Implementing Stereoscopic 3D in Your Applications
|
|
|
- Peter Robertson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Implementing Stereoscopic 3D in Your Applications Room C 09/20/ :00 17:20 Samuel Gateau, NVIDIA, Steve Nash, NVIDIA
2 Agenda How It Works NVIDIA 3D Vision Implementation Example Stereoscopic Basics Depth Perception Parallax Budget Rendering in Stereo What s Next?
3 3D vs Stereo In 3D is the new Stereo They are used interchangeably, stereoscopic rendering is the technical means to make an image In 3D Each eye gets its own view rendered with a slightly different camera location: usually about as far apart as your eyes Stereo displays and APIs are used to manage these two views Stereo Stereo Not Stereo
4 Stereoscopic Basics How It Works Applications render a Left Eye view and Right Eye view with slight offset between Left Eye view Right Eye view A Stereoscopic display then shows the left eye view for even frames (0, 2, 4, etc) and the right eye view for odd frames (1, 3, 5, etc).
5 Stereoscopic Basics How It Works In this example active shutter glasses black-out the right lens when the left eye view is shown on the display and black-out the left lens when the right eye view is shown on the display. Left eye view on, right lens blocked Right eye view on, left lens blocked This means that the refresh rate of the display is effectively cut in half for each eye. (e.g. a display running at 120 Hz is 60 Hz per eye) on off off on Left lens Right lens Left lens Right lens The resulting image for the end user is a combined image that appears to have depth in front of and behind the stereoscopic 3D Display.
6 NVIDIA 3D Vision Software 3D Vision SW automatically converts mono games to Stereo Direct X only Hardware IR communication 3D Vision certified displays Support for single screen or 1x3 configurations
7 NVIDIA 3D Vision Pro Software Supports Consumer 3D Vision SW or Quad Buffered Stereo QBS: OpenGL or DirectX For DX QBS, for help Hardware RF communication 3D Vision certified displays, Passive Displays, CRTs and projectors Up to 8 displays Mix Stereo and Regular Displays G-Sync support for multiple displays and systems Direct connection to GPU mini-din
8 NVIDIA 3D Vision Pro Hardware cont d Designed for multi-user professional installations No line of sight requirement, no dead spots, no cross talk RF bi-directional communication with UI 50m range Easily deploy in office no matter what the floor plan
9 Implementation Example
10 Implementation Example: OpenGL Step 1: Configure for Stereo
11 Implementation Example: OpenGL Step 2: Query and request PFD_STEREO ipixelformat = DescribePixelFormat(hdc, 1, sizeof(pixelformatdescriptor), &pfd); while (ipixelformat) { DescribePixelFormat(hdc, ipixelformat, sizeof(pixelformatdescriptor), &pfd); if (pfd.dwflags & PFD_STEREO){ istereopixelformats++; } ipixelformat--; } if (istereopixelformats== 0) // no stereo pixel formats available StereoIsAvailable = FALSE; else StereoIsAvailable = TRUE;
12 Implementation Example: OpenGL Step 2 cont d if (StereoIsAvailable){ ZeroMemory(&pfd, sizeof(pixelformatdescriptor)); pfd.nsize = sizeof(pixelformatdescriptor); pfd.nversion = 1; pfd.dwflags = PFD_DRAW_TO_WINDOW PFD_SUPPORT_OPENGL PFD_DOUBLEBUFFER PFD_STEREO; pfd.ipixeltype = PFD_TYPE_RGBA; pfd.ccolorbits = 24; ipixelformat = ChoosePixelFormat(hdc, &pfd); if (ipixelformat!= 0){ if (SetPixelFormat(hdc, ipixelformat, &pfd)){ hglrc = wglcreatecontext(hdc); if (hglrc!= NULL){ if (wglmakecurrent(hdc, hglrc)){
13 Implementation Example: OpenGL Step 3: Render to Left/Right buffer with offset between // Select back left buffer gldrawbuffer(gl_back_left); glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Setup the frustum for the left eye glmatrixmode(gl_projection); glloadidentity(); glfrustum(xmin - FrustumAssymmetry, Xmax FrustumAssymmetry, -0.75, 0.75, 0.65, 4.0); gltranslatef(eyeoffset, 0.0f, 0.0f); glmatrixmode(gl_modelview); glloadidentity(); <Rendering calls>
14 Implementation Example: OpenGL Step 3 cont d // Select back right buffer gldrawbuffer(gl_back_right); glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // Setup the frustum for the right eye. glmatrixmode(gl_projection); glloadidentity(); glfrustum(xmin + FrustumAssymmetry, Xmax + FrustumAssymmetry, -0.75, 0.75, 0.65, 4.0); gltranslatef(-eyeoffset, 0.0f, 0.0f); gltranslatef(0.0f, 0.0f, -PULL_BACK); glmatrixmode(gl_modelview); glloadidentity(); <Rendering calls> // Swaps both left and right buffers SwapBuffers(hdc);
15 Changes to the rendering pipe FROM MONO TO STEREO
16 In Mono Scene Scene is viewed from one eye and projected with a perspective projection along eye direction on Near plane in Viewport Mono Frustum Near plane Viewport Y Z X Eye space
17 In Stereo Scene Near plane Y Z X Eye space
18 In Stereo: Two eyes Scene Left and Right eyes Shifting the mono eye along the X axis Near plane Y Z X Eye space
19 In Stereo: Two eyes Scene Left and Right eyes Shifting the mono eye along the X axis Eye directions are parallels Near plane Y Z X Eye space
20 In Stereo: Two Eyes, One Screen Left and Right eyes Shifting the mono eye along the X axis Eye directions are parallels One virtual screen Virtual Screen Scene Near plane Y Z X Eye space
21 In Stereo: Two Eyes, One Screen Left and Right eyes Shifting the mono eye along the X axis Eye directions are parallels One virtual screen Where the left and right frustums converge Left Frustum Virtual Screen Scene Right Frustum Near plane Y Z X Eye space
22 In Stereo: Two Eyes, One Screen, Two Images Left and Right eyes Shifting the mono eye along the X axis Eye directions are parallels One virtual screen Where the left and right frustums converge Virtual Screen Scene Two images 2 images are generated at the near plane in each views Near plane Left Image Right Image Y Z X Eye space
23 In Stereo: Two Eyes, One Screen, Two Images Scene Left Image Right Image Real Screen Virtual Screen Two images 2 images are generated at the near plane in each views Near plane Left Image Right Image Presented independently to each eyes of the user on the real screen Y Z X Eye space
24 Stereoscopic Rendering Render geometry twice From left and right eyes Into left and right images
25 Basic definitions so we all speak English DEFINING STEREO PROJECTION
26 Stereo Projection Stereo projection matrix is a horizontally offset version of regular mono projection matrix Offset Left / Right eyes along X axis Screen Eye space Y Z X Left Eye Mono Eye Right Eye Mono Frustum
27 Stereo Projection Projection Direction is parallel to mono direction (NOT toed in) Left and Right frustums converge at virtual screen Virtual Screen Left Frustum Eye space Y Z X Left Eye Mono Eye Right Eye Right Frustum
28 Interaxial Distance between the 2 virtual eyes in eye space The mono, left & right eyes directions are all parallels Eye space Y Z X Left Eye Mono Eye Right Eye Interaxial
29 Separation The normalized version of interaxial by the virtual screen width More details in a few slides. Virtual Screen Eye space Left Eye Y Z Mono Eye Interaxial Screen width X Right Eye Separation = Interaxial / Screen Width
30 Convergence Virtual Screen s depth in eye space ( Screen Depth ) Plane where Left and Right Frustums intersect Virtual Screen Left Frustum Eye space Y Z X Left Eye Mono Eye Right Eye Right Frustum Convergence
31 Interaxial Parallax Signed Distance on the virtual screen between the projected positions of one vertex in left and right image Parallax is function of the depth of the vertex Virtual Screen Parallax Eye space Y Z X Left Eye Mono Eye Right Eye Convergence Vertex depth
32 Where the magic happens and more equations DEPTH PERCEPTION
33 Virtual vs. Real Screen Scene Left Image Real Screen Right Image The virtual screen is perceived AS the real screen Virtual Screen Parallax creates the depth perception for the user looking at the real screen presenting left and right images Y Z X Virtual Space
34 In / Out of the Screen Vertex Depth Parallax Vertex Appears Further than Convergence Positive In the Screen Equal Convergence Zero At the Screen Closer than Convergence Negative Out of the Screen Out of the Screen Screen In the Screen Left Eye Mono Eye Right Eye Eye space Y X Z Convergence
35 Parallax in normalized image space Convergence Parallax in normalized image space Parallax = Separation * ( 1 Convergence / W ) Separation Maximum Parallax at infinity is separation distance between the eyes Vertex Depth (W) Parallax is 0 at screen depth Parallax diverges quickly to negative infinity for object closer to the eye
36 Eye Separation Real Screen Interocular (distance between the eyes) is on average cm Equivalent to the visible parallax on screen for objects at infinity Depending on the screen width, we define a normalized Eye Separation Eye Separation = Interocular / Real Screen Width Different for each screen model A reference maximum value for the Separation used in the stereo projection for a comfortable experience Interocular Parallax at infinity Screen Width
37 Separation should be Comfortable The maximum parallax at infinity is Separation Eye Separation is an average, should be used as the very maximum Separation value Never make the viewer look diverge People don t have the same eyes For Interactive application, let the user adjust Separation When the screen is close to the user (PC scenario) most of the users cannot handle more than 50% of the Eye Separation Real Screen
38 Eye Separation is the Maximum Comfort Separation Real Screen Real Screen
39 Convergence Parallax Safe Parallax Range Eye Separation Separation 1 Separation 2 Depth -Eye Separation
40 PARALLAX BUDGET
41 Parallax Convergence Parallax Budget How much parallax variation is used in the frame Nearest pixel Farthest pixel Separation Parallax budget Depth
42 Parallax Convergence In Screen : Farthest Pixel At 100 * Convergence, Parallax is 99% of the Separation For pixels further than 100 * Convergence, Elements looks flat on the far distance with no depth differentiation Between 10 to 100 * Convergence, Parallax vary of only 9% Objects in that range have a subtle depth differentiation Separation Depth
43 Convergence Parallax Out of the Screen : Nearest pixel At Convergence / 2, Parallax is equal to -Separation, out of the screen Parallax is very large (> Separation) and can cause eye strains Separation Depth
44 Convergence 1 Convergence 2 Parallax Convergence sets the scene in the screen Defines the window into the virtual space Defines the style of stereo effect achieved (in / out of the screen) Near pixel Parallax budget 1 Far pixel Separation Depth Parallax budget 2
45 Convergence Parallax Separation scales the parallax budget Scales the depth perception of the frame Near pixel Far pixel Separation 1 Separation 2 Depth Parallax budget 21
46 Adjust Convergence Convergence must be controlled by the application Camera parameter driven by the look of the frame Artistic / Gameplay decision Should adjust for each camera shot / mode Make sure the scene elements are in the range [ Convergence / 2, 100 * Convergence ] Adjust it to use the Parallax Budget properly Cf Bob Whitehill Talk (Pixar Stereographer) at Siggraph 2010 Dynamic Convergence is a bad idea Except for specific transition cases Analyze frame depth through an Histogram and focus points? Ongoing projects at NV
47 Let s do it RENDERING IN STEREO
48 Stereoscopic Rendering Render geometry twice Do stereo drawcalls Duplicate drawcalls From left and right eyes Apply stereo projection Modify projection matrix Into left and right images Use stereo surfaces Duplicate render surfaces
49 How to implement stereo projection? Fully defined by mono projection and Separation & Convergence Replace the perspective projection matrix by an offset perspective projection horizontal offset of Interaxial Negative for Right eye Positive for Left eye Or just before rasterization in the vertex shader, offset the clip position by the parallax amount (Nvidia 3D vision driver solution) clippos.x += EyeSign * Separation * ( clippos.w Convergence ) EyeSign = +1 for right, -1 for left
50 Stereo Transformation Pipeline Standard Mono World space View Transform Vertex Shader Eye space Projection Transform Clip space Perspective Divide Rasterization Normalized space Viewport Transform Image space Pixel Shader Stereo Projection Matrix Eye Space Vertex Shader Stereo Projection Transform Stereo Clip space Perspective Divide Rasterization Stereo Normalized space Viewport Transform Stereo Image space Pixel Shader Stereo Separation on clip position Eye space Projection Transform Vertex Shader Clip space Stereo Separation Stereo Clip space Perspective Divide Rasterization Stereo Normalized space Viewport Transform Stereo Image space Pixel Shader
51 Stereo rendering surfaces View dependent render targets must be duplicated Back buffer Depth Stencil buffer Intermediate full screen render targets used to process final image High dynamic range, Blur, Bloom Screen Space Ambient Occlusion Left Image Right Image Screen Left Image Right Image
52 Mono rendering surfaces View independent render targets DON T need to be duplicated Shadow map Spot light maps projected in the scene Screen
53 How to do the stereo drawcalls? Simply draw the geometries twice, in left and right versions of stereo surfaces Can be executed per scene pass Draw left frame completely Then Draw right frame completely Need to modify the rendering loop Or for each individual objects Bind Left Render target, Setup state for left projection, Draw geometry Bind Right render target, Setup state for right projection, Draw Geometry Might be less intrusive in an engine Not everything in the scene needs to be drawn Just depends on the render target type
54 When to do what? Use Case Render Target Type Stereo Projection Stereo Drawcalls Shadow maps Mono No Use Shadow projection Draw Once Main frame Any Forward rendering pass Stereo Yes Draw Twice Reflection maps Stereo Yes Generate a stereo reflection projection Draw Twice Post processing effect (Drawing a full screen quad) Stereo No No Projection needed at all Draw Twice Deferred shading lighting pass (Drawing a full screen quad) Stereo G-buffers Yes Be careful of the Unprojection Should be stereo Draw twice
55 What could go possibly wrong? EVERYTHING IS UNDER CONTROL
56 3D Objects All the 3D objects in the scene should be rendered using a unique Perspective Projection in a given frame All the 3D objects must have a coherent depth relative to the scene Lighting effects are visible in 3D so should be computed correctly Highlight and specular are probably best looking evaluated with mono eye origin Reflection and Refraction should be evaluated with stereo eyes
57 Pseudo 3D objects : Sky box, Billboards Sky box should be drawn with a valid depth further than the regular scene Must be Stereo Projected Best is at a very Far distance so Parallax is maximum And cover the full screen Billboard elements (Particles, leaves ) should be rendered in a plane parallel to the viewing plane Doesn t look perfect Relief mapping looks bad
58 Several 3D scenes Different 3D scenes rendered in the same frame using different scales Portrait viewport of selected character Split screen Since scale of the scene is different, Must use a different Convergence to render each scene
59 Out of the screen objects The user s brain is fighting against the perception of hovering objects out of the screen Extra care must be taken to achieve a convincing effect Objects should not be clipped by the edges of the window Be aware of the extra horizontal guard bands Move object slowly from inside the screen to the outside area to give eyes time to adapt Make smooth visibility transitions No blinking Realistic rendering helps
60 2D Objects Starcraft2 screenshot, Courtesy of Blizzard 2D object in depth attached to 3D anchor point Billboards in depth Particles with 3D positions 2D object in depth attached to 3D anchor point
61 2D Objects must be drawn at a valid Depth With no stereo projection Head Up Display interface UI elements Either draw with no stereo projection or with stereo projection at Convergence At the correct depth when interacting with the 3D scene Labels or billboards in the scene Must be drawn with stereo projection Use the depth of the 3D anchor point used to define the position in 2D window space Needs to modify the 2D ortho projection to take into account Stereo
62 2D to 3D conversion shader function float4 2Dto3DclipPosition( in float2 posclip : POSITION, // Input position in clip space uniform float depth // Depth where to draw the 2D object ) : POSITION // Output the position in clip space { return float4( posclip.xy * depth, // Simply scale the posclip by the depth // to compensate for the division by W // performed before rasterization 0, // Z is not used if the depth buffer is not used // If needed Z = ( depth * f nf )/(f n); // ( For DirectX ) } depth ); // W is the Z in eye space
63 Selection, Pointing in S3D Selection or pointing UI interacting with the 3D scene don t work if drawn mono Mouse Cursor at the pointed object s depth Can not use the HW cursor Crosshair Needs to modify the projection to take into account depth of pointed elements Draw the UI as a 2D element in depth at the depth of the scene where pointed Compute the depth from the Graphics Engine or eval on the fly from the depth buffer (Contact me for more info) Selection Rectangle is not perfect, could be improved
64 3D Objects Culling When culling is done against the mono frustum Screen Left Frustum Eye space Y Z X Left Eye Mono Eye Right Eye Mono Frustum Right Frustum
65 3D Objects Culling Some in screen regions are missing in the right and left frustum They should be visible Screen Left Frustum Eye space Y Z X Left Eye Mono Eye Right Eye Mono Frustum Right Frustum
66 3D Objects Culling And we don t want to see out of the screen objects only in one eye It disturbs the stereo perception Screen Left Frustum Eye space Y Z X Left Eye Mono Eye Right Eye Mono Frustum Right Frustum
67 3D Objects Culling Here is the frustum we want to use for culling Screen Left Frustum Eye space Y Z X Left Eye Mono Eye Right Eye Mono Frustum Right Frustum
68 3D Objects Culling Computing Stereo Frustum origin offset Z = Convergence / ( / Separation ) Z Screen Left Frustum Eye space Y Z Interaxial Left Eye Mono Eye Screen Width Mono Frustum X Right Eye Right Frustum Convergence
69 3D Objects Culling Culling this area is not always a good idea Blacking out pixels in this area is better Through a shader Screen Left Frustum Left Eye Mono Eye Right Eye Mono Frustum Equivalent to the Floating window used in movies Right Frustum
70 Fetching Stereo Render Target When fetching from a stereo render target use the good texture coordinate Render target is addressed in STEREO IMAGE SPACE Use the pixel position provided in the pixel shader Or use a texture coordinate computed in the vertex shader correctly Pixel Shader Pixel Shader Mono Image Space uv Fetch Texel at uv Do something with it Stereo Image Space POSITION.xy Fetch Texel at POSITION.xy Do something with it Stereo Render Target Stereo Render Target
71 Unprojection in pixel shader When doing deferred shading technique, Pixel shader fetch the depth buffer (beware of the texcoord used, cf previous slide) And evaluate a 3D clip position from the Depth fetched and XY viewport position Make sure to use a Stereo Unprojection Inverse transformation to go to Mono Eye space Otherwise you will be in a Stereo Eye Space! Stereo Image Space POSITION.xy Fetch Depth at POSITION.xy Evaluate Image Space Position Image space Viewport Inverse Transform Pixel Shader Normalized space Perspective Multiply Clip space Mono Projection Inverse Transform Stereo Eye space Stereo Depth Buffer Stereo Image Space POSITION.xy Fetch Depth at POSITION.xy Evaluate Image Space Position Image space Viewport Inverse Transform Pixel Shader Normalized space Perspective Multiply Clip space Stereo Projection Inverse Transform Mono Eye space Stereo Depth Buffer
72 One or two things to look at WHAT S NEXT?
73 Performance considerations At worse the frame rate is divided by 2 But applications are rarely GPU bound so less expensive in practice Since using Vsynch when running in stereo, you see the standard Vsync frequence jumps Not all the rendering is executed twice (Shadow maps) Memory is allocated twice for all the stereo surfaces Try to reuse render targets when possible to save memory Get another GPU
74 Tessellation Works great with stereoscopy Unigine Demo
75 Letterbox Emphasize the out of the screen effect Simply Draw 2 extra horizontal bands at Convergence Out of the screen objects can overdraw the bands G-Force movie from Walt DIsney
76 Nvidia Demo Sled SHOW TIME
The In and Out: Making Games Play Right with Stereoscopic 3D Technologies. Samuel Gateau
 The In and Out: Making Games Play Right with Stereoscopic 3D Technologies Samuel Gateau Outline NVIDIA 3D Vision Stereoscopic driver & HW display solutions Stereoscopic basics Definitions and equations
The In and Out: Making Games Play Right with Stereoscopic 3D Technologies Samuel Gateau Outline NVIDIA 3D Vision Stereoscopic driver & HW display solutions Stereoscopic basics Definitions and equations
Image Processing and Computer Graphics. Rendering Pipeline. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Image Processing and Computer Graphics Rendering Pipeline Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction rendering pipeline vertex processing primitive processing
Image Processing and Computer Graphics Rendering Pipeline Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction rendering pipeline vertex processing primitive processing
INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES
 INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES 22 Mar. 212 Yanir Kleiman What is 3D Graphics? Why 3D? Draw one frame at a time Model only once X 24 frames per second Color / texture only once 15, frames for a feature
INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES 22 Mar. 212 Yanir Kleiman What is 3D Graphics? Why 3D? Draw one frame at a time Model only once X 24 frames per second Color / texture only once 15, frames for a feature
Shader Model 3.0. Ashu Rege. NVIDIA Developer Technology Group
 Shader Model 3.0 Ashu Rege NVIDIA Developer Technology Group Talk Outline Quick Intro GeForce 6 Series (NV4X family) New Vertex Shader Features Vertex Texture Fetch Longer Programs and Dynamic Flow Control
Shader Model 3.0 Ashu Rege NVIDIA Developer Technology Group Talk Outline Quick Intro GeForce 6 Series (NV4X family) New Vertex Shader Features Vertex Texture Fetch Longer Programs and Dynamic Flow Control
3D Stereoscopic Game Development. How to Make Your Game Look
 3D Stereoscopic Game Development How to Make Your Game Look Like Beowulf 3D 3D Stereoscopic Has Gone 3D Stereoscopic Has Gone Mainstream 3D Enabled Cinemas are Growing 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 2005
3D Stereoscopic Game Development How to Make Your Game Look Like Beowulf 3D 3D Stereoscopic Has Gone 3D Stereoscopic Has Gone Mainstream 3D Enabled Cinemas are Growing 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 2005
Beyond 2D Monitor NVIDIA 3D Stereo
 Beyond 2D Monitor NVIDIA 3D Stereo Agenda Basics of 3D Stereo on a PC NVIDIA GeForce 3D Stereo Drivers Maximizing 3D Stereo in Your Game 3D Stereoscopic Has Gone Mainstream Agenda Basics of 3D Stereo on
Beyond 2D Monitor NVIDIA 3D Stereo Agenda Basics of 3D Stereo on a PC NVIDIA GeForce 3D Stereo Drivers Maximizing 3D Stereo in Your Game 3D Stereoscopic Has Gone Mainstream Agenda Basics of 3D Stereo on
Optimizing Unity Games for Mobile Platforms. Angelo Theodorou Software Engineer Unite 2013, 28 th -30 th August
 Optimizing Unity Games for Mobile Platforms Angelo Theodorou Software Engineer Unite 2013, 28 th -30 th August Agenda Introduction The author and ARM Preliminary knowledge Unity Pro, OpenGL ES 3.0 Identify
Optimizing Unity Games for Mobile Platforms Angelo Theodorou Software Engineer Unite 2013, 28 th -30 th August Agenda Introduction The author and ARM Preliminary knowledge Unity Pro, OpenGL ES 3.0 Identify
Realtime 3D Computer Graphics Virtual Reality
 Realtime 3D Computer Graphics Virtual Realit Viewing and projection Classical and General Viewing Transformation Pipeline CPU Pol. DL Pixel Per Vertex Texture Raster Frag FB object ee clip normalized device
Realtime 3D Computer Graphics Virtual Realit Viewing and projection Classical and General Viewing Transformation Pipeline CPU Pol. DL Pixel Per Vertex Texture Raster Frag FB object ee clip normalized device
Optimizing AAA Games for Mobile Platforms
 Optimizing AAA Games for Mobile Platforms Niklas Smedberg Senior Engine Programmer, Epic Games Who Am I A.k.a. Smedis Epic Games, Unreal Engine 15 years in the industry 30 years of programming C64 demo
Optimizing AAA Games for Mobile Platforms Niklas Smedberg Senior Engine Programmer, Epic Games Who Am I A.k.a. Smedis Epic Games, Unreal Engine 15 years in the industry 30 years of programming C64 demo
Dynamic Resolution Rendering
 Dynamic Resolution Rendering Doug Binks Introduction The resolution selection screen has been one of the defining aspects of PC gaming since the birth of games. In this whitepaper and the accompanying
Dynamic Resolution Rendering Doug Binks Introduction The resolution selection screen has been one of the defining aspects of PC gaming since the birth of games. In this whitepaper and the accompanying
iz3d Stereo Driver Description (DirectX Realization)
 iz3d Stereo Driver Description (DirectX Realization) iz3d Driver v 1.08 April 15, 2008 1. Main Functionality 2. System Requirements 3. Installation 4. Driver Features 5. Special Points 6. Future Development
iz3d Stereo Driver Description (DirectX Realization) iz3d Driver v 1.08 April 15, 2008 1. Main Functionality 2. System Requirements 3. Installation 4. Driver Features 5. Special Points 6. Future Development
Outline. srgb DX9, DX10, XBox 360. Tone Mapping. Motion Blur
 Outline srgb DX9, DX10, XBox 360 Tone Mapping Motion Blur srgb Outline srgb & gamma review Alpha Blending: DX9 vs. DX10 & XBox 360 srgb curve: PC vs. XBox 360 srgb Review Terminology: Color textures are
Outline srgb DX9, DX10, XBox 360 Tone Mapping Motion Blur srgb Outline srgb & gamma review Alpha Blending: DX9 vs. DX10 & XBox 360 srgb curve: PC vs. XBox 360 srgb Review Terminology: Color textures are
Making natural looking Volumetric Clouds In Blender 2.48a
 I think that everyone using Blender has made some trials about making volumetric clouds. The truth is that a kind of volumetric clouds is already available in Blender for a long time, thanks to the 3D
I think that everyone using Blender has made some trials about making volumetric clouds. The truth is that a kind of volumetric clouds is already available in Blender for a long time, thanks to the 3D
3D Modeling Using Stereo Projection
 3D Modeling Using Stereo Projection TOMAS POPEK, MARTIN NEMEC, MICHAL KRUMNIKL, RADOSLAV FASUGA VSB-Technical University of Ostrava Department of Computer Science 17. Listopadu 15/2172 70030 Ostrava Czech
3D Modeling Using Stereo Projection TOMAS POPEK, MARTIN NEMEC, MICHAL KRUMNIKL, RADOSLAV FASUGA VSB-Technical University of Ostrava Department of Computer Science 17. Listopadu 15/2172 70030 Ostrava Czech
GPU(Graphics Processing Unit) with a Focus on Nvidia GeForce 6 Series. By: Binesh Tuladhar Clay Smith
 GPU(Graphics Processing Unit) with a Focus on Nvidia GeForce 6 Series By: Binesh Tuladhar Clay Smith Overview History of GPU s GPU Definition Classical Graphics Pipeline Geforce 6 Series Architecture Vertex
GPU(Graphics Processing Unit) with a Focus on Nvidia GeForce 6 Series By: Binesh Tuladhar Clay Smith Overview History of GPU s GPU Definition Classical Graphics Pipeline Geforce 6 Series Architecture Vertex
Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Sample Exam Questions 2007
 Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Questions 2007 INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions. Spend approximately 1 minute per mark. Question 1 30 Marks Total
Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Questions 2007 INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions. Spend approximately 1 minute per mark. Question 1 30 Marks Total
Deferred Shading & Screen Space Effects
 Deferred Shading & Screen Space Effects State of the Art Rendering Techniques used in the 3D Games Industry Sebastian Lehmann 11. Februar 2014 FREESTYLE PROJECT GRAPHICS PROGRAMMING LAB CHAIR OF COMPUTER
Deferred Shading & Screen Space Effects State of the Art Rendering Techniques used in the 3D Games Industry Sebastian Lehmann 11. Februar 2014 FREESTYLE PROJECT GRAPHICS PROGRAMMING LAB CHAIR OF COMPUTER
Advanced Visual Effects with Direct3D
 Advanced Visual Effects with Direct3D Presenters: Mike Burrows, Sim Dietrich, David Gosselin, Kev Gee, Jeff Grills, Shawn Hargreaves, Richard Huddy, Gary McTaggart, Jason Mitchell, Ashutosh Rege and Matthias
Advanced Visual Effects with Direct3D Presenters: Mike Burrows, Sim Dietrich, David Gosselin, Kev Gee, Jeff Grills, Shawn Hargreaves, Richard Huddy, Gary McTaggart, Jason Mitchell, Ashutosh Rege and Matthias
Stereo 3D Monitoring & Correction
 www.omnitek.tv Advanced Measurement Technology Stereo 3D Monitoring & Correction Roger Fawcett, Managing Director, OmniTek It has long been known that it is possible to give the impression of 3D scene
www.omnitek.tv Advanced Measurement Technology Stereo 3D Monitoring & Correction Roger Fawcett, Managing Director, OmniTek It has long been known that it is possible to give the impression of 3D scene
Using Photorealistic RenderMan for High-Quality Direct Volume Rendering
 Using Photorealistic RenderMan for High-Quality Direct Volume Rendering Cyrus Jam [email protected] Mike Bailey [email protected] San Diego Supercomputer Center University of California San Diego Abstract With
Using Photorealistic RenderMan for High-Quality Direct Volume Rendering Cyrus Jam [email protected] Mike Bailey [email protected] San Diego Supercomputer Center University of California San Diego Abstract With
Video in Logger Pro. There are many ways to create and use video clips and still images in Logger Pro.
 Video in Logger Pro There are many ways to create and use video clips and still images in Logger Pro. Insert an existing video clip into a Logger Pro experiment. Supported file formats include.avi and.mov.
Video in Logger Pro There are many ways to create and use video clips and still images in Logger Pro. Insert an existing video clip into a Logger Pro experiment. Supported file formats include.avi and.mov.
Computer Graphics. Introduction. Computer graphics. What is computer graphics? Yung-Yu Chuang
 Introduction Computer Graphics Instructor: Yung-Yu Chuang ( 莊 永 裕 ) E-mail: [email protected] Office: CSIE 527 Grading: a MatchMove project Computer Science ce & Information o Technolog og Yung-Yu Chuang
Introduction Computer Graphics Instructor: Yung-Yu Chuang ( 莊 永 裕 ) E-mail: [email protected] Office: CSIE 527 Grading: a MatchMove project Computer Science ce & Information o Technolog og Yung-Yu Chuang
Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline 1
 Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline 1 Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline Windows Embedded Compact 7 Technical Article Writers: David Franklin,
Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline 1 Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline Windows Embedded Compact 7 Technical Article Writers: David Franklin,
6 Space Perception and Binocular Vision
 Space Perception and Binocular Vision Space Perception and Binocular Vision space perception monocular cues to 3D space binocular vision and stereopsis combining depth cues monocular/pictorial cues cues
Space Perception and Binocular Vision Space Perception and Binocular Vision space perception monocular cues to 3D space binocular vision and stereopsis combining depth cues monocular/pictorial cues cues
2) A convex lens is known as a diverging lens and a concave lens is known as a converging lens. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Var: 1 Page Ref: Sec.
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 4e (Giancoli) Chapter 33 Lenses and Optical Instruments 33.1 Conceptual Questions 1) State how to draw the three rays for finding the image position due to a thin
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 4e (Giancoli) Chapter 33 Lenses and Optical Instruments 33.1 Conceptual Questions 1) State how to draw the three rays for finding the image position due to a thin
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics 3D views and projection Adapted from notes by Yong Cao 1 Overview of 3D rendering Modeling: *Define object in local coordinates *Place object in world coordinates (modeling transformation)
CS 4204 Computer Graphics 3D views and projection Adapted from notes by Yong Cao 1 Overview of 3D rendering Modeling: *Define object in local coordinates *Place object in world coordinates (modeling transformation)
GPU Architecture. Michael Doggett ATI
 GPU Architecture Michael Doggett ATI GPU Architecture RADEON X1800/X1900 Microsoft s XBOX360 Xenos GPU GPU research areas ATI - Driving the Visual Experience Everywhere Products from cell phones to super
GPU Architecture Michael Doggett ATI GPU Architecture RADEON X1800/X1900 Microsoft s XBOX360 Xenos GPU GPU research areas ATI - Driving the Visual Experience Everywhere Products from cell phones to super
Scan-Line Fill. Scan-Line Algorithm. Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list
 Scan-Line Fill Can also fill by maintaining a data structure of all intersections of polygons with scan lines Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list desired order Scan-Line
Scan-Line Fill Can also fill by maintaining a data structure of all intersections of polygons with scan lines Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list desired order Scan-Line
Blender Notes. Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 9 The Game Engine
 Blender Notes Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 9 The Game Engine The Blender Game Engine This week we will have an introduction to the Game Engine build
Blender Notes Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 9 The Game Engine The Blender Game Engine This week we will have an introduction to the Game Engine build
OpenGL Performance Tuning
 OpenGL Performance Tuning Evan Hart ATI Pipeline slides courtesy John Spitzer - NVIDIA Overview What to look for in tuning How it relates to the graphics pipeline Modern areas of interest Vertex Buffer
OpenGL Performance Tuning Evan Hart ATI Pipeline slides courtesy John Spitzer - NVIDIA Overview What to look for in tuning How it relates to the graphics pipeline Modern areas of interest Vertex Buffer
Performance Optimization and Debug Tools for mobile games with PlayCanvas
 Performance Optimization and Debug Tools for mobile games with PlayCanvas Jonathan Kirkham, Senior Software Engineer, ARM Will Eastcott, CEO, PlayCanvas 1 Introduction Jonathan Kirkham, ARM Worked with
Performance Optimization and Debug Tools for mobile games with PlayCanvas Jonathan Kirkham, Senior Software Engineer, ARM Will Eastcott, CEO, PlayCanvas 1 Introduction Jonathan Kirkham, ARM Worked with
VRayPattern also allows to curve geometry on any surface
 Introduction VrayPattern is a plug-in for 3dsmax and V-Ray VRayPattern allows to multiply geometry periodically without extra memory consumption. As a sample you can use any tiled geometry (or those with
Introduction VrayPattern is a plug-in for 3dsmax and V-Ray VRayPattern allows to multiply geometry periodically without extra memory consumption. As a sample you can use any tiled geometry (or those with
Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview
 Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview Graphics System Monitor Input devices CPU/Memory GPU Raster Graphics System Raster: An array of picture elements Based on raster-scan TV technology The screen (and
Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview Graphics System Monitor Input devices CPU/Memory GPU Raster Graphics System Raster: An array of picture elements Based on raster-scan TV technology The screen (and
DATA VISUALIZATION OF THE GRAPHICS PIPELINE: TRACKING STATE WITH THE STATEVIEWER
 DATA VISUALIZATION OF THE GRAPHICS PIPELINE: TRACKING STATE WITH THE STATEVIEWER RAMA HOETZLEIN, DEVELOPER TECHNOLOGY, NVIDIA Data Visualizations assist humans with data analysis by representing information
DATA VISUALIZATION OF THE GRAPHICS PIPELINE: TRACKING STATE WITH THE STATEVIEWER RAMA HOETZLEIN, DEVELOPER TECHNOLOGY, NVIDIA Data Visualizations assist humans with data analysis by representing information
Recent Advances and Future Trends in Graphics Hardware. Michael Doggett Architect November 23, 2005
 Recent Advances and Future Trends in Graphics Hardware Michael Doggett Architect November 23, 2005 Overview XBOX360 GPU : Xenos Rendering performance GPU architecture Unified shader Memory Export Texture/Vertex
Recent Advances and Future Trends in Graphics Hardware Michael Doggett Architect November 23, 2005 Overview XBOX360 GPU : Xenos Rendering performance GPU architecture Unified shader Memory Export Texture/Vertex
NVPRO-PIPELINE A RESEARCH RENDERING PIPELINE MARKUS TAVENRATH [email protected] SENIOR DEVELOPER TECHNOLOGY ENGINEER, NVIDIA
 NVPRO-PIPELINE A RESEARCH RENDERING PIPELINE MARKUS TAVENRATH [email protected] SENIOR DEVELOPER TECHNOLOGY ENGINEER, NVIDIA GFLOPS 3500 3000 NVPRO-PIPELINE Peak Double Precision FLOPS GPU perf improved
NVPRO-PIPELINE A RESEARCH RENDERING PIPELINE MARKUS TAVENRATH [email protected] SENIOR DEVELOPER TECHNOLOGY ENGINEER, NVIDIA GFLOPS 3500 3000 NVPRO-PIPELINE Peak Double Precision FLOPS GPU perf improved
Space Perception and Binocular Vision
 Space Perception and Binocular Vision Space Perception Monocular Cues to Three-Dimensional Space Binocular Vision and Stereopsis Combining Depth Cues 9/30/2008 1 Introduction to Space Perception Realism:
Space Perception and Binocular Vision Space Perception Monocular Cues to Three-Dimensional Space Binocular Vision and Stereopsis Combining Depth Cues 9/30/2008 1 Introduction to Space Perception Realism:
Binocular Vision and The Perception of Depth
 Binocular Vision and The Perception of Depth Visual Perception How one visually interprets a scene 4 forms of perception to be studied: Depth Color Temporal Motion Depth Perception How does one determine
Binocular Vision and The Perception of Depth Visual Perception How one visually interprets a scene 4 forms of perception to be studied: Depth Color Temporal Motion Depth Perception How does one determine
Real-Time Realistic Rendering. Michael Doggett Docent Department of Computer Science Lund university
 Real-Time Realistic Rendering Michael Doggett Docent Department of Computer Science Lund university 30-5-2011 Visually realistic goal force[d] us to completely rethink the entire rendering process. Cook
Real-Time Realistic Rendering Michael Doggett Docent Department of Computer Science Lund university 30-5-2011 Visually realistic goal force[d] us to completely rethink the entire rendering process. Cook
CSE 564: Visualization. GPU Programming (First Steps) GPU Generations. Klaus Mueller. Computer Science Department Stony Brook University
 GPU Generations CSE 564: Visualization GPU Programming (First Steps) Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University For the labs, 4th generation is desirable Graphics Hardware Pipeline
GPU Generations CSE 564: Visualization GPU Programming (First Steps) Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University For the labs, 4th generation is desirable Graphics Hardware Pipeline
Lesson 26: Reflection & Mirror Diagrams
 Lesson 26: Reflection & Mirror Diagrams The Law of Reflection There is nothing really mysterious about reflection, but some people try to make it more difficult than it really is. All EMR will reflect
Lesson 26: Reflection & Mirror Diagrams The Law of Reflection There is nothing really mysterious about reflection, but some people try to make it more difficult than it really is. All EMR will reflect
Image Synthesis. Transparency. computer graphics & visualization
 Image Synthesis Transparency Inter-Object realism Covers different kinds of interactions between objects Increasing realism in the scene Relationships between objects easier to understand Shadows, Reflections,
Image Synthesis Transparency Inter-Object realism Covers different kinds of interactions between objects Increasing realism in the scene Relationships between objects easier to understand Shadows, Reflections,
Intermediate Tutorials Modeling - Trees. 3d studio max. 3d studio max. Tree Modeling. 1.2206 2006 Matthew D'Onofrio Page 1 of 12
 3d studio max Tree Modeling Techniques and Principles 1.2206 2006 Matthew D'Onofrio Page 1 of 12 Modeling Trees Tree Modeling Techniques and Principles The era of sprites and cylinders-for-trunks has passed
3d studio max Tree Modeling Techniques and Principles 1.2206 2006 Matthew D'Onofrio Page 1 of 12 Modeling Trees Tree Modeling Techniques and Principles The era of sprites and cylinders-for-trunks has passed
EXPERIMENT 6 OPTICS: FOCAL LENGTH OF A LENS
 EXPERIMENT 6 OPTICS: FOCAL LENGTH OF A LENS The following website should be accessed before coming to class. Text reference: pp189-196 Optics Bench a) For convenience of discussion we assume that the light
EXPERIMENT 6 OPTICS: FOCAL LENGTH OF A LENS The following website should be accessed before coming to class. Text reference: pp189-196 Optics Bench a) For convenience of discussion we assume that the light
Lecture Notes, CEng 477
 Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make
Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make
Hi everyone, my name is Michał Iwanicki. I m an engine programmer at Naughty Dog and this talk is entitled: Lighting technology of The Last of Us,
 Hi everyone, my name is Michał Iwanicki. I m an engine programmer at Naughty Dog and this talk is entitled: Lighting technology of The Last of Us, but I should have called it old lightmaps new tricks 1
Hi everyone, my name is Michał Iwanicki. I m an engine programmer at Naughty Dog and this talk is entitled: Lighting technology of The Last of Us, but I should have called it old lightmaps new tricks 1
Computer Applications in Textile Engineering. Computer Applications in Textile Engineering
 3. Computer Graphics Sungmin Kim http://latam.jnu.ac.kr Computer Graphics Definition Introduction Research field related to the activities that includes graphics as input and output Importance Interactive
3. Computer Graphics Sungmin Kim http://latam.jnu.ac.kr Computer Graphics Definition Introduction Research field related to the activities that includes graphics as input and output Importance Interactive
How To Understand The Power Of Unity 3D (Pro) And The Power Behind It (Pro/Pro)
 Optimizing Unity Games for Mobile Platforms Angelo Theodorou Software Engineer Brains Eden, 28 th June 2013 Agenda Introduction The author ARM Ltd. What do you need to have What do you need to know Identify
Optimizing Unity Games for Mobile Platforms Angelo Theodorou Software Engineer Brains Eden, 28 th June 2013 Agenda Introduction The author ARM Ltd. What do you need to have What do you need to know Identify
The Limits of Human Vision
 The Limits of Human Vision Michael F. Deering Sun Microsystems ABSTRACT A model of the perception s of the human visual system is presented, resulting in an estimate of approximately 15 million variable
The Limits of Human Vision Michael F. Deering Sun Microsystems ABSTRACT A model of the perception s of the human visual system is presented, resulting in an estimate of approximately 15 million variable
GPU Christmas Tree Rendering. Evan Hart [email protected]
 GPU Christmas Tree Rendering Evan Hart [email protected] February 2007 Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change 0.9 2/20/2007 Ehart Betarelease February 2007 ii Beta Release This
GPU Christmas Tree Rendering Evan Hart [email protected] February 2007 Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change 0.9 2/20/2007 Ehart Betarelease February 2007 ii Beta Release This
Course Overview. CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 1. Administrative Issues Modeling Animation Rendering OpenGL Programming [Angel Ch.
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Course Overview January 14, 2013 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s13/ Administrative Issues Modeling Animation
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Course Overview January 14, 2013 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s13/ Administrative Issues Modeling Animation
2: Introducing image synthesis. Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system architecture Overview of OpenGL / GLU / GLUT
 COMP27112 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 2: Introducing image synthesis [email protected] 1 Introduction In these notes we ll cover: Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system
COMP27112 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 2: Introducing image synthesis [email protected] 1 Introduction In these notes we ll cover: Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system
B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS. NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions.
 B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER
B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER
GUI GRAPHICS AND USER INTERFACES. Welcome to GUI! Mechanics. Mihail Gaianu 26/02/2014 1
 Welcome to GUI! Mechanics 26/02/2014 1 Requirements Info If you don t know C++, you CAN take this class additional time investment required early on GUI Java to C++ transition tutorial on course website
Welcome to GUI! Mechanics 26/02/2014 1 Requirements Info If you don t know C++, you CAN take this class additional time investment required early on GUI Java to C++ transition tutorial on course website
Go to contents 18 3D Visualization of Building Services in Virtual Environment
 3D Visualization of Building Services in Virtual Environment GRÖHN, Matti Gröhn; MANTERE, Markku; SAVIOJA, Lauri; TAKALA, Tapio Telecommunications Software and Multimedia Laboratory Department of Computer
3D Visualization of Building Services in Virtual Environment GRÖHN, Matti Gröhn; MANTERE, Markku; SAVIOJA, Lauri; TAKALA, Tapio Telecommunications Software and Multimedia Laboratory Department of Computer
Protocol for Microscope Calibration
 Protocol for Microscope Calibration A properly calibrated system is essential for successful and efficient software use. The following are step by step instructions on how to calibrate the hardware using
Protocol for Microscope Calibration A properly calibrated system is essential for successful and efficient software use. The following are step by step instructions on how to calibrate the hardware using
Low power GPUs a view from the industry. Edvard Sørgård
 Low power GPUs a view from the industry Edvard Sørgård 1 ARM in Trondheim Graphics technology design centre From 2006 acquisition of Falanx Microsystems AS Origin of the ARM Mali GPUs Main activities today
Low power GPUs a view from the industry Edvard Sørgård 1 ARM in Trondheim Graphics technology design centre From 2006 acquisition of Falanx Microsystems AS Origin of the ARM Mali GPUs Main activities today
White Paper AMD HD3D Pro Technology: Stereoscopic 3D For Professionals. Table of Contents
 White Paper AMD HD3D Pro Technology: Stereoscopic 3D For Professionals Table of Contents INTRODUCTION 2 What is Stereoscopic 3D? 2 About this document 2 Professional Graphics applications of Stereo 3D
White Paper AMD HD3D Pro Technology: Stereoscopic 3D For Professionals Table of Contents INTRODUCTION 2 What is Stereoscopic 3D? 2 About this document 2 Professional Graphics applications of Stereo 3D
COMP175: Computer Graphics. Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies
 COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su ([email protected]) TA: Matt Menke
COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su ([email protected]) TA: Matt Menke
CUBE-MAP DATA STRUCTURE FOR INTERACTIVE GLOBAL ILLUMINATION COMPUTATION IN DYNAMIC DIFFUSE ENVIRONMENTS
 ICCVG 2002 Zakopane, 25-29 Sept. 2002 Rafal Mantiuk (1,2), Sumanta Pattanaik (1), Karol Myszkowski (3) (1) University of Central Florida, USA, (2) Technical University of Szczecin, Poland, (3) Max- Planck-Institut
ICCVG 2002 Zakopane, 25-29 Sept. 2002 Rafal Mantiuk (1,2), Sumanta Pattanaik (1), Karol Myszkowski (3) (1) University of Central Florida, USA, (2) Technical University of Szczecin, Poland, (3) Max- Planck-Institut
1051-232 Imaging Systems Laboratory II. Laboratory 4: Basic Lens Design in OSLO April 2 & 4, 2002
 05-232 Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 4: Basic Lens Design in OSLO April 2 & 4, 2002 Abstract: For designing the optics of an imaging system, one of the main types of tools used today is optical
05-232 Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 4: Basic Lens Design in OSLO April 2 & 4, 2002 Abstract: For designing the optics of an imaging system, one of the main types of tools used today is optical
Basic Principles of Stereoscopic 3D. Simon Reeve & Jason Flock Senior Editors, BSKYB [email protected] [email protected]
 Basic Principles of Stereoscopic 3D Simon Reeve & Jason Flock Senior Editors, BSKYB [email protected] [email protected] Stereoscopic 3D Shooting and transmitting images in Stereoscopic 3D is an
Basic Principles of Stereoscopic 3D Simon Reeve & Jason Flock Senior Editors, BSKYB [email protected] [email protected] Stereoscopic 3D Shooting and transmitting images in Stereoscopic 3D is an
The Evolution of Computer Graphics. SVP, Content & Technology, NVIDIA
 The Evolution of Computer Graphics Tony Tamasi SVP, Content & Technology, NVIDIA Graphics Make great images intricate shapes complex optical effects seamless motion Make them fast invent clever techniques
The Evolution of Computer Graphics Tony Tamasi SVP, Content & Technology, NVIDIA Graphics Make great images intricate shapes complex optical effects seamless motion Make them fast invent clever techniques
CS130 - Intro to computer graphics. Dr. Victor B. Zordan [email protected] www.cs.ucr.edu/~vbz. Objectives
 CS130 - Intro to computer graphics Dr. Victor B. Zordan [email protected] www.cs.ucr.edu/~vbz Objectives Explore basics of computer graphics Survey application areas Today, brief introduction to graphics
CS130 - Intro to computer graphics Dr. Victor B. Zordan [email protected] www.cs.ucr.edu/~vbz Objectives Explore basics of computer graphics Survey application areas Today, brief introduction to graphics
Modern Graphics Engine Design. Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation [email protected]
 Modern Graphics Engine Design Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation [email protected] Overview Modern Engine Features Modern Engine Challenges Scene Management Culling & Batching Geometry Management Collision
Modern Graphics Engine Design Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation [email protected] Overview Modern Engine Features Modern Engine Challenges Scene Management Culling & Batching Geometry Management Collision
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 12 (Part 1) Curves. Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics CS 54 Lecture 1 (Part 1) Curves Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) So Far Dealt with straight lines and flat surfaces Real world objects include
Computer Graphics CS 54 Lecture 1 (Part 1) Curves Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) So Far Dealt with straight lines and flat surfaces Real world objects include
SketchUp Instructions
 SketchUp Instructions Every architect needs to know how to use SketchUp! SketchUp is free from Google just Google it and download to your computer. You can do just about anything with it, but it is especially
SketchUp Instructions Every architect needs to know how to use SketchUp! SketchUp is free from Google just Google it and download to your computer. You can do just about anything with it, but it is especially
NVFX : A NEW SCENE AND MATERIAL EFFECT FRAMEWORK FOR OPENGL AND DIRECTX. TRISTAN LORACH Senior Devtech Engineer SIGGRAPH 2013
 NVFX : A NEW SCENE AND MATERIAL EFFECT FRAMEWORK FOR OPENGL AND DIRECTX TRISTAN LORACH Senior Devtech Engineer SIGGRAPH 2013 nvfx : Plan What is an Effect New Approach and new ideas of nvfx Examples Walkthrough
NVFX : A NEW SCENE AND MATERIAL EFFECT FRAMEWORK FOR OPENGL AND DIRECTX TRISTAN LORACH Senior Devtech Engineer SIGGRAPH 2013 nvfx : Plan What is an Effect New Approach and new ideas of nvfx Examples Walkthrough
1. INTRODUCTION Graphics 2
 1. INTRODUCTION Graphics 2 06-02408 Level 3 10 credits in Semester 2 Professor Aleš Leonardis Slides by Professor Ela Claridge What is computer graphics? The art of 3D graphics is the art of fooling the
1. INTRODUCTION Graphics 2 06-02408 Level 3 10 credits in Semester 2 Professor Aleš Leonardis Slides by Professor Ela Claridge What is computer graphics? The art of 3D graphics is the art of fooling the
L20: GPU Architecture and Models
 L20: GPU Architecture and Models scribe(s): Abdul Khalifa 20.1 Overview GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are large parallel structure of processing cores capable of rendering graphics efficiently on displays.
L20: GPU Architecture and Models scribe(s): Abdul Khalifa 20.1 Overview GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are large parallel structure of processing cores capable of rendering graphics efficiently on displays.
3D Computer Games History and Technology
 3D Computer Games History and Technology VRVis Research Center http://www.vrvis.at Lecture Outline Overview of the last 10-15 15 years A look at seminal 3D computer games Most important techniques employed
3D Computer Games History and Technology VRVis Research Center http://www.vrvis.at Lecture Outline Overview of the last 10-15 15 years A look at seminal 3D computer games Most important techniques employed
Color correction in 3D environments Nicholas Blackhawk
 Color correction in 3D environments Nicholas Blackhawk Abstract In 3D display technologies, as reviewers will say, color quality is often a factor. Depending on the type of display, either professional
Color correction in 3D environments Nicholas Blackhawk Abstract In 3D display technologies, as reviewers will say, color quality is often a factor. Depending on the type of display, either professional
Introduction to GPGPU. Tiziano Diamanti [email protected]
 [email protected] Agenda From GPUs to GPGPUs GPGPU architecture CUDA programming model Perspective projection Vectors that connect the vanishing point to every point of the 3D model will intersecate
[email protected] Agenda From GPUs to GPGPUs GPGPU architecture CUDA programming model Perspective projection Vectors that connect the vanishing point to every point of the 3D model will intersecate
Advanced Rendering for Engineering & Styling
 Advanced Rendering for Engineering & Styling Prof. B.Brüderlin Brüderlin,, M Heyer 3Dinteractive GmbH & TU-Ilmenau, Germany SGI VizDays 2005, Rüsselsheim Demands in Engineering & Styling Engineering: :
Advanced Rendering for Engineering & Styling Prof. B.Brüderlin Brüderlin,, M Heyer 3Dinteractive GmbH & TU-Ilmenau, Germany SGI VizDays 2005, Rüsselsheim Demands in Engineering & Styling Engineering: :
Digital Photography Composition. Kent Messamore 9/8/2013
 Digital Photography Composition Kent Messamore 9/8/2013 Photography Equipment versus Art Last week we focused on our Cameras Hopefully we have mastered the buttons and dials by now If not, it will come
Digital Photography Composition Kent Messamore 9/8/2013 Photography Equipment versus Art Last week we focused on our Cameras Hopefully we have mastered the buttons and dials by now If not, it will come
RADEON 9700 SERIES. User s Guide. Copyright 2002, ATI Technologies Inc. All rights reserved.
 RADEON 9700 SERIES User s Guide P/N 137-40361-30 Copyright 2002, ATI Technologies Inc. All rights reserved. ATI and all ATI product and product feature names are trademarks and/or registered trademarks
RADEON 9700 SERIES User s Guide P/N 137-40361-30 Copyright 2002, ATI Technologies Inc. All rights reserved. ATI and all ATI product and product feature names are trademarks and/or registered trademarks
How To Use 3D On A Computer Or Tv
 Display technologies seminar 3D Displays What is 3D? 3D History 3D production 3D Displays 3D now Agenda 13 May 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Lauri Virkki What is 3D? Eyes are average 64
Display technologies seminar 3D Displays What is 3D? 3D History 3D production 3D Displays 3D now Agenda 13 May 2010 Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Lauri Virkki What is 3D? Eyes are average 64
Introduction to Computer Graphics
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller TASC 8021 778-782-2215 [email protected] www.cs.sfu.ca/~torsten Today What is computer graphics? Contents of this course Syllabus Overview of course topics
Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller TASC 8021 778-782-2215 [email protected] www.cs.sfu.ca/~torsten Today What is computer graphics? Contents of this course Syllabus Overview of course topics
Optimization for DirectX9 Graphics. Ashu Rege
 Optimization for DirectX9 Graphics Ashu Rege Last Year: Batch, Batch, Batch Moral of the story: Small batches BAD What is a batch Every DrawIndexedPrimitive call is a batch All render, texture, shader,...
Optimization for DirectX9 Graphics Ashu Rege Last Year: Batch, Batch, Batch Moral of the story: Small batches BAD What is a batch Every DrawIndexedPrimitive call is a batch All render, texture, shader,...
A Crash Course on Programmable Graphics Hardware
 A Crash Course on Programmable Graphics Hardware Li-Yi Wei Abstract Recent years have witnessed tremendous growth for programmable graphics hardware (GPU), both in terms of performance and functionality.
A Crash Course on Programmable Graphics Hardware Li-Yi Wei Abstract Recent years have witnessed tremendous growth for programmable graphics hardware (GPU), both in terms of performance and functionality.
How To Run A Factory I/O On A Microsoft Gpu 2.5 (Sdk) On A Computer Or Microsoft Powerbook 2.3 (Powerpoint) On An Android Computer Or Macbook 2 (Powerstation) On
 User Guide November 19, 2014 Contents 3 Welcome 3 What Is FACTORY I/O 3 How Does It Work 4 I/O Drivers: Connecting To External Technologies 5 System Requirements 6 Run Mode And Edit Mode 7 Controls 8 Cameras
User Guide November 19, 2014 Contents 3 Welcome 3 What Is FACTORY I/O 3 How Does It Work 4 I/O Drivers: Connecting To External Technologies 5 System Requirements 6 Run Mode And Edit Mode 7 Controls 8 Cameras
Transformations in the pipeline
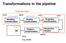 Transformations in the pipeline gltranslatef() Modeling transformation ModelView Matrix OCS WCS glulookat() VCS CCS Viewing transformation Projection transformation DCS Viewport transformation (e.g. pixels)
Transformations in the pipeline gltranslatef() Modeling transformation ModelView Matrix OCS WCS glulookat() VCS CCS Viewing transformation Projection transformation DCS Viewport transformation (e.g. pixels)
What is GPUOpen? Currently, we have divided console & PC development Black box libraries go against the philosophy of game development Game
 1 2 3 4 What is GPUOpen? Currently, we have divided console & PC development Black box libraries go against the philosophy of game development Game developers are smart and inquisitive Game devs extract
1 2 3 4 What is GPUOpen? Currently, we have divided console & PC development Black box libraries go against the philosophy of game development Game developers are smart and inquisitive Game devs extract
Introduction to Computer Graphics. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012 Today Course organization Course overview 2 Course Staff Instructor Jürgen Schulze,
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012 Today Course organization Course overview 2 Course Staff Instructor Jürgen Schulze,
Maxwell Render 1.5 complete list of new and enhanced features
 Maxwell Render 1.5 complete list of new and enhanced features Multiprocessor Maxwell Render can exploit all of the processors available on your system and can make them work simultaneously on the same
Maxwell Render 1.5 complete list of new and enhanced features Multiprocessor Maxwell Render can exploit all of the processors available on your system and can make them work simultaneously on the same
Our One-Year 3D Animation Program is a comprehensive training in 3D using Alias
 1 YEAR 3D ANIMATION Illusion is the first of all pleasures Oscar Wilde Our One-Year 3D Animation Program is a comprehensive training in 3D using Alias Oscar Winning software, Maya, the industry standard
1 YEAR 3D ANIMATION Illusion is the first of all pleasures Oscar Wilde Our One-Year 3D Animation Program is a comprehensive training in 3D using Alias Oscar Winning software, Maya, the industry standard
NVIDIA workstation 3D graphics card upgrade options deliver productivity improvements and superior image quality
 Hardware Announcement ZG09-0170, dated March 31, 2009 NVIDIA workstation 3D graphics card upgrade options deliver productivity improvements and superior image quality Table of contents 1 At a glance 3
Hardware Announcement ZG09-0170, dated March 31, 2009 NVIDIA workstation 3D graphics card upgrade options deliver productivity improvements and superior image quality Table of contents 1 At a glance 3
The Rocket Steam Locomotive - Animation
 Course: 3D Design Title: Rocket Steam Locomotive - Animation Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig ([email protected]) (May 2012) The Rocket Steam Locomotive - Animation In this tutorial
Course: 3D Design Title: Rocket Steam Locomotive - Animation Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig ([email protected]) (May 2012) The Rocket Steam Locomotive - Animation In this tutorial
High Dynamic Range and other Fun Shader Tricks. Simon Green
 High Dynamic Range and other Fun Shader Tricks Simon Green Demo Group Motto If you can t make it good, make it big. If you can t make it big, make it shiny. Overview The OpenGL vertex program and texture
High Dynamic Range and other Fun Shader Tricks Simon Green Demo Group Motto If you can t make it good, make it big. If you can t make it big, make it shiny. Overview The OpenGL vertex program and texture
Head-Coupled Perspective
 Head-Coupled Perspective Introduction Head-Coupled Perspective (HCP) refers to a technique of rendering a scene that takes into account the position of the viewer relative to the display. As a viewer moves
Head-Coupled Perspective Introduction Head-Coupled Perspective (HCP) refers to a technique of rendering a scene that takes into account the position of the viewer relative to the display. As a viewer moves
Writing Applications for the GPU Using the RapidMind Development Platform
 Writing Applications for the GPU Using the RapidMind Development Platform Contents Introduction... 1 Graphics Processing Units... 1 RapidMind Development Platform... 2 Writing RapidMind Enabled Applications...
Writing Applications for the GPU Using the RapidMind Development Platform Contents Introduction... 1 Graphics Processing Units... 1 RapidMind Development Platform... 2 Writing RapidMind Enabled Applications...
An introduction to Global Illumination. Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 An introduction to Global Illumination Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Isn t ray tracing enough? Effects to note in Global Illumination image:
An introduction to Global Illumination Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Isn t ray tracing enough? Effects to note in Global Illumination image:
How To Teach Computer Graphics
 Computer Graphics Thilo Kielmann Lecture 1: 1 Introduction (basic administrative information) Course Overview + Examples (a.o. Pixar, Blender, ) Graphics Systems Hands-on Session General Introduction http://www.cs.vu.nl/~graphics/
Computer Graphics Thilo Kielmann Lecture 1: 1 Introduction (basic administrative information) Course Overview + Examples (a.o. Pixar, Blender, ) Graphics Systems Hands-on Session General Introduction http://www.cs.vu.nl/~graphics/
Specular reflection. Dielectrics and Distribution in Ray Tracing. Snell s Law. Ray tracing dielectrics
 Specular reflection Dielectrics and Distribution in Ray Tracing CS 465 Lecture 22 Smooth surfaces of pure materials have ideal specular reflection (said this before) Metals (conductors) and dielectrics
Specular reflection Dielectrics and Distribution in Ray Tracing CS 465 Lecture 22 Smooth surfaces of pure materials have ideal specular reflection (said this before) Metals (conductors) and dielectrics
Q. Can an Exceptional3D monitor play back 2D content? A. Yes, Exceptional3D monitors can play back both 2D and specially formatted 3D content.
 FAQ Content Playback Q. What kind of computer do I need to run an Exceptional 3D display? A. Processor: Intel Core Duo Processor 2.5+GHz, 3M, 1066 Operating System: Windows 7 Memory: 4GB, DDR3, 1066MHz,
FAQ Content Playback Q. What kind of computer do I need to run an Exceptional 3D display? A. Processor: Intel Core Duo Processor 2.5+GHz, 3M, 1066 Operating System: Windows 7 Memory: 4GB, DDR3, 1066MHz,
GPU-Driven Rendering Pipelines
 SIGGRAPH 2015: Advances in Real-Time Rendering in Games GPU-Driven Rendering Pipelines Ulrich Haar, Lead Programmer 3D, Ubisoft Montreal Sebastian Aaltonen, Senior Lead Programmer, RedLynx a Ubisoft Studio
SIGGRAPH 2015: Advances in Real-Time Rendering in Games GPU-Driven Rendering Pipelines Ulrich Haar, Lead Programmer 3D, Ubisoft Montreal Sebastian Aaltonen, Senior Lead Programmer, RedLynx a Ubisoft Studio
Blender addons ESRI Shapefile import/export and georeferenced raster import
 Blender addons ESRI Shapefile import/export and georeferenced raster import This blender addon is a collection of 4 tools: ESRI Shapefile importer - Import point, pointz, polyline, polylinez, polygon,
Blender addons ESRI Shapefile import/export and georeferenced raster import This blender addon is a collection of 4 tools: ESRI Shapefile importer - Import point, pointz, polyline, polylinez, polygon,
REAL-TIME IMAGE BASED LIGHTING FOR OUTDOOR AUGMENTED REALITY UNDER DYNAMICALLY CHANGING ILLUMINATION CONDITIONS
 REAL-TIME IMAGE BASED LIGHTING FOR OUTDOOR AUGMENTED REALITY UNDER DYNAMICALLY CHANGING ILLUMINATION CONDITIONS Tommy Jensen, Mikkel S. Andersen, Claus B. Madsen Laboratory for Computer Vision and Media
REAL-TIME IMAGE BASED LIGHTING FOR OUTDOOR AUGMENTED REALITY UNDER DYNAMICALLY CHANGING ILLUMINATION CONDITIONS Tommy Jensen, Mikkel S. Andersen, Claus B. Madsen Laboratory for Computer Vision and Media
CLOUD GAMING WITH NVIDIA GRID TECHNOLOGIES Franck DIARD, Ph.D., SW Chief Software Architect GDC 2014
 CLOUD GAMING WITH NVIDIA GRID TECHNOLOGIES Franck DIARD, Ph.D., SW Chief Software Architect GDC 2014 Introduction Cloud ification < 2013 2014+ Music, Movies, Books Games GPU Flops GPUs vs. Consoles 10,000
CLOUD GAMING WITH NVIDIA GRID TECHNOLOGIES Franck DIARD, Ph.D., SW Chief Software Architect GDC 2014 Introduction Cloud ification < 2013 2014+ Music, Movies, Books Games GPU Flops GPUs vs. Consoles 10,000
