1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e.
|
|
|
- Alexandrina Ellis
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Which of the following is NOT part of the diencephalon? a. Pineal gland b. Tectum c. Interthalamic adhesion d. Hypothalamus e. Thalamus 2. The is the primary relay station for sensory information coming into the cerebral cortex. a. Hypothalamus b. Epithalamus c. Midbrain d. Thalamus e. Prosencephalon 3. The is attached to the hypothalamus by the infundibulum. a. Pineal gland b. Sella turcica of the sphenoid bone c. Thyroid gland d. Thalamus e. None of the above 4. The is the autonomic control center. a. Thalamus b. Pons c. Prefrontal cortex d. Hypothalamus e. Fornix 5. Which of the following secretes a hormone that plays a role in the regulation of sleep/wake cycles? a. Thalamus b. Pituitary gland c. Brainstem d. Pons e. Pineal gland 6. Which of the following is NOT found in the brain stem? a. Pons b. Midbrain c. Cerebral peduncles d. Decussation of the pyramids e. Lateral ventricle
2 7. The cerebral aqueduct connects the: a. Left and right lateral ventricles b. Lateral ventricles to the 3 rd ventricle c. 3 rd ventricle to the 4 th ventricle d. 4 th ventricle to the subarachnoid space e. Subarachnoid space to the dural sinuses 8. The pons contains: a. White matter linking the cerebral cortex and the spinal cord b. Nuclei involved in urination c. Nuclei involved in respiration d. Neurons and glial cells 9. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The deepest meninx is the pia mater b. The dura mater of the brain is a 2 layered structure c. The periosteal dura mater is deep to the meningeal dura mater d. The subarachnoid space contains cerebrospinal fluid e. The subarachnoid space is between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater 10. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. Venous sinuses are found between the 2 layers of the dura mater b. CSF travels from the subarachnoid space to the venous sinuses c. There are 4 ventricles in the brain d. Roughly 5000 ml of CSF is produced daily. e. CSF enters the subarachnoid space by way of the median and lateral apertures of the 4 th ventricle 11. Which of the following is TRUE? a. Capillary endothelial cells are linked by tight junctions. b. The brain is a very vascular organ c. The blood-brain barrier protects the brain from harmful substances in the brain d. The lateral ventricles are separated by the septum pellucidum Use the following answer choices for the next 6 items. Each may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a. CN VII b. Oculomotor nerve c. CN II d. Glossopharyngeal nerve e. None of the above 12. Controls the levator palpebrae superioris 13. Controls the submandibular and sublingual glands 14. Extends through the optic canals of the sphenoid bone. 15. Shrugs the shoulders. 16. Carries sensory information concerning blood pressure. 17. Releases ACh onto the heart.
3 18. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the cranial nerves. b. Vagus means wanderer. c. Damage to the trochlear nerve could result in double vision d. The cochlea of the inner ear is associated with CN VIII e. Fibers of CN I pass through the cribriform plate of the sphenoid bone 19. Which of the following nerves controls the motor functions of the tongue? a. CN V b. CN VII c. CN IX d. CN XI e. CN XII 20. Which of the following cranial nerves does NOT contain axons of parasympathetic motor neurons? a. CN III b. CN VII c. CN IX d. CN X e. CN XII 21. Inability to track the flight of an airplane could be indicative of damage to the: a. Inferior colliculus b. Superior colliculus c. Cerebral aqueduct d. 3 rd ventricle e. Central canal of the spinal cord 22. Which of the following cortical areas is associated with neurons extending through the cribriform plate? a. Gustatory cortex b. Olfactory cortex c. Primary somatosensory cortex d. Premotor cortex e. Frontal eye field 23. Which of the following brain areas would you expect to be most involved in coordinating the joint movements used in throwing a football? a. Cerebellum b. Epithalamus c. Hypothalamus d. Adenohypophysis e. Neurohypophysis 24. There are 24 cranial nerves. a. True b. False
4 25. Which of the following is NOT considered one of the 4 major regions of the brain? a. Cerebrum b. Prosencephalon c. Diencephalon d. Cerebellum e. Brainstem 26. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The cerebral hemispheres make up about 80% of the brain. b. Ridges in the cerebrum are called sulci c. The longitudinal fissure separates the 2 cerebral hemispheres d. The central sulcus separates the frontal and parietal lobes e. The parieto-occipital sulcus separates the parietal and occipital lobes 27. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The precentral gyrus is anterior to the central sulcus b. The precentral gyrus is anterior to the postcentral gyrus c. The lateral sulcus separates the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes d. Each cerebral hemisphere has a thin outer surface layer composed of myelinated axons e. The cerebral cortex is the site of the conscious mind 28. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The primary motor cortex is found in the postcentral gyrus. b. The precentral gyrus contains pyramidal neurons that control muscle movements. c. The motor homunculus has big hands d. The corticospinal tracts connect the spinal cord and the primary motor cortex e. The premotor cortex is anterior to the precentral gyrus 29. Damage to Broca s area would result in an inability to: a. See a pattern of flashing lights b. Smell organic compounds like freshly cut grass c. Smell volatile compounds like unleaded gasoline d. Say the word inconspicuous e. Hear sounds that are high in pitch 30. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The frontal eye field controls voluntary eye movements b. The somatosensory cortex is found in the postcentral gyrus c. The sensory homunculus has large lips d. Proprioceptors sense body position e. The somatosensory association cortex is just anterior to the postcentral gyrus
5 31. The number of cranial nerves with purely sensory function is the number of cranial nerves with purely motor function. a. Greater than b. Less/fewer than c. Stay the same 32. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The primary visual cortex is found in the occipital lobe b. The visual association area is found in the occipital lobe c. The primary auditory cortex is found in the temporal lobe d. Rodin is the artist who sculpted The Thinker e. The corpus callosum is a group of projection fibers 33. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. Wernicke s area is involved in understanding spoken language b. A frontal lobotomy can drastically alter an individual s personality c. Association fibers connect the 2 cerebral hemispheres d. Basal nuclei are deep to the cerebral cortex e. Basal nuclei play a role in performing voluntary movements 34. Movement of the right hand is caused by neural activity in the: a. Left precentral gyrus b. Right precentral gyrus c. Left postcentral gyrus d. Right postcentral gyrus 35. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The motor tracts descending toward the spinal cord cross over in the medulla oblongata b. The medulla oblongata contains nuclei involved in cardiac function c. The medulla oblongata is superior to the pons d. The medulla oblongata is superior to the spinal cord 36. Which of the following is NOT TRUE? a. The vermis is found in between the 2 cerebellar hemispheres. b. Munch painted The Scream c. The cerebellum plays a role in coordinating the movements involved in throwing a baseball. d. The cerebellum is anterior to the 4 th ventricle e. The cerebellum is inferior to the occipital lobe of the cerebrum 37. Mr. Drexler suffered a stroke. He is able to understand verbal and written language, but when he tries to speak, his words are garbled. What cortical region did the stroke damage? Broca s area
6 38. After Mr. Stockton s brain tumor was removed, he could no longer identify an object solely by touch. He can describe how the object feels when he touches it but he must look at it in order to name it. What cortical region could be malfunctioning? Somatosensory association cortex 39. Mr. Olajuwon was in a horrific snowmobile accident. Afterwards he had trouble walking and he had a loss of balance. Which of the 4 major brain regions was probably damaged? Cerebellum 40. Someone can survive the destruction of an entire cerebral hemisphere but cannot survive destruction of the hypothalamus. Why? b/c of the vital role the hypothalamus plays in maintaining homeostasis including the regulation of cardiac function and blood pressure. 41. Rank the following from most anterior to most posterior. Primary visual cortex 6 Central sulcus 4 Premotor area 2 Prefrontal cortex 1 Precentral gyrus 3 Wernicke s area Bogorad s syndrome (a.k.a. crocodile tears syndrome) is spontaneous lacrimation (crying) during eating. Damage to which of the following nerves is the likely cause of this disorder? a. Cranial nerve 5 b. Oculomotor nerve c. Facial nerve d. Cranial nerve An inability to shrug one s shoulders would be indicative of damage to which of the following nerves? a. Vagus b. Accessory c. Hypoglossal d. Hyperglossal e. Trapeziomatic f. All of the above g. 2 of the above 44. Cutting one of the cranial nerves will cause heart rate to go up. Which cranial nerve must it be? a. Vestibulocochlear b. Vagus c. Visceral d. Trigeminal e. CN VI
7 45. Meniere s disease is characterized by a loss of balance and a ringing in the ears. Inflammation of which of the following nerves is the likely cause? a. Trochlear b. Abducens c. Facial d. Vestibulocochlear 46. Which of the following cranial nerves is the odd one of the group? a. Trochlear b. Abducens c. Oculomotor d. Optic 47. Explain your reasoning behind your choice for #46. What commonality did the other 3 share that led you to select the odd one? It s the only sensory one. 48. Which cranial nerve is not really a cranial nerve? And why? Accessory b/c it is formed from the cervical spinal nerve roots. 49. Which of the following nerves carry sensory information about blood pressure? a. Vagus b. Accessory c. Hypoglossal d. Trochlear e. Glossopharyngeal f. All of the above g. 2 of the above
Lab Exercise 9. Nervous Tissue. Brain. Cranial Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Nerves
 Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
Lab Exercise 9 Nervous Tissue Brain Cranial Nerves Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Textbook Reference: See Chapter 11 for histology of nerve tissue and spinal cord See Chapter 12 for brain and spinal cord anatomy
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
THE BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, AND CRANIAL NERVES I. BRAIN ANATOMY A. Meninges (coverings) of the brain and spinal cord (Fig. [13.120 p. 452 [457]) Use text illustrations to study these. Note that the singular
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
Sheep Brain Dissection http://www.carolina.com/product/preserved+organisms/preserved+animals+%28mammal s%29/sheep+organs/preserved+sheep+dissection.do Michigan State University Neuroscience Program Brain
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline
 BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
BIO130 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture Outline Brain structure 1. Cerebrum Hemispheres: left & right Cerebral cortex Gyri Sulci Fissures Longitudinal fissure Corpus callosum Lobes Central
Nervous System: PNS and CNS
 Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System: PNS and CNS Biology 105 Lecture 10 Chapter 8 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous
Nervous System Organization. PNS and CNS. Nerves. Peripheral Nervous System. Peripheral Nervous System. Motor Component.
 Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
Nervous System Organization PNS and CNS Chapters 8 and 9 Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) connects CNS to sensory receptors, muscles and glands Central Nervous System (CNS) control/integrating center brain
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Brain Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 431 through 435 and 463-467 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Parts of the Brain. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Chapter 1 Parts of the Brain Living creatures are made up of cells. Groups of cells, similar in appearance and with the same function, form tissue. The brain is a soft mass of supportive tissues and nerve
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 8 Nervous System Quiz 1. The term central nervous system refers to the: A) autonomic and peripheral nervous systems B) brain, spinal cord, and cranial nerves
Human Neuroanatomy. Grades 9-12. Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today?
 Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12 Driving Question: How did the evolution of the human brain impact the structure and function it has today? Objectives: Students will be able to Describe the basic parts and
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.)
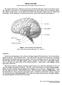 BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
BRAIN ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology by Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) The anatomy of the brain is often discussed in terms of either the embryonic scheme or the medical scheme. The embryonic
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES
 THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
THE BRAIN AND CRANIAL NERVES The Brain - made up of a trillion neurons - weighs about 3 lbs - has four principle parts 1. Brain stem - medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain (mesencephalon) 2. Diencephalon
3) Cerebral Cortex & Functions of the 4 LOBES. 5) Cranial Nerves (Nerves In the Cranium, i.e., Head)
 Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Lecture 5 (Oct 8 th ): ANATOMY and FUNCTION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Lecture Outline 1) Basic Divisions (CNS vs. PNS, Somatic vs. Autonomic) and Directional Terms 2) The Brain (Hindbrain/ Midbrain/ Forebrain)
Anatomy of the Brain > 1. Figure 1. Eight bones form the skull and fourteen bones form the face.
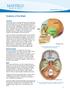 Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Anatomy of the Brain Overview The human brain is an amazing three-pound organ that controls all functions of the body, interprets information from the outside world, and embodies the essence of the mind
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
Chapter 7: The Nervous System I. Organization of the Nervous System Objectives: List the general functions of the nervous system Explain the structural and functional classifications of the nervous system
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach you one of the great methods of studying
Function (& other notes)
 LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
LAB 8. ANATOMY OF THE HUMAN BRAIN In this exercise you each will map the human brain both anatomy and function so that you can develop a more accurate picture of what s going on in your head :-) EXTERNAL
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Sensory Pathway (PNS) OVERVIEW OF SPINAL CORD ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD FUNCTIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Central nervous system (CNS) brain and spinal cord enclosed in bony coverings Functions of the spinal cord spinal cord reflexes integration ti (summation of inhibitory and excitatory)
Nervous System sensor input integration motor output sensory organs central nervous system
 Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Nervous System Nervous system performs three overlapping functions of sensor input, integration, and motor output. This process is generally the same even at a very primitive level of nervous system, but
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide
 Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Sheep Brain Dissection Picture Guide Figure 1: Right Hemisphere of Sheep s Brain Figure 2: Underside of Sheep s Brain Figure 3: Saggital cut of Sheep s Brain to reveal subcortical structures Figure 4:
Chapter 9 - Nervous System
 Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
Chapter 9 - Nervous System 9.1 Introduction (p. 215; Fig. 9.1) A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses along nerve fibers to other neurons. 2. Nerves
3. The neuron has many branch-like extensions called that receive input from other neurons. a. glia b. dendrites c. axons d.
 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer: A difficulty: 1 factual
Brain Tumor 101. Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center
 Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Brain Tumor 101 Shanna Armstrong, RN Neuro Oncology Nurse Clinician UC Brain Tumor Center Objectives Identify the different parts of the brain Describe how each part of the brain works Connect each part
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system
 Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Consists of: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves The autonomic nervous system Nerves and neurons Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs They are numbered according
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Chapter 9 Nervous System Nervous System function: The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. When sensory
Peripheral Nervous System
 Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Nervous system consists of: Peripheral Nervous System CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves, nerve plexuses & ganglia ~10% (10
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization
 Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain Organization Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Course Outline Lecture 1: Vocabulary & General Concepts of Brain
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain
 Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
Mini-atlas of the Marmoset Brain http://marmoset-brain.org Aya Senoo Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Hironobu Tokuno Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science Charles Watson Curtin
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling. Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy
 CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling CSE511 Brain & Memory Modeling Lect02: BOSS Discrete Event Simulator Lect04: Brain & Spine Neuroanatomy Appendix of Purves et al., 4e Larry Wittie Computer Science, StonyBrook
The brain structure and function
 The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
The brain structure and function This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding brain tumours. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a copy free see page 5. Contents Introduction
Brain Matters: Brain Anatomy
 1 : Brain Anatomy Lesson Overview Students share what they already know about brain structure and function, and then, guided by descriptions of brain regions explore the G2C Online 3-D Brain to learn more
1 : Brain Anatomy Lesson Overview Students share what they already know about brain structure and function, and then, guided by descriptions of brain regions explore the G2C Online 3-D Brain to learn more
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System
 Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
Chapter 3 The Anatomy of the Nervous System Systems, Structures, and Cells That Make Up Your Nervous System 1 General Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal
What is the basic component of the brain and spinal cord communication system?
 EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 Neural Communication Neurons How Neurons Communicate How Neurotransmitters Influence Us The Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System The
What role does the nucleolus have in cell functioning? Glial cells
 Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Nervous System Lab The nervous system of vertebrates can be divided into the central nervous system, which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which contains nerves,
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS) By the end of this unit, the learner will be able to: Describe the anatomy of the brain and the central nervous system Identify regions of the brain
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN
 BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
BIOLOGY STUDY PACKET THE BRAIN SC.912.L.14.26 AA Spring 2012 The intent of this packet is to supplement regular classroom instruction, not to replace it. This also supposes that the students have access
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B.
 U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
U N IT 10 NE RVOUS SYS TE M REVIEW 1. Which of the following is controlled by the somatic nervous system? A. rate of heartbeat B. contraction of skeletal muscles C. increased blood flow to muscle tissue
The Brain of a Normal Human
 The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
The Brain of a Normal Human Your Brain Evolved Over Time Human Brain Logic and reasoning Mammalian Brain More complex feelings and reactions Lizard Brain Basic functions The Brain Stem or Hindbrain (The
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Vision: Receptors. Modes of Perception. Vision: Summary 9/28/2012. How do we perceive our environment? Sensation and Perception Terminology
 How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
How do we perceive our environment? Complex stimuli are broken into individual features, relayed to the CNS, then reassembled as our perception Sensation and Perception Terminology Stimulus: physical agent
Slide 4: Forebrain Structures. Slide 5: 4 Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex. Slide 6: The Cerebral Hemispheres (L & R)
 Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
Slide 1: [Film Clip: The Brain #2- Phineas Gage] Integrated Bodily Communications Within Brain (Hemispheres and structures) The remaining Nervous System Endocrine System (Hormonal communication) Our bodies-
NEUROANATOMY 6 Limbic System
 NEUROANATOMY 6 Limbic System The Limbic System The part of the brain involved with learning, memory and emotion. It is affected in many neuropsychiatric diseases including schizophrenia, Alzheimer s disease
NEUROANATOMY 6 Limbic System The Limbic System The part of the brain involved with learning, memory and emotion. It is affected in many neuropsychiatric diseases including schizophrenia, Alzheimer s disease
Basic Brain Information
 Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic Brain Information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function
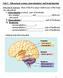 Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function Subcortical anatomy: Most of the five major subdivisions of the brain are subcortical. I. Telencephalon (cortical - part of forebrain) -
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function Subcortical anatomy: Most of the five major subdivisions of the brain are subcortical. I. Telencephalon (cortical - part of forebrain) -
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Integration and Coordination of the Human Body. Nervous System
 I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
I. General Info Integration and Coordination of the Human Body A. Both the and system are responsible for maintaining 1. Homeostasis is the process by which organisms keep internal conditions despite changes
1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS
 151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
151 Brain stem Pyramids/Corticospinal Tract 1 PYRAMIDS - CORTICOSPINAL FIBERS The pyramids are two elongated swellings on the ventral aspect of the medulla. Each pyramid contains approximately 1,000,000
Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Central Nervous System
 CHAPTER 3 Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Central Nervous System GENERAL TERMINOLOGY AN OVERVIEW OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Major Divisions
CHAPTER 3 Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Central Nervous System GENERAL TERMINOLOGY AN OVERVIEW OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Major Divisions
Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161
 116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
116 Lab 10: Muscle Tissue and Selected Muscles Unit 7: Muscle Tissue & Muscular System (p. 153-180) Ex. 7-1: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy & Muscle Tissue, p. 161 Muscle Tissue Sketch View of Muscle Tissue Under
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd.
 About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
About Brain Injury: A Guide to Brain Anatomy Information from http://www.waiting.com, 1997-2002, Becca, Ltd. Brain Anatomy Definitions Brainstem: The lower extension of the brain where it connects to the
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron
 Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
Diagram 2(i): Structure of the Neuron Generally speaking, we can divide the nervous system into different parts, according to location and function. So far we have mentioned the central nervous system
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
The Hypothalamus. Functions of the Hypothalamus. The Hypothalamus. Medical Neuroscience Dr. Wiegand
 The Medical Neuroscience Dr. Wiegand Neural Influences Neural Influences Hormonal Influences Hormonal Influences The Autonomic Nervous System Limbic System Endocrine System system Endocrine 1 The Diencephalon
The Medical Neuroscience Dr. Wiegand Neural Influences Neural Influences Hormonal Influences Hormonal Influences The Autonomic Nervous System Limbic System Endocrine System system Endocrine 1 The Diencephalon
Wessex Neurological Centre. Neuro-anatomy & Physiology Workbook
 Wessex Neurological Centre Neuro-anatomy & Physiology Workbook Sarah Irwin, Senior Sister NICU, SUHT & Rachel Palmer, Lecturer Practitioner Neurosciences (SUHT & School of Health Professionals, University
Wessex Neurological Centre Neuro-anatomy & Physiology Workbook Sarah Irwin, Senior Sister NICU, SUHT & Rachel Palmer, Lecturer Practitioner Neurosciences (SUHT & School of Health Professionals, University
MEDULLA OBLONGATA AND PONS form lower part of brainstem (oblongata, pons, midbrain)
 MEDULLA OBLONGATA AND PONS form lower part of brainstem (oblongata, pons, midbrain) Medulla oblongata - is uper continuation of the spinal cord Its caudal part is alike the spinal cord, while - its cranial
MEDULLA OBLONGATA AND PONS form lower part of brainstem (oblongata, pons, midbrain) Medulla oblongata - is uper continuation of the spinal cord Its caudal part is alike the spinal cord, while - its cranial
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3
 Slide 1 The Role of Experience on the Developing Brain Barb Jackson, Ph.D. Director, Education & Child Development Munroe-Meyer Institute University of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE USA The purpose
Slide 1 The Role of Experience on the Developing Brain Barb Jackson, Ph.D. Director, Education & Child Development Munroe-Meyer Institute University of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE USA The purpose
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Adrian Owens Research
 *Classic View: Not entirely correct Nervous System Central Nervous System is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System is broken down into a component called the somatic division.
*Classic View: Not entirely correct Nervous System Central Nervous System is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System is broken down into a component called the somatic division.
18. What is limbic system? A. The inner parts of cerebral hemispheres associated with deep structures and from a complex structure. 19.
 CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
CHAPTER 21 NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION One mark Questions: 1. Name the structural and functional unit of nervous system? A. Neuron. 2. What does central Nervous System consists of? A. Brain and spinal
1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera 10 Choroid
 Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
Anatomy and Physiology Quiz 1 Sample Question Answers Use the following table to answer Questions 1 2. 1 Cornea 6 Macula 2 Lens 7 Vitreous humor 3 Iris 8 Optic disc 4 Conjunctiva 9 Ciliary muscles 5 Sclera
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM)
 MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM) On the medial surface of the temporal lobe are three structures critical for normal human functioning. From rostral to caudal, they are the olfactory cortex, the
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM) On the medial surface of the temporal lobe are three structures critical for normal human functioning. From rostral to caudal, they are the olfactory cortex, the
7.4.3.2.2 Use internal and external anatomical structures to compare and infer relationships
 The Basics: from Neuron to Neuron to the Brain Document Overview: Description of Activity Part I. Neuron Part II. Action Potential Part III. Neurotransmission Part IV. Specific Neurotransmitters Part V.
The Basics: from Neuron to Neuron to the Brain Document Overview: Description of Activity Part I. Neuron Part II. Action Potential Part III. Neurotransmission Part IV. Specific Neurotransmitters Part V.
The Brainstem (or brain stem) Ventral Surface. The Cranial Nerves 4/5/2010. Review: Spinal Nerves
 The Brainstem (or brain stem) Like spinal cord, it is part of the cable connecting brain to body, and also has local functions. Like spinal cord, dorsal structures are usually sensory, ventral structures
The Brainstem (or brain stem) Like spinal cord, it is part of the cable connecting brain to body, and also has local functions. Like spinal cord, dorsal structures are usually sensory, ventral structures
Chapter 4. The Brain
 Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
Chapter 4 The Brain The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) receives, processes, interprets and stores info (taste, sound, smell, color etc.) Sends information to muscles, glands and internal organs
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
LECTURE 16 NEUROPATHOPHYSIOLOGY (HEAD INJURY)
 LECTURE 16 Copyright 2000 by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. The approach and organization of this material was developed by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. for specific use in online instruction. All rights reserved. No part
LECTURE 16 Copyright 2000 by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. The approach and organization of this material was developed by Bowman O. Davis, Jr. for specific use in online instruction. All rights reserved. No part
組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system
 組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system 實 驗 講 義 : 謝 侑 霖 老 師 Yu-Lin Hsieh, PhD. 劉 俊 馳 Chun-Chih Liu 李 怡 琛 Yi-Chen Lee 張 昭 元 Chao-Yuah Chang 張 瀛 双 Ying-Shuang Chang :07-3121101 ext 2144-18 :littlebu@kmu.edu.tw
組 織 學 實 驗 : 神 經 系 統 Histology Lab : Nervous system 實 驗 講 義 : 謝 侑 霖 老 師 Yu-Lin Hsieh, PhD. 劉 俊 馳 Chun-Chih Liu 李 怡 琛 Yi-Chen Lee 張 昭 元 Chao-Yuah Chang 張 瀛 双 Ying-Shuang Chang :07-3121101 ext 2144-18 :littlebu@kmu.edu.tw
The Brain. What is it? Neurons Glial Cells Connective Tissue Connective Fiber White Matter Grey Matter Cerebro-spinal Fluid
 The Brain What is it? Neurons Glial Cells Connective Tissue Connective Fiber White Matter Grey Matter Cerebro-spinal Fluid A More Realistic View When we look at the brain we see mostly the Cerebral Cortex
The Brain What is it? Neurons Glial Cells Connective Tissue Connective Fiber White Matter Grey Matter Cerebro-spinal Fluid A More Realistic View When we look at the brain we see mostly the Cerebral Cortex
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY
 NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
NEUROLOCALIZATION MADE EASY Jared B. Galle, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) Dogwood Veterinary Referral Center 4920 Ann Arbor-Saline Road Ann Arbor, MI 48103 Localizing a neurologic problem to an anatomical
6 Diagnosing Injuries of the Skull Base
 Flowchart Injuries of the Skull Base, Chapter 3, p. 17. Treatment of Injuries of the Skull Base, Chapter 17, p. 140. Surgical Anatomy n The bony architecture of the skull base can be divided into three
Flowchart Injuries of the Skull Base, Chapter 3, p. 17. Treatment of Injuries of the Skull Base, Chapter 17, p. 140. Surgical Anatomy n The bony architecture of the skull base can be divided into three
HEAD INJURY WITH HELMET USE
 HEAD INJURY WITH HELMET USE by Greg Doc TrojanIntroduction While motorcycling has been targeted as a public burden and garners most of the public attention concerning head injury, it is actually a minor
HEAD INJURY WITH HELMET USE by Greg Doc TrojanIntroduction While motorcycling has been targeted as a public burden and garners most of the public attention concerning head injury, it is actually a minor
Discuss risk factors and characteristics of various levels of brain injury from mild to severe
 Understanding Brain Injury and Effective Strategies for Communication Kristin A. King, PhD, CCC-SLP University of Tennessee kking29@uthsc.edu Objectives Participants will be able to: Discuss risk factors
Understanding Brain Injury and Effective Strategies for Communication Kristin A. King, PhD, CCC-SLP University of Tennessee kking29@uthsc.edu Objectives Participants will be able to: Discuss risk factors
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI
 Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
CHAPTER 14 NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES. On completion of this chapter, you will be able to:
 CHAPTER 14 NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the tissues of the nervous system. Describe nerve fibers, nerves, and tracts. Describe the transmission
CHAPTER 14 NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the tissues of the nervous system. Describe nerve fibers, nerves, and tracts. Describe the transmission
Rosen Educational Services materials copyright 2011 Rosen Educational Services, LLC. All rights reserved.
 Published in 2011 by Britannica Educational Publishing (a trademark of Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.) in association with Rosen Educational Services, LLC 29 East 21st Street, New York, NY 10010. Copyright
Published in 2011 by Britannica Educational Publishing (a trademark of Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.) in association with Rosen Educational Services, LLC 29 East 21st Street, New York, NY 10010. Copyright
To understand the nervous system, start by thinking of your
 Chapter The Nervous System 6 To understand the nervous system, start by thinking of your body as a biological machine that runs on electricity. In fact, this is true; your body does run on electricity!
Chapter The Nervous System 6 To understand the nervous system, start by thinking of your body as a biological machine that runs on electricity. In fact, this is true; your body does run on electricity!
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (ANSWERS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Somatic efferent and ANS Somatic Efferent Control is over skeletal muscles. External environment This division of the PNS responds to some change in the external environment. single
Name Date Hour. Nerve Histology Microscope Lab
 Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Name Date Hour Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB: Answer the following questions using your reading and class notes before starting the microscope lab. 1. What is the difference between the functions
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Central Nervous System Brain & Spinal Cord
 Brain Central Nervous System Brain & Spinal Cord one of largest organs in body: men: women: 1,600 g (3.5 lbs) 1,450g (3.2 lbs) [size is proportional to body size not intelligence! Neanderthals had larger
Brain Central Nervous System Brain & Spinal Cord one of largest organs in body: men: women: 1,600 g (3.5 lbs) 1,450g (3.2 lbs) [size is proportional to body size not intelligence! Neanderthals had larger
D.U.C. Assist. Lec. Faculty of Dentistry General Physiology Ihsan Dhari. The Autonomic Nervous System
 The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
The Autonomic Nervous System The portion of the nervous system that controls most visceral functions of the body is called the autonomic nervous system. This system helps to control arterial pressure,
Glossary. Activities of Daily Living (ADL): routine daily self care skills, including dressing, bathing, toileting, and feeding.
 Glossary Acoustic nerve: the nerve that is responsible for hearing. Activities of Daily Living (ADL): routine daily self care skills, including dressing, bathing, toileting, and feeding. Adaptive physical
Glossary Acoustic nerve: the nerve that is responsible for hearing. Activities of Daily Living (ADL): routine daily self care skills, including dressing, bathing, toileting, and feeding. Adaptive physical
Chapter 15. Neurotransmitters of the ANS
 Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Chapter 15 Neurotransmitters of the ANS Neurotransmitters and Receptors How can the same ANS neurons create different effects on different target tissue? Variety of neurotransmitters Secondly, different
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Basic brain information
 Basic brain information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Basic brain information Brain facts Your brain weighs about 3lbs, or just under 1.5Kg It has the texture of blancmange Your brain is connected to your spinal cord by the brain stem Behind your brain stem
Stress Psychophysiology. Introduction. The Brain. Chapter 2
 Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
Stress Psychophysiology Chapter 2 Introduction This chapter covers the process & structures activated during the physiological response to stress. Two stress pathways are available; one for short term
Chapter 2. The Biological Bases of Psychological Functioning
 Chapter 2 The Biological Bases of Psychological Functioning Outline I. Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System A. A neuron is a nerve cell that transmits information from one part of the body
Chapter 2 The Biological Bases of Psychological Functioning Outline I. Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System A. A neuron is a nerve cell that transmits information from one part of the body
Brain Power. Counseling and Mental Health
 Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Brain Power Counseling and Mental Health TEA COPYRIGHT Copyright Texas Education Agency, 2012. These Materials are copyrighted and trademarked as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may
Homework Help Stroke
 The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
The Brain & Strokes Your brain is the most complex organ in your body. It is the command centre for everything you do, think, sense and say! It has over 100 billion special nerve cells called neurons.
Nervous System Pathology
 Nervous System Pathology Nervous System Central Nervous System CNS Brain & Spinal cord Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System PNS Spinal and cranial nerves CNS Close relationship with endocrine system
Nervous System Pathology Nervous System Central Nervous System CNS Brain & Spinal cord Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System PNS Spinal and cranial nerves CNS Close relationship with endocrine system
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination
 Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Basic Cranial Nerve Examination WIPE Wash hands Introduce yourself Permission Position (Patient sitting facing you, maintain comparable eye level) Exposure (Face exposed only, i.e. remove hats etc) Identify
Lu L m u b m a b r a rta T p a Figure 12.30
 SPINAL CORD ANATOMY AND DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD FUNCTION SPINAL CORD ANATOMY Lumbar Tap Figure 12.30 Spinal Cord Figure 12.29a There are 31 spinal cord segments: 8 cervical segments 12 thoracic segments 5 lumbar
SPINAL CORD ANATOMY AND DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD FUNCTION SPINAL CORD ANATOMY Lumbar Tap Figure 12.30 Spinal Cord Figure 12.29a There are 31 spinal cord segments: 8 cervical segments 12 thoracic segments 5 lumbar
