Life; Ch. 14 Test; Circulation & Respiration
|
|
|
- Cassandra Cunningham
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Life; Ch. 14 Test; Circulation & Respiration Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these is NOT a function of the cardiovascular system? a. transporting cells that attack disease-causing microorganisms b. carrying oxygen, glucose, and other needed materials to cells c. carrying waste products away from cells d. controlling many body processes by means of chemicals 2. Needed substances are carried to the body cells by a. enzymes. b. blood. c. water. d. food. 3. The function of the atria is to a. pump blood to the lungs. b. pump blood to the body. c. receive blood that comes into the heart. d. deliver oxygen to body tissues. 4. Which of these heart structures prevents blood from flowing backward? a. aorta b. valve c. septum d. coronary artery 5. When the ventricles contract, blood is pumped a. out of the heart. b. into the heart. c. through the septum. d. into veins. 6. When blood flows into the right atrium from the body, it contains a. little oxygen and a lot of carbon dioxide. b. a lot of oxygen and little carbon dioxide. c. a lot of both oxygen and carbon dioxide. d. little of either oxygen or carbon dioxide. 7. Which chamber of the heart pumps oxygen-poor blood to the lungs? a. left atrium b. right atrium c. left ventricle d. right ventricle 8. How many loops does the human circulatory system contain? a. one b. two c. three
2 d. four 9. In which vessels are materials exchanged between the blood and the body cells? a. veins b. arteries c. capillaries d. lymphatic vessels 10. What causes blood pressure? a. the force with which the ventricles contract b. the rate at which blood flows through the heart c. the speed at which oxygen is returned to blood in the lungs d. the strength of the muscles in the walls of the capillaries 11. What layer or layers of veins have muscles? a. the outer layer only b. the middle layer only c. the inner layer only d. all three layers 12. If a person s blood lacked platelets, what process could not take place? a. carrying oxygen to cells b. carrying glucose to cells c. clotting of blood d. transfusing of blood 13. A heart attack affects heart cells by a. cutting off blood flow and oxygen and causing cells to die. b. creating a buildup of fatty substances such as cholesterol within cells. c. destroying white blood cells. d. preventing the ventricles from contracting. 14. What is the blood type of a person whose plasma contains only anti-b clumping proteins? a. type A b. type B c. type AB d. type O 15. What eventually happens to fluid that leaks from capillaries into the surrounding tissues? a. It undergoes chemical reactions and becomes fatty tissue. b. It replaces dead body cells. c. It returns to the blood through the lymphatic system. d. It replaces dead red blood cells. 16. What is the function of lymph nodes? a. to trap disease-causing bacteria b. to make new lymph c. to transfer oxygen d. to return lymph to the bloodstream 17. Which substances are produced during respiration? a. water and oxygen b. oxygen and red blood cells c. carbon dioxide and water
3 d. carbon dioxide and red blood cells 18. What term do scientists use to describe the chemical process in which oxygen and glucose react to release energy inside body cells? a. inhaling b. exhaling c. breathing d. respiration 19. What is the name of the small flap of tissue that seals off the trachea during swallowing? a. pharynx b. larynx c. epiglottis d. alveoli 20. Which parts of the respiratory system divide into smaller and smaller tubes in a pattern that resembles the branches of a tree? a. pharynx b. trachea c. bronchi d. epiglottis 21. Hairlike structures that line the nasal cavities and trachea are called a. cilia. b. mucus. c. bronchi. d. capillaries. 22. Where in the respiratory system does gas exchange occur? a. in the heart b. in the alveoli c. in the pharynx d. in the trachea 23. During gas exchange, which substance moves from the alveoli into the blood? a. carbon dioxide b. oxygen c. water d. nitrogen 24. What happens to cause air to be exhaled from the lungs? a. The rib muscles contract and move outward. b. The chest cavity expands and grows larger. c. The diaphragm relaxes and moves upward. d. The lungs contract and then expand. 25. What produces a person s voice? a. the lungs b. the diaphragm c. the vocal cords d. the alveoli 26. Why is atherosclerosis especially serious when it develops in the coronary arteries? a. It can then go on to affect the aorta.
4 b. It can make red blood cells die. c. It can lead to a heart attack. d. It can limit the functioning of white blood cells. 27. Hypertension is a condition in which a. blood pressure is consistently lower than normal. b. blood pressure is consistently higher than normal. c. fatty deposits build up on artery walls. d. some of the heart muscle dies. 28. Why is atherosclerosis especially serious when it develops in the coronary arteries? a. It can then go on to affect the aorta. b. It can make red blood cells die. c. It can lead to a heart attack. d. It can limit the functioning of white blood cells. 29. Over time, smoking can irritate the breathing passages, which may become clogged with mucus. This condition is called a. bronchitis. b. emphysema. c. lung cancer. d. heart attacks. 30. A tumor that develops in the lungs may be a sign of a. bronchitis. b. lung cancer. c. heart disease. d. emphysema. Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 31. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and lymph. _ 32. The two upper chambers of the heart are called atria. _ 33. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs. _ 34. As blood moves away from the heart, blood pressure increases. _ 35. White blood cells are the most numerous type of cells in whole blood. _ 36. People with blood type O can safely receive blood transfusions from people with blood type O. _ 37. Lymph nodes may enlarge when they are helping the body fight an infection. _ 38. The respiratory system removes oxygen and water from the body. _
5 39. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in capillaries that surround tiny sacs called bronchi. _ 40. In gas exchange, oxygen passes from the alveoli into the blood. _ Completion Complete each statement. 41. The circulatory system carries the needed materials oxygen and to the body cells. 42. The group of cells called the regulates the rate at which the heart beats. 43. A flap of tissue called a(n) separates the right atrium from the right ventricle. 44. Blood that contains large amounts of carbon dioxide flows from the body into the atrium of the heart. 45. A sphygmomanometer measures. 46. The force with which the contract causes blood pressure. 47. Fibrin is produced when the blood components called start a chain reaction that produces a blood clot. 48. The marker molecules on red blood cells determine a person s. 49. Fluid that has leaked out of capillaries is returned to the blood by the system. 50. Fluid from the blood that enters lymphatic vessels is known as. 51. The movement of air into and out of the lungs is called. 52. The process in which energy is released from glucose is called cellular. 53. After flowing through the nasal cavities, air enters the, or throat. 54. Dust in air that enters the nose is trapped by a sticky substance called. 55. Carbon dioxide and pass from the blood into the alveoli. 56. Your voice is produced by the rapid vibration of air molecules rushing through the opening of the. 57. The combined action of your rib muscles and your increase and decrease the size of your chest cavity, allowing inhalation and exhalation. 58. A high-fat diet and sedentary lifestyle might lead to in the coronary arteries. 59. People with hemophilia, a genetic disorder that prevents clotting of the blood, lack the ability to produce the protein.
6 60. _ is an infection that causes the alveoli to fill with fluid, impairing their ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Short Answer Use the diagram to answer each question. 61. What is the name for the structure labeled A? To which locations does it carry blood? 62. Identify structure B. 63. Identify structure G. Give the letter and name of the structure into which blood flows after leaving G. 64. What is the structure labeled C? What is its function? 65. Identify the structure labeled D. When blood enters structure D, is the blood low in oxygen or high in oxygen? Explain. 66. Identify structure E. What would happen to a person who had a hole in this structure? Use the diagram to answer each question.
7 67. Identify the type of cell shown by A. 68. What is the function of the type of cell indicated by A? 69. What is the function of the type of cell indicated by B? If the body did not have this type of cell, what would probably happen? 70. What blood component is shown by C? In what body process is it important? 71. Which type of cell does blood contain more of A or B? 72. Which major blood component is not labeled in the diagram? Essay 73. Describe the role of the cardiovascular system in helping the body get rid of carbon dioxide. 74. What is meant by the two loops pattern of blood flow? Explain your answer. 75. Describe how the muscles in an artery regulate blood flow. 76. Explain why people with type AB blood can accept transfusions of any type blood. 77. Explain where the lymph was before it entered the lymphatic system. Then explain how the lymphatic system returns lymph to the bloodstream. 78. Explain the difference between breathing and respiration. 79. Anemia is a severe iron deficiency. Explain why a person suffering from anemia might feel constantly tired and short of breath. 80. What is bronchitis? Describe the effects of bronchitis.
8 Life; Ch. 14 Test; Circulation & Respiration Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: D OBJ: CaLS Explain the functions of the cardiovascular system. 2. ANS: B OBJ: CaLS Explain the functions of the cardiovascular system. 3. ANS: C OBJ: CaLS Explain the functions of the cardiovascular system. STA: S 7.6.j BLM: comprehension 4. ANS: B OBJ: CaLS Describe the function and structure of the heart. 5. ANS: A OBJ: CaLS Describe the function and structure of the heart. 6. ANS: A OBJ: CaLS Sequence the path taken by blood through the cardiovascular system. STA: S 7.6.j BLM: comprehension 7. ANS: D OBJ: CaLS Sequence the path taken by blood through the cardiovascular system. 8. ANS: B OBJ: CaLS Sequence the path taken by blood through the cardiovascular system. 9. ANS: C OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions and structures of arteries, capillaries, and veins. 10. ANS: A OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions and structures of arteries, capillaries, and veins. 11. ANS: B OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions and structures of arteries, capillaries, and veins. STA: S 7.6.j BLM: comprehension 12. ANS: C OBJ: CaLS Describe the components of blood. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: comprehension 13. ANS: A OBJ: CaLS Describe the components of blood. STA: S 7.5.a BLM: comprehension
9 14. ANS: A OBJ: CaLS Explain what determines the type of blood that a person can receive in a transfusion. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: comprehension 15. ANS: C OBJ: CaLS Name the structures and functions of the lymphatic system. 16. ANS: A OBJ: CaLS Name the structures and functions of the lymphatic system. 17. ANS: C OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions of the respiratory system. 18. ANS: D OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions of the respiratory system. 19. ANS: C OBJ: CaLS Identify the structures that air passes through as it travels to the lungs. 20. ANS: C OBJ: CaLS Identify the structures that air passes through as it travels to the lungs. 21. ANS: A OBJ: CaLS Identify the structures that air passes through as it travels to the lungs. 22. ANS: B OBJ: CaLS Describe what happens during gas exchange and breathing. 23. ANS: B OBJ: CaLS Describe what happens during gas exchange and breathing. 24. ANS: C OBJ: CaLS Describe what happens during gas exchange and breathing. 25. ANS: C OBJ: CaLS Describe what happens during gas exchange and breathing. 26. ANS: C OBJ: CaLS Identify some diseases of the cardiovascular system. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: comprehension 27. ANS: B OBJ: CaLS Identify some diseases of the cardiovascular system. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: knowledge 28. ANS: C OBJ: CaLS Identify some diseases of the cardiovascular system. BLM: comprehension
10 29. ANS: A OBJ: CaLS Explain how tobacco smoke may affect the body. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: knowledge 30. ANS: B OBJ: CaLS Explain how tobacco smoke may affect the body. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: comprehension MODIFIED TRUE/FALSE 31. ANS: F, blood OBJ: CaLS Explain the functions of the cardiovascular system. 32. ANS: T OBJ: CaLS Describe the function and structure of the heart. 33. ANS: T OBJ: CaLS Sequence the path taken by blood through the cardiovascular system. 34. ANS: F, decreases OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions and structures of arteries, capillaries, and veins. STA: S 7.6.j BLM: comprehension 35. ANS: F, Red OBJ: CaLS Describe the components of blood. STA: S 7.5.a BLM: knowledge 36. ANS: T OBJ: CaLS Explain what determines the type of blood that a person can receive in a transfusion. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: comprehension 37. ANS: T OBJ: CaLS Name the structures and functions of the lymphatic system. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: comprehension 38. ANS: F, carbon dioxide OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions of the respiratory system. 39. ANS: F, alveoli OBJ: CaLS Identify the structures that air passes through as it travels to the lungs.
11 40. ANS: T OBJ: CaLS Describe what happens during gas exchange and breathing. COMPLETION 41. ANS: glucose OBJ: CaLS Explain the functions of the cardiovascular system. 42. ANS: pacemaker OBJ: CaLS Describe the function and structure of the heart. 43. ANS: valve OBJ: CaLS Describe the function and structure of the heart. 44. ANS: right OBJ: CaLS Sequence the path taken by blood through the cardiovascular system. STA: S 7.6.j BLM: comprehension 45. ANS: blood pressure OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions and structures of arteries, capillaries, and veins. 46. ANS: ventricles OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions and structures of arteries, capillaries, and veins. 47. ANS: platelets OBJ: CaLS Describe the components of blood. BLM: comprehension 48. ANS: blood type STA: S 7.5.a
12 OBJ: CaLS Explain what determines the type of blood that a person can receive in a transfusion. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: knowledge 49. ANS: lymphatic OBJ: CaLS Name the structures and functions of the lymphatic system. 50. ANS: lymph OBJ: CaLS Name the structures and functions of the lymphatic system. 51. ANS: breathing OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions of the respiratory system. 52. ANS: respiration OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions of the respiratory system. 53. ANS: pharynx OBJ: CaLS Identify the structures that air passes through as it travels to the lungs. 54. ANS: mucus OBJ: CaLS Identify the structures that air passes through as it travels to the lungs. 55. ANS: water OBJ: CaLS Describe what happens during gas exchange and breathing. 56. ANS: larynx OBJ: CaLS Describe what happens during gas exchange and breathing. 57. ANS: diaphragm
13 OBJ: CaLS Describe what happens during gas exchange and breathing. 58. ANS: atherosclerosis OBJ: CaLS Identify some diseases of the cardiovascular system. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: comprehension 59. ANS: fibrin. PTS: 1 DIF: L3 OBJ: CaLS Describe the components of blood. BLM: synthesis 60. ANS: Pneumonia STA: S 7.5.b OBJ: CaLS Identify respiratory diseases that result from infections or other physical conditions. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: comprehension SHORT ANSWER 61. ANS: A is the aorta, which carries blood from the heart to the body. OBJ: CaLS Describe the function and structure of the heart. CaLS Sequence the path taken by blood through the cardiovascular system. STA: S 7.6.j BLM: application 62. ANS: Structure B is the left atrium. OBJ: CaLS Describe the function and structure of the heart. STA: S 7.6.j BLM: application 63. ANS: G is the right atrium. After leaving G, blood flows into F, the right ventricle. OBJ: CaLS Describe the function and structure of the heart. CaLS Sequence the path taken by blood through the cardiovascular system. STA: S 7.6.j BLM: application 64. ANS: Structure C is the valve that separates the left atrium from the left ventricle. Its function is to prevent blood from flowing backward from the ventricle into the atrium.
14 OBJ: CaLS Describe the function and structure of the heart. STA: S 7.6.j BLM: application 65. ANS: D is the left ventricle. Blood entering the left ventricle is high in oxygen, because it has just come from the left atrium, which receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs. OBJ: CaLS Describe the function and structure of the heart. CaLS Sequence the path taken by blood through the cardiovascular system. STA: S 7.6.j BLM: application 66. ANS: Structure E is the septum. A hole in the septum would allow oxygen-poor blood to mix with oxygen-rich blood. As a result, less oxygen would go to body cells. PTS: 1 DIF: L3 OBJ: CaLS Describe the function and structure of the heart. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: synthesis 67. ANS: A is a red blood cell. OBJ: CaLS Describe the components of blood. BLM: application 68. ANS: A, a red blood cell, carries oxygen throughout the body. STA: S 7.5.a OBJ: CaLS Describe the components of blood. STA: S 7.5.a BLM: application 69. ANS: B is a white blood cell. If the body did not have white blood cells, its ability to fight disease would be weakened. PTS: 1 DIF: L3 OBJ: CaLS Describe the components of blood. BLM: synthesis 70. ANS: C is a platelet. Platelets are important in the clotting of blood. OBJ: CaLS Describe the components of blood. BLM: application 71. ANS: A, the red blood cell STA: S 7.5.b STA: S 7.5.a
15 OBJ: CaLS Describe the components of blood. BLM: application 72. ANS: plasma PTS: 1 DIF: L3 OBJ: CaLS Describe the components of blood. BLM: analysis STA: S 7.5.a STA: S 7.5.a ESSAY 73. ANS: Cells produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. The carbon dioxide passes from the cells into the blood. The cardiovascular system carries the carbon dioxide to the lungs. The carbon dioxide is exhaled. OBJ: CaLS Explain the functions of the cardiovascular system. 74. ANS: The overall pattern of blood flow through the body is somewhat like a figure eight with the heart at the center where the two loops cross. In the first loop, blood travels from the heart to the lungs and then back to the heart. In the second loop, blood is pumped from the heart throughout the body and then returns to the heart. OBJ: CaLS Sequence the path taken by blood through the cardiovascular system. STA: S 7.6.j BLM: comprehension 75. ANS: When the artery muscles contract, the opening in the artery becomes smaller. Less blood flows through them. When the artery muscles relax, the opening becomes larger. More blood flows through them. OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions and structures of arteries, capillaries, and veins. STA: S 7.6.j BLM: comprehension 76. ANS: Some blood types react to certain marker molecules by clumping. People with type AB blood do not produce clumping chemicals that act against either A or B markers. Type O blood does not contain either A or B markers. Therefore, a person with group AB blood can accept a transfusion of any blood type, because no clumping will occur. OBJ: CaLS Explain what determines the type of blood that a person can receive in a transfusion. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: comprehension
16 77. ANS: Before it entered the lymphatic system, the lymph was part of the blood. It then leaks out of blood vessels and bathes body tissues. The lymphatic system returns lymph to the bloodstream by emptying it into large veins in the chest. OBJ: CaLS Name the structures and functions of the lymphatic system. 78. ANS: Breathing is the movement of air into and out of the lungs. Respiration, which is also called cellular respiration, is the process in which oxygen and glucose chemically react to release energy from glucose. OBJ: CaLS Describe the functions of the respiratory system. STA: S 7.5.a BLM: analysis 79. ANS: Iron is needed for the production of the protein hemoglobin, which binds to oxygen so blood can transport the oxygen throughout the body. A person with anemia would not have enough iron to create needed hemoglobin. Without enough hemoglobin, the red blood cells would be unable to carry oxygen efficiently. Enough oxygen might not reach all the organs of the body. The lungs would have to work harder, and the anemic person would feel tired and short of breath. PTS: 1 DIF: L3 OBJ: CaLS Describe the components of blood. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: synthesis 80. ANS: Bronchitis is a narrowing of small air passages. Bronchitis makes breathing difficult and is often accompanied by infections of the respiratory system. Eventually, bronchitis may permanently damage the breathing passages. OBJ: CaLS Identify respiratory diseases that result from infections or other physical conditions. STA: S 7.5.b BLM: comprehension
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
33.1 The Circulatory System
 33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Blood vessels. transport blood throughout the body
 Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment
 Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series
 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Circulatory System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3135 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM from The Human Body Systems Series Teacher's Guide 1 The Circulatory System from The Human Body Systems Series catalog # 3135 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560
1. Our lungs are, essentially, a network of connected that bring
 The Respiratory System Webquest http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/health-and-human-body/human-body/lungs-article/ The Breath of Life-National Geographic 1. Our lungs are, essentially, a network
The Respiratory System Webquest http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/health-and-human-body/human-body/lungs-article/ The Breath of Life-National Geographic 1. Our lungs are, essentially, a network
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST
 REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
CHAPTER 5 - BREATHING "THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM"
 CHAPTER 5 - BREATHING "THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM" You have read how the blood transports oxygen from the lungs to cells and carries carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs. It is the function of the respiratory
CHAPTER 5 - BREATHING "THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM" You have read how the blood transports oxygen from the lungs to cells and carries carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs. It is the function of the respiratory
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School
 Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
Distance Learning Program Anatomy of the Human Heart/Pig Heart Dissection Middle School/ High School This guide is for middle and high school students participating in AIMS Anatomy of the Human Heart and
1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood?
 1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Cells, tissues and organs
 Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
Chapter 8: Cells, tissues and organs Cells: building blocks of life Living things are made of cells. Many of the chemical reactions that keep organisms alive (metabolic functions) take place in cells.
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system
 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes.
 Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM
 BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
In 2009, Canadian astronaut Robert Thirsk began a six-month stay
 Topic 1.4 How do systems work together in the human body? Key Concepts The respiratory system carries oxygen to and removes carbon dioxide from the blood. The circulatory system transports dissolved gases
Topic 1.4 How do systems work together in the human body? Key Concepts The respiratory system carries oxygen to and removes carbon dioxide from the blood. The circulatory system transports dissolved gases
How To Understand What You Know
 Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Heart Disorders Glossary ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) Test: A test that measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in the blood. Anemia: A condition in which there are low levels of red blood cells in
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Lesson 7: Respiratory and Skeletal Systems and Tuberculosis
 Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Circulatory System and Blood
 Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Circulatory System and Blood 1. Identify the arteries in the diagram and give one function for each. Y: Common carotid artery: sends oxygenated blood to the brain, provide nutrients. X: Subclavian artery:
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Transfusion. Red Blood Cells White Blood Cells Platelets
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions are very common. Each year, almost 5 million Americans need a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions are given to replace blood lost during surgery or serious
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions are very common. Each year, almost 5 million Americans need a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions are given to replace blood lost during surgery or serious
II. Fourth Grade, The Human Body 2002 Colorado Unit Writing Project 1
 The Human Body Grade Level or Special Area: 4 th Grade Written by: Krystal Kroeker, The Classical Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Length of Unit: 11 lessons (approximately 12 days, one day = 45 minutes)
The Human Body Grade Level or Special Area: 4 th Grade Written by: Krystal Kroeker, The Classical Academy, Colorado Springs, CO Length of Unit: 11 lessons (approximately 12 days, one day = 45 minutes)
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY MAINTENANCE 30
 Curriculum Development In the Fairfield Public Schools FAIRFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS FAIRFIELD, CONNECTICUT HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY MAINTENANCE 30 Board of Education Approved 05/22/2007 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
Curriculum Development In the Fairfield Public Schools FAIRFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS FAIRFIELD, CONNECTICUT HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY MAINTENANCE 30 Board of Education Approved 05/22/2007 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
About lung cancer. Contents. The lungs
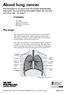 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
Breathing and Holding Your Breath copyright, 2005, Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania 1
 Breathing and Holding Your Breath copyright, 2005, Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania 1 Introduction Everybody breathes all day, every day. Why?
Breathing and Holding Your Breath copyright, 2005, Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania 1 Introduction Everybody breathes all day, every day. Why?
STAGE 5: Interacting Systems
 Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
Blood Transfusion. There are three types of blood cells: Red blood cells. White blood cells. Platelets.
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions can save lives. Every second, someone in the world needs a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions can replace the blood lost from a serious injury or surgery.
HEALTH EFFECTS. Inhalation
 Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
This interchange is simple
 3 Circulation This interchange is simple compared to how blood travels within your body. In this chapter, you will discover how complex your circulatory system is. You ll learn what blood is made of and
3 Circulation This interchange is simple compared to how blood travels within your body. In this chapter, you will discover how complex your circulatory system is. You ll learn what blood is made of and
GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
 GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GRADE: 5 LESSON: 1 THEME: BODY SYSTEMS CONCEPT: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM IS ESSENTIAL FOR GETTING OXYGEN INTO AND CARBON DIOXIDE OUT OF THE BODY PREPARATION:
GRADE 5 GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT GRADE: 5 LESSON: 1 THEME: BODY SYSTEMS CONCEPT: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM IS ESSENTIAL FOR GETTING OXYGEN INTO AND CARBON DIOXIDE OUT OF THE BODY PREPARATION:
Gas Exchange. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com)
 Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the alveoli
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the alveoli
Comparing Organs BIOLOGY SCIENCE INSTRUCTIONAL TASKS
 BIOLOGY SCIENCE INSTRUCTIONAL TASKS Comparing Organs Grade-Level Expectations The exercises in these instructional tasks address content related to the following science grade-level expectation: Contents
BIOLOGY SCIENCE INSTRUCTIONAL TASKS Comparing Organs Grade-Level Expectations The exercises in these instructional tasks address content related to the following science grade-level expectation: Contents
ANSWERS AND MARK SCHEMES. (a) 5 correct plots;;; (-1 mark each incorrect plot) 3
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 5 correct plots;;; (-1 mark each incorrect plot) 3 (b) 1600/4; = 400 kj; (i mark for correct working if answer incorrect) 2 (c) the more vigorous the activity the more energy used; 1 (d)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 5 correct plots;;; (-1 mark each incorrect plot) 3 (b) 1600/4; = 400 kj; (i mark for correct working if answer incorrect) 2 (c) the more vigorous the activity the more energy used; 1 (d)
What You Should Know About ASTHMA
 What You Should Know About ASTHMA 200 Hospital Drive Galax, VA 24333 (276) 236-8181 www.tcrh.org WHAT IS ASTHMA? It s a lung condition that makes breathing difficult. The cause of asthma is not known.
What You Should Know About ASTHMA 200 Hospital Drive Galax, VA 24333 (276) 236-8181 www.tcrh.org WHAT IS ASTHMA? It s a lung condition that makes breathing difficult. The cause of asthma is not known.
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.
 Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins?
 Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? Healthy Legs 2006 http://healthylegs.com Page 1 Venous disorders are widespread Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? Healthy Legs 2006 http://healthylegs.com Page 1 Venous disorders are widespread Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people
Cells and Systems Unit 2 Test
 Cells and Systems Unit 2 Test Student Name Class 1. Characteristics of living organisms include all of the following, EXCEPT... A. they need energy and produce wastes B. they reproduce and grow C. they
Cells and Systems Unit 2 Test Student Name Class 1. Characteristics of living organisms include all of the following, EXCEPT... A. they need energy and produce wastes B. they reproduce and grow C. they
Respiratory Disorders
 Respiratory Disorders Teaching Plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy
Respiratory Disorders Teaching Plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy
Department of Surgery
 What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
Your Body's Systems Literacy Foundations Science: Biology
 Version 01 Your Body's Systems Literacy Foundations Science: Biology 2012 by Open School BC This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. To view
Version 01 Your Body's Systems Literacy Foundations Science: Biology 2012 by Open School BC This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. To view
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
 Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Risk factors are traits and life-style habits that increase a person's chances of having coronary artery and vascular disease. Some risk factors cannot be changed or
BLOOD-Chp. Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? What is the composition of blood? 3 major types of plasma proteins
 6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition
 Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Phlebotomy Handbook Blood Collection Essentials Seventh Edition Diana Garza Kathleen Becan-McBride Chapter Four The Cardiovascular System Introduction Circulatory system is a transport system. Contributes
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions
 Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
Heart and Vascular System Practice Questions Student: 1. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich
GRADE 11F: Biology 3. UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours. Human gas exchange system and health. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision
 National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision Key Area 1: Structure and function of organs and organ systems and their role in sustaining life. What you must know: The basic structure and functions of main
National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision Key Area 1: Structure and function of organs and organ systems and their role in sustaining life. What you must know: The basic structure and functions of main
Circulation. What does a highway have to do with circulation? 62 D Steve Allen/Getty Images
 Circulation sections 1 The Circulatory System Lab The Heart as a Pump 2 Blood 3 The Lymphatic System Lab Blood Type Reactions Virtual Lab What factors affect the likelihood of hypertension? What does a
Circulation sections 1 The Circulatory System Lab The Heart as a Pump 2 Blood 3 The Lymphatic System Lab Blood Type Reactions Virtual Lab What factors affect the likelihood of hypertension? What does a
Advanced Subsidiary GCE Biology
 Advanced Subsidiary GCE Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport - High banded Candidate style answer Introduction OCR has produced these candidate style answers to support teachers in interpreting the
Advanced Subsidiary GCE Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport - High banded Candidate style answer Introduction OCR has produced these candidate style answers to support teachers in interpreting the
S.M.A.R.T.box. Circulatory System The Plasma Pipeline Teacher s Guide CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP. Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers
 CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM Circulatory System The Plasma Pipeline Teacher s Guide 33115 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher
CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM Circulatory System The Plasma Pipeline Teacher s Guide 33115 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher
H.W. 1 Bio 101 Prof. Fournier
 H.W. 1 Bio 101 Prof. Fournier 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a
H.W. 1 Bio 101 Prof. Fournier 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a
Emphysema. Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide.
 Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
ACTIVITY #3: LUNG HEALTH ASTHMA AND ALLERGIES
 ACTIVITY #3: LUNG HEALTH ASTHMA AND ALLERGIES TIME 50 minutes, computer lab REQUIRED RESOURCES Activity Computer lab with internet access for student research Notepaper and pencil for research Poster board
ACTIVITY #3: LUNG HEALTH ASTHMA AND ALLERGIES TIME 50 minutes, computer lab REQUIRED RESOURCES Activity Computer lab with internet access for student research Notepaper and pencil for research Poster board
The Immune System and Disease
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1029 1033) This section describes the causes of disease and explains how infectious diseases are transmitted Introduction
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
6023-1 - Page 1. Name: 4) The diagram below represents a beaker containing a solution of various molecules involved in digestion.
 Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Name: 6023-1 - Page 1 1) Which one of the following situations indicates a serious organ system malfunction? A) Mitochondria stop functioning in a unicellular organism exposed to pollutants. B) White blood
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? An informative guide for patients
 Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? An informative guide for patients Are You at Risk? Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people don t know is that approximately
Tired, Aching Legs? Swollen Ankles? Varicose Veins? An informative guide for patients Are You at Risk? Leg problems are widespread throughout the world, but what most people don t know is that approximately
These factors increase your chance of developing emphysema. Tell your doctor if you have any of these risk factors:
 Emphysema Pronounced: em-fiss-see-mah by Debra Wood, RN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Emphysema is a chronic obstructive disease of the lungs. The lungs contain millions of tiny air sacs called
Emphysema Pronounced: em-fiss-see-mah by Debra Wood, RN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Emphysema is a chronic obstructive disease of the lungs. The lungs contain millions of tiny air sacs called
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships
 Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Anatomy and Physiology
 Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
10. T and B cells are types of a. endocrine cells. c. lymphocytes. b. platelets. d. complement cells.
 Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Just as a plumbing system carries water through a series of
 37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Just as a plumbing system carries water through a series of pipes to different parts of a house, the circulatory system carries blood through a series of blood vessels
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Just as a plumbing system carries water through a series of pipes to different parts of a house, the circulatory system carries blood through a series of blood vessels
Blood: The Body s Vital Defense Force
 Blood: The body s vital defense force Ouch you ve cut your finger! A familiar red substance oozes out. As you reach for a bandage, take a moment to ponder the vital role this remarkable fluid performs.
Blood: The body s vital defense force Ouch you ve cut your finger! A familiar red substance oozes out. As you reach for a bandage, take a moment to ponder the vital role this remarkable fluid performs.
7 TH GRADE FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST. Part I: Cells. 1. The cell grows to its mature size during. a. mitosis b. prophase c. telophase d.
 7 TH GRADE FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST Part I: Cells 1. The cell grows to its mature size during a. mitosis b. prophase c. telophase d. interphase 2. The final stage of the cell cycle is called a. interphase
7 TH GRADE FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST Part I: Cells 1. The cell grows to its mature size during a. mitosis b. prophase c. telophase d. interphase 2. The final stage of the cell cycle is called a. interphase
Whooping Cough. The Lungs Whooping cough is an infection of the lungs and breathing tubes, both of which are parts of the respiratory system.
 Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
3. The Circulatory System
 3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
3. The Circulatory System A. Introduction B. Blood 1. Circulatory system transports water, electrolytes, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, cell, gases and nutrients to all cells and carries away metabolic
DIABETES. Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys. www.kidney.org
 DIABETES Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries that help
DIABETES Eyes, Heart, Nerves, Feet, and Kidneys www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation (NKF) offers guidelines and commentaries that help
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES. 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions.
 KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Lymph Nodes and Cancer What is the lymph system?
 Lymph Nodes and Cancer What is the lymph system? Our bodies have a network of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. (Lymph is pronounced limf.) This network is a part of the body s immune system. It collects
Lymph Nodes and Cancer What is the lymph system? Our bodies have a network of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. (Lymph is pronounced limf.) This network is a part of the body s immune system. It collects
Scheme of work Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610)
 Scheme of work Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) Unit 4: Respiration and the human transport system Recommended prior knowledge Students need to have some knowledge of energy transfer, and to be able understand
Scheme of work Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) Unit 4: Respiration and the human transport system Recommended prior knowledge Students need to have some knowledge of energy transfer, and to be able understand
The heart then repolarises (or refills) in time for the next stimulus and contraction.
 Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
Atrial Fibrillation BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART PUMP? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Breathless The Whys and Wherefores Living with Alpha-1-Antitrypsin Deficiency
 Breathless The Whys and Wherefores Living with Deficiency Patient Information Program Breathlessness Short of breath after running the marathon? Short of breath after climbing a flight of stairs? Short
Breathless The Whys and Wherefores Living with Deficiency Patient Information Program Breathlessness Short of breath after running the marathon? Short of breath after climbing a flight of stairs? Short
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
2.2.1 Pressure and flow rate along a pipe: a few fundamental concepts
 1.1 INTRODUCTION Single-cell organisms live in direct contact with the environment from where they derive nutrients and into where they dispose of their waste. For living systems containing multiple cells,
1.1 INTRODUCTION Single-cell organisms live in direct contact with the environment from where they derive nutrients and into where they dispose of their waste. For living systems containing multiple cells,
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
