BONES AND JOINTS. Axial Skeleton
|
|
|
- Philomena Holmes
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BONES AND JOINTS The adult human skeleton usually consists of 206 bones which are connected by various joints. Muscles produce force which causes movement at these joints. These bones can be grouped in two divisions: Axial skeleton and Appendicular skeleton. The 80 bones of the Axial skeleton form the vertical axis of the body. They include the bones of the skull, vertebral column, ribs and breastbone or sternum. The Appendicular skeleton consists of 126 bones and includes the free appendages and their attachments to the axial skeleton. The free appendages are the upper and lower extremities, or limbs, and their attachments that are called girdles. Axial Skeleton Skull: The skull consists of facial bones and cranial bones (cranium). The cranium is important, enclosing and protecting the brain as well as providing a site for attachment of head and neck muscles. Vertebral column: The vertebral column (spine) serves as an axial support for the trunk, protects the spinal cord, and provides attachment points for the ribs. It consists of the sacrum, coccyx and 24 individual vertebrae. These are divided into three divisions, the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae. Cervical vertebrae: Consists of the seven vertebrae of the neck and represents as a concave (lordotic) curve. These vertebrae are numbered from the top down (superior to inferior) and are identified as C1 C7. Thoracic vertebrae: The thoracic vertebrae all articulate with the ribs. There are 12 thoracic vertebrae and are numbered T1 T12 starting where the cervical vertebrae left off. The thoracic vertebrae represents as a convex (kyphotic) curve in the middle of the back. Fit College Bones & Joints v1.1 Mar
2 Lumbar vertebrae: Also referred to as the small of the back, the lumbar vertebrae are the largest of the vertebrae in the human spine. They provide the bulk of the weight bearing function of the spine and as such account for the majority of back injuries and complaints. There are 5 lumbar vertebrae numbered L1 L5 starting where the thoracic vertebrae left off. Sacrum: Formed by 5 fused vertebrae, the sacrum articulates with L5 and with the pelvis to form the sacroiliac joints of the body. It provides support for the pelvic organs of the body. Coccyx (Tail bone): Is a small triangular shaped bone formed by 4 fused vertebrae and articulates with the sacrum. Other then providing a small amount of support for the pelvic organs, the coccyx has very little purpose. Ribs: There are 12 pairs of ribs which all articulate with the thoracic vertebrae. The first 7 ribs attach to the sternum and are referred to as true ribs. The remaining ribs are called false ribs because they either indirectly attach to the sternum or have no attachment at all. The ribs and sternum join to make up the bony thorax, which forms a protective cavity around the bodies vital organs and the thoracic cavity. Sternum: Also known as the breastbone, the sternum is the result of three bones fused together, the manubrium, the body and the xiphoid process. Manubrium: The superior portion of the sternum, the manubrium articulates with the clavicles and the first 2 ribs. Body: Forms the bulk of the sternum and articulates with the 2 nd to 7 th ribs. Xiphoid Process: Forms the inferior end of the sternum and serves as an attachment point for the muscles of the abdomen. Fit College Bones & Joints v1.1 Mar
3 Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular skeleton consists of the bones of the limbs and their girdles and provides us with our mobility. Upper Body Clavicle: The clavicles articulate with the sternum and the scapulae, acting as a brace, holding the scapulae and arms out laterally. Scapulae: These are triangular flat bones that lie on the border of posterior surface of the rib cage between ribs 2 and 7. It articulates with the clavicle at the acromioclavicular joint and the humerus at the glenohumeral joint. Humerus: A typical long bone, the humerus articulates with the scapulae of the shoulder, and the radius and ulna of the forearm. Radius: The radius is one of two bones in the forearm. It articulates with the humerus, ulna and carpals of the wrist. In the anatomical position, the radius is positioned laterally to the ulna. Ulna: Slightly longer than the radius, the ulna is responsible for forming the elbow joint with the humerus. Carpals: The carpals are 8 small bones that make up the wrist. They articulate with each other, the metacarpals and the radius. There are 5 bones that radiate from the wrist to form the palm of the hand. Phalanges: Fingers or digits Lower Body Pelvis: The pelvis attaches the lower limbs to the axial skeleton and is secured in place with some of the strongest ligaments in the body. The pelvis articulates with the femur and sacrum. Fit College Bones & Joints v1.1 Mar
4 Femur: The longest, strongest bone in the human body, the femur articulates with the tibia, fibula and patella to also form the knee. Patella: A triangular sesamoid bone enclosed in the quadriceps tendon that secures the anterior thigh muscles to the tibia. Tibia: The tibia receives the weight of the body through the femur, transferring it to the foot. It lies anterior and medial to the fibula and articulates with the patella, femur, fibula, and tarsals. Fibula: Posterior and lateral to the tibia, it articulates with the tibia and tarsals. Tarsals: There are seven tarsal bones that make up the posterior half of the foot. Metatarsals: These are the long bones of the foot. The heads of the metatarsals make up the "ball" of the foot. The 1 st metatarsal corresponds to the big toe. The 5 th metatarsal corresponds to the smallest toe. Phalanges: There are 14 small bones that make up the toes. There are 2 phalanges in each large toe and 3 in each smaller toe. Fit College Bones & Joints v1.1 Mar
5 Structure of a long bone The shaft of a long bone is called the diaphysis and is made of thick compact bone. The ends of a long bone are called the epiphysis. The exterior of the epiphysis is made of compact bone while the interior is comprised of spongy bone. Hyaline or articular cartilage covers the epiphysis. Bone remodeling Our bones are not dormant but are continually changing. Bones can become weaker or stronger. The adult skeleton maintains itself and replaces mineral reserves by remodeling. Remodeling - recycles and renews bone matrix and involves osteocytes, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts. Bone degenerates quickly and up to 1/3 of bone mass can be lost in a few weeks of inactivity. Alcohol consumption and smoking can result in a lower bone density. Menopause which causes a decline in a females estrogen levels affects bone strength. Low body fat levels can inhibit the absorption of some fat soluble vitamins which can also weaken bones. Bones require many nutrients to stay healthy. Some of these include calcium, magnesium, protein, copper, and vitamins A, C, D and K. Vitamin C is required for collagen synthesis, and stimulates osteoblast differentiation Vitamin A stimulates osteoblast activity Vitamins K and B 12 help synthesize bone proteins A dietary source of calcium and phosphate salts plus small amounts of magnesium, fluoride, iron, and manganese are also important for normal bone growth and maintenance Hormones also influence bone growth and health Calcitriolis made in kidneys & helps absorb calcium & phosphorus from digestive tract. Calcitrolsynthesis requires vitamin D 3 (cholecalciferol) Growth hormone &thyroxine stimulate bone growth Estrogens & androgens stimulate osteoblasts Calcitonin & parathyroid hormone regulate calcium & phosphate levels Bones become thinner and weaker with age Osteopenia begins between ages 30 and 40 Women lose 8% of bone mass per decade, men 3% The epiphyses, vertebrae, & jaws are most affected resulting in fragile limbs, reduction in height, & tooth loss Osteoporosis is the result of severe bone loss and affects normal function. This normally occurs over age 45, and occurs in 29% of women & 18% of men. Fit College Bones & Joints v1.1 Mar
6 Resistance training and weight bearing exercise helps increase bone density as heavily stressed bones become thicker and stronger and the Mineral recycling allows bones to adapt to stress. Joints The weakest parts of the skeleton, joints are the point at which two bone meet. The range of movement at the joint is reliant on the structure, surrounding ligaments, tendons and muscles. As a result, joints enable movement whilst providing support against external forces (i.e. gravity) Joint types Joints can be classified according to the degree and type of movement: Fibrous (or Immovable) Joints These joints are firmly held together by a thin layer of strong connective tissue. There is no movement between the bones such as the sutures of the skull. Cartilaginous Joints: Cartilaginous joints are joints where the articular surfaces of the bones forming the joints are attached to each other by means of white fibrocartilaginous discs and ligaments. They allow only a limited degree of movement. Examples are the cartilaginous joints between the vertebrae. Synovial joints: Synovial joints make up the majority joints within the body. The articulating bones are separated by a fluid filled joint cavity. This allows synovial joints to be freely moveable. Source: Dorland's Medical Dictionary for Health Consumers Fit College Bones & Joints v1.1 Mar
7 Various kinds of joints: Fibrous: A,syndesmosis (tibiofibular); B, suture (skull). Cartilaginous: C,symphysis (vertebral bodies); D,synchondrosis (first rib and sternum). Synovial: E,condyloid (wrist); F, gliding (radioulnar); G, hinge or ginglymus (elbow); H, ball and socket (hip); I, saddle (carpometacarpal of thumb); J, pivot (atlantoaxial). Five classes of tissue make up synovial joints: Bone Cartilage Synovium Synovial fluid Tensile tissues: ligament and tendon, attached at entheses Bone The bone adjacent to a joint consists of an open spongy framework of calcified collagen in a tough outer shell. Immediately beneath articular cartilage there is a more or less continuous subchondral bony plate but this is often extremely thin. The bone can withstand thrust forces as long as it is covered in cartilage, which distributes load evenly. Without cartilage, the spongy bone collapses easily. Bone is a live tissue constantly remodelling in response to stresses. Articular Cartilage Hyaline cartilage Hyaline cartilage is the skeletal growth tissue. In many, but not all, joints a thin layer remains as the bearing surface in the adult. Hylaine cartilage is avascular. It contains type II collagen and giant molecular complexes of a proteoglycan called aggrecan. Load bearing normally occurs over small areas, varying with joint position. Cartilage does not normally wear despite decades of use, but will do if its composition or joint mechanics are abnormal. It can regenerate, and will do so at the margins of damaged joints as part of the osteochondral swellings known as osteophytes, but load bearing areas will rarely rethicken once damaged, so the tissue is unable to restore its normal shape after injury. Fibrocartilage Fibrocartilage occurs as intervertebral disc, and as discs, menisci or ring pads in many peripheral joints. It lacks the combination of collagen II and aggrecan seen in hyaline cartilage and blends in with fibrous synovial tissue. It will regenerate to fill a space e.g. in the case of repairing cartilage defects of the knee; it has lower mechanical properties compared to hialine. Fit College Bones & Joints v1.1 Mar
8 Synovium (articular capsule) Synovium is the name given to the soft tissue lining the cavities of joints, tendon sheaths and bursae. It is like other connective tissue packing, being a mixture of fatty, areolar and fibrous tissue. The surface of synovium is permeable to water, small molecules and proteins, but not to hyaluronan, which is the molecule that makes synovial fluid viscous. This allows synovium to trap synovial fluid within the cavity. Beneath the surface cell layer is a net of small blood vessels, important in the development of synovial inflammation. Joint, tendon sheath and bursalsynovium all have the same structure. Synovial Fluid Normal synovial fluid is clear, colourless and noticeably thick and stringy, like eggwhite. Hence the name syn-ovium ( with egg ). Its viscous and elastic properties are due to hyaluronan, a long chain glycosaminoglycan carbohydrate with a molecular mass of about 1 million. Synovial fluid is effectively a liquid connective tissue. Because there are no fibrous components to it, the water and the hyaluronan ground substance move around together within the synovial space, whereas in other tissues water moves and the ground substance stays put. Water diffuses in and out of the synovial cavity more easily than hyaluronan. The amount of water in a joint depends on passive equilibration of plasma with vascular and lymphatic compartments, as for all connective tissue fluid. It goes up and down with exercise and rest. Water can enter the joint rapidly during inflammation but once mixed with hyaluronan cannot leave so rapidly unless the joint ruptures. If joints are stretched suddenly, even the fluid does not fill all the space and the lining may jump into the vacuum formed, which is how people "click" their finger joints. Tendon sheaths and bursae: The synovial lining in these structures is similar to that within joints, with a slippery nonadherent surface allowing movement between planes of tissue. Synovial tendon sheaths line tendons only where they pass through narrow passages or retinacula, as in the palm, at the wrist and around the ankle. Elsewhere the tendon lies in a bed of loose fibrous tissue. Bursae occur at sites of shearing in subcutaneous tissue or between deeper tissues such as muscle groups and fascia. Many bursae develop during growth but new or adventitious bursae can occur at sites of occupational friction. Ligaments and tendons Ligaments hold bones together. They are variably elastic. Tendons transmit muscle power to bones and are inelastic (except in kangaroo legs). Joint "capsules" are composed of a basket work of independently moving ligaments and tendons associated with sheets of fascia. Some joints, such as the sacroiliac, are largely surrounded by ligament, others, such as the shoulder, with its rotator cuff, are surrounded by tendon. Tendons may also pass through joint cavities, e.g. long head of biceps. Fit College Bones & Joints v1.1 Mar
Chapter 11. What are the functions of the skeletal system? More detail on bone
 Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Skeletal System Chapter 11 11.1 Overview of the skeletal system What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. Supports the body 2. Protects the soft body parts 3. Produces blood cells 4. Stores minerals
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton is the body s bony framework which consists of 206 bones. The bones are made up of water(45%), calcium and phosphorous(35%) and other organic materials(20%). The calcium
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone
8/25/2014 JOINTS. The Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS The Skeletal System Made up of the numerous bones of the human body Gives support and framework to the body Protects vital organs Manufactures blood cells Storage of calcium
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
UNIT - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 18 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement is an important feature of living organism. Both the microbes and macrobes show wide range of movements. The movements results in change
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM Degrees of freedom Functional potential of the
9/3/2013 JOINTS. Joints. Axial Skeleton STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION:
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: JOINTS Joints A connection between 2 or more bones A pivot point for bony motion The features of the joint help determine The ROM freedom Functional potential of the joint Axial
Divisions of the Skeletal System
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
OpenStax-CNX module: m46344 1 Divisions of the Skeletal System OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this
SKELETON AND JOINTS G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Unit 1. Factors Affecting Participation and Performance. G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:.
 G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
G.C.S.E. PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 Factors Affecting Participation and Performance SKELETON AND JOINTS Name: G.C.S.E. P.E. Teacher:. By the end of this booklet you should be able to: Understand what the
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS. The Bones & Joints
 THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
THE SKELETAL & ARTICULAR SYSTEMS The Bones & Joints CLOSE YOUR POWERPOINT HANDOUTS!! Think-Pair-Share: Why do we need bones? Try to think of 3 reasons. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Is made up of numerous bones
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function
 7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
7. Skeletal System: Bone Structure and Function For the next two chapters (7 and 9) we will study the skeletal system. Although the major feature of this system is the bones, the skeletal system also consists
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
THE SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
 i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
i A Wealth of Information. A World of Ideas. Instructor s Guide The Human Body: How It Works Introduction This program is part of the nine-part series The Human Body: How It Works. The series uses physiologic
Skeletal system. 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
NURS1004 Week 6 Part I Prepared by Didy Button Skeletal system An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues 6-1
CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. 4. Name the three types of fibrous joints and give an example of each.
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. 2. Distinguish between the functional and structural classification of joints, and relate the terms that are essentially synonymous. 3. Compare and contrast
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body. 2. Supports soft tissue. 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments,
Classification of bones Any bone may be classified into one of the following groups:
 Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Skeletal system This system is made up of hard tissues like bone and cartilages. This system gives form and shape to animal body The skeleton of a living animal is made up living structures of bones. The
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
10/12/2011. Classification of Bones Every adult skeleton contains 206 bones which can be arranged into six broad categories according to shape
 Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
Primary Functions of Skeletal System 1. support 2. storage of minerals & lipids -calcium salts provide vital minerals -lipids are in stored yellow marrow 3. blood cell production -RBC s, WBC s, and other
Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN ACTIVITY ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES. Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21
 activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
activity 21 Human Bones BROWARD COUNTY ELEMENTARY SCIENCE BENCHMARK PLAN Grade 4 Quarter 3 Activity 21 SC.F.1.2.1 The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structures and functions
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam #2
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam #2 For questions 1 through 3, select your answers from the following responses: a. stratified squamous epithelium b. reticular connective tissue
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10
 Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Lab 5 Overview of the Skeleton: Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages Exercise 9 The Axial Skeleton Exercise 10 Overview of the Skeleton Locate the important cartilages in the human skeleton
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
Chapter 6: The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Chapter Objectives FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. Discuss the functions of support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, blood cell
Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3)
 Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3) Anatomy: The structure and organization of the body and its organs. From Greek Origin: Anatome dissection Physiology: The function of the body
Anatomical Terminology: Planes Axes Direction (Text Pg 2 3) Anatomy: The structure and organization of the body and its organs. From Greek Origin: Anatome dissection Physiology: The function of the body
Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
Chapter 9 1 JOINTS Chapter 9 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 9 2 JOINTS (Bones are too rigid to bend without causing damage.) (Bones are held together at joints by flexible connective tissue.) (Imagine
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES. for Massage Therapists. Online!
 CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES for Massage Therapists Online! ccmh Halifax Canadian College of Massage & Hydrotherapy Online Continuing Education Program CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education
Brunswick School Department: Grades 11-12. Essential Understandings
 Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Bones provide invaluable structure and support for the body. There are a variety of bone shapes. Joints connect bones. The skeletal system is divided
Understandings Questions Knowledge Vocabulary Skills Bones provide invaluable structure and support for the body. There are a variety of bone shapes. Joints connect bones. The skeletal system is divided
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES
 CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
CHS 06-07 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES This chapter provides a review of bone and skeletal tissue. The human skeleton is composed primarily of two connective tissues: (1) cartilage and (2) bone. CHARACTERISTICS
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System
 Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
Animal Systems: The Musculoskeletal System Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Cells, Cell Division, and Animal Systems and Plant Systems Cell Specialization Human Systems The Digestive The Circulatory
The skeletal and muscular systems
 anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
anatomy and physiology The skeletal and muscular systems CHAPTER 1: Anatomy and physiology LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe an overview of the skeletal system
Lumbar Spine Anatomy. eorthopod.com 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 info@eorthopod.
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spine Anatomy 228 West Main St., Suite D Missoula, MT 59802-4345 Phone: 406-721-3072 Fax: 406-721-2619 [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Anatomy of Skeletal System
 Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
Anatomy of Skeletal System two main subdivisions of skeletal system: axial : skull, vertebral column, rib cage appendicular: arms and legs and girdles Bone Markings: Foramen: opening in bone passageway
BONE BINGO. Blood Production Red and white blood cells are produced in the bone marrow, a substance found inside the larger bones of the body.
 BONE BINGO Background: The human skeleton is a framework of bones that is held together by ligaments and joints. Our skeleton has four major functions: Support The main job of the skeleton is to provide
BONE BINGO Background: The human skeleton is a framework of bones that is held together by ligaments and joints. Our skeleton has four major functions: Support The main job of the skeleton is to provide
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION
 LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
LABORATORY EXERCISE 12 BONE STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION FIG. 12.1 1. Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) 6. Periosteum 2. Spongy bone (red marrow) 7. Proximal epiphysis 3. Medullary cavity 8. Diaphysis
E. Blood cells production. Blood cells are produced within the cavities of bones.
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. The skeletal system consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments (attach bone to another bone), and tendons (attach muscle to bone). 2. Functions. A. Support. Bone helps to
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. The skeletal system consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments (attach bone to another bone), and tendons (attach muscle to bone). 2. Functions. A. Support. Bone helps to
Skeletal System. Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs
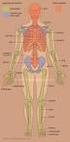 Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
Skeletal System Axial Skeleton: Vertebral Column and Ribs Functions Regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Primary & secondary curvatures There are three major functions of the vertebral column. First,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 The Human Skeletal System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton. 4-2. Name
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 The Human Skeletal System. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Define skeleton. 4-2. Name
SKELETAL SYSTEM GRADE 3-6 BACKGROUND
 SKELETAL SYSTEM GRADE 3-6 BACKGROUND The Skeletal System is made up of the bones of the body and the joints between the bones, as well as certain connective tissue (cartilage and ligaments.) This lesson
SKELETAL SYSTEM GRADE 3-6 BACKGROUND The Skeletal System is made up of the bones of the body and the joints between the bones, as well as certain connective tissue (cartilage and ligaments.) This lesson
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Lectures of Human Anatomy Vertebral Column-I By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D. "Anatomy and Embryology"
Osseous Tissue & Structure. The skeletal system includes: Storage of minerals: calcium salts
 Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
Chapter 15 Lecture The Skeletal System: Osseous Tissue & Skeletal Structure The Skeletal System The skeletal system includes: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Bone tissue = osseous tissue Includes living cells
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 1 Body systems and the effects of physical activity K/507/4452 Guided learning hours: 90 Version 2 - Revised content - March 2016
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Thoracic Spine Anatomy 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: [email protected] DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy Lecture 2: Fossil Record Segmentation Cyclic genescreate segme ntation clock for somite production Final #s 4 occipital 8
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 5: Bone Development & Trunk Anatomy Lecture 2: Fossil Record Segmentation Cyclic genescreate segme ntation clock for somite production Final #s 4 occipital 8
Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education. Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh
 Tendons - connect Muscle to Bone Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh Tendons are fibrous cords of
Tendons - connect Muscle to Bone Middle California Region USPC Upper Level Horse Management Education Tendons, Ligaments, Joints & the Skeletal System By Claudia Deffenbaugh Tendons are fibrous cords of
o Understand the anatomy of the covered areas. This includes bony, muscular and ligamentous anatomy.
 COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller [email protected] Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
COURSE TITLE Kin 505 Activities, Injuries Disease in the Larger Society On-Line offering Instructor Dr. John Miller [email protected] Course Description. Sports and exercise are a part of American society
ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions *
 ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions * Finding the ICD-10 equivalent for an ICD-9 code can be a challenge. This resource of frequently used codes can help when
ICD-10 Cheat Sheet Frequently Used ICD-10 Codes for Musculoskeletal Conditions * Finding the ICD-10 equivalent for an ICD-9 code can be a challenge. This resource of frequently used codes can help when
BONES AND BONE TISSUE
 BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
BIO 2401 BONES & BONE TISSUE page 1 BONES AND BONE TISSUE Organization of the Skeletal System components: 1) bone 2) skeletal cartilage: surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue which acts to girdle
Observing Vertebrate Skeletons
 Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
Name Class Date Chapter 33 Comparing Chordates Observing Vertebrate Skeletons Introduction One characteristic common to all vertebrates is the presence of a skeleton. The endoskeleton provides support,
Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510
 Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510 Functions of the Musculoskeletal System Support and protect the body and its organs. Provide motion. Musculoskeletal
Structure and Function of the Musculoskeletal System Professor Alan Hedge DEA 3250/6510 Functions of the Musculoskeletal System Support and protect the body and its organs. Provide motion. Musculoskeletal
OBJECTIVE: List and describe the functions of the skeletal system. D. Storage depot for minerals and homeostasis
 Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
Text Reference: Chapters 6 and 7 Pages 1-6 are mostly a review from lab Know this material before you come to lecture. Lecture will begin on page 7 Read text and complete packet before lecture. I. Introduction
Function of Bones. Bone Tissue and Bones BONE CLASSIFICATION. Long Bones Gross Anatomy. Lab Activity 1 - Gross Anatomy of a Long Bone
 Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
Function of Bones Bone Tissue and Bones Bones form the framework of the skeleton. Anatomy and Physiology Text and Laboratory Workbook, Stephen G. Davenport, Copyright 2006, All Rights Reserved, no part
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) Introduction Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) is a phenomenon that more commonly affects older males. It is associated
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
The Search for the Missing Bones
 The Magic School Bus A Science Chapter Book #2 The Search for the Missing Bones Lapbook by Amy Yee. Yee Shall Know http:///www.yeeshallknow.com Lapbook Basics Follow the instructions in the following page(s)
The Magic School Bus A Science Chapter Book #2 The Search for the Missing Bones Lapbook by Amy Yee. Yee Shall Know http:///www.yeeshallknow.com Lapbook Basics Follow the instructions in the following page(s)
1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen
 I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
I. cartilage A. perichondrium 1. outer fibrous layer contains fibroblasts that secrete collagen 2. inner chondrogenic layer contains cells that can proliferate and turn into chondroblasts B. cartilage
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins
 Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
Skeletal Development Multiple Cellular Origins 1 - Paraxial Mesoderm Somite, Sclerotome Axial Skeleton (e.g. vertebra) 2 - Lateral Plate Mesoderm Appendicular Skeleton (e.g. limb) 3 - Neural Crest Head
The Pilates Studio of Los Angeles / PilatesCertificationOnline.com
 Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
Anatomy Review Part I Anatomical Terminology and Review Questions (through pg. 80) Define the following: 1. Sagittal Plane 2. Frontal or Coronal Plane 3. Horizontal Plane 4. Superior 5. Inferior 6. Anterior
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE. Chapter 6. Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 Chapter 6 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 6 2 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Bone (Osseous) Tissue forms most of the skeleton: Skeletal System - the
Chapter 6 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 6 2 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: BONE TISSUE Bone (Osseous) Tissue forms most of the skeleton: Skeletal System - the
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine. Bones of the Spine (Vertebrae)
 Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List
 Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of common ICD-10 codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
Chiropractic ICD-10 Common Codes List This is a preliminary list of common ICD-10 codes for chiropractic diagnoses. This is a common code list to be used as a guide for coding and is not intended to represent
Appendix A Partial Pick List of Injury and Sequelae Codes (ICD-10-CA)
 What are ICD-10 and ICD-10-CA? The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is an international standard for reporting diseases, injuries,
What are ICD-10 and ICD-10-CA? The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems - Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is an international standard for reporting diseases, injuries,
Clients w/ Orthopedic, Injury and Rehabilitation Concerns. Chapter 21
 Clients w/ Orthopedic, Injury and Rehabilitation Concerns Chapter 21 Terminology Macrotrauma A specific, sudden episode of overload injury to a given tissue, resulting in disrupted tissue integrity (Acute)
Clients w/ Orthopedic, Injury and Rehabilitation Concerns Chapter 21 Terminology Macrotrauma A specific, sudden episode of overload injury to a given tissue, resulting in disrupted tissue integrity (Acute)
its lifetime. The skeletal system is divided into: 1. Axial Division: bones of the body s axis (skulll, ribs, vertebrae)
 The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
Chiropractic ICD 9 Code List
 Use of valid ICD 9 codes, billed with appropriate and corresponding CPT codes, benefits providers by facilitating treatment authorization and claims payment. The use of valid and appropriate codes also
Use of valid ICD 9 codes, billed with appropriate and corresponding CPT codes, benefits providers by facilitating treatment authorization and claims payment. The use of valid and appropriate codes also
www.roylco.com EDUCATION SUPPLY ACTIVITY No. 60558 Newspaper Skeleton
 EDUCATION SUPPLY ACTIVITY www.roylco.com Canada: 30 Northland Road, Waterloo, Ontario, N2V 1Y1 USA: PO Box 13409 Anderson, SC 29624 No. 60558 Newspaper Skeleton Teach students about human bone structure
EDUCATION SUPPLY ACTIVITY www.roylco.com Canada: 30 Northland Road, Waterloo, Ontario, N2V 1Y1 USA: PO Box 13409 Anderson, SC 29624 No. 60558 Newspaper Skeleton Teach students about human bone structure
Spinal Anatomy. * MedX research contends that the lumbar region really starts at T-11, based upon the attributes of the vertebra.
 Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Spinal Anatomy Overview Neck and back pain, especially pain in the lower back, is one of the most common health problems in adults. Fortunately, most back and neck pain is temporary, resulting from short-term
Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I
 Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Fall 2016 Biology 141 Anatomy and Physiology I COURSE OUTLINE Faculty Name: Enter Faculty Name Here Program Head: Enter Program Head Here Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Fall
Online! CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES
 Online! CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES CCMH Halifax CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education Courses ONLINE* allowing therapists across the country to avoid the cost of travel and accommodation,
Online! CONTINUING EDUCATION COURSES CCMH Halifax CCMH Halifax offers a variety of Continuing Education Courses ONLINE* allowing therapists across the country to avoid the cost of travel and accommodation,
The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle
 The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle The shoulder complex 4 articulations involving The sternum The clavicle The ribs The scapula and The humerus Bony Landmarks provide attachment points for muscles
The Shoulder Complex & Shoulder Girdle The shoulder complex 4 articulations involving The sternum The clavicle The ribs The scapula and The humerus Bony Landmarks provide attachment points for muscles
Surgical Art. Formulaic Drawing Method. DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes
 DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
DRAWING WORKSHOP Learning to sketch for patient notes Surgical Art Formulaic Drawing Method Formulaic figure drawing systems involve using abstract rhythms and interlocking shapes to construct the human
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013
 Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Locating Common Bones*
 4H1656 4ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ACTIVITY Locating Common Bones* Skill Level: 4Beginner to advanced Life Skills: 4Communication, critical thinking, decision-making and teamwork Setting: 4Room with chairs arranged
4H1656 4ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ACTIVITY Locating Common Bones* Skill Level: 4Beginner to advanced Life Skills: 4Communication, critical thinking, decision-making and teamwork Setting: 4Room with chairs arranged
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 36 1 The Skeletal System (pages 921 925) This section describes the skeletal system and its functions. Introduction (page 921) 1. What forms
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions
 Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Laboratory 1 Anatomical Planes and Regions Goals: Define the anatomical position, including the application of the terms right and left. List and correctly use the major directional terms used in anatomy.
Biomechanics of Joints, Ligaments and Tendons.
 Hippocrates (460-377 B.C.) Biomechanics of Joints, s and Tendons. Course Text: Hamill & Knutzen (some in chapter 2 and 3, but ligament and tendon mechanics is not well covered in the text) Nordin & Frankel
Hippocrates (460-377 B.C.) Biomechanics of Joints, s and Tendons. Course Text: Hamill & Knutzen (some in chapter 2 and 3, but ligament and tendon mechanics is not well covered in the text) Nordin & Frankel
www.ghadialisurgery.com
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE
 UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
UNIT 5: FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE TOPIC 1: TOPIC 2: BASIC ANATOMY MAJOR MUSCLE GROUPS & BONES PROPER STRETCHING TECHNIQUE GRADES 6-7 UNIT 5 FITNESS BASIC ANATOMY & GRADES PROPER
S.M.A.R.T.box. Skeletal System The Infrastructure Teacher s Guide CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP. Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers
 CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM Skeletal System The Infrastructure Teacher s Guide 33118 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher s
CURRICULUM MEDIA GROUP S.M.A.R.T.box Standards-based MediA Resource for Teachers TM Skeletal System The Infrastructure Teacher s Guide 33118 A DIVISION OF FILMS MEDIA GROUP INTRODUCTION This Teacher s
Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques
 Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques If you ve ever strained your back while lifting something, you ll know the importance of lifting safely. Agenda Introduction About the Back The
Avoid The Dreaded Back Injury by Proper Lifting Techniques If you ve ever strained your back while lifting something, you ll know the importance of lifting safely. Agenda Introduction About the Back The
RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES
 RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE. 1. Without the aid of references, given a casualty and standard combat lifesaver medical equipment set, perform splinting techniques,
RP0807 - PERFORM SPLINTING TECHNIQUES TERMINAL LEARNING OBJECTIVE. 1. Without the aid of references, given a casualty and standard combat lifesaver medical equipment set, perform splinting techniques,
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES. Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132
 SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
SPINE ANATOMY AND PROCEDURES Tulsa Spine & Specialty Hospital 6901 S. Olympia Avenue Tulsa, Oklahoma 74132 SPINE ANATOMY The spine consists of 33 bones called vertebrae. The top 7 are cervical, or neck
The Many Causes of Joint Pain
 I n t r o d u c t i o n The Many Causes of Joint Pain there are about a hundred different forms of arthritis, an umbrella term for diseases with symptoms that include joint and musculoskeletal pain. And
I n t r o d u c t i o n The Many Causes of Joint Pain there are about a hundred different forms of arthritis, an umbrella term for diseases with symptoms that include joint and musculoskeletal pain. And
Skeletal System -Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science
 Skeletal System -Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science INTERACTION OF SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS: Skeletal and Muscular systems works together to allow movement
Skeletal System -Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science INTERACTION OF SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS: Skeletal and Muscular systems works together to allow movement
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS
 Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
Module F SKELETAL SYSTEM & ARTICULATIONS Topic from General functions of bone & the skeletal system Structural components microscopic anatomy Structural components gross anatomy Physiology of embryonic
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Objectives Identify the meaning of 10 or more terms relating to the organization of the body Describe the properties of life Describe the function for the structures of the
67 The Human Skeleton
 67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
67 The Human Skeleton Skull SCIENCE EXPLORER Focus on Life Science Prentice-Hall, Inc. Clavicle (collarbone) Scapula (shoulder blade) Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Femur Tibia Humerus Ulna Sternum (breastbone)
