ANALYSIS OF ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEM USING THE TRANSFER MATRIX METHOD
|
|
|
- Neal Hodges
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
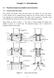
1 ANALYSIS OF ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEM USING THE TRANSFER MATRIX METHOD Mohammad T. Ahmadian Department of Mehanial Engineering Omid Ghasemaliadeh Department of Mehanial Engineering Center of Eellene in Dnamis, rootis, and Automation, Sharif Universit of Tehnolog, Tehran , Iran. Hossein Sadeghi Department of Mehanial Engineering Mohammad Bonadar Department of Mehanial Engineering ABSTRACT One of the methods to find the natural frequenies of rotating sstems is the appliation of the transfer matri method. In this method the rotor is modeled as several elements along the shaft whih have their own mass and moment of inertia. Using these elements, the entire ontinuous sstem is disretied and the orresponding differential equation an e stated in matri form. The earings at the end of the shaft are modeled as equivalent spring and dampers whih are applied as oundar onditions to the disretied sstem. In this paper the dnamis of a rotor-earing sstem is analed, onsidering the grosopi effet. The thiness of the dis and earings is also taen into aount. Continuous model is used for shaft. Results Show that, the stiffness of the shaft and the natural frequenies of the sstem inrease, while the amplitude of viration dereases as a onsequene of inreasing the thiness of the earing. 1 INTRODUCTION Rotating shafts have an important role in power transmission and are used etensivel in mahines suh as turines, generators, eletrial motors and et. Various methods have een used in analing rotar sstems. The Jeffott model [1] for rotors assumes a massless shaft having a rigid rotor on it. The transfer matri is a useful method for analing elasti strutures []. The transfer matries of man standard parts are given in handoos. Sometimes, however, the required transfer matri is not atalogued. It is often possile to find the transfer matri using simple dnami equations or using results that are taulated in engineering handoos. The merit of transfer matri method lies in the fat that the dnamis of ompliated sstems an e simplified into a sstem of algerai equations. Prohl [3] in 195 suggested the transfer matri method. lund and orutt [] in 1967 used this method with the ontinuous model for shaft and unalane in dis taen into aount. Kir and Bansal [5] in 1975 used the transfer matri method for alulating damped natural frequenies. Kang and Tan [6] in 1998 investigated disontinuit in shafts using this method. In this paper a Continuous model is used for the shaft and the grosopi effet is also taen into aount. The e feature of this stud is that the thiness of the dis is onsidered and the width of supporting end earings is also modeled. dnamis of the shaft. This theor assumes a onstant transversal shear strain at the diretion of thiness of the eam. To determine the shear fores, a orretion fator (K) is used. Eah setion of the shaft is assumed to have two translational and two rotational motions aout the perpendiular aes. In this paper the fluid film journal earing is onsidered for oth ends of the shaft. Sine the earings have muh more damping effet than the shaft, this effet is negleted for the shaft and the motion of shaft is assumed to e undamped. The earings are modeled as equivalent spring and dampers whih are applied as oundar onditions to the disretied sstem. The transfer matri of the shaft and the dis are otained assuming that the grosopi effet is present and the dis has a finite thiness. 3 SHAFT TRANSFER MATRIX An element of the defleted shaft in the and planes is depited in figs.1 and, respetivel. The susripts l and r orrespond to left and right sides of the element. The righthanded loal oordinate sstem 1, 1, 1 stis to the shaft having its 1 ais in the aial diretion of the shaft. As shown elow, the variation of shear fores and ending moments at the oth ends of the element is alulated using partial derivatives. Figure 1. Element of shaft in plane MODELING ASSUMPTIONS In this analsis the viration amplitude is assumed to e small. The Timosheno eam theor is used for epressing the 1
2 Figure. Element of shaft in plane The resultant moment vetors for the element with unit length ( d 1) is M Q M M Q (1) 0 and the angular momentum vetor is I t H I t () I Where and are the rotation of shaft aout and ais, repetivel and are assumed to e small as a onsequene of assuming the viration amplitude to e small, and is the spin veloit and I and I are the seond moments of area whih are assumed to e equal. Newton s seond law for rotation is epressed as; [7] dh M ( ) ΩH (3) dt where T Ω () t t is the angular veloit of the loal oordinate sstem. Sustituting equs. 1, and into equ. 3 results in M Q I I I t t t (5) M Q I I I t t t the resultant eternal fore vetor eerted on the element is Q Q F (6) 0 Appling the Newton s seond law to the element results in Q, Q A A (7) t t Equations 5 and 7 onstitute the partial differential equation of the shaft. The following equations govern the ending moment and shear fore in the shaft. [8] M EI, M EI (8) Q KAG, Q KAG B replaing equ. 8 into equs. 5 and 7 the governing differential equations of the shaft in and planes are otained, whih simplifies to: KG E t KEG t 3 3 A 0 3 EI t E t KG t (9) KG E t KEG t 3 3 A 0 3 EI t E t KG t The general solution to these PDEs is in the form of: ˆ ˆ os ts sin t (10) os ˆ sin ˆ t s t where ˆ is the natural frequen of the sstem. Sustituting equ. 10 into equ. 9 results in four ODEs whih require that the fators of Sin and Cos to e ero in order to have a nontrivial solution. The solution to the aove set of ODE is in the form of: ue, s ue s (11) ve, s vse B sustituting the assumed solution into the four equations that have een reated, a set of algerai equations is otained whih is not stated here for the sae of revit. In order to have a nontrivial solution the determinant of the oeffiient matri should vanish whih results in the following harateristi equation: 3 A KG I I E I I KG KGEI KGI (1) 3 A KG I I E I 0 I KG KGEI KGI
3 The aove equation has the following eight roots: 1, i, 3, i, whih result the following statements for the four unnowns us, u, vs, v us v, u vs, fori, 1 (13) us v, u vs, fori, 3 Using the otained roots, the displaement amplitudes ma e epressed as; 1osh 1sinh 13os sin 5osh 36sinh 37os 8sin s 9osh 110sinh 111os 1sin 13 osh 31 sinh 315 os 16 sin (1) 1osh 1sinh 13os sin 5osh 36sinh 37 os8sin s 9osh 110sinh 111os 1sin osh sinh os sin All the i oeffiients in the aove equation are olleted into the vetor B. B i 16 1 (15) To otain the transfer matri of the shaft it is neessar to epress the state vetor in one side of the element in terms of the state vetor in the other side. The state vetor for the shaft is: S { s s s s (16) T M Ms M M s Q Qs Q Qs} where s and indies orrespond to the sin and os epressions as stated for and in equ. 10. A vetor of position derivatives is also defined as; W { s s s s (17) T s s s s } At two ends of the element, the aove vetor is equal to: W 0 A0B (18) W A B L L where A 0 and are given in appendi 1. B omitting the Bvetor in equs. 16 we onlude that; 1 WL AL A0 WL A W 0 (19) B epanding the omponents in the W vetor, the relation etween W and S ma e found. Q M 1,, ( A ) KAG EI KAG 1 Q ( ) ( Q I I ) EI KG KAG Q M 1 (0),, ( A ) KAG EI KAG 1 Q ( Q I I ) ( ) EI KG KAG B olleting the aove relations into matri form, the following relation is resulted W F S (1) where F is given in appendi 1. Using equs. 19 and 1 the state vetor in one side of the element ma e related to that of the other side as follows: 1 1 S F W F A W L L 0 1 F AFS TS 0 0 () So the transfer matri of the shaft is otained from. 1 1 T F A A F (3) 1616 L 0 DISK TRANSFER MATRIX The dis free od diagram is depited in Fig. 3. () M l (M ) l Q l Q r (Q ) r h (Q ) l M r (M ) r 0 (0 ) Figure 3. Free od diagram of dis Here it is assumed that the dis is nonhomogeneous suh that its enter of mass is loated a small distane r off the geometri enter. It is also assumed that r is suh small that its effet on the inertia tensor ma e negleted. So the inertia tensor of the dis is written as: Id 0 0 I 0 Id 0 () 0 0 I d where I d is the mass moment of inertia of the dis aout an ais passing through its enter of gravit (CG). Again the Newton s seond law is used to otain the equations of motion for the dis. Appliation of Newton s seond law to translational motion of the dis results in: l r m( r os t) Ql Qr (5) l r m( r sin t) Ql Qr Newton s seond law in rotational motion is given in equ. 3. The angular momentum of dis is H I Ω (6) where Ω is the same as than in equ.. The otained angular momentum should e transformed into the gloal oordinate sstem using a rotation matri R t. M R( t) H Ω( R( t) H) (7) The resultant of moment vetors ating on the dis is:
4 h M Mr ( Q Qr) h M M r M ( Q Qr ) (8) 0 Sustituting equs. 6 and 8 into equ. 7 ields the equation of motion for rotation of the dis. Again writing the degrees of freedom as in equ. 10, the aove governing differential equations are simplified to some algerai equations. Using the following additional equations; r l, r l (9) r l h l, r l h l the state vetor at oth ends of the dis ma now e related and the transfer matri is otained. 5 BEARING TRANSFER MATRIX A linear model is assumed for earings whih uses two equivalent pairs of spring and dampers for eah earing as shown in fig.. X (Y) Q l M l t M r Q r K/ C/ K/ C/ Figure. Bearing model In this figure t represents the length of the shaft that lies in the aring and or is the foundation displaement. This model assumes that eah earing an withstand moment in addition to transversal load. In a simplified model we assume that the earing fore vetor an e written as; F f(, ) iˆg(, ) ˆj (30) where f (, ) (31) g(, ) the fore and moment resultants are as follows; 0 Z F Ql Qr l l r r l l r r F Ql Qr l l r r l l r r M M r M l l t t Ql Qr l t r t (3) r t l t l t r t r t M Ml Mr l t t Ql Qr l t r t r t l t l t r t r t Using the Newton s seond law in rotation and translation and using the following geometrial additional equations; r l, r l (33) r l t, r l t the governing differential equation of the earing is otained. Again assuming harmoni motion for all degrees of freedom (as equ. 10), the governing algerai equation is otained whih is used to alulate the transfer matri of the earing. To otain the transfer matri etween two desired points of the sstem, the transfer matries of the individual elements loated etween the points should e multiplied onsequentl. If the transfer matri of the whole sstem is availale, appling the oundar onditions on the state vetor of oth ends will result in a relation among the unnown properties of the sstem. 6 RESULTS To investigate the appliailit of this method in dnami analsis of rotor-earing sstems, an eample is provided. A shaft arring several diss is supported on two earings on oth ends as shown in fig. 5.
5 Figure 5. Shemati figure of a rotor In this eample a fleile shaft is arring three similar diss and two earings are supporting the shaft. The parameters of the sstem are given in tale 1. Tale 1. Parameters of the rotor-earing sstem. Modulus of elastiit N / m Shear modulus N / m Densit g / m Dis mass g 13.7 Polar moment of inertia g. m 100 Mass moment of inertia g. m 51 Unalane of dis g. m Shaft diameter m When the dis width is ignored the amplitude-rotational speed urve in fig. 6 is otained. Figure 6. response of the sstem when onsidering the dis width It is shown that the first natural frequen of the sstem has inreased ompared to the previous ase. The inrease of the natural frequen is attriuted to the fat that onsidering the dis width, the effetive length of the shaft dereases and hene the sstem eomes more rigid. The derease in the amplitude of viration is another onsequene of thiening the dis. The real ase an e ahieved when oth the dis and earing thinesses are taen into aount. Figure 7 orresponds to this ase. Figure 5. response of the sstem when ignoring the dis width In the aove figure the pi amplitude orresponds to the first natural frequen of the sstem whih agrees with approimate methods availale suh as the Dunerle s method. When the thiness of the dis is also taen into aount, the response urve hanges signifiantl as depited in fig. 6. Figure 7. response of the sstem when onsidering oth the dis and earing widths It is oserved from fig. 7 that onsidering the width of earing the natural frequen inreases again while the amplitude of viration has dereased. 7 CONCLUSIONS In this paper the matri transfer method is applied to rotorearing sstem. The transfer matri of individual elements inluding the shaft, dis and the earing are otained. The
6 merit of this approah over the onventional approimate methods is that the thiness of the diss and the earings ma also e onsidered. It is shown that the thiness of diss and earing have a onsiderale effet on the viration ehavior of the sstem. This method an e applied to rotor-earing sstems with various onfigurations. 6 REFERENCES [1] Rao, S.S., 1983, Rotor Dnamis, John Wile & Sons, Newor [] Pestel, E. C., and Leie, F. A., 1963, Matri Methods in Elastomehanis, MGrawHill, New or. [3] Prohl, M. A., 195, "A General Method for Calulating Critial Speeds of Fleile Rotors", ASME J. Appl. Meh., Vol. 67, p. 1. [] Lund, J. W., and Orut, F.K., 1967, Calulations and Eperiments on the Unalane Response of a Fleile Rotor, ASME Journal of Engineering for Industr, Vol. 89 (), pp [5] Bansal, P. N., and Kir, R. G., 1975, "Stailit and Damped Critial Speeds of a Fleile Rotor in Fluid Film Bearings," ASME J. Ind., Series B, 97(), pp [6] Tan, C.A., Kang. B., 1999, Free viration of aiall loaded, rotating Timosheno shaft sstems the wavetrain losure priniple, International Journal of Solids and Strutures, Vol 36, pp [7] Meriam, J.L, Kraige L.G, 1998, Dnamis, John Wile & Sons, New or. [8] Beer, F.P, Johnston, J.R., 199, Mehanis of materials, M Graw Hill, Singapore. APPENDIX 1- SOME TRANSFER MATRICES A ,1...8 osh( 1L) sinh( 1L) os( L) sin( 1L) osh( 3L) sinh( 1L) os( L) sin( 1L) sinh( 1L) 1 osh( 1L) 1 sin( L) os( L) sinh( 3L) 3 osh( 3L) 3 sin( L) os( L) osh( 1L) 1 sinh( 1L) 1 os( L) sin( L) osh( 3L) 3 sinh( 3L) 3 os( L) sin( L) sinh( 1L) 1 osh( 1L) 1 sinh( L) os( L) sinh( 3L) 3 osh( 3L) 3 sinh( L) os( L)
7 1...8, osh( L) sinh( L) os( L) sin( L) osh( L) sinh( L) os( L) sin( L) sinh( 1L) 1 osh( 1L) 1 sin( L) os( L) sinh( 3L) 3 osh( 3L) 3 sin( L) os( L) osh( 1L) 1 sinh( 1L) 1 os( L) sin( L) osh( 3L) 3 sinh( 3L) 3 os( L) sin( L) sinh( 1L) 1 osh( 1L) 1 sin( L) os( L) sinh( 3L) 3 osh( 3L) 3 sin( L) os( L) ,1...8 osh( 1L) sinh( 1L) os( L) sin( L) osh( 3L) sinh( 3L) os( L) sin( L) sinh( 1L) 1 osh( 1L) 1 sin( L) os( L) sinh( 3L) osh( 3L) sin( L) os( L) osh( 1L) 1 sinh( 1L) 1 os( L) sin( L) osh( 3L) 3 sinh( 3L) 3 os( L) sin( L) sinh( 1L) 1 osh( 1L) 1 sin( L) os( L) sinh( 3L) 3 osh( 3L) 3 sin( L) os( L) , osh( 1L) sinh( 1L) os( L) sin( 1L) osh( 3L) sinh( 1L) os( L) sin( 1L) sinh( 1L) 1 osh( 1L) 1 sin( L) os( L) sinh( 3L) 3 osh( 3L) 3 sin( L) os( L) osh( 1L) 1 sinh( 1L) 1 os( L) sin( L) osh( 3L) 3 sinh( 3L) 3 os( L) sin( L) sinh( 1L) 1 osh( 1L) 1 sin( L) os( L) sinh( 3L) 3 osh( 3L) 3 sin( L) os( L)
SHAFTS: TORSION LOADING AND DEFORMATION
 ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
Relativity in the Global Positioning System
 Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: [email protected] July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
Relativity in the Global Positioning System Neil Ashby Department of Physis,UCB 390 University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-00390 NIST Affiliate Email: [email protected] July 0, 006 AAPT workshop
HEAT CONDUCTION. q A q T
 HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
The analysis of brushing tool characteristics
 ARCHIVES OF CIVIL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Vol. IV 004 No. 4 The analysis of rushing tool harateristis Kiele University of Tehnology, al. Tysiąleia P. P. 7, 5-34 Kiele In this paper, an analytial proedure
ARCHIVES OF CIVIL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Vol. IV 004 No. 4 The analysis of rushing tool harateristis Kiele University of Tehnology, al. Tysiąleia P. P. 7, 5-34 Kiele In this paper, an analytial proedure
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
Fig. 1.1 Rectangular foundation plan.
 Footings Example 1 Design of a square spread footing of a seven-story uilding Design and detail a typial square spread footing of a six ay y five ay seven-story uilding, founded on stiff soil, supporting
Footings Example 1 Design of a square spread footing of a seven-story uilding Design and detail a typial square spread footing of a six ay y five ay seven-story uilding, founded on stiff soil, supporting
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
10.1 The Lorentz force law
 Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismic Code IS 1893 (Part I)
 Doument No. :: IITK-GSDMA-EQ1-V.0 inal Report :: A - Earthquake Codes IITK-GSDMA Projet on Building Codes Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismi Code IS 1893 (Part I) by Dr. Sudhir K Jain Department of
Doument No. :: IITK-GSDMA-EQ1-V.0 inal Report :: A - Earthquake Codes IITK-GSDMA Projet on Building Codes Explanatory Examples on Indian Seismi Code IS 1893 (Part I) by Dr. Sudhir K Jain Department of
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
tr(a + B) = tr(a) + tr(b) tr(ca) = c tr(a)
 Chapter 3 Determinant 31 The Determinant Funtion We follow an intuitive approah to introue the efinition of eterminant We alreay have a funtion efine on ertain matries: the trae The trae assigns a numer
Chapter 3 Determinant 31 The Determinant Funtion We follow an intuitive approah to introue the efinition of eterminant We alreay have a funtion efine on ertain matries: the trae The trae assigns a numer
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow Behaviour through Industrial Processing Lines
 Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Measurement of Powder Flow Properties that relate to Gravity Flow ehaviour through Industrial Proessing Lines A typial industrial powder proessing line will inlude several storage vessels (e.g. bins, bunkers,
Dynamic Model of the Spacecraft Position and Attitude
 Dnami Model of the Spaeraft Position and Attitude Basilio BNA, nrio CANUT Dipartimento di Automatia e Informatia, Politenio di Torino Corso Dua degli Abruzzi 4 9 Torino, Ital tel. 564 76, fa 564 799 [email protected]
Dnami Model of the Spaeraft Position and Attitude Basilio BNA, nrio CANUT Dipartimento di Automatia e Informatia, Politenio di Torino Corso Dua degli Abruzzi 4 9 Torino, Ital tel. 564 76, fa 564 799 [email protected]
10 UNSTEADY FLOW IN OPEN CHANNELS
 0 UNTEY FLOW IN OEN CHNNEL 0. Introdution Unsteady flow in open hannels differs from that in losed onduits in that the eistene of a free surfae allows the flow ross-setion to freely hange, a fator whih
0 UNTEY FLOW IN OEN CHNNEL 0. Introdution Unsteady flow in open hannels differs from that in losed onduits in that the eistene of a free surfae allows the flow ross-setion to freely hange, a fator whih
Programming Basics - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physics.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html
 CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
Equivalent Spring Stiffness
 Module 7 : Free Undamped Vibration of Single Degree of Freedom Systems; Determination of Natural Frequency ; Equivalent Inertia and Stiffness; Energy Method; Phase Plane Representation. Lecture 13 : Equivalent
Module 7 : Free Undamped Vibration of Single Degree of Freedom Systems; Determination of Natural Frequency ; Equivalent Inertia and Stiffness; Energy Method; Phase Plane Representation. Lecture 13 : Equivalent
5.2 The Master Theorem
 170 CHAPTER 5. RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 5.2 The Master Theorem Master Theorem In the last setion, we saw three different kinds of behavior for reurrenes of the form at (n/2) + n These behaviors depended
170 CHAPTER 5. RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 5.2 The Master Theorem Master Theorem In the last setion, we saw three different kinds of behavior for reurrenes of the form at (n/2) + n These behaviors depended
Modeling Mechanical Systems
 chp3 1 Modeling Mechanical Systems Dr. Nhut Ho ME584 chp3 2 Agenda Idealized Modeling Elements Modeling Method and Examples Lagrange s Equation Case study: Feasibility Study of a Mobile Robot Design Matlab
chp3 1 Modeling Mechanical Systems Dr. Nhut Ho ME584 chp3 2 Agenda Idealized Modeling Elements Modeling Method and Examples Lagrange s Equation Case study: Feasibility Study of a Mobile Robot Design Matlab
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsica, vol. 21, no. 4, Dezembro, 1999 469. Surface Charges and Electric Field in a Two-Wire
 Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsia, vol., no. 4, Dezembro, 999 469 Surfae Charges and Eletri Field in a Two-Wire Resistive Transmission Line A. K. T.Assis and A. J. Mania Instituto de Fsia Gleb Wataghin'
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsia, vol., no. 4, Dezembro, 999 469 Surfae Charges and Eletri Field in a Two-Wire Resistive Transmission Line A. K. T.Assis and A. J. Mania Instituto de Fsia Gleb Wataghin'
Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. [email protected] Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. [email protected] Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in.
ES240 Solid Mechanics Fall 2007. Stress field and momentum balance. Imagine the three-dimensional body again. At time t, the material particle ( x, y,
 S40 Solid Mechanics Fall 007 Stress field and momentum balance. Imagine the three-dimensional bod again. At time t, the material particle,, ) is under a state of stress ij,,, force per unit volume b b,,,.
S40 Solid Mechanics Fall 007 Stress field and momentum balance. Imagine the three-dimensional bod again. At time t, the material particle,, ) is under a state of stress ij,,, force per unit volume b b,,,.
CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS
 J-1 CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS INTRODUCTION Chapter J of the addresses the design and heking of onnetions. The hapter s primary fous is the design of welded and bolted onnetions. Design requirements
J-1 CHAPTER J DESIGN OF CONNECTIONS INTRODUCTION Chapter J of the addresses the design and heking of onnetions. The hapter s primary fous is the design of welded and bolted onnetions. Design requirements
VOLTAGE CONTROL WITH SHUNT CAPACITANCE ON RADIAL DISTRIBUTION LINE WITH HIGH R/X FACTOR. A Thesis by. Hong-Tuan Nguyen Vu
 VOLTAGE CONTROL WITH SHUNT CAPACITANCE ON RADIAL DISTRIBUTION LINE WITH HIGH R/X FACTOR A Thesis by Hong-Tuan Nguyen Vu Eletrial Engineer, Polytehni University of HCMC, 1993 Submitted to the College of
VOLTAGE CONTROL WITH SHUNT CAPACITANCE ON RADIAL DISTRIBUTION LINE WITH HIGH R/X FACTOR A Thesis by Hong-Tuan Nguyen Vu Eletrial Engineer, Polytehni University of HCMC, 1993 Submitted to the College of
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topical Insights from our Subject Matter Experts
 FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
SUBSTRUCTURE EXAMPLE. Full Height Abutment on Spread Footing
 SUBSTRUCTURE EXAMPLE Full Height Abutment on Spread Footing This example illustrates the design of a full height abutment on spread footings for a single span ast-in-plae post-tensioned onrete box girder
SUBSTRUCTURE EXAMPLE Full Height Abutment on Spread Footing This example illustrates the design of a full height abutment on spread footings for a single span ast-in-plae post-tensioned onrete box girder
Effects of Inter-Coaching Spacing on Aerodynamic Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains
 Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Unit - 6 Vibrations of Two Degree of Freedom Systems
 Unit - 6 Vibrations of Two Degree of Freedom Systems Dr. T. Jagadish. Professor for Post Graduation, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bangalore Institute of Technology, Bangalore Introduction A two
Unit - 6 Vibrations of Two Degree of Freedom Systems Dr. T. Jagadish. Professor for Post Graduation, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bangalore Institute of Technology, Bangalore Introduction A two
Recovering Articulated Motion with a Hierarchical Factorization Method
 Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Slide 10.1. Basic system Models
 Slide 10.1 Basic system Models Objectives: Devise Models from basic building blocks of mechanical, electrical, fluid and thermal systems Recognize analogies between mechanical, electrical, fluid and thermal
Slide 10.1 Basic system Models Objectives: Devise Models from basic building blocks of mechanical, electrical, fluid and thermal systems Recognize analogies between mechanical, electrical, fluid and thermal
1.3 Complex Numbers; Quadratic Equations in the Complex Number System*
 04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
04 CHAPTER Equations and Inequalities Explaining Conepts: Disussion and Writing 7. Whih of the following pairs of equations are equivalent? Explain. x 2 9; x 3 (b) x 29; x 3 () x - 2x - 22 x - 2 2 ; x
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Rotation: Moment of Inertia and Torque
 Rotation: Moment of Inertia and Torque Every time we push a door open or tighten a bolt using a wrench, we apply a force that results in a rotational motion about a fixed axis. Through experience we learn
Rotation: Moment of Inertia and Torque Every time we push a door open or tighten a bolt using a wrench, we apply a force that results in a rotational motion about a fixed axis. Through experience we learn
Derivation of Einstein s Equation, E = mc 2, from the Classical Force Laws
 Apeiron, Vol. 14, No. 4, Otober 7 435 Derivation of Einstein s Equation, E = m, from the Classial Fore Laws N. Hamdan, A.K. Hariri Department of Physis, University of Aleppo, Syria [email protected],
Apeiron, Vol. 14, No. 4, Otober 7 435 Derivation of Einstein s Equation, E = m, from the Classial Fore Laws N. Hamdan, A.K. Hariri Department of Physis, University of Aleppo, Syria [email protected],
Impedance Method for Leak Detection in Zigzag Pipelines
 10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
Earthquake Loss for Reinforced Concrete Building Structures Before and After Fire damage
 Earthquake Loss for Reinfored Conrete Building Strutures Before and After Fire damage Pai-Mei LIU, Yi-Hsuan Tu and Maw-Shyong SHEU 3 ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to propose a rational analytial
Earthquake Loss for Reinfored Conrete Building Strutures Before and After Fire damage Pai-Mei LIU, Yi-Hsuan Tu and Maw-Shyong SHEU 3 ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to propose a rational analytial
Physical and mathematical postulates behind relativity
 Physial and mathematial postulates behind relativity Tuomo Suntola Physis Foundations Soiety, Finland, www.physisfoundations.org In this presentation we look for answers to questions: What was the problem
Physial and mathematial postulates behind relativity Tuomo Suntola Physis Foundations Soiety, Finland, www.physisfoundations.org In this presentation we look for answers to questions: What was the problem
4/3 Problem for the Gravitational Field
 4/3 Proble for the Gravitational Field Serey G. Fedosin PO bo 6488 Sviazeva str. -79 Per Russia E-ail: [email protected] Abstrat The ravitational field potentials outside and inside a unifor assive ball
4/3 Proble for the Gravitational Field Serey G. Fedosin PO bo 6488 Sviazeva str. -79 Per Russia E-ail: [email protected] Abstrat The ravitational field potentials outside and inside a unifor assive ball
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Source Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings
 Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Section 0.3 Power and exponential functions
 Section 0.3 Power and eponential functions (5/6/07) Overview: As we will see in later chapters, man mathematical models use power functions = n and eponential functions =. The definitions and asic properties
Section 0.3 Power and eponential functions (5/6/07) Overview: As we will see in later chapters, man mathematical models use power functions = n and eponential functions =. The definitions and asic properties
Relativistic Kinematics -a project in Analytical mechanics Karlstad University
 Relativisti Kinematis -a projet in Analytial mehanis Karlstad University Carl Stigner 1th January 6 Abstrat The following text is a desription of some of the ontent in hapter 7 in the textbook Classial
Relativisti Kinematis -a projet in Analytial mehanis Karlstad University Carl Stigner 1th January 6 Abstrat The following text is a desription of some of the ontent in hapter 7 in the textbook Classial
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
CHAP 4 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF BEAMS AND FRAMES INTRODUCTION
 CHAP FINITE EEMENT ANAYSIS OF BEAMS AND FRAMES INTRODUCTION We learned Direct Stiffness Method in Chapter imited to simple elements such as D bars we will learn Energ Method to build beam finite element
CHAP FINITE EEMENT ANAYSIS OF BEAMS AND FRAMES INTRODUCTION We learned Direct Stiffness Method in Chapter imited to simple elements such as D bars we will learn Energ Method to build beam finite element
Income Protection CLAIM FORM
 Inome Protetion CLAIM FORM PLEASE COMPLETE THIS APPLICATION IN BLACK PEN ONLY USING BLOCK LETTERS 1 PERSONAL DETAILS Poliy numer Important notes: a This form must e ompleted in full and returned to PO
Inome Protetion CLAIM FORM PLEASE COMPLETE THIS APPLICATION IN BLACK PEN ONLY USING BLOCK LETTERS 1 PERSONAL DETAILS Poliy numer Important notes: a This form must e ompleted in full and returned to PO
TS150 Visible (exposed) fixing with screws on a timber sub-frame
 TS150 Visile (exposed) fixing with srews on a timer su-frame This system offers a ost effetive solution for installing Trespa Meteon panels in a large variety of panel dimensions. Trespa Meteon panels
TS150 Visile (exposed) fixing with srews on a timer su-frame This system offers a ost effetive solution for installing Trespa Meteon panels in a large variety of panel dimensions. Trespa Meteon panels
Modelling and Simulation of Closed Loop Controlled Buck Converter Fed Pmbldc Drive System
 Researh Journal of Applied Sienes, Engineering and Tehnology 3(4): 284-289, 2011 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Sientifi Organization, 2011 Reeived: Feruary 14, 2011 Aepted: Marh 15, 2011 Pulished: April 20,
Researh Journal of Applied Sienes, Engineering and Tehnology 3(4): 284-289, 2011 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Sientifi Organization, 2011 Reeived: Feruary 14, 2011 Aepted: Marh 15, 2011 Pulished: April 20,
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review 6 (5) (2013) 143-148. Research Article
 Jestr Journal o Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review 6 (5) (13) 143-148 Researh Artile JOURNAL OF Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review www.jestr.org Numerial Analyses on Seismi Behaviour o Conrete-illed
Jestr Journal o Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review 6 (5) (13) 143-148 Researh Artile JOURNAL OF Engineering Siene and Tehnology Review www.jestr.org Numerial Analyses on Seismi Behaviour o Conrete-illed
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Introduction to Mechanical Behavior of Biological Materials
 Introduction to Mechanical Behavior of Biological Materials Ozkaya and Nordin Chapter 7, pages 127-151 Chapter 8, pages 173-194 Outline Modes of loading Internal forces and moments Stiffness of a structure
Introduction to Mechanical Behavior of Biological Materials Ozkaya and Nordin Chapter 7, pages 127-151 Chapter 8, pages 173-194 Outline Modes of loading Internal forces and moments Stiffness of a structure
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynamic Cycles of Reciprocating and Rotary Engines - R.S.
 THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
TOP VIEW. FBD s TOP VIEW. Examination No. 2 PROBLEM NO. 1. Given:
 RLEM N. 1 Given: Find: vehicle having a mass of 500 kg is traveling on a banked track on a path with a constant radius of R = 1000 meters. t the instant showing, the vehicle is traveling with a speed of
RLEM N. 1 Given: Find: vehicle having a mass of 500 kg is traveling on a banked track on a path with a constant radius of R = 1000 meters. t the instant showing, the vehicle is traveling with a speed of
Intuitive Guide to Principles of Communications By Charan Langton www.complextoreal.com
 Intuitive Guide to Priniples of Communiations By Charan Langton www.omplextoreal.om Understanding Frequeny Modulation (FM), Frequeny Shift Keying (FSK), Sunde s FSK and MSK and some more The proess of
Intuitive Guide to Priniples of Communiations By Charan Langton www.omplextoreal.om Understanding Frequeny Modulation (FM), Frequeny Shift Keying (FSK), Sunde s FSK and MSK and some more The proess of
Affine Transformations
 A P P E N D I X C Affine Transformations CONTENTS C The need for geometric transformations 335 C2 Affine transformations 336 C3 Matri representation of the linear transformations 338 C4 Homogeneous coordinates
A P P E N D I X C Affine Transformations CONTENTS C The need for geometric transformations 335 C2 Affine transformations 336 C3 Matri representation of the linear transformations 338 C4 Homogeneous coordinates
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: [email protected] 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: [email protected] 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
( 1 ) Obtain the equation of the circle passing through the points ( 5, - 8 ), ( - 2, 9 ) and ( 2, 1 ).
 PROBLEMS 03 CIRCLE Page ( ) Obtain the equation of the irle passing through the points ( 5 8 ) ( 9 ) and ( ). [ Ans: x y 6x 48y 85 = 0 ] ( ) Find the equation of the irumsribed irle of the triangle formed
PROBLEMS 03 CIRCLE Page ( ) Obtain the equation of the irle passing through the points ( 5 8 ) ( 9 ) and ( ). [ Ans: x y 6x 48y 85 = 0 ] ( ) Find the equation of the irumsribed irle of the triangle formed
Another Look at Gaussian CGS Units
 Another Look at Gaussian CGS Units or, Why CGS Units Make You Cool Prashanth S. Venkataram February 24, 202 Abstrat In this paper, I ompare the merits of Gaussian CGS and SI units in a variety of different
Another Look at Gaussian CGS Units or, Why CGS Units Make You Cool Prashanth S. Venkataram February 24, 202 Abstrat In this paper, I ompare the merits of Gaussian CGS and SI units in a variety of different
CHAPTER 13 SIMPLE LINEAR REGRESSION. Opening Example. Simple Regression. Linear Regression
 Opening Example CHAPTER 13 SIMPLE LINEAR REGREION SIMPLE LINEAR REGREION! Simple Regression! Linear Regression Simple Regression Definition A regression model is a mathematical equation that descries the
Opening Example CHAPTER 13 SIMPLE LINEAR REGREION SIMPLE LINEAR REGREION! Simple Regression! Linear Regression Simple Regression Definition A regression model is a mathematical equation that descries the
Lecture L22-2D Rigid Body Dynamics: Work and Energy
 J. Peraire, S. Widnall 6.07 Dynamics Fall 008 Version.0 Lecture L - D Rigid Body Dynamics: Work and Energy In this lecture, we will revisit the principle of work and energy introduced in lecture L-3 for
J. Peraire, S. Widnall 6.07 Dynamics Fall 008 Version.0 Lecture L - D Rigid Body Dynamics: Work and Energy In this lecture, we will revisit the principle of work and energy introduced in lecture L-3 for
COMPLEX STRESS TUTORIAL 3 COMPLEX STRESS AND STRAIN
 COMPLX STRSS TUTORIAL COMPLX STRSS AND STRAIN This tutorial is not part of the decel unit mechanical Principles but covers elements of the following sllabi. o Parts of the ngineering Council eam subject
COMPLX STRSS TUTORIAL COMPLX STRSS AND STRAIN This tutorial is not part of the decel unit mechanical Principles but covers elements of the following sllabi. o Parts of the ngineering Council eam subject
Center of Gravity. We touched on this briefly in chapter 7! x 2
 Center of Gravity We touched on this briefly in chapter 7! x 1 x 2 cm m 1 m 2 This was for what is known as discrete objects. Discrete refers to the fact that the two objects separated and individual.
Center of Gravity We touched on this briefly in chapter 7! x 1 x 2 cm m 1 m 2 This was for what is known as discrete objects. Discrete refers to the fact that the two objects separated and individual.
The Reduced van der Waals Equation of State
 The Redued van der Waals Equation of State The van der Waals equation of state is na + ( V nb) n (1) V where n is the mole number, a and b are onstants harateristi of a artiular gas, and R the gas onstant
The Redued van der Waals Equation of State The van der Waals equation of state is na + ( V nb) n (1) V where n is the mole number, a and b are onstants harateristi of a artiular gas, and R the gas onstant
INVESTIGATION OF STABILITY ON NONLINEAR OSCILATIONS WITH ONE DEGREE OF FREEDOM
 91 Kragujeva J. Math. 25 (2003) 91 96. INVESTIGATION OF STABILITY ON NONLINEAR OSCILATIONS WITH ONE DEGREE OF FREEDOM Julka Knežević-Miljanović 1 and Ljubia Lalović 2 1 Mathematis faulty of Belgrade, Serbia
91 Kragujeva J. Math. 25 (2003) 91 96. INVESTIGATION OF STABILITY ON NONLINEAR OSCILATIONS WITH ONE DEGREE OF FREEDOM Julka Knežević-Miljanović 1 and Ljubia Lalović 2 1 Mathematis faulty of Belgrade, Serbia
cos t sin t sin t cos t
 Exerise 7 Suppose that t 0 0andthat os t sin t At sin t os t Compute Bt t As ds,andshowthata and B ommute 0 Exerise 8 Suppose A is the oeffiient matrix of the ompanion equation Y AY assoiated with the
Exerise 7 Suppose that t 0 0andthat os t sin t At sin t os t Compute Bt t As ds,andshowthata and B ommute 0 Exerise 8 Suppose A is the oeffiient matrix of the ompanion equation Y AY assoiated with the
BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL
 BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL Dr. S. K. Prasad Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering, Mysore 7.0 Syllabus. Definition of ultimate, net and safe bearing apaities, Allowable bearing pressure
BEARING CAPACITY OF SOIL Dr. S. K. Prasad Professor of Civil Engineering S. J. College of Engineering, Mysore 7.0 Syllabus. Definition of ultimate, net and safe bearing apaities, Allowable bearing pressure
Research on Virtual Vehicle Driven with Vision
 I.J. Information Tehnolog and Computer Siene, 2011, 4, 29-35 Published Online August 2011 in MECS http://.mes-press.org/) Researh on Virtual Vehile Driven ith Vision Youquan Liu and Yu Cui Shool of Information
I.J. Information Tehnolog and Computer Siene, 2011, 4, 29-35 Published Online August 2011 in MECS http://.mes-press.org/) Researh on Virtual Vehile Driven ith Vision Youquan Liu and Yu Cui Shool of Information
THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT ALBANY, NY
 P THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT ALBANY, NY 4 Referene Tables for Physial Setting/PHYSICS 006 Edition List of Physial Constants Name Symbol Value Universal gravitational
P THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT ALBANY, NY 4 Referene Tables for Physial Setting/PHYSICS 006 Edition List of Physial Constants Name Symbol Value Universal gravitational
Bypassing Space Explosion in Regular Expression Matching for Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
 Bypassing Spae Explosion in Regular Expression Mathing for Network Intrusion Detetion and Prevention Systems Jignesh Patel Alex X. Liu Eri Torng Department of Computer Siene and Engineering Mihigan State
Bypassing Spae Explosion in Regular Expression Mathing for Network Intrusion Detetion and Prevention Systems Jignesh Patel Alex X. Liu Eri Torng Department of Computer Siene and Engineering Mihigan State
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability
 Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Availability, Reliability, Maintainability, and Capability H. Paul Barringer, P.E. Barringer & Assoiates, In. Humble, TX Triplex Chapter Of The Vibrations Institute Hilton Hotel Beaumont, Texas February
Conversion of short optical pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 35114 007 Conversion of short optial pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory N. N. Zinov ev* Department of Physis, University of Durham, Durham
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 35114 007 Conversion of short optial pulses to terahertz radiation in a nonlinear medium: Experiment and theory N. N. Zinov ev* Department of Physis, University of Durham, Durham
Forward Dynamics of Flexible Multibody Systems
 11 Forward Dynamics of Flexile Multiody Systems So far, several approaches to the solution of the kinematics and dynamics of multiody systems have een presented. It has een assumed in these approaches
11 Forward Dynamics of Flexile Multiody Systems So far, several approaches to the solution of the kinematics and dynamics of multiody systems have een presented. It has een assumed in these approaches
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Acceleration due to Gravity
 Acceleration due to Gravity 1 Object To determine the acceleration due to gravity by different methods. 2 Apparatus Balance, ball bearing, clamps, electric timers, meter stick, paper strips, precision
Acceleration due to Gravity 1 Object To determine the acceleration due to gravity by different methods. 2 Apparatus Balance, ball bearing, clamps, electric timers, meter stick, paper strips, precision
2D Geometrical Transformations. Foley & Van Dam, Chapter 5
 2D Geometrical Transformations Fole & Van Dam, Chapter 5 2D Geometrical Transformations Translation Scaling Rotation Shear Matri notation Compositions Homogeneous coordinates 2D Geometrical Transformations
2D Geometrical Transformations Fole & Van Dam, Chapter 5 2D Geometrical Transformations Translation Scaling Rotation Shear Matri notation Compositions Homogeneous coordinates 2D Geometrical Transformations
Propagation in Lossy Rectangular Waveguides
 10 Propagation in Lossy Retangular Waveguides Kim Ho Yeap 1, Choy Yoong Tham, Ghassan Yassin 3 and Kee Choon Yeong 1 1 Tunku Abdul Rahman University Wawasan Open University 3 University of Oxford 1, Malaysia
10 Propagation in Lossy Retangular Waveguides Kim Ho Yeap 1, Choy Yoong Tham, Ghassan Yassin 3 and Kee Choon Yeong 1 1 Tunku Abdul Rahman University Wawasan Open University 3 University of Oxford 1, Malaysia
Lecture L5 - Other Coordinate Systems
 S. Widnall, J. Peraire 16.07 Dynamics Fall 008 Version.0 Lecture L5 - Other Coordinate Systems In this lecture, we will look at some other common systems of coordinates. We will present polar coordinates
S. Widnall, J. Peraire 16.07 Dynamics Fall 008 Version.0 Lecture L5 - Other Coordinate Systems In this lecture, we will look at some other common systems of coordinates. We will present polar coordinates
Beam Deflections: Second-Order Method
 10 eam Deflections: Second-Order Method 10 1 Lecture 10: EM DEFLECTIONS: SECOND-ORDER METHOD TLE OF CONTENTS Page 10.1 Introduction..................... 10 3 10.2 What is a eam?................... 10 3
10 eam Deflections: Second-Order Method 10 1 Lecture 10: EM DEFLECTIONS: SECOND-ORDER METHOD TLE OF CONTENTS Page 10.1 Introduction..................... 10 3 10.2 What is a eam?................... 10 3
Complex Numbers. w = f(z) z. Examples
 omple Numbers Geometrical Transformations in the omple Plane For functions of a real variable such as f( sin, g( 2 +2 etc ou are used to illustrating these geometricall, usuall on a cartesian graph. If
omple Numbers Geometrical Transformations in the omple Plane For functions of a real variable such as f( sin, g( 2 +2 etc ou are used to illustrating these geometricall, usuall on a cartesian graph. If
Lab 7: Rotational Motion
 Lab 7: Rotational Motion Equipment: DataStudio, rotary motion sensor mounted on 80 cm rod and heavy duty bench clamp (PASCO ME-9472), string with loop at one end and small white bead at the other end (125
Lab 7: Rotational Motion Equipment: DataStudio, rotary motion sensor mounted on 80 cm rod and heavy duty bench clamp (PASCO ME-9472), string with loop at one end and small white bead at the other end (125
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization
 Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Soft-Edge Flip-flops for Improved Timing Yield: Design and Optimization Abstrat Parameter variations ause high yield losses due to their large impat on iruit delay. In this paper, we propose the use of
Lecture 16. Newton s Second Law for Rotation. Moment of Inertia. Angular momentum. Cutnell+Johnson: 9.4, 9.6
 Lecture 16 Newton s Second Law for Rotation Moment of Inertia Angular momentum Cutnell+Johnson: 9.4, 9.6 Newton s Second Law for Rotation Newton s second law says how a net force causes an acceleration.
Lecture 16 Newton s Second Law for Rotation Moment of Inertia Angular momentum Cutnell+Johnson: 9.4, 9.6 Newton s Second Law for Rotation Newton s second law says how a net force causes an acceleration.
Winners First Place: Kay Gemba (University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa, USA)
 Aoustial Soiety of Ameria International Student Challenge Problem in Aousti Signal Proessing 14 Student Entry Evaluation Report by the Tehnial Committee on Signal Proessing in Aoustis Bakground Bakground
Aoustial Soiety of Ameria International Student Challenge Problem in Aousti Signal Proessing 14 Student Entry Evaluation Report by the Tehnial Committee on Signal Proessing in Aoustis Bakground Bakground
Lecture 24: Spinodal Decomposition: Part 3: kinetics of the
 Leture 4: Spinodal Deoposition: Part 3: kinetis of the oposition flutuation Today s topis Diffusion kinetis of spinodal deoposition in ters of the onentration (oposition) flutuation as a funtion of tie:
Leture 4: Spinodal Deoposition: Part 3: kinetis of the oposition flutuation Today s topis Diffusion kinetis of spinodal deoposition in ters of the onentration (oposition) flutuation as a funtion of tie:
Asimple analytic method for transistor
 A Simple Analyti Method for ransistor Osillator Design his straightforward mathematial tehnique helps optimize osillator designs By Andrei Grennikov Institute of Miroeletronis, Singapore Asimple analyti
A Simple Analyti Method for ransistor Osillator Design his straightforward mathematial tehnique helps optimize osillator designs By Andrei Grennikov Institute of Miroeletronis, Singapore Asimple analyti
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES
 THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
Recent Progress in Brillouin Scattering Based Fiber Sensors
 Sensors 011, 11, 415-4187; doi:10.3390/s11040415 OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 144-80 www.mdpi.om/journal/sensors Review Reent Progress in rillouin Sattering ased Fiber Sensors Xiaoyi ao * and Liang Chen Physis
Sensors 011, 11, 415-4187; doi:10.3390/s11040415 OPEN ACCESS sensors ISSN 144-80 www.mdpi.om/journal/sensors Review Reent Progress in rillouin Sattering ased Fiber Sensors Xiaoyi ao * and Liang Chen Physis
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Active Load Balancing in a Three-Phase Network by Reactive Power Compensation
 Ative Load Balaning in a hree-phase Network by eative Power Compensation Adrian Pană Politehnia University of imisoara omania. ntrodution. Brief overview of the auses, effets and methods to redue voltage
Ative Load Balaning in a hree-phase Network by eative Power Compensation Adrian Pană Politehnia University of imisoara omania. ntrodution. Brief overview of the auses, effets and methods to redue voltage
