Steffen Lindert, René Staritzbichler, Nils Wötzel, Mert Karakaş, Phoebe L. Stewart, and Jens Meiler
|
|
|
- Osborne Norman Stokes
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Structure 17 Supplemental Data EM-Fold: De Novo Folding of α-helical Proteins Guided by Intermediate-Resolution Electron Microscopy Density Maps Steffen Lindert, René Staritzbichler, Nils Wötzel, Mert Karakaş, Phoebe L. Stewart, and Jens Meiler SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES EM-Fold uses knowledge-based scores Both in the EM-Fold assembly as well as refinement protocol, knowledge-based scores are used. A full evaluation of the scores will be published shortly (N. Woetzel, R. Staritzbichler, R. Mueller, E. Durham, M. Karakas, J. Meiler, unpublished results). Only a brief description of the knowledge-based scores will be given here. Amino acid pair distance potential This score was derived by evaluating the distribution of Cβ atom distances between pairs of amino acids in the protein data bank. All distances between amino acids that are separated at least 10 residues in sequence and up to 50 Å in distance contributed to the statistics. This score checks whether pairs of amino acids in the computational model are placed in their preferred distance. Neighbor count score The neighbor count score constitutes an amino acid environment potential in that it captures the preference of an amino acid to either be exposed to solvent or buried in the core of the protein. It was implemented by counting the number of neighbors within a radius of 11.4 Å around an amino acid of interest (with a sinusoidal down-weighting of neighbors more than 4 Å away) within the protein data bank. Loop score The loop score is central in the EM-Fold algorithm as it is the only knowledge-based score that is used in both the assembly and refinement protocol. The loop score was derived by comprising information on the sequence length of loops and the Euclidian distance these loops are bridging. There are preferences for a combination of certain lengths with specific distances that are bridged. Secondary structure element packing score EM-Fold utilized exclusively the α-helix α-helix packing component of a more general secondary structural element packing score. The score has been derived by gathering statistics over the distance and twist angle between helical axes for contacting helices in the protein data bank. Two helices prefer to pack with an angle of -45º and a distance of 10 Å. Radius of gyration score The radius of gyration is proportional to the square root of the mean square distance of all Cβ atom coordinates to their mean position. It basically describes the compactness of a protein and is used to assemble proteins in a compact manner. Occupancy score favors models with filled density rods The occupancy score is one of the three scores used in the assembly step of EM-Fold (as described in Experimental Procedures). It was introduced to drive EM-Fold to build models that have as many helices placed into the identified density rods as possible, with the fit of the helices into the density rods optimized. Supplemental Figure 1 summarizes the occupancy score. The length of the density rod (A) as well as the length of the helix (B) that is placed into it, are measured. Depending the deviation of these lengths, the occupancy scores takes on values between 0 (for deviations larger than 3 residues and empty density rods) and -1 (for deviations up to one residue). This rewards models with filled density rods.
2 Connectivity score favors models that connect density rods with strong density between them The connectivity score is one of the three scores used in the assembly step of EM-Fold (as described in Experimental Procedures). It measures the strength of the connection between two density rods. Supplemental Figure 2 exemplifies that some pairs of density rods are connected by stronger density than others. If two helices are placed into density rods with a strong connection between them, the connectivity score rewards this model. EM-Fold refinement protocol improves α-helical orientations It was pointed out in the results section that the refinement protocol generally improves the ranking and the quality of the true model. This is mainly due to the identification of native α- helical orientations. Supplemental Figure 3 illustrates the improvement of α-helix orientation during the refinement step on three examples. ROSETTA iterative high resolution refinement achieves enrichment in true topology models All the seven proteins where EM-Fold was able to find the correct topology (1IE9, 1N83, 1OUV, 1QKM, 1TBF, 1Z1L and 2AX6) were subjected to an iterative ROSETTA refinement protocol (see Experimental Procedures). Supplemental Figure 4 shows the total full-atom ROSETTA energy for all the models and the native structure plotted versus the RMSD of the model for all seven proteins. Refined Ad35F map shows better FSC curve The published Ad35F density map (Saban et al., 2006) was refined further by including more particle images and refining the magnification value of each particle with Frealign (Grigorieff, 2007) until large aromatic side chains could be observed. A FSC plot of the refined Ad35F density map is shown in Figure S5. The additional refinement made a relatively small change in the FSC 0.5 resolution (6.9 to 6.8 Å). However, the extra refinement made more significant improvements in the FSC 0.3 (6.1 to 5.8 Å) and FSC (5.4 to 5.2 Å) resolutions. Trp side chain density can be clearly identified in hexon The refined Ad35F density map exhibits clear density bumps corresponding to large aromatic side chains. Comparison of the density map with the docked penton base and hexon crystal structures indicates that the Trp side chains have the most prominent bumps in the density map. Bumps for other aromatic sidechains are observed but with lower isosurface values. The density and docked hexon crystal structure in the vicinity of the two Trp side chains in hexon helices are shown in Figure S6. Computation The EM-Fold and ROSETTA calculations were performed on the ACCRE Linux cluster at Vanderbilt University which has a total of ~1,400 processors.
3 Figure S1. Schematic Representation of the Occupancy Score Used in the EM-Fold Assembly and Refinement Steps (A) The length of a density rod (in α-helical residues) is determined. (B) The length of the α-helix that is placed into the density rod (in α-helical residues) is determined. (C) Plot of occupancy score vs. the absolute difference between the length of the α-helix and the length of the density into which it is placed. If the length of the α-helix and density rod do not differ by more than one residue, the maximum reward (-1.0) is given. If they differ by more than the assigned length tolerance (3 residues), or if the density rod is left empty, no reward is given. For any length deviation in between these two extremes a partial reward is given.
4 Figure S2. Conceptual Scheme of the Connectivity Score Panels A and B show simulated density for protein 1OUV, while panels C through F show experimental cryoem density assigned to adenovirus protein IIIa (Saban et al., 2006). Each density region is shown at high isosurface (red) and at lower isosurface (grey in panels B,D,F) revealing additional weak density. Some density rods are connected by density (black arrows). For 1OUV these connections represent true peptide links between helices. The connectivity score captures the strength of these density connections between ends of density rods that are closer than 10 Å in space.
5 Figure S3. Three Examples of Improved α-helical Orientations after the EM-Fold Refinement Protocol Black: model before refinement step. Red: native α-helix from PDB. Blue: model after refinement step. (A, C, and E) The α-helix in the model before refinement is turned by approximately 180 around the α-helical axis with respect to the native structure. (B, D, and F) The refinement was able to correctly turn the α-helix with respect to the native structure. Generally, only a slight shift along the α-helical axis remains between the model after refinement and the native α-helix.
6 Figure S1. ROSETTA full-atom score vs. rmsd-to-native (over α-helical residues) after 8 rounds of iterative side chain repacking and backbone relaxation for 1IE9 (A), 1N83 (B), 1OUV (C), 1QKM (D), 1TBF (E), 1Z1L (F) and 2AX6 (G). The red data points represent the final full atom models that went through the whole assembly, loop building and refinement protocol. The black data points show the native after 8 rounds of repacking and relaxation for comparison. For all seven proteins the relaxed native structure scores better than any of the full-atom models built. Within the best 10% scoring models there is an enrichment for the correct topology in six out of seven cases: 7.6 (1Z1L), 4.0 (1IE9), 3.8 (1OUV), 2.6 (1QKM), 1.6 (1TBF) and 1.2 (1N83). Figure S2. FSC Curve for Refined Ad35F Density Map
7 The final Ad35F structure is based on 3040 particle images and has a resolution of 6.8 Å at the FSC 0.5 threshold (and 5.8 Å at the FSC 0.3, and 5.2 Å at the FSC thresholds). Figure S3. Density bumps for the only two Trp sidechains in helices 3 (A, B) and 6 (C, D) of hexon. Panels A and C show the hexon crystal structure for residues (helix 3, panel A) and residues (helix 6, panel C) with the Trp side chain coordinates. Panels B and D show the crystal structure for the same helices overlaid with the refined Ad35F density map. For both Trp side chains clear density bumps are visible. The black arrows represent the position of the Trp side chain. SUPPLEMENTAL REFERNCES Grigorieff, N. (2007). FREALIGN: High-resolution refinement of single particle structures. Journal of Structural Biology 157, Saban, S.D., Silvestry, M., Nemerow, G.R., and Stewart, P.L. (2006). Visualization of alphahelices in a 6-angstrom resolution cryoelectron microscopy structure of adenovirus allows refinement of capsid protein assignments. J Virol 80,
8 Table S1. Overview over the ten proteins used in the assembly benchmark PDB-ID Description residues α- helices a helical residues b resolution [Å] 1IE9 Vitamin D3 receptor N83 Nuclear receptor ROR-alpha OUV Conserved hypothetical secreted protein QKM Estrogen receptor beta TBF cgmp-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase V9M V-type ATP synthase subunit C XQO 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase Z1L cgmp-dependent 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase AX6 Androgen receptor CWC ADP-ribosylglycohydrolase GZM Bovine Rhodopsin a All α-helices with at least 12 residues are shown b The total helical content per protein varies from 60 to 68% contact order c c Contact order is defined as the average sequence separation of all residues that are in contact within the protein. The higher the contact order, the more complex the fold is. Values above 40 are considered to reflect very complex folds.
9 Table S2. Evaluation of different secondary structure prediction pools Pool A a Pool B b Pool C c protein deviation d (residues) number helices deviation d (residues) number helices deviation d (residues) number helices 1IE N OUV QKM TBF V9M XQO Z1L AX CWC average prediction number helices number helices number helices shorter longer equal a Pool A contains predictions from jufo, psipred, sam; a consensus of the three; and a consensus where long helices are broken into smaller pieces. b Pool B replaces all of the helices in pool A with copies that have one residue added to both the N-terminal and C- terminal ends of each helix. c Pool C contains all of the helices in pool A and additional longer copies with one residue added to the N-terminal end, one residue added to the C-terminal end, and one residue added to both the N-terminal and C-terminal ends of each helix. d Average deviation (in residues) of helix lengths between the PDB structure and the best predicted helix in the pool
Hydrogen Bonds The electrostatic nature of hydrogen bonds
 Hydrogen Bonds Hydrogen bonds have played an incredibly important role in the history of structural biology. Both the structure of DNA and of protein a-helices and b-sheets were predicted based largely
Hydrogen Bonds Hydrogen bonds have played an incredibly important role in the history of structural biology. Both the structure of DNA and of protein a-helices and b-sheets were predicted based largely
Peptide Bonds: Structure
 Peptide Bonds: Structure Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence, from - to C-terminus, determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide
Peptide Bonds: Structure Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence, from - to C-terminus, determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide
Disulfide Bonds at the Hair Salon
 Disulfide Bonds at the Hair Salon Three Alpha Helices Stabilized By Disulfide Bonds! In order for hair to grow 6 inches in one year, 9 1/2 turns of α helix must be produced every second!!! In some proteins,
Disulfide Bonds at the Hair Salon Three Alpha Helices Stabilized By Disulfide Bonds! In order for hair to grow 6 inches in one year, 9 1/2 turns of α helix must be produced every second!!! In some proteins,
Refinement of a pdb-structure and Convert
 Refinement of a pdb-structure and Convert A. Search for a pdb with the closest sequence to your protein of interest. B. Choose the most suitable entry (or several entries). C. Convert and resolve errors
Refinement of a pdb-structure and Convert A. Search for a pdb with the closest sequence to your protein of interest. B. Choose the most suitable entry (or several entries). C. Convert and resolve errors
Peptide bonds: resonance structure. Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains. Dihedral angles. Peptide bond. Protein physics, Lecture 5
 Protein physics, Lecture 5 Peptide bonds: resonance structure Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains Proteins are linear polymers However, the peptide binds and side chains restrict conformational
Protein physics, Lecture 5 Peptide bonds: resonance structure Properties of proteins: Peptide bonds and side chains Proteins are linear polymers However, the peptide binds and side chains restrict conformational
(c) How would your answers to problem (a) change if the molecular weight of the protein was 100,000 Dalton?
 Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
Problem 1. (12 points total, 4 points each) The molecular weight of an unspecified protein, at physiological conditions, is 70,000 Dalton, as determined by sedimentation equilibrium measurements and by
Amino Acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain. Alpha Carbon. Carboxyl. Group.
 Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Recap. Lecture 2. Protein conformation. Proteins. 8 types of protein function 10/21/10. Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell
 Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Lecture 2 Protein conformation ecap Proteins.. > 50% dry weight of a cell ell s building blocks and molecular tools. More important than genes A large variety of functions http://www.tcd.ie/biochemistry/courses/jf_lectures.php
Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture
 CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
Functional Architecture of RNA Polymerase I
 Cell, Volume 131 Supplemental Data Functional Architecture of RNA Polymerase I Claus-D. Kuhn, Sebastian R. Geiger, Sonja Baumli, Marco Gartmann, Jochen Gerber, Stefan Jennebach, Thorsten Mielke, Herbert
Cell, Volume 131 Supplemental Data Functional Architecture of RNA Polymerase I Claus-D. Kuhn, Sebastian R. Geiger, Sonja Baumli, Marco Gartmann, Jochen Gerber, Stefan Jennebach, Thorsten Mielke, Herbert
This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are
 This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are put together. 1 A more detailed view of a single protein
This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are put together. 1 A more detailed view of a single protein
Consensus alignment server for reliable comparative modeling with distant templates
 W50 W54 Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, Vol. 32, Web Server issue DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh456 Consensus alignment server for reliable comparative modeling with distant templates Jahnavi C. Prasad 1, Sandor Vajda
W50 W54 Nucleic Acids Research, 2004, Vol. 32, Web Server issue DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh456 Consensus alignment server for reliable comparative modeling with distant templates Jahnavi C. Prasad 1, Sandor Vajda
INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE
 Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview
 18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
PROTEINS THE PEPTIDE BOND. The peptide bond, shown above enclosed in the blue curves, generates the basic structural unit for proteins.
 Ca 2+ The contents of this module were developed under grant award # P116B-001338 from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), United States Department of Education. However, those
Ca 2+ The contents of this module were developed under grant award # P116B-001338 from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), United States Department of Education. However, those
PyRy3D: a software tool for modeling of large macromolecular complexes MODELING OF STRUCTURES FOR LARGE MACROMOLECULAR COMPLEXES
 MODELING OF STRUCTURES FOR LARGE MACROMOLECULAR COMPLEXES PyRy3D is a method for building low-resolution models of large macromolecular complexes. The components (proteins, nucleic acids and any other
MODELING OF STRUCTURES FOR LARGE MACROMOLECULAR COMPLEXES PyRy3D is a method for building low-resolution models of large macromolecular complexes. The components (proteins, nucleic acids and any other
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids
 Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Built from 20 kinds of amino acids Each Protein has a three dimensional structure. Majority of proteins are compact. Highly convoluted molecules. Proteins are folded polypeptides. There are four levels
Supplementary Figures S1 - S11
 1 Membrane Sculpting by F-BAR Domains Studied by Molecular Dynamics Simulations Hang Yu 1,2, Klaus Schulten 1,2,3, 1 Beckman Institute, University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois, USA 2 Center of Biophysics
1 Membrane Sculpting by F-BAR Domains Studied by Molecular Dynamics Simulations Hang Yu 1,2, Klaus Schulten 1,2,3, 1 Beckman Institute, University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois, USA 2 Center of Biophysics
Helices From Readily in Biological Structures
 The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
The α Helix and the β Sheet Are Common Folding Patterns Although the overall conformation each protein is unique, there are only two different folding patterns are present in all proteins, which are α
MASCOT Search Results Interpretation
 The Mascot protein identification program (Matrix Science, Ltd.) uses statistical methods to assess the validity of a match. MS/MS data is not ideal. That is, there are unassignable peaks (noise) and usually
The Mascot protein identification program (Matrix Science, Ltd.) uses statistical methods to assess the validity of a match. MS/MS data is not ideal. That is, there are unassignable peaks (noise) and usually
Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK
 Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK Dai Lu, Ph.D. dlu@tamhsc.edu Tel: 361-221-0745 Office: RCOP, Room 307 Drug Discovery and Development Drug Molecules Medicinal
Advanced Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry CHEM 5412 Dept. of Chemistry, TAMUK Dai Lu, Ph.D. dlu@tamhsc.edu Tel: 361-221-0745 Office: RCOP, Room 307 Drug Discovery and Development Drug Molecules Medicinal
The peptide bond is rigid and planar
 Level Description Bonds Primary Sequence of amino acids in proteins Covalent (peptide bonds) Secondary Structural motifs in proteins: α- helix and β-sheet Hydrogen bonds (between NH and CO groups in backbone)
Level Description Bonds Primary Sequence of amino acids in proteins Covalent (peptide bonds) Secondary Structural motifs in proteins: α- helix and β-sheet Hydrogen bonds (between NH and CO groups in backbone)
Structure Determination
 5 Structure Determination Most of the protein structures described and discussed in this book have been determined either by X-ray crystallography or by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Although
5 Structure Determination Most of the protein structures described and discussed in this book have been determined either by X-ray crystallography or by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Although
Pipe Cleaner Proteins. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their function in the cell?
 Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
Pipe Cleaner Proteins GPS: SB1 Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. Essential question: How does the structure of proteins relate to their
Section I Using Jmol as a Computer Visualization Tool
 Section I Using Jmol as a Computer Visualization Tool Jmol is a free open source molecular visualization program used by students, teachers, professors, and scientists to explore protein structures. Section
Section I Using Jmol as a Computer Visualization Tool Jmol is a free open source molecular visualization program used by students, teachers, professors, and scientists to explore protein structures. Section
Phase determination methods in macromolecular X- ray Crystallography
 Phase determination methods in macromolecular X- ray Crystallography Importance of protein structure determination: Proteins are the life machinery and are very essential for the various functions in the
Phase determination methods in macromolecular X- ray Crystallography Importance of protein structure determination: Proteins are the life machinery and are very essential for the various functions in the
K'NEX DNA Models. Developed by Dr. Gary Benson Department of Biomathematical Sciences Mount Sinai School of Medicine
 KNEX DNA Models Introduction Page 1 of 11 All photos by Kevin Kelliher. To download an Acrobat pdf version of this website Click here. K'NEX DNA Models Developed by Dr. Gary Benson Department of Biomathematical
KNEX DNA Models Introduction Page 1 of 11 All photos by Kevin Kelliher. To download an Acrobat pdf version of this website Click here. K'NEX DNA Models Developed by Dr. Gary Benson Department of Biomathematical
Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7. 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0?
 Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0? A) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 ) B) H 2 PO - 4 (Ka =
Paper: 6 Chemistry 2.130 University I Chemistry: Models Page: 2 of 7 4. Which of the following weak acids would make the best buffer at ph = 5.0? A) Acetic acid (Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 ) B) H 2 PO - 4 (Ka =
Student name ID # 2. (4 pts) What is the terminal electron acceptor in respiration? In photosynthesis? O2, NADP+
 1. Membrane transport. A. (4 pts) What ion couples primary and secondary active transport in animal cells? What ion serves the same function in plant cells? Na+, H+ 2. (4 pts) What is the terminal electron
1. Membrane transport. A. (4 pts) What ion couples primary and secondary active transport in animal cells? What ion serves the same function in plant cells? Na+, H+ 2. (4 pts) What is the terminal electron
CSC 2427: Algorithms for Molecular Biology Spring 2006. Lecture 16 March 10
 CSC 2427: Algorithms for Molecular Biology Spring 2006 Lecture 16 March 10 Lecturer: Michael Brudno Scribe: Jim Huang 16.1 Overview of proteins Proteins are long chains of amino acids (AA) which are produced
CSC 2427: Algorithms for Molecular Biology Spring 2006 Lecture 16 March 10 Lecturer: Michael Brudno Scribe: Jim Huang 16.1 Overview of proteins Proteins are long chains of amino acids (AA) which are produced
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Experimental Methods for Macromolecular Structure Determination
 Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Experimental Methods for Macromolecular Structure Determination Introduction Knowing the exact 3D-structure of bio-molecules is essential for any attempt to understand
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Experimental Methods for Macromolecular Structure Determination Introduction Knowing the exact 3D-structure of bio-molecules is essential for any attempt to understand
3D structure visualization and high quality imaging. Chimera
 3D structure visualization and high quality imaging. Chimera Vincent Zoete 2008 Contact : vincent.zoete@isb sib.ch 1/27 Table of Contents Presentation of Chimera...3 Exercise 1...4 Loading a structure
3D structure visualization and high quality imaging. Chimera Vincent Zoete 2008 Contact : vincent.zoete@isb sib.ch 1/27 Table of Contents Presentation of Chimera...3 Exercise 1...4 Loading a structure
The peptide bond Peptides and proteins are linear polymers of amino acids. The amino acids are
 Introduction to Protein Structure Proteins are large heteropolymers usually comprised of 50 2500 monomer units, although larger proteins are observed 7. The monomer units of proteins are amino acids. The
Introduction to Protein Structure Proteins are large heteropolymers usually comprised of 50 2500 monomer units, although larger proteins are observed 7. The monomer units of proteins are amino acids. The
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Sindelar et al. 10.1073/pnas.0911208107 SI Text Supplementary Methods. Sample preparation. Preparation of the no-nucleotide K349-microtubule complex and subsequent data collection
Supporting Information Sindelar et al. 10.1073/pnas.0911208107 SI Text Supplementary Methods. Sample preparation. Preparation of the no-nucleotide K349-microtubule complex and subsequent data collection
Protein Studies Using CAChe
 Protein Studies Using CAChe Exercise 1 Building the Molecules of Interest, and Using the Protein Data Bank In the CAChe workspace, click File / pen, and navigate to the C:\Program Files\Fujitsu\ CAChe\Fragment
Protein Studies Using CAChe Exercise 1 Building the Molecules of Interest, and Using the Protein Data Bank In the CAChe workspace, click File / pen, and navigate to the C:\Program Files\Fujitsu\ CAChe\Fragment
Translation Study Guide
 Translation Study Guide This study guide is a written version of the material you have seen presented in the replication unit. In translation, the cell uses the genetic information contained in mrna to
Translation Study Guide This study guide is a written version of the material you have seen presented in the replication unit. In translation, the cell uses the genetic information contained in mrna to
Protein 3D-structure analysis. why and how
 Protein 3D-structure analysis why and how 3D-structures are precious sources of information Shape and domain structure Protein classification Prediction of function for uncharacterized proteins Interaction
Protein 3D-structure analysis why and how 3D-structures are precious sources of information Shape and domain structure Protein classification Prediction of function for uncharacterized proteins Interaction
Chapter 3. Protein Structure and Function
 Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain.
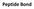 Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Structure Tools and Visualization
 Structure Tools and Visualization Gary Van Domselaar University of Alberta gary.vandomselaar@ualberta.ca Slides Adapted from Michel Dumontier, Blueprint Initiative 1 Visualization & Communication Visualization
Structure Tools and Visualization Gary Van Domselaar University of Alberta gary.vandomselaar@ualberta.ca Slides Adapted from Michel Dumontier, Blueprint Initiative 1 Visualization & Communication Visualization
REMOTE CONTROL by DNA as a Bio-sensor -antenna.
 REMOTE CONTROL by DNA as a Bio-sensor -antenna. "Piezoelectric quantum transduction is a fundamental property of at- distance induction of genetic control " Paolo Manzelli: pmanzelli@gmail.com ; www.edscuola.it/lre.html;www.egocreanet.it
REMOTE CONTROL by DNA as a Bio-sensor -antenna. "Piezoelectric quantum transduction is a fundamental property of at- distance induction of genetic control " Paolo Manzelli: pmanzelli@gmail.com ; www.edscuola.it/lre.html;www.egocreanet.it
Secondary Structure Prediction. Michael Tress CNIO
 Secondary Structure Prediction Michael Tress CNIO Why do we Need to Know About Secondary Structure? Secondary structure prediction is a step towards deducing the fold. In order to arrive at the correct
Secondary Structure Prediction Michael Tress CNIO Why do we Need to Know About Secondary Structure? Secondary structure prediction is a step towards deducing the fold. In order to arrive at the correct
Overview'of'Solid-Phase'Peptide'Synthesis'(SPPS)'and'Secondary'Structure'Determination'by'FTIR'
 verviewofsolid-phasepeptidesynthesis(spps)andsecondarystructuredeterminationbyftir Introduction Proteinsareubiquitousinlivingorganismsandcells,andcanserveavarietyoffunctions.Proteinscanactas enzymes,hormones,antibiotics,receptors,orserveasstructuralsupportsintissuessuchasmuscle,hair,and
verviewofsolid-phasepeptidesynthesis(spps)andsecondarystructuredeterminationbyftir Introduction Proteinsareubiquitousinlivingorganismsandcells,andcanserveavarietyoffunctions.Proteinscanactas enzymes,hormones,antibiotics,receptors,orserveasstructuralsupportsintissuessuchasmuscle,hair,and
Proteins and Nucleic Acids
 Proteins and Nucleic Acids Chapter 5 Macromolecules: Proteins Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group of biomolecules. : o Involved in almost everything o Enzymes o Structure (keratin,
Proteins and Nucleic Acids Chapter 5 Macromolecules: Proteins Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group of biomolecules. : o Involved in almost everything o Enzymes o Structure (keratin,
Discrete representations of the protein C. chain Xavier F de la Cruz 1, Michael W Mahoney 2 and Byungkook Lee
 Research Paper 223 Discrete representations of the protein C chain Xavier F de la Cruz 1, Michael W Mahoney 2 and Byungkook Lee Background: When a large number of protein conformations are generated and
Research Paper 223 Discrete representations of the protein C chain Xavier F de la Cruz 1, Michael W Mahoney 2 and Byungkook Lee Background: When a large number of protein conformations are generated and
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
 Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Myoglobin and hemoglobin are hemeproteins whose physiological importance is principally related to their ability to bind molecular oxygen. Myoglobin (Mb) The oxygen storage protein
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Myoglobin and hemoglobin are hemeproteins whose physiological importance is principally related to their ability to bind molecular oxygen. Myoglobin (Mb) The oxygen storage protein
4. Which carbohydrate would you find as part of a molecule of RNA? a. Galactose b. Deoxyribose c. Ribose d. Glucose
 1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
1. How is a polymer formed from multiple monomers? a. From the growth of the chain of carbon atoms b. By the removal of an OH group and a hydrogen atom c. By the addition of an OH group and a hydrogen
Bioinformatics for Biologists. Protein Structure
 Bioinformatics for Biologists Comparative Protein Analysis: Part III. Protein Structure Prediction and Comparison Robert Latek, PhD Sr. Bioinformatics Scientist Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research
Bioinformatics for Biologists Comparative Protein Analysis: Part III. Protein Structure Prediction and Comparison Robert Latek, PhD Sr. Bioinformatics Scientist Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research
Protein annotation and modelling servers at University College London
 Nucleic Acids Research Advance Access published May 27, 2010 Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 1 6 doi:10.1093/nar/gkq427 Protein annotation and modelling servers at University College London D. W. A. Buchan*,
Nucleic Acids Research Advance Access published May 27, 2010 Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 1 6 doi:10.1093/nar/gkq427 Protein annotation and modelling servers at University College London D. W. A. Buchan*,
Linear Sequence Analysis. 3-D Structure Analysis
 Linear Sequence Analysis What can you learn from a (single) protein sequence? Calculate it s physical properties Molecular weight (MW), isoelectric point (pi), amino acid content, hydropathy (hydrophilic
Linear Sequence Analysis What can you learn from a (single) protein sequence? Calculate it s physical properties Molecular weight (MW), isoelectric point (pi), amino acid content, hydropathy (hydrophilic
H H N - C - C 2 R. Three possible forms (not counting R group) depending on ph
 Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
Amino acids - 0 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently - Common structure for amino acid - C, -N, and functional groups all attached to the alpha carbon N - C - C
Structures of Proteins. Primary structure - amino acid sequence
 Structures of Proteins Primary structure - amino acid sequence Secondary structure chain of covalently linked amino acids folds into regularly repeating structures. Secondary structure is the result of
Structures of Proteins Primary structure - amino acid sequence Secondary structure chain of covalently linked amino acids folds into regularly repeating structures. Secondary structure is the result of
Biological Molecules
 Biological Molecules I won t lie. This is probably the most boring topic you have ever done in any science. It s pretty much as simple as this: learn the material deal with it. Enjoy don t say I didn t
Biological Molecules I won t lie. This is probably the most boring topic you have ever done in any science. It s pretty much as simple as this: learn the material deal with it. Enjoy don t say I didn t
Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction
 Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction The function and chemical properties of proteins are determined by its three-dimensional structure. The final architecture of the protein
Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction The function and chemical properties of proteins are determined by its three-dimensional structure. The final architecture of the protein
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
 Vol 466 5 August 2010 doi:10.1038/nature09304 LETTERS Predicting protein structures with a multiplayer online game Seth Cooper 1, Firas Khatib 2, Adrien Treuille 1,3, Janos Barbero 1, Jeehyung Lee 3, Michael
Vol 466 5 August 2010 doi:10.1038/nature09304 LETTERS Predicting protein structures with a multiplayer online game Seth Cooper 1, Firas Khatib 2, Adrien Treuille 1,3, Janos Barbero 1, Jeehyung Lee 3, Michael
Chapter-21b: Hormones and Receptors
 1 hapter-21b: Hormones and Receptors Hormone classes Hormones are classified according to the distance over which they act. 1. Autocrine hormones --- act on the same cell that released them. Interleukin-2
1 hapter-21b: Hormones and Receptors Hormone classes Hormones are classified according to the distance over which they act. 1. Autocrine hormones --- act on the same cell that released them. Interleukin-2
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon. V. Polypeptides and Proteins
 IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
IV. -Amino Acids: carboxyl and amino groups bonded to -Carbon A. Acid/Base properties 1. carboxyl group is proton donor! weak acid 2. amino group is proton acceptor! weak base 3. At physiological ph: H
Protein Physics. A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1
 Protein Physics A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1 PROTEINS Functions in a Cell MOLECULAR MACHINES BUILDING BLOCKS of a CELL ARMS of a CELL ENZYMES - enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions
Protein Physics A. V. Finkelstein & O. B. Ptitsyn LECTURE 1 PROTEINS Functions in a Cell MOLECULAR MACHINES BUILDING BLOCKS of a CELL ARMS of a CELL ENZYMES - enzymatic catalysis of biochemical reactions
Analysis of structural dynamics by H/D-exchange coupled to mass spectrometry HDX-MS
 Analysis of structural dynamics by H/D-exchange coupled to mass spectrometry () New Approaches in Drug Design & Discovery 2014 25 th of March 2014 Introduction What are the challenges in structure-based
Analysis of structural dynamics by H/D-exchange coupled to mass spectrometry () New Approaches in Drug Design & Discovery 2014 25 th of March 2014 Introduction What are the challenges in structure-based
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY
 2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
2007 7.013 Problem Set 1 KEY Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, February 16, 2007. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. Where in a eukaryotic cell do you
Papers listed: Cell2. This weeks papers. Chapt 4. Protein structure and function
 Papers listed: Cell2 During the semester I will speak of information from several papers. For many of them you will not be required to read these papers, however, you can do so for the fun of it (and it
Papers listed: Cell2 During the semester I will speak of information from several papers. For many of them you will not be required to read these papers, however, you can do so for the fun of it (and it
Replication Study Guide
 Replication Study Guide This study guide is a written version of the material you have seen presented in the replication unit. Self-reproduction is a function of life that human-engineered systems have
Replication Study Guide This study guide is a written version of the material you have seen presented in the replication unit. Self-reproduction is a function of life that human-engineered systems have
Deep profiling of multitube flow cytometry data Supplemental information
 Deep profiling of multitube flow cytometry data Supplemental information Kieran O Neill et al December 19, 2014 1 Table S1: Markers in simulated multitube data. The data was split into three tubes, each
Deep profiling of multitube flow cytometry data Supplemental information Kieran O Neill et al December 19, 2014 1 Table S1: Markers in simulated multitube data. The data was split into three tubes, each
Biochemistry 462a Hemoglobin Structure and Function Reading - Chapter 7 Practice problems - Chapter 7: 1-6; Proteins extra problems
 Biochemistry 462a Hemoglobin Structure and Function Reading - Chapter 7 Practice problems - Chapter 7: 1-6; Proteins extra problems Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Oxygen is required for oxidative metabolism
Biochemistry 462a Hemoglobin Structure and Function Reading - Chapter 7 Practice problems - Chapter 7: 1-6; Proteins extra problems Myoglobin and Hemoglobin Oxygen is required for oxidative metabolism
FTIR Analysis of Protein Structure
 FTIR Analysis of Protein Structure Warren Gallagher A. Introduction to protein structure The first structures of proteins at an atomic resolution were determined in the late 1950 s. 1 From that time to
FTIR Analysis of Protein Structure Warren Gallagher A. Introduction to protein structure The first structures of proteins at an atomic resolution were determined in the late 1950 s. 1 From that time to
Structure Check. Authors: Eduard Schreiner Leonardo G. Trabuco. February 7, 2012
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign NIH Resource for Macromolecular Modeling and Bioinformatics Beckman Institute Computational Biophysics Workshop Structure Check Authors: Eduard Schreiner Leonardo
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign NIH Resource for Macromolecular Modeling and Bioinformatics Beckman Institute Computational Biophysics Workshop Structure Check Authors: Eduard Schreiner Leonardo
Heuristics for the Sorting by Length-Weighted Inversions Problem on Signed Permutations
 Heuristics for the Sorting by Length-Weighted Inversions Problem on Signed Permutations AlCoB 2014 First International Conference on Algorithms for Computational Biology Thiago da Silva Arruda Institute
Heuristics for the Sorting by Length-Weighted Inversions Problem on Signed Permutations AlCoB 2014 First International Conference on Algorithms for Computational Biology Thiago da Silva Arruda Institute
BIOC351: Proteins. PyMOL Laboratory #1. Installing and Using
 BIOC351: Proteins PyMOL Laboratory #1 Installing and Using Information and figures for this handout was obtained from the following sources: Introduction to PyMOL (2009) DeLano Scientific LLC. Installing
BIOC351: Proteins PyMOL Laboratory #1 Installing and Using Information and figures for this handout was obtained from the following sources: Introduction to PyMOL (2009) DeLano Scientific LLC. Installing
Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?)
 ChemActivity 46 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins 1 ChemActivity 46 Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?) Model 1: The 20 Amino Acids at Biological p See
ChemActivity 46 Amino Acids, Polypeptides and Proteins 1 ChemActivity 46 Part A: Amino Acids and Peptides (Is the peptide IAG the same as the peptide GAI?) Model 1: The 20 Amino Acids at Biological p See
Computational Systems Biology. Lecture 2: Enzymes
 Computational Systems Biology Lecture 2: Enzymes 1 Images from: David L. Nelson, Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, IV Edition, Freeman ed. or under creative commons license (search for images at http://search.creativecommons.org/)
Computational Systems Biology Lecture 2: Enzymes 1 Images from: David L. Nelson, Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, IV Edition, Freeman ed. or under creative commons license (search for images at http://search.creativecommons.org/)
T cell Epitope Prediction
 Institute for Immunology and Informatics T cell Epitope Prediction EpiMatrix Eric Gustafson January 6, 2011 Overview Gathering raw data Popular sources Data Management Conservation Analysis Multiple Alignments
Institute for Immunology and Informatics T cell Epitope Prediction EpiMatrix Eric Gustafson January 6, 2011 Overview Gathering raw data Popular sources Data Management Conservation Analysis Multiple Alignments
High Resolution Epitope Mapping of Human Autoimmune Sera against Antigens CENPA and KDM6B. PEPperPRINT GmbH Heidelberg, 06/2014
 High Resolution Epitope Mapping of Human Autoimmune Sera against Antigens CENPA and KDM6B PEPperPRINT GmbH Heidelberg, 06/2014 Introduction This report describes the epitope mapping of autoimmune sera
High Resolution Epitope Mapping of Human Autoimmune Sera against Antigens CENPA and KDM6B PEPperPRINT GmbH Heidelberg, 06/2014 Introduction This report describes the epitope mapping of autoimmune sera
http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri
 http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri Definition: Proteins are macromolecules with a backbone formed by polymerization of amino acids. Proteins carry out a number of functions in living organisms: - They
http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/h.alshehri Definition: Proteins are macromolecules with a backbone formed by polymerization of amino acids. Proteins carry out a number of functions in living organisms: - They
Increase the measurement speed with NOVA
 Increase the measurement speed with NOVA Case study: how to increase the measurement speed by optimizing the USB communication with the Autolab? 1 USB 1.1 vs USB 2.0 Although the Autolab uses a USB 1.1
Increase the measurement speed with NOVA Case study: how to increase the measurement speed by optimizing the USB communication with the Autolab? 1 USB 1.1 vs USB 2.0 Although the Autolab uses a USB 1.1
VTT TECHNICAL RESEARCH CENTRE OF FINLAND
 Figure from: http://www.embl.de/nmr/sattler/teaching Why NMR (instead of X ray crystallography) a great number of macromolecules won't crystallize) natural environmant (water) ligand binding and inter
Figure from: http://www.embl.de/nmr/sattler/teaching Why NMR (instead of X ray crystallography) a great number of macromolecules won't crystallize) natural environmant (water) ligand binding and inter
High flexibility of DNA on short length scales probed by atomic force microscopy
 High flexibility of DNA on short length scales probed by atomic force microscopy Wiggins P. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnology (2006) presented by Anja Schwäger 23.01.2008 Outline Theory/Background Elasticity
High flexibility of DNA on short length scales probed by atomic force microscopy Wiggins P. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnology (2006) presented by Anja Schwäger 23.01.2008 Outline Theory/Background Elasticity
Atomic Force Microscope and Magnetic Force Microscope Background Information
 Atomic Force Microscope and Magnetic Force Microscope Background Information Lego Building Instructions There are several places to find the building instructions for building the Lego models of atomic
Atomic Force Microscope and Magnetic Force Microscope Background Information Lego Building Instructions There are several places to find the building instructions for building the Lego models of atomic
Structure of proteins
 Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
Lab # 12: DNA and RNA
 115 116 Concepts to be explored: Structure of DNA Nucleotides Amino Acids Proteins Genetic Code Mutation RNA Transcription to RNA Translation to a Protein Figure 12. 1: DNA double helix Introduction Long
115 116 Concepts to be explored: Structure of DNA Nucleotides Amino Acids Proteins Genetic Code Mutation RNA Transcription to RNA Translation to a Protein Figure 12. 1: DNA double helix Introduction Long
Amino Acids and Proteins
 Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
Amino Acids and Proteins Proteins are composed of amino acids. There are 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. All have: N2 C α R COO Amino acids at neutral p are dipolar ions (zwitterions) because
A successful market segmentation initiative answers the following critical business questions: * How can we a. Customer Status.
 MARKET SEGMENTATION The simplest and most effective way to operate an organization is to deliver one product or service that meets the needs of one type of customer. However, to the delight of many organizations
MARKET SEGMENTATION The simplest and most effective way to operate an organization is to deliver one product or service that meets the needs of one type of customer. However, to the delight of many organizations
Protein Sequence Analysis - Overview -
 Protein Sequence Analysis - Overview - UDEL Workshop Raja Mazumder Research Associate Professor, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Georgetown University Medical Center Topics Why do protein
Protein Sequence Analysis - Overview - UDEL Workshop Raja Mazumder Research Associate Professor, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Georgetown University Medical Center Topics Why do protein
Multiobjective Robust Design Optimization of a docked ligand
 Multiobjective Robust Design Optimization of a docked ligand Carlo Poloni,, Universitaʼ di Trieste Danilo Di Stefano, ESTECO srl Design Process DESIGN ANALYSIS MODEL Dynamic Analysis Logistics & Field
Multiobjective Robust Design Optimization of a docked ligand Carlo Poloni,, Universitaʼ di Trieste Danilo Di Stefano, ESTECO srl Design Process DESIGN ANALYSIS MODEL Dynamic Analysis Logistics & Field
NO CALCULATORS OR CELL PHONES ALLOWED
 Biol 205 Exam 1 TEST FORM A Spring 2008 NAME Fill out both sides of the Scantron Sheet. On Side 2 be sure to indicate that you have TEST FORM A The answers to Part I should be placed on the SCANTRON SHEET.
Biol 205 Exam 1 TEST FORM A Spring 2008 NAME Fill out both sides of the Scantron Sheet. On Side 2 be sure to indicate that you have TEST FORM A The answers to Part I should be placed on the SCANTRON SHEET.
Tutorial for Proteomics Data Submission. Katalin F. Medzihradszky Robert J. Chalkley UCSF
 Tutorial for Proteomics Data Submission Katalin F. Medzihradszky Robert J. Chalkley UCSF Why Have Guidelines? Large-scale proteomics studies create huge amounts of data. It is impossible/impractical to
Tutorial for Proteomics Data Submission Katalin F. Medzihradszky Robert J. Chalkley UCSF Why Have Guidelines? Large-scale proteomics studies create huge amounts of data. It is impossible/impractical to
Lecture 8. Protein Trafficking/Targeting. Protein targeting is necessary for proteins that are destined to work outside the cytoplasm.
 Protein Trafficking/Targeting (8.1) Lecture 8 Protein Trafficking/Targeting Protein targeting is necessary for proteins that are destined to work outside the cytoplasm. Protein targeting is more complex
Protein Trafficking/Targeting (8.1) Lecture 8 Protein Trafficking/Targeting Protein targeting is necessary for proteins that are destined to work outside the cytoplasm. Protein targeting is more complex
R. Fonseca, M. Paluszewski and P. Winter
 Protein Structure Prediction Using Bee Colony Optimization Metaheuristic R. Fonseca, M. Paluszewski and P. Winter Technical Report no. 08-12 ISSN: 0107-8283 Dept. of Computer Science University of Copenhagen
Protein Structure Prediction Using Bee Colony Optimization Metaheuristic R. Fonseca, M. Paluszewski and P. Winter Technical Report no. 08-12 ISSN: 0107-8283 Dept. of Computer Science University of Copenhagen
Christopher W Wood 1,2,*, Marc Bruning 1, Amaurys Á Ibarra 2, Gail J Bartlett 1, Andrew R Thomson
 Bioinformatics Advance Access published July 26, 2014 Structural Bioinformatics CCBuilder: an interactive web-based tool for building, designing and assessing coiled-coil-protein assemblies Christopher
Bioinformatics Advance Access published July 26, 2014 Structural Bioinformatics CCBuilder: an interactive web-based tool for building, designing and assessing coiled-coil-protein assemblies Christopher
A reduced model of short range interactions in polypeptide chains
 A reduced model of short range interactions in polypeptide chains Andrzej Kolinski a) Department of Chemistry, University of Warsaw, Pasteura 1, 0-093 Warsaw, Poland (and Department of Molecular Biology,
A reduced model of short range interactions in polypeptide chains Andrzej Kolinski a) Department of Chemistry, University of Warsaw, Pasteura 1, 0-093 Warsaw, Poland (and Department of Molecular Biology,
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids
 Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES Macromolecules: polymers with molecular weights >1,000 Functional groups THE FOUR MACROMOLECULES IN LIFE Molecules in living organisms: proteins,
The Molecules of Cells
 The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
The Molecules of Cells I. Introduction A. Most of the world s population cannot digest milk-based foods. 1. These people are lactose intolerant because they lack the enzyme lactase. 2. This illustrates
Scoring Functions and Docking. Keith Davies Treweren Consultants Ltd 26 October 2005
 Scoring Functions and Docking Keith Davies Treweren Consultants Ltd 26 October 2005 Overview Applications Docking Algorithms Scoring Functions Results Demonstration Docking Applications Drug Design Lead
Scoring Functions and Docking Keith Davies Treweren Consultants Ltd 26 October 2005 Overview Applications Docking Algorithms Scoring Functions Results Demonstration Docking Applications Drug Design Lead
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159. Date Submitted: 12-11-09
 Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Title: Mapping T cell epitopes in PCV2 capsid protein - NPB #08-159 Investigator: Institution: Carol Wyatt Kansas State University Date Submitted: 12-11-09 Industry summary: Effective circovirus vaccines
Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) State of the Art. Prof. Dr. T. Nouri Computer Science Department FHNW Switzerland
 Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) State of the Art Prof. Dr. T. Nouri Computer Science Department FHNW Switzerland 1 Conference overview 1. Overview of KDD and data mining 2. Data
Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) State of the Art Prof. Dr. T. Nouri Computer Science Department FHNW Switzerland 1 Conference overview 1. Overview of KDD and data mining 2. Data
Covalent bonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to the protein structure A peptide bond is formed between with of the following?
 MCAT Question Covalent bonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to the protein structure A peptide bond is formed between with of the following? A. Carboxylic group and amino group B. Two carboxylic
MCAT Question Covalent bonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to the protein structure A peptide bond is formed between with of the following? A. Carboxylic group and amino group B. Two carboxylic
Biological molecules:
 Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Biological molecules: All are organic (based on carbon). Monomers vs. polymers: Monomers refer to the subunits that, when polymerized, make up a larger polymer. Monomers may function on their own in some
Solving NP Hard problems in practice lessons from Computer Vision and Computational Biology
 Solving NP Hard problems in practice lessons from Computer Vision and Computational Biology Yair Weiss School of Computer Science and Engineering The Hebrew University of Jerusalem www.cs.huji.ac.il/ yweiss
Solving NP Hard problems in practice lessons from Computer Vision and Computational Biology Yair Weiss School of Computer Science and Engineering The Hebrew University of Jerusalem www.cs.huji.ac.il/ yweiss
Integrating DNA Motif Discovery and Genome-Wide Expression Analysis. Erin M. Conlon
 Integrating DNA Motif Discovery and Genome-Wide Expression Analysis Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Massachusetts Amherst Statistics in Functional Genomics Workshop Ascona, Switzerland
Integrating DNA Motif Discovery and Genome-Wide Expression Analysis Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Massachusetts Amherst Statistics in Functional Genomics Workshop Ascona, Switzerland
NMR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
 NMR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is an effect whereby magnetic nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic (EM) energy. This energy is at a specific resonance
NMR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is an effect whereby magnetic nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic (EM) energy. This energy is at a specific resonance
