Coclia: Deep Space Neck Infections:
|
|
|
- Baldwin Logan
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Coclia: Deep Space Neck Infections: 1. Describe the anatomy of the cervical fascia. AL - From Cummings b Investing-----~="HI layer Muscularportion,------~'**~~ """"~~~r==~~'""::-~~,-----prevertebral pretracheallayer Visceralportion,---~~~{!kjj~~--~~=----=> pretracheallayer layer E Fascial relationships in the neck b Left lateral view. Midsagittal section showing the prevertebrallayer.
2 The two main fascial divisions of the neck are the superficial cervical fascia and the deep cervical fascia, which further divides into three layers. Superficial Cervical Fascia -The superficial cervical fascia, deep to the dermis, envelops the platysma and muscles of facial expression. It incorporates the superficial muscu- loaponeurotic system and extends from the zygoma to the axillae, clavicles, and deltopectoral region. Deep to the platysma, a potential space separates the superficial and deep cervical fasciae. This space houses adipose tissue, sensory nerves, and blood vessels, such as the anterior and external jugular veins, and facilitates free movement of the skin. Deep Cervical Fascia -The deep cervical fascia is divided into three layers: the superficial, middle, and deep. The superficial layer of deep cervical fascia, or invest- ing fascia, surrounds the neck. Posteriorly it attaches to the superior nuchal line, the ligamentum nuchae of the cervical vertebrae, and the mastoid process. As it transmits anteriorly, it splits and re-fuses to sur- round the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles. Anterosuperi- orly, this layer attaches to the inferior zygomatic arch. As it proceeds inferiorly, it splits to enclose the parotid gland, forming the parotid fascia superficially, and extends along the temporal bone to the carotid canal deeply. It envelops the muscles of mastication and covers the submandibular gland. This layer also forms the stylomandibular liga- ment, which separates the parotid from the submandibular gland. Infe- riorly the investing fascia attaches to the hyoid, clavicle, acromion, and spine of the scapula, but first splits to encompass the intermediate tendon of the omohyoid and form the suprasternal space. The super- ficial layer of deep cervical fascia contributes to the lateral aspect of the carotid sheath. The middle layer of deep cervical fascia, or visceral fascia, is com- posed of a muscular and visceral division. The muscular division sur- rounds the strap muscles (sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid, omohyoid). The visceral division surrounds the buccinator, pharyngeal constrictor muscles, larynx, trachea, esophagus, thyroid, and parathy- roid glands. The visceral division forms a pretracheal fascia that overlies the trachea. The visceral division also contributes the buccopharyngeal fascia posterior to the esophagus, which separates the esophagus from the deep layer of deep cervical fascia and forms the anterior border of the retropharyngeal space. The buccopharyngeal fascia forms two raphae: (1) one in the posterior midline that adheres to the alar layer of the deep layer, and (2) the pterygomandibular raphe of the lateral pharynx. The middle layer also contributes to the medial aspect of the carotid sheath. The deep layer of deep cervical fascia, or prevertebral fascia, divides into two layers: the prevertebral and alar layers. The prevertebral layer envelops the paraspinous muscles and cervical vertebrae, lying anterior to the vertebral bodies from the skull base to the coccyx, and attaching laterally to the transverse processes. It covers the scalene muscles and forms the floor of the posterior triangle. As it courses anteromedially, it contributes to the posterior carotid sheath and splits to form the alar layer. The alar layer lies between the prevertebral layer and the buccopharyngeal fascia of the visceral middle layer. The alar fascia separates the retropharyngeal and danger spaces and covers the cervical sympathetic trunk. The carotid sheath extends from the skull base to the thorax, and is a confluence of each layer of deep fascia. The sheath contains the common carotid artery, internal jugular vein, vagus nerve, and ansa cervicalis.
3 2.Name the deep neck spaces. Be prepared to draw pictures to help us understand. AL 1 1 Anatomy ofthe Neck: General Considerations 509 Muscles I. Scalene group 2. Levator of the scapula 3. Splenius of the head 4. Semispinal of the head 5. Rhomboids 6. Prevertebral group Nerves I. Brachial plexus 2. Cervical plexus 3. Phrenic nerve THE FASCIAE OF THE NECK (FIG. 11.1) Superficial Fascia Comprises two layers: Supraplatysmal Infraplatysmal Superficial Space #4 Space of Middle Layer Deep Fascia (Anterior Visceral) Trachea
4 Esophagus Retropharyngeal Space #3 (Posterior Visceral) B uccopharyngeal Middle Layer Deep Prevertebral Space #5 Danger Space #4 Prevertebral Fascia Superficial Fascia Superficial Layer Deep Fascia Deep Layer Deep Fascia Lateral Pharyngeal Space
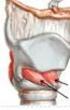
5 Visceral Vascular Space Space of Superficial Layer Deep Fascia Space of Deep Layer Deep Fascia A Fasciae Spaces FIG A,B: Fasciae and spaces of the neck. Neck Spaces The above fasciae and the structures within the neck form real and potential spaces. Many of these compartments openly communicate with each other, and some spaces are contiguous with distant regions of the body, offering a route of rapid transit for infections. The neck spaces can be organized by their location: the face (buccal, canine, masticator, parotid), suprahyoid neck (peritonsillar, submandibular, sublingual, parapharyngeal), infrahyoid neck (anterior visceral), and along the length of the neck (retropharyngeal, danger, prevertebral, carotid). Parapharyngeal Space Also called the lateral pharyngeal or pharyngomaxillary space, the para- pharyngeal space is an inverted pyramid with its superior base at the skull base and its inferior apex at the junction of the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and greater cornu of the hyoid bone. The pterygomandibular raphe and medial pterygoid muscle bound the space anteriorly, while the prevertebral fascia bounds it posteriorly. The supe- rior constrictor, tensor, and levator veli palatini muscles form the medial boundary, and the parotid gland, mandible, and lateral pterygoid muscle bound it laterally. The styloid process divides the space into two compartments: the prestyloid compartment, which is anterior to the styloid process, and the post-styloid compartment, which is posterior to the process. The prestyloid compartment contains fat, muscle (styloglossus and stylo- pharyngeus), lymph nodes, deep lobe of the parotid, internal maxillary artery, inferior alveolar, lingual, and auriculotemporal nerves. The post- styloid compartment contains neurovascular structures: carotid artery, internal jugular vein, sympathetic chain, and cranial nerves IX, X, XI, and XII. The parapharyngeal space provides a central connection for the major deep neck spaces. It connects posteromedially with the retropha- ryngeal space, inferiorly with the submandibular space, and laterally with the masticator space. The carotid sheath courses through the space into the mediastinum. Lateral extension from the peritonsillar space directly invades the parapharyngeal space.
6 Submandibular and Sublingual Spaces These two spaces are best discussed together, because they functionally comprise a single space. The mucosa of the floor of the mouth forms the superior border of the submandibular space, and the digastric muscle and hyoid bone form the inferior. Anteriorly, the mylohyoid muscle and anterior belly of digastric bound the submandibular space, with the posterior belly of the digastric and stylomandibular ligament serving as its posterior borders. The hyoglossus, mylohyoid, styloglos- sus, genioglossus, and geniohyoid muscles are medial, with the platysma and mandible being lateral. The mylohyoid muscle divides the submandibular space into a superior sublingual compartment and an inferior submaxillary com- partment. This sublingual compartment is also called the sublingual space, and contains the sublingual gland and Wharton s duct. The supramylohyoid sublingual space is lateral to the geniohyoid and gen- ioglossus muscles. The sublingual space openly connects to the sub- maxillary compartment around the free posterior edge of the mylohyoid. The inframylohyoid submaxillary compartment, sometimes itself called the submandibular space, connects to its corresponding space contralat- erally and contains the submandibular gland and lymph nodes. The relationship of the mylohyoid to the tooth apices, the mylo- hyoid line, determines the most likely route of odontogenic infectious spread. The teeth apices anterior to the second molar lie superior to the mylohyoid line and thus involve the sublingual space. Infections of the second and third molars initially involve the submandibular or para- pharyngeal space, because their roots extend below the mylohyoid line. Retropharyngeal Space The retropharyngeal space, extending from the skull base to the medi- astinum at the tracheal bifurcation, refers to the lymph node and con- nective tissue containing potential space between the middle and deep layers of deep cervical fasciae. The space lies anterior to the alar fascia of the deep layer and posterior to the buccopharyngeal fascia of the middle layer that lines the posterior pharynx and esophagus. The carotid sheath is lateral to the space. It typically becomes involved by direct spread from the parapharyngeal space, or lymphatic spread from the paranasal sinuses or nasopharyngeal region, primarily in children. Danger Space The danger space, so named because of the potential for rapid inferior spread of infection to the posterior mediastinum through its loose areolar tissue, extends from the skull base to the diaphragm. This poten- tial space lies between the retropharyngeal and prevertebral spaces. The deep layer of deep cervical fascia subdivisions bound this space. The alar layer forms its anterior border, and the prevertebral layer forms its posterior border. Laterally, the transverse processes of the vertebrae enclose the danger space. The sympathetic trunk courses through this space. Infectious infiltration from the retropharyngeal, parapharyngeal, or prevertebral spaces are the primary routes to the danger space.
7 Prevertebral Space The prevertebral space is enclosed by the prevertebral fascia, vertebral bodies and transverse processes, and extends from the clivus of the skull base to the coccyx. It is a compact potential space that contains dense areolar tissue and lies posterior to the danger space. In addition to the paraspinous, prevertebral, and scalene muscles, it contains the vertebral artery and vein, brachial plexus, and phrenic nerve. The main pathways of spread to the prevertebral space are from infection of the vertebral bodies and penetrating injuries. Tuberculosis of the spine may breach the space and form a Pott s abscess. Masticator Space The superficial layer of deep cervical fascia defines the masticator space upon splitting at the inferior border of the mandible to cover the medial pterygoid and masseter muscles. Next, the fascia continues superiorly to cover the inferior tendon of the temporalis muscle and incorporate with the superficial temporalis fascia. It contains the mandible and muscles of mastication (masseter, temporalis, medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid). The masticator space also contains the third portion of the trigeminal nerve, which enters through the foramen ovale, the internal maxillary artery, and much of the buccal fat pad. This space occupies a position anterolateral to the parapharyngeal space. The masticator space is also further divided into subspaces: the masseteric space between the masseter muscle and ramus of mandible, the pterygoid space between the pterygoid muscles and ramus, the superficial temporal space between the superficial temporal fascia and temporalis muscle, and the deep temporal space between the deep temporal fascia and temporal bone. Transmission of infection into the masticator space is most commonly from the third mandibular molars. Peritonsillar Space The peritonsillar space consists of loose connective tissue between the capsule of the palatine tonsil and the superior constrictor muscle. The anterior and posterior tonsillar pillars contribute to its anterior and posterior borders, respectively. The posterior tongue forms the inferior boundary. Peritonsillar infections may readily spread to the parapha- ryngeal space. Parotid Space The superficial layer of deep cervical fascia forms the parotid space as it splits to surround the parotid gland. However, the fascia, which does not enclose the superomedial aspect of the gland, permits communica- tion with the prestyloid compartment of the parapharyngeal space. The space also contains the facial nerve, external carotid artery, and posterior facial vein. It occupies a position lateral to the parapharyngeal space. Carotid Space The carotid, or visceral vascular, space is the potential space within the carotid sheath containing the carotid artery, internal jugular vein, vagus nerve, and sympathetic plexus. Infection from the
8 surrounding para- pharyngeal space, penetrating trauma, or intravenous drug use may potentiate spread into this space. Anterior Visceral Space The visceral division of the middle layer of deep cervical fascia encloses the anterior visceral space, or pretracheal space, which lies immediately anterior to the trachea. It extends from the thyroid cartilage to the superior mediastinum. It contains the pharynx, esophagus, larynx, trachea, and thyroid gland. Perforation of the anterior esophageal wall by endoscopic instrumentation, foreign bodies, or trauma may intro- duce infection to this space. 3.Where is the Lincoln Highway and what is the importance? CB 4.Microbiology of deep neck infections. CB 5.Most common etiology of deep neck infections. Name some others. TT 6.You order a lateral neck film to rule out a retropharyngeal abscess. What are the radiographic criteria for widening of this space? AL Lateral neck films are useful for quickly evaluating the upper aerodiges- tive tract in cases of suspected retropharyngeal abscess or supraglottitis. Presence of an air-fluid level or greater than 5mm of thickening in a child or greater than 7 mm of thickening in an adult of the prevertebral tissue at C2 indicate retropharyngeal infection until proven otherwise. 7.Indications for surgical management of deep neck infections. CB 8.What is Ludwig s angina? TT 9.Your friend wants to get a cat, but is worried about possible infections. What can you tell her? CB 10.Scrofula vs. non tuberculosis infections of the neck. HH 11.A patient presents with a slow growing, painless submandibular mass. Biopsies reveal gram-positive anaerobic bacillus with sulfur granules. What is the diagnosis and how should it be treated? HH
Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy
 Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy Kris Cummings, M.D. Axial CT Unlabeled Labeled Deep s/lymph Node Chains s/lymph Nodes Temporalis Muscle Occipitalis Muscle s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph
Soft Tissue Neck CT Anatomy Kris Cummings, M.D. Axial CT Unlabeled Labeled Deep s/lymph Node Chains s/lymph Nodes Temporalis Muscle Occipitalis Muscle s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph Nodes s/lymph
IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Level IA: Submental Group
 IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Fig. 1 The level system is used for describing the location of lymph nodes in the neck: Level I, submental and submandibular group; Level II, upper jugular
IV. DEFINITION OF LYMPH NODE GROUPS (FIGURE 1) Fig. 1 The level system is used for describing the location of lymph nodes in the neck: Level I, submental and submandibular group; Level II, upper jugular
Cranial Nerve I Name: Foramen: Fiber Type: Function: Branches: Embryo:
 Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Cranial Nerve I Olfactory nerve Cribiform plate Special sensory Olfactory bulbs, Smell Olfactory filaments CNS (ectoderm) cribiform plate sensory = Cranial Nerve II Other: Optic nerve Optic canal Special
Deep Neck Spaces and Infections
 Deep Neck Spaces and Infections Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Faculty Advisor: Byron J. Bailey, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation April 17, 2002
Deep Neck Spaces and Infections Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Faculty Advisor: Byron J. Bailey, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation April 17, 2002
Key Points. Eric R. Oliver M. Boyd Gillespie
 Eric R. Oliver M. Boyd Gillespie Key Points Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is an increasingly common cause of deep neck space infections. Ultrasound will likely be applied more frequently
Eric R. Oliver M. Boyd Gillespie Key Points Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is an increasingly common cause of deep neck space infections. Ultrasound will likely be applied more frequently
Infection of the neck is a common clinical. Deep Neck Spaces radiology and review of deep neck infections at King Abdulaziz University Hospital
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Deep Neck Spaces radiology and review of deep neck infections at King Abdulaziz University Hospital Khaled Al-Noury a, Alsaid Lotfy b Otolaryngology Department a, King Abdulaziz University,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Deep Neck Spaces radiology and review of deep neck infections at King Abdulaziz University Hospital Khaled Al-Noury a, Alsaid Lotfy b Otolaryngology Department a, King Abdulaziz University,
by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin
 by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin body mechanics palpation of the anterior neck ESOUCES For more information go to www.medlineplus.gov and search under anterior neck. The anterior
by joseph e. muscolino, DO photography by yanik chauvin body mechanics palpation of the anterior neck ESOUCES For more information go to www.medlineplus.gov and search under anterior neck. The anterior
Deep Neck Space Infections. Michael D. Puricelli, M.D. Jeffrey B. Jorgensen, M.D.
 Deep Neck Space Infections Michael D. Puricelli, M.D. Jeffrey B. Jorgensen, M.D. Goals Review fascia and fascial spaces to facilitate understanding of how infections move through the neck. Provide current
Deep Neck Space Infections Michael D. Puricelli, M.D. Jeffrey B. Jorgensen, M.D. Goals Review fascia and fascial spaces to facilitate understanding of how infections move through the neck. Provide current
CMEArticle Infections of the deep neck spaces
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(5) : 305 CMEArticle Infections of the deep neck spaces Amogh Hegde 1, MD, FRCR, Suyash Mohan 2, MD, PDCC, Winston Eng Hoe Lim 3, FRCR ABSTRACT Deep neck infections (DNI) have a
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(5) : 305 CMEArticle Infections of the deep neck spaces Amogh Hegde 1, MD, FRCR, Suyash Mohan 2, MD, PDCC, Winston Eng Hoe Lim 3, FRCR ABSTRACT Deep neck infections (DNI) have a
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck. Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW
 Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System of the Neck Adam Koleśnik, MD Department of Descriptive and Clinical Anatomy Center of Biostructure Research, MUW Autonomic nervous system sympathetic parasympathetic enteric Autonomic
Deeper: geniohyoid, cricothyroid
 VitalStim Therapy ELECTRODE PLACEMENT WITH NECK MUSCLES Electrode Placements Placement 1 - All electrodes aligned vertically along midline - First electrode is placed well above hyoid bone - Second electrode
VitalStim Therapy ELECTRODE PLACEMENT WITH NECK MUSCLES Electrode Placements Placement 1 - All electrodes aligned vertically along midline - First electrode is placed well above hyoid bone - Second electrode
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions
 The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
The Axial Skeleton Eighty bones segregated into three regions Skull Vertebral column Bony thorax Bones of the Axial Skeleton Figure 7.1 The Skull The skull, the body s most complex bony structure, is formed
Suprahyoid Neck Lesions. C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Professor of Radiology Weill Cornell Medical College NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital
 Suprahyoid Neck Lesions C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Professor of Radiology Weill Cornell Medical College NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital Objectives To introduce spatial concept of neck anatomy with imaging
Suprahyoid Neck Lesions C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Professor of Radiology Weill Cornell Medical College NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital Objectives To introduce spatial concept of neck anatomy with imaging
Spread of Dental Infection
 Spread of Dental Infection The healthy body usually lives in balance with a number of resident normal flora. However, pathogens can invade and initiate an infectious process. 1 Dental infections involving
Spread of Dental Infection The healthy body usually lives in balance with a number of resident normal flora. However, pathogens can invade and initiate an infectious process. 1 Dental infections involving
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON. 1. Frontal Bone. 2. Parietal Bones. 3. Temporal Bones. CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired)
 Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Objectives AXIAL SKELETON SKULL 1. On a skull or diagram, identify and name the bones of the skull 2. Identify the structure and function of the bones of the skull 3. Describe how a fetal skull differs
Anatomy of Human Muscles
 Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Anatomy of Human Muscles PURPOSE: To develop skill in identifying muscle names and locations relative to other regional structures. To determine origin, insertion and principle action of muscles through
Recurrent & Persistent Papillary Thyroid Cancer Central Nodal Dissection vs. Node-Picking Patterns of Nodal Metastases Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve,
 Recurrent & Persistent Papillary Thyroid Cancer Central Nodal Dissection vs. Node-Picking Patterns of Nodal Metastases Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve, Larynx, Trachea, & Esophageal Management Robert C. Wang,
Recurrent & Persistent Papillary Thyroid Cancer Central Nodal Dissection vs. Node-Picking Patterns of Nodal Metastases Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve, Larynx, Trachea, & Esophageal Management Robert C. Wang,
TNM Staging of Head and Neck Cancer and Neck Dissection Classification
 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE TO TNM Staging of Head and Neck Cancer and Neck Dissection Classification Fourth Edition 2014 All materials in this ebook are copyrighted by the American Academy of Otolaryngology
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE TO TNM Staging of Head and Neck Cancer and Neck Dissection Classification Fourth Edition 2014 All materials in this ebook are copyrighted by the American Academy of Otolaryngology
LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE
 ZOO 4377L - VERTEBRATE MORPHOLOGY LAB LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE Name: Name: SSN: SSN: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZOO 4377L - VERTEBRATE MORPHOLOGY LAB LABS 8 & 9: CAT MUSCULATURE Name: Name: SSN: SSN: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Upper Limb QUESTIONS UPPER LIMB: QUESTIONS
 1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
1 Upper Limb QUESTIONS 1.1 Which of the following statements best describes the scapula? a. It usually overlies the 2nd to 9th ribs. b. The spine continues laterally as the coracoid process. c. The suprascapular
Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
 Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Sean M. Healy, D.D.S. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Francis B. Quinn, M.D., FACS Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery The University of Texas
Local Anesthesia Techniques in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Sean M. Healy, D.D.S. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Francis B. Quinn, M.D., FACS Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery The University of Texas
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
Clarification of Terms
 Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
Shoulder Girdle Clarification of Terms Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus What is the purpose (or function) of the shoulder and entire upper
ENT Emergencies. Injuries of the Neck. Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital
 ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
ENT Emergencies Injuries of the Neck Registrar Dept Trauma and emergency Medicine Tygerberg Hospital Neck Injuries Blunt and Penetrating Trauma Blunt Injuries Blunt trauma direct/indirect Trauma to larynx
Respiratory System. Chapter 21
 Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
TNM Staging of Head and Neck Cancer and Neck Dissection Classification
 QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE TO TNM Staging of Head and Neck Cancer and Neck Dissection Classification Fourth Edition 2014 All materials in this ebook are copyrighted by the American Academy of Otolaryngology
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE TO TNM Staging of Head and Neck Cancer and Neck Dissection Classification Fourth Edition 2014 All materials in this ebook are copyrighted by the American Academy of Otolaryngology
Buccinator Presses cheek against molar teeth Facial (CNVII) wrinkles forehead
 Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Muscles to Identify on the Cadaver and/or Models You are required to identify each of the following muscles or associated structures on the cadavers and/or models in lab. If the box is shaded in a particular
Maxillary Sinus. (Antrum of Higmore)
 Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Developmental Cysts. Non-odontogenic Cysts. Nasopalatine duct cyst. Palatal and gingival cysts of newborns
 Non-odontogenic Cysts Dr. Ioannis G. Koutlas Division of Oral Pathology Developmental Cysts a.k.a. fissural cysts Exact pathogenesis of some of them uncertain Generally, slow increase May be identified
Non-odontogenic Cysts Dr. Ioannis G. Koutlas Division of Oral Pathology Developmental Cysts a.k.a. fissural cysts Exact pathogenesis of some of them uncertain Generally, slow increase May be identified
The Muscular System Interactions of Skeletal Muscles in the Body (p. 321)
 The Muscular System Interactions of Skeletal Muscles in the Body (p. 321) Naming Skeletal Muscles (pp. 321 322) Muscle Mechanics: Importance of Fascicle Arrangement and Leverage (pp. 322 324) Arrangement
The Muscular System Interactions of Skeletal Muscles in the Body (p. 321) Naming Skeletal Muscles (pp. 321 322) Muscle Mechanics: Importance of Fascicle Arrangement and Leverage (pp. 322 324) Arrangement
DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE
 2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
2012-2013 ORAL BIOLOGY DEVELOPMENT AND GROWTH OF THE MANDIBLE Ass. Prof. Dr. Heba M. Elsabaa Development and Growth of the Mandible DEVELOPMENT OF THE MANDIBLE The Mandible Is the largest and strongest
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM - THE AXIAL SKELETON Chapter 7 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 1 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON Skeletal System forms the framework of the body. TYPES OF BONES: FOUR PRINCIPAL
TMJ Dysfunction & Pain
 TMJ Dysfunction & Pain The temporomandibular joints (TMJs) are two of the most functionally important and frequently used joints in the body. It is with these joints that important processes such as chewing,
TMJ Dysfunction & Pain The temporomandibular joints (TMJs) are two of the most functionally important and frequently used joints in the body. It is with these joints that important processes such as chewing,
Oct 17:Deep Neck Space Infections (updated 08/06) Oct 17: Deep Neck Space Infections (updated 08/06) Vacation: none! ; Preceptor
 Oct 17: Deep Neck Space Infections (updated 08/06) Vacation: none! ; Preceptor 1. (Deya) Describe the anatomy of the cervical fascia. 2. (Deya) Name the deep neck spaces. Be prepared to draw pictures to
Oct 17: Deep Neck Space Infections (updated 08/06) Vacation: none! ; Preceptor 1. (Deya) Describe the anatomy of the cervical fascia. 2. (Deya) Name the deep neck spaces. Be prepared to draw pictures to
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Topography of the Mouth and Tooth Structure. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Topography of the Mouth and Tooth Structure. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Topography of the Mouth and Tooth Structure. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Identify
Muscular System. Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body
 Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Muscular System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major muscles of the body Identify the action of major muscles of the body Structures to be identified: Muscle actions: Extension Flexion Abduction
Laerdal' Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton
 Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
Human Anatomy Manual The Skeleton Laerdal Texas P.O. Box 38.226 EM. 116 Gatesville,Texas U.S.A.76528 U.S.A.1-800-433-5539 IntemationaI1-254-865-7221 24 Hour Fax 254-865-8011 ~ Laerdal' TABLE OF CONTENTS
6. Histopathology of Alveoli 7. Surfactant 8. Blood supply of lungs 9. Lymphatics of Lungs 10. Nerve supply of Lungs 11. Pleura 12.
 ANATOMY OF LUNGS - 1. Gross Anatomy of Lungs 2. Surfaces and Borders of Lungs 3. Hilum and Root of Lungs 4. Fissures and Lobes of Lungs 5. Bronchopulmonary segments 6. Histopathology of Alveoli 7. Surfactant
ANATOMY OF LUNGS - 1. Gross Anatomy of Lungs 2. Surfaces and Borders of Lungs 3. Hilum and Root of Lungs 4. Fissures and Lobes of Lungs 5. Bronchopulmonary segments 6. Histopathology of Alveoli 7. Surfactant
Muscles of the Spinal Column. Chapter 12
 Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
Muscles of the Spinal Column Chapter 12 Cervical Muscles Splenius Splenius (capitis and cervicis) Origin: Cervicis spinous process of T3-T6 Capitis - lower half of ligmentum nuchea & spinous process of
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology Bio 110 lab quiz study guide Bio 110 lab quiz study guide By: Darrell Davies !!!CAUTION!!! This power point presentation is intended to be used as an add on
Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology Bio 110 lab quiz study guide Bio 110 lab quiz study guide By: Darrell Davies !!!CAUTION!!! This power point presentation is intended to be used as an add on
Digestive System AKA. GI System. Overview. GI Process Process Includes. G-I Tract Alimentary Canal
 Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Digestive System AKA G-I Tract Alimentary Canal Overview GI System Consists of Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus About 30 in length Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
its lifetime. The skeletal system is divided into: 1. Axial Division: bones of the body s axis (skulll, ribs, vertebrae)
 The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
The Axial Skeleton The basic features of the human skeleton have been shaped by evolution, but the detailed characteristics of each bone reflect the stresses put on it. As a result, the skeleton changes
Medical Terminology, Anatompy & Physiology
 1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
1. Which of the following BEST describes the anatomical position? a. Supine with arms crossed over the chest and knees slightly bent b. Standing, facing forward, with arms raised above the head c. Standing,
Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis
 2 Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis Intra-Abdominal Anatomy of the Male Pelvic Region Bladder Medial Umbilical Ligaments Lateral Umbilical Ligaments Spermatic Cords Iliac Vessels Ureters Seminal Vesicular
2 Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis Intra-Abdominal Anatomy of the Male Pelvic Region Bladder Medial Umbilical Ligaments Lateral Umbilical Ligaments Spermatic Cords Iliac Vessels Ureters Seminal Vesicular
Carotid Endarterectomy. Mark Shikhman, MD, Ph.D., CSA Andrea Scott, CST
 Carotid Endarterectomy Mark Shikhman, MD, Ph.D., CSA Andrea Scott, CST This lecture presents one of the most often vascular surgical procedures carotid endarterectomy. This type of surgery is performed
Carotid Endarterectomy Mark Shikhman, MD, Ph.D., CSA Andrea Scott, CST This lecture presents one of the most often vascular surgical procedures carotid endarterectomy. This type of surgery is performed
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Vertebral
Chapter 11 The Muscular System. Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin and Insertion
 Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
Chapter 11 The Muscular System Skeletal muscle major groupings How movements occur at specific joints Learn the origin, insertion, function and innervation of all major muscles Important to allied health
The Abdominal Wall And Hernias. Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK
 The Abdominal Wall And Hernias Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK The Abdominal Wall The structure of the abdominal wall is similar in principle to the thoracic wall. There are
The Abdominal Wall And Hernias Stanley Kurek, DO, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery UTMCK The Abdominal Wall The structure of the abdominal wall is similar in principle to the thoracic wall. There are
Chapter 21 Fractures of the Upper Thoracic Spine: Approaches and Surgical Management
 Chapter 21 Fractures of the Upper Thoracic Spine: Approaches and Surgical Management Sean D Christie, M.D., John Song, M.D., and Richard G Fessler, M.D., Ph.D. INTRODUCTION Fractures occurring in the thoracic
Chapter 21 Fractures of the Upper Thoracic Spine: Approaches and Surgical Management Sean D Christie, M.D., John Song, M.D., and Richard G Fessler, M.D., Ph.D. INTRODUCTION Fractures occurring in the thoracic
Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body
 Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
Epicranius Anatomy and Physiology 121: Muscles of the Human Body Covers upper cranium Raises eyebrows, surprise, headaches Parts Frontalis Occipitalis Epicranial aponeurosis Orbicularis oculi Ring (sphincter)
21140 Closed treatment of reimplantation. mandibular or maxillary and/or stabilization. alveolar ridge fracture of accidentally
 Medical in Nature Oral Surgery CDT Code Description (CDT code) CPT Code Description (CPT Code) D7270 Tooth 21140 Closed treatment of reimplantation mandibular or maxillary and/or stabilization alveolar
Medical in Nature Oral Surgery CDT Code Description (CDT code) CPT Code Description (CPT Code) D7270 Tooth 21140 Closed treatment of reimplantation mandibular or maxillary and/or stabilization alveolar
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review
 Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Name: Period: Unit 4: Skeletal System Test Review Test Review 1. List four functions of the skeletal system: a. b. c. d. 2. Define ossification and identify the roles of the osteoblasts, osteocytes, and
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Chapter 10: The Muscular System
 Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Chapter 10: The Muscular System Objectives: 1. Describe the function of prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. 2. List the criteria used in naming muscles. Provide an example to illustrate
Regional Anesthesia Blocks in Head and Face
 Regional Anesthesia Blocks in Head and Face Resident Physician: Leon Martinez, MD Faculty Mentor: Paul Brindley, MD, FACS The University of Texas Medical Branch UTMB Health Department of Otolaryngology
Regional Anesthesia Blocks in Head and Face Resident Physician: Leon Martinez, MD Faculty Mentor: Paul Brindley, MD, FACS The University of Texas Medical Branch UTMB Health Department of Otolaryngology
MD 2016. Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy. A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience
 MD 2016 Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
MD 2016 Back Muscles & Movements Applied Anatomy A/Prof Chris Briggs Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
SECTION 2. Oral Maxillofacial Surgeon Services. Table of Contents
 SECTION 2 Table of Contents Table of Contents 1. GENERAL POLICY (Updated 4/1/12)... 3 1-1 Credentials... 3 1-2 Clients Enrolled in a Managed Care Plan... 3 1-3 Clients NOT Enrolled in a Managed Care Plan...
SECTION 2 Table of Contents Table of Contents 1. GENERAL POLICY (Updated 4/1/12)... 3 1-1 Credentials... 3 1-2 Clients Enrolled in a Managed Care Plan... 3 1-3 Clients NOT Enrolled in a Managed Care Plan...
Dentistry Students (2014/2015 entry) Session 2015-2016, Term 2
 Number of Units Dentistry Students (2014/2015 entry) Session 2015-2016, Term 2 Course Name 2.0 Anatomical Sciences II (theory) 1.0 Anatomical Sciences II (practical) 1.0 Parasitology 2.0 Psychology 1.5
Number of Units Dentistry Students (2014/2015 entry) Session 2015-2016, Term 2 Course Name 2.0 Anatomical Sciences II (theory) 1.0 Anatomical Sciences II (practical) 1.0 Parasitology 2.0 Psychology 1.5
Atlas of Human Anatomy By Frank H. Netter, MD (5e to 6e)
 5e to 6e, see pages 1-13 Atlas of Human Anatomy By Frank H. Netter, MD (5e to 6e) 5e Plate # 6e Plate # Plate Title 1 1 Head and Neck: Surface Anatomy 2 2 Cutaneous Nerves of Head and Neck 3 3 Superficial
5e to 6e, see pages 1-13 Atlas of Human Anatomy By Frank H. Netter, MD (5e to 6e) 5e Plate # 6e Plate # Plate Title 1 1 Head and Neck: Surface Anatomy 2 2 Cutaneous Nerves of Head and Neck 3 3 Superficial
10. The Muscular System Text The McGraw Hill Companies, 2003 CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 Muscles of the thigh to upper calf (MRI) The Muscular System CHAPTER OUTLINE The Structural and Functional Organization of Muscles 326 The Functions of Muscles 326 Connective Tissues of a Muscle
CHAPTER 10 Muscles of the thigh to upper calf (MRI) The Muscular System CHAPTER OUTLINE The Structural and Functional Organization of Muscles 326 The Functions of Muscles 326 Connective Tissues of a Muscle
Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions
 Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions I. Exercise Generalizations: A. Patients with post-traumatic TMJ problems or with recent-onset dysfunction that is largely posture-related will generally
Temporo-Mandibular Joint Complex Exercise Suggestions I. Exercise Generalizations: A. Patients with post-traumatic TMJ problems or with recent-onset dysfunction that is largely posture-related will generally
MOLLOY COLLEGE DIVISION OF NURSING NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAMS. Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam
 DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
DIVISION OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2009). (10 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination and history
Anatomy & Physiology 120. Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Anatomy & Physiology 120 Lab #7 Muscle Tissue and Skeletal Muscles What you Need to Know Look briefly at the Structure of: 1) Skeletal, 2) Smooth & 3) Cardiac Muscle Naming, Identification, Functions You
Alimentary canal (gastrointestinal or GI tract) continuous coiled hollow tube
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Gross Anatomy Function The Digestive System Functions Ingestion taking in food Digestion breaking food down both physically and chemically Absorption movement of
I. The basic function of the digestive system is
 Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Chapter 15, Digestive System - ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. The basic function of the digestive system is. This process is called. II. List 2 other names for the digestive tract: A. B. III. The digestive
Examine the neck. Lumps in the neck. - thyroglossal cyst - pharyngeal pouch
 Lumps in the neck Midline - goitre - thyroglossal cyst - pharyngeal pouch Examine the neck Lateral - lymph node - sebaceous cyst / lipoma - cystic hygroma/ branchial cyst - vascular: aneurysm, tumour -
Lumps in the neck Midline - goitre - thyroglossal cyst - pharyngeal pouch Examine the neck Lateral - lymph node - sebaceous cyst / lipoma - cystic hygroma/ branchial cyst - vascular: aneurysm, tumour -
Head and Neck Exam. Charlie Goldberg, M.D. [email protected]
 Head and Neck Exam Charlie Goldberg, M.D. [email protected] Hammer & Nails icon indicates A Slide Describing Skills You Should Perform In Lab Observation and Palpation Note right sided neck/jaw area
Head and Neck Exam Charlie Goldberg, M.D. [email protected] Hammer & Nails icon indicates A Slide Describing Skills You Should Perform In Lab Observation and Palpation Note right sided neck/jaw area
The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
14 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The Central Nervous System
Introduction to Dental Anatomy
 Introduction to Dental Anatomy Vickie P. Overman, RDH, MEd Continuing Education Units: N/A This continuing education course is intended for dental students and dental hygiene students. Maintaining the
Introduction to Dental Anatomy Vickie P. Overman, RDH, MEd Continuing Education Units: N/A This continuing education course is intended for dental students and dental hygiene students. Maintaining the
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation
 Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
TNM STAGING OF HEAD AND NECK CANCER AND NECK DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION
 Pocket Guide To TNM STAGING OF HEAD AND NECK CANCER AND NECK DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION Edited by Daniel G. Deschler, MD Terry Day, MD AAO HNS/F American Head and Neck Society Pocket Guide to NECK DISSECTION
Pocket Guide To TNM STAGING OF HEAD AND NECK CANCER AND NECK DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION Edited by Daniel G. Deschler, MD Terry Day, MD AAO HNS/F American Head and Neck Society Pocket Guide to NECK DISSECTION
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI
 Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Orbit & Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, & VI PCC Year 1, Spring Quarter Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Life Sciences Building 123 OBJECTIVES: to understand the anatomy of the bony orbit and its contents, in particular,
Chapter 15. Sympathetic Nervous System
 Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Chapter 15 Sympathetic Nervous System Somatic versus Autonomic Pathways Somatic efferent innervation ACh Myelinated fiber Somatic effectors (skeletal muscles) Autonomic efferent innervation ACh ACh or
Navigating Anorectal Anatomy: Terms, Planes, Spaces, Structures
 Navigating Anorectal Anatomy: Terms, Planes, Spaces, Structures Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Department of Biomedical Sciences College of Osteopathic Medicine Ohio University Athens,
Navigating Anorectal Anatomy: Terms, Planes, Spaces, Structures Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Lawrence M. Witmer, PhD Department of Biomedical Sciences College of Osteopathic Medicine Ohio University Athens,
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine. Bones of the Spine (Vertebrae)
 Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine The spine, also called the spinal column, vertebral column or backbone, consists of bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and joints. In addition, the spine serves
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015. Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey.
 Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Vertebral anatomy study guide. Human Structure Summer 2015 Prepared by Daniel Schmitt, Angel Zeininger, and Karyne Rabey. 1. Plan of Action: In this guide you will learn to identify these structures: Cervical
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot
 Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
Reavis High School Anatomy and Physiology Curriculum Snapshot Unit 1: Introduction to the Human Body 10 days As part of this unit, students will define anatomy, physiology, and pathology. They will identify
LUMBAR LAMINECTOMY AND DISCECTOMY. Basic Anatomical Landmarks: Posterior View Lumbar Spine
 Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between the ribs and the pelvis. In the spinal column, the last five vertebrae (from superior to inferior, L1-L5) Laminectomy Surgical
Lumbar Relating to the loins or the section of the back and sides between the ribs and the pelvis. In the spinal column, the last five vertebrae (from superior to inferior, L1-L5) Laminectomy Surgical
Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic System
 Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic System Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, Chapter 3 2. Dissection Guide for Human Anatomy, Lab 4 Objectives: 1. Osteocartilaginous thoracic
Dr. Weyrich G04: Anterior Thoracic Wall, Breast and Lymphatic System Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, Chapter 3 2. Dissection Guide for Human Anatomy, Lab 4 Objectives: 1. Osteocartilaginous thoracic
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014
 PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, [email protected] Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, [email protected] Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
PRIMARY HUMAN ANATOMY: BIOL20600 SPRING 2014 Instructors: Kit Muma, Rm. 158 CNS, (607) 274-3610, [email protected] Michelle Bamberger, Rm. 118A Williams Hall, [email protected] Mark Baustian, Rm. 118A
UNMH Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinical Privileges
 All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees effective: 09/26/2014 INSTRUCTIONS Applicant: Check off the "Requested" box for each privilege requested.
All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees effective: 09/26/2014 INSTRUCTIONS Applicant: Check off the "Requested" box for each privilege requested.
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Histological Organization. Overview of Digestive System. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Skin of eyebrows galea aponeurotica. Muscle and skin of mouth
 : SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
: SEE ALSO THE AP SITE FOR OTHER TABLES GROSS ANATOMY OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEMM Muscles of the Head and Neck: Occipitofrontalis Frontalis Occipitalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Buccinator Masseter
Anatomy of Bones and Joints
 C HAPTER 7 Learning Outcomes AFTER YOU COMPLETE THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Anatomy of Bones and Joints 7.1 General Considerations of Bones 150 1. Define the general anatomical terms for various
C HAPTER 7 Learning Outcomes AFTER YOU COMPLETE THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Anatomy of Bones and Joints 7.1 General Considerations of Bones 150 1. Define the general anatomical terms for various
Unilateral Nasal Polyps
 Unilateral Nasal Polyps This tutorial follows on from the rhinosinusitis tutorial but only concerns itself with the unilateral nasal polyp. The majority of unilateral nasal polyps form in the same way
Unilateral Nasal Polyps This tutorial follows on from the rhinosinusitis tutorial but only concerns itself with the unilateral nasal polyp. The majority of unilateral nasal polyps form in the same way
Page 1 of 9 BDS FINAL PROFESSIONAL EXAMINATION 2007 ORAL SURGERY (MCQs) Model Paper
 Page 1 of 9 Marks: 45 Total No. of MCQs 45 One mark for each Time: 45 minutes Q-1: Long term effect of radiotherapy to oral mucosa is characterized by: a) Epithelium becomes more keratinized. b) Sub mucosa
Page 1 of 9 Marks: 45 Total No. of MCQs 45 One mark for each Time: 45 minutes Q-1: Long term effect of radiotherapy to oral mucosa is characterized by: a) Epithelium becomes more keratinized. b) Sub mucosa
