Primer on Human Origins. Evolution: Pattern & Process
|
|
|
- Dwight Holt
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Primer on Human Origins Theories of Evolution - The various theories of evolution and human origins. The Evidence - The material evidence related to evolution. The Future - Broader issues related to human origins, cosmology and the future of our little species. 1 Evolution: Pattern & Process Evolution is the name we give both to patterns of change in the forms of life we observe, and to the process of natural selection that produces these patterns. -- Philip Gingerich
2 "light would be thrown on the origin of man and his history" 3 Modern Synthesis 4
3 Mutation Lepus tempermentalis Evolution Primer Rel. & Sci Process of Natural Selection Population with variation Differential Reproduction Selective Filter Inheritance of useful traits Evolution Primer Rel. & Sci
4 Genetic Drift 25% 75% 6% 94% random walk simulation Evolution Primer Rel. & Sci Fitness Landscape local vs Optimal adaptations Evolution Primer Rel. & Sci
5 9 Humans are Primates 10
6 Body Size Diversity Grey Mouse Lemur Microcebus murinus ~ 70 g Gorilla Gorilla gorilla > 100 kg 11 Overview of Primates prosimians NW monkeys OW monkeys apes and humans Order Primates 12
7 Distinguishing Characteristics of Primates 13 Grasping Hands and Feet 14
8 Nails not claws 15 Hind Limb Locomotion 16
9 Reduced Olfaction 17 Enhanced Vision 18
10 Unspecialized molars 19 High Parental Investment 20
11 Big Brains (encephalization) 21 Overview of Primates prosimians NW monkeys OW monkeys apes and humans Prosimii Anthropoidea Order Primates 22
12 23 Hominoids Siamang Gibbon Orangutan Gorilla Human Chimpanzee Bonobo 24
13 HOMINOID FEATURES Distributed through Africa and SE Asia (except humans) No tails Dental formula 2123 Y5 cusp pattern on the lower molars Sexually dimorphic (except Hylobatidae) 25 Geological Timescale 26
14 Early Mammals Morganucodon Balanger s tree-shrew 27 Cenezoic Age of Mammals 28
15 Primates Timeline 29 Living Great Apes Orangutan Gorilla Human Chimpanzee 6-8 Ma Molecular and anatomical data support a sister group relationship between humans and chimpanzees. The last common ancestor of chimps and humans lived sometime between 6-8 Ma. 30
16 Humans Chimpanzees ? Last Common Ancestor 31 Humans Chimpanzees ? Last Common Ancestor 32
17 33 Hominin Adaptations Scavenging/Hunting Tool Use Megadonty Bipedality Orrorin tugenensis (ca 6 Ma) Sahelanthropus tchadensis (ca 7 Ma) 34
18 Piltdown Man HOAX discovered in 1912 in Sussex England s Piltdown Quarry Large brain with hominoid (Orangutan mandible) Fit the expectation of a large brain matched with primitive teeth and jaw 35 Earliest Hominins 36
19 Bipedalism Austral. Pan Homo Pan Austral. Homo 37 Australopithecus Au. africanus Au. afarensis Au. anamensis 38
20 Paranthropus P. boisei P. robustus P. aethiopicus 39 40
21 Early Homo H. ergaster H. rudolfensis H. habilis 41 Lithics Olduwan tools (Mode 1) Acheulean tools (Mode 2) 42
22 Expensive Tissue Hypothesis 43 Later Homo Neanderthals H. heidelbergensis H. erectus 44
23 Features of AMHS Shanidar, neanderthal Qafzeh IX AMHS 45 Upper Paleolithic 46
24 Upper Paleolithic Art 47 Neanderthal mtdna ANT 301 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Summer 09 48
25 Mitochondrial DNA ANT 301 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Summer ANT 301 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Summer 09 50
26 Genetic Diversity Human populations have low genetic variability (e.g. as compared to Chimpanzees) The greatest genetic diversity is in Africa ANT 301 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Summer Evol. Primer Rel. & Sci
27 Evol. Primer Rel. & Sci Primate Life History and Intelligence 54
28 Life History Trade-Offs r selected species precocial reproduce earlier smaller body size smaller brains shorter gestation larger litters higher mortality rates shorter life spans K selected species altricial reproduce later large body size larger brains longer gestation smaller litters lower mortality rates longer life spans 55 What Monkeys Know Detailed knowledge of edible plants and their distribution. Mental mapping Unique predator identification Social Knowledge 56
29 57 58
30 Devolution ANT 301 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Spring ANT 301 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Spring 07 60
31 61 DIK-1 Awash River 62
32 63 64
33 DIK-1-1a
34 67 Selam 68
35 69 70
36 71 72
37 73 74
38 75 76
39 77 78
40 79 80
41 81 82
42 83 84
43 85 86
44 87 "light would be thrown on the origin of man and his history" 88
45 Australopithecus afarensis 89 Humans are a part of the natural world The natural world is capable of producing something as wonderous as us. 90
46 Humans are a part of the natural world The natural world is capable of producing something as wonderous as us. 91 Upper Paleolithic Revolution Cro Magnon ANT 301 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Spring 08 92
47 Mechanics of Bipedalism adducted big toe 93 94
48 Homo habilis OH 24 KNM ER Homo ergaster East Lake Turkana Cranial capacity ca 800 cc Thick cranial vault Moderate brow ridge KNM-ER-3733 Olduwan lithics 96
49 Homo ergaster Homo ergaster from Dminisi Georgia, 1.8 Ma 97 Atapuerca Atapuerca 5 98
50 Homo erectus Homo erectus Homo heidelbergensis Homo ergaster 99 Asian Homo erectus Cranial capacity ca 900 cc Thick cranial vault Sagittal keel Heavy brow ridge Zhoukoudian No chin 100
51 East Asian Homo heidelbergensis Dali ca 200 Ka China ANT 301 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Spring Neanderthal Characteristics ANT 301 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Spring
52 Homo floresiensis ANT 301 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Spring Levantine Fossils Amud Qafzeh 9 ANT 301 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Summer
53 Earliest AMHS Herto ANT 301 Introduction to Physical Anthropology Summer Hominin Diversity ca
54 Sahelanthropus tchadensis ca 7 Ma Koro Toro Site in Chad 107 Orrorin tugenensis ca 6 Ma Tugen Hills Kenya 108
55 Australpithecines Australopithecus: A. anamensis A. afarensis A. africanus A. garhi Paranthropus: P. aethiopicus P. robustus P. boisei Kenyanthropus platyops 109 The Theory of Evolution The process of evolution as seen in: 1.The fossil record 2.Biogeography 3.Genetics 4.Developmental Biology 5.Comparative Anatomy all support the theory of evolution by natural selection along with other evolutionary mechanisms such as genetic drift. 110
56 What Monkeys Know Unique predator identification. Third-party relationships Kinship relationships Dominance hierarchies
57 Reciprocal Altruism frequent interaction record keeping limit support to reciprocators 113 Simple Phylogeny Homo sapiens Homo erectus (ca 1.8 Ma) Homo habilis (ca 2 Ma) Paranthropus boisei (ca Ma) Paranthropus robustus (ca 1.8) Au. africanus (ca 2.6 Ma) Australopithecus afarensis (ca Ma) 114
58 (not so) Simple Phylogeny Homo sapiens Homo erectus (ca 1.8 Ma) Homo ergaster Homo rudolfensis Homo habilis (ca 2 Ma) Homo neanderthalensis Homo heidelbergesis Paranthropus boisei (ca Ma) Paranthropus robustus (ca 1.8) Paranthropus aethiopicus (ca 2 Ma) Au. africanus (ca 2.6 Ma) Au. garhi (ca 2.5 Ma) Kenyanthropus platyops (ca 3.5 Ma) Au. bahrelghazali (ca 3 Ma) Australopithecus afarensis (ca Ma) Australopithecus anamensis (ca 4 Ma) Ardipithecus ramidus (ca 4.4 Ma) Ardipithecus kadabba (ca 5.6 Ma) Orrorin tugenensis (ca 6 Ma) Sahalanthropus tchadensis (ca 7 Ma) 115 Hominoid Phylogeny Molecular data (DNA sequence and DNA-DNA hybridization) consistently point to a Pan as the sister group to Homo 116
59 Siamang Gibbon Orangutan Gorilla Human Chimpanzee Bonobo
60 Nicholas Steno Anatomist who worked for the Grand Duke of Tuscany, Ferdinand II Principle of original horizontality and superposition 119 Alfred Russel Wallace Co-Discoverer of Natural Selection 120
61 Brain Size 121 Australopithecus africanus South Africa (Taung, Sterkfontein and others) ca 3 to 2.2 Ma Taung 122
62 P. robustus SK OH 5 Zinj Paranthropus boisei 124
63 P. robustus KNM ER P. robustus 126
64 Comparision Au. afarensis Au. aethiopicus Au. boisei 127 Strapping Youth KNM-WT year-old male 1.6 m tall (5 ft. 4 in) adult stature approx. 1.9 m (6 ft.) 128
65 Strapping Youth KNM-WT year-old male 1.6 m tall (5 ft. 4 in) adult stature approx. 1.9 m (6 ft.) 129 Homo ergaster East Lake Turkana KNM-ER
66 Homo rudolfensis KNM ER How Many Species? KNM ER 1470 KNM ER 1813 Homo rudolfensis Homo habilis 132
67 Homologous Structures
68
69 137 Modern Synthesis 138
70 Evolutionary rates 139
Outline 22: Hominid Fossil Record
 Outline 22: Hominid Fossil Record Human ancestors A.=Australopithicus Assumed direct lineage to modern humans Babcock textbook Collecting hominid fossils in East Africa Using Stratigraphy and Radiometric
Outline 22: Hominid Fossil Record Human ancestors A.=Australopithicus Assumed direct lineage to modern humans Babcock textbook Collecting hominid fossils in East Africa Using Stratigraphy and Radiometric
The facts most scientists agree on
 Extant Apes Even though chimps look more similar to gorillas and orangutans, they re actually more closely related to humans according to current genetic data. The facts most scientists agree on Brains:
Extant Apes Even though chimps look more similar to gorillas and orangutans, they re actually more closely related to humans according to current genetic data. The facts most scientists agree on Brains:
Last class. What species of hominid are found in the early Pliocene? Where are they found? What are their distinguishing anatomical characteristics?
 Last class What species of hominid are found in the early Pliocene? Where are they found? What are their distinguishing anatomical characteristics? How do the Australopithecines differ from the possible
Last class What species of hominid are found in the early Pliocene? Where are they found? What are their distinguishing anatomical characteristics? How do the Australopithecines differ from the possible
Introduction to Physical Anthropology - Study Guide - Focus Topics
 Introduction to Physical Anthropology - Study Guide - Focus Topics Chapter 1 Species: Recognize all definitions. Evolution: Describe all processes. Culture: Define and describe importance. Biocultural:
Introduction to Physical Anthropology - Study Guide - Focus Topics Chapter 1 Species: Recognize all definitions. Evolution: Describe all processes. Culture: Define and describe importance. Biocultural:
On side: Classification of Humans
 1 The modern human, known as the species homo sapien, is characterized by a large and well-developed brain compared to early species of humans.this increased mental capacity has allowed people to excel
1 The modern human, known as the species homo sapien, is characterized by a large and well-developed brain compared to early species of humans.this increased mental capacity has allowed people to excel
Tracing the evolution of the genus Homo is important for understanding the ancestry of humans; the only living species of Homo.
 Section 3: Tracing the evolution of the genus Homo is important for understanding the ancestry of humans; the only living species of Homo. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential
Section 3: Tracing the evolution of the genus Homo is important for understanding the ancestry of humans; the only living species of Homo. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential
The Story of Human Evolution Part 1: From ape-like ancestors to modern humans
 The Story of Human Evolution Part 1: From ape-like ancestors to modern humans Slide 1 The Story of Human Evolution This powerpoint presentation tells the story of who we are and where we came from - how
The Story of Human Evolution Part 1: From ape-like ancestors to modern humans Slide 1 The Story of Human Evolution This powerpoint presentation tells the story of who we are and where we came from - how
Phylogeny and the dispersal of Homo. David S. Strait, U Albany
 Phylogeny and the dispersal of Homo David S. Strait, U Albany Biogeography g The study of how and why organisms are distributed across the landscape Darwin s voyage to the Galapagos Islands Darwin s finches
Phylogeny and the dispersal of Homo David S. Strait, U Albany Biogeography g The study of how and why organisms are distributed across the landscape Darwin s voyage to the Galapagos Islands Darwin s finches
Classification and Evolution
 Classification and Evolution Starter: How many different ways could I split these objects into 2 groups? Classification All living things can also be grouped how do we decide which groups to put them into?
Classification and Evolution Starter: How many different ways could I split these objects into 2 groups? Classification All living things can also be grouped how do we decide which groups to put them into?
Defining the Genus Homo
 Defining the Genus Homo Mark Collard and Bernard Wood Contents Introduction... 2108 Changing Interpretations of Genus Homo... 2109 Is Genus Homo a Good Genus?... 2114 Updating Wood and Collard s (1999)
Defining the Genus Homo Mark Collard and Bernard Wood Contents Introduction... 2108 Changing Interpretations of Genus Homo... 2109 Is Genus Homo a Good Genus?... 2114 Updating Wood and Collard s (1999)
In 1871 Charles Darwin published another groundbreaking
 23 How Humans Evolved Concept Outline 23.1 The evolutionary path to humans starts with the advent of primates. The Evolutionary Path to Apes. Primates first evolved 65 million years ago, giving rise first
23 How Humans Evolved Concept Outline 23.1 The evolutionary path to humans starts with the advent of primates. The Evolutionary Path to Apes. Primates first evolved 65 million years ago, giving rise first
EARLY AND LATE ARCHAIC HOMO SAPIENS AND ANATOMICALLY MODERN HOMO SAPIENS
 ANTH 310 Human Origins LABORATORY #5 EARLY AND LATE ARCHAIC HOMO SAPIENS AND ANATOMICALLY MODERN HOMO SAPIENS Traditionally, the hominins after the middle Pleistocene (middle Homo) belong to Homo sapiens.
ANTH 310 Human Origins LABORATORY #5 EARLY AND LATE ARCHAIC HOMO SAPIENS AND ANATOMICALLY MODERN HOMO SAPIENS Traditionally, the hominins after the middle Pleistocene (middle Homo) belong to Homo sapiens.
Level 3 Biology, 2012
 90719 907190 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Biology, 2012 90719 Describe trends in human evolution 2.00 pm Tuesday 13 November 2012 Credits: Three Check that the National Student Number (NSN) on your admission
90719 907190 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Biology, 2012 90719 Describe trends in human evolution 2.00 pm Tuesday 13 November 2012 Credits: Three Check that the National Student Number (NSN) on your admission
ANTH 215 Physical Anthropology Study Guide for Exam-III
 ANTH 215 Physical Anthropology Study Guide for Exam-III General: The final exam covers all the lectures and reading in Jurmain et al. (Chapters 8-13 &17) since the last exam. This exam is worth 30% of
ANTH 215 Physical Anthropology Study Guide for Exam-III General: The final exam covers all the lectures and reading in Jurmain et al. (Chapters 8-13 &17) since the last exam. This exam is worth 30% of
he standard uniform for paleontologists is casual. T-shirts, cutoffs, and floppy old hats are common
 NOT FOR SALE A New Kind of Ape T 14 Reprinted from The Tangled Bank: An Introduction to Evolution, Second Edition by Carl Zimmer. Permission granted by Roberts and Company Publishers. http://bit.ly/1bwx1qt
NOT FOR SALE A New Kind of Ape T 14 Reprinted from The Tangled Bank: An Introduction to Evolution, Second Edition by Carl Zimmer. Permission granted by Roberts and Company Publishers. http://bit.ly/1bwx1qt
Fossils, feet and the evolution of human bipedal locomotion
 J. Anat. (2004) 204, pp403 416 Blackwell Publishing, Ltd. REVIEW Fossils, feet and the evolution of human bipedal locomotion W. E. H. Harcourt-Smith 1 and L. C. Aiello 2 1 Division of Vertebrate Paleontology,
J. Anat. (2004) 204, pp403 416 Blackwell Publishing, Ltd. REVIEW Fossils, feet and the evolution of human bipedal locomotion W. E. H. Harcourt-Smith 1 and L. C. Aiello 2 1 Division of Vertebrate Paleontology,
The First Female Homo erectus Pelvis, from Gona, Afar, Ethiopia
 PRESS RELEASE The First Female Homo erectus Pelvis, from Gona, Afar, Ethiopia To be published in the Journal Science 14 November, 2008 Prepared by the Gona Palaeoanthropological Research Project Stone
PRESS RELEASE The First Female Homo erectus Pelvis, from Gona, Afar, Ethiopia To be published in the Journal Science 14 November, 2008 Prepared by the Gona Palaeoanthropological Research Project Stone
Chapter 11: The Origins and Evolution of Early Homo
 Chapter 11: The Origins and Evolution of Early Homo 1. Homo habilis: The First Species of the Genus Homo a. The Path to Humanness: Bigger Brains, Tool Use, and Adaptive Flexibility i. First discovered
Chapter 11: The Origins and Evolution of Early Homo 1. Homo habilis: The First Species of the Genus Homo a. The Path to Humanness: Bigger Brains, Tool Use, and Adaptive Flexibility i. First discovered
Principles of Evolution - Origin of Species
 Theories of Organic Evolution X Multiple Centers of Creation (de Buffon) developed the concept of "centers of creation throughout the world organisms had arisen, which other species had evolved from X
Theories of Organic Evolution X Multiple Centers of Creation (de Buffon) developed the concept of "centers of creation throughout the world organisms had arisen, which other species had evolved from X
A Quick Taxonomy of the Primate Order (See University of Manitoba for an excellent and very thorough primate taxonomy)
 PRIMATE TAXONOMY Apes are no monkeys! The best way to insult a scientist working on chimpanzees is to say he/she is working with monkeys. We, humans, belong to the same family as the anthropoid (human-like)
PRIMATE TAXONOMY Apes are no monkeys! The best way to insult a scientist working on chimpanzees is to say he/she is working with monkeys. We, humans, belong to the same family as the anthropoid (human-like)
Cotlow Award Application Form 2009
 Cotlow Award Application Form 2009 Department of Anthropology The George Washington University Washington, DC 20052 1. Personal Information Applicant s name: Degree sought: Katherine E. Schroer PhD Field
Cotlow Award Application Form 2009 Department of Anthropology The George Washington University Washington, DC 20052 1. Personal Information Applicant s name: Degree sought: Katherine E. Schroer PhD Field
Chapter 00. Chapter 13. The Early Hominins. Chapter Outline
 Chapter 00 Chapter 13 The Early Hominins e are all united by our past, that we all hae a common history and though... wwe may be astly different, our origins all lead back to the crucible of human eolution
Chapter 00 Chapter 13 The Early Hominins e are all united by our past, that we all hae a common history and though... wwe may be astly different, our origins all lead back to the crucible of human eolution
ONCE we TODAYWETAKE FOR GRANTED THAT HOMO SAPIENS FOUR MILLION YEARS MANY HOMINID SPECIES EMERGENCE
 EMERGENCE TODAYWETAKE FOR GRANTED THAT HOMO SAPIENS FOUR MILLION YEARS MANY HOMINID SPECIES ONCE we SHARING A SINGLE LANDSCAPE, four kinds of hominids lived about 1.8 million years ago in what is now part
EMERGENCE TODAYWETAKE FOR GRANTED THAT HOMO SAPIENS FOUR MILLION YEARS MANY HOMINID SPECIES ONCE we SHARING A SINGLE LANDSCAPE, four kinds of hominids lived about 1.8 million years ago in what is now part
Homo erectus Infancy and Childhood The Turning Point in the Evolution of Behavioral Development in Hominids
 10 Homo erectus Infancy and Childhood The Turning Point in the Evolution of Behavioral Development in Hominids Sue Taylor Parker In man, attachment is mediated by several different sorts of behaviour of
10 Homo erectus Infancy and Childhood The Turning Point in the Evolution of Behavioral Development in Hominids Sue Taylor Parker In man, attachment is mediated by several different sorts of behaviour of
The femur of Orrorin tugenensis exhibits morphometric affinities with both Miocene apes and later hominins Supplementary Information
 The femur of Orrorin tugenensis exhibits morphometric affinities with both Miocene apes and later hominins Supplementary Information Sergio Almécija, Melissa Tallman, David M. Alba, Marta Pina, Salvador
The femur of Orrorin tugenensis exhibits morphometric affinities with both Miocene apes and later hominins Supplementary Information Sergio Almécija, Melissa Tallman, David M. Alba, Marta Pina, Salvador
Smithsonian Books, 2001. 1 Groves, Colin P. Primate Taxonomy. Smithsonian Series in Comparative Evolutionary Biology. Washington, D.C.
 Primates at Woodland Park Zoo Pre-visit Information for Teachers If you are planning a field trip to the zoo and wish to have your students focus on or study primates during their zoo visit, this pre-visit
Primates at Woodland Park Zoo Pre-visit Information for Teachers If you are planning a field trip to the zoo and wish to have your students focus on or study primates during their zoo visit, this pre-visit
Section 3 Ape Physical Characteristics
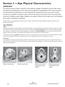 Section 3 Ape Physical Characteristics OVERVIEW The physical anatomy of apes is essential to their adaptive strategies. Compared to humans, their closest living relatives, ape skeletons are more robust
Section 3 Ape Physical Characteristics OVERVIEW The physical anatomy of apes is essential to their adaptive strategies. Compared to humans, their closest living relatives, ape skeletons are more robust
Phylogenetic trees have a long history of representing
 Deep Time in Perspective: An Animated Fossil Hominin Timeline HOLLY M. DUNSWORTH Department of Anthropology, 5500 N. St. Louis Ave., Northeastern Illionois University, Chicago, IL 60625, USA; h-dunsworth@neiu.edu
Deep Time in Perspective: An Animated Fossil Hominin Timeline HOLLY M. DUNSWORTH Department of Anthropology, 5500 N. St. Louis Ave., Northeastern Illionois University, Chicago, IL 60625, USA; h-dunsworth@neiu.edu
These two species overlapped temporally for 700,000 years or more and at location of Koobi Fora, overlapped geographically.
 Earl hominans: Homo habilis and Homo rudolfensis Homo habilis (2.3-16 mya) Female height about 3.3 ft. Male? Weight 72-83 lbs. Brain size 509-674 cc May have had much in common with South African A. africanus
Earl hominans: Homo habilis and Homo rudolfensis Homo habilis (2.3-16 mya) Female height about 3.3 ft. Male? Weight 72-83 lbs. Brain size 509-674 cc May have had much in common with South African A. africanus
Biology 1406 - Notes for exam 5 - Population genetics Ch 13, 14, 15
 Biology 1406 - Notes for exam 5 - Population genetics Ch 13, 14, 15 Species - group of individuals that are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring; genetically similar 13.7, 14.2 Population
Biology 1406 - Notes for exam 5 - Population genetics Ch 13, 14, 15 Species - group of individuals that are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring; genetically similar 13.7, 14.2 Population
FUSSING OVER FOSSILS
 CHRISTIAN RESEARCH INSTITUTE PO Box 8500, Charlotte, NC 28271 Review: JAR1356 FUSSING OVER FOSSILS a book review of The Fossil Chronicles: How Two Controversial Discoveries Changed Our View of Human Evolution
CHRISTIAN RESEARCH INSTITUTE PO Box 8500, Charlotte, NC 28271 Review: JAR1356 FUSSING OVER FOSSILS a book review of The Fossil Chronicles: How Two Controversial Discoveries Changed Our View of Human Evolution
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional background reading and information about their work. Supplement to: Roffman I, Nevo E. Can Chimpanzee Biology
Supplementary Material This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional background reading and information about their work. Supplement to: Roffman I, Nevo E. Can Chimpanzee Biology
A model of Homo naledi, a newly discovered species of ape, at the Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site, Maropeng, South Africa, September 2015
 1 of 10 10/30/2015 10:25 AM Font Size: A A Steven Mithen NOVEMBER 19, 2015 ISSUE The Real Planet of the Apes: A New Story of Human Origins by David R. Begun Princeton University Press, 246 pp., $29.95
1 of 10 10/30/2015 10:25 AM Font Size: A A Steven Mithen NOVEMBER 19, 2015 ISSUE The Real Planet of the Apes: A New Story of Human Origins by David R. Begun Princeton University Press, 246 pp., $29.95
Evolutionary Studies Institute, University of the Witwatersrand Student number: 763068
 A M O R P H O M E T R I C A N A L Y S I S O F H O M I N I N T E E T H A T T R I B U T E D T O D I F F E R E N T S P E C I E S O F A U S T R A L O P I T H E C U S, P A R A N T H R O P U S A N D H O M O
A M O R P H O M E T R I C A N A L Y S I S O F H O M I N I N T E E T H A T T R I B U T E D T O D I F F E R E N T S P E C I E S O F A U S T R A L O P I T H E C U S, P A R A N T H R O P U S A N D H O M O
Once We Were Not. Today we take for granted that Homo sapiens is the only hominid on Earth.Yet for at least four million years many
 Today we take for granted that Homo sapiens is the only hominid on Earth.Yet for at least four million years many Once We Were Not PARANTHROPUS BOISEI had massive jaws, equipped with huge grinding teeth
Today we take for granted that Homo sapiens is the only hominid on Earth.Yet for at least four million years many Once We Were Not PARANTHROPUS BOISEI had massive jaws, equipped with huge grinding teeth
HUMAN ORIGINS, DISPERSAL AND ASSOCIATED ENVIRONMENTS: AN AFRICAN PERSPECTIVE
 HUMAN ORIGINS, DISPERSAL AND ASSOCIATED ENVIRONMENTS: AN AFRICAN PERSPECTIVE Amanuel Beyin University of Southern Indiana, Evansville, Indiana, U.S.A. Keywords: Modern humans (Homo sapiens), hominins,
HUMAN ORIGINS, DISPERSAL AND ASSOCIATED ENVIRONMENTS: AN AFRICAN PERSPECTIVE Amanuel Beyin University of Southern Indiana, Evansville, Indiana, U.S.A. Keywords: Modern humans (Homo sapiens), hominins,
From Africa to Aotearoa Part 1: Out of Africa
 From Africa to Aotearoa Part 1: Out of Africa The spread of modern humans out of Africa started around 65,000 years ago, and ended with the settlement of New Zealand 750 years ago. These PowerPoint presentations
From Africa to Aotearoa Part 1: Out of Africa The spread of modern humans out of Africa started around 65,000 years ago, and ended with the settlement of New Zealand 750 years ago. These PowerPoint presentations
STEP BY STEP: THE EVOLUTION OF BIPEDALISM Lesson Overview - Intermediate & Advanced
 Lesson Overview - Intermediate & Advanced Overview: Bipedalism is a defining characteristic of modern humans that evolved over millions of years. Therefore, identifying evidence for bipedalism in the fossil
Lesson Overview - Intermediate & Advanced Overview: Bipedalism is a defining characteristic of modern humans that evolved over millions of years. Therefore, identifying evidence for bipedalism in the fossil
Psychomotorický vývoj.
 $% & ' (!! " # OR 15 - Antropologie Auxologie ) & % & && & & * $! Psychomotorický vývoj. " & & & Osnova + & 1. Prenatální růst a vývoj, + *!- & & &." &! * & & &/$ 2. Postnatální růst a vývoj 3. Principy
$% & ' (!! " # OR 15 - Antropologie Auxologie ) & % & && & & * $! Psychomotorický vývoj. " & & & Osnova + & 1. Prenatální růst a vývoj, + *!- & & &." &! * & & &/$ 2. Postnatální růst a vývoj 3. Principy
CCR Biology - Chapter 10 Practice Test - Summer 2012
 Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 10 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the term for a feature
Name: Class: Date: CCR Biology - Chapter 10 Practice Test - Summer 2012 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the term for a feature
Evidence for evolution factsheet
 The theory of evolution by natural selection is supported by a great deal of evidence. Fossils Fossils are formed when organisms become buried in sediments, causing little decomposition of the organism.
The theory of evolution by natural selection is supported by a great deal of evidence. Fossils Fossils are formed when organisms become buried in sediments, causing little decomposition of the organism.
Human Nature A look at the ways in which monkeys and apes are similar to humans, not just biologically but mentally and socially
 Lesson Title: Life As We Know It Grade Level: 9-12 Time Allotment: 3 45-minute class periods Overview Where did life on Earth come from, and how did it become what it is today? Students will explore the
Lesson Title: Life As We Know It Grade Level: 9-12 Time Allotment: 3 45-minute class periods Overview Where did life on Earth come from, and how did it become what it is today? Students will explore the
Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions
 Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions Grade 7 (Evolution) 3.a Students know both genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and diversity of organisms. (pg. 109 Science
Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions Grade 7 (Evolution) 3.a Students know both genetic variation and environmental factors are causes of evolution and diversity of organisms. (pg. 109 Science
5 The Origins of Bipedal Locomotion
 The Origins of Bipedal Locomotion William E. H. Harcourt Smith Abstract Bipedalism is a highly specialized and unusual form of primate locomotion that is found today only in modern humans. The majority
The Origins of Bipedal Locomotion William E. H. Harcourt Smith Abstract Bipedalism is a highly specialized and unusual form of primate locomotion that is found today only in modern humans. The majority
Evolution, Natural Selection, and Adaptation
 Evolution, Natural Selection, and Adaptation Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution. (Theodosius Dobzhansky) Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Voyage of HMS Beagle (1831-1836) Thinking
Evolution, Natural Selection, and Adaptation Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution. (Theodosius Dobzhansky) Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Voyage of HMS Beagle (1831-1836) Thinking
WHO IS LUCY? Lesson Overview
 Lesson Overview Overview: In this lesson, you will be introduced to Lucy, one of the most famous fossils ever found. You ll learn details about Lucy including her relationship to humans, her diet, her
Lesson Overview Overview: In this lesson, you will be introduced to Lucy, one of the most famous fossils ever found. You ll learn details about Lucy including her relationship to humans, her diet, her
6 LUCY & THE LEAKEYS BIOGRAPHY 770L
 6 LUCY & THE LEAKEYS BIOGRAPHY 770L LUCY & THE LEAKEYS HOMININE FOSSILS AND PALEOARCHAEOLOGISTS Louis Leakey Mary Leakey Lucy c. 3.2 MYA Afar, Ethiopia Born August 7, 1903 Kabete, Kenya Died October 1,
6 LUCY & THE LEAKEYS BIOGRAPHY 770L LUCY & THE LEAKEYS HOMININE FOSSILS AND PALEOARCHAEOLOGISTS Louis Leakey Mary Leakey Lucy c. 3.2 MYA Afar, Ethiopia Born August 7, 1903 Kabete, Kenya Died October 1,
Name Class Date. binomial nomenclature. MAIN IDEA: Linnaeus developed the scientific naming system still used today.
 Section 1: The Linnaean System of Classification 17.1 Reading Guide KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. VOCABULARY taxonomy taxon binomial nomenclature genus MAIN IDEA:
Section 1: The Linnaean System of Classification 17.1 Reading Guide KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. VOCABULARY taxonomy taxon binomial nomenclature genus MAIN IDEA:
ARCH 1616 Between Sahara and Sea: North Africa from Human Origins to Islam
 ARCH 1616 Between Sahara and Sea: North Africa from Human Origins to Islam Brett Kaufman brett_kaufman@brown.edu Office Hours week of September 22: Monday, 2:30-4:30 pm Rhode Island Hall 007 Hominid Evolution
ARCH 1616 Between Sahara and Sea: North Africa from Human Origins to Islam Brett Kaufman brett_kaufman@brown.edu Office Hours week of September 22: Monday, 2:30-4:30 pm Rhode Island Hall 007 Hominid Evolution
Evolution of Human Parental Behavior and the Human Family
 PARENTING: SCIENCE AND PRACTICE Copyright 2001, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. January June 2001 Volume 1 Numbers 1 and 2 Pages 5 61 Evolution of Human Parental Behavior and the Human Family David C.
PARENTING: SCIENCE AND PRACTICE Copyright 2001, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. January June 2001 Volume 1 Numbers 1 and 2 Pages 5 61 Evolution of Human Parental Behavior and the Human Family David C.
Social cooperation, niche construction, and the core role of intergenerational bonding in human evolution. Agustín Fuentes University of Notre Dame
 Social cooperation, niche construction, and the core role of intergenerational bonding in human evolution Agustín Fuentes University of Notre Dame Complexity in evolutionary theory helps think about human
Social cooperation, niche construction, and the core role of intergenerational bonding in human evolution Agustín Fuentes University of Notre Dame Complexity in evolutionary theory helps think about human
This is a series of skulls and front leg fossils of organisms believed to be ancestors of the modern-day horse.
 Evidence of Evolution Background When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide as much evidence as
Evidence of Evolution Background When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide as much evidence as
Practice Questions 1: Evolution
 Practice Questions 1: Evolution 1. Which concept is best illustrated in the flowchart below? A. natural selection B. genetic manipulation C. dynamic equilibrium D. material cycles 2. The diagram below
Practice Questions 1: Evolution 1. Which concept is best illustrated in the flowchart below? A. natural selection B. genetic manipulation C. dynamic equilibrium D. material cycles 2. The diagram below
INTRODUCTION. Stage 1: Bipedal hominins
 INTRODUCTION There is fairly general agreement that language is a uniquely human accomplishment. Although other species communicate in diverse ways, human language has properties that stand out as special.
INTRODUCTION There is fairly general agreement that language is a uniquely human accomplishment. Although other species communicate in diverse ways, human language has properties that stand out as special.
Hominid evolution and the emergence of the genus Homo
 Pontifical Academy of Sciences, Scripta Varia 121, Vatican City 2013 www.casinapioiv.va/content/dam/accademia/pdf/sv121/sv121-coppens.pdf Hominid evolution and the emergence of the genus Homo Yves Coppens
Pontifical Academy of Sciences, Scripta Varia 121, Vatican City 2013 www.casinapioiv.va/content/dam/accademia/pdf/sv121/sv121-coppens.pdf Hominid evolution and the emergence of the genus Homo Yves Coppens
Chordates (phylum Chordata) are bilaterian animals that belong to the clade of animals known as Deuterostomia
 Ch 34 Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates Chordates Chordates (phylum Chordata) are bilaterian animals that belong to the clade of animals known as Deuterostomia Chordates comprise all vertebrates and two
Ch 34 Origin & Evolution of Vertebrates Chordates Chordates (phylum Chordata) are bilaterian animals that belong to the clade of animals known as Deuterostomia Chordates comprise all vertebrates and two
Lab 2/Phylogenetics/September 16, 2002 1 PHYLOGENETICS
 Lab 2/Phylogenetics/September 16, 2002 1 Read: Tudge Chapter 2 PHYLOGENETICS Objective of the Lab: To understand how DNA and protein sequence information can be used to make comparisons and assess evolutionary
Lab 2/Phylogenetics/September 16, 2002 1 Read: Tudge Chapter 2 PHYLOGENETICS Objective of the Lab: To understand how DNA and protein sequence information can be used to make comparisons and assess evolutionary
Rethinking Polynesian Origins: Human Settlement of the Pacific
 LENScience Senior Biology Seminar Series Rethinking Polynesian Origins: Human Settlement of the Pacific Michal Denny, and Lisa Matisoo-Smith Our Polynesian ancestors are renowned as some of the world s
LENScience Senior Biology Seminar Series Rethinking Polynesian Origins: Human Settlement of the Pacific Michal Denny, and Lisa Matisoo-Smith Our Polynesian ancestors are renowned as some of the world s
Regardless of who you are or where you came from
 We Are All African! Can scientific proof of our commonality save us? Christopher dicarlo Regardless of who you are or where you came from despite ethnic differences, political distinctions, and racial
We Are All African! Can scientific proof of our commonality save us? Christopher dicarlo Regardless of who you are or where you came from despite ethnic differences, political distinctions, and racial
Chapter 25: The History of Life on Earth
 Overview Name Period 1. In the last chapter, you were asked about macroevolution. To begin this chapter, give some examples of macroevolution. Include at least one novel example not in your text. Concept
Overview Name Period 1. In the last chapter, you were asked about macroevolution. To begin this chapter, give some examples of macroevolution. Include at least one novel example not in your text. Concept
Australopithecus and Homo habilis Pre-Human Ancestors?
 Australopithecus and Homo habilis Pre-Human Ancestors? A. W. MEHLERT ABSTRACT A survey of the palaeoanthropological literature reveals the controversies raging between various discoverers of australopithecine
Australopithecus and Homo habilis Pre-Human Ancestors? A. W. MEHLERT ABSTRACT A survey of the palaeoanthropological literature reveals the controversies raging between various discoverers of australopithecine
Animal Models of Human Behavioral and Social Processes: What is a Good Animal Model? Dario Maestripieri
 Animal Models of Human Behavioral and Social Processes: What is a Good Animal Model? Dario Maestripieri Criteria for assessing the validity of animal models of human behavioral research Face validity:
Animal Models of Human Behavioral and Social Processes: What is a Good Animal Model? Dario Maestripieri Criteria for assessing the validity of animal models of human behavioral research Face validity:
Conference Report: Paleoanthropology of the Mani Peninsula (Greece)
 News and Views K. Harvati & E. Delson Conference Report: Paleoanthropology of the Mani Peninsula (Greece) NYCEP; Department of Anthropology, City University of New York Graduate School; and Department
News and Views K. Harvati & E. Delson Conference Report: Paleoanthropology of the Mani Peninsula (Greece) NYCEP; Department of Anthropology, City University of New York Graduate School; and Department
Were Australopithecines Ape Human Intermediates or Just Apes? A Test of Both Hypotheses Using the Lucy Skeleton
 article Were Australopithecines Ape Human Intermediates or Just Apes? A Test of Both Hypotheses Using the Lucy Skeleton Phil Senter Abstrac t Mainstream scientists often claim that australopithecines such
article Were Australopithecines Ape Human Intermediates or Just Apes? A Test of Both Hypotheses Using the Lucy Skeleton Phil Senter Abstrac t Mainstream scientists often claim that australopithecines such
Curriculum Vitae Karen L. Baab
 Curriculum Vitae Karen L. Baab Department of Anthropology Office (631) 632-5755 Stony Brook University Fax (631) 632-9165 Stony Brook, New York 11794 Karen.Baab@stonybrook.edu Education 2007 PhD, City
Curriculum Vitae Karen L. Baab Department of Anthropology Office (631) 632-5755 Stony Brook University Fax (631) 632-9165 Stony Brook, New York 11794 Karen.Baab@stonybrook.edu Education 2007 PhD, City
IDENTIFICATION OF ORGANISMS
 reflect Take a look at the pictures on the right. Think about what the two organisms have in common. They both need food and water to survive. They both grow and reproduce. They both have similar body
reflect Take a look at the pictures on the right. Think about what the two organisms have in common. They both need food and water to survive. They both grow and reproduce. They both have similar body
Is Homo Defined by Culture?
 Is Homo Defined by Culture? BERNARD WOOD & MARK COLLARD The changing face of Homo THE GENUS HOMO was established by Carolus Linnaeus as part of the 1758 edition of his monumental review, the Systema Naturae.
Is Homo Defined by Culture? BERNARD WOOD & MARK COLLARD The changing face of Homo THE GENUS HOMO was established by Carolus Linnaeus as part of the 1758 edition of his monumental review, the Systema Naturae.
Chapter 34 Vertebrates Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is a shared characteristic of all chordates? A) scales B) jaws C) vertebrae
 Chapter 34 Vertebrates Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is a shared characteristic of all chordates? A) scales B) jaws C) vertebrae D) dorsal, hollow nerve cord E) four-chambered heart
Chapter 34 Vertebrates Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is a shared characteristic of all chordates? A) scales B) jaws C) vertebrae D) dorsal, hollow nerve cord E) four-chambered heart
Part 1: Evolutionary Psychology (Colarelli) Part 2: Behavioral Genetics (Arvey)
 Evolutionary Psychology, Behavioral Genetics, and Leadership Academy of Management Professional Development Workshop Richard D. Arvey Stephen M. Colarelli August 8, 2008 Part 1: Evolutionary Psychology
Evolutionary Psychology, Behavioral Genetics, and Leadership Academy of Management Professional Development Workshop Richard D. Arvey Stephen M. Colarelli August 8, 2008 Part 1: Evolutionary Psychology
Evolutionary Evidence
 Evolutionary Evidence 7th Grade, Science and English/Language Arts: Age of Mammals Make the most of your Museum field trip by integrating it into your classroom curriculum. These lesson plans provide a
Evolutionary Evidence 7th Grade, Science and English/Language Arts: Age of Mammals Make the most of your Museum field trip by integrating it into your classroom curriculum. These lesson plans provide a
Mendelian and Non-Mendelian Heredity Grade Ten
 Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
Ohio Standards Connection: Life Sciences Benchmark C Explain the genetic mechanisms and molecular basis of inheritance. Indicator 6 Explain that a unit of hereditary information is called a gene, and genes
Problem Set 5 BILD10 / Winter 2014 Chapters 8, 10-12
 Chapter 8: Evolution and Natural Selection 1) A population is: a) a group of species that shares the same habitat. b) a group of individuals of the same species that lives in the same general location
Chapter 8: Evolution and Natural Selection 1) A population is: a) a group of species that shares the same habitat. b) a group of individuals of the same species that lives in the same general location
Taxonomy and Classification
 Taxonomy and Classification Taxonomy = the science of naming and describing species Wisdom begins with calling things by their right names -Chinese Proverb museums contain ~ 2 Billion specimens worldwide
Taxonomy and Classification Taxonomy = the science of naming and describing species Wisdom begins with calling things by their right names -Chinese Proverb museums contain ~ 2 Billion specimens worldwide
Summary. 16 1 Genes and Variation. 16 2 Evolution as Genetic Change. Name Class Date
 Chapter 16 Summary Evolution of Populations 16 1 Genes and Variation Darwin s original ideas can now be understood in genetic terms. Beginning with variation, we now know that traits are controlled by
Chapter 16 Summary Evolution of Populations 16 1 Genes and Variation Darwin s original ideas can now be understood in genetic terms. Beginning with variation, we now know that traits are controlled by
Centre for Archaeological Science Dr Adam Brumm
 Centre for Archaeological Science Dr Adam Brumm ARC Postdoctoral Research Fellow Room: 41.266 Phone No: +61 2 4221 5946 Email: abrumm@uow.edu.au Professional Profile Qualifications: BA (Hons), PhD Awards:
Centre for Archaeological Science Dr Adam Brumm ARC Postdoctoral Research Fellow Room: 41.266 Phone No: +61 2 4221 5946 Email: abrumm@uow.edu.au Professional Profile Qualifications: BA (Hons), PhD Awards:
The Presbyterian Association on Science, Technology, and the Christian Faith THE JOURNAL h AUGUST 2015 h VOLUME 24, NUMBER 3. Creation Affirming
 SciTech The Presbyterian Association on Science, Technology, and the Christian Faith THE JOURNAL h AUGUST 2015 h VOLUME 24, NUMBER 3 Creation Affirming A Call to the Presbyterian Church (USA) In the beginning
SciTech The Presbyterian Association on Science, Technology, and the Christian Faith THE JOURNAL h AUGUST 2015 h VOLUME 24, NUMBER 3 Creation Affirming A Call to the Presbyterian Church (USA) In the beginning
Culture (from the Encarta Encyclopedia)
 Culture (from the Encarta Encyclopedia) 1. Introduction Culture, in anthropology, is the patterns of behavior and thinking that people living in social groups learn, create, and share. Culture distinguishes
Culture (from the Encarta Encyclopedia) 1. Introduction Culture, in anthropology, is the patterns of behavior and thinking that people living in social groups learn, create, and share. Culture distinguishes
AP Biology Essential Knowledge Student Diagnostic
 AP Biology Essential Knowledge Student Diagnostic Background The Essential Knowledge statements provided in the AP Biology Curriculum Framework are scientific claims describing phenomenon occurring in
AP Biology Essential Knowledge Student Diagnostic Background The Essential Knowledge statements provided in the AP Biology Curriculum Framework are scientific claims describing phenomenon occurring in
11, Olomouc, 783 71, Czech Republic. Version of record first published: 24 Sep 2012.
 This article was downloaded by: [Knihovna Univerzity Palackeho], [Vladan Ondrej] On: 24 September 2012, At: 05:24 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954
This article was downloaded by: [Knihovna Univerzity Palackeho], [Vladan Ondrej] On: 24 September 2012, At: 05:24 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954
Introduction to Anthropology
 Introduction to Anthropology Course Information Organization Mercer County Community College Developers Nichol Wilson Killian; Gianna Durso-Finley Development Date 200122 Course Number ANT 101 Instructional
Introduction to Anthropology Course Information Organization Mercer County Community College Developers Nichol Wilson Killian; Gianna Durso-Finley Development Date 200122 Course Number ANT 101 Instructional
STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words BIOLOGY. Written examination 2. Monday 5 November 2007
 Victorian CertiÞcate of Ed ucation 2007 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words BIOLOGY Written examination 2 Monday 5 November 2007 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15
Victorian CertiÞcate of Ed ucation 2007 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words BIOLOGY Written examination 2 Monday 5 November 2007 Reading time: 9.00 am to 9.15
A Correlation of Pearson Miller & Levine Biology 2014 To the Utah Core State Standards for Biology Grades 9-12
 A Correlation of Pearson To the Utah Core State Standards Resource Title: Publisher: Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall ISBN (10 or 13 digit unique identifier is required): SE: 9780133242003
A Correlation of Pearson To the Utah Core State Standards Resource Title: Publisher: Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall ISBN (10 or 13 digit unique identifier is required): SE: 9780133242003
Theory of Evolution. A. the beginning of life B. the evolution of eukaryotes C. the evolution of archaebacteria D. the beginning of terrestrial life
 Theory of Evolution 1. In 1966, American biologist Lynn Margulis proposed the theory of endosymbiosis, or the idea that mitochondria are the descendents of symbiotic, aerobic eubacteria. What does the
Theory of Evolution 1. In 1966, American biologist Lynn Margulis proposed the theory of endosymbiosis, or the idea that mitochondria are the descendents of symbiotic, aerobic eubacteria. What does the
Nutrition and Zoo Animals
 Nutrition and Zoo Animals Nutrition All animals need nutrition to survive. Nutrition can have a large effect on basic health as well as physical and mental development, ability to reproduce, emotions and
Nutrition and Zoo Animals Nutrition All animals need nutrition to survive. Nutrition can have a large effect on basic health as well as physical and mental development, ability to reproduce, emotions and
Experimental Perspective on Fallback Foods and Dietary Adaptations in Early Hominins
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Publications Department of Anthropology -0 Experimental Perspective on Fallback Foods and Dietary Adaptations in Early Hominins Jeremiah E. Scott Southern
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Publications Department of Anthropology -0 Experimental Perspective on Fallback Foods and Dietary Adaptations in Early Hominins Jeremiah E. Scott Southern
Mechanisms of Evolution
 page 2 page 3 Teacher's Notes Mechanisms of Evolution Grades: 11-12 Duration: 28 mins Summary of Program Evolution is the gradual change that can be seen in a population s genetic composition, from one
page 2 page 3 Teacher's Notes Mechanisms of Evolution Grades: 11-12 Duration: 28 mins Summary of Program Evolution is the gradual change that can be seen in a population s genetic composition, from one
Tuesday 14 May 2013 Morning
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION H Tuesday 14 May 2013 Morning GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A A161/02 Modules B1 B2 B3 (Higher Tier) *A137150613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. A calculator
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION H Tuesday 14 May 2013 Morning GCSE TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE BIOLOGY A A161/02 Modules B1 B2 B3 (Higher Tier) *A137150613* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. A calculator
Genetic Variation and Human Evolution Lynn B. Jorde, Ph.D. Department of Human Genetics University of Utah School of Medicine.
 Genetic Variation and Human Evolution Lynn B. Jorde, Ph.D. Department of Human Genetics University of Utah School of Medicine. The past two decades have witnessed an explosion of human genetic data. Innumerable
Genetic Variation and Human Evolution Lynn B. Jorde, Ph.D. Department of Human Genetics University of Utah School of Medicine. The past two decades have witnessed an explosion of human genetic data. Innumerable
Hoofdstuk 8.1., bijlage 1, noten
 Hoofdstuk 8.1., bijlage 1, noten 1 Mensapen Mioceen: Begun, (2007) ~ zie ook: Dennell, (2010); Elton, (2008) 2 Spanje, Dryonpithecus: Almécija, (2007); Begun, (2005) 3 Landbrug: Begun, (2007); Begun, (2005);
Hoofdstuk 8.1., bijlage 1, noten 1 Mensapen Mioceen: Begun, (2007) ~ zie ook: Dennell, (2010); Elton, (2008) 2 Spanje, Dryonpithecus: Almécija, (2007); Begun, (2005) 3 Landbrug: Begun, (2007); Begun, (2005);
AP Biology 2015 Free-Response Questions
 AP Biology 2015 Free-Response Questions College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online home
AP Biology 2015 Free-Response Questions College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online home
Comparative Primate Psychology
 Comparative Primate Psychology D Maestripieri, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA ã 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Glossary Adaptation A genetically controlled trait that has evolved
Comparative Primate Psychology D Maestripieri, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA ã 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Glossary Adaptation A genetically controlled trait that has evolved
Recovering the Romanovs
 Recovering the Romanovs Description of activity Recovering the Romanovs is an excellent opening to any unit on human genetics. To complete the three parts of this module, approximately three 40-minute
Recovering the Romanovs Description of activity Recovering the Romanovs is an excellent opening to any unit on human genetics. To complete the three parts of this module, approximately three 40-minute
The Evolution of Language. W. Tecumseh Fitch INSTANT EXPERT 6
 The Evolution of Language W. Tecumseh Fitch INSTANT EXPERT 6 Linguists define language as any system which allows the free and unfettered expression of thoughts into signals, and the complementary interpretation
The Evolution of Language W. Tecumseh Fitch INSTANT EXPERT 6 Linguists define language as any system which allows the free and unfettered expression of thoughts into signals, and the complementary interpretation
1. Over the past century, several scientists around the world have made the following observations:
 Evolution Keystone Review 1. Over the past century, several scientists around the world have made the following observations: New mitochondria and plastids can only be generated by old mitochondria and
Evolution Keystone Review 1. Over the past century, several scientists around the world have made the following observations: New mitochondria and plastids can only be generated by old mitochondria and
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Bio EOC Questions for Cell Reproduction:
 Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Bio EOC Topics for Cell Reproduction: Asexual vs. sexual reproduction Mitosis steps, diagrams, purpose o Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis Meiosis steps, diagrams, purpose
Notes on Science & Christian Belief - Chapter 7 2009. Chapter 7 EVOLUTION AND CREATION. Allan J Day. Author: Allan J Day 7-1
 Chapter 7 EVOLUTION AND CREATION Allan J Day Author: Allan J Day 7-1 CONTENTS CHAPTER 7 Chapter 7 EVOLUTION AND CREATION... 7-1 7.1 INTRODUCTION... 7-3 7.2 INTERPRETING THE SCIENTIFIC DATA... 7-3 7.2.1
Chapter 7 EVOLUTION AND CREATION Allan J Day Author: Allan J Day 7-1 CONTENTS CHAPTER 7 Chapter 7 EVOLUTION AND CREATION... 7-1 7.1 INTRODUCTION... 7-3 7.2 INTERPRETING THE SCIENTIFIC DATA... 7-3 7.2.1
Variation in enamel development of South African fossil hominids
 Journal of Human Evolution 51 (2006) 580e590 Variation in enamel development of South African fossil hominids Rodrigo S. Lacruz a, *, Fernando Ramirez Rozzi b,c, Timothy G. Bromage d a Institute for Human
Journal of Human Evolution 51 (2006) 580e590 Variation in enamel development of South African fossil hominids Rodrigo S. Lacruz a, *, Fernando Ramirez Rozzi b,c, Timothy G. Bromage d a Institute for Human
Diversity through time...
 Diversity through time... Changes in dinosaur diversity by continent Count species? genera? families? through time 1) steady increase in diversity through time 2) Compare changes in diversity within each
Diversity through time... Changes in dinosaur diversity by continent Count species? genera? families? through time 1) steady increase in diversity through time 2) Compare changes in diversity within each
The assassination of JFK
 The assassination of JFK John Fitzgerald Kennedy, the 35th President of the United States, was assassinated on Friday, November 22, 1963, in Dealey Plaza, Dallas, Texas. Kennedy was fatally shot by a sniper
The assassination of JFK John Fitzgerald Kennedy, the 35th President of the United States, was assassinated on Friday, November 22, 1963, in Dealey Plaza, Dallas, Texas. Kennedy was fatally shot by a sniper
17.1. The Tree of Life CHAPTER 17. Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. Linnaean taxonomy. names.
 SECTION 17.1 THE LINNAEAN SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. VOCABULARY taxonomy taxon binomial nomenclature genus MAIN IDEA: Linnaeus
SECTION 17.1 THE LINNAEAN SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Organisms can be classified based on physical similarities. VOCABULARY taxonomy taxon binomial nomenclature genus MAIN IDEA: Linnaeus
