Intelligent Measurement Processes in 3D Optical Metrology: Producing More Accurate Point Clouds
|
|
|
- Ira Carr
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intelligent Measurement Proesses in 3D Optial Metrology: Produing More Aurate Point Clouds Charles Mony, Ph.D. 1 President Creaform in. [email protected] Daniel Brown, Eng. 1 Produt Manager Creaform in. [email protected] Patrik Hébert, Ph.D. 1 3D Optial Metrology Advaned Researh Creaform in. [email protected] 1 Creaform 5825, rue St-Georges Lévis (Québe) Canada G6V 4L2 Word Count: 4488 Number of Images Submitted: 6 Abstrat This paper introdues the new paradigm of intelligent measurement proess in the ontext of 3D optial metrology. Sine new 3D sensor tehnologies an apture 3D points at very high rates on the surfae of objets, it is now possible to quikly apture very dense sets of points on an objet s surfae. This very large quantity of 3D point observations allows one to examine the loal distribution of these points on setion areas before validating their onsisteny with the expeted error model developed at the alibration stage. From these dense point observations, higher quality surfae point measurements an be produed for metrology. An intelligent measurement proess will integrate these steps in real time during apture. We desribe a framework adapted for implementing suh a proess. The result setion presents some appliation ases in metrology. The paper onludes with prospetive omments on intelligent measurement systems. 1. Introdution It is interesting to note that sientifi and tehnologial advanes have always been tightly oupled with the improvement of measuring systems. The 21 st entury has already witnessed the explosion of the ability to measure in several domains. Probably the most signifiant examples are the experiments with the CERN s Large Hadron Collider, eah generating several terabytes of observation data. Closer to our domain, existing 3D optial sensing tehnologies allow quik generation of a tremendous amount of dense points on the surfae of an objet. Indeed, apturing to more than a million 3D points per seond is no longer exoti. This ever growing apability to ollet observations ombined with the improved omputational tehnologies not only paves the way to, but leads us inevitably towards the new paradigm of intelligent measurement. Intelligent measurement is the proess that produes onsistent measurement obtained from a set of basi observations, and whih onsisteny is verified against a model of the measuring proess (the aquisition model) during apture. Reading an ambient temperature of 60 C in a onferene room from a thermometer, or reading a diameter of 100 mm for a oin with a aliper, obviously makes no sense. One would at least make one or several additional readings before providing a reliable measurement or reporting a problem with the devie. Indeed, the observation is not onsistent with the expeted range of values in the urrent ontext of measurement. Several
2 observations (readings) would be neessary to be able to onfirm the onsisteny of eah observation. Consisteny is verified with respet to the aquisition model whih integrates knowledge on the measuring devie and hypotheses on the objet to be measured. These knowledge and hypotheses may be as simple as the typial range of values and the resolution, repeatability and auray of the measurement that an be produed by the devie. When observations are onsistent, improved measurements an also be produed after reduing error due to noise, from several observations. Let s now onsider that the aquisition model is integrated within the measurement proess; that would yield an intelligent measuring system. In the preeding examples, the human is the intelligent agent in the measurement proess. Preferably, intelligene would be integrated into the omputerized system when the quantity of observations inreases and beomes intratable for the human. Integration of intelligene then beomes partiularly valuable with the enormous amount of observations that an be aquired in real time with 3D optial sensors. In this paper, it is shown how to build an intelligent measurement proess in 3D optial metrology. After explaining why optial sensing tehnologies are well suited for the new paradigm in setion 2, we will revisit the whole paradigm of raw 3D points in setion 3. Atually, in any measuring system, 3D point oordinates are the results of several alulations on the observations. Moreover, their noise error distribution is not stritly idential. Setion 4 develops on the priniples for developing an intelligent measuring system. In setion 5, we present the bases of a framework developed for implementing an intelligent measurement proess. Setion 6 shows various results following the appliation of the framework. Finally setion 7 disusses the prospetive in this new paradigm. 2. Capturing a large number of 3D points with optial sensors In metrology, it is ommon pratie to inspet parts by extrating measured harateristis from geometri entities suh as spheres or planes, for instane. The harateristis are based on a limited number of alulated points from touh probe or high density loud of points from an optial 3D sensor. It is also more and more ommon to evaluate the geometri onformity after omparing a 3D point loud with a referene CAD model. During this inspetion, statistis are omputed on the distane between 3D points and their putative mathing points that are the losest on the aligned surfae model. Besides measuring points at higher density on the surfae, optial sensors make it possible to avoid ompensation for the radius of a tatile probe during alignment. Due to the higher point density, it is also possible to apture a dense set of points that are very lose to the boundaries and rease edges. One must keep in mind that the primary objetive while inspeting a part is not to measure 3D points, but the onformity with geometri dimension and tolerane model (GD&T) in order to respet funtional speifiations and assembly of the produt using surfae geometri harateristis. Typially, 3D points measurement is a preliminary step beause it is a simple and flexible way to extrat surfae harateristis and ompare two surfaes. For instane, one may onsider measuring the distane or the angle between two planes. It is lear that 3D points onsidered solely are of no utility sine they annot be ompared. It is the underlying surfae shape that is of interest. Measuring a large number of points makes it possible to better define the surfaes and entities for measuring harateristis but, furthermore, a better sampling will also allow one to haraterize the error loally. The very large number of observations that is possible with a 3D optial sensor allows the appliation of the new intelligent measurement paradigm desribed below.
3 3. Revisiting the paradigm of raw 3D points In metrology, it is ommon pratie to measure harateristis or to ompare a 3D point loud arising from a sensor to the referene surfae. These observations are onsidered raw points, whih errors are independent and identially distributed. Unfortunately, raw points do not exist, and it is erroneous to onsider these measurements as raw observations. They are rather the result of several alulation steps. For instane, in the ase of a CMM-mounted touh probe, basi observations are olleted from the linear or angular enoders of the system. A 3D point is then alulated from the parameters of the mehanial model of the devie and the probe. These parameters are alibrated beforehand. Any error in these parameters will affet several 3D points differently and will not be independent from the measured geometry (e.g.: starting from a simple radius orretion of the probe). A similar situation arises with optial sensors. Let s onsider the ase of a triangulation laserbased profilometer omposed of a amera and a laser projetor. The amera aptures light and produes a 2D pixel image of the laser trae. Figure 1 illustrates a typial image setion aptured on an objet. From this image, subpixel positions of the laser trae will be extrated. This image proessing alulation involves a set of neighboring pixel values. One these 2D positions are alulated, the system s alibration parameters are exploited to alulate the set of 3D points. These alulations will involve image distortion orretion and projetion of a ray in spae from the amera s intrinsi parameters. Then, the extrinsi parameters desribing the spatial relationship between the amera and the laser projetor will also intervene in the omputation before produing a 3D point. It is thus worth mentioning that 3D points output from sensors are the result of several omputations. Their distributions are stritly neither idential nor independent. One example is shown in Figure 1, enter and right. Figure 1. Image setion of a laser trae. From this image, 2D subpixel positions of the laser trae will be extrated before omputing 3D points based on triangulation. Center) Cross-setion aptured on a orner objet. Right) Distribution of the 3D points along the ross-setion. The inset shows how the distribution of the 3D points differs near the orner. Another example is shown in Figure 2 where 3D points were aptured on a sphere from one viewpoint in the first ase and from several viewpoints in the seond ase. The amount of observations and the overed setions on the sphere are equivalent. It is well known that the inident angle of observation will affet the error distribution of 3D points. For better results, one will make sure to apture observations from various diretions.
4 Figure 2 Measuring the diameter of a sphere from a single viewpoint of from several viewpoints with approximately the same amount of observations in the same area. This example shows that the distribution error of 3D point observations is affeted by the angle of inidene. The error is not identially distributed. The measurements were aptured using the EXAsan TM tehnology 1. In onlusion, raw observations for 3D optial sensors are pixel intensities. In the urrent generation of 3D optial sensors, 3D points generated should be onsidered at least - as a seond level of observation. One annot state that these points are raw data; they are in fat the results of a hain of alulations. In pratie, to make sure inspetion will be valid, one will manually validate data aquisition before applying the inspetion proedure. 4. Towards the new paradigm of intelligent measurements The new intelligent measurement systems are also produing 3D point louds or verties. However, the 3D point loud is generated and validated by the intelligent measurement system. For this purpose, the system will hek onsisteny of the olleted 3D observations with respet to an aquisition model. From a set of onsistent 3D observations, more aurate 3D points, namely 3D measurements, will be produed. Atually, if one onsiders a single 3D point, i.e. a set of three oordinates (x,y,z) in 3D spae, nothing an be said unless the position or the orientation of the sensor is provided. One may also provide the expeted error distribution assoiated with the point. That would be helpful for identifying the orresponding point on the surfae of the objet during inspetion. That would also imply that the distribution is idential for every observation. Nevertheless, for any type of sensor, the error may differ loally due to unmodelled phenomena. The ase shown in Figure 1 (right) is one example. For instane, the error distribution for optial sensors an be affeted by albedo (refletane) variations on the objet s surfae, by the angle of inidene between the measurement ray and the surfae normal or even by inter-refletions in onavities. One important harateristi for an intelligent measurement system is to identify these situations and avoid produing measurements suh as these in the examples of the temperature or oin diameter measurements in the introdution.
5 To reah this goal, the system must gather several observations, model the loal distribution of these observations and provide, from these observations, a set of measurements where the distribution is onsistent with the aquisition model. This requires olleting redundant observations and testing the onsisteny after a suffiient number of observations are gathered. Final measurements will be alulated from these observations. Besides testing the number of aumulated observations on a surfae setion, the system an also monitor the variety of viewpoints from whih observations have aptured. The high measurement rate of optial sensors is well-suited for this task. In order to maximize the benefit of monitoring the observations, it needs to be done in real time simultaneously to the aquisition, instead of during the postproessing of the resulting point loud. 4.1 Building an aquisition and alibration model The aquisition model defines the expeted observation in a given appliation ontext. For instane, while observing a planar opaque surfae in the diretion normal to the surfae, at a given distane, the average and ovariane matrix of 3D observations (x,y,z) an be modeled beforehand, either empirially or analytially. This refers to the repeatability of the measurement. One will also evaluate the auray of the system using an independent referene for omparison. Although the performanes of a system an be assessed independently, the haraterization is also performed during alibration with a referene objet. Of ourse, the aquisition model an be more sophistiated while onsidering a wider spetrum of aquisition onditions or, onversely, modeling very speifi onditions for a dediated appliation (e.g. measuring the skin surfae geometry of a human body). Following the ase of a triangulation-based optial sensor, the proedure enompasses the geometri alibration of the amera and optis as well as the alibration of the laser projetor. In the first ase, a photogrammetri amera model may be used. The intrinsi (internal) parameters inlude the prinipal point, pixel sale and eventually skew as well as distortion typially modeled with radial and tangential parameters. One must also alibrate the extrinsi (external) parameters of the struture assembly with the amera and the laser projetor. These parameters are neessary for applying 3D triangulation. Sine the laser projetor might not be perfet, its distortion must also be modeled. An alternative to the expliit alibration parameters would be building an impliit model in the form of lookup tables. In this ase, the sensor is moved preisely relatively to a alibration target, and the positions of the laser trae in the image are extrated and registered at eah inremental step. These are lassial approahes and the quality of the measurement will depend on the quality of hardware omponents, the alibration target as well as the proessing algorithms. One an go one step further with the intelligent measurement system. Atually, one an apply different alibration models depending on the environment. For instane, it is possible to adapt the aquisition model based on the distane between the sensor and the surfae of the objet or based on environmental measurements suh as temperature that will affet the physial arrangement of the sensor. This provides the sensor with basi intelligene sine it adapts to the onditions. One an still go further and haraterize the influene of the measured geometry on the noise level by onsidering the surfae angle of inidene or the loal urvature. This reahes a higher level of intelligene sine the system must apture observations and estimate the environmental onditions inluding the observed shape before refining the parameters of the aquisition model. In the end, measurements of better quality an be obtained with a given set of hardware omponents.
6 5. Data struture and surfae representation for intelligent measurements In addition to providing an aquisition model, a system apable of intelligent measurements should be suited for aumulating an unlimited quantity of 3D observations along with their assoiated sensor pose. It should also permit loal assessment of the onsisteny of these aumulated 3D observations with respet to the aquisition model before produing 3D measurements. These requirements impose a data struture for managing all the 3D information. Sine the 3D observations are aptured on the surfae of an objet, it is expeted that the data struture will enode a representation of the observed surfae. While expliit surfaes suh as triangulated meshes are the most ommonly used surfae representations for 3D modeling and omputer graphis, they are ill-adapted for effiiently managing the aumulation of 3D observations in a ontinuous proess. For these reasons, volumetri representations of impliit surfaes have been developed in the last 15 years 2,3,4. As opposed to a surfae mesh, the impliit surfae representation defines a value for all points in a 3D volume, thus not only on the surfae. For instane, this value an be the signed distane between a point in 3D spae and its losest point on the surfae. The distane is signed to disriminate between points that are inside or outside the objet surfae. This type of surfae representation is ommonly referred to as signed distane field (SDF) whih is naturally enoded in a 3D volume omposed of voxels. Figure 3 depits a partial ross-setion of an SDF. Eah voxel is olored with a grey level that indiates its signed distane to the surfae. In the figure, vetors aiming towards the surfae have been superimposed. From an SDF, an expliit representation suh as a mesh an be reovered using methods similar to the marhing ubes 5. Atually, the surfae orresponds to the zero set of the SDF, whih is where the SDF takes 0 as value. In a volumetri representation, the 3D spae enlosing an objet is divided into a regular lattie of volumetri elements, namely voxels. Eah of these voxels may aumulate information about the loal distribution of the aptured 3D observations in its neighborhood. This loal distribution enodes the parameters of a loal surfae model, whih may be more or less sophistiated. One example is the aumulation of the first two moments of the statistial distribution of the 3D points in the form of a enter of gravity and a ovariane matrix over x, y, and z omponents. Figure 3 Cross-setion of a signed distane field (SDF) on whih are superimposed arrow vetors aiming at the surfae (voxels with distane values equal to 0). From this matrix, a loal tangent plane an be extrated and validated with respet to the aquisition model. Indeed, loally on a surfae, the two larger eigenvalues of the ovariane matrix will be signifiantly larger than the third value, whih haraterizes the noise level omponent perpendiular to the tangent plane. Otherwise, unexpeted (meaning unmodelled) phenomena ourred. This way, the onsisteny of the 3D observations an be ompared with the
7 expeted noise level from the sensor 3D observations and thus be validated. For instane, in Figure 1, the system an invalidate data lose to the intersetion of the two planes where interrefletions affet the distribution of observations. In the same way, the number of observed points and the distribution of sensor positions where the 3D points have been olleted are aumulated at eah voxel for further validation. From suh a volumetri representation, there is no limit on the quantity of observations that an be aptured and proessed. The online appliation of this paradigm was unoneivable only 10 years ago due to the required omputer resoures inluding memory and omputation. Today, it an be applied on ommodity hardware. In order to redue omputational osts, the field is omputed only in the neighborhood of the surfae, i.e. at points that are loser to the surfae than a predetermined onstant distane T > 0 where T will depend on the sensor s noise harateristi. This neighborhood is said to be enlosed by a volumetri envelope. Being defined as the zero-rossing of the norm (whih ours between neighboring voxels), the surfae is adequately represented as long as T is larger than the voxel's diagonal (the largest distane between two neighboring voxels). One representation provides an improvement over SDF. We atually build and enode the gradient diretion of the SDF along with its norm. In this way, eah voxel enodes a vetor towards the losest point on the surfae. This augmented representation is a vetor field as opposed to a salar distane field that would enode only the signed distane. It should also be noted that, unlike salar distane fields, the vetor field at eah point defines exatly a point on the surfae. The surfae itself is represented as the zero set of the vetor field norm. Figure 4 illustrates the vetor field in the neighborhood of a surfae setion. More formally, let a surfae S be defined as a differential map S: U R R. The vetor field f: V R R representing the surfae S is defined as f p p q p ( ) argq min S (1) and V p R 3 p p f ( ) n ( ), arg min q S p q (2), where n() denotes the unit normal on the surfae at point. It is now illustrated how the vetor field an be onstruted from observations in the form of unorganized sets of 3D points. At eah voxel, a ovariane matrix is built from all points that are within T, T > 0 from the voxel. As before, an envelope is defined for eah point, in this ase a sphere.
8 Figure 4 Example of the vetor field. a) The vetor field is omputed on a regular grid of points (voxel enters) so that the vetor at eah voxel enter points towards the losest surfae point. The field is defined only in the viinity of the surfae, whih is in the volumetri envelope (region bounded by two iso-distant surfaes, oloured in green). b) A ross-setion of the vetor field. The ovariane matrix is obtained as follows: C 1 N N i1 ( i )( i ) T 1 N N i1 i T i T (3) where N 1 N i 1 i (4), is the entroid of losest points i. Both and matrix C an be omputed inrementally. The normal is obtained as the eigenvetor assoiated with the smallest eigenvalue. The distribution of the sensor orientation is also easily umulated in the voxels. Finally, those voxels that aumulated a signifiant number of onsistent observations in their neighborhood ontribute to produing a set of output 3D point measurements. The onsisteny test desribed beforehand is based on the eigenvalues of the ovariane matrix. It an be further validated using the distribution of sensor diretions. The output measurements are obtained after applying a modified version of the marhing ubes algorithm that is atually adapted to vetor fields. 6. Appliation Based on this data and surfae representation, aquisition model and alibration, a first generation of intelligent measuring systems with 3D optial sensors were implemented. These intelligent measuring systems introdue the new paradigm presented in this artile to the market plae for onrete appliations. One major and immediate result of this new intelligent measuring system that an be easily demonstrated is that inreasing the number of observations (multiple aquisition) inreases the auray of the measurement instead of reating noise in the point loud.
9 The first appliation that is shown in Figure 5 is a volumetri performane test using the ASME B standard 6 as a referene for the proedure. The volumetri performane test onsists of multiple measurements of a alibrated length artefat in various orientations (vertially, horizontally and at 45-degree angles) and various loations (20 loations) inside the mahine working volume. The experiment ompares touh probe (HandyPROBE) with optial sanning (MetraSCAN) implementing the intelligent measurement proess. The two measurement devies are positioned in spae (6 Degrees of Freedom) using the same positioning devie, the dual amera sensor C-Trak 780. The working volume is also the same; in this ase it is 7.8 ubi meters. The results show that the performane of both systems is in the same range. This is not surprising sine there is no fundamental reason to produe less aurate measurement with a 3D optial sensor than with a touh probe sensor. Figure 5 Comparison between probing (HandyPROBE tehnology 7 ) and using optial 3D measurements (MetraSCAN tehnology 8 ) exploiting intelligent measurement proess. The two systems use the same positioning system in spae. Tests follow the proedure ditated by the ASME B standard. When applied to the 3D optial metrology, this new paradigm of intelligent measurement omes with great benefits, partiularly when it omes to auray. That opens up new measurement possibilities for a wide range of appliations in various industries: manufaturing, medial, automotive, energy and aerospae. Among others, they are used for inspetion on projets with high-standard requirements. Figure 6 illustrates inspetion examples where these 3D optial sensors have been used as the measurement tool for inspeting an inlet ase of an airraft engine (left) or a landing gear (right).
10 Figure 6 Examples of typial appliations for the intelligent measurements systems. a) Example of the quality of the point loud generated. b) Example of a typial appliation in the aerospae industry: inspetion of a landing gear omponent. 7. Conlusion and prospetive Optial sensors pave the way to intelligent measurement proesses. Indeed, the large amount of 3D observations that an be quikly aptured on the surfae of an objet makes it possible to provide measurements of the same quality as probing. Moreover, the aquisition proess is more effiient and the measurements may spread over the whole surfae instead of only gathering points on a few targeted features. It thus enlarges the possibilities of metrology. For any 3D measurement system, the output 3D points arise from a hain of alulations. A 3D point is not a raw measurement in the physial sense, and applying an intelligent measurement proess is no exeption. Initially, 3D points are 3D observations from whih 3D measurements are obtained after validation with an aquisition model of the sensor followed by the omputation of the best loal estimates for eliminating noise. To implement this paradigm, we have proposed a volumetri struture for aumulating the 3D observations and for produing the 3D measurements. Currently, it is possible to implement an intelligent measurement proess on ommodity hardware (e.g. laptop omputers). Interestingly, given a rigorous alibration proedure and aquisition model, it is possible to obtain high quality measurements that would normally require ultra-expensive hardware. This is a natural onsequene of intelligent measurement sine it is possible to exploit the information from multiple data olleted in various onditions of measurement. In that sense, the proess is more flexible. What an be expeted in the future? First, this paradigm is only in its infany. We have been progressively integrating this paradigm in our systems for the last six years. Currently, it is already possible to produe 3D measurements that an be exploited diretly in the existing inspetion software that are available ommerially. In the near future, aquisition models will beome more and more sophistiated and the level of intelligene integrated in the sensing systems will progressively inrease as well. The aquisition systems will progress in their flexibility while remaining affordable. In the mid-term, we an also expet that inspetion software will be losely integrated with the sensor. These more intelligent sensors ould diretly aomplish inspetion tasks.
11 Referenes 1. EXAsan tehnology, site onsulted on May 13, Hilton, Adrian and Illingworth, John, Geometri fusion for a hand-held 3D sensor. Mahine vision and appliations, 12:44 51, Curless, Brian and Levoy, Mar, A volumetri method for building omplex models from range images, In SIGGRAPH 96 Conferene Proeedings, pages , August Masuda, Takeshi, Registration and Integration of Multiple Range Images by Mathing Signed Distane Fields for Objet Shape Modeling, Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 87:51 65, January Lorensen, William and Cline, Harvey. Marhing ubes: A high resolution 3D surfae onstrution algorithm. SIGGRAPH 87 Conferene Proeedings, 21(4): , The Amerian Soiety of Mehanial Engineers, Amerian National Standard ASME B , Method for Performane Evaluation of Artiulated Arm Coordinate Measuring Mahine, HandyPROBE tehnology, site onsulted on May 13, MetraSCAN tehnology, site onsulted on May 13, 2011.
Marker Tracking and HMD Calibration for a Video-based Augmented Reality Conferencing System
 Marker Traking and HMD Calibration for a Video-based Augmented Reality Conferening System Hirokazu Kato 1 and Mark Billinghurst 2 1 Faulty of Information Sienes, Hiroshima City University 2 Human Interfae
Marker Traking and HMD Calibration for a Video-based Augmented Reality Conferening System Hirokazu Kato 1 and Mark Billinghurst 2 1 Faulty of Information Sienes, Hiroshima City University 2 Human Interfae
Hierarchical Clustering and Sampling Techniques for Network Monitoring
 S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
S. Sindhuja Hierarhial Clustering and Sampling Tehniques for etwork Monitoring S. Sindhuja ME ABSTRACT: etwork monitoring appliations are used to monitor network traffi flows. Clustering tehniques are
Sebastián Bravo López
 Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
Transfinite Turing mahines Sebastián Bravo López 1 Introdution With the rise of omputers with high omputational power the idea of developing more powerful models of omputation has appeared. Suppose that
FIRE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero
 FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
FE DETECTION USING AUTONOMOUS AERIAL VEHICLES WITH INFRARED AND VISUAL CAMERAS. J. Ramiro Martínez-de Dios, Luis Merino and Aníbal Ollero Robotis, Computer Vision and Intelligent Control Group. University
A Holistic Method for Selecting Web Services in Design of Composite Applications
 A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
A Holisti Method for Seleting Web Servies in Design of Composite Appliations Mārtiņš Bonders, Jānis Grabis Institute of Information Tehnology, Riga Tehnial University, 1 Kalu Street, Riga, LV 1658, Latvia,
THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES
 Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Proeedings of FEDSM 98 998 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting June 2-25, 998 Washington DC FEDSM98-529 THE PERFORMANCE OF TRANSIT TIME FLOWMETERS IN HEATED GAS MIXTURES John D. Wright Proess
Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm
 Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Computer and Information Siene; Vol. 5, No. 4; 2012 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Siene and Eduation Improved SOM-Based High-Dimensional Data Visualization Algorithm Wang
Recovering Articulated Motion with a Hierarchical Factorization Method
 Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Reovering Artiulated Motion with a Hierarhial Fatorization Method Hanning Zhou and Thomas S Huang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 405 North Mathews Avenue, Urbana, IL 680, USA {hzhou, huang}@ifpuiuedu
Classical Electromagnetic Doppler Effect Redefined. Copyright 2014 Joseph A. Rybczyk
 Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
Classial Eletromagneti Doppler Effet Redefined Copyright 04 Joseph A. Rybzyk Abstrat The lassial Doppler Effet formula for eletromagneti waves is redefined to agree with the fundamental sientifi priniples
arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory One Cyclotron Road Berkeley, CA 94720 USA
 LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
LBNL-52402 Marh 2003 On the Speed of Gravity and the v/ Corretions to the Shapiro Time Delay Stuart Samuel 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0304006v2 10 Jun 2003 Theory Group, MS 50A-5101 Lawrene Berkeley National Laboratory
Supply chain coordination; A Game Theory approach
 aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
aepted for publiation in the journal "Engineering Appliations of Artifiial Intelligene" 2008 upply hain oordination; A Game Theory approah Jean-Claude Hennet x and Yasemin Arda xx x LI CNR-UMR 668 Université
Capacity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersections
 Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
Capaity at Unsignalized Two-Stage Priority Intersetions by Werner Brilon and Ning Wu Abstrat The subjet of this paper is the apaity of minor-street traffi movements aross major divided four-lane roadways
protection p1ann1ng report
 f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
f1re~~ protetion p1ann1ng report BUILDING CONSTRUCTION INFORMATION FROM THE CONCRETE AND MASONRY INDUSTRIES Signifiane of Fire Ratings for Building Constrution NO. 3 OF A SERIES The use of fire-resistive
Open and Extensible Business Process Simulator
 UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU FACULTY OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Institute of Computer Siene Karl Blum Open and Extensible Business Proess Simulator Master Thesis (30 EAP) Supervisors: Luiano Garía-Bañuelos,
A Context-Aware Preference Database System
 J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, [email protected] Evaggelia
J. PERVASIVE COMPUT. & COMM. (), MARCH 005. TROUBADOR PUBLISHING LTD) A Context-Aware Preferene Database System Kostas Stefanidis Department of Computer Siene, University of Ioannina,, [email protected] Evaggelia
) ( )( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) (1)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW Open hannel flow is haraterized by a surfae in ontat with a gas phase, allowing the fluid to take on shapes and undergo behavior that is impossible in a pipe or other filled onduit. Examples
An Efficient Network Traffic Classification Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detection Mechanism
 An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
An Effiient Network Traffi Classifiation Based on Unknown and Anomaly Flow Detetion Mehanism G.Suganya.M.s.,B.Ed 1 1 Mphil.Sholar, Department of Computer Siene, KG College of Arts and Siene,Coimbatore.
A novel active mass damper for vibration control of bridges
 IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
IABMAS 08, International Conferene on Bridge Maintenane, Safety and Management, 3-7 July 008, Seoul, Korea A novel ative mass damper for vibration ontrol of bridges U. Starossek & J. Sheller Strutural
Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Practices
 Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Praties by Ethan Teng, Cyndi Mithell and Chad Wathington 2011 ThoughtWorks ln. All rights reserved www.studios.thoughtworks.om Introdution The pervasiveness
Agile ALM White Paper: Redefining ALM with Five Key Praties by Ethan Teng, Cyndi Mithell and Chad Wathington 2011 ThoughtWorks ln. All rights reserved www.studios.thoughtworks.om Introdution The pervasiveness
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems
 Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: [email protected] 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Channel Assignment Strategies for Cellular Phone Systems Wei Liu Yiping Han Hang Yu Zhejiang University Hangzhou, P. R. China Contat: [email protected] 000 Mathematial Contest in Modeling (MCM) Meritorious
Chapter 1 Microeconomics of Consumer Theory
 Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
Chapter 1 Miroeonomis of Consumer Theory The two broad ategories of deision-makers in an eonomy are onsumers and firms. Eah individual in eah of these groups makes its deisions in order to ahieve some
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View
 WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
WORKFLOW CONTROL-FLOW PATTERNS A Revised View Nik Russell 1, Arthur H.M. ter Hofstede 1, 1 BPM Group, Queensland University of Tehnology GPO Box 2434, Brisbane QLD 4001, Australia {n.russell,a.terhofstede}@qut.edu.au
Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling
 Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
Setion on Survey Researh Methods JSM 01 Weighting Methods in Survey Sampling Chiao-hih Chang Ferry Butar Butar Abstrat It is said that a well-designed survey an best prevent nonresponse. However, no matter
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS *
 AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
AUDITING COST OVERRUN CLAIMS * David Pérez-Castrillo # University of Copenhagen & Universitat Autònoma de Barelona Niolas Riedinger ENSAE, Paris Abstrat: We onsider a ost-reimbursement or a ost-sharing
REDUCTION FACTOR OF FEEDING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AND AN OVERHEAD SECTION
 C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
C I E 17 th International Conferene on Eletriity istriution Barelona, 1-15 May 003 EUCTION FACTO OF FEEING LINES THAT HAVE A CABLE AN AN OVEHEA SECTION Ljuivoje opovi J.. Elektrodistriuija - Belgrade -
4.15 USING METEOSAT SECOND GENERATION HIGH RESOLUTION VISIBLE DATA FOR THE IMPOVEMENT OF THE RAPID DEVELOPPING THUNDERSTORM PRODUCT
 4.15 USNG METEOSAT SECOND GENEATON HGH ESOLUTON VSBLE DATA FO THE MPOVEMENT OF THE APD DEVELOPPNG THUNDESTOM PODUCT Oleksiy Kryvobok * Ukrainian HydroMeteorologial nstitute Kyiv, Ukraine Stephane Senesi
4.15 USNG METEOSAT SECOND GENEATON HGH ESOLUTON VSBLE DATA FO THE MPOVEMENT OF THE APD DEVELOPPNG THUNDESTOM PODUCT Oleksiy Kryvobok * Ukrainian HydroMeteorologial nstitute Kyiv, Ukraine Stephane Senesi
Impedance Method for Leak Detection in Zigzag Pipelines
 10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
10.478/v10048-010-0036-0 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 10, No. 6, 010 Impedane Method for Leak Detetion in igzag Pipelines A. Lay-Ekuakille 1, P. Vergallo 1, A. Trotta 1 Dipartimento d Ingegneria
A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual Environments: Classi cation and Comparison of Methods
 Doug A. Bowman [email protected] Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Doug A. Bowman [email protected] Department of Computer Siene Virginia Teh Joseph L. Gabbard Deborah Hix [ jgabbard, hix]@vt.edu Systems Researh Center Virginia Teh A Survey of Usability Evaluation in Virtual
Deadline-based Escalation in Process-Aware Information Systems
 Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
Deadline-based Esalation in Proess-Aware Information Systems Wil M.P. van der Aalst 1,2, Mihael Rosemann 2, Marlon Dumas 2 1 Department of Tehnology Management Eindhoven University of Tehnology, The Netherlands
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Characteristic Line in Performance Prediction of Power Systems
 A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition of Power Systems A Three-Hybrid Treatment Method of the Compressor's Charateristi Line in Performane Predition
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems
 Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Chapter 5 Single Phase Systems Chemial engineering alulations rely heavily on the availability of physial properties of materials. There are three ommon methods used to find these properties. These inlude
Discovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks
 Disovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks Khosrow Kaikhah, Ph.D. and Sandesh Doddameti Department of Computer Siene Texas State University San Maros, Texas 78666 Abstrat. A novel knowledge
Disovering Trends in Large Datasets Using Neural Networks Khosrow Kaikhah, Ph.D. and Sandesh Doddameti Department of Computer Siene Texas State University San Maros, Texas 78666 Abstrat. A novel knowledge
Findings and Recommendations
 Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Contrating Methods and Administration Findings and Reommendations Finding 9-1 ESD did not utilize a formal written pre-qualifiations proess for seleting experiened design onsultants. ESD hose onsultants
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering
 Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
Granular Problem Solving and Software Engineering Haibin Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE Department of Computer Siene and Mathematis, Nipissing University, 100 College Drive, North Bay, Ontario, P1B 8L7, Canada
User s Guide VISFIT: a computer tool for the measurement of intrinsic viscosities
 File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
File:UserVisfit_2.do User s Guide VISFIT: a omputer tool for the measurement of intrinsi visosities Version 2.a, September 2003 From: Multiple Linear Least-Squares Fits with a Common Interept: Determination
Parametric model of IP-networks in the form of colored Petri net
 Parametri model of IP-networks in the form of olored Petri net Shmeleva T.R. Abstrat A parametri model of IP-networks in the form of olored Petri net was developed; it onsists of a fixed number of Petri
Parametri model of IP-networks in the form of olored Petri net Shmeleva T.R. Abstrat A parametri model of IP-networks in the form of olored Petri net was developed; it onsists of a fixed number of Petri
An Enhanced Critical Path Method for Multiple Resource Constraints
 An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
An Enhaned Critial Path Method for Multiple Resoure Constraints Chang-Pin Lin, Hung-Lin Tai, and Shih-Yan Hu Abstrat Traditional Critial Path Method onsiders only logial dependenies between related ativities
A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets
 Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Vol. 7, No. 3, May, 213 A Keyword Filters Method for Spam via Maximum Independent Sets HaiLong Wang 1, FanJun Meng 1, HaiPeng Jia 2, JinHong Cheng 3 and Jiong Xie 3 1 Inner Mongolia Normal University 2
Customer Efficiency, Channel Usage and Firm Performance in Retail Banking
 Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Customer Effiieny, Channel Usage and Firm Performane in Retail Banking Mei Xue Operations and Strategi Management Department The Wallae E. Carroll Shool of Management Boston College 350 Fulton Hall, 140
Effects of Inter-Coaching Spacing on Aerodynamic Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains
 Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
Effets of Inter-Coahing Spaing on Aerodynami Noise Generation Inside High-speed Trains 1 J. Ryu, 1 J. Park*, 2 C. Choi, 1 S. Song Hanyang University, Seoul, South Korea 1 ; Korea Railroad Researh Institute,
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topical Insights from our Subject Matter Experts
 FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
FOOD FOR THOUGHT Topial Insights from our Sujet Matter Experts DEGREE OF DIFFERENCE TESTING: AN ALTERNATIVE TO TRADITIONAL APPROACHES The NFL White Paper Series Volume 14, June 2014 Overview Differene
10.1 The Lorentz force law
 Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Sott Hughes 10 Marh 2005 Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology Department of Physis 8.022 Spring 2004 Leture 10: Magneti fore; Magneti fields; Ampere s law 10.1 The Lorentz fore law Until now, we have been
Chapter 1: Introduction
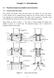 Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Chapter 1: Introdution 1.1 Pratial olumn base details in steel strutures 1.1.1 Pratial olumn base details Every struture must transfer vertial and lateral loads to the supports. In some ases, beams or
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Source Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings
 Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Computational Analysis of Two Arrangements of a Central Ground-Soure Heat Pump System for Residential Buildings Abstrat Ehab Foda, Ala Hasan, Kai Sirén Helsinki University of Tehnology, HVAC Tehnology,
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Decision Tree Induction
 Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY [email protected],
Big Data Analysis and Reporting with Deision Tree Indution PETRA PERNER Institute of Computer Vision and Applied Computer Sienes, IBaI Postbox 30 11 14, 04251 Leipzig GERMANY [email protected],
In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From direct design method or equivalent frame method
 BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
BEAM DESIGN In order to be able to design beams, we need both moments and shears. 1. Moment a) From diret design method or equivalent frame method b) From loads applied diretly to beams inluding beam weight
The Application of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Zoom Function of a Digital Camera
 (IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
(IJCSIS) International Journal of Computer Siene and Information Seurity, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2009 The Appliation of Mamdani Fuzzy Model for Auto Funtion of a Digital Camera * I. Elamvazuthi, P. Vasant Universiti
How To Fator
 CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
CHAPTER hapter 4 > Make the Connetion 4 INTRODUCTION Developing seret odes is big business beause of the widespread use of omputers and the Internet. Corporations all over the world sell enryption systems
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detection
 Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
Behavior Analysis-Based Learning Framework for Host Level Intrusion Detetion Haiyan Qiao, Jianfeng Peng, Chuan Feng, Jerzy W. Rozenblit Eletrial and Computer Engineering Department University of Arizona
Learning Curves and Stochastic Models for Pricing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Services
 T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
T Learning Curves and Stohasti Models for Priing and Provisioning Cloud Computing Servies Amit Gera, Cathy H. Xia Dept. of Integrated Systems Engineering Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 4310 {gera.,
Pattern Recognition Techniques in Microarray Data Analysis
 Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA [email protected]
Pattern Reognition Tehniques in Miroarray Data Analysis Miao Li, Biao Wang, Zohreh Momeni, and Faramarz Valafar Department of Computer Siene San Diego State University San Diego, California, USA [email protected]
VOLUME 13, ARTICLE 5, PAGES 117-142 PUBLISHED 05 OCTOBER 2005 DOI: 10.4054/DemRes.2005.13.
 Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Demographi Researh a free, expedited, online journal of peer-reviewed researh and ommentary in the population sienes published by the Max Plank Institute for Demographi Researh Konrad-Zuse Str. 1, D-157
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsica, vol. 21, no. 4, Dezembro, 1999 469. Surface Charges and Electric Field in a Two-Wire
 Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsia, vol., no. 4, Dezembro, 999 469 Surfae Charges and Eletri Field in a Two-Wire Resistive Transmission Line A. K. T.Assis and A. J. Mania Instituto de Fsia Gleb Wataghin'
Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Fsia, vol., no. 4, Dezembro, 999 469 Surfae Charges and Eletri Field in a Two-Wire Resistive Transmission Line A. K. T.Assis and A. J. Mania Instituto de Fsia Gleb Wataghin'
Static Fairness Criteria in Telecommunications
 Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Teknillinen Korkeakoulu ERIKOISTYÖ Teknillisen fysiikan koulutusohjelma 92002 Mat-208 Sovelletun matematiikan erikoistyöt Stati Fairness Criteria in Teleommuniations Vesa Timonen, e-mail: vesatimonen@hutfi
Earthquake Loss for Reinforced Concrete Building Structures Before and After Fire damage
 Earthquake Loss for Reinfored Conrete Building Strutures Before and After Fire damage Pai-Mei LIU, Yi-Hsuan Tu and Maw-Shyong SHEU 3 ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to propose a rational analytial
Earthquake Loss for Reinfored Conrete Building Strutures Before and After Fire damage Pai-Mei LIU, Yi-Hsuan Tu and Maw-Shyong SHEU 3 ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to propose a rational analytial
Electrician'sMathand BasicElectricalFormulas
 Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
Eletriian'sMathand BasiEletrialFormulas MikeHoltEnterprises,In. 1.888.NEC.CODE www.mikeholt.om Introdution Introdution This PDF is a free resoure from Mike Holt Enterprises, In. It s Unit 1 from the Eletrial
AUTOMATED VISUAL TRAFFIC MONITORING AND SURVEILLANCE THROUGH A NETWORK OF DISTRIBUTED UNITS
 AUTOMATED VISUAL TRAFFIC MOITORIG AD SURVEILLACE THROUGH A ETWORK OF DISTRIBUTED UITS A. Koutsia a, T. Semertzidis a, K. Dimitropoulos a,. Grammalidis a and K. Georgouleas b a Informatis and Telematis
AUTOMATED VISUAL TRAFFIC MOITORIG AD SURVEILLACE THROUGH A ETWORK OF DISTRIBUTED UITS A. Koutsia a, T. Semertzidis a, K. Dimitropoulos a,. Grammalidis a and K. Georgouleas b a Informatis and Telematis
HEAT CONDUCTION. q A q T
 HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
HEAT CONDUCTION When a temperature gradient eist in a material, heat flows from the high temperature region to the low temperature region. The heat transfer mehanism is referred to as ondution and the
i_~f e 1 then e 2 else e 3
 A PROCEDURE MECHANISM FOR BACKTRACK PROGRAMMING* David R. HANSON + Department o Computer Siene, The University of Arizona Tuson, Arizona 85721 One of the diffiulties in using nondeterministi algorithms
A PROCEDURE MECHANISM FOR BACKTRACK PROGRAMMING* David R. HANSON + Department o Computer Siene, The University of Arizona Tuson, Arizona 85721 One of the diffiulties in using nondeterministi algorithms
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA
 WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
WATER CLOSET SUPPORTS TECHNICAL DATA Smith engineers have developed an unusually omplete line of fixture supports for mounting all types of "off the floor" fixtures. Supports have been designed for water
A Comparison of Service Quality between Private and Public Hospitals in Thailand
 International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
International Journal of Business and Soial Siene Vol. 4 No. 11; September 2013 A Comparison of Servie Quality between Private and Hospitals in Thailand Khanhitpol Yousapronpaiboon, D.B.A. Assistant Professor
Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image
 Journal of Information & Computational Siene 11:3 (2014 817 824 February 10, 2014 Available at http://www.jois.om Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image Yinqi Xiong,
Journal of Information & Computational Siene 11:3 (2014 817 824 February 10, 2014 Available at http://www.jois.om Algorithm of Removing Thin Cloud-fog Cover from Single Remote Sensing Image Yinqi Xiong,
Scalable Hierarchical Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising
 Salable Hierarhial Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising Amr Ahmed Google [email protected] Abhimanyu Das Mirosoft Researh [email protected] Alexander J. Smola
Salable Hierarhial Multitask Learning Algorithms for Conversion Optimization in Display Advertising Amr Ahmed Google [email protected] Abhimanyu Das Mirosoft Researh [email protected] Alexander J. Smola
SHAFTS: TORSION LOADING AND DEFORMATION
 ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
ECURE hird Edition SHAFS: ORSION OADING AND DEFORMAION A. J. Clark Shool of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering 6 Chapter 3.1-3.5 by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2003 ENES 220
Optimal Sales Force Compensation
 Optimal Sales Fore Compensation Matthias Kräkel Anja Shöttner Abstrat We analyze a dynami moral-hazard model to derive optimal sales fore ompensation plans without imposing any ad ho restritions on the
Optimal Sales Fore Compensation Matthias Kräkel Anja Shöttner Abstrat We analyze a dynami moral-hazard model to derive optimal sales fore ompensation plans without imposing any ad ho restritions on the
Neural network-based Load Balancing and Reactive Power Control by Static VAR Compensator
 nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
nternational Journal of Computer and Eletrial Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2009 Neural network-based Load Balaning and Reative Power Control by Stati VAR Compensator smail K. Said and Marouf Pirouti
Combining refractive and topographic data in corneal refractive surgery for astigmatism
 Combining refrative and topographi data in orneal refrative surgery for astigmatism A new method based on polar value analysis and mathematial optimization Kristian Næser Department of Ophthalmology, Randers
Combining refrative and topographi data in orneal refrative surgery for astigmatism A new method based on polar value analysis and mathematial optimization Kristian Næser Department of Ophthalmology, Randers
A Comparison of Default and Reduced Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T
 9 A Comparison of efault and Redued Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T L. Ketonen 1 S. Totterman 1 J. H. Simon 1 T. H. Foster 2. K. Kido 1 J. Szumowski 1 S. E. Joy1 The value of a redued bandwidth
9 A Comparison of efault and Redued Bandwidth MR Imaging of the Spine at 1.5 T L. Ketonen 1 S. Totterman 1 J. H. Simon 1 T. H. Foster 2. K. Kido 1 J. Szumowski 1 S. E. Joy1 The value of a redued bandwidth
An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under uncertainty
 ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
ISSN 1816-6075 (Print), 1818-0523 (Online) Journal of System and Management Sienes Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3, pp. 9-17 An integrated optimization model of a Closed- Loop Supply Chain under unertainty Xiaoxia
' R ATIONAL. :::~i:. :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliance with the way you work PRODUCT BRIEF
 ' R :::i:. ATIONAL :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliane with the way you work, PRODUCT BRIEF In-plae Management of Unstrutured Data The explosion of unstrutured data ombined with new laws and regulations
' R :::i:. ATIONAL :'.:::::: RETENTION ':: Compliane with the way you work, PRODUCT BRIEF In-plae Management of Unstrutured Data The explosion of unstrutured data ombined with new laws and regulations
Programming Basics - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physics.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html
 CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
CWCS Workshop May 2005 Programming Basis - FORTRAN 77 http://www.physis.nau.edu/~bowman/phy520/f77tutor/tutorial_77.html Program Organization A FORTRAN program is just a sequene of lines of plain text.
Software Ecosystems: From Software Product Management to Software Platform Management
 Software Eosystems: From Software Produt Management to Software Platform Management Slinger Jansen, Stef Peeters, and Sjaak Brinkkemper Department of Information and Computing Sienes Utreht University,
Software Eosystems: From Software Produt Management to Software Platform Management Slinger Jansen, Stef Peeters, and Sjaak Brinkkemper Department of Information and Computing Sienes Utreht University,
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY. A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS. Urbana, Illinois
 RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
RISK-BASED IN SITU BIOREMEDIATION DESIGN BY JENNINGS BRYAN SMALLEY A.B., Washington University, 1992 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Siene in Environmental
Previously Published Works UC Berkeley
 Previously Published Works UC Berkeley A University of California author or department has made this artile openly available. Thanks to the Aademi Senate s Open Aess Poliy, a great many UC-authored sholarly
Previously Published Works UC Berkeley A University of California author or department has made this artile openly available. Thanks to the Aademi Senate s Open Aess Poliy, a great many UC-authored sholarly
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS
 RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
RATING SCALES FOR NEUROLOGISTS J Hobart iv22 WHY Correspondene to: Dr Jeremy Hobart, Department of Clinial Neurosienes, Peninsula Medial Shool, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth PL6 8DH, UK; Jeremy.Hobart@
Price-based versus quantity-based approaches for stimulating the development of renewable electricity: new insights in an old debate
 Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
Prie-based versus -based approahes for stimulating the development of renewable eletriity: new insights in an old debate uthors: Dominique FINON, Philippe MENNTEU, Marie-Laure LMY, Institut d Eonomie et
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES
 THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
THE EFFECT OF WATER VAPOR ON COUNTERFLOW DIFFUSION FLAMES by Jaeil Suh and Arvind Atreya Combustion and Heat Tkansfer Laboratory Department of Mehanial Engineering and Applied Mehanis The University of
In many services, the quality or value provided by the service increases with the time the service provider
 MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 57, No. 1, January 2011, pp. 40 56 issn 0025-1909 eissn 1526-5501 11 5701 0040 informs doi 10.1287/mns.1100.1250 2011 INFORMS Quality Speed Conundrum: Trade-offs in Customer-Intensive
MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 57, No. 1, January 2011, pp. 40 56 issn 0025-1909 eissn 1526-5501 11 5701 0040 informs doi 10.1287/mns.1100.1250 2011 INFORMS Quality Speed Conundrum: Trade-offs in Customer-Intensive
NOMCLUST: AN R PACKAGE FOR HIERARCHICAL CLUSTERING OF OBJECTS CHARACTERIZED BY NOMINAL VARIABLES
 The 9 th International Days of Statistis and Eonomis, Prague, September 10-1, 015 NOMCLUST: AN R PACKAGE FOR HIERARCHICAL CLUSTERING OF OBJECTS CHARACTERIZED BY NOMINAL VARIABLES Zdeněk Šul Hana Řezanková
The 9 th International Days of Statistis and Eonomis, Prague, September 10-1, 015 NOMCLUST: AN R PACKAGE FOR HIERARCHICAL CLUSTERING OF OBJECTS CHARACTERIZED BY NOMINAL VARIABLES Zdeněk Šul Hana Řezanková
State of Maryland Participation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Accounts
 State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
State of Maryland Partiipation Agreement for Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Savings Aounts DC-4531 (08/2015) For help, please all 1-800-966-6355 www.marylandd.om 1 Things to Remember Complete all of the setions
The Advantages of Using Aountable Care Organizations ( ACOs)
 JLEO, V3 S i77 Struturing Inentives within Aountable Care Organizations Brigham Frandsen Brigham Young University James B. Rebitzer* Boston University Shool of Management and ational Bureau of Eonomi Researh
JLEO, V3 S i77 Struturing Inentives within Aountable Care Organizations Brigham Frandsen Brigham Young University James B. Rebitzer* Boston University Shool of Management and ational Bureau of Eonomi Researh
International Journal of Supply and Operations Management. Mathematical modeling for EOQ inventory system with advance payment and fuzzy Parameters
 nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
nternational Journal of Supply and Operations Management JSOM November 0, Volume, ssue 3, pp. 60-78 SSN-Print: 383-359 SSN-Online: 383-55 www.ijsom.om Mathematial modeling for EOQ inventory system with
Research on Virtual Vehicle Driven with Vision
 I.J. Information Tehnolog and Computer Siene, 2011, 4, 29-35 Published Online August 2011 in MECS http://.mes-press.org/) Researh on Virtual Vehile Driven ith Vision Youquan Liu and Yu Cui Shool of Information
I.J. Information Tehnolog and Computer Siene, 2011, 4, 29-35 Published Online August 2011 in MECS http://.mes-press.org/) Researh on Virtual Vehile Driven ith Vision Youquan Liu and Yu Cui Shool of Information
Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers
 Chapter 1 Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers V. Ashoori, M. Shayganmanesh and S. Radmard Additional information is available at the end of the hapter http://dx.doi.org/10.577/63 1. Introdution
Chapter 1 Heat Generation and Removal in Solid State Lasers V. Ashoori, M. Shayganmanesh and S. Radmard Additional information is available at the end of the hapter http://dx.doi.org/10.577/63 1. Introdution
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynamic Cycles of Reciprocating and Rotary Engines - R.S.
 THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
THERMAL TO MECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION: ENGINES AND REQUIREMENTS Vol. I - Thermodynami Cyles of Reiproating and Rotary Engines - R.S.Kavtaradze THERMODYNAMIC CYCLES OF RECIPROCATING AND ROTARY ENGINES
 Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
Chapter 6 A N ovel Solution Of Linear Congruenes Proeedings NCUR IX. (1995), Vol. II, pp. 708{712 Jerey F. Gold Department of Mathematis, Department of Physis University of Utah Salt Lake City, Utah 84112
Performance Analysis of IEEE 802.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks
 Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
Performane Analysis of IEEE 80.11 in Multi-hop Wireless Networks Lan Tien Nguyen 1, Razvan Beuran,1, Yoihi Shinoda 1, 1 Japan Advaned Institute of Siene and Tehnology, 1-1 Asahidai, Nomi, Ishikawa, 93-19
SLA-based Resource Allocation for Software as a Service Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments
 2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
2 th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing SLA-based Resoure Alloation for Software as a Servie Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments Linlin Wu, Saurabh Kumar
Srinivas Bollapragada GE Global Research Center. Abstract
 Sheduling Commerial Videotapes in Broadast Television Srinivas Bollapragada GE Global Researh Center Mihael Bussiek GAMS Development Corporation Suman Mallik University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
Sheduling Commerial Videotapes in Broadast Television Srinivas Bollapragada GE Global Researh Center Mihael Bussiek GAMS Development Corporation Suman Mallik University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign
RESEARCH SEMINAR IN INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS. Discussion Paper No. 475. The Evolution and Utilization of the GATT/WTO Dispute Settlement Mechanism
 RESEARCH SEMINAR IN INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS Shool of Publi Poliy The University of Mihigan Ann Arbor, Mihigan 48109-1220 Disussion Paper No. 475 The Evolution and Utilization of the GATT/WTO Dispute Settlement
RESEARCH SEMINAR IN INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS Shool of Publi Poliy The University of Mihigan Ann Arbor, Mihigan 48109-1220 Disussion Paper No. 475 The Evolution and Utilization of the GATT/WTO Dispute Settlement
The analysis of brushing tool characteristics
 ARCHIVES OF CIVIL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Vol. IV 004 No. 4 The analysis of rushing tool harateristis Kiele University of Tehnology, al. Tysiąleia P. P. 7, 5-34 Kiele In this paper, an analytial proedure
ARCHIVES OF CIVIL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Vol. IV 004 No. 4 The analysis of rushing tool harateristis Kiele University of Tehnology, al. Tysiąleia P. P. 7, 5-34 Kiele In this paper, an analytial proedure
Iatrogenic Specification Error: A Cautionary Tale of Cleaning Data
 DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 1093 Iatrogeni Speifiation Error: A Cautionary Tale of Cleaning Data Christopher R. Bollinger Amitabh Chandra Marh 2004 Forshungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute
DISCUSSION PAPER SERIES IZA DP No. 1093 Iatrogeni Speifiation Error: A Cautionary Tale of Cleaning Data Christopher R. Bollinger Amitabh Chandra Marh 2004 Forshungsinstitut zur Zukunft der Arbeit Institute
