SoCLib : Une plate-forme de prototypage virtuel pour systèmes multi-processeurs intégrés sur puce
|
|
|
- Tabitha Barnett
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SoCLib : Une plate-forme de prototypage virtuel pour systèmes multi-processeurs intégrés sur puce FETCH 07
2 Outline SoCLib goals SystemC modeling principles The Mutek Real-Time Operating System The MWMR communication middleware The DSX hardware/software codesign tool An application example : Stereovision
3 Example of a multi-processor architecture Input Engine Ext. RAM ctrl Ext. RAM ctrl Output Engine VCI VCI/OCP network (DSPIN) VCI VCI/OCP Local Crossbar VCI/OCP Local Crossbar VCI Proc Proc RAM Locks Proc Proc RAM Locks Sub-system 5 Sub-system 9
4 GOALS Design Space Exploration : fast performance evaluation for the mapping of a multi-threaded software application on a multi-processor hardware architecture. Plat-form based design : provide the system designer one (or several) generic hardware/software multi-processor architecture(s). IP reuse : clear separation between computing ressources and communication ressources : VCI/OCP standard.
5 SoCLib : Industrial Partners ST Micro-electronics Grenoble (B.Jego) Thales Paris (P.Kajfasz) Thomson SC Rennes (H.Heijnen) Silicomp Grenoble (V.Joloboff) Prosilog Cergy (M.Saussay) TurboConcept Brest (J.Tousch)
6 SoCLib : Académic Partners LIP6 Paris (A.Greiner) INRIA Orsay (O.Temam) LISIF Paris (P. Garda) CEA-LIST Saclay (F.Derepas) ENST Paris (A.Polti) IRISA Rennes (F.Charot) LESTER Lorient (P.Coussy) IETR Rennes (D. Houzet) CEA-LETI Grenoble (J-R. Lequepeys) TIMA Grenoble (F.Petrot) CITI Lyon (T. Risset)
7 SoCLib : General Principles The modeling language is SystemC. Two simulation models for each hardware component: CABA (Cycle-Accurate / Bit-Accurate) TLMT (Transaction Level Model with Time) All hardware components respect the same (VCI/OCP) communication protocol. All simulation models will be available as free software. For each SoCLib component, there is a - commercially available - synthezisable RTL model.
8 SoCLib : Planned Components COMPONENTS ORIGINE General Purpose Processors Digital Signal Processors MIPS R3000 SPARC V8 OpenRISC 1000 ARM 7 ARM 9 PowerPC 450 PowerPC 750 ST200 C6X Texas LIP6 ENST LIP6 LIP6 CEA LRI CEA ST / LRI IRISA System Utilities VCI/OCP Interconnects Interrupt controler Locks engine DMA controler MWMR controler VCI Generic VCI on DSPIN VCI on AMBA VCI on AVALON LIP6 LIP6 IETR LIP6 LIP6 LIP6 PROSILOG IRISA
9 SoCLib : Planned Components COMPOSANT ORIGINE Memory Controlers Embedded SRAM External SDRAM External DDR/SDRAM LIP6 PROSILOG PROSILOG Dedicated Coprocessors Turbodecodeur TC1000 Turbodecodeur TC3000 LDPC DWT MOD DEM TURBOCONCEPT TURBOCONCEPT ENST LESTER LESTER LESTER I/O Controlers VCI / PCI bridge VCI / USB bridge VCI / CAN bridge VCI / I2C bridge IETR ENST ENST LISIF
10 Outline SoCLib goals SystemC modeling principles The Mutek Real-Time Operating System The MWMR communication middleware The DSX hardware/software codesign environment An application example : Stereovision
11 Communicating Synchronous FSM Model T0 T1 T2 CK R0 R1 R2 G0 G1 G2
12 Component Modeling E TRANSITION method STATE GENMEALY method GENMOORE method S S
13 The Mealy FSMs issue... The general behaviour of the cache component is a Mealy FSM, because there is a combinational dependency between ADR signal and INST signal PROCESSOR PC IR ADR INST => The PROCESSOR component must be evaluated before the CACHE component! combi CACHE
14 Mealy Dependency Graph The nodes are the signals The arrows are Mealy dependencies between signals X Y X Y Z Z
15 Static Scheduling As there is no cycle in the Mealy Dependency Graph, it is possible to define a static scheduling that respects all dependencies: For (cycle = 0 ; cycle < MAX ; cycle++) { MODULE_0::Transition() ;... MODULE_N::Transition() ; MODULE_0::genMoore() MODULE_N::genMoore() ; MODULE_0::genMealy() ; MODULE_N::genMealy() ; } The genmealy methods ordering must respect the dependencies, and can be derived from the sensitivity sets of the methods.
16 The Sensitivity Lists SC_METHOD(transition); sensitive_pos << CLK; SC_METHOD(genMoore); sensitive_neg << CLK; SC_METHOD(genMealy); sensitive_neg << CLK; sensitive << input0; sensitive << input1; To precisely describe the input -> output dependancies, there is one genmealy method per output signal for each hardware component.
17 SystemCASS All SocLib models can be efficiently used with the standard OSCI SystemC simulation engine that uses dynamic scheduling technics: All Transition» & «GenMoore» methods will be evaluated only one time per cycle The SoCLib models can be simulated with the SystemCASS simulation engine that uses static sceduling, and provides a simulation speedup of one order of magnitude!
18 Outline SoCLib goals The SoCLib virtual prototyping platform SystemC modeling principles The Mutek Real-Time Operating System The MWMR communication middleware The DSX hardware/software codesign environment An application example : Stereovision
19 Mutek : Embedded Operating System MUTEK is an embedded OS for MP-SoC : POSIX compliant : The multi-threaded software application can be executed on any workstation. Distributed scheduler : one scheduler per processor, for true scalability. Real-Time support : provides automatic re-initialisation in case of dead-line violation (soft real-time constraints). Controled Placement : allows the system designer to statically place the tasks on the processors, and the communication buffers on the memory banks. small foot-print : about 25 kbytes.
20 Mutek : status and evolution Mutek is jointly developped by several french laboratories (LIP6, TIMA, IRISA, CITI) The present version supports only symmetric, homogeneous multi-processor architectures, and has been ported on several micro-processor (MIPS, SPARC, OPENRISC, ARM). Two evolutions are in progress at LIP6 MUTEK/S : Static version (faster, but without POSIX compatibility) MUTEK/H : Heterogeneous version (supporting mixed hardware architectures, with both General Purposes Processors & Digital Signal Processors)
21 H-EXO layer H-EXO is a very thin hardware abstraction layer (exo-kernel), defined to support heterogeneous multi-processor architectures APPLICATIONS THREADS POSIX MUTEK/S MUTEK/H H-EXO HARDWARE
22 Outline SoCLib goals The SoCLib virtual prototyping platform SystemC modeling principles The Mutek Real-Time Operating System The MWMR communication middleware The DSX hardware/software codesign environment An application example : Stereovision
23 Software application modeling A parallel application is described with two types of components: A set of concurrent tasks A set of MWMR communication channels Each communication channel is implemented as a software FIFO. Each FIFO can have several writers and several readers. Software tasks use only two (blocking) communication functions : MWMR_read(channel, Buf_address, item_number) MWMR_write(channel, Buf_address, item_number) Each software task can be implemented as A software thread (without modification) A synthesized hardware coprocessor.
24 Task & Communication Graph T1 Ti Software task T0 Communication channel IN T2 OUT T1 T3
25 MWMR communication channel MWMR communication channels are implemented as software FIFOs, in a shared memory segment. Each MWMR FIFO is protected by a system lock. A FIFO can have several «producer» tasks and several «consumer» tasks, and each of those tasks can be implemented as hardware, or software : Both hardware and software implementations use the same protocol to acces the software FIFO. In the MWMR acces protocol, each MWMR acces generates six memory transactions. The software implementation of the MWMR_write() & MWMR_read() primitives is based on the POSIX threads => It can be directly simulated on any POSIX compliant workstation. The hardware implementation of the MWMR_write() & MWMR_read() primitives is based on a generic - VCI compliant - MWMR initiator. This hardware «wrapper» provides the synthesized hardware coprocessor a simple FIFO interface.
26 MWMR «wrapper» FIFO VCI HARDWARE COPROCESSOR (IP CORE) VCI_MWMR_INITIATOR WRAPPER VCI_RAM (containing the MWMR software FIFO) VCI interconnect The VCI_MWMR_initiator wrapper is a generic hardware component, that implements a variable number of read or write MWMR FIFO channels.
27 Outline SoCLib goals The SoCLib virtual prototyping platform SystemC modeling principles The Mutek Real-Time Operating System The MWMR communication middleware The DSX hardware/software codesign environment An application example : Stereovision
28 DSX : Design Space exploration The DSX environment provides 3 services : define the hardware architecture parameters (using several generic, parameterized platforms) define the software application architecture (Tasks & Communication Graph) map the software application on the architecture (memory space segmentation & placement constraints) This tool is based on the Python language. It generates : A SystemC description of the hardware architecture All script files for the binary code generation (GCC) /
29 DSX : Mapping Multi-thread application The system designer can : choose the hard/soft implementation for each task map the software tasks on the programmable processors and the hardware tasks on synthesized Multi-processor architecture (or existing) coprocessors map the inter-tasks communication buffers on the physical memory banks. map for each task, the private code & data segments on the physical memory banks.
30 Outline SoCLib goals The SoCLib virtual prototyping platform SystemC modeling principles The Mutek Real-Time Operating System The MWMR communication middleware The DSX hardware/software codesign environment An application example : Stereovision
31 An example : stéreo-vision The goal is obstacle detection for cars, by stereo-vision technics, using two synchronized cameras. Image size : 256 * 512 pixels (8 bits pixel) Fréquence : 40 couple of images per second The stereo-vision algorithm and the sequential software application have been developed by the LIVIC laboratory. We want to parallelize the algorithm and to map the corresponding multi-threaded software application on a MP-SoC architecture.
32 Stereo-vision : Genera Principle
33 Generic Hardware Architecture Sub-system 0 Sub-system 1 AQUIS/L MWMR µ Proc RAM Timer + Locks RAM Timer + Locks µ Proc AQUIS/R MWMR VCI Local Crossbar Local Crossbar VCI micro- network (DSPIN) VCI Local Crossbar Local Crossbar VCI µ Proc µ Proc RAM Timer + Locks µ Proc µ Proc RAM Timer + Locks Sub-system 2 Sub-system n
34 Stereo-Vision : Résults Hardware 8 clusters : (6 computation clusters, 2 acquisition clusters) 30 general purpose processors (MIPS R3000) 16 embedded memory banks (total memory capacity : 700 Koctets) silicon area (estimated) : 60 mm2 Software : 30 threads exécuting under the MUTEK OS Optimized task & communication channels placement (DSX) Soft real time violation management. Virtual prototyping (Cycle Accurate) : Simulation speed : cycles/s (on a 3GHz PC workstation) results : 6.8 million cycles per couple of images. => 22.6 ms at 300 MHz
35 Conclusion La plate-forme SoCLib vise le prototypage virtuel d applications logicielles embarquées complexes sur systèmes multi-processeurs intégrés sur puce. Cette plate-forme, financée par l ANR, sera accessible aux industriels et aux universitaires sous forme de logiciel libre : modèles de simulation des composants matériels, et outils logiciels de base. La première version accessible au public est prévue fin Cette plate-forme a clairement vocation à s intégrer dans un projet européen, qui reste à définir
Virtual Prototyping of NoC-based MPSoC : Fundamentals & Case Studies
 Virtual Prototyping of NoC-based MPSoC : Fundamentals & Case Studies Virtual Prototyping principles Virtual prototyping with TLM2.0, Laurent Maillet-Contoz, STMicro SystemC, and the various abstraction
Virtual Prototyping of NoC-based MPSoC : Fundamentals & Case Studies Virtual Prototyping principles Virtual prototyping with TLM2.0, Laurent Maillet-Contoz, STMicro SystemC, and the various abstraction
Outline. Introduction. Multiprocessor Systems on Chip. A MPSoC Example: Nexperia DVP. A New Paradigm: Network on Chip
 Outline Modeling, simulation and optimization of Multi-Processor SoCs (MPSoCs) Università of Verona Dipartimento di Informatica MPSoCs: Multi-Processor Systems on Chip A simulation platform for a MPSoC
Outline Modeling, simulation and optimization of Multi-Processor SoCs (MPSoCs) Università of Verona Dipartimento di Informatica MPSoCs: Multi-Processor Systems on Chip A simulation platform for a MPSoC
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms
 7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
7a. System-on-chip design and prototyping platforms Labros Bisdounis, Ph.D. Department of Computer and Communication Engineering 1 What is System-on-Chip (SoC)? System-on-chip is an integrated circuit
Architectures and Platforms
 Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
Hardware/Software Codesign Arch&Platf. - 1 Architectures and Platforms 1. Architecture Selection: The Basic Trade-Offs 2. General Purpose vs. Application-Specific Processors 3. Processor Specialisation
A New, High-Performance, Low-Power, Floating-Point Embedded Processor for Scientific Computing and DSP Applications
 1 A New, High-Performance, Low-Power, Floating-Point Embedded Processor for Scientific Computing and DSP Applications Simon McIntosh-Smith Director of Architecture 2 Multi-Threaded Array Processing Architecture
1 A New, High-Performance, Low-Power, Floating-Point Embedded Processor for Scientific Computing and DSP Applications Simon McIntosh-Smith Director of Architecture 2 Multi-Threaded Array Processing Architecture
Operating System Support for Multiprocessor Systems-on-Chip
 Operating System Support for Multiprocessor Systems-on-Chip Dr. Gabriel marchesan almeida Agenda. Introduction. Adaptive System + Shop Architecture. Preliminary Results. Perspectives & Conclusions Dr.
Operating System Support for Multiprocessor Systems-on-Chip Dr. Gabriel marchesan almeida Agenda. Introduction. Adaptive System + Shop Architecture. Preliminary Results. Perspectives & Conclusions Dr.
A Generic Network Interface Architecture for a Networked Processor Array (NePA)
 A Generic Network Interface Architecture for a Networked Processor Array (NePA) Seung Eun Lee, Jun Ho Bahn, Yoon Seok Yang, and Nader Bagherzadeh EECS @ University of California, Irvine Outline Introduction
A Generic Network Interface Architecture for a Networked Processor Array (NePA) Seung Eun Lee, Jun Ho Bahn, Yoon Seok Yang, and Nader Bagherzadeh EECS @ University of California, Irvine Outline Introduction
Digitale Signalverarbeitung mit FPGA (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007. Jens Onno Krah
 (DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
(DSF) Soft Core Prozessor NIOS II Stand Mai 2007 Jens Onno Krah Cologne University of Applied Sciences www.fh-koeln.de [email protected] NIOS II 1 1 What is Nios II? Altera s Second Generation
Agenda. Michele Taliercio, Il circuito Integrato, Novembre 2001
 Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
Agenda Introduzione Il mercato Dal circuito integrato al System on a Chip (SoC) La progettazione di un SoC La tecnologia Una fabbrica di circuiti integrati 28 How to handle complexity G The engineering
1-20020138637 26-sept-2002 Computer architecture and software cells for broadband networks Va avec 6526491
 Les brevets CELL 14 décembre 2006 1 ARCHITECTURE GENERALE 1-20020138637 26-sept-2002 Computer architecture and software cells for broadband networks 6526491 2-6526491 25-févr-03 Memory protection system
Les brevets CELL 14 décembre 2006 1 ARCHITECTURE GENERALE 1-20020138637 26-sept-2002 Computer architecture and software cells for broadband networks 6526491 2-6526491 25-févr-03 Memory protection system
Chapter 1 Computer System Overview
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 1 Computer System Overview Eighth Edition By William Stallings Operating System Exploits the hardware resources of one or more processors Provides
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 1 Computer System Overview Eighth Edition By William Stallings Operating System Exploits the hardware resources of one or more processors Provides
Introduction to Exploration and Optimization of Multiprocessor Embedded Architectures based on Networks On-Chip
 Introduction to Exploration and Optimization of Multiprocessor Embedded Architectures based on Networks On-Chip Cristina SILVANO [email protected] Politecnico di Milano, Milano (Italy) Talk Outline
Introduction to Exploration and Optimization of Multiprocessor Embedded Architectures based on Networks On-Chip Cristina SILVANO [email protected] Politecnico di Milano, Milano (Italy) Talk Outline
Introduction to System-on-Chip
 Introduction to System-on-Chip COE838: Systems-on-Chip Design http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~courses/coe838/ Dr. Gul N. Khan http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~gnkhan Electrical and Computer Engineering Ryerson University
Introduction to System-on-Chip COE838: Systems-on-Chip Design http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~courses/coe838/ Dr. Gul N. Khan http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~gnkhan Electrical and Computer Engineering Ryerson University
All Programmable Logic. Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems. Zürcher Fachhochschule
 All Programmable Logic Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Institute of Embedded Systems 31 Assistants 10 Professors 7 Technical Employees 2 Secretaries www.ines.zhaw.ch Research: Education:
All Programmable Logic Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Institute of Embedded Systems 31 Assistants 10 Professors 7 Technical Employees 2 Secretaries www.ines.zhaw.ch Research: Education:
Operating Systems 4 th Class
 Operating Systems 4 th Class Lecture 1 Operating Systems Operating systems are essential part of any computer system. Therefore, a course in operating systems is an essential part of any computer science
Operating Systems 4 th Class Lecture 1 Operating Systems Operating systems are essential part of any computer system. Therefore, a course in operating systems is an essential part of any computer science
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory
 ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-17: Memory organisation, and types of memory 1 1. Memory Organisation 2 Random access model A memory-, a data byte, or a word, or a double
Networking Virtualization Using FPGAs
 Networking Virtualization Using FPGAs Russell Tessier, Deepak Unnikrishnan, Dong Yin, and Lixin Gao Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Massachusetts,
Networking Virtualization Using FPGAs Russell Tessier, Deepak Unnikrishnan, Dong Yin, and Lixin Gao Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Massachusetts,
What is a System on a Chip?
 What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
What is a System on a Chip? Integration of a complete system, that until recently consisted of multiple ICs, onto a single IC. CPU PCI DSP SRAM ROM MPEG SoC DRAM System Chips Why? Characteristics: Complex
Multiprocessor System-on-Chip
 http://www.artistembedded.org/fp6/ ARTIST Workshop at DATE 06 W4: Design Issues in Distributed, CommunicationCentric Systems Modelling Networked Embedded Systems: From MPSoC to Sensor Networks Jan Madsen
http://www.artistembedded.org/fp6/ ARTIST Workshop at DATE 06 W4: Design Issues in Distributed, CommunicationCentric Systems Modelling Networked Embedded Systems: From MPSoC to Sensor Networks Jan Madsen
Introducción. Diseño de sistemas digitales.1
 Introducción Adapted from: Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) www.cse.psu.edu/~cg431 [Original from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005, UCB] Diseño de sistemas digitales.1
Introducción Adapted from: Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) www.cse.psu.edu/~cg431 [Original from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005, UCB] Diseño de sistemas digitales.1
Chapter 02: Computer Organization. Lesson 04: Functional units and components in a computer organization Part 3 Bus Structures
 Chapter 02: Computer Organization Lesson 04: Functional units and components in a computer organization Part 3 Bus Structures Objective: Understand the IO Subsystem and Understand Bus Structures Understand
Chapter 02: Computer Organization Lesson 04: Functional units and components in a computer organization Part 3 Bus Structures Objective: Understand the IO Subsystem and Understand Bus Structures Understand
Introduction to Cloud Computing
 Introduction to Cloud Computing Parallel Processing I 15 319, spring 2010 7 th Lecture, Feb 2 nd Majd F. Sakr Lecture Motivation Concurrency and why? Different flavors of parallel computing Get the basic
Introduction to Cloud Computing Parallel Processing I 15 319, spring 2010 7 th Lecture, Feb 2 nd Majd F. Sakr Lecture Motivation Concurrency and why? Different flavors of parallel computing Get the basic
Linux A multi-purpose executive support for civil avionics applications?
 August 2004 Serge GOIFFON Pierre GAUFILLET AIRBUS France Linux A multi-purpose executive support for civil avionics applications? Civil avionics software context Main characteristics Required dependability
August 2004 Serge GOIFFON Pierre GAUFILLET AIRBUS France Linux A multi-purpose executive support for civil avionics applications? Civil avionics software context Main characteristics Required dependability
SOC architecture and design
 SOC architecture and design system-on-chip (SOC) processors: become components in a system SOC covers many topics processor: pipelined, superscalar, VLIW, array, vector storage: cache, embedded and external
SOC architecture and design system-on-chip (SOC) processors: become components in a system SOC covers many topics processor: pipelined, superscalar, VLIW, array, vector storage: cache, embedded and external
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow. uk.ni.com ireland.ni.com
 Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
Best Practises for LabVIEW FPGA Design Flow 1 Agenda Overall Application Design Flow Host, Real-Time and FPGA LabVIEW FPGA Architecture Development FPGA Design Flow Common FPGA Architectures Testing and
OpenSPARC T1 Processor
 OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
OpenSPARC T1 Processor The OpenSPARC T1 processor is the first chip multiprocessor that fully implements the Sun Throughput Computing Initiative. Each of the eight SPARC processor cores has full hardware
System Considerations
 System Considerations Interfacing Performance Power Size Ease-of Use Programming Interfacing Debugging Cost Device cost System cost Development cost Time to market Integration Peripherals Different Needs?
System Considerations Interfacing Performance Power Size Ease-of Use Programming Interfacing Debugging Cost Device cost System cost Development cost Time to market Integration Peripherals Different Needs?
Codesign: The World Of Practice
 Codesign: The World Of Practice D. Sreenivasa Rao Senior Manager, System Level Integration Group Analog Devices Inc. May 2007 Analog Devices Inc. ADI is focused on high-end signal processing chips and
Codesign: The World Of Practice D. Sreenivasa Rao Senior Manager, System Level Integration Group Analog Devices Inc. May 2007 Analog Devices Inc. ADI is focused on high-end signal processing chips and
Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation
 Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation 386-Class Performance, Enhanced System Integration, and Built-in SRAM Problem with External RAM All embedded systems require RAM Low density SRAM moving
Am186ER/Am188ER AMD Continues 16-bit Innovation 386-Class Performance, Enhanced System Integration, and Built-in SRAM Problem with External RAM All embedded systems require RAM Low density SRAM moving
A Scalable VISC Processor Platform for Modern Client and Cloud Workloads
 A Scalable VISC Processor Platform for Modern Client and Cloud Workloads Mohammad Abdallah Founder, President and CTO Soft Machines Linley Processor Conference October 7, 2015 Agenda Soft Machines Background
A Scalable VISC Processor Platform for Modern Client and Cloud Workloads Mohammad Abdallah Founder, President and CTO Soft Machines Linley Processor Conference October 7, 2015 Agenda Soft Machines Background
DS1104 R&D Controller Board
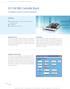 DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
DS1104 R&D Controller Board Cost-effective system for controller development Highlights Single-board system with real-time hardware and comprehensive I/O Cost-effective PCI hardware for use in PCs Application
Control 2004, University of Bath, UK, September 2004
 Control, University of Bath, UK, September ID- IMPACT OF DEPENDENCY AND LOAD BALANCING IN MULTITHREADING REAL-TIME CONTROL ALGORITHMS M A Hossain and M O Tokhi Department of Computing, The University of
Control, University of Bath, UK, September ID- IMPACT OF DEPENDENCY AND LOAD BALANCING IN MULTITHREADING REAL-TIME CONTROL ALGORITHMS M A Hossain and M O Tokhi Department of Computing, The University of
Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System
 Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System First Prize Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System Institution: Participants: Instructor: National Chung Hsing University
Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System First Prize Networking Remote-Controlled Moving Image Monitoring System Institution: Participants: Instructor: National Chung Hsing University
CHAPTER 1: OPERATING SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS
 CHAPTER 1: OPERATING SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS What is an operating? A collection of software modules to assist programmers in enhancing efficiency, flexibility, and robustness An Extended Machine from the users
CHAPTER 1: OPERATING SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS What is an operating? A collection of software modules to assist programmers in enhancing efficiency, flexibility, and robustness An Extended Machine from the users
Hardware Acceleration for Just-In-Time Compilation on Heterogeneous Embedded Systems
 Hardware Acceleration for Just-In-Time Compilation on Heterogeneous Embedded Systems A. Carbon, Y. Lhuillier, H.-P. Charles CEA LIST DACLE division Embedded Computing Embedded Software Laboratories France
Hardware Acceleration for Just-In-Time Compilation on Heterogeneous Embedded Systems A. Carbon, Y. Lhuillier, H.-P. Charles CEA LIST DACLE division Embedded Computing Embedded Software Laboratories France
OC By Arsene Fansi T. POLIMI 2008 1
 IBM POWER 6 MICROPROCESSOR OC By Arsene Fansi T. POLIMI 2008 1 WHAT S IBM POWER 6 MICROPOCESSOR The IBM POWER6 microprocessor powers the new IBM i-series* and p-series* systems. It s based on IBM POWER5
IBM POWER 6 MICROPROCESSOR OC By Arsene Fansi T. POLIMI 2008 1 WHAT S IBM POWER 6 MICROPOCESSOR The IBM POWER6 microprocessor powers the new IBM i-series* and p-series* systems. It s based on IBM POWER5
Trampoline OSEK-VDX & AUTOSAR Compliant Open Source Real-Time Operating System
 Trampoline OSEK-VDX & AUTOSAR Compliant Open Source Real-Time Operating System Jean-Luc Béchennec, Mikaël Briday, Sylvain Cotard, Sébastien Faucou, Yvon Trinquet Journée ACTRISS Outils. November 7, 2012
Trampoline OSEK-VDX & AUTOSAR Compliant Open Source Real-Time Operating System Jean-Luc Béchennec, Mikaël Briday, Sylvain Cotard, Sébastien Faucou, Yvon Trinquet Journée ACTRISS Outils. November 7, 2012
ESE566 REPORT3. Design Methodologies for Core-based System-on-Chip HUA TANG OVIDIU CARNU
 ESE566 REPORT3 Design Methodologies for Core-based System-on-Chip HUA TANG OVIDIU CARNU Nov 19th, 2002 ABSTRACT: In this report, we discuss several recent published papers on design methodologies of core-based
ESE566 REPORT3 Design Methodologies for Core-based System-on-Chip HUA TANG OVIDIU CARNU Nov 19th, 2002 ABSTRACT: In this report, we discuss several recent published papers on design methodologies of core-based
Computer System Design. System-on-Chip
 Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2171000/ Computer System Design. System-on-Chip Description: The next generation of computer system designers will be less concerned
Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2171000/ Computer System Design. System-on-Chip Description: The next generation of computer system designers will be less concerned
A Comparison of Distributed Systems: ChorusOS and Amoeba
 A Comparison of Distributed Systems: ChorusOS and Amoeba Angelo Bertolli Prepared for MSIT 610 on October 27, 2004 University of Maryland University College Adelphi, Maryland United States of America Abstract.
A Comparison of Distributed Systems: ChorusOS and Amoeba Angelo Bertolli Prepared for MSIT 610 on October 27, 2004 University of Maryland University College Adelphi, Maryland United States of America Abstract.
Breaking the Interleaving Bottleneck in Communication Applications for Efficient SoC Implementations
 Microelectronic System Design Research Group University Kaiserslautern www.eit.uni-kl.de/wehn Breaking the Interleaving Bottleneck in Communication Applications for Efficient SoC Implementations Norbert
Microelectronic System Design Research Group University Kaiserslautern www.eit.uni-kl.de/wehn Breaking the Interleaving Bottleneck in Communication Applications for Efficient SoC Implementations Norbert
Contents. Chapter 1. Introduction
 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Computer-System Structures 3. Operating-System Structures 4. Processes 5. Threads 6. CPU Scheduling 7. Process Synchronization 8. Deadlocks 9. Memory Management 10. Virtual
Contents 1. Introduction 2. Computer-System Structures 3. Operating-System Structures 4. Processes 5. Threads 6. CPU Scheduling 7. Process Synchronization 8. Deadlocks 9. Memory Management 10. Virtual
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren. Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor
 Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
Von der Hardware zur Software in FPGAs mit Embedded Prozessoren Alexander Hahn Senior Field Application Engineer Lattice Semiconductor AGENDA Overview Mico32 Embedded Processor Development Tool Chain HW/SW
Logical Operations. Control Unit. Contents. Arithmetic Operations. Objectives. The Central Processing Unit: Arithmetic / Logic Unit.
 Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Objectives The Central Processing Unit: What Goes on Inside the Computer Chapter 4 Identify the components of the central processing unit and how they work together and interact with memory Describe how
Weighted Total Mark. Weighted Exam Mark
 CMP2204 Operating System Technologies Period per Week Contact Hour per Semester Total Mark Exam Mark Continuous Assessment Mark Credit Units LH PH TH CH WTM WEM WCM CU 45 30 00 60 100 40 100 4 Rationale
CMP2204 Operating System Technologies Period per Week Contact Hour per Semester Total Mark Exam Mark Continuous Assessment Mark Credit Units LH PH TH CH WTM WEM WCM CU 45 30 00 60 100 40 100 4 Rationale
Code generation under Control
 Code generation under Control Rencontres sur la compilation / Saint Hippolyte Henri-Pierre Charles CEA Laboratoire LaSTRE / Grenoble 12 décembre 2011 Introduction Présentation Henri-Pierre Charles, two
Code generation under Control Rencontres sur la compilation / Saint Hippolyte Henri-Pierre Charles CEA Laboratoire LaSTRE / Grenoble 12 décembre 2011 Introduction Présentation Henri-Pierre Charles, two
Applying the Benefits of Network on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design
 Applying the Benefits of on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design WP-01149-1.1 White Paper This document describes the advantages of network on a chip (NoC) architecture in Altera FPGA system design.
Applying the Benefits of on a Chip Architecture to FPGA System Design WP-01149-1.1 White Paper This document describes the advantages of network on a chip (NoC) architecture in Altera FPGA system design.
Chapter 18: Database System Architectures. Centralized Systems
 Chapter 18: Database System Architectures! Centralized Systems! Client--Server Systems! Parallel Systems! Distributed Systems! Network Types 18.1 Centralized Systems! Run on a single computer system and
Chapter 18: Database System Architectures! Centralized Systems! Client--Server Systems! Parallel Systems! Distributed Systems! Network Types 18.1 Centralized Systems! Run on a single computer system and
Real-Time Operating Systems for MPSoCs
 Real-Time Operating Systems for MPSoCs Hiroyuki Tomiyama Graduate School of Information Science Nagoya University http://member.acm.org/~hiroyuki MPSoC 2009 1 Contributors Hiroaki Takada Director and Professor
Real-Time Operating Systems for MPSoCs Hiroyuki Tomiyama Graduate School of Information Science Nagoya University http://member.acm.org/~hiroyuki MPSoC 2009 1 Contributors Hiroaki Takada Director and Professor
Computer Organization
 Computer Organization and Architecture Designing for Performance Ninth Edition William Stallings International Edition contributions by R. Mohan National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli PEARSON
Computer Organization and Architecture Designing for Performance Ninth Edition William Stallings International Edition contributions by R. Mohan National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli PEARSON
The Orca Chip... Heart of IBM s RISC System/6000 Value Servers
 The Orca Chip... Heart of IBM s RISC System/6000 Value Servers Ravi Arimilli IBM RISC System/6000 Division 1 Agenda. Server Background. Cache Heirarchy Performance Study. RS/6000 Value Server System Structure.
The Orca Chip... Heart of IBM s RISC System/6000 Value Servers Ravi Arimilli IBM RISC System/6000 Division 1 Agenda. Server Background. Cache Heirarchy Performance Study. RS/6000 Value Server System Structure.
Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics
 Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics Paul Chow High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Who
Seeking Opportunities for Hardware Acceleration in Big Data Analytics Paul Chow High-Performance Reconfigurable Computing Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Who
PikeOS: Multi-Core RTOS for IMA. Dr. Sergey Tverdyshev SYSGO AG 29.10.2012, Moscow
 PikeOS: Multi-Core RTOS for IMA Dr. Sergey Tverdyshev SYSGO AG 29.10.2012, Moscow Contents Multi Core Overview Hardware Considerations Multi Core Software Design Certification Consideratins PikeOS Multi-Core
PikeOS: Multi-Core RTOS for IMA Dr. Sergey Tverdyshev SYSGO AG 29.10.2012, Moscow Contents Multi Core Overview Hardware Considerations Multi Core Software Design Certification Consideratins PikeOS Multi-Core
Centralized Systems. A Centralized Computer System. Chapter 18: Database System Architectures
 Chapter 18: Database System Architectures Centralized Systems! Centralized Systems! Client--Server Systems! Parallel Systems! Distributed Systems! Network Types! Run on a single computer system and do
Chapter 18: Database System Architectures Centralized Systems! Centralized Systems! Client--Server Systems! Parallel Systems! Distributed Systems! Network Types! Run on a single computer system and do
Network connectivity controllers
 Network connectivity controllers High performance connectivity solutions Factory Automation The hostile environment of many factories can have a significant impact on the life expectancy of PCs, and industrially
Network connectivity controllers High performance connectivity solutions Factory Automation The hostile environment of many factories can have a significant impact on the life expectancy of PCs, and industrially
Operating Systems for Parallel Processing Assistent Lecturer Alecu Felician Economic Informatics Department Academy of Economic Studies Bucharest
 Operating Systems for Parallel Processing Assistent Lecturer Alecu Felician Economic Informatics Department Academy of Economic Studies Bucharest 1. Introduction Few years ago, parallel computers could
Operating Systems for Parallel Processing Assistent Lecturer Alecu Felician Economic Informatics Department Academy of Economic Studies Bucharest 1. Introduction Few years ago, parallel computers could
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 MOTIVATION OF RESEARCH Multicore processors have two or more execution cores (processors) implemented on a single chip having their own set of execution and architectural recourses.
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 MOTIVATION OF RESEARCH Multicore processors have two or more execution cores (processors) implemented on a single chip having their own set of execution and architectural recourses.
Throughput constraint for Synchronous Data Flow Graphs
 Throughput constraint for Synchronous Data Flow Graphs *Alessio Bonfietti Michele Lombardi Michela Milano Luca Benini!"#$%&'()*+,-)./&0&20304(5 60,7&-8990,.+:&;/&."!?@A>&"'&=,0B+C. !"#$%&'()* Resource
Throughput constraint for Synchronous Data Flow Graphs *Alessio Bonfietti Michele Lombardi Michela Milano Luca Benini!"#$%&'()*+,-)./&0&20304(5 60,7&-8990,.+:&;/&."!?@A>&"'&=,0B+C. !"#$%&'()* Resource
Open Source Software
 Open Source Software Title Experiences and considerations about open source software for standard software components in automotive environments 2 Overview Experiences Project Findings Considerations X-by-wire
Open Source Software Title Experiences and considerations about open source software for standard software components in automotive environments 2 Overview Experiences Project Findings Considerations X-by-wire
System Design Issues in Embedded Processing
 System Design Issues in Embedded Processing 9/16/10 Jacob Borgeson 1 Agenda What does TI do? From MCU to MPU to DSP: What are some trends? Design Challenges Tools to Help 2 TI - the complete system The
System Design Issues in Embedded Processing 9/16/10 Jacob Borgeson 1 Agenda What does TI do? From MCU to MPU to DSP: What are some trends? Design Challenges Tools to Help 2 TI - the complete system The
Architekturen und Einsatz von FPGAs mit integrierten Prozessor Kernen. Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Professur für Mikroelektronik
 Architekturen und Einsatz von FPGAs mit integrierten Prozessor Kernen Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Professur für Mikroelektronik Contents Überblick: Aufbau moderner FPGA Einblick: Eigenschaften
Architekturen und Einsatz von FPGAs mit integrierten Prozessor Kernen Hans-Joachim Gelke Institute of Embedded Systems Professur für Mikroelektronik Contents Überblick: Aufbau moderner FPGA Einblick: Eigenschaften
Overview. Surveillance Systems. The Smart Camera - Hardware
 Overview A Mobile AgentAgent-based System for Dynamic Task Allocation in Clusters of Embedded Smart Cameras Introduction The Smart Camera Michael Bramberger1,, Bernhard Rinner1, and Helmut Schwabach Surveillance
Overview A Mobile AgentAgent-based System for Dynamic Task Allocation in Clusters of Embedded Smart Cameras Introduction The Smart Camera Michael Bramberger1,, Bernhard Rinner1, and Helmut Schwabach Surveillance
High Performance or Cycle Accuracy?
 CHIP DESIGN High Performance or Cycle Accuracy? You can have both! Bill Neifert, Carbon Design Systems Rob Kaye, ARM ATC-100 AGENDA Modelling 101 & Programmer s View (PV) Models Cycle Accurate Models Bringing
CHIP DESIGN High Performance or Cycle Accuracy? You can have both! Bill Neifert, Carbon Design Systems Rob Kaye, ARM ATC-100 AGENDA Modelling 101 & Programmer s View (PV) Models Cycle Accurate Models Bringing
Computer Performance. Topic 3. Contents. Prerequisite knowledge Before studying this topic you should be able to:
 55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
55 Topic 3 Computer Performance Contents 3.1 Introduction...................................... 56 3.2 Measuring performance............................... 56 3.2.1 Clock Speed.................................
GEDAE TM - A Graphical Programming and Autocode Generation Tool for Signal Processor Applications
 GEDAE TM - A Graphical Programming and Autocode Generation Tool for Signal Processor Applications Harris Z. Zebrowitz Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Laboratories 1 Federal Street Camden, NJ 08102
GEDAE TM - A Graphical Programming and Autocode Generation Tool for Signal Processor Applications Harris Z. Zebrowitz Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Laboratories 1 Federal Street Camden, NJ 08102
Performance Comparison of RTOS
 Performance Comparison of RTOS Shahmil Merchant, Kalpen Dedhia Dept Of Computer Science. Columbia University Abstract: Embedded systems are becoming an integral part of commercial products today. Mobile
Performance Comparison of RTOS Shahmil Merchant, Kalpen Dedhia Dept Of Computer Science. Columbia University Abstract: Embedded systems are becoming an integral part of commercial products today. Mobile
Chapter 13 Embedded Operating Systems
 Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 13 Embedded Operating Systems Eighth Edition By William Stallings Embedded System Refers to the use of electronics and software within a product
Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles Chapter 13 Embedded Operating Systems Eighth Edition By William Stallings Embedded System Refers to the use of electronics and software within a product
Master Interface For On-Chip Hardware Accelerator Burst Communications
 Master Interface For On-Chip Hardware Accelerator Burst Communications Antoine Fraboulet Compsys, Lip 46 Allée d Italie 69363 Lyon cedex 07 France [email protected] Tanguy Risset Citi, Insa-Lyon,
Master Interface For On-Chip Hardware Accelerator Burst Communications Antoine Fraboulet Compsys, Lip 46 Allée d Italie 69363 Lyon cedex 07 France [email protected] Tanguy Risset Citi, Insa-Lyon,
Design and Implementation of the Heterogeneous Multikernel Operating System
 223 Design and Implementation of the Heterogeneous Multikernel Operating System Yauhen KLIMIANKOU Department of Computer Systems and Networks, Belarusian State University of Informatics and Radioelectronics,
223 Design and Implementation of the Heterogeneous Multikernel Operating System Yauhen KLIMIANKOU Department of Computer Systems and Networks, Belarusian State University of Informatics and Radioelectronics,
Computer System: User s View. Computer System Components: High Level View. Input. Output. Computer. Computer System: Motherboard Level
 System: User s View System Components: High Level View Input Output 1 System: Motherboard Level 2 Components: Interconnection I/O MEMORY 3 4 Organization Registers ALU CU 5 6 1 Input/Output I/O MEMORY
System: User s View System Components: High Level View Input Output 1 System: Motherboard Level 2 Components: Interconnection I/O MEMORY 3 4 Organization Registers ALU CU 5 6 1 Input/Output I/O MEMORY
Introduction to Virtual Machines
 Introduction to Virtual Machines Introduction Abstraction and interfaces Virtualization Computer system architecture Process virtual machines System virtual machines 1 Abstraction Mechanism to manage complexity
Introduction to Virtual Machines Introduction Abstraction and interfaces Virtualization Computer system architecture Process virtual machines System virtual machines 1 Abstraction Mechanism to manage complexity
Architecture of Hitachi SR-8000
 Architecture of Hitachi SR-8000 University of Stuttgart High-Performance Computing-Center Stuttgart (HLRS) www.hlrs.de Slide 1 Most of the slides from Hitachi Slide 2 the problem modern computer are data
Architecture of Hitachi SR-8000 University of Stuttgart High-Performance Computing-Center Stuttgart (HLRS) www.hlrs.de Slide 1 Most of the slides from Hitachi Slide 2 the problem modern computer are data
FPGA-based Multithreading for In-Memory Hash Joins
 FPGA-based Multithreading for In-Memory Hash Joins Robert J. Halstead, Ildar Absalyamov, Walid A. Najjar, Vassilis J. Tsotras University of California, Riverside Outline Background What are FPGAs Multithreaded
FPGA-based Multithreading for In-Memory Hash Joins Robert J. Halstead, Ildar Absalyamov, Walid A. Najjar, Vassilis J. Tsotras University of California, Riverside Outline Background What are FPGAs Multithreaded
Software engineering for real-time systems
 Introduction Software engineering for real-time systems Objectives To: Section 1 Introduction to real-time systems Outline the differences between general-purpose applications and real-time systems. Give
Introduction Software engineering for real-time systems Objectives To: Section 1 Introduction to real-time systems Outline the differences between general-purpose applications and real-time systems. Give
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-12: ARM
 ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-12: ARM 1 The ARM architecture processors popular in Mobile phone systems 2 ARM Features ARM has 32-bit architecture but supports 16 bit
ADVANCED PROCESSOR ARCHITECTURES AND MEMORY ORGANISATION Lesson-12: ARM 1 The ARM architecture processors popular in Mobile phone systems 2 ARM Features ARM has 32-bit architecture but supports 16 bit
Red Hat Linux Internals
 Red Hat Linux Internals Learn how the Linux kernel functions and start developing modules. Red Hat Linux internals teaches you all the fundamental requirements necessary to understand and start developing
Red Hat Linux Internals Learn how the Linux kernel functions and start developing modules. Red Hat Linux internals teaches you all the fundamental requirements necessary to understand and start developing
Reconfigurable Architecture Requirements for Co-Designed Virtual Machines
 Reconfigurable Architecture Requirements for Co-Designed Virtual Machines Kenneth B. Kent University of New Brunswick Faculty of Computer Science Fredericton, New Brunswick, Canada [email protected] Micaela Serra
Reconfigurable Architecture Requirements for Co-Designed Virtual Machines Kenneth B. Kent University of New Brunswick Faculty of Computer Science Fredericton, New Brunswick, Canada [email protected] Micaela Serra
Making Multicore Work and Measuring its Benefits. Markus Levy, president EEMBC and Multicore Association
 Making Multicore Work and Measuring its Benefits Markus Levy, president EEMBC and Multicore Association Agenda Why Multicore? Standards and issues in the multicore community What is Multicore Association?
Making Multicore Work and Measuring its Benefits Markus Levy, president EEMBC and Multicore Association Agenda Why Multicore? Standards and issues in the multicore community What is Multicore Association?
Building Blocks for PRU Development
 Building Blocks for PRU Development Module 1 PRU Hardware Overview This session covers a hardware overview of the PRU-ICSS Subsystem. Author: Texas Instruments, Sitara ARM Processors Oct 2014 2 ARM SoC
Building Blocks for PRU Development Module 1 PRU Hardware Overview This session covers a hardware overview of the PRU-ICSS Subsystem. Author: Texas Instruments, Sitara ARM Processors Oct 2014 2 ARM SoC
ELEC 5260/6260/6266 Embedded Computing Systems
 ELEC 5260/6260/6266 Embedded Computing Systems Spring 2016 Victor P. Nelson Text: Computers as Components, 3 rd Edition Prof. Marilyn Wolf (Georgia Tech) Course Topics Embedded system design & modeling
ELEC 5260/6260/6266 Embedded Computing Systems Spring 2016 Victor P. Nelson Text: Computers as Components, 3 rd Edition Prof. Marilyn Wolf (Georgia Tech) Course Topics Embedded system design & modeling
FRANCIS XAVIER ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 EC2042-Embedded and Real time Systems Unit I - I INTRODUCTION TO EMBEDDED COMPUTING Part-A (2 Marks) 1. What is an embedded system? An embedded system employs a combination of hardware & software (a computational
EC2042-Embedded and Real time Systems Unit I - I INTRODUCTION TO EMBEDDED COMPUTING Part-A (2 Marks) 1. What is an embedded system? An embedded system employs a combination of hardware & software (a computational
A case study of mobile SoC architecture design based on transaction-level modeling
 A case study of mobile SoC architecture design based on transaction-level modeling Eui-Young Chung School of Electrical & Electronic Eng. Yonsei University 1 EUI-YOUNG(EY) CHUNG, EY CHUNG Outline Introduction
A case study of mobile SoC architecture design based on transaction-level modeling Eui-Young Chung School of Electrical & Electronic Eng. Yonsei University 1 EUI-YOUNG(EY) CHUNG, EY CHUNG Outline Introduction
Module 8. Industrial Embedded and Communication Systems. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 8 Industrial Embedded and Communication Systems Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 37 Real-Time Operating Systems: Introduction and Process Management Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional
Module 8 Industrial Embedded and Communication Systems Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 37 Real-Time Operating Systems: Introduction and Process Management Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional
From Bus and Crossbar to Network-On-Chip. Arteris S.A.
 From Bus and Crossbar to Network-On-Chip Arteris S.A. Copyright 2009 Arteris S.A. All rights reserved. Contact information Corporate Headquarters Arteris, Inc. 1741 Technology Drive, Suite 250 San Jose,
From Bus and Crossbar to Network-On-Chip Arteris S.A. Copyright 2009 Arteris S.A. All rights reserved. Contact information Corporate Headquarters Arteris, Inc. 1741 Technology Drive, Suite 250 San Jose,
Special FEATURE. By Heinrich Munz
 Special FEATURE By Heinrich Munz Heinrich Munz of KUKA Roboter discusses in this article how to bring Microsoft Windows CE and WindowsXP together on the same PC. He discusses system and application requirements,
Special FEATURE By Heinrich Munz Heinrich Munz of KUKA Roboter discusses in this article how to bring Microsoft Windows CE and WindowsXP together on the same PC. He discusses system and application requirements,
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output
 Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
Computer Systems Structure Input/Output Peripherals Computer Central Processing Unit Main Memory Computer Systems Interconnection Communication lines Input Output Ward 1 Ward 2 Examples of I/O Devices
Comparative Performance Review of SHA-3 Candidates
 Comparative Performance Review of the SHA-3 Second-Round Candidates Cryptolog International Second SHA-3 Candidate Conference Outline sphlib sphlib sphlib is an open-source implementation of many hash
Comparative Performance Review of the SHA-3 Second-Round Candidates Cryptolog International Second SHA-3 Candidate Conference Outline sphlib sphlib sphlib is an open-source implementation of many hash
Lesson 7: SYSTEM-ON. SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN TECHNOLOGY. Chapter-1L07: "Embedded Systems - ", Raj Kamal, Publs.: McGraw-Hill Education
 Lesson 7: SYSTEM-ON ON-CHIP (SoC( SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN TECHNOLOGY 1 VLSI chip Integration of high-level components Possess gate-level sophistication in circuits above that of the counter,
Lesson 7: SYSTEM-ON ON-CHIP (SoC( SoC) AND USE OF VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN TECHNOLOGY 1 VLSI chip Integration of high-level components Possess gate-level sophistication in circuits above that of the counter,
Principles and characteristics of distributed systems and environments
 Principles and characteristics of distributed systems and environments Definition of a distributed system Distributed system is a collection of independent computers that appears to its users as a single
Principles and characteristics of distributed systems and environments Definition of a distributed system Distributed system is a collection of independent computers that appears to its users as a single
Early Hardware/Software Integration Using SystemC 2.0
 Early Hardware/Software Integration Using SystemC 2.0 Jon Connell, ARM. Bruce Johnson, Synopsys, Inc. Class 552, ESC San Francisco 2002 Abstract Capabilities added to SystemC 2.0 provide the needed expressiveness
Early Hardware/Software Integration Using SystemC 2.0 Jon Connell, ARM. Bruce Johnson, Synopsys, Inc. Class 552, ESC San Francisco 2002 Abstract Capabilities added to SystemC 2.0 provide the needed expressiveness
CS550. Distributed Operating Systems (Advanced Operating Systems) Instructor: Xian-He Sun
 CS550 Distributed Operating Systems (Advanced Operating Systems) Instructor: Xian-He Sun Email: [email protected], Phone: (312) 567-5260 Office hours: 2:10pm-3:10pm Tuesday, 3:30pm-4:30pm Thursday at SB229C,
CS550 Distributed Operating Systems (Advanced Operating Systems) Instructor: Xian-He Sun Email: [email protected], Phone: (312) 567-5260 Office hours: 2:10pm-3:10pm Tuesday, 3:30pm-4:30pm Thursday at SB229C,
The Temporal Firewall--A Standardized Interface in the Time-Triggered Architecture
 1 The Temporal Firewall--A Standardized Interface in the Time-Triggered Architecture H. Kopetz TU Vienna, Austria July 2000 Outline 2 Introduction Temporal Accuracy of RT Information The Time-Triggered
1 The Temporal Firewall--A Standardized Interface in the Time-Triggered Architecture H. Kopetz TU Vienna, Austria July 2000 Outline 2 Introduction Temporal Accuracy of RT Information The Time-Triggered
Going Linux on Massive Multicore
 Embedded Linux Conference Europe 2013 Going Linux on Massive Multicore Marta Rybczyńska 24th October, 2013 Agenda Architecture Linux Port Core Peripherals Debugging Summary and Future Plans 2 Agenda Architecture
Embedded Linux Conference Europe 2013 Going Linux on Massive Multicore Marta Rybczyńska 24th October, 2013 Agenda Architecture Linux Port Core Peripherals Debugging Summary and Future Plans 2 Agenda Architecture
Designing and Embodiment of Software that Creates Middle Ware for Resource Management in Embedded System
 , pp.97-108 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2014.8.6.08 Designing and Embodiment of Software that Creates Middle Ware for Resource Management in Embedded System Suk Hwan Moon and Cheol sick Lee Department
, pp.97-108 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijseia.2014.8.6.08 Designing and Embodiment of Software that Creates Middle Ware for Resource Management in Embedded System Suk Hwan Moon and Cheol sick Lee Department
SYSTEM ecos Embedded Configurable Operating System
 BELONGS TO THE CYGNUS SOLUTIONS founded about 1989 initiative connected with an idea of free software ( commercial support for the free software ). Recently merged with RedHat. CYGNUS was also the original
BELONGS TO THE CYGNUS SOLUTIONS founded about 1989 initiative connected with an idea of free software ( commercial support for the free software ). Recently merged with RedHat. CYGNUS was also the original
