www.howstuffworks.com/immune-system.htm http://www.thebody.com/step/immune.html http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookIMMUN.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 16 Lymphatic System URLs http://www.howstuffworks.com/immune-system.htm http://www.thebody.com/step/immune.html http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/ BioBookIMMUN.html
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology
 Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
Chapter 18: Applications of Immunology 1. Vaccinations 2. Monoclonal vs Polyclonal Ab 3. Diagnostic Immunology 1. Vaccinations What is Vaccination? A method of inducing artificial immunity by exposing
02/08/2010. 1. Background. Outline
 Identification of immunodominant T-cell eptitopes in matrix protein of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus Ya-Xin Wang, PhD Student Outline 1. Background 2. Research Contents
Identification of immunodominant T-cell eptitopes in matrix protein of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus Ya-Xin Wang, PhD Student Outline 1. Background 2. Research Contents
Principles of Vaccination
 Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Immunology is a complicated subject, and a detailed discussion of it is beyond the scope of this text. However, an understanding of the basic function of the
Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Immunology is a complicated subject, and a detailed discussion of it is beyond the scope of this text. However, an understanding of the basic function of the
KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. binomial nomenclature
 Section 17.1: The Linnaean System of Classification Unit 9 Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. VOCABULARY taxonomy taxon binomial nomenclature genus MAIN
Section 17.1: The Linnaean System of Classification Unit 9 Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. VOCABULARY taxonomy taxon binomial nomenclature genus MAIN
JIANGSU CARTMAY INDUSTRIAL CO.,LTD www.labfurniture.asia mail: info@labfurniture.asia
 The basic layout, the main functions and instrumentation concept of micro Inspection Division laboratory, 1, Virology Laboratory 1. Functions: for the city to monitor the prevalence of HIV disease, dealing
The basic layout, the main functions and instrumentation concept of micro Inspection Division laboratory, 1, Virology Laboratory 1. Functions: for the city to monitor the prevalence of HIV disease, dealing
Uses of Flow Cytometry
 Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Activation and effector functions of HMI
 Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Activation and effector functions of HMI Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 August 2015 ว ตถ ประสงค หล งจากช วโมงบรรยายน แล วน กศ กษาสามารถ
Ph.D. Program Molecular Microbiology and Immunology (MMI) Saint Louis University School of Medicine
 Ph.D. Program Molecular Microbiology and Immunology (MMI) Saint Louis University School of Medicine I. Overview The Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology and Immunology (MMI) offers a graduate
Ph.D. Program Molecular Microbiology and Immunology (MMI) Saint Louis University School of Medicine I. Overview The Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology and Immunology (MMI) offers a graduate
Graduate Certificate Pre-Med Program Course Descriptions For Year 2015-2016 FALL
 Graduate Certificate Pre-Med Program Course Descriptions For Year 2015-2016 FALL COURSE TITLE: BIOCHEMISTRY COURSE NUMBER: 5104 This course emphasizes biochemical compounds, processes and systems, designed
Graduate Certificate Pre-Med Program Course Descriptions For Year 2015-2016 FALL COURSE TITLE: BIOCHEMISTRY COURSE NUMBER: 5104 This course emphasizes biochemical compounds, processes and systems, designed
Clinic Infectious Disease Control
 Chapter 2 - Lesson 4 Clinic Infectious Disease Control Introduction Infectious and parasitic disease control is important in veterinary clinics. The main objective is to prevent the spread of infections
Chapter 2 - Lesson 4 Clinic Infectious Disease Control Introduction Infectious and parasitic disease control is important in veterinary clinics. The main objective is to prevent the spread of infections
