Laboratory 7 Brain Anatomy
|
|
|
- Reynard Andrews
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Laboratory 7 Brain Anatomy Goals: Describe the organization & function of the three meningeal layers. Explain where cerebrospinal fluid is found in the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the human brain using models. Identify the major structures of the sheep brain by dissection. Identify selected cranial nerves on the human and sheep brains. 1. Coverings of the Brain: The brain and spinal cord are protected by multiple layers of tissue. Most external is the skin, followed by the skull. Underneath the skull are three layers of connective tissue membranes collectively referred to as meninges. The outer most layer is called the dura mater (literally, hard or tough mother). It is a tough, double- layered membrane. The most superficial layer of the dura mater forms the inner periosteum of the cranial bones. The middle layer, the arachnoid mater (think spider) has a delicate spider web- like appearance and helps to cushion the brain. The innermost layer, the pia mater (literally soft mother), is a thin, waterproof layer that adheres to the outer surface of the brain and spinal cord. Identification: On the sheep brain, identify the three layers of the meninges. Identify & remove the dura and arachnoid maters. 2. Regions of the Brain: The cerebral hemispheres form the largest part of the human brain and are situated above most other brain structures. They are covered with a cortical layer with many bumps and grooves called the cerebrum. The visible part of the cerebrum is the neocortex. Interior to the cortex is the midbrain. Underneath the cerebrum lies the brainstem, resembling handle underneath the main portion of the brain. At the rear of the brain, beneath the cerebrum and behind the brainstem, is the cerebellum, a structure with a much finer bumps than the cerebrum. The same structures are present in other mammals, although the cerebellum is not so large relative to the rest of the brain. During development, the brain develops from three expansions of the embryonic neural tube referred to as the forebrain (also called the proencephalon), midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon). The forebrain forms the largest region of the human brain form forming the telencephelon or cerebrum, and the diencephalon. The diencephalon becomes the thalamus and hypothalamus controlling movement and autonomic/endocrine function, respectively. The midbrain is the smallest region and is located between the forebrain and hindbrain. The midbrain contains a number 91
2 of nuclei involved in relaying auditory and visual information and in regulating voluntary muscle movement. The hindbrain is closest to the spinal cord and forms the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata. Figure 2. Developmental brain regions in the mammalian brain. Some brain systems transverse multiple brain regions. For example, voluntary movement begins in the neocortex, but normal voluntary movement also requires input from the cerebellum and midbrain and signals are relayed in the thalamus. Identification: On the sheep brain, identify the telencephalon (or cerebrum), cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata. The diencephalon and midbrain will not be visible. On a human brain model, identify all six brain regions. 3. Surface anatomy of the brain Cerebral lobes The cerebrum is forms the most superior portion of the brain and is divided by a prominent longitudinal fissure into right and left hemispheres. These hemispheres are further dived into five cerebral lobes. The four cerebral lobes on the surface of the brain are named after the skull bones under which they lie: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital. The insular lobe can be found interior to the lateral sulcus separating the parietal and temporal lobes. 92
3 Note that the surface of the cerebral hemispheres has ridges of tissue called gyri (singular gyrus) separated by grooves called sulci (singular sulcus). Deeper sulci are referred to as fissures that separate the cerebrum into five cerebral lobes. Forming the border between the frontal and parietal lobes, the central sulcus is perpendicular to the longitudinal fissure on each lateral aspect of the brain. The lateral sulcus separates the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes. The transverse fissure separates the neocortex from the cerebellum. Importantly, the precentral and postcentral gyri are anterior and posterior to the central sulcus. The precentral gyrus is also known as the primary motor cortex. Neurons in this cortical region are responsible for initiating voluntary movement. The postcentral gyrus is also known as the primary somatosensory cortex and the region responsible for conscious sensation from our tactile senses for the body, Connecting the right and left cerebral hemispheres, and visible from the dorsal (superior) aspect if you gently pull apart the hemispheres along the longitudinal fissure is the corpus collusum. This structure is comprised of white matter tracts that allow communication between the two cortical hemispheres. Identification: On the sheep brain and a human brain model, identify gyri, sulci, the 4 primary lobes of the cerebral hemispheres and the major grooves & fissures. 93
4 4.Surface anatomy of the brain Ventral aspect: From the ventral or inferior aspect of the brain, the frontal and temporal lobes are apparent as well as the midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata. All twelve cranial nerve are also visible from the ventral view. The cranial nerves and their locations are described in the next laboratory. The olfactory bulbs, the neural tissue responsible for the sense of smell, are found on the underside of the frontal lobes. These give rise to the first set of cranial nerves, the olfactory nerve. The optic nerves form an X at the optic chiasm and continues as the optic tract until the synapsing in the thalamus. The rest of the cranial nerves can be seen along the pons and brainstem. Just posterior to the optic chiasm, you can see the infundibular stalk which connects to the pituitary gland and the mammillary bodies. Posterior to the hypothalamus are two large tracts called the cerebral peduncles and this represents the part of the midbrain viewable from this aspect. The medial gyrus on the temporal lobe is the parahippocampal gyrus. Immediately deep to this gyrus is the hippocampus, part of the limbic system. 94
5 5. Anatomy of the Midsaggital Section: The midsaggital section is a view of the brain bisected along the longitudinal fissure. From this view, the frontal, parietal and occipital lobes are seen. Two white matter tracts are readily apparent: the larger corpus collosum which allows communication between the hemisphere and the fornix which is the white matter tract leaving the hippocampus. White matter in the brain consists of myelinated axons as compared to gray matter that consists of cells bodies and unmyelinated neurites. The opening seen between the two white matter structures is the lateral ventricle. The third ventricle is the space medial to the hypothalamus connected to the fourth ventricle between the cerebellum and brainstem by the cerebral aquaduct. Immediately inferior to the fornix is a largish rounded area of the thalamus. Anterior and slightly inferior is the triangularly shaped hypothalamus. The infidibulum is a stalk projecting from the anterior point of the hypothalamus and is attached to the pituaitary. Immediately caudal to the hypothalamus is the rounded mammillary body. The midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata are seen as the cerebellum with the cerebellar white matter tracts known as the arbor vitae. Identification: On the sheep brain and a human brain model, identify as many of the surface structures shown in the above illustrations as possible. 95
6 6. Cerebellum: The cerebellum is located on the caudal aspect of the brain, with the large mass of the cerebral cortex above it and the portion of the brainstem called the pons anterior. The cerebellum is divided into right and left halves with the vermis (latin for worm) protruding midline. The cerebellum, responsible for fine control of voluntary movement, is composed of a gray matter cortex and a white matter arbor vitae. 7. Ventricles: There are a series of hollow spaces within the brain called ventricles. The ventricles are continuous with each other as well as the central canal of the spinal Figure 7. Posterior view of the cerebellum. cord through a series of canals. The two large, C- shaped lateral ventricles encircle the two thalamic lobes and connect medially (via interventricular foramina) to a centrally located third ventricle. Arising from the posterior- ventral wall of the third ventricle, the cerebral aqueduct runs inferior to the corpora quadrigemina of the midbrain to the fourth ventricle, which lies inferior to the cerebrum. The central canal of the spinal cord begins at the base of the fourth ventricle. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is produced by special vascularized patches of tissue within the ventricles called choroid plexus, fills the ventricles, ducts, central canal. CSF flows from the ventricles to the central canal, which is continuous with the subarachnoid space surrounding the entire central nervous system. Once the CSF returns to the head, it is drained through specialized shunts called arachoid villi and returned to the circulatory system. Cerebral Aquaduct Identification: On the sheep brain and a human brain model, identify the choroid plexus, lateral ventricles, third ventricle, cerebral aqueduct & fourth ventricle. 96
7 8. Sheep Brain Dissection Use the following link for guidance on sheep brain dissection: Use a digital camera or cell phone camera, take pictures of the sheep brain as you dissect it. You should have at least (but are not limited to) one image from each of the different primary views (inferior, superior, lateral & midsagital section), Place images into a Powerpoint or Google presentation (ASK YOUR INSTRUCTOR IF THEY HAVE A PREFERENCE) and label as many of the following structures as you can in each image (you should be able to label all the structures on the list at least once): Cerebrum Frontal lobe Temporal lobe Parietal lobe Occipital lobe Precentral gyrus Postcentral gyrus Central sulcus Lateral sulcus Transverse fissure Longitudinal fissure Corpus collosum Fornix Thalamus Hypothalamus Lateral ventricles Third ventricle Cerebral aquaduct Fourth ventricle Cerebellum Vermis Arbor vitae Midbrain Pons Medulla Olfactory bulb Optic nerve Optic chiasm Optic tract Attach the Word document to the back of your lab report or share and the Google Doc to your instructor. ASK YOUR INSTRUCTOR WHICH THEY PREFER. 97
8 Attributions: Figure 1. National Cancer Institute (n.d.). [Meninges of the CNS]. SEER Training Modules, The Central Nervous System. Retrieved July 12, 2012 from Figure 2. Nrets (2007). [Encephalon]. and Looie496(2008). [Vertebrate- brain- regions]. Wikimedia Coomons. Retrieved August 16, 2012 from brain- regions.pn. Figure 3. Looie496. (2011). [Vertebrate brain regions]. Wikimedia Commons. Retrieved July 12, 2012 from brain- regions_small.png. Figure 4. NEUROtiker. (2007). [Brain, lateral, medial and inferior views]. Wikimedia Commons. Retrieved July 12, 2012 from _Hauptsulci_beschriftet.svg.. Figure 5. Modified from Beal, J.A. (2005). [Human brain view on traverse temporal and isular gyri description]. Wikimedia Commons. Retrieved July 12, 2012 from description.jpg. Figure 6. Beal, J.A. (2006). [Human brain midsagittal cut description]. Wikimedia Commons. Retrieved July 12, 2012 from Figure 7. Figure 8. Modified from Was a bee. (2009). [Third ventricle]. Wikimedia Commons. Retrieved July 12, 2012 from 98
9 Lab 07 Brain CNS Name Lab Section 1. Briefly define the following terms: Meninges Hemisphere Lobe Sulcus Fissure Cerebral Cortex Ventricle (brain) Choroid Plexus 2. Name the adult brain structures that arise from each of the following embryonic regions: Prosencephalon Mesencephalon Rhombencephalon 3. Name the groove/fissure/sulcus that separates the following brain regions: Left & Right Cerebral Hemispheres Cerebrum & Cerebellum Frontal & Parietal Lobes Parietal & Temporal Lobes Parietal & Occipital Lobes 99
10 4. Describe the position of the insula: 5. Briefly differentiate between White Matter & Grey Matter 6. Supply the missing terms in the following sentences that describes the LONGEST possible route that CSF can take from its production till it reaches the central canal of the spinal cord: CSF is produced by in one of the two. From there it flows through a into the. From there it flows through the into the, and then into the central canal of the spinal cord. 7. You have likely noticed that the Sheep s olfactory bulbs are much larger (both their actual size as well as their size compared to the overall size of the brain) than the human s. Why might this be the case? 8. Attach your pictures of the sheep brain dissection or submit to your instructor online (ask your instructor which). 100
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.)
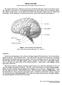 BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline
 BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e.
 1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Brain Matters: Brain Anatomy
 1 : Brain Anatomy Lesson Overview Students share what they already know about brain structure and function, and then, guided by descriptions of brain regions explore the G2C Online 3-D Brain to learn more
1 : Brain Anatomy Lesson Overview Students share what they already know about brain structure and function, and then, guided by descriptions of brain regions explore the G2C Online 3-D Brain to learn more
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Anatomy of the Brain > 1. Figure 1. Eight bones form the skull and fourteen bones form the face.
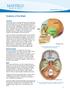 Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
The brain structure and function
 The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
Function (& other notes)
 LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain
 Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
NEUROANATOMY 6 Limbic System
 NEUROANATOMY 6 Limbic System The Limbic System The part of the brain involved with learning, memory and emotion. It is affected in many neuropsychiatric diseases including schizophrenia, Alzheimer s disease
NEUROANATOMY 6 Limbic System The Limbic System The part of the brain involved with learning, memory and emotion. It is affected in many neuropsychiatric diseases including schizophrenia, Alzheimer s disease
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN
 BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
7.4.3.2.2 Use internal and external anatomical structures to compare and infer relationships
 The Basics: from Neuron to Neuron to the Brain Document Overview: Description of Activity Part I. Neuron Part II. Action Potential Part III. Neurotransmission Part IV. Specific Neurotransmitters Part V.
The Basics: from Neuron to Neuron to the Brain Document Overview: Description of Activity Part I. Neuron Part II. Action Potential Part III. Neurotransmission Part IV. Specific Neurotransmitters Part V.
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Central Nervous System
 CHAPTER 3 Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Central Nervous System GENERAL TERMINOLOGY AN OVERVIEW OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Major Divisions
CHAPTER 3 Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Central Nervous System GENERAL TERMINOLOGY AN OVERVIEW OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Major Divisions
Chapter 9 - Nervous System
 Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function
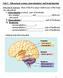 Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function Subcortical anatomy: Most of the five major subdivisions of the brain are subcortical. I. Telencephalon (cortical - part of forebrain) -
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function Subcortical anatomy: Most of the five major subdivisions of the brain are subcortical. I. Telencephalon (cortical - part of forebrain) -
The Brain. What is it? Neurons Glial Cells Connective Tissue Connective Fiber White Matter Grey Matter Cerebro-spinal Fluid
 The Brain What is it? Neurons Glial Cells Connective Tissue Connective Fiber White Matter Grey Matter Cerebro-spinal Fluid A More Realistic View When we look at the brain we see mostly the Cerebral Cortex
The Brain What is it? Neurons Glial Cells Connective Tissue Connective Fiber White Matter Grey Matter Cerebro-spinal Fluid A More Realistic View When we look at the brain we see mostly the Cerebral Cortex
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM)
 MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM) On the medial surface of the temporal lobe are three structures critical for normal human functioning. From rostral to caudal, they are the olfactory cortex, the
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM) On the medial surface of the temporal lobe are three structures critical for normal human functioning. From rostral to caudal, they are the olfactory cortex, the
1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera 10 Choroid
 Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes I. General Organization of the Nervous System, p. 422 Objectives 1. Describe the basic structural and organizational characteristics of the
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine. Bones of the Spine (Vertebrae)
 Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
LECTURE 16 NEUROPATHOPHYSIOLOGY (HEAD INJURY)
 LECTURE 16 Copyright 2000 by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. The approach and organization of this material was developed by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. for specific use in online instruction. All rights reserved. No part
LECTURE 16 Copyright 2000 by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. The approach and organization of this material was developed by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. for specific use in online instruction. All rights reserved. No part
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Brain Power. Counseling and Mental Health
 Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
An Introduction To Human Neuroanatomy
 An Introduction To Human Neuroanatomy Harvard Brain Tissue Resource Center, McLean Hospital, Belmont, MA 02478, 1-800-BRAIN BANK. Created by Tim Wheelock, Assistant Director of Neuropathology/Instructor
An Introduction To Human Neuroanatomy Harvard Brain Tissue Resource Center, McLean Hospital, Belmont, MA 02478, 1-800-BRAIN BANK. Created by Tim Wheelock, Assistant Director of Neuropathology/Instructor
The Brain of a Normal Human
 The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
Slide 4: Forebrain Structures. Slide 5: 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex. Slide 6: The Cerebral Hemispheres (L & R)
 Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
The Hypothalamus. Functions of the Hypothalamus. The Hypothalamus. Medical Neuroscience Dr. Wiegand
 The Medical Neuroscience Dr. Wiegand Neural Influences Neural Influences Hormonal Influences Hormonal Influences The Autonomic Nervous System Limbic System Endocrine System system Endocrine 1 The Diencephalon
The Medical Neuroscience Dr. Wiegand Neural Influences Neural Influences Hormonal Influences Hormonal Influences The Autonomic Nervous System Limbic System Endocrine System system Endocrine 1 The Diencephalon
Nervous System. from the Human Body Systems Series. catalog # 2890. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Nervous System from the Human Body Systems Series catalog # 2890 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
18. What is limbic system? A. The inner parts of cerebral hemispheres associated with deep structures and from a complex structure. 19.
 CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
Nervous System Pathology
 Nervous System Pathology Nervous System Central Nervous System CNS Brain & Spinal cord Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System PNS Spinal and cranial nerves CNS Close relationship with endocrine system
Nervous System Pathology Nervous System Central Nervous System CNS Brain & Spinal cord Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System PNS Spinal and cranial nerves CNS Close relationship with endocrine system
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Wessex Neurological Centre. Neuro-anatomy & Physiology Workbook
 Wessex Neurological Centre Neuro-anatomy & Physiology Workbook Sarah Irwin, Senior Sister NICU, SUHT & Rachel Palmer, Lecturer Practitioner Neurosciences (SUHT & School of Health Professionals, University
Wessex Neurological Centre Neuro-anatomy & Physiology Workbook Sarah Irwin, Senior Sister NICU, SUHT & Rachel Palmer, Lecturer Practitioner Neurosciences (SUHT & School of Health Professionals, University
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
Central Nervous System Brain & Spinal Cord
 Brain Central Nervous System Brain & Spinal Cord one of largest organs in body: men: women: 1,600 g (3.5 lbs) 1,450g (3.2 lbs) [size is proportional to body size not intelligence! Neanderthals had larger
Brain Central Nervous System Brain & Spinal Cord one of largest organs in body: men: women: 1,600 g (3.5 lbs) 1,450g (3.2 lbs) [size is proportional to body size not intelligence! Neanderthals had larger
組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system
 組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system 實 驗 講 義 : 謝 侑 霖 老 師 Yu-Lin Hsieh, PhD. 劉 俊 馳 Chun-Chih Liu 李 怡 琛 Yi-Chen Lee 張 昭 元 Chao-Yuah Chang 張 瀛 双 Ying-Shuang Chang :07-3121101 ext 2144-18 :[email protected]
組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system 實 驗 講 義 : 謝 侑 霖 老 師 Yu-Lin Hsieh, PhD. 劉 俊 馳 Chun-Chih Liu 李 怡 琛 Yi-Chen Lee 張 昭 元 Chao-Yuah Chang 張 瀛 双 Ying-Shuang Chang :07-3121101 ext 2144-18 :[email protected]
BIO 150 (3 credits) & BIO 150L (1 credit) Nazareth College Department of Biology Rochester, NY 14618 (585) 389-2554
 BIO 150 (3 credits) & BIO 150L (1 credit) HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Nazareth College Department of Biology Rochester, NY 14618 (585) 389-2554 1 PREREQUISITE: You must have completed BIO 103/103L (or
BIO 150 (3 credits) & BIO 150L (1 credit) HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Nazareth College Department of Biology Rochester, NY 14618 (585) 389-2554 1 PREREQUISITE: You must have completed BIO 103/103L (or
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
OLFACTORY PATHWAYS AND LIMBIC SYSTEM
 903 Olfactory and Limbic OLFACTORY PATHWAYS AND LIMBIC SYSTEM I. OLFACTORY PATHWAYS The sense of smell is much less essential than vision, audition or the somatic senses, and will therefore receive less
903 Olfactory and Limbic OLFACTORY PATHWAYS AND LIMBIC SYSTEM I. OLFACTORY PATHWAYS The sense of smell is much less essential than vision, audition or the somatic senses, and will therefore receive less
Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System.
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 11: Nervous System Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System. I have 19 goals for you in this lesson: 1. Name
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 11: Nervous System Welcome to Lesson 11 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Nervous System. I have 19 goals for you in this lesson: 1. Name
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
CHAPTER 14 NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES. On completion of this chapter, you will be able to:
 CHAPTER 14 NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the tissues of the nervous system. Describe nerve fibers, nerves, and tracts. Describe the transmission
CHAPTER 14 NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the tissues of the nervous system. Describe nerve fibers, nerves, and tracts. Describe the transmission
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161
 116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
Introduction. I. Objectives. II. Introduction. A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location.
 E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
E X E R C I S E Introduction I. Objectives A. To become familiar with the terms of direction and location. B. To become familiar with different types of planes and sections. C. To learn the names and locations
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3
 Slide 1 The Role of Experience on the Developing Brain Barb Jackson, Ph.D. Director, Education & Child Development Munroe-Meyer Institute University of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE USA The purpose
Slide 1 The Role of Experience on the Developing Brain Barb Jackson, Ph.D. Director, Education & Child Development Munroe-Meyer Institute University of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE USA The purpose
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology
 Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Welcome to Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 -Human Organization What do you need to do to pass this class? MEMORIZE! The Scope of Human Anatomy Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body.
Glossary. Activities of Daily Living (ADL): routine daily self care skills, including dressing, bathing, toileting, and feeding.
 Glossary Acoustic nerve: the nerve that is responsible for hearing. Activities of Daily Living (ADL): routine daily self care skills, including dressing, bathing, toileting, and feeding. Adaptive physical
Glossary Acoustic nerve: the nerve that is responsible for hearing. Activities of Daily Living (ADL): routine daily self care skills, including dressing, bathing, toileting, and feeding. Adaptive physical
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College
 Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Primary Sources for figures and content: Eastern Campus Marieb,
HEAD INJURY WITH HELMET USE
 HEAD INJURY WITH HELMET USE by Greg Doc TrojanIntroduction While motorcycling has been targeted as a public burden and garners most of the public attention concerning head injury, it is actually a minor
HEAD INJURY WITH HELMET USE by Greg Doc TrojanIntroduction While motorcycling has been targeted as a public burden and garners most of the public attention concerning head injury, it is actually a minor
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY
 NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
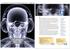
Brain Anatomy on CT & MRI. Department of Radiation Oncology
 Brain Anatomy on CT & MRI Rebecca L. Frame, BS, CMD Rebecca L. Frame, BS, CMD Department of Radiation Oncology Objectives 1. Brain Facts 2. MRI Imaging Techniques 3. How the Various Imaging Helps Us in
Brain Anatomy on CT & MRI Rebecca L. Frame, BS, CMD Rebecca L. Frame, BS, CMD Department of Radiation Oncology Objectives 1. Brain Facts 2. MRI Imaging Techniques 3. How the Various Imaging Helps Us in
To understand the nervous system, start by thinking of your
 Chapter The Nervous System 6 To understand the nervous system, start by thinking of your body as a biological machine that runs on electricity. In fact, this is true; your body does run on electricity!
Chapter The Nervous System 6 To understand the nervous system, start by thinking of your body as a biological machine that runs on electricity. In fact, this is true; your body does run on electricity!
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
 151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
LESSON 4: BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 LESSON 4: BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION THE TRIUNE BRAIN Neo? axon brain stem cerebral hemispheres cortex dendrite limbic system neural plasticity neurons neurotransmitter sensory flooding sensory gating
LESSON 4: BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION THE TRIUNE BRAIN Neo? axon brain stem cerebral hemispheres cortex dendrite limbic system neural plasticity neurons neurotransmitter sensory flooding sensory gating
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
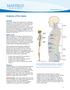 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
 The Great Diseases A collaborative approach to real world science in the classroom Infectious Diseases Neurological Disorders Metabolic Disease Cancer NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS Katherine Malanson and Karina
The Great Diseases A collaborative approach to real world science in the classroom Infectious Diseases Neurological Disorders Metabolic Disease Cancer NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS Katherine Malanson and Karina
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord
 Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Transverse Sections of the Spinal Cord The spinal cord is perhaps the most simply arranged part of the CNS. Its basic structure, indicated in a schematic drawing of the eighth cervical segment (Figure
Chapter 15: Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 Chapter 15: Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System I. An Overview of Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System, p. 496 Figure 15-1 Specialized cells called sensory
Chapter 15: Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System I. An Overview of Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System, p. 496 Figure 15-1 Specialized cells called sensory
MEDULLA OBLONGATA AND PONS form lower part of brainstem (oblongata, pons, midbrain)
 MEDULLA OBLONGATA AND PONS form lower part of brainstem (oblongata, pons, midbrain) Medulla oblongata - is uper continuation of the spinal cord Its caudal part is alike the spinal cord, while - its cranial
MEDULLA OBLONGATA AND PONS form lower part of brainstem (oblongata, pons, midbrain) Medulla oblongata - is uper continuation of the spinal cord Its caudal part is alike the spinal cord, while - its cranial
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
of computational neuroscience. The chapter is organized as follows. Section 1 describes the
 Chapter 1 This chapter presents elements of neurobiology that form the necessary preparation for a student of computational neuroscience. The chapter is organized as follows. Section 1 describes the biology
Chapter 1 This chapter presents elements of neurobiology that form the necessary preparation for a student of computational neuroscience. The chapter is organized as follows. Section 1 describes the biology
M2 Pathology Course Phone: 312-996-1772 Lecture # 72 e-mail: [email protected] Tuesday, February 11, 2003 9:30 10:20
 Tibor Valyi-Nagy, M.D., Ph.D. UIC College of Medicine Assistant Professor of Pathology, UIC M2 Pathology Course Phone: 312-996-1772 Lecture # 72 e-mail: [email protected] Tuesday, February 11, 2003 9:30 10:20
Tibor Valyi-Nagy, M.D., Ph.D. UIC College of Medicine Assistant Professor of Pathology, UIC M2 Pathology Course Phone: 312-996-1772 Lecture # 72 e-mail: [email protected] Tuesday, February 11, 2003 9:30 10:20
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Human Anatomy & Physiology Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes 13-1 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes 13-2 Overview of Spinal Cord Information
Sensory Organs (Receptors) Sensory Physiology. Sensory Adaptation. Four Steps to Sensation. Types of Sensors Structural Design
 Sensory Organs (Receptors) Sensory Physiology Chapter 10 Monitor the internal and external environment Transmit peripheral signals to CNS for processing Critical for homeostasis Types of Sensors Structural
Sensory Organs (Receptors) Sensory Physiology Chapter 10 Monitor the internal and external environment Transmit peripheral signals to CNS for processing Critical for homeostasis Types of Sensors Structural
