Solar Wind Heating by MHD Turbulence
|
|
|
- Nora Barton
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Solar Wind Heating by MHD Turbulence C. S. Ng, A. Bhattacharjee, and D. Munsi Space Science Center University of New Hampshire Acknowledgment: P. A. Isenberg Work partially supported by NSF, NASA CMSO General Meeting, June 4, 2007 University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH
2 Hydrodynamic turbulence Kolmogorov (1941): can get energy spectrum by dimensional analysis Energy cascade rate:!(k) " k # E(k) $! " = 5/ 2, # = 3/ 2 Kolmogorov spectrum: { Energy spectrum: Kolmogorov constant: C K ~ 1.4! 2 = constant E(k) ~ C K! 2 / 3 k "5/ 3! E(k) dk = total energy
3 MHD turbulence Additional dependence on the Alfvén speed V A!(k) " k # E(k) $ % Energy cascade rate: V A! " = (5 #$ ) / 2, % = (3 #$ ) / 2 Spectral index: ν = α / β = (5 γ ) (3 γ ) = constant! = 0 : Kolmogorov spectrum E(k) ~ C K! 2 / 3 k "5/ 3 E(k) ~ C IK ε 1/ 2 1/ 2 3/ 2 γ = 1 : IK spectrum V A k Iroshnikov (1963), Kraichnan (1965) C IK ~ Dimensionless parameter:! " k1/ 2 E k 1/ 2 V A #1 = v k / V A << 1
4 Weak MHD turbulence Energy cascade possible only if two Alfvén wave packets propagating in opposite directions collide Weak turbulence: χ << 1 Time scales: Eddy turn-over time! N ~ 1/ kv k Alfvén time! A ~ 1/ kv A = "! N <<! N Energy cascade time! E ~! A / " 2 =! N / " >>! N Kolmogorov cascade rate:! K ~ v k 2 / " N ~ k 5/ 2 E k 3/ 2 IK cascade rate:! IK ~ v k 2 / " E ~! K # ~ k 3 E k 2 V A $1 <<! K
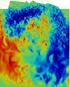
5 simulations of 2D MHD turbulence no B 0 k - 3/2 energy spectrum [Ng et al. 2003] 1D energy spectrum decaying periodic in x,y consistent with IK spectrum magnetic energy kinetic energy
6 Energy cascade rate! Fit numerical values of or #3 / " = C 2 K " K = C #2 IK " IK where ε IK = k 3 E 2 1 k V! A by IK theory ε K = k 5 / 2 E k 3/ 2 by Kolmogorov theory E(k) = C K " 2 / 3 k #5 / 3 = C IK " 1/ 2 V A 1/ 2 k #3 / 2 C IK 1.8 C K More consistent with IK theory c.f. usually found values: C K ~ 1.4 2, C IK ~
7 Energy cascade rate ! E energy cascade rate ε IK = k 3 E k 2 VA 1 ε A amplitude changing rate ε K = k 5/ 2 E k 3/2 More consistent with IK theory
8 Energy cascade rate -- observations From [Vasquez et al. 2007, preprint], scatter plot of the Kolmogorov cascade rate (red diamonds - left), the IK cascade rate (red diamonds -right), and expected heating rate (blue crosses) as a function of proton temperature T pr. The Kolmogorov rate exceeds the expected one by a factor of 10 or more, while the IK rate is roughly in agreement.
9 Solar wind turbulence model The steady state solar wind turbulence model developed by [Matthaeus et al. 1994, 1996] and later developments: Assumptions: Steady state Radially expanding solar wind with uniform speed V sw 1D (radial position r) Turbulence characterized by two fields: fluctuation velocity (Z) and correlation length (λ) Kolmogorov type cascade rate Solar wind (proton) temperature can be calculated passively
10 Solar wind turbulence model The steady state solar wind turbulence model developed by [Matthaeus et al. 1994, 1996] and later developments: dz 2 dr = " AZ 2 r " #Z 3 $V SW + Q V SW d" dr = # C" r + $Z V SW # $"Q V SW Z 2! dt dr = " 4T 3r + m#z 3 3k B $V SW Z 2 :! average turbulence energy with Z = Z " λ: turbulence correlation length T: solar! wind proton temperature Q: turbulence generation rate due to pickup ions (interstellar neutral particles entering the! heliosphere and get ionized)
11 Solar wind turbulence model vs observations From [Smith et al. 2001]
12 Temperature comparison with pickup ions From [Isenberg et al. 2003]
13 Solar wind model with IK cascade The solar wind turbulence model changed to [Matthaeus et al. 1994, Hossain et al. 1995]: dz 2 dr = " AZ 2 r " #Z 4 $V SW V A + Q V SW d" dr = # C" r + $ % Z 4 ( ' * # $"Q V SW & V A ) V SW Z 2! dt dr = " 4T 3r + m#z 4 3k B $V SW V A Z 2!: average turbulence energy with Z = Z " λ: turbulence correlation length T:! solar wind temperature Q: turbulence generation rate due to pickup ions! 1/ 3
14 Comparisons with observations IK without Q IK with Q Kolmogorov with Q Kolmogorov without Q c.f. [Isenberg et al. 2003]
15 Comparisons with observations Kolmogorov without Q Kolmogorov with Q C.f. [Smith et al. 2001], with corrected temperature equation.
16 Comparisons with observations Kolmogorov without Q Kolmogorov with Q IK without Q C.f. [Smith et al. 2001], with corrected temperature equation.
17 Comparisons with observations Kolmogorov without Q Kolmogorov with Q IK without Q IK with Q C.f. [Smith et al. 2001], with corrected temperature equation.
18 Conclusion 2D MHD turbulence is found in simulations to be weak 3 /2 with IK spectrum E(k) k and the energy cascade rate is found to be more consistent with IK scaling. Although a solar wind model based on Kolmogorov cascade compares well with proton temperature observations with contributions from pickup ions, it is also consistent with IK cascade with or without that. The predication of correlation length based on IK cascade with or without pickup ions agrees better with data than Kolmogorov cascade with pickup ions. Ion heating based on IK cascade is a possible alternative to Kolmogorov based theories and should be investigated more extensively.
Kolmogorov versus Iroshnikov-Kraichnan spectra: Consequences for ion heating in
 Kolmogorov versus Iroshnikov-Kraichnan spectra: Consequences for ion heating in the solar wind C. S. Ng 1, A. Bhattacharjee 2, D. Munsi 2, P. A. Isenberg 2, and C. W. Smith 2 1 Geophysical Institute, University
Kolmogorov versus Iroshnikov-Kraichnan spectra: Consequences for ion heating in the solar wind C. S. Ng 1, A. Bhattacharjee 2, D. Munsi 2, P. A. Isenberg 2, and C. W. Smith 2 1 Geophysical Institute, University
Coronal Heating Problem
 Mani Chandra Arnab Dhabal Raziman T V PHY690C Course Project Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Outline 1 2 3 Source of the energy Mechanism of energy dissipation Proposed mechanisms Regions of the
Mani Chandra Arnab Dhabal Raziman T V PHY690C Course Project Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Outline 1 2 3 Source of the energy Mechanism of energy dissipation Proposed mechanisms Regions of the
Kinetic effects in the turbulent solar wind: capturing ion physics with a Vlasov code
 Kinetic effects in the turbulent solar wind: capturing ion physics with a Vlasov code Francesco Valentini [email protected] S. Servidio, D. Perrone, O. Pezzi, B. Maruca, F. Califano, W.
Kinetic effects in the turbulent solar wind: capturing ion physics with a Vlasov code Francesco Valentini [email protected] S. Servidio, D. Perrone, O. Pezzi, B. Maruca, F. Califano, W.
Temperature anisotropy in the solar wind
 Introduction Observations Simulations Summary in the solar wind Petr Hellinger Institute of Atmospheric Physics & Astronomical Institute AS CR, Prague, Czech Republic Kinetic Instabilities, Plasma Turbulence
Introduction Observations Simulations Summary in the solar wind Petr Hellinger Institute of Atmospheric Physics & Astronomical Institute AS CR, Prague, Czech Republic Kinetic Instabilities, Plasma Turbulence
Wave-particle and wave-wave interactions in the Solar Wind: simulations and observations
 Wave-particle and wave-wave interactions in the Solar Wind: simulations and observations Lorenzo Matteini University of Florence, Italy In collaboration with Petr Hellinger, Simone Landi, and Marco Velli
Wave-particle and wave-wave interactions in the Solar Wind: simulations and observations Lorenzo Matteini University of Florence, Italy In collaboration with Petr Hellinger, Simone Landi, and Marco Velli
Sound. References: L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol. 2, Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8
 References: Sound L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol., Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8 1 Speed of sound The phenomenon of sound waves is one that
References: Sound L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol., Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8 1 Speed of sound The phenomenon of sound waves is one that
11 Navier-Stokes equations and turbulence
 11 Navier-Stokes equations and turbulence So far, we have considered ideal gas dynamics governed by the Euler equations, where internal friction in the gas is assumed to be absent. Real fluids have internal
11 Navier-Stokes equations and turbulence So far, we have considered ideal gas dynamics governed by the Euler equations, where internal friction in the gas is assumed to be absent. Real fluids have internal
Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2)
 Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2) In this lecture How does turbulence affect the ensemble-mean equations of fluid motion/transport? Force balance in a quasi-steady turbulent boundary
Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2) In this lecture How does turbulence affect the ensemble-mean equations of fluid motion/transport? Force balance in a quasi-steady turbulent boundary
Coronal expansion and solar wind
 Coronal expansion and solar wind The solar corona over the solar cycle Coronal and interplanetary temperatures Coronal expansion and solar wind acceleration Origin of solar wind in magnetic network Multi-fluid
Coronal expansion and solar wind The solar corona over the solar cycle Coronal and interplanetary temperatures Coronal expansion and solar wind acceleration Origin of solar wind in magnetic network Multi-fluid
Kinetic physics of the solar wind
 "What science do we need to do in the next six years to prepare for Solar Orbiter and Solar Probe Plus?" Kinetic physics of the solar wind Eckart Marsch Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung Complementary
"What science do we need to do in the next six years to prepare for Solar Orbiter and Solar Probe Plus?" Kinetic physics of the solar wind Eckart Marsch Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung Complementary
Kinetic processes and wave-particle interactions in the solar wind
 Kinetic processes and wave-particle interactions in the solar wind Eckart Marsch Institute for Experimental and Applied Physics (IEAP), Christian Albrechts University at Kiel, 24118 Kiel, Germany Seminar
Kinetic processes and wave-particle interactions in the solar wind Eckart Marsch Institute for Experimental and Applied Physics (IEAP), Christian Albrechts University at Kiel, 24118 Kiel, Germany Seminar
Solar Wind: Theory. Parker s solar wind theory
 Solar Wind: Theory The supersonic outflow of electrically charged particles, mainly electrons and protons from the solar CORONA, is called the SOLAR WIND. The solar wind was described theoretically by
Solar Wind: Theory The supersonic outflow of electrically charged particles, mainly electrons and protons from the solar CORONA, is called the SOLAR WIND. The solar wind was described theoretically by
Heating & Cooling in Molecular Clouds
 Lecture 8: Cloud Stability Heating & Cooling in Molecular Clouds Balance of heating and cooling processes helps to set the temperature in the gas. This then sets the minimum internal pressure in a core
Lecture 8: Cloud Stability Heating & Cooling in Molecular Clouds Balance of heating and cooling processes helps to set the temperature in the gas. This then sets the minimum internal pressure in a core
Chapter 9 Summary and outlook
 Chapter 9 Summary and outlook This thesis aimed to address two problems of plasma astrophysics: how are cosmic plasmas isotropized (A 1), and why does the equipartition of the magnetic field energy density
Chapter 9 Summary and outlook This thesis aimed to address two problems of plasma astrophysics: how are cosmic plasmas isotropized (A 1), and why does the equipartition of the magnetic field energy density
Interstellar Cosmic-Ray Spectrum from Gamma Rays and Synchrotron
 Interstellar Cosmic-Ray Spectrum from Gamma Rays and Synchrotron Chuck Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC [email protected] Andy Strong Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik,
Interstellar Cosmic-Ray Spectrum from Gamma Rays and Synchrotron Chuck Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC [email protected] Andy Strong Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik,
The heliosphere-interstellar medium interaction: One shock or two?
 1 The heliosphere-interstellar medium interaction: One shock or two? John D. Richardson M.I.T. Abstract. The issue of whether a shock forms in the interstellar medium as it approaches the heliopause has
1 The heliosphere-interstellar medium interaction: One shock or two? John D. Richardson M.I.T. Abstract. The issue of whether a shock forms in the interstellar medium as it approaches the heliopause has
The Solar Wind. Chapter 5. 5.1 Introduction. 5.2 Description
 Chapter 5 The Solar Wind 5.1 Introduction The solar wind is a flow of ionized solar plasma and an associated remnant of the solar magnetic field that pervades interplanetary space. It is a result of the
Chapter 5 The Solar Wind 5.1 Introduction The solar wind is a flow of ionized solar plasma and an associated remnant of the solar magnetic field that pervades interplanetary space. It is a result of the
MHD Modeling of the Interaction Between the Solar Wind and Solar System Objects
 554 MHD Modeling of the Interaction Between the Solar Wind and Solar System Objects Andreas Ekenbäck and Mats Holmström Swedish Institute of Space Physics (IRF) P.O. Box 81 98134 Kiruna, Sweden {andreas.ekenback,mats.holmstrom}@irf.se
554 MHD Modeling of the Interaction Between the Solar Wind and Solar System Objects Andreas Ekenbäck and Mats Holmström Swedish Institute of Space Physics (IRF) P.O. Box 81 98134 Kiruna, Sweden {andreas.ekenback,mats.holmstrom}@irf.se
Proton temperature and Plasma Volatility
 The microstate of the solar wind Radial gradients of kinetic temperatures Velocity distribution functions Ion composition and suprathermal electrons Coulomb collisions in the solar wind Waves and plasma
The microstate of the solar wind Radial gradients of kinetic temperatures Velocity distribution functions Ion composition and suprathermal electrons Coulomb collisions in the solar wind Waves and plasma
Graduate Certificate Program in Energy Conversion & Transport Offered by the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
 Graduate Certificate Program in Energy Conversion & Transport Offered by the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Intended Audience: Main Campus Students Distance (online students) Both Purpose:
Graduate Certificate Program in Energy Conversion & Transport Offered by the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Intended Audience: Main Campus Students Distance (online students) Both Purpose:
Physics 9e/Cutnell. correlated to the. College Board AP Physics 1 Course Objectives
 Physics 9e/Cutnell correlated to the College Board AP Physics 1 Course Objectives Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Enduring
Physics 9e/Cutnell correlated to the College Board AP Physics 1 Course Objectives Big Idea 1: Objects and systems have properties such as mass and charge. Systems may have internal structure. Enduring
Solar Wind and Pickup Protons
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.109/005ja011533, 006 A three-dimensional MHD solar wind model with pickup protons A. V. Usmanov 1, and M. L. Goldstein 3 Received
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.109/005ja011533, 006 A three-dimensional MHD solar wind model with pickup protons A. V. Usmanov 1, and M. L. Goldstein 3 Received
Vacuum Evaporation Recap
 Sputtering Vacuum Evaporation Recap Use high temperatures at high vacuum to evaporate (eject) atoms or molecules off a material surface. Use ballistic flow to transport them to a substrate and deposit.
Sputtering Vacuum Evaporation Recap Use high temperatures at high vacuum to evaporate (eject) atoms or molecules off a material surface. Use ballistic flow to transport them to a substrate and deposit.
Conceptual: 1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 16, 18, 19. Problems: 4, 6, 8, 11, 16, 20, 23, 27, 34, 41, 45, 56, 60, 65. Conceptual Questions
 Conceptual: 1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 16, 18, 19 Problems: 4, 6, 8, 11, 16, 20, 23, 27, 34, 41, 45, 56, 60, 65 Conceptual Questions 1. The magnetic field cannot be described as the magnetic force per unit charge
Conceptual: 1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 16, 18, 19 Problems: 4, 6, 8, 11, 16, 20, 23, 27, 34, 41, 45, 56, 60, 65 Conceptual Questions 1. The magnetic field cannot be described as the magnetic force per unit charge
The solar wind (in 90 minutes) Mathew Owens
 The solar wind (in 90 minutes) Mathew Owens 5 th Sept 2013 STFC Advanced Summer School [email protected] Overview There s simply too much to cover in 90 minutes Hope to touch on: Formation of the
The solar wind (in 90 minutes) Mathew Owens 5 th Sept 2013 STFC Advanced Summer School [email protected] Overview There s simply too much to cover in 90 minutes Hope to touch on: Formation of the
Indiana's Academic Standards 2010 ICP Indiana's Academic Standards 2016 ICP. map) that describe the relationship acceleration, velocity and distance.
 .1.1 Measure the motion of objects to understand.1.1 Develop graphical, the relationships among distance, velocity and mathematical, and pictorial acceleration. Develop deeper understanding through representations
.1.1 Measure the motion of objects to understand.1.1 Develop graphical, the relationships among distance, velocity and mathematical, and pictorial acceleration. Develop deeper understanding through representations
Diagnostics. Electric probes. Instituto de Plasmas e Fusão Nuclear Instituto Superior Técnico Lisbon, Portugal http://www.ipfn.ist.utl.
 C. Silva Lisboa, Jan. 2014 IST Diagnostics Electric probes Instituto de Plasmas e Fusão Nuclear Instituto Superior Técnico Lisbon, Portugal http://www.ipfn.ist.utl.pt Langmuir probes Simplest diagnostic
C. Silva Lisboa, Jan. 2014 IST Diagnostics Electric probes Instituto de Plasmas e Fusão Nuclear Instituto Superior Técnico Lisbon, Portugal http://www.ipfn.ist.utl.pt Langmuir probes Simplest diagnostic
Sporadic E A Mystery Solved?
 Sporadic E A Mystery Solved? In Part 1 of this QST exclusive, one of the world s leading ionospheric scientists explains the physics of sporadic E and discusses unresolved problems in understanding its
Sporadic E A Mystery Solved? In Part 1 of this QST exclusive, one of the world s leading ionospheric scientists explains the physics of sporadic E and discusses unresolved problems in understanding its
Keywords: Geomagnetic storms Dst index Space Weather Recovery phase.
 MAGNETOSPHERE BEHAVIOUR DURING THE RECOVERY PHASE OF GEOMAGNETIC STORMS JESÚS AGUADO, CONSUELO CID, YOLANDA CERRATO, ELENA SAIZ Departamento de Física. Universidad de Alcalá, E-28871 Alcalá de Henares,
MAGNETOSPHERE BEHAVIOUR DURING THE RECOVERY PHASE OF GEOMAGNETIC STORMS JESÚS AGUADO, CONSUELO CID, YOLANDA CERRATO, ELENA SAIZ Departamento de Física. Universidad de Alcalá, E-28871 Alcalá de Henares,
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECTS OF WIND ON BUILDING STRUCTURES
 Vol. XX 2012 No. 4 28 34 J. ŠIMIČEK O. HUBOVÁ NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECTS OF WIND ON BUILDING STRUCTURES Jozef ŠIMIČEK email: [email protected] Research field: Statics and Dynamics Fluids mechanics
Vol. XX 2012 No. 4 28 34 J. ŠIMIČEK O. HUBOVÁ NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE EFFECTS OF WIND ON BUILDING STRUCTURES Jozef ŠIMIČEK email: [email protected] Research field: Statics and Dynamics Fluids mechanics
Indiana Content Standards for Educators
 Indiana Content for Educators SCIENCE PHYSICAL SCIENCE teachers are expected to have a broad understanding of the knowledge and skills needed for this educator license, and to use that knowledge to help
Indiana Content for Educators SCIENCE PHYSICAL SCIENCE teachers are expected to have a broad understanding of the knowledge and skills needed for this educator license, and to use that knowledge to help
Chapter 19 Magnetic Forces and Fields
 Chapter 19 Magnetic Forces and Fields Student: 3. The magnetism of the Earth acts approximately as if it originates from a huge bar magnet within the Earth. Which of the following statements are true?
Chapter 19 Magnetic Forces and Fields Student: 3. The magnetism of the Earth acts approximately as if it originates from a huge bar magnet within the Earth. Which of the following statements are true?
Photons. ConcepTest 27.1. 1) red light 2) yellow light 3) green light 4) blue light 5) all have the same energy. Which has more energy, a photon of:
 ConcepTest 27.1 Photons Which has more energy, a photon of: 1) red light 2) yellow light 3) green light 4) blue light 5) all have the same energy 400 nm 500 nm 600 nm 700 nm ConcepTest 27.1 Photons Which
ConcepTest 27.1 Photons Which has more energy, a photon of: 1) red light 2) yellow light 3) green light 4) blue light 5) all have the same energy 400 nm 500 nm 600 nm 700 nm ConcepTest 27.1 Photons Which
SPACE WEATHER INTERPRETING THE WIND. Petra Vanlommel & Luciano Rodriguez
 SPACE WEATHER INTERPRETING THE WIND Petra Vanlommel & Luciano Rodriguez THE SUN LOSES ENERGY Radiation Mass Particles THE SUN LOSES ENERGY PHYSICAL REPHRASING Total Solar Irradiance Solar Wind Fast Particles
SPACE WEATHER INTERPRETING THE WIND Petra Vanlommel & Luciano Rodriguez THE SUN LOSES ENERGY Radiation Mass Particles THE SUN LOSES ENERGY PHYSICAL REPHRASING Total Solar Irradiance Solar Wind Fast Particles
PS-6.2 Explain the factors that determine potential and kinetic energy and the transformation of one to the other.
 PS-6.1 Explain how the law of conservation of energy applies to the transformation of various forms of energy (including mechanical energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, light energy, sound energy,
PS-6.1 Explain how the law of conservation of energy applies to the transformation of various forms of energy (including mechanical energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, light energy, sound energy,
39th International Physics Olympiad - Hanoi - Vietnam - 2008. Theoretical Problem No. 3
 CHANGE OF AIR TEMPERATURE WITH ALTITUDE, ATMOSPHERIC STABILITY AND AIR POLLUTION Vertical motion of air governs many atmospheric processes, such as the formation of clouds and precipitation and the dispersal
CHANGE OF AIR TEMPERATURE WITH ALTITUDE, ATMOSPHERIC STABILITY AND AIR POLLUTION Vertical motion of air governs many atmospheric processes, such as the formation of clouds and precipitation and the dispersal
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) and Remote Sensing
 Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) and Remote Sensing 1 Atmosphere Anything missing in between? Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) is radiated by atomic particles at the source (the Sun), propagates through
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) and Remote Sensing 1 Atmosphere Anything missing in between? Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) is radiated by atomic particles at the source (the Sun), propagates through
The Birth of the Universe Newcomer Academy High School Visualization One
 The Birth of the Universe Newcomer Academy High School Visualization One Chapter Topic Key Points of Discussion Notes & Vocabulary 1 Birth of The Big Bang Theory Activity 4A the How and when did the universe
The Birth of the Universe Newcomer Academy High School Visualization One Chapter Topic Key Points of Discussion Notes & Vocabulary 1 Birth of The Big Bang Theory Activity 4A the How and when did the universe
Lecture 8 - Turbulence. Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics
 Lecture 8 - Turbulence Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics Instructor: André Bakker http://www.bakker.org André Bakker (2002-2006) Fluent Inc. (2002) 1 Turbulence What is turbulence? Effect of turbulence
Lecture 8 - Turbulence Applied Computational Fluid Dynamics Instructor: André Bakker http://www.bakker.org André Bakker (2002-2006) Fluent Inc. (2002) 1 Turbulence What is turbulence? Effect of turbulence
Turbulence Modeling in CFD Simulation of Intake Manifold for a 4 Cylinder Engine
 HEFAT2012 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta Turbulence Modeling in CFD Simulation of Intake Manifold for a 4 Cylinder Engine Dr MK
HEFAT2012 9 th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics 16 18 July 2012 Malta Turbulence Modeling in CFD Simulation of Intake Manifold for a 4 Cylinder Engine Dr MK
Three-dimensional Simulation of Magnetized Cloud Fragmentation Induced by Nonlinear Flows and Ambipolar Diffusion
 accepted by Astrophysical Journal Letters Three-dimensional Simulation of Magnetized Cloud Fragmentation Induced by Nonlinear Flows and Ambipolar Diffusion Takahiro Kudoh 1 and Shantanu Basu 2 ABSTRACT
accepted by Astrophysical Journal Letters Three-dimensional Simulation of Magnetized Cloud Fragmentation Induced by Nonlinear Flows and Ambipolar Diffusion Takahiro Kudoh 1 and Shantanu Basu 2 ABSTRACT
Lesson 3: Isothermal Hydrostatic Spheres. B68: a self-gravitating stable cloud. Hydrostatic self-gravitating spheres. P = "kt 2.
 Lesson 3: Isothermal Hydrostatic Spheres B68: a self-gravitating stable cloud Bok Globule Relatively isolated, hence not many external disturbances Though not main mode of star formation, their isolation
Lesson 3: Isothermal Hydrostatic Spheres B68: a self-gravitating stable cloud Bok Globule Relatively isolated, hence not many external disturbances Though not main mode of star formation, their isolation
Physics 30 Worksheet #10 : Magnetism From Electricity
 Physics 30 Worksheet #10 : Magnetism From Electricity 1. Draw the magnetic field surrounding the wire showing electron current below. x 2. Draw the magnetic field surrounding the wire showing electron
Physics 30 Worksheet #10 : Magnetism From Electricity 1. Draw the magnetic field surrounding the wire showing electron current below. x 2. Draw the magnetic field surrounding the wire showing electron
A subgrid-scale model for the scalar dissipation rate in nonpremixed combustion
 Center for Turbulence Research Proceedings of the Summer Program 1998 11 A subgrid-scale model for the scalar dissipation rate in nonpremixed combustion By A. W. Cook 1 AND W. K. Bushe A subgrid-scale
Center for Turbulence Research Proceedings of the Summer Program 1998 11 A subgrid-scale model for the scalar dissipation rate in nonpremixed combustion By A. W. Cook 1 AND W. K. Bushe A subgrid-scale
Theory of electrons and positrons
 P AUL A. M. DIRAC Theory of electrons and positrons Nobel Lecture, December 12, 1933 Matter has been found by experimental physicists to be made up of small particles of various kinds, the particles of
P AUL A. M. DIRAC Theory of electrons and positrons Nobel Lecture, December 12, 1933 Matter has been found by experimental physicists to be made up of small particles of various kinds, the particles of
Heating & Cooling in the Interstellar Medium
 Section 7 Heating & Cooling in the Interstellar Medium 7.1 Heating In general terms, we can imagine two categories of heating processes in the diuse ISM: 1 large-scale (mechanical, e.g., cloud-cloud collisions),
Section 7 Heating & Cooling in the Interstellar Medium 7.1 Heating In general terms, we can imagine two categories of heating processes in the diuse ISM: 1 large-scale (mechanical, e.g., cloud-cloud collisions),
Basic Equations, Boundary Conditions and Dimensionless Parameters
 Chapter 2 Basic Equations, Boundary Conditions and Dimensionless Parameters In the foregoing chapter, many basic concepts related to the present investigation and the associated literature survey were
Chapter 2 Basic Equations, Boundary Conditions and Dimensionless Parameters In the foregoing chapter, many basic concepts related to the present investigation and the associated literature survey were
Solar Wind Control of Density and Temperature in the Near-Earth Plasma Sheet: WIND-GEOTAIL Collaboration. Abstract
 1 Geophys. Res. Letters, 24, 935-938, 1997. Solar Wind Control of Density and Temperature in the Near-Earth Plasma Sheet: WIND-GEOTAIL Collaboration T. Terasawa 1, M. Fujimoto 2, T. Mukai 3, I. Shinohara
1 Geophys. Res. Letters, 24, 935-938, 1997. Solar Wind Control of Density and Temperature in the Near-Earth Plasma Sheet: WIND-GEOTAIL Collaboration T. Terasawa 1, M. Fujimoto 2, T. Mukai 3, I. Shinohara
Heating diagnostics with MHD waves
 Heating diagnostics with MHD waves R. Erdélyi & Y. Taroyan [email protected] SP 2 RC, Department of Applied Mathematics, The University of Sheffield (UK) The solar corona 1860s coronium discovered
Heating diagnostics with MHD waves R. Erdélyi & Y. Taroyan [email protected] SP 2 RC, Department of Applied Mathematics, The University of Sheffield (UK) The solar corona 1860s coronium discovered
Lecture 14. Introduction to the Sun
 Lecture 14 Introduction to the Sun ALMA discovers planets forming in a protoplanetary disc. Open Q: what physics do we learn about the Sun? 1. Energy - nuclear energy - magnetic energy 2. Radiation - continuum
Lecture 14 Introduction to the Sun ALMA discovers planets forming in a protoplanetary disc. Open Q: what physics do we learn about the Sun? 1. Energy - nuclear energy - magnetic energy 2. Radiation - continuum
Interpolation error in DNS simulations of turbulence: consequences for particle tracking
 Interpolation error in DNS simulations of turbulence: consequences for particle tracking Michel van Hinsberg Department of Physics, Eindhoven University of Technology, PO Box 513, 5600MB Eindhoven, The
Interpolation error in DNS simulations of turbulence: consequences for particle tracking Michel van Hinsberg Department of Physics, Eindhoven University of Technology, PO Box 513, 5600MB Eindhoven, The
Meeting the Grand Challenge of Protecting an Astronaut s Health: Electrostatic Active Space Radiation Shielding for Deep Space Missions
 Meeting the Grand Challenge of Protecting an Astronaut s Health: Electrostatic Active Space Radiation Shielding for Deep Space Missions Ram Tripathi NASA Langley Research Center NIAC 2012 Spring Symposium,
Meeting the Grand Challenge of Protecting an Astronaut s Health: Electrostatic Active Space Radiation Shielding for Deep Space Missions Ram Tripathi NASA Langley Research Center NIAC 2012 Spring Symposium,
Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Structure 1
 Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Structure 1 INTRODUCTION The word atom is derived from the Greek word, atomos, which means uncut or indivisible. It was Dalton (1808) who established that elementary constituents
Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Structure 1 INTRODUCTION The word atom is derived from the Greek word, atomos, which means uncut or indivisible. It was Dalton (1808) who established that elementary constituents
O.F.Wind Wind Site Assessment Simulation in complex terrain based on OpenFOAM. Darmstadt, 27.06.2012
 O.F.Wind Wind Site Assessment Simulation in complex terrain based on OpenFOAM Darmstadt, 27.06.2012 Michael Ehlen IB Fischer CFD+engineering GmbH Lipowskystr. 12 81373 München Tel. 089/74118743 Fax 089/74118749
O.F.Wind Wind Site Assessment Simulation in complex terrain based on OpenFOAM Darmstadt, 27.06.2012 Michael Ehlen IB Fischer CFD+engineering GmbH Lipowskystr. 12 81373 München Tel. 089/74118743 Fax 089/74118749
Cross section, Flux, Luminosity, Scattering Rates
 Cross section, Flux, Luminosity, Scattering Rates Table of Contents Paul Avery (Andrey Korytov) Sep. 9, 013 1 Introduction... 1 Cross section, flux and scattering... 1 3 Scattering length λ and λ ρ...
Cross section, Flux, Luminosity, Scattering Rates Table of Contents Paul Avery (Andrey Korytov) Sep. 9, 013 1 Introduction... 1 Cross section, flux and scattering... 1 3 Scattering length λ and λ ρ...
Measurement and Simulation of Electron Thermal Transport in the MST Reversed-Field Pinch
 1 EX/P3-17 Measurement and Simulation of Electron Thermal Transport in the MST Reversed-Field Pinch D. J. Den Hartog 1,2, J. A. Reusch 1, J. K. Anderson 1, F. Ebrahimi 1,2,*, C. B. Forest 1,2 D. D. Schnack
1 EX/P3-17 Measurement and Simulation of Electron Thermal Transport in the MST Reversed-Field Pinch D. J. Den Hartog 1,2, J. A. Reusch 1, J. K. Anderson 1, F. Ebrahimi 1,2,*, C. B. Forest 1,2 D. D. Schnack
Atomic Calculations. 2.1 Composition of the Atom. number of protons + number of neutrons = mass number
 2.1 Composition of the Atom Atomic Calculations number of protons + number of neutrons = mass number number of neutrons = mass number - number of protons number of protons = number of electrons IF positive
2.1 Composition of the Atom Atomic Calculations number of protons + number of neutrons = mass number number of neutrons = mass number - number of protons number of protons = number of electrons IF positive
Charges, voltage and current
 Charges, voltage and current Lecture 2 1 Atoms and electrons Atoms are built up from Positively charged nucleus Negatively charged electrons orbiting in shells (or more accurately clouds or orbitals) -
Charges, voltage and current Lecture 2 1 Atoms and electrons Atoms are built up from Positively charged nucleus Negatively charged electrons orbiting in shells (or more accurately clouds or orbitals) -
Energy. Mechanical Energy
 Principles of Imaging Science I (RAD119) Electromagnetic Radiation Energy Definition of energy Ability to do work Physicist s definition of work Work = force x distance Force acting upon object over distance
Principles of Imaging Science I (RAD119) Electromagnetic Radiation Energy Definition of energy Ability to do work Physicist s definition of work Work = force x distance Force acting upon object over distance
Numerical Model for the Study of the Velocity Dependence Of the Ionisation Growth in Gas Discharge Plasma
 Journal of Basrah Researches ((Sciences)) Volume 37.Number 5.A ((2011)) Available online at: www.basra-science -journal.org ISSN 1817 2695 Numerical Model for the Study of the Velocity Dependence Of the
Journal of Basrah Researches ((Sciences)) Volume 37.Number 5.A ((2011)) Available online at: www.basra-science -journal.org ISSN 1817 2695 Numerical Model for the Study of the Velocity Dependence Of the
Physical Principle of Formation and Essence of Radio Waves
 Physical Principle of Formation and Essence of Radio Waves Anatoli Bedritsky Abstract. This article opens physical phenomena which occur at the formation of the radio waves, and opens the essence of the
Physical Principle of Formation and Essence of Radio Waves Anatoli Bedritsky Abstract. This article opens physical phenomena which occur at the formation of the radio waves, and opens the essence of the
Neutralization Reactions. Evaluation copy
 Neutralization Reactions Computer 6 If an acid is added to a base, a chemical reaction called neutralization occurs. An example is the reaction between nitric acid, HNO 3, and the base potassium hydroxide,
Neutralization Reactions Computer 6 If an acid is added to a base, a chemical reaction called neutralization occurs. An example is the reaction between nitric acid, HNO 3, and the base potassium hydroxide,
Magnetism. d. gives the direction of the force on a charge moving in a magnetic field. b. results in negative charges moving. clockwise.
 Magnetism 1. An electron which moves with a speed of 3.0 10 4 m/s parallel to a uniform magnetic field of 0.40 T experiences a force of what magnitude? (e = 1.6 10 19 C) a. 4.8 10 14 N c. 2.2 10 24 N b.
Magnetism 1. An electron which moves with a speed of 3.0 10 4 m/s parallel to a uniform magnetic field of 0.40 T experiences a force of what magnitude? (e = 1.6 10 19 C) a. 4.8 10 14 N c. 2.2 10 24 N b.
DEM modelling of the dynamic penetration process on Mars as a part of the NASA InSight Mission
 Proceedings of the 4th European Young Geotechnical Engineers Conference (EYGEC), Durham, UK Osman, A.S. & Toll, D.G. (Eds.) 05 ISBN 978-0-9933836-0 DEM modelling of the dynamic penetration process on Mars
Proceedings of the 4th European Young Geotechnical Engineers Conference (EYGEC), Durham, UK Osman, A.S. & Toll, D.G. (Eds.) 05 ISBN 978-0-9933836-0 DEM modelling of the dynamic penetration process on Mars
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Introduction to Energy. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Get Energized! What are two types of energy? Energy is the ability to cause change. Energy takes many different forms and causes many different effects. There are two general types of energy: kinetic energy
Get Energized! What are two types of energy? Energy is the ability to cause change. Energy takes many different forms and causes many different effects. There are two general types of energy: kinetic energy
Kinetic Models of Solar Wind Electrons, Protons and Heavy Ions
 10 Kinetic Models of Solar Wind Electrons, Protons and Heavy Ions Viviane Pierrard Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy and Université Catholique de Louvain Belgium 1. Introduction In the present chapter,
10 Kinetic Models of Solar Wind Electrons, Protons and Heavy Ions Viviane Pierrard Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy and Université Catholique de Louvain Belgium 1. Introduction In the present chapter,
Fundamentals of Plasma Physics Waves in plasmas
 Fundamentals of Plasma Physics Waves in plasmas APPLAuSE Instituto Superior Técnico Instituto de Plasmas e Fusão Nuclear Vasco Guerra 1 Waves in plasmas What can we study with the complete description
Fundamentals of Plasma Physics Waves in plasmas APPLAuSE Instituto Superior Técnico Instituto de Plasmas e Fusão Nuclear Vasco Guerra 1 Waves in plasmas What can we study with the complete description
AZ State Standards. Concept 3: Conservation of Energy and Increase in Disorder Understand ways that energy is conserved, stored, and transferred.
 Forms of Energy AZ State Standards Concept 3: Conservation of Energy and Increase in Disorder Understand ways that energy is conserved, stored, and transferred. PO 1. Describe the following ways in which
Forms of Energy AZ State Standards Concept 3: Conservation of Energy and Increase in Disorder Understand ways that energy is conserved, stored, and transferred. PO 1. Describe the following ways in which
Chapter 2. Derivation of the Equations of Open Channel Flow. 2.1 General Considerations
 Chapter 2. Derivation of the Equations of Open Channel Flow 2.1 General Considerations Of interest is water flowing in a channel with a free surface, which is usually referred to as open channel flow.
Chapter 2. Derivation of the Equations of Open Channel Flow 2.1 General Considerations Of interest is water flowing in a channel with a free surface, which is usually referred to as open channel flow.
PHYS 1624 University Physics I. PHYS 2644 University Physics II
 PHYS 1624 Physics I An introduction to mechanics, heat, and wave motion. This is a calculus- based course for Scientists and Engineers. 4 hours (3 lecture/3 lab) Prerequisites: Credit for MATH 2413 (Calculus
PHYS 1624 Physics I An introduction to mechanics, heat, and wave motion. This is a calculus- based course for Scientists and Engineers. 4 hours (3 lecture/3 lab) Prerequisites: Credit for MATH 2413 (Calculus
Ion Propulsion Engine Simulation
 Ion Propulsion Ion Propulsion Engine Simulation STUDENT ACTIVITY AND REPORT SHEET This activity must be completed at a computer with Internet access. Part 1: Procedure 1. Go to http://dawn.jpl.nasa.gov/mission/ion_engine_interactive/index.html
Ion Propulsion Ion Propulsion Engine Simulation STUDENT ACTIVITY AND REPORT SHEET This activity must be completed at a computer with Internet access. Part 1: Procedure 1. Go to http://dawn.jpl.nasa.gov/mission/ion_engine_interactive/index.html
Data representation and analysis in Excel
 Page 1 Data representation and analysis in Excel Let s Get Started! This course will teach you how to analyze data and make charts in Excel so that the data may be represented in a visual way that reflects
Page 1 Data representation and analysis in Excel Let s Get Started! This course will teach you how to analyze data and make charts in Excel so that the data may be represented in a visual way that reflects
7. DYNAMIC LIGHT SCATTERING 7.1 First order temporal autocorrelation function.
 7. DYNAMIC LIGHT SCATTERING 7. First order temporal autocorrelation function. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) studies the properties of inhomogeneous and dynamic media. A generic situation is illustrated
7. DYNAMIC LIGHT SCATTERING 7. First order temporal autocorrelation function. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) studies the properties of inhomogeneous and dynamic media. A generic situation is illustrated
Free Convection Film Flows and Heat Transfer
 Deyi Shang Free Convection Film Flows and Heat Transfer With 109 Figures and 69 Tables < J Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Scope 1 1.2 Application Backgrounds 1 1.3 Previous Developments 2 1.3.1
Deyi Shang Free Convection Film Flows and Heat Transfer With 109 Figures and 69 Tables < J Springer Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Scope 1 1.2 Application Backgrounds 1 1.3 Previous Developments 2 1.3.1
What is the most obvious difference between pipe flow and open channel flow????????????? (in terms of flow conditions and energy situation)
 OPEN CHANNEL FLOW 1 3 Question What is the most obvious difference between pipe flow and open channel flow????????????? (in terms of flow conditions and energy situation) Typical open channel shapes Figure
OPEN CHANNEL FLOW 1 3 Question What is the most obvious difference between pipe flow and open channel flow????????????? (in terms of flow conditions and energy situation) Typical open channel shapes Figure
AP Physics 1 and 2 Lab Investigations
 AP Physics 1 and 2 Lab Investigations Student Guide to Data Analysis New York, NY. College Board, Advanced Placement, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks
AP Physics 1 and 2 Lab Investigations Student Guide to Data Analysis New York, NY. College Board, Advanced Placement, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks
Waves - Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
 Waves - Transverse and Longitudinal Waves wave may be defined as a periodic disturbance in a medium that carries energy from one point to another. ll waves require a source and a medium of propagation.
Waves - Transverse and Longitudinal Waves wave may be defined as a periodic disturbance in a medium that carries energy from one point to another. ll waves require a source and a medium of propagation.
8 Radiative Cooling and Heating
 8 Radiative Cooling and Heating Reading: Katz et al. 1996, ApJ Supp, 105, 19, section 3 Thoul & Weinberg, 1995, ApJ, 442, 480 Optional reading: Thoul & Weinberg, 1996, ApJ, 465, 608 Weinberg et al., 1997,
8 Radiative Cooling and Heating Reading: Katz et al. 1996, ApJ Supp, 105, 19, section 3 Thoul & Weinberg, 1995, ApJ, 442, 480 Optional reading: Thoul & Weinberg, 1996, ApJ, 465, 608 Weinberg et al., 1997,
CFD Based Air Flow and Contamination Modeling of Subway Stations
 CFD Based Air Flow and Contamination Modeling of Subway Stations Greg Byrne Center for Nonlinear Science, Georgia Institute of Technology Fernando Camelli Center for Computational Fluid Dynamics, George
CFD Based Air Flow and Contamination Modeling of Subway Stations Greg Byrne Center for Nonlinear Science, Georgia Institute of Technology Fernando Camelli Center for Computational Fluid Dynamics, George
Chemical Waves in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction: Determining a Rate Constant with a Ruler
 Chemical Waves in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction: Determining a Rate Constant with a Ruler John A. Pojman Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, The University of Southern Mississippi, Hattiesburg,
Chemical Waves in the Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction: Determining a Rate Constant with a Ruler John A. Pojman Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, The University of Southern Mississippi, Hattiesburg,
Heat Transfer Prof. Dr. Ale Kumar Ghosal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Heat Transfer Prof. Dr. Ale Kumar Ghosal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module No. # 04 Convective Heat Transfer Lecture No. # 03 Heat Transfer Correlation
Heat Transfer Prof. Dr. Ale Kumar Ghosal Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module No. # 04 Convective Heat Transfer Lecture No. # 03 Heat Transfer Correlation

