Technical Note: Analysis of microrna function using mircury LNA TM microrna Inhibitors
|
|
|
- Myra Skinner
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Technical note: Analysis of microrna function using mircury LNA microrna Inhibitors Introduction The study of micrornas has come a long way since the discovery of these small RNAs some fifteen years ago. We now know that micrornas are involved in a number of important biological processes such as embryonic development and cell differentiation and they have been linked to several important diseases such as cancer and heart disease. In addition, micrornas have been found in a large number of different organisms including single cell alga, plants, vertebrates and their associated viruses. However, out of the more than 9000 micrornas currently annotated in mirbase (v.12.0), only a fraction have been characterized in terms of their biological role. Clearly, a great challenge ahead will be to elucidate the function of these micrornas and to identify their mrna targets. One of the most powerful and straight forward ways of determining the function of a microrna is by performing inhibition experiments. In such experiments, the phenotypic changes of cells transfected with antisense oligonucleotides are closely monitored to elucidate the biological role of the targeted microrna. In addition to their role in characterizing micrornas of unknown function, inhibition experiments can also be used for validating bioinformatically predicted mrna targets. Although a very powerful method, a number of technical challenges have to be overcome in order to get quality microrna inhibition data. First, the silencing technology used must be effective under physiological conditions. Second, the oligonucleotide must be optimally delivered to the cells and, third, the effect of the inhibition has to be monitored in an efficient way. Here, we discuss these challenges and outline guidelines for the design of knockdown experiments using mircury LNA microrna Inhibitors. Experimental design In the early stages of planning a microrna inhibition experiment, it is important to ensure that the microrna is actually expressed in the cells. If the endogenous microrna is not expressed in the cell line, then you are unlikely to observe any effect of silencing that microrna. Figure I Fold Up-regulation FL(RLU) / RL(RLU) Mismatch discrimination ability of mircury LNA Knockdown Probes mircury mircury 1MM 5 nm 20 nm 100 nm mircury 2MM mircury 4MM Figure I. Mismatch discrimination of mircury LNA microrna Inhibitors. The pmir- 21 luciferase reporter is upregulated compared to the no-oligonucleotide control when HeLa cells are transfected with perfectly matched and mismatched (MM) antisense inhibitors targeting hsa-mir-21. There is a sharp drop in luciferase expression when comparing the perfectly matched microrna inhibitor to the single (1MM) and double (2MM) mismatched inhibitors, indicating that mircury LNA microrna inhibitors are very specific and can distinguish between single nucleotide mismatches. Luciferase expression levels were measured using Dual-Glo Luciferase 24 h after transfection. FL, firefly luciferase signal; RL, Renilla luciferase signal; RLU, relative light units. 1
2 Another consideration that should be addressed early in the planning stages is whether to knock down just a few micrornas or to perform high throughput screens. In addition to individual antisense inhibitors, Exiqon offers the mircury LNA microrna Inhibitor Library, which contains over 900 antisense oligonucleotides and has been specifically developed for high throughput screens. Other considerations include which method to use for the delivery of the antisense inhibitors and how to determine the effect of the silencing. These topics will be discussed in greater detail below. An important aspect of any silencing experiment is the use of proper controls. It is always reassuring to verify that the observed phenotype is not reproduced when using a negative control (scrambled) LNA microrna inhibitor. In addition, a custom designed mismatch control LNA microrna inhibitor can be used to assess the specificity of the silencing (Figure I). Designing efficient inhibitors There are a number of challenges in designing efficient LNA microrna inhibitors. Mature micrornas are only around 20 nucleotides in length, which means that even full length traditional antisense inhibitors (such as 2 -O-Me) will have poor affinity for their microrna targets. This is especially problematic for AT-rich target sequences as the melting temperature of such duplexes will be relatively low. The use of full length oligonucleotides is further complicated by the fact that many micrornas have autocomplementary end sequences, which may result in extensive self-annealing of the microrna inhibitors. By incorporating Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA ) monomers into the microrna inhibitors, the affinity of the inhibitors for their target micrornas is greatly increased and the resistance to enzymatic degradation is improved. This means that shorter oligonucleotides can be designed, thus avoiding the problem of using full length sequences. We have taken advantage of this to develop new sophisticated inhibitor design algorithms that calculate the most efficient inhibitors by adjusting the length and the LNA spiking pattern of the oligonucleotides. This has allowed us to design second generation antisense inhibitors with uniform and very high potency by normalizing their T m and by minimizing problems of autocomplementarity (Figure II). Furthermore, this means that all our microrna inhibitors have high silencing efficiency at low concentrations, which reduces the risk of negative side-effects. Figure II Fold upregulation of microrna reporter gene expression Product A Product B microrna inhibitor 1 nm 5 nm 20 nm 2 -OMe mircury LNA Figure II. mircury LNA microrna inhibitors are more efficient than competing technologies at inhibiting micrornas. The expression of the pmir-21 luciferase reporter is upregulated compared to the no-oligonucleotide control when MCF7 cells are transfected with antisense inhibitors directed against hsa-mir-21. This effect is significantly stronger in cells transfected with LNA oligonucleotides than cells transfected with DNA (Product A and B) or 2 -O-Me oligonucleotides. Measurements were taken 60 h after transfection. 2
3 Delivery of mircury LNA microrna Inhibitors The mircury LNA microrna Inhibitors can be delivered efficiently into a variety of cell lines using any method suited for the delivery of small RNA molecules (e.g. sirnas). In general, delivery can be achieved using either chemical transfection (lipid or amine based transfection reagents) or electroporation. Which method to use depends on the cell line and may have to be empirically determined on a case-by-case basis. Table I presents some of the transfection reagents and cell lines that have been used successfully with the mircury LNA microrna Inhibitors. Optimal transfection conditions can be found by identifying efficient transfection reagents for each cell line and by adjusting: The amount of transfection reagent The amount of inhibitor Cell density at the time of transfection The order of transfection (plating cells before transfection or plating cells at the moment of transfection) The length of exposure of cells to the transfection reagent/ oligonucleotide complex Most protocols recommend maintaining mammalian cells in the transfection medium for 24 hours at which time it should be replaced with fresh medium to maximize the viability of the cell culture. Table I Cell type Transfection reagent Reference A172 Lipofectamine , 3 CTC12 Lipofectamine H19 Lipofectamine 5 HCT116 Lipofectamine HEK293 Lipofectamine , 7 HeLa X-tremeGENE 8 HeLa S3 Lipofectamine Jurkat cells Nucleofector II Device 9 LN229 Lipofectamine LN308 Lipofectamine MCF-7 Lipofectamine MDA-MB- 435S Lipofectamine MEL X-tremeGENE 11 Myoblast C2C12 Lipofectamine 1, 5 NB4 Lipofectamine NPC C17.2 Lipofectamine PC3 Lipofectamine U87 Lipofectamine , 3 Table I. Some of the cell lines and transfection reagents that have been used with the mircury LNA TM microrna Knockdown Probes. 3 Normally, mircury LNA microrna Inhibitors display potent activity at final concentrations of 1-25 nm, but an extended range of nm may be appropriate for optimization purposes. Measuring transfection efficiency Once the cells have been transfected, it is important to determine the transfection efficiency. When deciding on a method to accomplish this, it is important to understand the mode of action of our microrna inhibitors. Our oligonucleotides do not stimulate enzymatic degradation of their target microrna. Instead, they inhibit micrornas by sequestering them in tight and stable complexes 14. Usually one of the following methods is used for determining the transfection efficiency. 1. Real-time PCR and Northern blot analysis Quantitative real-time PCR and Northern blots are commonly used to measure microrna inhibitor transfection efficiency. MicroRNAs in complex with antisense inhibitors can not be detected by real time PCR, since the reverse transcription step in particular, is sensitive to
4 antisense compounds targeting the microrna template. Similarly, strong complexes between mircury LNA inhibitors and micrornas are not dissociated even in highly denaturing gels 15. Such complexes can therefore be visualized in Northern blots as bands that migrate at a higher molecular weight than unbound mature micrornas. However, we do not recommend these methods to estimate transfection efficiency. When transfection is inefficient it is very often because the microrna inhibitoris retained on the outside of the cell membrane or is sequestered in internal vesicles, physically separated from their microrna targets in the cytoplasm. However, during cell lysis these oligonucleotides are released and will interact with micrornas in the lysate. Real-time PCR and Northern blot analysis therefore, can not distinguish between biologically relevant complexes that formed in the cytoplasm of transfected cells and complexes that formed following cell lysis. 2. Western blot analysis For micrornas with well characterized mrna targets, we instead recommend monitoring transfection efficiency by measuring target mrna encoded protein levels by Western blotting. 3. MicroRNA reporter assays If suitable antibodies are not available, we instead recommend using a microrna reporter assay. An example of such an assay could be a plasmid encoded Renilla luciferase gene in which a target site complementary to the studied microrna has been introduced into the 3 -UTR of the reporter. Consequently, the expression of the luciferase protein from this plasmid will be repressed when this particular microrna is present in the cell. However, antisense-mediated inhibition of the microrna results in a derepression of the reporter and an upregulated luciferase expression. Thus, a reporter system needs to be constructed for each microrna in the study and the background expression of the reporter depends on the expression level of the studied microrna in the cell. 4 In addition to the microrna reporter vector, a control vector constitutively expressing a different reporter molecule, e.g., firefly luciferase or betagalactosidase should be used for normalization of transfection efficiency. 4. Fluorescently labeled microrna inhibitors A very convenient way of measuring transfection efficiency is by using fluorescently labeled mircury LNA microrna Inhibitors. Flow cytometry can be used to sort the cells transfected with these oligonucleotides. While direct visualization of the LNA microrna Inhibitors
5 in the cells is convenient, it is important to ensure that the signal is diffusely distributed in the cytoplasm. If there is a granular distribution in the cytoplasm or if the signal is concentrated to the cell surface, this indicates that the oligonucleotide has been sequestered in vesicles or at the cell membrane, respectively. For this reason, we only recommend this procedure for scientists experienced in confocal microscopy. Monitoring the effect(s) of the microrna inhibition There are a number of different ways of monitoring the effects of a microrna silencing. The choice of method depends on how much is known about the microrna and its targets and the phenotype of the affected cells. For scientists who wish to monitor changes in the cell population following microrna silencing, we recommend phenotypic assays such as cell proliferation, cell differentiation and apoptosis (caspase) assays. The choice of assay will depend on the biological process being studied. In addition to monitoring transfection efficiency, reporter vectors can also be used to demonstrate interactions between a microrna and a predicted target site 1. A predicted microrna binding site, or an entire 3 UTR sequence, can be cloned downstream of the luciferase reporter. Since micrornas cause translational inhibition and in some cases mrna degradation, the effect of the silencing on known or predicted target genes can also be measured on the mrna and/or protein levels. Since validated target genes are not available for the majority of micrornas, a number of algorithms have been developed for the prediction of microrna target genes (Table II). Such prediction tools aid in the validation of new microrna targets. 5 Furthermore, global changes in mrna levels following a microrna inhibition can be monitored using microarray analysis. This approach is not without risk as it may be difficult to distinguish between primary and secondary effects of the silencing. However, by monitoring mrna levels over time this problem can be alleviated.
6 Table II 6 Method Type of Method Reference Method Availability Stark et al. Complementary (Stark et al., 2003) miranda Complementary (John et al., 2004) miranda MiRBase Target Scan Lipofectamine Complementary Seed Complementary DIANA microt Thermodynamics (Enright et al., 2003) (Lewis et al., 2005) (Kirakidou et al., 2004) PicTar Thermodynamics (Krek et al., 2005) RNAHybrid mirgen++ MiTarget MiTarget2 TarBase Data Resource Availability Online search Yes micrornas Download Yes Online search Yes Online search Yes Download Yes N/A Yes Thermodynamics (Rehmsmeier Download Yes & Statistical model et al., 2004) Bayesian Inference (Huang et al., Mathlab Code Yes b) genmir Support Vector Machine Support Vector Machine Experimentally Validated Targets (Kim et al., 2006) Online search Yes (Wang and El Online search Yes Naqa, 2008) (Sethupathy et al., 2006) N/A Yes tarbase/ Table II. Methods and resources for microrna target prediction. Reprinted from Enright in microrna Research-Fundamentals, Reviews and Perspectives. Conclusions MicroRNAs have the potential to inhibit multiple target genes or potentially an entire pathway, which make them attractive targets for antisense inhibition studies. Our mircury LNA microrna Inhibitors offer a convenient and powerful way of silencing micrornas and elucidating their function. However, whether you are inhibiting single micrornas or using the mircury LNA microrna Inhibitor Library for high throughput screens, careful planning of the experimental set-up is crucial for the outcome of the experiment. Also, it is important to bear in mind that networks of several different micrornas may act cooperatively in the translational regulation of individual mrnas. Therefore, simultaneous disruption of multiple micrornas may be required to elicit a biological phenotype. This can only be achieved using mircury LNA microrna Inhibitors, as only they have the high potency needed for the cotransfection of several oligonucleotides at non-cytotoxic concentrations.
7 Scientific contributors Anna Karina Busch, Niels M. Frandsen, Hazel Pinheiro, Johan Wahlin Exiqon A/S, Vedbæk, Denmark. References 1. The microrna mir-181 targets the homeobox protein Hox-A11 during mammalian myoblast differentiation. Naguibneva et al. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8: MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Chan et al. Cancer Res. 2005, 65: MicroRNA-21 knockdown disrupts glioma growth in vivo and displays synergistic cytotoxicity with neural precursor cell delivered S-TRAIL in human gliomas. Corsten et al. Cancer Res. 2007, 67: MicroRNAs regulate the expression of the alternative splicing factor nptb during muscle development. Boutz et al. Genes Dev. 2007, 21: An LNA TM -based loss-of-function assay for micrornas. Naguibneva et al. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2006, 60: Transcripts targeted by the microrna-16 family cooperatively regulate cell cycle progression. Linsley et al. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27: Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microrna mir- 21 in breast cancer cells. Frankel et al. 2008, 283: X-tremeGene sirna transfection reagent: A powerful tool for antisense inhibition of microrna in human cells with mircury LNA TM Knockdown Probes. Watzele et al. Biochemica, 2006, 2: Suppression of microrna-silencing pathway by HIV-1 during virus replication. Triboulet et al. Science, 2007, 315: mir-200b mediates post-transcriptional repression of ZFHX1B. Christoffersen et al. RNA, 2007, 13: MicroRNA expression dynamics during murine and human erythroid differentiation. Zhan et al. Exp. Hematol. 2007, 35: A minicircuitry comprised of microrna-223 and transcription factors NFI-A and C/ EBPalpha regulates human granulopoiesis. Fazi et al. Cell, 2005, 123: mir-221 and mir-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27kip1. Galardi et al. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282: Antagonism of microrna-122 in mice by systemically administered LNA-antimiR leads to up-regulation of a large set of predicted target mrnas in the liver. Elmén et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 306: mir-122 targeting with LNA/2 -O-methyl oligonucleotide mixmers, peptide nucleic acids (PNA), and PNA-peptide conjugates. Fabani & Gait. RNA. 2008, 14:
岑 祥 股 份 有 限 公 司 技 術 專 員 費 軫 尹 20100803
 技 術 專 員 費 軫 尹 20100803 Overview of presentation Basic Biology of RNA interference Application of sirna for gene function? How to study mirna? How to deliver sirna and mirna? New prospects on RNAi research
技 術 專 員 費 軫 尹 20100803 Overview of presentation Basic Biology of RNA interference Application of sirna for gene function? How to study mirna? How to deliver sirna and mirna? New prospects on RNAi research
Functional Analysis. mircury LNA microrna Mimics
 Functional Analysis mircury LNA microrna Mimics Instruction manual v1.0 April 2014 Table of Contents Product summary......................................................... 3 Content..................................................................
Functional Analysis mircury LNA microrna Mimics Instruction manual v1.0 April 2014 Table of Contents Product summary......................................................... 3 Content..................................................................
Relative Quantification of mirna Target mrnas by Real-Time qpcr. 1 Introduction. Gene Expression Application Note No. 4
 Gene Expression Application Note No. 4 Relative Quantification of mirna Target mrnas by Real-Time qpcr Ute Ernst, Jitao David Zhang, Anja Irsigler, Stefan Wiemann, Ulrich Tschulena Division: Molecular
Gene Expression Application Note No. 4 Relative Quantification of mirna Target mrnas by Real-Time qpcr Ute Ernst, Jitao David Zhang, Anja Irsigler, Stefan Wiemann, Ulrich Tschulena Division: Molecular
TOOLS sirna and mirna. User guide
 TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
TOOLS sirna and mirna User guide Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is a powerful tool for suppression gene expression by causing the destruction of specific mrna molecules. Small Interfering RNAs (sirnas)
A role of microrna in the regulation of telomerase? Yuan Ming Yeh, Pei Rong Huang, and Tzu Chien V. Wang
 A role of microrna in the regulation of telomerase? Yuan Ming Yeh, Pei Rong Huang, and Tzu Chien V. Wang Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Chang Gung University, Kwei San, Tao Yuan 333, Taiwan
A role of microrna in the regulation of telomerase? Yuan Ming Yeh, Pei Rong Huang, and Tzu Chien V. Wang Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Chang Gung University, Kwei San, Tao Yuan 333, Taiwan
OriGene Technologies, Inc. MicroRNA analysis: Detection, Perturbation, and Target Validation
 OriGene Technologies, Inc. MicroRNA analysis: Detection, Perturbation, and Target Validation -Optimal strategies to a successful mirna research project Optimal strategies to a successful mirna research
OriGene Technologies, Inc. MicroRNA analysis: Detection, Perturbation, and Target Validation -Optimal strategies to a successful mirna research project Optimal strategies to a successful mirna research
Notch 1 -dependent regulation of cell fate in colorectal cancer
 Notch 1 -dependent regulation of cell fate in colorectal cancer Referees: PD Dr. Tobias Dick Prof. Dr. Wilfried Roth http://d-nb.info/1057851272 CONTENTS Summary 1 Zusammenfassung 2 1 INTRODUCTION 3 1.1
Notch 1 -dependent regulation of cell fate in colorectal cancer Referees: PD Dr. Tobias Dick Prof. Dr. Wilfried Roth http://d-nb.info/1057851272 CONTENTS Summary 1 Zusammenfassung 2 1 INTRODUCTION 3 1.1
Micro RNAs: potentielle Biomarker für das. Blutspenderscreening
 Micro RNAs: potentielle Biomarker für das Blutspenderscreening micrornas - Background Types of RNA -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) -Non-coding (examples): Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
Micro RNAs: potentielle Biomarker für das Blutspenderscreening micrornas - Background Types of RNA -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) -Non-coding (examples): Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
Thermo Scientific DharmaFECT Transfection Reagents
 Thermo Scientific Transfection Reagents Maintain cell viability with lipids specially formulated to deliver sirna Achieve robust sirna uptake for dependable gene silencing Expand your RNAi applications
Thermo Scientific Transfection Reagents Maintain cell viability with lipids specially formulated to deliver sirna Achieve robust sirna uptake for dependable gene silencing Expand your RNAi applications
Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology
 Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology Chapter 18 Lecture Objectives What Is Recombinant DNA? How Are New Genes Inserted into Cells? What Sources of DNA Are Used in Cloning? What Other Tools Are Used to Study
Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology Chapter 18 Lecture Objectives What Is Recombinant DNA? How Are New Genes Inserted into Cells? What Sources of DNA Are Used in Cloning? What Other Tools Are Used to Study
Essentials of Real Time PCR. About Sequence Detection Chemistries
 Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
Essentials of Real Time PCR About Real-Time PCR Assays Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the ability to monitor the progress of the PCR as it occurs (i.e., in real time). Data is therefore collected
MicroRNA formation. 4th International Symposium on Non-Surgical Contraceptive Methods of Pet Population Control
 MicroRNA formation mirna s are processed from several precursor stages Mammalian genomes seem to have 100 s of mirna s Nucleotides in positions 2-8 of an mirna are considered the mirna seed 5 Methyl-G
MicroRNA formation mirna s are processed from several precursor stages Mammalian genomes seem to have 100 s of mirna s Nucleotides in positions 2-8 of an mirna are considered the mirna seed 5 Methyl-G
LightSwitch Luciferase Assay System
 Constructs, Assays & Services Assay System Promoter GoClones Synthetic Response Elements Pathway Cell Lines 3 UTR GoClones mirna Mimics & Inhibitors Synthetic mirna Targets Transfection Reagents Assay
Constructs, Assays & Services Assay System Promoter GoClones Synthetic Response Elements Pathway Cell Lines 3 UTR GoClones mirna Mimics & Inhibitors Synthetic mirna Targets Transfection Reagents Assay
RNA Interference. - Localization - Labeling - Expression Profiling - In Vivo Delivery - Transfection
 RNA Interference - Localization - Labeling - Expression Profiling - In Vivo Delivery - Transfection Rna interference x RNAi Pathways RNA interference x Tools and Multiplexing RNAi Tools pri-mirna Application
RNA Interference - Localization - Labeling - Expression Profiling - In Vivo Delivery - Transfection Rna interference x RNAi Pathways RNA interference x Tools and Multiplexing RNAi Tools pri-mirna Application
mirnaselect pep-mir Cloning and Expression Vector
 Product Data Sheet mirnaselect pep-mir Cloning and Expression Vector CATALOG NUMBER: MIR-EXP-C STORAGE: -80ºC QUANTITY: 2 vectors; each contains 100 µl of bacterial glycerol stock Components 1. mirnaselect
Product Data Sheet mirnaselect pep-mir Cloning and Expression Vector CATALOG NUMBER: MIR-EXP-C STORAGE: -80ºC QUANTITY: 2 vectors; each contains 100 µl of bacterial glycerol stock Components 1. mirnaselect
micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved
 microrna 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions of target mrnas Act as negative
microrna 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions of target mrnas Act as negative
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products
 Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
Validating Microarray Data Using RT 2 Real-Time PCR Products Introduction: Real-time PCR monitors the amount of amplicon as the reaction occurs. Usually, the amount of product is directly related to the
2.1.2 Characterization of antiviral effect of cytokine expression on HBV replication in transduced mouse hepatocytes line
 i 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Human Hepatitis B virus (HBV) 1 1.1.1 Pathogenesis of Hepatitis B 1 1.1.2 Genome organization of HBV 3 1.1.3 Structure of HBV virion 5 1.1.4 HBV life cycle 5 1.1.5 Experimental models
i 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Human Hepatitis B virus (HBV) 1 1.1.1 Pathogenesis of Hepatitis B 1 1.1.2 Genome organization of HBV 3 1.1.3 Structure of HBV virion 5 1.1.4 HBV life cycle 5 1.1.5 Experimental models
Transfection-Transfer of non-viral genetic material into eukaryotic cells. Infection/ Transduction- Transfer of viral genetic material into cells.
 Transfection Key words: Transient transfection, Stable transfection, transfection methods, vector, plasmid, origin of replication, reporter gene/ protein, cloning site, promoter and enhancer, signal peptide,
Transfection Key words: Transient transfection, Stable transfection, transfection methods, vector, plasmid, origin of replication, reporter gene/ protein, cloning site, promoter and enhancer, signal peptide,
TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent
 Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5400 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent
Quick Reference Protocol, MSDS and Certificate of Analysis available at mirusbio.com/5400 INTRODUCTION TransIT -2020 Transfection Reagent is a high-performance, animal-origin free, broad spectrum reagent
Understanding the immune response to bacterial infections
 Understanding the immune response to bacterial infections A Ph.D. (SCIENCE) DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO JADAVPUR UNIVERSITY SUSHIL KUMAR PATHAK DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY BOSE INSTITUTE 2008 CONTENTS Page SUMMARY
Understanding the immune response to bacterial infections A Ph.D. (SCIENCE) DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO JADAVPUR UNIVERSITY SUSHIL KUMAR PATHAK DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY BOSE INSTITUTE 2008 CONTENTS Page SUMMARY
HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook
 Fifth Edition October 2010 HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook For transfection of eukaryotic cells with sirna and mirna Sample & Assay Technologies QIAGEN Sample and Assay Technologies QIAGEN is the
Fifth Edition October 2010 HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook For transfection of eukaryotic cells with sirna and mirna Sample & Assay Technologies QIAGEN Sample and Assay Technologies QIAGEN is the
Profiling of microrna in Blood Serum/Plasma. Guidelines for the mircury LNA TM Universal RT microrna PCR System
 Profiling of microrna in Blood Serum/Plasma Guidelines for the mircury LNA TM Universal RT microrna PCR System Table of Contents 2 Introduction.....................................................................................
Profiling of microrna in Blood Serum/Plasma Guidelines for the mircury LNA TM Universal RT microrna PCR System Table of Contents 2 Introduction.....................................................................................
Thermo Scientific Dharmacon sirna Libraries
 Thermo Scientific Dharmacon sirna Libraries Scientific innovation in sirna potency, specificity and delivery Superior sirna in comprehensive collections for reliable screens Market leading products for
Thermo Scientific Dharmacon sirna Libraries Scientific innovation in sirna potency, specificity and delivery Superior sirna in comprehensive collections for reliable screens Market leading products for
Thermo Scientific Dharmacon ON-TARGETplus sirna The Standard for sirna Specificity
 Thermo Scientific Dharmacon sirna The Standard for sirna Specificity Reduce off-targets up to 90% with the market-leading sirna Combine higher target specificity with guaranteed silencing Increase confidence
Thermo Scientific Dharmacon sirna The Standard for sirna Specificity Reduce off-targets up to 90% with the market-leading sirna Combine higher target specificity with guaranteed silencing Increase confidence
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp MicroRNAs are predicted to regulate thousands of mammalian genes, but relatively
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp MicroRNAs are predicted to regulate thousands of mammalian genes, but relatively
Product: Expression Arrest TM egfp control shrna vector
 Product: Expression Arrest TM egfp control vector Catalog #: RHS1702 Product Description The laboratory of Dr. Greg Hannon at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) has created an RNAi Clone Library comprised
Product: Expression Arrest TM egfp control vector Catalog #: RHS1702 Product Description The laboratory of Dr. Greg Hannon at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) has created an RNAi Clone Library comprised
Innate Immunity. Insects rely solely on an innate immune system for defense against infection
 Innate Immunity Insects rely solely on an innate immune system for defense against infection The importance of mammalian innate immunity has only recently become appreciated The innate immune response
Innate Immunity Insects rely solely on an innate immune system for defense against infection The importance of mammalian innate immunity has only recently become appreciated The innate immune response
MAB Solut. MABSolys Génopole Campus 1 5 rue Henri Desbruères 91030 Evry Cedex. www.mabsolut.com. is involved at each stage of your project
 Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
Mabsolus-2015-UK:Mise en page 1 03/07/15 14:13 Page1 Services provider Department of MABSolys from conception to validation MAB Solut is involved at each stage of your project Creation of antibodies Production
Microarray Technology
 Microarrays And Functional Genomics CPSC265 Matt Hudson Microarray Technology Relatively young technology Usually used like a Northern blot can determine the amount of mrna for a particular gene Except
Microarrays And Functional Genomics CPSC265 Matt Hudson Microarray Technology Relatively young technology Usually used like a Northern blot can determine the amount of mrna for a particular gene Except
Optimized Protocol sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells
 page 1 of 8 sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells Kit principle Co-transfection of pmaxgfp, encoding the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from Pontellina p. with an sirna directed against
page 1 of 8 sirna Test Kit for Cell Lines and Adherent Primary Cells Kit principle Co-transfection of pmaxgfp, encoding the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from Pontellina p. with an sirna directed against
Functional and Biomedical Aspects of Genome Research
 Functional and Biomedical Aspects of Genome Research 20 11 35 Vorlesung SS 04 Bartsch, Jockusch & Schmitt-John Mi. 9:15-10:00, in W7-135 13 Functional RNAs Thomas Schmitt-John micro RNAs small interfering
Functional and Biomedical Aspects of Genome Research 20 11 35 Vorlesung SS 04 Bartsch, Jockusch & Schmitt-John Mi. 9:15-10:00, in W7-135 13 Functional RNAs Thomas Schmitt-John micro RNAs small interfering
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005. Lectures 1 2
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 1 2 Lecture 1 We will begin this course with the question: What is a gene? This question will take us four lectures to answer because there are actually several
Co Extra (GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability) Outcomes of Co Extra
 GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability Outcomes of Co Extra Comparison of different real time PCR chemistries and their suitability for detection and quantification of genetically
GM and non GM supply chains: Their CO EXistence and TRAceability Outcomes of Co Extra Comparison of different real time PCR chemistries and their suitability for detection and quantification of genetically
INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL. 1 Standard sirna transfection of adherent cells... 2
 INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTERFERin is a powerful sirna/mirna transfection reagent that ensures efficient gene silencing and reproducible transfection in
INTERFERin in vitro sirna/mirna transfection reagent PROTOCOL DESCRIPTION INTERFERin is a powerful sirna/mirna transfection reagent that ensures efficient gene silencing and reproducible transfection in
Instructions. Torpedo sirna. Material. Important Guidelines. Specifications. Quality Control
 is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
is a is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically designed for the transfer of sirna and mirna into a variety of eukaryotic cell types. is a state of the art transfection reagent, specifically
Manual for: sirna-trans Maximo Reagent
 Manual for: sirna-trans Maximo Reagent Contact: info@geneon.net; www.geneon.net GeneON GmbH Germany GeneON GmbH / Protocol sirna-trans reagent vs. 1.3 / www.geneon.net / - 0 - sirna-trans reagent Instruction
Manual for: sirna-trans Maximo Reagent Contact: info@geneon.net; www.geneon.net GeneON GmbH Germany GeneON GmbH / Protocol sirna-trans reagent vs. 1.3 / www.geneon.net / - 0 - sirna-trans reagent Instruction
Lezioni Dipartimento di Oncologia Farmacologia Molecolare. RNA interference. Giovanna Damia 29 maggio 2006
 Lezioni Dipartimento di Oncologia Farmacologia Molecolare RNA interference Giovanna Damia 29 maggio 2006 RNA INTERFERENCE Sequence-specific gene suppression by dsrnas Gene silencing by dsrna: C. elegans
Lezioni Dipartimento di Oncologia Farmacologia Molecolare RNA interference Giovanna Damia 29 maggio 2006 RNA INTERFERENCE Sequence-specific gene suppression by dsrnas Gene silencing by dsrna: C. elegans
Outline. MicroRNA Bioinformatics. microrna biogenesis. short non-coding RNAs not considered in this lecture. ! Introduction
 Outline MicroRNA Bioinformatics Rickard Sandberg Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology (CMB) Karolinska Institutet! Introduction! microrna target site prediction! Useful resources 2 short non-coding RNAs
Outline MicroRNA Bioinformatics Rickard Sandberg Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology (CMB) Karolinska Institutet! Introduction! microrna target site prediction! Useful resources 2 short non-coding RNAs
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) MicroRNA 212 enhances IS from pancreatic β-cells. INS-1 832/3 β-cells were transfected with precursors for mirnas 212, 375, or negative control oligonucleotides. 48 hrs after
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) MicroRNA 212 enhances IS from pancreatic β-cells. INS-1 832/3 β-cells were transfected with precursors for mirnas 212, 375, or negative control oligonucleotides. 48 hrs after
INTERPRETATION INFORMATION SHEET
 Creative Testing Solutions 2424 West Erie Dr. 2205 Highway 121 10100 Martin Luther King Jr. St. No. Tempe, AZ 85282 Bedford, TX 76021 St. Petersburg, FL 33716 INTERPRETATION INFORMATION SHEET Human Immunodeficiency
Creative Testing Solutions 2424 West Erie Dr. 2205 Highway 121 10100 Martin Luther King Jr. St. No. Tempe, AZ 85282 Bedford, TX 76021 St. Petersburg, FL 33716 INTERPRETATION INFORMATION SHEET Human Immunodeficiency
QIAGEN Transfection Technologies
 QIAGEN Transfection Technologies Efficient and robust transfection for all your applications Sample & Assay Technologies Table of contents QIAGEN solutions for efficient transfection Transfection is a
QIAGEN Transfection Technologies Efficient and robust transfection for all your applications Sample & Assay Technologies Table of contents QIAGEN solutions for efficient transfection Transfection is a
sirna Duplexes & RNAi Explorer
 P r o d u c t S p e c i f i c a t i o n s Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fl/Dabcyl Molecular Beacon Catalog No.:27-6402-01 Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fluorescein/Tamra TaqMan Catalog No.:27-6402-01
P r o d u c t S p e c i f i c a t i o n s Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fl/Dabcyl Molecular Beacon Catalog No.:27-6402-01 Guaranteed RNAi Explorer kit with Fluorescein/Tamra TaqMan Catalog No.:27-6402-01
SmartFlare RNA Detection Probes: Principles, protocols and troubleshooting
 Technical Guide SmartFlare RNA Detection Probes: Principles, protocols and troubleshooting Principles of SmartFlare technology RNA detection traditionally requires transfection, laborious sample prep,
Technical Guide SmartFlare RNA Detection Probes: Principles, protocols and troubleshooting Principles of SmartFlare technology RNA detection traditionally requires transfection, laborious sample prep,
Investigating the role of a Cryptosporidium parum apyrase in infection
 Investigating the role of a Cryptosporidium parum apyrase in infection David Riccardi and Patricio Manque Abstract This project attempted to characterize the function of a Cryptosporidium parvum apyrase
Investigating the role of a Cryptosporidium parum apyrase in infection David Riccardi and Patricio Manque Abstract This project attempted to characterize the function of a Cryptosporidium parvum apyrase
Biotechnology: DNA Technology & Genomics
 Chapter 20. Biotechnology: DNA Technology & Genomics 2003-2004 The BIG Questions How can we use our knowledge of DNA to: diagnose disease or defect? cure disease or defect? change/improve organisms? What
Chapter 20. Biotechnology: DNA Technology & Genomics 2003-2004 The BIG Questions How can we use our knowledge of DNA to: diagnose disease or defect? cure disease or defect? change/improve organisms? What
Gene Expression Assays
 APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
APPLICATION NOTE TaqMan Gene Expression Assays A mpl i fic ationef ficienc yof TaqMan Gene Expression Assays Assays tested extensively for qpcr efficiency Key factors that affect efficiency Efficiency
Dicer Substrate RNAi Design
 INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES, INC. Dicer Substrate RNAi Design How to design and order 27-mer Dicer-substrate Duplex RNAs for use as RNA interference reagents The following document provides a summary of
INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES, INC. Dicer Substrate RNAi Design How to design and order 27-mer Dicer-substrate Duplex RNAs for use as RNA interference reagents The following document provides a summary of
Name Class Date. Figure 13 1. 2. Which nucleotide in Figure 13 1 indicates the nucleic acid above is RNA? a. uracil c. cytosine b. guanine d.
 13 Multiple Choice RNA and Protein Synthesis Chapter Test A Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Which of the following are found in both
13 Multiple Choice RNA and Protein Synthesis Chapter Test A Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Which of the following are found in both
MicroRNA Mike needs help to degrade all the mrna transcripts! Aaron Arvey ISMB 2010
 Target mrna abundance dilutes microrna and sirna activity MicroRNA Mike needs help to degrade all the mrna transcripts! Aaron Arvey ISMB 2010 Target mrna abundance dilutes microrna and sirna activity Erik
Target mrna abundance dilutes microrna and sirna activity MicroRNA Mike needs help to degrade all the mrna transcripts! Aaron Arvey ISMB 2010 Target mrna abundance dilutes microrna and sirna activity Erik
User Manual/Hand book. qpcr mirna Arrays ABM catalog # MA003 (human) and MA004 (mouse)
 User Manual/Hand book qpcr mirna Arrays ABM catalog # MA003 (human) and MA004 (mouse) Kit Components Cat. No. MA003...Human Whole Genome mirna qpcr Profiling Kit (-20 C) The following components are sufficient
User Manual/Hand book qpcr mirna Arrays ABM catalog # MA003 (human) and MA004 (mouse) Kit Components Cat. No. MA003...Human Whole Genome mirna qpcr Profiling Kit (-20 C) The following components are sufficient
Approaches that can be used to study expression of specific proteins
 Approaches that can be used to study expression of specific proteins Receptors and transporters Homogenate binding studies Receptor autoradiography Radiochemical Western blotting Immunohistochemistry/cytochemistry
Approaches that can be used to study expression of specific proteins Receptors and transporters Homogenate binding studies Receptor autoradiography Radiochemical Western blotting Immunohistochemistry/cytochemistry
Effects of Antibiotics on Bacterial Growth and Protein Synthesis: Student Laboratory Manual
 Effects of Antibiotics on Bacterial Growth and Protein Synthesis: Student Laboratory Manual I. Purpose...1 II. Introduction...1 III. Inhibition of Bacterial Growth Protocol...2 IV. Inhibition of in vitro
Effects of Antibiotics on Bacterial Growth and Protein Synthesis: Student Laboratory Manual I. Purpose...1 II. Introduction...1 III. Inhibition of Bacterial Growth Protocol...2 IV. Inhibition of in vitro
quantitative real-time PCR, grain, simplex DNA extraction: PGS0426 RT-PCR: PGS0494 & PGS0476
 BioScience quantitative real-time PCR, grain, simplex DNA extraction: PGS0426 RT-PCR: PGS0494 & PGS0476 This method describes a Real-time semi-quantitative TaqMan PCR procedure for the determination of
BioScience quantitative real-time PCR, grain, simplex DNA extraction: PGS0426 RT-PCR: PGS0494 & PGS0476 This method describes a Real-time semi-quantitative TaqMan PCR procedure for the determination of
Analysis of gene expression data. Ulf Leser and Philippe Thomas
 Analysis of gene expression data Ulf Leser and Philippe Thomas This Lecture Protein synthesis Microarray Idea Technologies Applications Problems Quality control Normalization Analysis next week! Ulf Leser:
Analysis of gene expression data Ulf Leser and Philippe Thomas This Lecture Protein synthesis Microarray Idea Technologies Applications Problems Quality control Normalization Analysis next week! Ulf Leser:
Viruses. Viral components: Capsid. Chapter 10: Viruses. Viral components: Nucleic Acid. Viral components: Envelope
 Viruses Chapter 10: Viruses Lecture Exam #3 Wednesday, November 22 nd (This lecture WILL be on Exam #3) Dr. Amy Rogers Office Hours: MW 9-10 AM Too small to see with a light microscope Visible with electron
Viruses Chapter 10: Viruses Lecture Exam #3 Wednesday, November 22 nd (This lecture WILL be on Exam #3) Dr. Amy Rogers Office Hours: MW 9-10 AM Too small to see with a light microscope Visible with electron
Supplemental Information. McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data
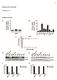 1 Supplemental Information McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data 2 Figure S1. Glucose consumption rates of MM cell lines exceed that of normal PBMC. (A) Normal PBMC isolated from three healthy donors were
1 Supplemental Information McBrayer et al. Supplemental Data 2 Figure S1. Glucose consumption rates of MM cell lines exceed that of normal PBMC. (A) Normal PBMC isolated from three healthy donors were
RNA Viruses. A Practical Approac h. Alan J. Cann
 RNA Viruses A Practical Approac h Alan J. Cann List of protocols page xiii Abbreviations xvii Investigation of RNA virus genome structure 1 A j. Easton, A.C. Marriott and C.R. Pringl e 1 Introduction-the
RNA Viruses A Practical Approac h Alan J. Cann List of protocols page xiii Abbreviations xvii Investigation of RNA virus genome structure 1 A j. Easton, A.C. Marriott and C.R. Pringl e 1 Introduction-the
Gene Silencing Oligos (GSOs) Third Generation Antisense
 Gene Silencing Oligos (GSOs) Third Generation Antisense Walter R. Strapps, Ph.D. Executive Director, RNA Therapeutics Idera Pharmaceuticals Cambridge, MA NASDAQ: IDRA www.iderapharma.com Idera is a leader
Gene Silencing Oligos (GSOs) Third Generation Antisense Walter R. Strapps, Ph.D. Executive Director, RNA Therapeutics Idera Pharmaceuticals Cambridge, MA NASDAQ: IDRA www.iderapharma.com Idera is a leader
DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis. This isn t a baaaaaaaddd chapter!!!
 DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis This isn t a baaaaaaaddd chapter!!! The Discovery of DNA s Structure Watson and Crick s discovery of DNA s structure was based on almost fifty years of research by other
DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis This isn t a baaaaaaaddd chapter!!! The Discovery of DNA s Structure Watson and Crick s discovery of DNA s structure was based on almost fifty years of research by other
Profiling of non-coding RNA classes Gunter Meister
 Profiling of non-coding RNA classes Gunter Meister RNA Biology Regensburg University Universitätsstrasse 31 93053 Regensburg Overview Classes of non-coding RNAs Profiling strategies Validation Protein-RNA
Profiling of non-coding RNA classes Gunter Meister RNA Biology Regensburg University Universitätsstrasse 31 93053 Regensburg Overview Classes of non-coding RNAs Profiling strategies Validation Protein-RNA
Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit
 Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit Item No. 10009349 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Safety
Cell Cycle Phase Determination Kit Item No. 10009349 Customer Service 800.364.9897 * Technical Support 888.526.5351 www.caymanchem.com TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials Supplied 3 Safety
Chapter 8. Summary and Perspectives
 Chapter 8 Summary and Perspectives 131 Chapter 8 Summary Overexpression of the multidrug resistance protein MRP1 confer multidrug resistance (MDR) to cancer cells. The contents of this thesis describe
Chapter 8 Summary and Perspectives 131 Chapter 8 Summary Overexpression of the multidrug resistance protein MRP1 confer multidrug resistance (MDR) to cancer cells. The contents of this thesis describe
Creating Standard Curves with Genomic DNA or Plasmid DNA Templates for Use in Quantitative PCR
 Creating Standard Curves with Genomic DNA or Plasmid DNA Templates for Use in Quantitative PCR Overview Genomic DNA (gdna) and plasmids containing cloned target sequences are commonly used as standards
Creating Standard Curves with Genomic DNA or Plasmid DNA Templates for Use in Quantitative PCR Overview Genomic DNA (gdna) and plasmids containing cloned target sequences are commonly used as standards
博 士 論 文 ( 要 約 ) A study on enzymatic synthesis of. stable cyclized peptides which. inhibit protein-protein interactions
 博 士 論 文 ( 要 約 ) 論 文 題 目 A study on enzymatic synthesis of stable cyclized peptides which inhibit protein-protein interactions ( 蛋 白 質 間 相 互 作 用 を 阻 害 する 安 定 な 環 状 化 ペプチドの 酵 素 合 成 に 関 する 研 究 ) 氏 名 張 静 1
博 士 論 文 ( 要 約 ) 論 文 題 目 A study on enzymatic synthesis of stable cyclized peptides which inhibit protein-protein interactions ( 蛋 白 質 間 相 互 作 用 を 阻 害 する 安 定 な 環 状 化 ペプチドの 酵 素 合 成 に 関 する 研 究 ) 氏 名 張 静 1
CHAPTER 6: RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY YEAR III PHARM.D DR. V. CHITRA
 CHAPTER 6: RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY YEAR III PHARM.D DR. V. CHITRA INTRODUCTION DNA : DNA is deoxyribose nucleic acid. It is made up of a base consisting of sugar, phosphate and one nitrogen base.the
CHAPTER 6: RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY YEAR III PHARM.D DR. V. CHITRA INTRODUCTION DNA : DNA is deoxyribose nucleic acid. It is made up of a base consisting of sugar, phosphate and one nitrogen base.the
Five-year relative survival rates. Cancer. Age-adjusted cancer death rates. Proteomic Technologies for Cancer Biomarker Discovery 2010/3/22
 Cancer Five-year relative survival rates Basal lamina Underlyig tissue Normal tissue Carcinoma Invasive carcinoma 1 http://www.cancer.org/docroot/home/index.asp 2 Proteomic Technologies for Cancer Biomarker
Cancer Five-year relative survival rates Basal lamina Underlyig tissue Normal tissue Carcinoma Invasive carcinoma 1 http://www.cancer.org/docroot/home/index.asp 2 Proteomic Technologies for Cancer Biomarker
Structure and Function of DNA
 Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
Structure and Function of DNA DNA and RNA Structure DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. They consist of chemical units called nucleotides. The nucleotides are joined by a sugar-phosphate backbone. The four
Practical Cell Analysis
 Practical Cell Analysis Dimitri Pappas Dept of Chemistry & Biochemistry, Texas Tech University, USA WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd, Publication Contents Preface Acknowledgments xiii xix 1 Getting Started
Practical Cell Analysis Dimitri Pappas Dept of Chemistry & Biochemistry, Texas Tech University, USA WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd, Publication Contents Preface Acknowledgments xiii xix 1 Getting Started
RNA & Protein Synthesis
 RNA & Protein Synthesis Genes send messages to cellular machinery RNA Plays a major role in process Process has three phases (Genetic) Transcription (Genetic) Translation Protein Synthesis RNA Synthesis
RNA & Protein Synthesis Genes send messages to cellular machinery RNA Plays a major role in process Process has three phases (Genetic) Transcription (Genetic) Translation Protein Synthesis RNA Synthesis
EXPRESSION ARREST shrna mir GENOME- WIDE LIBRARIES
 C GUGAAG EXPRESSION ARREST shrna mir GENOME- WIDE LIBRARIES MicroRNA-adapted shrna (shrna mir ) for increased, specific and consistent knockdown. MicroRNA PROCESSING PATHWAY UTILIZED FOR shrna mir Developed
C GUGAAG EXPRESSION ARREST shrna mir GENOME- WIDE LIBRARIES MicroRNA-adapted shrna (shrna mir ) for increased, specific and consistent knockdown. MicroRNA PROCESSING PATHWAY UTILIZED FOR shrna mir Developed
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
QPCR Applications using Stratagene s Mx Real-Time PCR Platform
 QPCR Applications using Stratagene s Mx Real-Time PCR Platform Dan Schoeffner, Ph.D Field Applications Scientist Dan.Schoeffner@Stratagene.com Tech. Services 800-894-1304 Polymerase Chain Reaction Melt
QPCR Applications using Stratagene s Mx Real-Time PCR Platform Dan Schoeffner, Ph.D Field Applications Scientist Dan.Schoeffner@Stratagene.com Tech. Services 800-894-1304 Polymerase Chain Reaction Melt
Viral Infection: Receptors
 Viral Infection: Receptors Receptors: Identification of receptors has come from expressing the gene for the receptor in a cell to which a virus does not normally bind -OR- By blocking virus attachment
Viral Infection: Receptors Receptors: Identification of receptors has come from expressing the gene for the receptor in a cell to which a virus does not normally bind -OR- By blocking virus attachment
Given these characteristics of life, which of the following objects is considered a living organism? W. X. Y. Z.
 Cell Structure and Organization 1. All living things must possess certain characteristics. They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on to their offspring.
Cell Structure and Organization 1. All living things must possess certain characteristics. They are all composed of one or more cells. They can grow, reproduce, and pass their genes on to their offspring.
Head of College Scholars List Scheme. Summer Studentship. Report Form
 Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the project
Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the project
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA 1
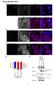 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Overexpression of untagged Ago2 inhibits the nuclear transport of the dotted foci of GFP-signal of myc-gfp-tnrc6a-nes-mut. (A C) HeLa cells expressing myc-gfp-tnrc6a-nes-mut
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Overexpression of untagged Ago2 inhibits the nuclear transport of the dotted foci of GFP-signal of myc-gfp-tnrc6a-nes-mut. (A C) HeLa cells expressing myc-gfp-tnrc6a-nes-mut
Module 3 Questions. 7. Chemotaxis is an example of signal transduction. Explain, with the use of diagrams.
 Module 3 Questions Section 1. Essay and Short Answers. Use diagrams wherever possible 1. With the use of a diagram, provide an overview of the general regulation strategies available to a bacterial cell.
Module 3 Questions Section 1. Essay and Short Answers. Use diagrams wherever possible 1. With the use of a diagram, provide an overview of the general regulation strategies available to a bacterial cell.
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
 Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
Name Period Concept 5.1 Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Circle the three classes that are called
REAL TIME PCR USING SYBR GREEN
 REAL TIME PCR USING SYBR GREEN 1 THE PROBLEM NEED TO QUANTITATE DIFFERENCES IN mrna EXPRESSION SMALL AMOUNTS OF mrna LASER CAPTURE SMALL AMOUNTS OF TISSUE PRIMARY CELLS PRECIOUS REAGENTS 2 THE PROBLEM
REAL TIME PCR USING SYBR GREEN 1 THE PROBLEM NEED TO QUANTITATE DIFFERENCES IN mrna EXPRESSION SMALL AMOUNTS OF mrna LASER CAPTURE SMALL AMOUNTS OF TISSUE PRIMARY CELLS PRECIOUS REAGENTS 2 THE PROBLEM
Biacore X BIACORE. The versatile high sensitivity system
 Biacore X The versatile high sensitivity system Work with high sensitivity Study binding in non-aqueous and aqueous samples Reduce sample consumption Perform the most advanced kinetic evaluation Use proven
Biacore X The versatile high sensitivity system Work with high sensitivity Study binding in non-aqueous and aqueous samples Reduce sample consumption Perform the most advanced kinetic evaluation Use proven
Just the Facts: A Basic Introduction to the Science Underlying NCBI Resources
 1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
1 of 8 11/7/2004 11:00 AM National Center for Biotechnology Information About NCBI NCBI at a Glance A Science Primer Human Genome Resources Model Organisms Guide Outreach and Education Databases and Tools
RNAi. Martin Latterich
 RNAi Martin Latterich Contributors Abbreviations Preface i x ( xi xiii 1 Methods in RNA interference 1 Martin Latterich and Dalia Halawan i References 2 2 RNAi reagent design 3 Bernd Jagla and Nathalie
RNAi Martin Latterich Contributors Abbreviations Preface i x ( xi xiii 1 Methods in RNA interference 1 Martin Latterich and Dalia Halawan i References 2 2 RNAi reagent design 3 Bernd Jagla and Nathalie
Diabetes and Drug Development
 Diabetes and Drug Development Metabolic Disfunction Leads to Multiple Diseases Hypertension ( blood pressure) Metabolic Syndrome (Syndrome X) LDL HDL Lipoproteins Triglycerides FFA Hyperinsulinemia Insulin
Diabetes and Drug Development Metabolic Disfunction Leads to Multiple Diseases Hypertension ( blood pressure) Metabolic Syndrome (Syndrome X) LDL HDL Lipoproteins Triglycerides FFA Hyperinsulinemia Insulin
Real-time PCR: Understanding C t
 APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
APPLICATION NOTE Real-Time PCR Real-time PCR: Understanding C t Real-time PCR, also called quantitative PCR or qpcr, can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE Q5B
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY OF BIOTECHNOLOGICAL PRODUCTS: ANALYSIS
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE QUALITY OF BIOTECHNOLOGICAL PRODUCTS: ANALYSIS
VLLM0421c Medical Microbiology I, practical sessions. Protocol to topic J10
 Topic J10+11: Molecular-biological methods + Clinical virology I (hepatitis A, B & C, HIV) To study: PCR, ELISA, your own notes from serology reactions Task J10/1: DNA isolation of the etiological agent
Topic J10+11: Molecular-biological methods + Clinical virology I (hepatitis A, B & C, HIV) To study: PCR, ELISA, your own notes from serology reactions Task J10/1: DNA isolation of the etiological agent
Superior TrueMAB TM monoclonal antibodies for the recognition of proteins native epitopes
 Superior TrueMAB TM monoclonal antibodies for the recognition of proteins native epitopes Outlines Brief introduction of OriGene s mission on gene-centric product solution. TrueMAB monoclonal antibody
Superior TrueMAB TM monoclonal antibodies for the recognition of proteins native epitopes Outlines Brief introduction of OriGene s mission on gene-centric product solution. TrueMAB monoclonal antibody
Uses of Flow Cytometry
 Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
Uses of Flow Cytometry 1. Multicolour analysis... 2 2. Cell Cycle and Proliferation... 3 a. Analysis of Cellular DNA Content... 4 b. Cell Proliferation Assays... 5 3. Immunology... 6 4. Apoptosis... 7
PRODUCT INFORMATION...
 VIROMER RED In vitro plasmid DNA and mrna Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 RED OR YELLOW?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 FORWARD/REVERSE
VIROMER RED In vitro plasmid DNA and mrna Standard Transfection PRODUCT INFORMATION... 2 GENERAL... 2 RED OR YELLOW?... 3 PROTOCOL GUIDELINES... 4 GENERAL REMARKS... 4 CELL CULTURE AND PLATING... 4 FORWARD/REVERSE
Outline. interfering RNA - What is dat? Brief history of RNA interference. What does it do? How does it work?
 Outline Outline interfering RNA - What is dat? Brief history of RNA interference. What does it do? How does it work? What is RNA interference? Recently discovered regulatory level. Genome immune system.
Outline Outline interfering RNA - What is dat? Brief history of RNA interference. What does it do? How does it work? What is RNA interference? Recently discovered regulatory level. Genome immune system.
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr)
 Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Introduction To Real Time Quantitative PCR (qpcr) SABiosciences, A QIAGEN Company www.sabiosciences.com The Seminar Topics The advantages of qpcr versus conventional PCR Work flow & applications Factors
Molecular Genetics: Challenges for Statistical Practice. J.K. Lindsey
 Molecular Genetics: Challenges for Statistical Practice J.K. Lindsey 1. What is a Microarray? 2. Design Questions 3. Modelling Questions 4. Longitudinal Data 5. Conclusions 1. What is a microarray? A microarray
Molecular Genetics: Challenges for Statistical Practice J.K. Lindsey 1. What is a Microarray? 2. Design Questions 3. Modelling Questions 4. Longitudinal Data 5. Conclusions 1. What is a microarray? A microarray
The world of non-coding RNA. Espen Enerly
 The world of non-coding RNA Espen Enerly ncrna in general Different groups Small RNAs Outline mirnas and sirnas Speculations Common for all ncrna Per def.: never translated Not spurious transcripts Always/often
The world of non-coding RNA Espen Enerly ncrna in general Different groups Small RNAs Outline mirnas and sirnas Speculations Common for all ncrna Per def.: never translated Not spurious transcripts Always/often
SUPER SENSITIVE TM. mirna in FFPE. Next-Gen in situ Tissue Signature Markers Potential tool for Characterization of CUP
 SUPER SENSITIVE TM mirn in FFPE Next-Gen in situ Tissue Signature Markers Potential tool for haracterization of UP mirn in FFPE mirn Processing MicroRNs (mirns) are endogenous, non-coding RNs known to
SUPER SENSITIVE TM mirn in FFPE Next-Gen in situ Tissue Signature Markers Potential tool for haracterization of UP mirn in FFPE mirn Processing MicroRNs (mirns) are endogenous, non-coding RNs known to
Lecture Series 7. From DNA to Protein. Genotype to Phenotype. Reading Assignments. A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides
 Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
Translation Study Guide
 Translation Study Guide This study guide is a written version of the material you have seen presented in the replication unit. In translation, the cell uses the genetic information contained in mrna to
Translation Study Guide This study guide is a written version of the material you have seen presented in the replication unit. In translation, the cell uses the genetic information contained in mrna to
Application Note No. 2 / July 2012. Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation. System
 Application Note No. 2 / July 2012 Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation System Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation Introduction In vitro
Application Note No. 2 / July 2012 Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation System Quantitative Assessment of Cell Quality, Viability and Proliferation Introduction In vitro
GeneCopoeia Genome Editing Tools for Safe Harbor Integration in. Mice and Humans. Ed Davis, Liuqing Qian, Ruiqing li, Junsheng Zhou, and Jinkuo Zhang
 G e n e C o p o eia TM Expressway to Discovery APPLICATION NOTE Introduction GeneCopoeia Genome Editing Tools for Safe Harbor Integration in Mice and Humans Ed Davis, Liuqing Qian, Ruiqing li, Junsheng
G e n e C o p o eia TM Expressway to Discovery APPLICATION NOTE Introduction GeneCopoeia Genome Editing Tools for Safe Harbor Integration in Mice and Humans Ed Davis, Liuqing Qian, Ruiqing li, Junsheng
Molecular Biology Techniques: A Classroom Laboratory Manual THIRD EDITION
 Molecular Biology Techniques: A Classroom Laboratory Manual THIRD EDITION Susan Carson Heather B. Miller D.Scott Witherow ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN
Molecular Biology Techniques: A Classroom Laboratory Manual THIRD EDITION Susan Carson Heather B. Miller D.Scott Witherow ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN
