GEOGRAPHY AND CLIMATE
|
|
|
- Grant Allison
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Web Japan GEOGRAPHY AND CLIMATE A country of diverse topography and climate Geography A Pacific Island Country Japan is an island country forming an arc in the Pacific Ocean to the east of the Asian continent. The land comprises four large islands named (in decreasing order of size) Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku, together with many smaller islands. The Pacific Ocean lies to the east while the Sea of Japan and the East China Sea separate Japan from the Asian continent. In terms of latitude, Japan coincides approximately with the Mediterranean Sea and with the city of Los Angeles in North America. Paris and London have latitudes somewhat to the north of the northern tip of Hokkaido. Japan s total land area is about 378,000 square kilometers. It is thus approximately the same size as Germany, Finland, Vietnam, or Malaysia. It is only 1/25 the size of the United States and is smaller than the state of California. Japan s coastline is quite varied. In some places, such as Kujukurihama in Chiba Prefecture, there are long sandy beaches continuing fairly straight and uninterrrupted for 60 kilometers or so, while the coast of Nagasaki Prefecture is an example of an area characterized by peninsulas and inlets and offshore islands (like the Goto archipelago and the islands of Tsushima and Iki, which are part of that prefecture). There are also accidented areas of the coast with many inlets and steep cliffs caused by the submersion of part of the former coastline due to changes in the Earth s crust. A warm ocean current known as the Kuroshio (or Japan Current) flows northeastward along the southern part of the Japanese archipelago, and a branch of it, known as the Tsushima Current, flows into the Sea of Japan along the west side of the country. From the north, a cold current known as the Oyashio (or Chishima Current) flows south along Japan s east coast, and a branch of it, called the Liman Current, enters the Sea of Japan from the north. The mixing of these warm and cold currents helps produce abundant fish resources in waters near Japan. A Land of hot springs and attractive scenary About three-fourths of Japan s land surface is mountainous. The Chubu Region of central Honshu is known as the roof of Japan and has many mountains which are more than 3,000 meters high. Japan s highest mountain is Mt. Fuji (3,776 meters) on the border of Yamanashi and Shizuoka prefectures. Japan s secondhighest peak is Kitadake in Yamanashi Prefecture, at 3,192 meters, and its thirdhighest peak is Hotakadake at 3,190 meters, on the border between Nagano and Gifu prefectures. Mt. Fuji Japan s highest peak, Mt. Fuji, is seen here from Lake Kawaguchi in April. It remains covered in snow until June. 1 GEOGRAPHY AND CLIMATE
2 As it is situated along the circum-pacific volcanic belt, Japan has several volcanic regions usually considered to number seven from the far north to the far south. Of the total number of volcanoes, approximately 80 are active, including Mt. Mihara on Izu Oshima island, Mt. Asama on the border between Nagano and Gunma Prefectures, and Mt. Aso in Kumamoto Prefecture. Japan has almost 1/10 of the world s approximately 840 active volcanoes, even though it has only about l/400 of the world s land area. Mt. Fuji, which has been dormant since its last eruption in 1707, is by no means incapable of erupting again in our lifetimes. Though volcanoes can cause great harm through large eruptions, they also contribute an incalculable tourist resource. Touristic areas such as Nikko, Hakone, and the Izu Peninsula, for example, are famous for their hot springs and attractive scenery of volcanic mountains. As all these volcanoes attest, the Earth s crust beneath the Japanese archipelago is unstable and full of energy. Thus Japan is among those countries most likely to suffer from earthquakes. Every year there are approximately 1,000 earthquakes which are strong enough to be felt. In January 1995, the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake killed approximately 6,000 people, injured over 40,000, and left 200,000 homeless. An earthquake in Niigata Prefecture in October 2004 left over 60 people dead and more than 4,700 injured. In March 2011, a magnitude 9 earthquake was recorded off the coast of Sanriku (Tohoku) in the Pacific Ocean, and the ensuing tsunami, more than 10m high in places, hit the coast across a vast region from Tohoku to Kanto. The number of dead and missing after the earthquake and tsunami reached nearly 19,000. Fast-Flowing Rivers Mountainous Japan is blessed with many rivers. Most of Japan s rivers flow very fast, their waters reaching the ocean not long after leaving mountain valleys and basins. An example of the steepness of river flows is the Kurobe River, which joins the Sea of Japan after flowing only 83 kilometers from its source in the Japan Alps at an altitude of over 2,900 meters. Japan s longest river is the Shinano River, which flows 367 kilometers from the mountains of the Chubu region through Niigata Prefecture to the Sea of Japan. Second in length is the Tone River, which flows through the Kanto Plain to the Pacific Ocean, and third in length is the Ishikari River in Hokkaido, at 268 kilometers. The many rivers descending from mountainous areas have done much to mold Japan s topography, creating large and small valleys and basins and producing fan-shaped deltas near the points where they flow into the sea. Most of the country s plains are small. The largest is the Kanto Plain, which includes parts of Tochigi, Ibaraki, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba, Tokyo, and Kanagawa prefectures. Other relatively large areas of flat land are the Echigo Plain (Niigata Prefecture), the Ishikari Plain (Hokkaido), and the Nobi Plain (Aichi and Gifu prefectures). Climate A major feature of Japan s climate is the clear-cut temperature changes between the four seasons. From north to south, Japan covers a range of latitude of some 25 degrees and is influenced in the winter by seasonal winds blowing from Siberia and in the summer by seasonal winds blowing from the Pacific Ocean. In spite of its rather small area, Japan is characterized by four different climatic patterns. Hokkaido, with a subarctic weather pattern, has a yearly average temperature of eight degrees centigrade and receives an average annual precipitation of 1,150 millimeters. The Pacific Ocean side of Japan, from the Tohoku region of northern Honshu to Kyushu, belongs to the temperate zone, and its summers are hot, influenced by seasonal winds from the Pacific. The side of the country which faces the Sea of Japan has a climate with much rain and snow, produced when cold, moisture-bearing seasonal winds from the continent are stopped in their advance by the Central Alps and other mountains which run along Japan s center like a backbone. The southwestern islands of Okinawa Prefecture belong to the subtropical climate zone and have a yearly average temperate of over 22 degrees, while receiving over 2,000 millimeters of precipitation. 2 GEOGRAPHY AND CLIMATE
3 Cherry blossoms Cherry blossoms the symbol of spring in Japan. Firework displays Firework displays like this one are an essential part of the Japanese summer. Spring (March, April, May) When winter nears its end, the cold seasonal winds blowing from the continent become weaker and more intermittent. At this time, low pressure air masses originating in China enter the Sea of Japan; these give rise to strong, warm southerly winds which travel toward this low-pressure zone from the Pacific Ocean. The first of these winds is called haru ichiban. While it announces the warmth of the coming spring, it sometimes causes avalanches and, crossing the mountains to the side of the country facing the Sea of Japan, it is at times responsible for exceptionally hot and dry weather and can even become the cause of large fires. In early spring, plum blossoms start to bloom, followed by peach blossoms. During the last ten days or so of March, the cherry blossoms so beloved by the Japanese people begin to bloom. Summer (June, July, August) Before the arrival of real summerlike weather, Japan has a damp rainy season known as tsuyu. From May until July, there is a highpressure mass of cold air above the Sea of Okhotsk to the north of Japan, while over the Pacific Ocean there develops a high-pressure mass of warm, moist air. Along the line where these cold and warm air masses meet, known as the baiu zensen, or rainy season front, there often develop areas of low-pressure warm air. Thus the baiu zensen, which extends from southern China over the Japanese archipelago, causes prolonged periods of continuous rainfall. After the middle of July, high-pressure air masses over the Pacific Ocean become predominant and the rainy season comes to an end as the baiu zensen is pushed northward. Seasonal winds from the Pacific Ocean bring warm, moist air to Japan, and the country has hot summer weather with many days when temperatures rise to more than 30 degrees centigrade. Autumn (September, October, November) From the end of summer through September, Japan is often struck by typhoons. Typhoons originate from large masses of tropical lowpressure air in the North Pacific between the latitudes of approximately 5 and 20 degrees, and are the same phenomenon as hurricanes and cyclones in other parts of the world. When a typhoon begins to take shape, it gradually moves north. Every year, during this period, around 30 typhoons form, of which on the average about 4 reach Japan, sometimes causing great destruction. After the middle or latter part of October, Japan enjoys generally clear weather; it is neither hot nor cold. The country also enjoys especially fine weather at the beginning of November. Many of the trees take on bright autumn colors, making this time of the year, together with the time of new greenery in the spring, a truly beautiful season. Autumn leaves Colorful foliage is the symbol of autumn throughout Japan. Winter (December, January, February) Toward the end of November, cold seasonal winds begin blowing over Japan from the continent. These northwesterly winds pick up moisture over the Sea of Japan and drop much of this moisture in the form of rain and snow on the western side of Japan as they are impeded in their eastern advance by the ridge of mountains that runs through the central part of the country. The Hokuriku region (Fukui, Ishikawa, Toyama, and Niigata prefectures), which faces the Sea of Japan 3 GEOGRAPHY AND CLIMATE
4 Cherry blossoms Cherry blossoms the symbol of spring in Japan. and is separated from other regions of Japan by high mountains, is known for its deep snows. By contrast, the Pacific side of the country enjoys generally clear skies during the winter season. In Tokyo, despite the fair skies, winter temperatures average around 5 degrees, a difference of 25 degrees from summer temperatures of 30 degrees or more. The islands of Okinawa Prefecture in the far southwest have a subtropical climate with less marked temperature differences between the seasons. Winter temperatures there are much more moderate than in other parts of the country. Shirakawa-go in Winter The gassho-zukuri style farmhouses of Shirakawa village in Gifu Prefecture were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in (Photo courtesy of AFLO) 3 GEOGRAPHY AND CLIMATE
5 3 GEOGRAPHY AND CLIMATE
The number of policy holders has exceeded 100,000 individuals. Highly acceptance by the child-raising generations mainly 20s and 30s
 February 26, 2013 Haruaki Deguchi, President/Founder LIFENET INSURANCE COMPANY (Securities Code: 7157, TSE Mothers) The number of policy holders has exceeded 100,000 individuals Highly acceptance by the
February 26, 2013 Haruaki Deguchi, President/Founder LIFENET INSURANCE COMPANY (Securities Code: 7157, TSE Mothers) The number of policy holders has exceeded 100,000 individuals Highly acceptance by the
Climate, Vegetation, and Landforms
 Climate, Vegetation, and Landforms Definitions Climate is the average weather of a place over many years Geographers discuss five broad types of climates Moderate, dry, tropical, continental, polar Vegetation:
Climate, Vegetation, and Landforms Definitions Climate is the average weather of a place over many years Geographers discuss five broad types of climates Moderate, dry, tropical, continental, polar Vegetation:
Geography affects climate.
 KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
KEY CONCEPT Climate is a long-term weather pattern. BEFORE, you learned The Sun s energy heats Earth s surface unevenly The atmosphere s temperature changes with altitude Oceans affect wind flow NOW, you
CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS THINGS
 CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS NAME THE SIX MAJOR CLIMATE REGIONS DESCRIBE EACH CLIMATE REGION TELL THE FIVE FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE EXPLAIN HOW THOSE FACTORS AFFECT CLIMATE DESCRIBE HOW CLIMATES
CLIMATE, WATER & LIVING PATTERNS NAME THE SIX MAJOR CLIMATE REGIONS DESCRIBE EACH CLIMATE REGION TELL THE FIVE FACTORS THAT AFFECT CLIMATE EXPLAIN HOW THOSE FACTORS AFFECT CLIMATE DESCRIBE HOW CLIMATES
2. The map below shows high-pressure and low-pressure weather systems in the United States.
 1. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? 1) thermometer 3) weather satellite 2) sling psychrometer 4) weather balloon 6. Wind velocity is
1. Which weather instrument has most improved the accuracy of weather forecasts over the past 40 years? 1) thermometer 3) weather satellite 2) sling psychrometer 4) weather balloon 6. Wind velocity is
Present Status of Coastal Environmental Monitoring in Korean Waters. Using Remote Sensing Data
 Present Status of Coastal Environmental Monitoring in Korean Waters Using Remote Sensing Data Sang-Woo Kim, Young-Sang Suh National Fisheries Research & Development Institute #408-1, Shirang-ri, Gijang-up,
Present Status of Coastal Environmental Monitoring in Korean Waters Using Remote Sensing Data Sang-Woo Kim, Young-Sang Suh National Fisheries Research & Development Institute #408-1, Shirang-ri, Gijang-up,
CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate
 Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate Chapter 12 in the Making Connections textbook deals with Climate Connections. Use pages 127-144 to fill
Name: Date: Day/Period: CGC1D1: Interactions in the Physical Environment Factors that Affect Climate Chapter 12 in the Making Connections textbook deals with Climate Connections. Use pages 127-144 to fill
TECTONICS ASSESSMENT
 Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
Tectonics Assessment / 1 TECTONICS ASSESSMENT 1. Movement along plate boundaries produces A. tides. B. fronts. C. hurricanes. D. earthquakes. 2. Which of the following is TRUE about the movement of continents?
What Causes Climate? Use Target Reading Skills
 Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Climate and Climate Change Name Date Class Climate and Climate Change Guided Reading and Study What Causes Climate? This section describes factors that determine climate, or the average weather conditions
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather
 Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Name Period 4 th Six Weeks Notes 2015 Weather Radiation Convection Currents Winds Jet Streams Energy from the Sun reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves This energy fuels all life on Earth including the
Chapter Overview. Seasons. Earth s Seasons. Distribution of Solar Energy. Solar Energy on Earth. CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 6 Air-Sea Interaction The atmosphere and the ocean are one independent system. Earth has seasons because of the tilt on its axis. There are three major wind belts in each hemisphere.
FLOOD FORECASTING PRACTICE IN NORTHERN CALIFORNIA
 FLOOD FORECASTING PRACTICE IN NORTHERN CALIFORNIA California Department of Water Resources Post Office Box 219000, Sacramento, California 95821 9000 USA By Maurice Roos, Chief Hydrologist ABSTRACT Although
FLOOD FORECASTING PRACTICE IN NORTHERN CALIFORNIA California Department of Water Resources Post Office Box 219000, Sacramento, California 95821 9000 USA By Maurice Roos, Chief Hydrologist ABSTRACT Although
1. Japan's basic flood protection system. 2. Preparedness for major floods. Past major floods and state-level efforts Role of MLIT
 1. Japan's basic flood protection system 2. Preparedness for major floods Past major floods and state-level efforts Role of MLIT 8 Flood caused by Typhoon Kathleen (1947) Higashi-mura (present-day Otone-machi)
1. Japan's basic flood protection system 2. Preparedness for major floods Past major floods and state-level efforts Role of MLIT 8 Flood caused by Typhoon Kathleen (1947) Higashi-mura (present-day Otone-machi)
Climates are described by the same conditions used to describe
 58 The Causes of Climate R E A D I N G Climates are described by the same conditions used to describe weather, such as temperature, precipitation, and wind. You now know that oceans have an important effect
58 The Causes of Climate R E A D I N G Climates are described by the same conditions used to describe weather, such as temperature, precipitation, and wind. You now know that oceans have an important effect
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Echo Sounding Record. Measuring Bathymetry. CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces The study of bathymetry charts ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
Air Masses and Fronts
 Air Masses and Fronts Air Masses The weather of the United States east of the Rocky Mountains is dominated by large masses of air that travel south from the wide expanses of land in Canada, and north from
Air Masses and Fronts Air Masses The weather of the United States east of the Rocky Mountains is dominated by large masses of air that travel south from the wide expanses of land in Canada, and north from
Chapter 18 Introduction to. A f r i c a
 Chapter 18 Introduction to A f r i c a Ch. 18:1 Landforms & Resources 1. Africa s shape & landforms are the result of its location in the southern part of the ancient supercontinent of. Pangaea Over thousands
Chapter 18 Introduction to A f r i c a Ch. 18:1 Landforms & Resources 1. Africa s shape & landforms are the result of its location in the southern part of the ancient supercontinent of. Pangaea Over thousands
LANDFORMS OF THE EARTH STD VIII
 LANDFORMS OF THE EARTH STD VIII 1) What do you understand by the term geomorphology? A) Geomorphology is the systematic study of the Earth s relief features. Geo means earth; morph meaning form and ology
LANDFORMS OF THE EARTH STD VIII 1) What do you understand by the term geomorphology? A) Geomorphology is the systematic study of the Earth s relief features. Geo means earth; morph meaning form and ology
Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource
 Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource Vol. 9 No. 5 Spring 2003 Editor: Lauren Bell In this issue: g Climate Creations exploring mother nature s remote control for weather and Climate. g Crazy Climate
Southern AER Atmospheric Education Resource Vol. 9 No. 5 Spring 2003 Editor: Lauren Bell In this issue: g Climate Creations exploring mother nature s remote control for weather and Climate. g Crazy Climate
Disaster Risk Reduction through people centered National Multi-hazard Early Warning System in the context of Maldives
 Disaster Risk Reduction through people centered National Multi-hazard Early Warning System in the context of Maldives Abdul Muhusin, Deputy Director Department of Meteorology, Maldives Fourth Technical
Disaster Risk Reduction through people centered National Multi-hazard Early Warning System in the context of Maldives Abdul Muhusin, Deputy Director Department of Meteorology, Maldives Fourth Technical
Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Natural Disasters 6 th Grade
 The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved instructional plans are
7613-1 - Page 1. Weather Unit Exam Pre-Test Questions
 Weather Unit Exam Pre-Test Questions 7613-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) Equal quantities of water are placed in four uncovered containers with different shapes and left on a table at room temperature. From which
Weather Unit Exam Pre-Test Questions 7613-1 - Page 1 Name: 1) Equal quantities of water are placed in four uncovered containers with different shapes and left on a table at room temperature. From which
The Pennsylvania Observer
 The Pennsylvania Observer August 3, 2009 July 2009 - Pennsylvania Weather Recap Written by: Dan DePodwin After a cool month of June, some hoped July would bring usual summertime warmth to the state of
The Pennsylvania Observer August 3, 2009 July 2009 - Pennsylvania Weather Recap Written by: Dan DePodwin After a cool month of June, some hoped July would bring usual summertime warmth to the state of
8.5 Comparing Canadian Climates (Lab)
 These 3 climate graphs and tables of data show average temperatures and precipitation for each month in Victoria, Winnipeg and Whitehorse: Figure 1.1 Month J F M A M J J A S O N D Year Precipitation 139
These 3 climate graphs and tables of data show average temperatures and precipitation for each month in Victoria, Winnipeg and Whitehorse: Figure 1.1 Month J F M A M J J A S O N D Year Precipitation 139
1. Incredible India. Shade the map on the next page, to show India s relief. The correct shading is shown on the final page! Incredible India India
 1. Incredible India Shade the map on the next page, to show India s relief. The correct shading is shown on the final page! Incredible India India The DCSF supported Action plan for Geography is delivered
1. Incredible India Shade the map on the next page, to show India s relief. The correct shading is shown on the final page! Incredible India India The DCSF supported Action plan for Geography is delivered
Week 1. Week 2. Week 3
 Week 1 1. What US city has the largest population? 2. Where is Aachen? 3. What is the capitol of Florida? 4. What is the longest mountain range in Spain? 5. What countries border Equador? Week 2 1. What
Week 1 1. What US city has the largest population? 2. Where is Aachen? 3. What is the capitol of Florida? 4. What is the longest mountain range in Spain? 5. What countries border Equador? Week 2 1. What
Summary Report of Basic Survey on Wage Structure (starting salary)
 Summary Report of Basic Survey on Wage Structure (starting ) 2011 Contents Outline of Survey Page 1 Definitions Page 3 Summary of Results 1. Starting by school career Page 4 2. Starting by enterprise size
Summary Report of Basic Survey on Wage Structure (starting ) 2011 Contents Outline of Survey Page 1 Definitions Page 3 Summary of Results 1. Starting by school career Page 4 2. Starting by enterprise size
How to analyze synoptic-scale weather patterns Table of Contents
 How to analyze synoptic-scale weather patterns Table of Contents Before You Begin... 2 1. Identify H and L pressure systems... 3 2. Locate fronts and determine frontal activity... 5 3. Determine surface
How to analyze synoptic-scale weather patterns Table of Contents Before You Begin... 2 1. Identify H and L pressure systems... 3 2. Locate fronts and determine frontal activity... 5 3. Determine surface
Globalization of Higher Education in Japan
 Globalization of Higher Education in Japan: ( Made by Office for International Planning Higher Education Bureau ) 10 th of March, 2014 Hideshi SEMBA, Mission of Japan to the EU Globalization of Higher
Globalization of Higher Education in Japan: ( Made by Office for International Planning Higher Education Bureau ) 10 th of March, 2014 Hideshi SEMBA, Mission of Japan to the EU Globalization of Higher
EL Civics Objective 16 (Emergencies) Level: Beginning Low & Beginning High Task #1: Identify Emergencies & Disasters
 EL Civics Objective 16 (Emergencies) Level: Beginning Low & Beginning High Task #1: Identify Emergencies & Disasters Language & Literacy Objectives: 1. Identify what constitutes an emergency or disaster,
EL Civics Objective 16 (Emergencies) Level: Beginning Low & Beginning High Task #1: Identify Emergencies & Disasters Language & Literacy Objectives: 1. Identify what constitutes an emergency or disaster,
Hurricanes. Characteristics of a Hurricane
 Hurricanes Readings: A&B Ch. 12 Topics 1. Characteristics 2. Location 3. Structure 4. Development a. Tropical Disturbance b. Tropical Depression c. Tropical Storm d. Hurricane e. Influences f. Path g.
Hurricanes Readings: A&B Ch. 12 Topics 1. Characteristics 2. Location 3. Structure 4. Development a. Tropical Disturbance b. Tropical Depression c. Tropical Storm d. Hurricane e. Influences f. Path g.
The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation
 The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events 2 How do changes
The IPCC Special Report on Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events 2 How do changes
Mount Fuji. Grade Level This lesson plan can be adjusted for grades 5-12
 Grade Level This lesson plan can be adjusted for grades 5-12 Mount Fuji Purpose The purpose of this lesson is to consider the cultural significance of Mt. Fuji to the Japanese, use it as a tool to consider
Grade Level This lesson plan can be adjusted for grades 5-12 Mount Fuji Purpose The purpose of this lesson is to consider the cultural significance of Mt. Fuji to the Japanese, use it as a tool to consider
Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface
 TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
TEKS investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and landslides Rapid Changes in Earth s Surface Constant Changes Earth s surface is constantly changing. Wind,
Tectonic plates push together at convergent boundaries.
 KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. BEFORE, you learned Plates move apart at divergent boundaries In the oceans, divergent boundaries mark where the sea floor spreads apart On land,
KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. BEFORE, you learned Plates move apart at divergent boundaries In the oceans, divergent boundaries mark where the sea floor spreads apart On land,
11A Plate Tectonics. What is plate tectonics? Setting up. Materials
 11A Plate Tectonics What is plate tectonics? Earth s crust plus the upper mantle forms the lithosphere. Earth s lithosphere is broken in a number of different pieces. How these pieces move and interact
11A Plate Tectonics What is plate tectonics? Earth s crust plus the upper mantle forms the lithosphere. Earth s lithosphere is broken in a number of different pieces. How these pieces move and interact
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel
 Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries Deborah Jordan and Samuel Spiegel Jordan, Deborah and Spiegel, Samuel: Learning Research Development Center, University of Pittsburgh. Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries.
Storms Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Storms Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A(n) thunderstorm forms because of unequal heating
Name: Class: Date: Storms Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A(n) thunderstorm forms because of unequal heating
Chapter 3 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems
 Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
Communities, Biomes, and Ecosystems Section 1: Community Ecology Section 2: Terrestrial Biomes Section 3: Aquatic Ecosystems Click on a lesson name to select. 3.1 Community Ecology Communities A biological
WEATHER AND CLIMATE practice test
 WEATHER AND CLIMATE practice test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What role does runoff play in the water cycle? a. It is the process in
WEATHER AND CLIMATE practice test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What role does runoff play in the water cycle? a. It is the process in
Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist. Introduction. Climatic controls
 Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist Introduction Illinois lies midway between the Continental Divide and the Atlantic Ocean, and the state's southern tip is 500 miles north of
Climate of Illinois Narrative Jim Angel, state climatologist Introduction Illinois lies midway between the Continental Divide and the Atlantic Ocean, and the state's southern tip is 500 miles north of
Deserts, Wind Erosion and Deposition
 Deserts, Wind Erosion and Deposition By definition, a desert has less than 10 in (25 cm) of precipitation per year. Deserts occur at 30 o and 60 o in regions of descending air. Deserts can be hot or cold.
Deserts, Wind Erosion and Deposition By definition, a desert has less than 10 in (25 cm) of precipitation per year. Deserts occur at 30 o and 60 o in regions of descending air. Deserts can be hot or cold.
Lecture 4: Pressure and Wind
 Lecture 4: Pressure and Wind Pressure, Measurement, Distribution Forces Affect Wind Geostrophic Balance Winds in Upper Atmosphere Near-Surface Winds Hydrostatic Balance (why the sky isn t falling!) Thermal
Lecture 4: Pressure and Wind Pressure, Measurement, Distribution Forces Affect Wind Geostrophic Balance Winds in Upper Atmosphere Near-Surface Winds Hydrostatic Balance (why the sky isn t falling!) Thermal
The Polar Climate Zones
 The Polar Climate Zones How cold is it in the polar climate? Polar areas are the coldest of all the major climate zones The Sun is hardly ever high enough in the sky to cause the plentiful ice to melt,
The Polar Climate Zones How cold is it in the polar climate? Polar areas are the coldest of all the major climate zones The Sun is hardly ever high enough in the sky to cause the plentiful ice to melt,
7) Coastal Storms: Multi-Hazard Analysis for New York City
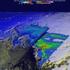 7) Coastal Storms: Multi-Hazard Analysis for New York City a) Hazard Profile i) Hazard Description Coastal storms, including nor'easters, tropical storms, and hurricanes, can and do affect New York City.
7) Coastal Storms: Multi-Hazard Analysis for New York City a) Hazard Profile i) Hazard Description Coastal storms, including nor'easters, tropical storms, and hurricanes, can and do affect New York City.
Climate Change on the Prairie:
 Climate Change on the Prairie: A Basic Guide to Climate Change in the High Plains Region - UPDATE Global Climate Change Why does the climate change? The Earth s climate has changed throughout history and
Climate Change on the Prairie: A Basic Guide to Climate Change in the High Plains Region - UPDATE Global Climate Change Why does the climate change? The Earth s climate has changed throughout history and
Kindergarten Seasons and Weather Assessment
 Kindergarten Seasons and Weather Assessment 1a. Circle the pictures that represent the four seasons: snowman going to a teacher harvest fruits colorful flowers the beach 1b. Write the name of the season
Kindergarten Seasons and Weather Assessment 1a. Circle the pictures that represent the four seasons: snowman going to a teacher harvest fruits colorful flowers the beach 1b. Write the name of the season
6. Base your answer to the following question on the graph below, which shows the average monthly temperature of two cities A and B.
 1. Which single factor generally has the greatest effect on the climate of an area on the Earth's surface? 1) the distance from the Equator 2) the extent of vegetative cover 3) the degrees of longitude
1. Which single factor generally has the greatest effect on the climate of an area on the Earth's surface? 1) the distance from the Equator 2) the extent of vegetative cover 3) the degrees of longitude
Advice For the multiple-choice questions, completely fill in the circle alongside the appropriate answer(s).
 SPECIMEN ASSESSMENT MATERIAL GCSE GEOGRAPHY Paper 1 Living with the physical environment Specimen Materials For this paper you must have: a pencil a ruler. Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes Instructions
SPECIMEN ASSESSMENT MATERIAL GCSE GEOGRAPHY Paper 1 Living with the physical environment Specimen Materials For this paper you must have: a pencil a ruler. Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes Instructions
EMERGENCY-RESPONSE CAPACITY OF LIFELINES AFTER WIDE-AREA EARTHQUAKE DISASTERS
 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Lessons Learned from the 211 Great East Japan Earthquake, March 1-4, 212, Tokyo, Japan EMERGENCY-RESPONSE CAPACITY OF LIFELINES AFTER WIDE-AREA
Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering Lessons Learned from the 211 Great East Japan Earthquake, March 1-4, 212, Tokyo, Japan EMERGENCY-RESPONSE CAPACITY OF LIFELINES AFTER WIDE-AREA
Seasonal & Daily Temperatures. Seasons & Sun's Distance. Solstice & Equinox. Seasons & Solar Intensity
 Seasonal & Daily Temperatures Seasons & Sun's Distance The role of Earth's tilt, revolution, & rotation in causing spatial, seasonal, & daily temperature variations Please read Chapter 3 in Ahrens Figure
Seasonal & Daily Temperatures Seasons & Sun's Distance The role of Earth's tilt, revolution, & rotation in causing spatial, seasonal, & daily temperature variations Please read Chapter 3 in Ahrens Figure
AN ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF HIGH-SPEED RAILWAY ON INTER-REGIONAL MIGRATION AND TRAFFIC FLOW IN JAPAN
 AN ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF HIGH-SPEED RAILWAY ON INTER-REGIONAL MIGRATION AND TRAFFIC FLOW IN JAPAN Shigeru Morichi Professor & Dr. of Eng. Dept. of Civil Engineering University of Address: 7-3-1 Hongo,
AN ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECT OF HIGH-SPEED RAILWAY ON INTER-REGIONAL MIGRATION AND TRAFFIC FLOW IN JAPAN Shigeru Morichi Professor & Dr. of Eng. Dept. of Civil Engineering University of Address: 7-3-1 Hongo,
Earth Science Chapter 14 Section 2 Review
 Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 14 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the three
Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 14 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the three
 Disaster Prevention Measures in Global-Local Context 4 th World Water Forum Dr. Yoshihiko Yamashita CTI Engineering Co., Ltd Association of Japanese Consulting Engineers Outline of Presentation Up-to to-date
Disaster Prevention Measures in Global-Local Context 4 th World Water Forum Dr. Yoshihiko Yamashita CTI Engineering Co., Ltd Association of Japanese Consulting Engineers Outline of Presentation Up-to to-date
Geography at GISSV: An Introduction to the Curriculum
 Geography at GISSV: An Introduction to the Curriculum Classes Geography is taught for two hours per week in Grades 5-9. The only exception is in Grade 8, where class is taught for one hour per week for
Geography at GISSV: An Introduction to the Curriculum Classes Geography is taught for two hours per week in Grades 5-9. The only exception is in Grade 8, where class is taught for one hour per week for
California Standards Grades 9 12 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping
 California Standards Grades 912 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping Earth Sciences Earth s Place in the Universe 1. Astronomy and planetary exploration reveal the solar system s structure,
California Standards Grades 912 Boardworks 2009 Science Contents Standards Mapping Earth Sciences Earth s Place in the Universe 1. Astronomy and planetary exploration reveal the solar system s structure,
WEATHERING, EROSION, AND DEPOSITION PRACTICE TEST. Which graph best shows the relative stream velocities across the stream from A to B?
 NAME DATE WEATHERING, EROSION, AND DEPOSITION PRACTICE TEST 1. The diagram below shows a meandering stream. Measurements of stream velocity were taken along straight line AB. Which graph best shows the
NAME DATE WEATHERING, EROSION, AND DEPOSITION PRACTICE TEST 1. The diagram below shows a meandering stream. Measurements of stream velocity were taken along straight line AB. Which graph best shows the
Water & Climate Review
 Water & Climate Review 1. The cross section below shows the direction of air flowing over a mountain. Points A and B are at the same elevation on opposite sides of the mountain. 4. The graph below shows
Water & Climate Review 1. The cross section below shows the direction of air flowing over a mountain. Points A and B are at the same elevation on opposite sides of the mountain. 4. The graph below shows
Regional Atlas: Introduction to South Asia
 Name Regional Atlas: Introduction to South Asia Study the map on page 593 of the textbook. 1. The Khyber Pass connects which two countries? CHAPTER 28 2. What capital city is located at 80 E longitude?
Name Regional Atlas: Introduction to South Asia Study the map on page 593 of the textbook. 1. The Khyber Pass connects which two countries? CHAPTER 28 2. What capital city is located at 80 E longitude?
Anyone Else Notice That Its Been Windy Lately?
 National Weather Service Aberdeen, South Dakota January 2014 Inside this issue: Has it Been Windy Lately or What? 2013 Year in Review 2013 Year in Review (cont.) 1 2 3 Has it Been Windy Lately or What?
National Weather Service Aberdeen, South Dakota January 2014 Inside this issue: Has it Been Windy Lately or What? 2013 Year in Review 2013 Year in Review (cont.) 1 2 3 Has it Been Windy Lately or What?
CLIMATE OF RWANDA. Overview. Linked to other lessons
 Geography S6 GENERAL PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY OF RWANDA Lesson 75 Developed by (Niwagaba Innocent) Subtopic Climate and factors influencing it in Rwanda Specific Objectives The learners must be able to: Describe
Geography S6 GENERAL PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY OF RWANDA Lesson 75 Developed by (Niwagaba Innocent) Subtopic Climate and factors influencing it in Rwanda Specific Objectives The learners must be able to: Describe
defined largely by regional variations in climate
 1 Physical Environment: Climate and Biomes EVPP 110 Lecture Instructor: Dr. Largen Fall 2003 2 Climate and Biomes Ecosystem concept physical and biological components of environment are considered as single,
1 Physical Environment: Climate and Biomes EVPP 110 Lecture Instructor: Dr. Largen Fall 2003 2 Climate and Biomes Ecosystem concept physical and biological components of environment are considered as single,
How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form?
 298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
298 10.14 INVESTIGATION How Did These Ocean Features and Continental Margins Form? The terrain below contains various features on the seafloor, as well as parts of three continents. Some general observations
Full name:.. Date:. School: Teacher: Contents:
 Contents: 1.- The atmosphere. 2.- Weather and climate. 3.- The elements of climate 3.1 Temperatures 3.2 Rainfalls 3.3 Atmospheric pressure 3.4 Wind 4.-The Natural Environment. Full name:.. Date:. Class:
Contents: 1.- The atmosphere. 2.- Weather and climate. 3.- The elements of climate 3.1 Temperatures 3.2 Rainfalls 3.3 Atmospheric pressure 3.4 Wind 4.-The Natural Environment. Full name:.. Date:. Class:
Using a Concept Definition Map
 Lesson Plan Using a Concept Definition Map 1. Set Expectations Print Disaster on the board. Tell students, You are going to come up with as many words as you can that are related to the word disaster,
Lesson Plan Using a Concept Definition Map 1. Set Expectations Print Disaster on the board. Tell students, You are going to come up with as many words as you can that are related to the word disaster,
When Things Go Wrong
 When Things Go Wrong When Things Go Wrong Our planet has many wondrous things. We plant a tiny sapling and it becomes a mighty tree. Water runs in rivers. Rainbows appear in the sky. But it is not always
When Things Go Wrong When Things Go Wrong Our planet has many wondrous things. We plant a tiny sapling and it becomes a mighty tree. Water runs in rivers. Rainbows appear in the sky. But it is not always
WeatherBug Vocabulary Bingo
 Type of Activity: Game: Interactive activity that is competitive, and allows students to learn at the same time. Activity Overview: WeatherBug Bingo is a fun and engaging game for you to play with students!
Type of Activity: Game: Interactive activity that is competitive, and allows students to learn at the same time. Activity Overview: WeatherBug Bingo is a fun and engaging game for you to play with students!
6.E.2.2 Plate Tectonics, Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Name: Date: 1. The road shown below was suddenly broken by a natural event. 3. The convergence of two continental plates would produce Which natural event most likely caused the crack in the road? island
Name: Date: 1. The road shown below was suddenly broken by a natural event. 3. The convergence of two continental plates would produce Which natural event most likely caused the crack in the road? island
ENVIRONMENTAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION: CLIMATE SYSTEM Vol. II - Low-Latitude Climate Zones and Climate Types - E.I. Khlebnikova
 LOW-LATITUDE CLIMATE ZONES AND CLIMATE TYPES E.I. Khlebnikova Main Geophysical Observatory, St. Petersburg, Russia Keywords: equatorial continental climate, ITCZ, subequatorial continental (equatorial
LOW-LATITUDE CLIMATE ZONES AND CLIMATE TYPES E.I. Khlebnikova Main Geophysical Observatory, St. Petersburg, Russia Keywords: equatorial continental climate, ITCZ, subequatorial continental (equatorial
FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY! - TRIAL PASSWORD USERS MAY NOT REPRODUCE AND DISTRIBUTE PRINTABLE MATERIALS OFF THE SOLPASS WEBSITE!
 FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY! - TRIAL PASSWORD USERS MAY NOT REPRODUCE AND DISTRIBUTE PRINTABLE MATERIALS OFF THE SOLPASS WEBSITE! 1 NAME DATE GRADE 5 SCIENCE SOL REVIEW WEATHER LABEL the 3 stages of the water
FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY! - TRIAL PASSWORD USERS MAY NOT REPRODUCE AND DISTRIBUTE PRINTABLE MATERIALS OFF THE SOLPASS WEBSITE! 1 NAME DATE GRADE 5 SCIENCE SOL REVIEW WEATHER LABEL the 3 stages of the water
Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica
Name: Class: Date: Plate Tectonics Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The existence of coal beds in Antarctica
The Oceans Role in Climate
 The Oceans Role in Climate Martin H. Visbeck A Numerical Portrait of the Oceans The oceans of the world cover nearly seventy percent of its surface. The largest is the Pacific, which contains fifty percent
The Oceans Role in Climate Martin H. Visbeck A Numerical Portrait of the Oceans The oceans of the world cover nearly seventy percent of its surface. The largest is the Pacific, which contains fifty percent
ES Chapter 10 Review. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Name: Class: Date: ES Chapter 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Scientists used the pattern of alternating normal and reversed
Jessica Blunden, Ph.D., Scientist, ERT Inc., Climate Monitoring Branch, NOAA s National Climatic Data Center
 Kathryn Sullivan, Ph.D, Acting Under Secretary of Commerce for Oceans and Atmosphere and NOAA Administrator Thomas R. Karl, L.H.D., Director,, and Chair of the Subcommittee on Global Change Research Jessica
Kathryn Sullivan, Ph.D, Acting Under Secretary of Commerce for Oceans and Atmosphere and NOAA Administrator Thomas R. Karl, L.H.D., Director,, and Chair of the Subcommittee on Global Change Research Jessica
Physiography, Geography and Climate of Latin America (Lecture 3)
 Physiography, Geography and Climate of Latin America (Lecture 3) Natural Landmarks in Latin America World's longest and second highest mountain range, and the world's highest active volcanoes. Biggest
Physiography, Geography and Climate of Latin America (Lecture 3) Natural Landmarks in Latin America World's longest and second highest mountain range, and the world's highest active volcanoes. Biggest
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
Unit 6 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Earthquakes and Volcanoes: Essential Questions What evidence can students observe that the Earth is changing? How do scientists know what s inside the Earth? What processes
Interactive Plate Tectonics
 Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
Interactive Plate Tectonics Directions: Go to the following website and complete the questions below. http://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/index.html How do scientists learn about the interior
2013 Annual Climate Summary for the Southeast United States
 Months of heavy rain forced the U.S. Army Corp of Engineers to open the spillways at Lake Hartwell, located at the headwaters of the Savannah River along the South Carolina-Georgia border, on July 9,.
Months of heavy rain forced the U.S. Army Corp of Engineers to open the spillways at Lake Hartwell, located at the headwaters of the Savannah River along the South Carolina-Georgia border, on July 9,.
Multi-Jurisdictional Hazard Mitigation Plan
 Flooding General Flooding is the leading cause of death among all types of natural disasters throughout the United States, with its ability to roll boulders the size of cars, tear out trees, and destroy
Flooding General Flooding is the leading cause of death among all types of natural disasters throughout the United States, with its ability to roll boulders the size of cars, tear out trees, and destroy
Flood After Fire Fact Sheet
 FACT SHEET Flood After Fire Fact Sheet Risks and Protection Floods are the most common and costly natural hazard in the nation. Whether caused by heavy rain, thunderstorms, or the tropical storms, the
FACT SHEET Flood After Fire Fact Sheet Risks and Protection Floods are the most common and costly natural hazard in the nation. Whether caused by heavy rain, thunderstorms, or the tropical storms, the
IX Geography CHEPTER-4 CLIMATE
 IX Geography CHEPTER-4 CLIMATE Introduction: Climate refers to the sum total of weather conditions and variations over a large area for a long period of time (more than thirty years). Weather refers to
IX Geography CHEPTER-4 CLIMATE Introduction: Climate refers to the sum total of weather conditions and variations over a large area for a long period of time (more than thirty years). Weather refers to
How To Predict Climate Change
 A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events the focus of Chapter 3 Presented by: David R. Easterling Chapter 3:Changes in Climate Extremes & their Impacts on the Natural Physical
A changing climate leads to changes in extreme weather and climate events the focus of Chapter 3 Presented by: David R. Easterling Chapter 3:Changes in Climate Extremes & their Impacts on the Natural Physical
Climate Change Impacts in the Asia/Pacific Region
 Climate Change Impacts in the Asia/Pacific Region Global CC threat CC in the A/P region The Stern Review and IPCC 4 th Assessment Report both state that climate change will have adverse impact on people
Climate Change Impacts in the Asia/Pacific Region Global CC threat CC in the A/P region The Stern Review and IPCC 4 th Assessment Report both state that climate change will have adverse impact on people
Hot Spots & Plate Tectonics
 Hot Spots & Plate Tectonics Activity I: Hawaiian Islands Procedures: Use the map and the following information to determine the rate of motion of the Pacific Plate over the Hawaiian hot spot. The volcano
Hot Spots & Plate Tectonics Activity I: Hawaiian Islands Procedures: Use the map and the following information to determine the rate of motion of the Pacific Plate over the Hawaiian hot spot. The volcano
5 th Grade Science Vocabulary Words
 5 th Grade Science Vocabulary Words abiotic factor A nonliving part of an ecosystem. acceleration Change in velocity with respect to time. action The force one object applies to a second, as in Newton
5 th Grade Science Vocabulary Words abiotic factor A nonliving part of an ecosystem. acceleration Change in velocity with respect to time. action The force one object applies to a second, as in Newton
Quarterly Securities Report
 Quarterly Securities Report (The second quarter of the 39th fiscal year) ACOM CO., LTD. Quarterly Securities Report 1. This document has been outputted and printed by adding a table of contents and page
Quarterly Securities Report (The second quarter of the 39th fiscal year) ACOM CO., LTD. Quarterly Securities Report 1. This document has been outputted and printed by adding a table of contents and page
Chapter 2 Earthquake Insurance System in Japan. Chapter 2
 Chapter 2 Section 1 Difficulties of Making Seismic Risk Insurable Every time a great earthquake disaster occurred after the latter half of the 19 th century in Japan, establishment of insurance compensating
Chapter 2 Section 1 Difficulties of Making Seismic Risk Insurable Every time a great earthquake disaster occurred after the latter half of the 19 th century in Japan, establishment of insurance compensating
6 th Grade Science Assessment: Weather & Water Select the best answer on the answer sheet. Please do not make any marks on this test.
 Select the be answer on the answer sheet. Please do not make any marks on this te. 1. Weather is be defined as the A. changes that occur in cloud formations from day to day. B. amount of rain or snow that
Select the be answer on the answer sheet. Please do not make any marks on this te. 1. Weather is be defined as the A. changes that occur in cloud formations from day to day. B. amount of rain or snow that
Heavy Rainfall from Hurricane Connie August 1955 By Michael Kozar and Richard Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803
 Heavy Rainfall from Hurricane Connie August 1955 By Michael Kozar and Richard Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803 1. Introduction Hurricane Connie became the first hurricane of the
Heavy Rainfall from Hurricane Connie August 1955 By Michael Kozar and Richard Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803 1. Introduction Hurricane Connie became the first hurricane of the
Modified Richter Scale
 Name Date ID Grade 7 - Science Interim Assessment Third Grading Period 1. Which of the following is NOT affected by the tilt of Earth's axis? Length of day Type of climate Change of seasons Length of year
Name Date ID Grade 7 - Science Interim Assessment Third Grading Period 1. Which of the following is NOT affected by the tilt of Earth's axis? Length of day Type of climate Change of seasons Length of year
Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage
 Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage Title: Exploring Our Nation 20 minutes *Have students complete group work prior to going to the computer lab. 2.List of themes 3. Computer lab 4. Student
Exploring Our World with GIS Lesson Plans Engage Title: Exploring Our Nation 20 minutes *Have students complete group work prior to going to the computer lab. 2.List of themes 3. Computer lab 4. Student
Module 11: The Cruise Ship Sector. Destination #3
 Module 11: The Cruise Ship Sector Destination #3 Cruise Destinations Welcome to your third destination. Use the following resource article to learn about the different oceans and time zones. Seen from
Module 11: The Cruise Ship Sector Destination #3 Cruise Destinations Welcome to your third destination. Use the following resource article to learn about the different oceans and time zones. Seen from
Design and Re-Use Of Shovadans In Today's Architecture "With Due Attention To Have Thermal Energy Of The Earth"
 RESEARCH INVENTY: International Journal of Engineering and Science ISBN: 2319-6483, ISSN: 2278-4721, Vol. 1, Issue 8 (November 2012), PP 60-64 www.researchinventy.com Design and Re-Use Of Shovadans In
RESEARCH INVENTY: International Journal of Engineering and Science ISBN: 2319-6483, ISSN: 2278-4721, Vol. 1, Issue 8 (November 2012), PP 60-64 www.researchinventy.com Design and Re-Use Of Shovadans In
FOOD INFORMATION EXCHANGE
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMERS DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Directorate E - Safety of the food chain E2 Food hygiene, Alert system and Training Brussels, 6 April, 2011 R A S F F N E W S FOOD INFORMATION
EUROPEAN COMMISSION HEALTH & CONSUMERS DIRECTORATE-GENERAL Directorate E - Safety of the food chain E2 Food hygiene, Alert system and Training Brussels, 6 April, 2011 R A S F F N E W S FOOD INFORMATION
Flood Facts 2F.1. Flood Facts
 Flood Facts 2F.1 Engage Flood Facts To introduce students to the causes and effects of flooding in Western Australia. Flooding occurs in the Australian environment as part of the natural water or hydrologic
Flood Facts 2F.1 Engage Flood Facts To introduce students to the causes and effects of flooding in Western Australia. Flooding occurs in the Australian environment as part of the natural water or hydrologic
LEARNING THE LANDFORMS Grade Level: Third Presented by: Elizabeth Turcott, Endeavor Charter Academy, Springfield, Michigan Length of Unit: 14 lessons
 LEARNING THE LANDFORMS Grade Level: Third Presented by: Elizabeth Turcott, Endeavor Charter Academy, Springfield, Michigan Length of Unit: 14 lessons I. ABSTRACT This unit develops an understanding of
LEARNING THE LANDFORMS Grade Level: Third Presented by: Elizabeth Turcott, Endeavor Charter Academy, Springfield, Michigan Length of Unit: 14 lessons I. ABSTRACT This unit develops an understanding of
The concepts developed in this standard include the following: Oceans cover about 70% of the surface of the Earth.
 Name Date Grade 5 SOL 5.6 Review Oceans Made by SOLpass - www.solpass.org solpass100@comcast.net Reproduction is permitted for SOLpass subscribers only. The concepts developed in this standard include
Name Date Grade 5 SOL 5.6 Review Oceans Made by SOLpass - www.solpass.org solpass100@comcast.net Reproduction is permitted for SOLpass subscribers only. The concepts developed in this standard include
Rocks and Plate Tectonics
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Rocks and Plate Tectonics Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is a naturally occurring, solid mass of mineral or
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Rocks and Plate Tectonics Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is a naturally occurring, solid mass of mineral or
Allows teachers to print reports for individual students or an entire class.
 Map and Globe Skills Developed by teachers and geography specialists, Map and Globe Skills provides the strategies, skills and practice your students need to develop a strong understanding of basic mapping
Map and Globe Skills Developed by teachers and geography specialists, Map and Globe Skills provides the strategies, skills and practice your students need to develop a strong understanding of basic mapping
NATURAL REGIONS OF KENTUCKY
 NATURAL WONDERS As you travel around Kentucky taking pictures, you are excited by what you see. Kentucky offers diverse and amazing sights. The Six Regions In the West, you see the Mississippi River, the
NATURAL WONDERS As you travel around Kentucky taking pictures, you are excited by what you see. Kentucky offers diverse and amazing sights. The Six Regions In the West, you see the Mississippi River, the
