Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 13 The Respiratory System. Short Answer. Figure 13.1
|
|
|
- Dortha Thomas
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
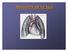
1 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Short Answer Figure 13.1 Using Figure 13.1, identify the following: 1) The nasal cavity is indicated by the letter. Answer: A 2) The right primary bronchus is indicated by letter. Answer: H 3) The trachea is indicated by letter. Answer: I 4) The diaphragm muscle is indicated by letter. Answer: G 5) The oral cavity is indicated by letter. Answer: C 6) The base of the right lung is indicated by letter. Answer: F 1
2 7) The nostrils are indicated by letter. 8) The apex of the right lung is indicated by letter. Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: 446 9) The larynx is indicated by letter. Answer: D 10) The pharynx is indicated by letter. Answer: J Fill in the blank or provide a short answer: 11) The three mucosa-covered projections into the nasal cavity that greatly increase surface area of mucosa exposed to air are called. Answer: conchae Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) The anterior portion of the palate that is supported by bone is called the. Answer: hard palate 13) The throat is also known as the. Answer: pharynx Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Inflammation of the sinuses that can cause marked changes in voice quality is called. Answer: sinusitis Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The large shield-shaped thyroid cartilage that protrudes anteriorly is commonly called the. Answer: Adam's apple 16) The mucosa-lined windpipe that extends from the larynx to the level of the fifth thoracic vertebra is called the. Answer: trachea 17) The tonsils found in the nasopharynx are called or. Answer: pharyngeal tonsils; adenoids Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The opening between the vocal folds is called the. Answer: glottis 2
3 19) The C-shaped rings that reinforce the trachea are constructed of cartilage. Answer: hyaline Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The flap of elastic cartilage that protects the opening of the larynx is called the. Answer: epiglottis 21) A procedure in which air within the lungs is used to forcibly expel an obstructing piece of food to avoid suffocation is called the. Answer: Heimlich maneuver 22) The central area between the two lungs that houses the heart, great blood vessels, bronchi, and esophagus is called the. Answer: mediastinum Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The smallest conducting passageways of the lungs are called. Answer: bronchioles Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) "Dust cells" that wander in and out of the alveoli, picking up bacteria, carbon particles, and other debris, are actually. Answer: macrophages Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) The air sacs of the lungs are called. Answer: alveoli Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The process of moving air into and out of the lungs is commonly called breathing or. Answer: pulmonary ventilation Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Gas exchange between the blood and tissue cells is called. Answer: internal respiration Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The inspiratory muscles that contract so we can inspire air are the and. Answer: diaphragm; external intercostals Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The presence of air in the intrapleural space is known as. Answer: pneumothorax Diff: 2 Page Ref:
4 30) Normal quiet breathing moves about ml of air into and out of the lungs with each breath. Answer: ) A mechanism that clears the upper respiratory passages, which is similar to a cough except that the expelled air is directed through the nasal cavities instead of the oral cavity, is called a. Answer: sneeze Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Air that remains in the conducting zone passageways and never reaches the alveoli is called the. Answer: dead space volume Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Respiratory capacities are measured with a. Answer: spirometer Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) An abnormal bubbling sound caused by diseased respiratory tissue, mucus, or pus is called. Answer: crackle Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Oxygen bound to hemoglobin molecules on RBCs is called. Answer: oxyhemoglobin Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Most carbon dioxide is dissolved in blood plasma and transported as. Answer: bicarbonate ion Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Inadequate oxygen delivery to body tissues is called. Answer: hypoxia Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) During internal respiration, the blood gas is loaded into the bloodstream. Answer: carbon dioxide Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) A normal respiratory rate of about breaths per minute is called. Answer: eupnea Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) The most important stimulus for breathing in a healthy person is the body's need to rid itself of the blood gas called. Answer: carbon dioxide Diff: 3 Page Ref: 457; 460 4
5 41) Enlargement of the alveoli and chronic inflammation of the lungs are characteristics of a respiratory disease called. Answer: emphysema Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Chronically inflamed, hypersensitive bronchial passages that can be irritated by dust mite and cockroach droppings are indicative of. Answer: asthma Diff: 2 Page Ref: 464 Multiple Choice 1) The conducting passageways of the respiratory system include all of the following structures EXCEPT: A) nose B) pharynx C) larynx D) trachea E) alveoli Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: 441 2) The respiratory conducting passageways perform all of the following functions EXCEPT: A) allow air to reach the lungs B) purify air C) humidify air D) exchange gases E) warm incoming air Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 441 3) Which one of the following terms does not apply to the nose: A) external nares B) nasopharynx C) nostrils D) nasal cavity E) nasal septum Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) What is the role of mucus in the nasal cavity: A) increase the air turbulence in the nasal cavity B) separate the oral from the nasal cavity C) lighten the skull D) act as a resonance chamber for speech E) trap incoming bacteria and other foreign debris Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: 442 5
6 5) The nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity by: A) the hard palate B) the nasal conchae C) the soft palate D) both the hard and soft palate E) both the nasal conchae and hard palate Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 442 6) Which one of the following bones does NOT contain paranasal sinuses: A) frontal B) sphenoid C) mandible D) ethmoid E) maxilla Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 442 7) Which one of the following is NOT a function of the paranasal sinuses: A) they lighten the skull B) they act as resonance chambers for speech C) they produce mucus D) they are olfactory receptors for smell E) they help to moisten air Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 443 8) Air from the nasal cavity enters the superior portion of the pharynx called the: A) nasopharynx B) oropharynx C) palatopharynx D) laryngopharynx E) tracheopharynx Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 443 9) The pharynogotympanic tubes, which drain the middle ear, open into the: A) nasopharynx B) oropharynx C) palatopharynx D) laryngopharynx E) tracheopharynx Answer: A 6
7 10) Tonsils that lie at the base of the tongue are called: A) adenoids B) pharyngeal tonsils C) palatine tonsils D) lingual tonsils E) pharyngotympanic tonsils Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Following the removal of the larynx, a person would be unable to: A) speak B) sneeze C) eat D) hear E) breathe Answer: A Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) The opening between the vocal cords is called the: A) epiglottis B) glottis C) larynx D) thyroid cartilage E) esophagus Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The flap of elastic cartilage that protects food from entering the larynx when swallowing is the: A) glottis B) thyroid cartilage C) Adam's apple D) epiglottis E) trachea Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Vibration due to exhaled air that results in speech is a function of the: A) complete voice box B) true vocal cords C) false vocal cords D) glottis E) epiglottis 7
8 15) Cilia of the trachea that beat continually propel contaminated mucus: A) toward the throat to be swallowed or spat out B) toward the nose to be sneezed out C) toward the epiglottis to be coughed out D) toward the lungs to be encapsulated E) toward the glottis to be hiccupped out Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The serous membrane covering the surface of the lungs is called the: A) mediastinum B) visceral pleura C) parietal pleura D) main (primary) bronchi E) pleurisy Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Which one of the following is NOT true of the lungs: A) the narrower portion of each lung is called the apex B) the bases rest on the diaphragm C) the left lung has two lobes D) the right lung has three lobes E) both lungs have two lobes Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: 445; ) When oxygen enters the respiratory system, what is the next structure to which it travels immediately upon leaving the trachea: A) bronchioles B) alveoli C) pleura D) main (primary) bronchi E) tertiary bronchi Answer: D Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Which one of the following structures is NOT part of the respiratory zone: A) respiratory bronchioles B) alveolar ducts C) alveolar sacs D) alveoli E) primary bronchi Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: 447 8
9 20) The walls of the alveoli are composed largely of: A) simple squamous epithelium B) stratified squamous epithelium C) simple cuboidal epithelium D) stratified cuboidal epithelium E) pseudostratified epithelium Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Exchange of both oxygen and carbon dioxide through the respiratory membrane occurs by: A) osmosis B) simple diffusion C) facilitated diffusion D) active transport E) passive transport Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The lipid molecule critical to lung function that coats the gas-exposed alveolar surfaces is called: A) surfactant B) interferon C) kinin D) renin E) lecithin Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Air moving in and out of the lungs is called: A) internal respiration B) inspiration C) external respiration D) expiration E) pulmonary ventilation Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Which one of the following is NOT true of inspiration: A) contraction of the diaphragm muscle helps increase the size of the thoracic cavity B) relaxation of the external intercostal muscles helps increase the size of the thoracic cavity C) increased intrapulmonary volume causes inhaled gases to spread out D) the decreased gas pressure produces a partial vacuum that forcibly sucks air in E) air continues to move into the lungs until intrapulmonary pressure equals atmospheric pressure Diff: 3 Page Ref: 451 9
10 25) The gas exchange that occurs between blood and tissue cells at systemic capillaries is called: A) pulmonary ventilation B) expiration C) internal respiration D) external respiration E) respiratory gas transport Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) In order to inspire: A) gas pressure in the lungs must increase B) the intrapulmonary volume must increase C) the diaphragm relaxes D) the intrapulmonary volume must decrease E) the external intercostal muscles relax Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) An emotionally-induced response during which air movement is similar to crying is: A) coughing B) sneezing C) laughing D) hiccupping E) yawning Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) A very deep inspiration that ventilates all alveoli is: A) coughing B) sneezing C) crying D) hiccupping E) yawning Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The respiratory movement representing the total amount of exchangeable air is the: A) tidal volume B) inspiratory reserve volume C) expiratory reserve volume D) vital capacity E) dead space volume Answer: D 10
11 30) The amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled after a tidal expiration is about: A) 500 ml B) 1200 ml C) 2100 ml D) 4800 ml E) 6000 ml 31) The amount of air exchanged during normal quiet breathing is about: A) 500 ml B) 1200 ml C) 2100 ml D) 4800 ml E) 6000 ml Answer: A 32) Most carbon dioxide is transported within blood plasma as: A) carbohemoglobin B) bicarbonate ion C) oxyhemoglobin D) hydrogen ion E) carbonic acid Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Oxygen binds with hemoglobin in the blood to form: A) bicarbonate ion B) oxyhemoglobin C) carbonic acid D) carbon dioxide E) plasma Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The bluish cast that results from inadequate oxygenation of the skin and mucosa is called: A) cyanosis B) xanthosis C) melanosis D) albinism E) erythema Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref:
12 35) Which one of the following is NOT a factor influencing respiratory rate and depth: A) physical exercise B) volition C) emotional factors D) enzymatic factors E) levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Cessation of breathing is called: A) apnea B) dyspnea C) eupnea D) hyperpnea E) tachypnea Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Hypoventilation dramatically increases carbonic acid concentration and involves: A) extremely deep breathing B) extremely fast breathing C) extremely slow breathing D) intermittent breathing E) irregular breathing Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Hyperventilation leads to all of the following EXCEPT: A) brief periods of apnea B) cyanosis C) dizziness D) fainting E) buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The most important chemical stimuli leading to increased rate and depth of breathing is: A) decreased oxygen level in the blood B) increased blood ph C) increased carbon dioxide in the blood D) increased hydrogen ion in the blood E) decreased carbon dioxide in the blood Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 457;
13 40) Which one of the following is NOT a feature of COPD: A) most patients have a genetic predisposition to COPD B) dyspnea becomes progressively more severe C) frequent pulmonary infections are common D) most COPD victims are hypoxic E) most patients have a history of smoking Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Emphysema results in all of the following EXCEPT: A) enlarged alveoli B) lung fibrosis C) expanded barrel chest D) decreased lung elasticity E) moon face Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The molecule that prevents lung collapse by lowering the surface tension of the water film lining each alveolar sac is called: A) resorbin B) renin C) lecithin D) surfactant E) fibrosin Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Surfactant is usually present in fetal lungs in adequate quantities by: A) weeks of pregnancy B) weeks of pregnancy C) weeks of pregnancy D) weeks of pregnancy E) weeks of pregnancy Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The abbreviation IRDS stands for: A) infant respiratory disease state B) intermittent respiratory distress state C) infant respiratory distress syndrome D) intermittent respiratory disease syndrome E) infant respiratory disease syndrome Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref:
14 45) Which one of the following is NOT true of cystic fibrosis: A) it is the most common lethal genetic disease in the U.S. B) it causes oversecretion of thick mucus that clogs the respiratory passages C) it impairs food digestion D) it causes sweat glands to produce an extremely salty perspiration E) it is rarely fatal Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: 461; ) The respiratory rate in adults is: A) 5-10 respirations per minute B) respirations per minute C) respirations per minute D) 30 respirations per minute E) over 40 respirations per minute Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The homeostatic imbalance associated with the death of many full-term newborn infants is called: A) CF B) SIDS C) CTRL D) COPD E) IRDS Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Obstruction of the trachea by a piece of food can lead to: A) hemothorax B) pleurisy C) aspiration pneumonia D) pneumothorax E) pulmonary tamponade Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Which of the following are currently the most damaging and disabling respiratory diseases in the U.S.: A) tuberculosis and COPD B) COPD and lung cancer C) lung cancer and asthma D) asthma and tuberculosis E) tuberculosis and pneumonia Diff: 2 Page Ref:
15 True/False 50) Which one of the following is NOT true of lung cancer: A) it accounts for one-third of all cancer deaths in the U.S. B) its incidence is currently increasing C) it is generally more prevalent in males than females D) most types of lung cancer are very aggressive E) lung cancers often metastasize rapidly and widely Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The ciliated cells of the nasal mucosa propel contaminated mucus posteriorly toward the pharynx. 2) The nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity by the nasal conchae. Answer: FALSE 3) There are only three paranasal sinuses located in the frontal, sphenoid, and parietal bones. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 442 4) Inflammation of the nasal mucosa by cold viruses and various antigens is called rhinitis. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 443 5) The larynx serves as a passageway for both food and air. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 443 6) The larynx routes air and food into their proper channel and plays an important role in speech production. 7) The "guardian of the airways" that prevents food from entering the superior opening of the larynx is the thyroid cartilage. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 444 8) The pharyngeal tonsils are also known as the adenoids. 9) The emergency surgical opening of the trachea is called a tracheostomy. 15
16 10) The C-shaped rings of cartilage that reinforce the trachea are made of elastic cartilage. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) The superior portion of the lung is called the base. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 445; ) The bronchioles are the smallest of the conducting passageways in the lungs. Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Inflammation of the pleura is often caused by decreased secretion of pleural fluid called pleurisy. Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The respiratory membrane is the air-blood barrier, where gases are exchanged. Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The respiratory zone includes the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli. Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The process of breathing is known as pulmonary ventilation. Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Inspiration results when the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles relax. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Expiration occurs when the thoracic and intrapulmonary volumes decrease and the intrapulmonary pressure increases. Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) The amount of air that can be forcibly inhaled over the tidal volume is about 2100 to 3200 ml. 20) The total amount of exchangeable air in a healthy young male is typically around 4800 ml. 21) Sudden inspirations resulting from spasms of the diaphragm are hiccups. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
17 22) The amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled after a normal tidal expiration is the residual volume. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Wheezing is a whistling sound associated with diseased respiratory tissue, mucus, or pus. Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) According to the laws of diffusion, movement of a respiratory gas occurs toward the area of higher concentration of that particular respiratory gas. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The general term for inadequate oxygen delivery to body tissues regardless of the cause is called hypoxia. Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Venous blood in systemic circulation is poorer in oxygen and richer in carbon dioxide. Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Inspiration by the diaphragm muscle is regulated by the phrenic nerves. Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The lungs of the fetus are filled with air late in pregnancy. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The faulty gene associated with cystic fibrosis codes for the CFTR protein, which controls the flow of chloride in and out of cells. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 461;
18 Matching Match the following structure with its description: 1) Throat A) alveoli Diff: 1 Page Ref: 443 B) larynx 2) Windpipe C) trachea 3) Voice box D) glottis E) esophagus 4) Opening to the larynx F) bronchioles Diff: 2 Page Ref: 444 5) The trachea branches into G) main (primary) bronchi these tubes Diff: 2 Page Ref: 445 H) pharynx 6) Tube posterior to the trachea 7) Smallest conducting passageways in the lungs Diff: 1 Page Ref: 447 8) Air sacs within the lungs Diff: 1 Page Ref: 447 1) H 2) C 3) B 4) D 5) G 6) E 7) F 8) A 18
19 Match the following mechanism with its associated nonrespiratory movement: 9) Involves using the uvula to A) yawning close the oral cavity off from the pharynx in order to clear the upper respiratory passages B) laughing C) coughing D) throat-clearing 10) An emotionally induced E) hiccupping response that produces air movements similar to crying F) sneezing 11) A very deep inspiration formerly believed to be triggered by low oxygen G) crying 12) Primarily an emotionally induced mechanism that involves release of air in a number of short breaths, similar to laughing 13) Blast of upward rushing air that clears the lower respiratory passageways 14) Sudden inspirations resulting from spasms of the diaphragm 9) F 10) B 11) A 12) G 13) C 14) E 19
20 Match the following definitions with their associated respiratory volume or capacity: 15) Amount of air that can be A) conducting zone volume forcibly exhaled after a normal tidal expiration B) total lung capacity C) dead space volume 16) Normal, quiet breathing D) tidal volume which moves approximately 500 ml of air per breath E) expiratory reserve volume 17) Air that enters the respiratory tract and remains within the conducting zone passageways F) vital capacity G) residual volume Diff: 2 Page Ref: 453 H) inspiratory reserve volume 18) Amount of air that can be inhaled forcibly over the tidal volume 19) Total amount of exchangeable air 20) Air that remains in the lungs even after the most strenuous expiration 21) Sum total of tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and expiratory reserve volume 15) E 16) D 17) C 18) H 19) F 20) G 21) F 20
21 Essay 1) Explain the roles of mucus and cilia in the respiratory system. Answer: Respiratory mucosa lines the nasal cavity which produces sticky mucus. This mucus moistens the air and traps incoming bacteria and other foreign debris entering the nasal cavity. The ciliated cells of the nasal mucosa move this contaminated mucus posteriorly toward the pharynx where it can be swallowed. The trachea is also lined with ciliated mucosa. These cilia move contaminated mucus toward the throat where it either can be swallowed or spat out. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 442; ) List the three regions of the pharynx and identify their relative superior and inferior endpoints in the respiratory passageway. Answer: The three portions of the pharynx are the nasopharynx, the oropharynx, and the laryngopharynx. The nasopharynx is the superior portion that extends from the nasal cavity to the soft palate. The oropharynx is the central portion that lies between the soft palate and the upper epiglottis. The laryngopharynx is the most inferior portion and is the connecting point to the larynx below. Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Explain the role of the epiglottis in the respiratory system. Answer: The epiglottis is a part of the larynx. This structure is made of elastic cartilage. The epiglottis protects the superior opening (glottis) of the trachea. When we swallow foods or fluids, the larynx is pulled upward and the epiglottis tips to form a lid over the opening of the larynx. Food and fluids are then forced into the posterior tube called the esophagus. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 444 4) Identify the two pleural membranes and describe them under normal and disease conditions. Answer: The pleural membranes, the visceral pleura and the parietal pleura, produce a slippery serous secretion that allows the lungs to glide easily over the thorax wall during breathing. This serous fluid causes the two pleural layers to cling together. They can slide easily from side to side across one another, but they cannot easily be pulled apart. As surface tension of water holds them tightly to each other, the lungs are held tightly to the thorax wall. The pleural space is more of a potential space than an actual space, and it is only during illness or injury that this space becomes apparent, such as with a pneumothorax that can lead to atelectasis. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 447 5) Explain the structure and function of the respiratory membrane. Answer: The respiratory membrane, also known as the air-blood barrier, is comprised of the fused basement membranes of the alveolar and capillary walls. It has gas flowing past on one side and blood flowing past on the other. Gas exchanges occur by simple diffusion through the respiratory membrane. Oxygen passes from the alveolar air into the capillary blood and carbon dioxide leaves the blood to enter the gas-filled alveoli. Diff: 3 Page Ref:
22 6) Identify and describe the four distinct events that are collectively called respiration. Answer: Pulmonary ventilation is commonly called breathing and involves the movement of air into and out of the lungs. External respiration is the exchange of gases between the pulmonary blood and the alveoli. Respiratory gas transport is the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from the lungs and tissue cells of the body via the bloodstream. Internal respiration is the exchange of gases between the blood and tissue cells. Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Describe how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood. Answer: Oxygen is transported in two ways: 1. Most oxygen attaches to hemoglobin molecules on the RBCs to form oxyhemoglobin. 2. A small amount of oxygen dissolves in the plasma for transport. Carbon dioxide is also transported in two ways: 1. Most carbon dioxide dissolves in the plasma as the bicarbonate ion. 2. A small amount of carbon dioxide is carried inside the RBCs bound to hemoglobin (bound to a different site from oxygen). Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Describe some of the major and minor effects of smoking on the human body. Answer: Answers will vary depending on what effects were discussed in class, since smoking has numerous effects on the body. Respiratory effects include airway obstruction, dyspnea, coughing, frequent infections, breakdown of elastin in the connective tissue in the lungs, continual bronchial irritation and inflammation, hypoxia, respiratory acidosis, and respiratory failure. Other effects include clubbing of the fingers due to hypoxia, impotence, and impairment of the immune system. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system
 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Human Anatomy and Physiology The Respiratory System Basic functions of the respiratory system: as a Gas exchange supply oxygen to aerobic tissues in the body and remove carbon dioxide waste product. in-
Respiratory System. Chapter 21
 Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
Respiratory System Chapter 21 Structural Anatomy Upper respiratory system Lower respiratory system throat windpipe voice box Function of Respiratory System Gas exchange Contains receptors for sense of
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
 A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
A. function: supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide 1. ventilation = movement of air into and out of lungs 2. diffusion: B. organization a. O2 diffuses from air into pulmonary capillary blood
CHAPTER 19: RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Fully explain the process (5 parts of) respiration. 2. Describe the significance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in human cells. 3. Explain the structure and function of mucous membranes that
OBJECTIVES: 1. Fully explain the process (5 parts of) respiration. 2. Describe the significance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in human cells. 3. Explain the structure and function of mucous membranes that
Anatomy of the Respiratory System. The Respiratory System. Respiratory system functions mainly as gas exchange system for O 2 andco 2.
 The Respiratory System Respiratory system functions mainly as gas exchange system for O 2 andco 2! cellular respiration (energy production) closely tied to circulatory system General Functions of Respiratory
The Respiratory System Respiratory system functions mainly as gas exchange system for O 2 andco 2! cellular respiration (energy production) closely tied to circulatory system General Functions of Respiratory
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System
 Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
Chapter 2 - Anatomy & Physiology of the Respiratory System Written by - AH Kendrick & C Newall 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Gross Anatomy of the Lungs, 2.3 Anatomy of the Thorax, 2.4 Anatomy and Histology of the
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
A. All cells need oxygen and release carbon dioxide why?
 I. Introduction: Describe how the cardiovascular and respiratory systems interact to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2. A. All cells need oxygen and release carbon dioxide why? B. Two systems that help to
I. Introduction: Describe how the cardiovascular and respiratory systems interact to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2. A. All cells need oxygen and release carbon dioxide why? B. Two systems that help to
CHAPTER 5 - BREATHING "THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM"
 CHAPTER 5 - BREATHING "THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM" You have read how the blood transports oxygen from the lungs to cells and carries carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs. It is the function of the respiratory
CHAPTER 5 - BREATHING "THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM" You have read how the blood transports oxygen from the lungs to cells and carries carbon dioxide from the cells to the lungs. It is the function of the respiratory
Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14
 Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14 Functions: Fluid balance by returning excess tissue fluid to the blood; returning solutes (especially plasma proteins) to the blood; filter body
Biology 2402 A&P II - Lymphatic System and Immunity Ch. 14 Functions: Fluid balance by returning excess tissue fluid to the blood; returning solutes (especially plasma proteins) to the blood; filter body
What, roughly, is the dividing line between the upper and lower respiratory tract? The larynx. What s the difference between the conducting zone and
 What, roughly, is the dividing line between the upper and lower respiratory tract? The larynx. What s the difference between the conducting zone and the respiratory zone? Conducting zone is passageways
What, roughly, is the dividing line between the upper and lower respiratory tract? The larynx. What s the difference between the conducting zone and the respiratory zone? Conducting zone is passageways
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANIMAL SCIENCE 8646-B THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Respiration* is a physical process by which living organisms inhale oxygen from the surrounding atmosphere and then exhale carbon dioxide. The
ANIMAL SCIENCE 8646-B THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Respiration* is a physical process by which living organisms inhale oxygen from the surrounding atmosphere and then exhale carbon dioxide. The
RESPIRATORY VENTILATION Page 1
 Page 1 VENTILATION PARAMETERS A. Lung Volumes 1. Basic volumes: elements a. Tidal Volume (V T, TV): volume of gas exchanged each breath; can change as ventilation pattern changes b. Inspiratory Reserve
Page 1 VENTILATION PARAMETERS A. Lung Volumes 1. Basic volumes: elements a. Tidal Volume (V T, TV): volume of gas exchanged each breath; can change as ventilation pattern changes b. Inspiratory Reserve
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY KNR 182
 Human Anatomy and Physiology Notes (KNR 182) ; Page 92 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY KNR 182 Lecture Packet for Unit V Respiratory System Professor: Dale D. Brown, Ph.D. 5120 Dept of KNR Horton Fieldhouse
Human Anatomy and Physiology Notes (KNR 182) ; Page 92 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY KNR 182 Lecture Packet for Unit V Respiratory System Professor: Dale D. Brown, Ph.D. 5120 Dept of KNR Horton Fieldhouse
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Respiratory System Questions
 1. Which of the following bones does NOT contain a paranasal sinus? a. Sphenoid b. Maxillary c. Ethmoid d. Nasal e. Frontal 2. Which of the following muscles contracts during quiet expiration? a. Diaphragm
1. Which of the following bones does NOT contain a paranasal sinus? a. Sphenoid b. Maxillary c. Ethmoid d. Nasal e. Frontal 2. Which of the following muscles contracts during quiet expiration? a. Diaphragm
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley
 Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Human Anatomy & Physiology II with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam III Name: Instructions This exam consists of 50 questions. You may write on the exam itself, but be sure to answer all your questions on a Scantron
Influenza (Flu) Influenza is a viral infection that may affect both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are three types of flu virus:
 Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Respiratory Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology General Manifestations of Respiratory Disease Sneezing is a reflex response to irritation in the upper respiratory tract and is associated with inflammation
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Pulmonary Ventilation
 Pulmonary Ventilation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Pulmonary ventilation, or breathing, is the
Pulmonary Ventilation Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Pulmonary ventilation, or breathing, is the
Lab #11: Respiratory Physiology
 Lab #11: Respiratory Physiology Background The respiratory system enables the exchange of O 2 and CO 2 between the cells and the atmosphere, thus enabling the intake of O 2 into the body for aerobic respiration
Lab #11: Respiratory Physiology Background The respiratory system enables the exchange of O 2 and CO 2 between the cells and the atmosphere, thus enabling the intake of O 2 into the body for aerobic respiration
Oxygenation. Chapter 21. Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing. Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing*
 Oxygenation Chapter 21 Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing Inspiration ~ breathing in Expiration ~ breathing out Ventilation ~ Movement of air in & out of the lungs Respiration ~ exchange of O2 & carbon
Oxygenation Chapter 21 Anatomy and Physiology of Breathing Inspiration ~ breathing in Expiration ~ breathing out Ventilation ~ Movement of air in & out of the lungs Respiration ~ exchange of O2 & carbon
Respiratory Disorders
 Respiratory Disorders Teaching Plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy
Respiratory Disorders Teaching Plan To use this lesson for self-study, the learner should read the material, do the activity, and take the test. For group study, the leader may give each learner a copy
33.1 The Circulatory System
 33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
What You Should Know About ASTHMA
 What You Should Know About ASTHMA 200 Hospital Drive Galax, VA 24333 (276) 236-8181 www.tcrh.org WHAT IS ASTHMA? It s a lung condition that makes breathing difficult. The cause of asthma is not known.
What You Should Know About ASTHMA 200 Hospital Drive Galax, VA 24333 (276) 236-8181 www.tcrh.org WHAT IS ASTHMA? It s a lung condition that makes breathing difficult. The cause of asthma is not known.
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
The Lymphatic System Dr. Naim Kittana, PhD 1 Disclosure The material and the illustrations are adopted from the textbook Human Anatomy and Physiology / Ninth edition/ Eliane N. Marieb 2013 Dr. Naim Kittana,
GRADE 11F: Biology 3. UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours. Human gas exchange system and health. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
Whooping Cough. The Lungs Whooping cough is an infection of the lungs and breathing tubes, both of which are parts of the respiratory system.
 Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
Whooping Cough Introduction Whooping cough is a serious bacterial infection of the lungs and breathing tubes. It is also called pertussis. About 16 million cases of whooping cough happen worldwide each
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Characterize each subdivision of the respiratory system (larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli). 36 Identify
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 42 Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A&M University Objectives Characterize each subdivision of the respiratory system (larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveoli). 36 Identify
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment
 Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Fourth Grade The Human Body: The Respiratory System Assessment 1a. The brings air in and out of the body. a. respiratory system b. circulatory system 1b. The system is the part of the body responsible
Lesson 7: Respiratory and Skeletal Systems and Tuberculosis
 Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Glossary 1. asthma: when the airways of the lungs narrow, making breathing difficult 2. bacteria: tiny living creatures that can only be seen with a microscope; some bacteria help the human body, and other
Gas Exchange and Respiratory Systems
 Gas Exchange and Respiratory Systems Modified from: Biology in the laboratory. 3 rd edition. Helms, Helms, Kosinski and Cummings. Helms, Helms, Kosinski, Cummings. Biology in the Laboratory, 3 rd edition.
Gas Exchange and Respiratory Systems Modified from: Biology in the laboratory. 3 rd edition. Helms, Helms, Kosinski and Cummings. Helms, Helms, Kosinski, Cummings. Biology in the Laboratory, 3 rd edition.
Human Body Vocabulary Words Week 1
 Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
Vocabulary Words Week 1 1. arteries Any of the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body 2. heart The muscular organ inside the chest that pumps blood through the body
ACTIVITY #3: LUNG HEALTH ASTHMA AND ALLERGIES
 ACTIVITY #3: LUNG HEALTH ASTHMA AND ALLERGIES TIME 50 minutes, computer lab REQUIRED RESOURCES Activity Computer lab with internet access for student research Notepaper and pencil for research Poster board
ACTIVITY #3: LUNG HEALTH ASTHMA AND ALLERGIES TIME 50 minutes, computer lab REQUIRED RESOURCES Activity Computer lab with internet access for student research Notepaper and pencil for research Poster board
1. Our lungs are, essentially, a network of connected that bring
 The Respiratory System Webquest http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/health-and-human-body/human-body/lungs-article/ The Breath of Life-National Geographic 1. Our lungs are, essentially, a network
The Respiratory System Webquest http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/health-and-human-body/human-body/lungs-article/ The Breath of Life-National Geographic 1. Our lungs are, essentially, a network
Understanding Hypoventilation and Its Treatment by Susan Agrawal
 www.complexchild.com Understanding Hypoventilation and Its Treatment by Susan Agrawal Most of us have a general understanding of what the term hyperventilation means, since hyperventilation, also called
www.complexchild.com Understanding Hypoventilation and Its Treatment by Susan Agrawal Most of us have a general understanding of what the term hyperventilation means, since hyperventilation, also called
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
COPD. Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
 COPD Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. CONTENTS What does COPD mean?...04 What are the symptoms of COPD?...06 What causes COPD?...09 Treating COPD...10 Valve therapy in COPD...12
COPD Information brochure for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. CONTENTS What does COPD mean?...04 What are the symptoms of COPD?...06 What causes COPD?...09 Treating COPD...10 Valve therapy in COPD...12
NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax
 NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax By: Steven Jones, NREMT-P Pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural space of the lung, causing the lung to collapse. Pneumothorax
NEEDLE THORACENTESIS Pneumothorax / Hemothorax By: Steven Jones, NREMT-P Pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural space of the lung, causing the lung to collapse. Pneumothorax
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology Bio 110 lab quiz study guide Bio 110 lab quiz study guide By: Darrell Davies !!!CAUTION!!! This power point presentation is intended to be used as an add on
Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology Bio 110 lab quiz study guide Bio 110 lab quiz study guide By: Darrell Davies !!!CAUTION!!! This power point presentation is intended to be used as an add on
Section B: Epithelial Tissue 1. Where are epithelial tissues found within the body? 2. What are the functions of the epithelial tissues?
 Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissue worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Histology Cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I.
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE PULMONARY SYSTEM Section 1 Part B Reading Assignment: Des Jardins - Chapter 1, pp. THE LOWER AIRWAY I. Cartilaginous Airways A. Trachea 1. extends from the cricoid cartilage
Divisions of Digestive System. Organs of the Alimentary Canal. Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal. CHAPTER 14 p.
 Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
Divisions of Digestive System Anatomy of the Digestive System: Organs of the Alimentary Canal CHAPTER 14 p. 412-423 1. Alimentary Canal or Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)-digests and absorbs food coiled hollow
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE. Includes: Bronchitis (chronic and acute) Emphysema
 THE BASICS OF BREATHING: Assessment & Treatment Approaches for the Patient with COPD Jocelyn Alexander, MA CCC-SLP Director of Program Development Therapy Partners of Ohio LEARNER OBJECTIVES: Identify
THE BASICS OF BREATHING: Assessment & Treatment Approaches for the Patient with COPD Jocelyn Alexander, MA CCC-SLP Director of Program Development Therapy Partners of Ohio LEARNER OBJECTIVES: Identify
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships
 Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Ventilation Perfusion Relationships VENTILATION PERFUSION RATIO Ideally, each alveolus in the lungs would receive the same amount of ventilation and pulmonary capillary blood flow (perfusion). In reality,
Pre-lab homework Lab 6: Respiration and Gas exchange
 Lab Section: Pre-lab homework Lab 6: Respiration and Gas exchange Name: 1. Name the organs used for gas exchange in each of the following organisms: Humans Fish Insects 2. What are three features common
Lab Section: Pre-lab homework Lab 6: Respiration and Gas exchange Name: 1. Name the organs used for gas exchange in each of the following organisms: Humans Fish Insects 2. What are three features common
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley. Practice Exam 1
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
Human Anatomy & Physiology I with Dr. Hubley Practice Exam 1 1. Which definition is the best definition of the term gross anatomy? a. The study of cells. b. The study of tissues. c. The study of structures
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
SYMPTOMS OF RESPIRATORY DISORDERS THE PHYSICAL EXAMINATION AND THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 134 The Body Systems: Clinical and Applied Topics
 34 The Body Systems: Clinical and Applied Topics The Respiratory System The anatomical components of the respiratory system can be divided into an upper respiratory system, which includes the nose, nasal
34 The Body Systems: Clinical and Applied Topics The Respiratory System The anatomical components of the respiratory system can be divided into an upper respiratory system, which includes the nose, nasal
These factors increase your chance of developing emphysema. Tell your doctor if you have any of these risk factors:
 Emphysema Pronounced: em-fiss-see-mah by Debra Wood, RN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Emphysema is a chronic obstructive disease of the lungs. The lungs contain millions of tiny air sacs called
Emphysema Pronounced: em-fiss-see-mah by Debra Wood, RN En Español (Spanish Version) Definition Emphysema is a chronic obstructive disease of the lungs. The lungs contain millions of tiny air sacs called
Asthma Glossary. Allergen
 Action plan Acute Adverse Allergen Allergic asthma Allergic rhinitis Allergist Allergy Allergy shots Alveoli Anaphylaxis Antibiotic Antibodies Antihistamine Asthma Asthma Attack Breath sounds Bronchi (singular,
Action plan Acute Adverse Allergen Allergic asthma Allergic rhinitis Allergist Allergy Allergy shots Alveoli Anaphylaxis Antibiotic Antibodies Antihistamine Asthma Asthma Attack Breath sounds Bronchi (singular,
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Normal CT scan of the chest
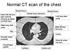 Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Normal CT scan of the chest Heart with left and right ventricle showing up lighter (contrast dye) Breast tissue Breast bone (sternum) Breast tissue Left lung (dark area) Right lung (dark area) Rib Main
Histology. Epithelial Tissue
 Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
Histology Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Lines internal and external body surfaces Forms glands Epithelial Tissue Little extracellular matrix Attached on one side Avascular Basement membrane Apical
ANSWERS AND MARK SCHEMES. (a) 5 correct plots;;; (-1 mark each incorrect plot) 3
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 5 correct plots;;; (-1 mark each incorrect plot) 3 (b) 1600/4; = 400 kj; (i mark for correct working if answer incorrect) 2 (c) the more vigorous the activity the more energy used; 1 (d)
QUESTIONSHEET 1 5 correct plots;;; (-1 mark each incorrect plot) 3 (b) 1600/4; = 400 kj; (i mark for correct working if answer incorrect) 2 (c) the more vigorous the activity the more energy used; 1 (d)
Airways Resistance and Airflow through the Tracheobronchial Tree
 Airways Resistance and Airflow through the Tracheobronchial Tree Lecturer: Sally Osborne, Ph.D. Department of Cellular & Physiological Sciences Email: sosborne@interchange.ubc.ca Useful links: www.sallyosborne.com
Airways Resistance and Airflow through the Tracheobronchial Tree Lecturer: Sally Osborne, Ph.D. Department of Cellular & Physiological Sciences Email: sosborne@interchange.ubc.ca Useful links: www.sallyosborne.com
Each gland has at least one duct that takes saliva to the oral cavity.
 kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
kufa university Physiology College of Nursing first year student Ass. Lect :- Hisham Qassem M. Lecture No :-3 The Digestive System Digestive system consists of: 1. Gastrointestinal Tract (GIT). 2. Accessory
Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange
 Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
Name: Questions on The Nervous System and Gas Exchange Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topics 6.4 (Gas Exchange) and 6.5 (Nerves, hormones and homeostasis).
2012 Anatomy & Physiology C Division. National Competition-Science
 2012 Anatomy & Physiology C Division National Competition-Science Olympiad 1. The alimentary canal includes 8 different parts and 4 accessory organs. Name 5 parts from the alimentary canal and 3 accessory
2012 Anatomy & Physiology C Division National Competition-Science Olympiad 1. The alimentary canal includes 8 different parts and 4 accessory organs. Name 5 parts from the alimentary canal and 3 accessory
KIDNEY Locate the following structures on the sheep kidney and human kidney models:
 Laboratory Handouts 163 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1:
Laboratory Handouts 163 Lab 11: Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology, Reproductive System Anatomy Unit 15: Urinary System Unit 16: Reproductive Systems Cat Dissection: Photo Atlas, Chapter 19 Ex. 15-1:
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
HEALTH EFFECTS. Inhalation
 Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
Health Effects HEALTH EFFECTS Asbestos can kill you. You must take extra precautions when you work with asbestos. Just because you do not notice any problems while you are working with asbestos, it still
Human Digestive System Anatomy
 Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Human Digestive System Anatomy Biology 104 Objectives: 1. Learn the anatomy of the digestive system. You should be able to find all terms in bold on the human torso models. 2. Relate structure of the system
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.
 Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between
MECHINICAL VENTILATION S. Kache, MD
 MECHINICAL VENTILATION S. Kache, MD Spontaneous respiration vs. Mechanical ventilation Natural spontaneous ventilation occurs when the respiratory muscles, diaphragm and intercostal muscles pull on the
MECHINICAL VENTILATION S. Kache, MD Spontaneous respiration vs. Mechanical ventilation Natural spontaneous ventilation occurs when the respiratory muscles, diaphragm and intercostal muscles pull on the
ASTHMA IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN
 ASTHMA IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. Symptoms of asthma are variable. That means that they can be mild to severe, intermittent to
ASTHMA IN INFANTS AND YOUNG CHILDREN What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. Symptoms of asthma are variable. That means that they can be mild to severe, intermittent to
About lung cancer. Contents. The lungs
 This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
This information is an extract from the booklet Understanding lung cancer. You may find the full booklet helpful. We can send you a free copy see page 7. The lungs Contents The lungs Types of lung cancer
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School. Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Hanover Area Jr./Sr. High School Chapter 1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Maxillary Sinus. (Antrum of Higmore)
 Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Maxillary Sinus (Antrum of Higmore) The maxillary sinus is a pneumatic space. It is the largest bilateral air sinus located in the body of the maxilla and opens in the middle nasal meatus of the nasal
Department of Surgery
 What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
What is emphysema? 2004 Regents of the University of Michigan Emphysema is a chronic disease of the lungs characterized by thinning and overexpansion of the lung-like blisters (bullae) in the lung tissue.
Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and asthma
 Chapter 31 Drugs Used to Treat Lower Respiratory Disease Learning Objectives Describe the physiology of respirations Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis,
Chapter 31 Drugs Used to Treat Lower Respiratory Disease Learning Objectives Describe the physiology of respirations Compare the physiologic responses of the respiratory system to emphysema, chronic bronchitis,
PULMONARY PHYSIOLOGY
 I. Lung volumes PULMONARY PHYSIOLOGY American College of Surgeons SCC Review Course Christopher P. Michetti, MD, FACS and Forrest O. Moore, MD, FACS A. Tidal volume (TV) is the volume of air entering and
I. Lung volumes PULMONARY PHYSIOLOGY American College of Surgeons SCC Review Course Christopher P. Michetti, MD, FACS and Forrest O. Moore, MD, FACS A. Tidal volume (TV) is the volume of air entering and
6. Histopathology of Alveoli 7. Surfactant 8. Blood supply of lungs 9. Lymphatics of Lungs 10. Nerve supply of Lungs 11. Pleura 12.
 ANATOMY OF LUNGS - 1. Gross Anatomy of Lungs 2. Surfaces and Borders of Lungs 3. Hilum and Root of Lungs 4. Fissures and Lobes of Lungs 5. Bronchopulmonary segments 6. Histopathology of Alveoli 7. Surfactant
ANATOMY OF LUNGS - 1. Gross Anatomy of Lungs 2. Surfaces and Borders of Lungs 3. Hilum and Root of Lungs 4. Fissures and Lobes of Lungs 5. Bronchopulmonary segments 6. Histopathology of Alveoli 7. Surfactant
Emphysema. Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide.
 Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects about 64 million people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This
Diseases. Inflammations Non-inflammatory pleural effusions Pneumothorax Tumours
 Pleura Visceral pleura covers lungs and extends into fissures Parietal pleura limits mediastinum and covers dome of diaphragm and inner aspect of chest wall. Two layers between them (pleural cavity) contains
Pleura Visceral pleura covers lungs and extends into fissures Parietal pleura limits mediastinum and covers dome of diaphragm and inner aspect of chest wall. Two layers between them (pleural cavity) contains
The EMT Instructional Guidelines in this section include all the topics and material at the EMR level PLUS the following material:
 Airway Management, Respiration and Artificial Ventilation EMR Applies knowledge (fundamental depth, foundational breadth) of general anatomy and physiology to assure a patent airway, adequate mechanical
Airway Management, Respiration and Artificial Ventilation EMR Applies knowledge (fundamental depth, foundational breadth) of general anatomy and physiology to assure a patent airway, adequate mechanical
Animal Tissues. I. Epithelial Tissue
 Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
Animal Tissues There are four types of tissues found in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. In this lab you will learn the major characteristics of each tissue
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary
 X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
X-Plain Sinus Surgery Reference Summary Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237)
 Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
 The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
The Gastrointestinal System It consists of: The digestive tract Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine The digestive organs Teeth Tongue Salivary glands Liver Gall bladder Pancreas
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
Name Class Date Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 386-394 in your textbook for a general discussion of the integumentary
The Human Immune System
 The Human Immune System What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles The First Line of Defense Skin The dead, outer layer
The Human Immune System What is the immune system? The body s defense against disease causing organisms, malfunctioning cells, and foreign particles The First Line of Defense Skin The dead, outer layer
How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion. How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion. How Organisms Exchange Gases: Respiratory Organs
 How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion Gas is exchanged between respiratory medium and body fluids through diffusion across a respiratory surface To effectively exchange gases, the surface must
How Organisms Exchange Gases: Simple Diffusion Gas is exchanged between respiratory medium and body fluids through diffusion across a respiratory surface To effectively exchange gases, the surface must
Gas Exchange. Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com)
 Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the alveoli
Gas Exchange Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse between the alveoli
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
Cystic Fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis affects various systems in children and young adults, including the following:
 Cystic Fibrosis What is cystic fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus. It is chronic, progressive, and is usually
Cystic Fibrosis What is cystic fibrosis? Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus. It is chronic, progressive, and is usually
National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision
 National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision Key Area 1: Structure and function of organs and organ systems and their role in sustaining life. What you must know: The basic structure and functions of main
National 3- Multicellular Organisms Revision Key Area 1: Structure and function of organs and organ systems and their role in sustaining life. What you must know: The basic structure and functions of main
The Digestive System. Chapter 15
 The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
The Digestive System Chapter 15 Introduction Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food so the nutrients can be absorbed by cells Carried out by the digestive system Consists of
Objectives COPD. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) 4/19/2011
 Objectives Discuss assessment findings and treatment for: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema Asthma Anaphylaxis Other respiratory issues Provide some definitions Chronic Obstructive
Objectives Discuss assessment findings and treatment for: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Emphysema Asthma Anaphylaxis Other respiratory issues Provide some definitions Chronic Obstructive
General Thoracic Surgery ICD9 to ICD10 Crosswalks. C34.11 Malignant neoplasm of upper lobe, right bronchus or lung
 ICD-9 Code ICD-9 Description ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description 150.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus 150.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle
ICD-9 Code ICD-9 Description ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Description 150.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus 150.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook The Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of the lungs and air passages. The lungs are the part of the body where gases are exchanged
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patient Guidebook The Respiratory System The respiratory system consists of the lungs and air passages. The lungs are the part of the body where gases are exchanged
Chapter 10. All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES
 Chapter 10 All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES The sinuses are air filled cavities contained within the bones of
Chapter 10 All chapters, full text, free download, available at http://www.divingmedicine.info SINUS BAROTRAUMA ANATOMY OF THE SINUSES The sinuses are air filled cavities contained within the bones of
Pediatric Airway Management
 Pediatric Airway Management Dec 2003 Dr. Shapiro I., PICU Adult Chain of Survival EMS CPR ALS Early Defibrillation Pediatric Chain of Survival Prevention CPR EMS ALS Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest SIDS
Pediatric Airway Management Dec 2003 Dr. Shapiro I., PICU Adult Chain of Survival EMS CPR ALS Early Defibrillation Pediatric Chain of Survival Prevention CPR EMS ALS Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest SIDS
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids
 Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: COPD and Steroids Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Head, Centre of Heart
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities: Years 7-8 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8
 Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
Investigating the Human Body On-site student activities Years 7 8 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to use as guides and focus material during
