Introduzione ad OpenGL
|
|
|
- Earl Gibbs
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduzione ad OpenGL
2 Cosa è OpenGL E una interfaccia so8ware all hardware grafico, rendering API Indipendente dal sistema di windowing Indipendente dal sistema operabvo
3 Evoluzione di OpenGL Viene gesbta da una Architectural Review Board (ARB) SGI, Microso8, Nvidia, Apple, HP, IBM Stabile e retrocompabbile (è nata nel 1992 e adesso siamo alla versione 4.3) Estensioni plauorm specific
4 API di supporto AGL, GLX, WGL Interfaccia con i sistemi di windowing GLU (OpenGL UBlity Library) Parte di opengl NURBS, tesselators, quadric etc GLUT API di windowing e gesbone evenb cross- plauorm Non è parte ufficiale di OpenGL
5 OpenGL e API di supporto applica>on program OpenGL Mo>f widget or similar GLX, AGL or WGL X, Win32, Mac O/S GLUT GLU GL so7ware and/or hardware
6 Macchina a StaB Le funzioni OpenGL sono di due Bpi: Cambio di Stato Colore corrente, modalità di shading etc., Generazione di primibve Possono generare un output visuale se la primibva è visibile Le primibve vengono processate in accordo allo stato corrente
7 Macchina a StaB Macchina a stab con input e output L input è la geometria in ingresso, l output è un set di pixel La macchina a stab converte una collezione di oggea geometrici in 3D in una immagine. Questo processo è controllato dallo stato. Gli stab specificano come gli oggea sono proiedab sul piano immagine, come vengono colorab ecc.
8 Formato comandi OpenGL glvertex3fv( v ) Number of components 2 - (x,y) 3 - (x,y,z) 4 - (x,y,z,w) Data Type b - byte ub - unsigned byte s - short us - unsigned short i - int ui - unsigned int f - float d - double Vector omit v for scalar form glvertex2f( x, y )
9 PrimiBve OpenGL Rappresentazione poligonale GL_POINTS GL_LINES GL_LINE_STRIP GL_LINE_LOOP GL_POLYGON GL_TRIANGLES GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP GL_TRIANGLE_FAN GL_QUADS GL_QUAD_STRIP
10 Poligoni OpenGL renderizzerà correcamente solo poligoni che sono: Semplici (lab che non si intersecano) Convessi Piani Polygon Issues OpenGL will only display polygons correctly that are - Simple: edges cannot cross - Convex: All points on line segment between two points in a polygon are also in the polygon - Flat: all vertices are in the same plane OpenGL User program non controlla must check se if le above condizioni true sopraelencate sono verificate Triangles satisfy all conditions nonsimple polygon nonconvex polygon 20
11 Vector V V 1 SECTION 1.3 Shading Normals 9 Normali Figure 1.6 Computing a surface normal from edge cross-product. Vector U V 0 V 2 Vector V V 2 V 1 Vector V V 1 V 3 Vector U.6 Computing a surface normal from edge cross-product. 10 CHAPTER 1 Geometry Representation and Modeling V 0 Vector U V 0 Figure 1.7 Computing quadrilateral surface normal from vertex cross-product. V 2 poly 00 V 1 Vector V Vector U.7 Computing quadrilateral surface normal from vertex cross-product. r polygons with more than four vertices it canfigure be difficult 1.8 Splitting to choose normals the best for hard vertices edges. for the cross product. One method is to to choose vertices that are the furthest rom each other, or to average the result of several vertex cross products. V 0 V 3 poly 10 v 0 Spliang normals poly 11 v 1 poly 12 v 2 poly 01 For polygons with more than four vertices it can be difficult to choose the best verti to use poly02 for the cross product. One method is to to choose vertices that are the furth apart from each other, or to average the result of several vertex cross products. poly 03 Hard edge Smooth Shading v 3 poly 04 To smoothly shade an object, a given vertex normal should be used by all polygo v poly 05 4 that share that vertex. Ideally, this vertex normal is the same as the surface normal the corresponding point on v 5 the original surface. However, if the true surface norm poly13 isn t available, the simplest way to approximate one is to add all (normalized) norm v from the common facets then renormalize 6 poly the result (Gouraud, 1971). This provid 14 reasonable results for surfaces that are fairly smooth, but does not look good for surfa with sharp edges. poly 15 In general, the polygonal nature of models can be hidden by smoothing the transiti between adjacent polygons. However, an object that should have hard edges, such a TEAM L
12 is straightforward to connect the triangles together into longer strips. Decide whether the first triangle should have a clockwise or counterclockwise winding, then ensure all subsequent triangles in the list alternate windings (as shown in Figure 1.10). Triangle fans 1 must also be started with the correct winding, but all subsequent triangles are wound in 3 5 the same direction (Figure 1.11). VerBci Since OpenGL does not have a way to specify generalized triangle strips, the user must choose between GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP and GL_TRIANGLE_FAN. In general, the triangle strip is the more (a.k.a. versatile primitive. While vertex triangle fans are winding ideal for large convex order) polygons that need to be converted to triangles or for triangulating geometry that is cone-shaped, most other cases are best converted to triangle strips. Ordinamento dell avvolgimento dei 7 SECTION 1.3 Shad Figure 1.10 Triangle strip winding. 6 Figure 1.10 Triangle strip winding. In base a come sono ordinab I verbci, si capisce come è orientata una faccia. 0 E possibile infaa scartare ( cull ) dal processo di rasterizzazione le facce che sono viste da dietro Figure 1.9 Proper winding for shared edge of adjoining facets. correct 1 results For 6 an object such as a cube, three hard edges will share one comm case the edge-splitting algorithm needs to be repeated for the third ed Vertex Winding Order Some 3D models come with polygons that are not 3 all wound in a cloc clockwise direction, but are a4 mixture of both. Since the polygon win 1 2
13 Semplice Esempio
14 Controllare lo stato corrente Sedare lo stato glpointsize( size ); gllinesbpple( repeat, padern ); glshademodel( GL_SMOOTH); Abilitare features glenable(gl_lighting); gldisable(gl_texture_2d);
15 Camera Analogy viewing volume camera tripod model
16 Stadi della Vertex TrasformaBon
17 Trasformazioni Semplici gltranslate{fd}(type x, TYPE y, TYPE z); glrotate{fd}(type angle, TYPE x, TYPE y, TYPE z); glscale{fd}(type, x, TYPE y, TYPE z);
18 glulookat void glulookat( GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble eyex, eyey, eyez, centerx, centery, centerz, upx, upy, upz);
19 Ordine delle Trasformazioni V = {vx,vy,vz,vw} Modelview M1 * M2*.Mn* V
20 Ordine delle trasformazioni Dato il seguente ordine gltranslate=mattrans glrotate=matrot glscale=matscale drawcube=v La matrice Modelview sarà IdenBty- >Trans- >Trans*Rot- >Trans*Rot*Scale Trans(Rot(Scale*v)))
21 Ordine delle trasformazioni Sistema di coordinate globali Le trasformazioni vengono applicate a parbre dall ulbma Sistema di coordinate locali Le trasformazioni vengono applicate a parbre dalla prima Non funziona per scalature non omogenee
22 Also let Scaling Matrici RisultanB S = Translation 0 z' y' z' 0 x' y' x' 0 and M = u The call glscale*(x, y, z) generates S, where gltranslate*(x, The call gltranslate*(x, y,z); glscale*(x, y, y,z); generates T, Then glrotate*(a,x,y,z) where 1 x x x x m y T = and T y S = = 0 y 0 0 and S z 1 z m m 0 m y m 0 0m 0 = R = 0 0 z 0 m m 0 1 m z Scaling Notice that S806 1 is defined Appendix only C: if Homogeneous x, y, and z are C Rotation The call glscale*(x, y, z) generates S, where The call glrotate*(a, 1 x, y, z) generates R as foll x T T
23 Matrix Stack glpushmatrix(): aggiunge la matrice corrente nello stack glpopmatrix(): preleva la matrice corrente dallo stack glloadiden>ty(): seda la matrice corrente all idenbtà glloadmatrix{fd}(m): seda la matrice corrente ad m glloadtransposematrix{fd}(m):sosbtuisce la matrice corrente con la matrice m (ordinata per righe) glmultmatrix{fd}(m): molbplica la matrice corrente per la matrice m e carica il valore nella matrice corrente glmulttransposematrix{fd}(m):molbplica la matrice corrente per la matrice ordinata per righe m, e carica il valore nella matrice corrente glgetfloatv(gl_modelview_matrix,m): carica in m I 16 valori della matrice GL_MODELVIEW
24 //... gltranslatef(x,y,z); // 1) posi*on for drawing torso DrawTorso(); // 2) draw torso glpushmatrix(); // 3) save torso matrix gltranslatef(x,y,z); // 4) posi*on for drawing arm DrawArm(); // 5) draw arm glpushmatrix(); // 6) save arm matrix gltranslatef(x,y,z); // 7) posi*on for drawing hand DrawHand(); // 8) draw hand glpushmatrix(); // 9) save hand matrix gltranslatef(x,y,z); // 10) posi*on for drawing first finger DrawFinger(); // 11) draw first finger glpopmatrix(); // 12) load hand matrix glpushmatrix(); // 13) save hand matrix again gltranslatef(x,y,z); // 14) posi*on for drawing second finger DrawFinger(); // 15) draw second finger glpopmatrix(); // 16) load hand matrix glpushmatrix(); // 17) save hand matrix again gltranslatef(x,y,z); // 18) posi*on for drawing third finger DrawFinger(); // 19) draw third finger glpopmatrix(); // 20) load hand matrix glpopmatrix(); // 21) load arm matrix glpopmatrix(); // 22) load torso matrix
25 camera transformation, we take the camera s actor transform and fli camera backward is equivalent to moving the whole world forward Tipico Display Loop the left is equivalent to rotating the whole world to the right. To ren sually take the approach outlined in Figure Loop Save Identity Matrix Apply camera transform Draw stuff that doesn t move Draw moving stuff (Actors) Save camera transform Loop Apply actor transform Draw actor geometry Restore camera transform Restore identity matrix 0 Typical rendering loop for a 3D environment.
26 or OpenGL represents the approach a 4 4 orientation matrix of the two-dimensional not (vectors as a here two-dimensional are array used (the to second represent array option of a flo in di glloadmatrixd(glfloat m); but as a single in array space. out of in For 16 a row-major most floating-point purposes, order. In values. these math terms, three This the vectors approach two orientations are always is diffea math libraries, which another. Most OpenGL implementations and are usually store do take and each manipulate the of two-dimensional unit pipeline length data as (unless floats array and you notapproach. are also app Fo doubles; consequently, using second variation may incur some performance penalty prefers the first mathematical of these two term examples: for this (in case you want to impress yo because 16 double-precision numbers must be converted into single-precision a 0 floats. a 4 a 8 a 12 the vectors are unit length, and orthogonal when they are n The GLfloat following matrix[16]; code shows an array being loaded // Nice with the OpenGL identity matrix friendly and a 1 then a 5 matrix abeing 9 a 13 loaded into the modelview transformation matrix stack. This matrix example with is equivalent the column to callingvectors highlighted GLfloat matrix[4][4]; // Popular, but not aas 2 aefficient 6 a 10 a 14 for O glloadidentity using the matrix higher-level is all functions: 0s with the exception of the very last elem // Load an identity matrix GLfloat OpenGL m[] = can { 1.0f, use 0.0f, the 0.0f, second 0.0f, variation, // X Column but the first is a more efficient FIGURE 4.27 Column-major matrix ordering. 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // Y Column reason for this will become clear in a moment. These 16 elements repr 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // Z Column matrix, as shown 0.0f, 0.0f, in The 0.0f, Figure real 1.0f magic }; lies When // in Translation the the fact array that these elements 16 values traverse represent dow a columns one by one, and we an call orientation this column-major of the three axes matrix with respect ordering. to the In eye mem co glmatrixmode(gl_modelview); glloadmatrixf(m); glloadtransposematrix*(type* m); that fixed, unchanging coordinate system we talked about earl numbers is not hard at all. The four columns each represent a things simple for this book, we focus our attention on just the X vectors. The fourth column vector contains x Y the x Z x, x T y, and x z valu dinate system s origin. When you call gltranslate X y Y y Z y on T y the iden your values for x, y, and z in the 12th, 13th, X z Yand z Z z 14th T z position The first three elements of the first three 0columns 0 0 are 1 just dire sent the orientation (vectors here are used to represent a direct in space. For most purposes, these three vectors are always at 9 FIGURE 4.28 a 3 X axis direction a 7 Y axis direction a 11 Z axis direction a 15 Translation/location How a 4 4 matrix represents a position and o
27 Matrix Modes Matrix Mode(glMatrixMode) ModelView Matrix (GL_MODELVIEW) ProjecBon Matrix (GL_PROJECTION)
28 glfrustum void glfrustum ( GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble le8, right, bodom, top, nearval, farval);
29 sion of the z-buffer is influenced by the values of z near and z fa too large, roundoff errors in the hidden surface algorithm can be et z near =0. nt projection matrix can be retrieved using the command loatv(gl PROJECTION MATRIX, GLfloat *params);. glfrustum matrix Figure 2: View Frustum () creates a transformation matrix M C that maps the view f [ 1, 1] [ 1, 1]: M C = 2 z near right left z near top bottom right+left right left 0 top+bottom top bottom 0 2 z far z near z far z near 0 0 z far+z near z far z near
30 gluperspecbve void gluperspecbve( GLdouble fovy, GLdouble aspect, GLdouble znear, GLdouble zfar);
31 glortho void glortho( GLdouble le8, GLdouble right, GLdouble bodom, GLdouble top, GLdouble nearval, GLdouble farval);
32 glorhto Matrix Orthographic Projection The call glortho(l, r, b, t, n, f ) generates R, where R 2 r l 0 0 r+ l r l 0 r l t b 0 t + b t b = t b and R 1 = f + n f n f n R is defined as long as l r, t b, and n f.
33 gluortho2d void gluortho2d( GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble GLdouble le8, right, bodom, top); Come glortho, con near = - 1 e far = +1
34 e thought of as a unit viewport; the final transformation that we e viewport in pixel coordinates. Assume that the trueviewport Viewport TransformaBon lf-widths V x,v y. Then one final matrix is needed to map to the V x 0 0 V cx 0 V y 0 V cy el coordinates are now ( Px P w, P ) y P w C x C y C z C w = P x P y P z P w and the z value for the point, is P z P w. Points Vcx e Vcy on è il centro the della near viewport clipping plane end up with a z valu Vx = width/2 inate system, and points on the far clipping plane have z coord Vy = height/2 ate system. Il punto Think window of coordinates the z coordinate sarà (Px/Pw, Py/Pw) as a normalized distanc I punb con z minore saranno quelli che passeranno il test Z Buffer n doing z-buffering, you want to retain the color of points with th
35 glviewport void glviewport( GLint x, GLint y, GLsizei width, GLsizei height);
36 Architedura
37 GLUT Strudura della applicazione Configurare ed aprire una nuova finestra Inizializzare lo stato OpenGL Registrare le funzioni di callback Render Resize Input: keyboard, mouse, etc Idle Far parbre il main loop
38 Esempio void main( int argc, char** argv ) { int mode = GLUT_RGB GLUT_DOUBLE; glutinitdisplaymode( mode ); glutcreatewindow( argv[0] ); init(); glutdisplayfunc( display ); glutreshapefunc( resize ); glutkeyboardfunc( key ); glutidlefunc( idle ); glutmainloop(); }
39 OpenGL IniBalizaBon void init( void ) { glclearcolor( 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 ); glcleardepth( 1.0 ); } glenable( GL_LIGHT0 ); glenable( GL_LIGHTING ); glenable( GL_DEPTH_TEST );
40 GLUT Callback FuncBons RouBne eseguite in base all evento Window resize o redraw User input AnimaBon Registrare le callback: glutdisplayfunc( cbdisplay ); glutdisplayfunc( cbidle); glutkeyboardfunc(cbkeyboard);
41 Display Callback void display( void ) { glclear( GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT ); glbegin( GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP ); glvertex3fv( v[0] ); glvertex3fv( v[1] ); glvertex3fv( v[2] ); glvertex3fv( v[3] ); glend(); glutswapbuffers(); }
42 Idle Callbacks Usata per le anmazioni e per l aggiornamento glutidlefunc(cbidle); void idle( void ) { t += dt; glutpostredisplay(); }
43 User Input Callback void keyboard( char key, int x, int y ) { switch( key ) { case q : case Q : exit( EXIT_SUCCESS ); break; case r : case R : rotate = GL_TRUE; break; } }
44 Reshape Callback void reshape (int w, int h) { glviewport (0, 0, (GLsizei) w, (GLsizei) h); glmatrixmode (GL_PROJECTION); glloadidenbty (); gluortho2d (0.0, 4, 0, 4); }
OpenGL & Delphi. Max Kleiner. http://max.kleiner.com/download/openssl_opengl.pdf 1/22
 OpenGL & Delphi Max Kleiner http://max.kleiner.com/download/openssl_opengl.pdf 1/22 OpenGL http://www.opengl.org Evolution of Graphics Assembler (demo pascalspeed.exe) 2D 3D Animation, Simulation (Terrain_delphi.exe)
OpenGL & Delphi Max Kleiner http://max.kleiner.com/download/openssl_opengl.pdf 1/22 OpenGL http://www.opengl.org Evolution of Graphics Assembler (demo pascalspeed.exe) 2D 3D Animation, Simulation (Terrain_delphi.exe)
Graphics Pipeline in a Nutshell
 Graphics Pipeline in a Nutshell How do we create a rendering such as this? CS334 Spring 2008 Design the scene (technical drawing in wireframe ) Apply perspective transformations to the scene geometry for
Graphics Pipeline in a Nutshell How do we create a rendering such as this? CS334 Spring 2008 Design the scene (technical drawing in wireframe ) Apply perspective transformations to the scene geometry for
Aston University. School of Engineering & Applied Science
 CS2150 Aston University School of Engineering & Applied Science CS2150: Computer Graphics January Examinations 2010 Date: XXX Time: XXX Instructions to Candidates: 1. Answer Question ONE and any other
CS2150 Aston University School of Engineering & Applied Science CS2150: Computer Graphics January Examinations 2010 Date: XXX Time: XXX Instructions to Candidates: 1. Answer Question ONE and any other
An Introduction to. Graphics Programming
 An Introduction to Graphics Programming with Tutorial and Reference Manual Toby Howard School of Computer Science University of Manchester V3.3, January 13, 2010 Contents 1 About this manual 1 1.1 How
An Introduction to Graphics Programming with Tutorial and Reference Manual Toby Howard School of Computer Science University of Manchester V3.3, January 13, 2010 Contents 1 About this manual 1 1.1 How
Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Sample Exam Questions 2007
 Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Questions 2007 INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions. Spend approximately 1 minute per mark. Question 1 30 Marks Total
Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Questions 2007 INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions. Spend approximately 1 minute per mark. Question 1 30 Marks Total
Computer Graphics Labs
 Computer Graphics Labs Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Beira Interior Portugal 2011 Copyright 2009-2011 All rights reserved. LAB. 2 1. Learning goals
Computer Graphics Labs Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Beira Interior Portugal 2011 Copyright 2009-2011 All rights reserved. LAB. 2 1. Learning goals
Android and OpenGL. Android Smartphone Programming. Matthias Keil. University of Freiburg
 Android and OpenGL Android Smartphone Programming Matthias Keil Institute for Computer Science Faculty of Engineering 16. Dezember 2013 Outline 1 OpenGL Introduction 2 Displaying Graphics 3 Interaction
Android and OpenGL Android Smartphone Programming Matthias Keil Institute for Computer Science Faculty of Engineering 16. Dezember 2013 Outline 1 OpenGL Introduction 2 Displaying Graphics 3 Interaction
Graphics Input Primitives. 5. Input Devices Introduction to OpenGL. String Choice/Selection Valuator
 4ICT10 Computer Graphics and Virtual Reality 5. Input Devices Introduction to OpenGL Dr Ann McNamara String Choice/Selection Valuator Graphics Input Primitives Locator coordinate pair x,y Pick required
4ICT10 Computer Graphics and Virtual Reality 5. Input Devices Introduction to OpenGL Dr Ann McNamara String Choice/Selection Valuator Graphics Input Primitives Locator coordinate pair x,y Pick required
CMSC 427 Computer Graphics 1
 CMSC 427 Computer Graphics 1 David M. Mount Department of Computer Science University of Maryland Spring 2004 1 Copyright, David M. Mount, 2004, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Maryland, College
CMSC 427 Computer Graphics 1 David M. Mount Department of Computer Science University of Maryland Spring 2004 1 Copyright, David M. Mount, 2004, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Maryland, College
3D Viewing. Chapter 7. Projections. 3D clipping. OpenGL viewing functions and clipping planes
 3D Viewing Chapter 7 Projections 3D clipping OpenGL viewing functions and clipping planes 1 Projections Parallel Perspective Coordinates are transformed along parallel lines Relative sizes are preserved
3D Viewing Chapter 7 Projections 3D clipping OpenGL viewing functions and clipping planes 1 Projections Parallel Perspective Coordinates are transformed along parallel lines Relative sizes are preserved
2: Introducing image synthesis. Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system architecture Overview of OpenGL / GLU / GLUT
 COMP27112 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 2: Introducing image synthesis [email protected] 1 Introduction In these notes we ll cover: Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system
COMP27112 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 2: Introducing image synthesis [email protected] 1 Introduction In these notes we ll cover: Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system
Methodology for Lecture. Review of Last Demo
 Basic Geometry Setup Methodology for Lecture Make mytest1 more ambitious Sequence of steps Demo Review of Last Demo Changed floor to all white, added global for teapot and teapotloc, moved geometry to
Basic Geometry Setup Methodology for Lecture Make mytest1 more ambitious Sequence of steps Demo Review of Last Demo Changed floor to all white, added global for teapot and teapotloc, moved geometry to
Input and Interaction. Project Sketchpad. Graphical Input. Physical Devices. Objectives
 Input and Interaction Project Sketchpad Objectives Introduce the basic input devices - Physical Devices - Logical Devices - Input Modes Event-driven input Introduce double buffering for smooth animations
Input and Interaction Project Sketchpad Objectives Introduce the basic input devices - Physical Devices - Logical Devices - Input Modes Event-driven input Introduce double buffering for smooth animations
Computer Graphics Labs
 Computer Graphics Labs Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 3 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Beira Interior Portugal 2011 Copyright 2009-2011 All rights reserved. 1. Learning goals 2. Timing
Computer Graphics Labs Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 3 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Beira Interior Portugal 2011 Copyright 2009-2011 All rights reserved. 1. Learning goals 2. Timing
CMSC 427 Computer Graphics 1
 CMSC 427 Computer Graphics 1 David M. Mount Department of Computer Science University of Maryland Fall 2010 1 Copyright, David M. Mount, 2010, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Maryland, College
CMSC 427 Computer Graphics 1 David M. Mount Department of Computer Science University of Maryland Fall 2010 1 Copyright, David M. Mount, 2010, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Maryland, College
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics 2D and 3D Transformations Doug Bowman Adapted from notes by Yong Cao Virginia Tech 1 Transformations What are they? changing something to something else via rules mathematics:
CS 4204 Computer Graphics 2D and 3D Transformations Doug Bowman Adapted from notes by Yong Cao Virginia Tech 1 Transformations What are they? changing something to something else via rules mathematics:
Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction)
 Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction) Thilo Kielmann Fall 2008 Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam [email protected] http://www.cs.vu.nl/ graphics/ Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and
Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction) Thilo Kielmann Fall 2008 Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam [email protected] http://www.cs.vu.nl/ graphics/ Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and
Input and Interaction
 Input and Interaction 1 Objectives Introduce basic input devices Physical Devices Logical Devices Input Modes Event-driven input Introduce double buffering for smooth animations Programming event input
Input and Interaction 1 Objectives Introduce basic input devices Physical Devices Logical Devices Input Modes Event-driven input Introduce double buffering for smooth animations Programming event input
4BA6 - Topic 4 Dr. Steven Collins. Chap. 5 3D Viewing and Projections
 4BA6 - Topic 4 Dr. Steven Collins Chap. 5 3D Viewing and Projections References Computer graphics: principles & practice, Fole, vandam, Feiner, Hughes, S-LEN 5.644 M23*;-6 (has a good appendix on linear
4BA6 - Topic 4 Dr. Steven Collins Chap. 5 3D Viewing and Projections References Computer graphics: principles & practice, Fole, vandam, Feiner, Hughes, S-LEN 5.644 M23*;-6 (has a good appendix on linear
Computer Graphics. Anders Hast
 Computer Graphics Anders Hast Who am I?! 5 years in Industry after graduation, 2 years as high school teacher.! 1996 Teacher, University of Gävle! 2004 PhD, Computerised Image Processing " Computer Graphics!
Computer Graphics Anders Hast Who am I?! 5 years in Industry after graduation, 2 years as high school teacher.! 1996 Teacher, University of Gävle! 2004 PhD, Computerised Image Processing " Computer Graphics!
Programmable Graphics Hardware
 Programmable Graphics Hardware Alessandro Martinelli [email protected] 6 November 2011 Rendering Pipeline (6): Programmable Graphics Hardware Rendering Architecture First Rendering Pipeline
Programmable Graphics Hardware Alessandro Martinelli [email protected] 6 November 2011 Rendering Pipeline (6): Programmable Graphics Hardware Rendering Architecture First Rendering Pipeline
Transformations in the pipeline
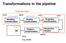 Transformations in the pipeline gltranslatef() Modeling transformation ModelView Matrix OCS WCS glulookat() VCS CCS Viewing transformation Projection transformation DCS Viewport transformation (e.g. pixels)
Transformations in the pipeline gltranslatef() Modeling transformation ModelView Matrix OCS WCS glulookat() VCS CCS Viewing transformation Projection transformation DCS Viewport transformation (e.g. pixels)
Introduction to Computer Graphics Techniques and Applications. Hong Qin Center for Visual Computing (CVC) Stony Brook University
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Techniques and Applications Hong Qin Center for Visual Computing (CVC) Stony Brook University Presentation Outline What is computer graphics? 3D graphics pipeline Programming
Introduction to Computer Graphics Techniques and Applications Hong Qin Center for Visual Computing (CVC) Stony Brook University Presentation Outline What is computer graphics? 3D graphics pipeline Programming
Image Processing and Computer Graphics. Rendering Pipeline. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Image Processing and Computer Graphics Rendering Pipeline Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction rendering pipeline vertex processing primitive processing
Image Processing and Computer Graphics Rendering Pipeline Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction rendering pipeline vertex processing primitive processing
The mouse callback. Positioning. Working with Callbacks. Obtaining the window size. Objectives
 Objectives Working with Callbacks Learn to build interactive programs using GLUT callbacks - Mouse - Keyboard - Reshape Introduce menus in GLUT The mouse callback glutmousefunc(mymouse) void mymouse(glint
Objectives Working with Callbacks Learn to build interactive programs using GLUT callbacks - Mouse - Keyboard - Reshape Introduce menus in GLUT The mouse callback glutmousefunc(mymouse) void mymouse(glint
Chapter 1 Introduction to OpenGL
 OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 1 Introduction to OpenGL Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Appreciate in general terms
OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 1 Introduction to OpenGL Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Appreciate in general terms
Input and Interaction. CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science
 Input and Interaction CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science E. Angel and D. Shreiner : Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 1 Objectives
Input and Interaction CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science E. Angel and D. Shreiner : Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 1 Objectives
Introduction to Computer Graphics
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller TASC 8021 778-782-2215 [email protected] www.cs.sfu.ca/~torsten Today What is computer graphics? Contents of this course Syllabus Overview of course topics
Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller TASC 8021 778-782-2215 [email protected] www.cs.sfu.ca/~torsten Today What is computer graphics? Contents of this course Syllabus Overview of course topics
How To Draw A Billiards Ball In Gta 3D With Texture Mapping (Gta 3) On A Computer Or 2D Or Gta 2D (Gt) On Your Computer Or Computer Or Your Computer (Or Your Computer)
 Pool Billiard An OpenGL-based billiard simulation Stefan HUBER Kamran SAFDAR Andreas SCHRÖCKER Fachbereich Computerwissenschaften Universität Salzburg June 10, 2009 S. Huber, K. Safdar, A. Schröcker: Pool
Pool Billiard An OpenGL-based billiard simulation Stefan HUBER Kamran SAFDAR Andreas SCHRÖCKER Fachbereich Computerwissenschaften Universität Salzburg June 10, 2009 S. Huber, K. Safdar, A. Schröcker: Pool
Lecture Notes. Fundamentals of Computer Graphics. Prof. Michael Langer School of Computer Science McGill University
 COMP 557 Winter 2015 Lecture Notes Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Prof. Michael Langer School of Computer Science McGill University NOTE: These lecture notes are dynamic. The initial version of the
COMP 557 Winter 2015 Lecture Notes Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Prof. Michael Langer School of Computer Science McGill University NOTE: These lecture notes are dynamic. The initial version of the
3D Math Overview and 3D Graphics Foundations
 Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4132 Rev. 0, 05/2010 3D Math Overview and 3D Graphics Foundations by Multimedia Applications Division Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX
Freescale Semiconductor Application Note Document Number: AN4132 Rev. 0, 05/2010 3D Math Overview and 3D Graphics Foundations by Multimedia Applications Division Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. Austin, TX
Realtime 3D Computer Graphics Virtual Reality
 Realtime 3D Computer Graphics Virtual Realit Viewing and projection Classical and General Viewing Transformation Pipeline CPU Pol. DL Pixel Per Vertex Texture Raster Frag FB object ee clip normalized device
Realtime 3D Computer Graphics Virtual Realit Viewing and projection Classical and General Viewing Transformation Pipeline CPU Pol. DL Pixel Per Vertex Texture Raster Frag FB object ee clip normalized device
INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES
 INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES 22 Mar. 212 Yanir Kleiman What is 3D Graphics? Why 3D? Draw one frame at a time Model only once X 24 frames per second Color / texture only once 15, frames for a feature
INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES 22 Mar. 212 Yanir Kleiman What is 3D Graphics? Why 3D? Draw one frame at a time Model only once X 24 frames per second Color / texture only once 15, frames for a feature
Given a point cloud, polygon, or sampled parametric curve, we can use transformations for several purposes:
 3 3.1 2D Given a point cloud, polygon, or sampled parametric curve, we can use transformations for several purposes: 1. Change coordinate frames (world, window, viewport, device, etc). 2. Compose objects
3 3.1 2D Given a point cloud, polygon, or sampled parametric curve, we can use transformations for several purposes: 1. Change coordinate frames (world, window, viewport, device, etc). 2. Compose objects
An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June
 An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June Chapter 11 Animation 11.1 Introduction Animation is an optical illusion of motion due to the phenomenon
An Introduction to 3D Computer Graphics, Stereoscopic Image, and Animation in OpenGL and C/C++ Fore June Chapter 11 Animation 11.1 Introduction Animation is an optical illusion of motion due to the phenomenon
Introduction to GPGPU. Tiziano Diamanti [email protected]
 [email protected] Agenda From GPUs to GPGPUs GPGPU architecture CUDA programming model Perspective projection Vectors that connect the vanishing point to every point of the 3D model will intersecate
[email protected] Agenda From GPUs to GPGPUs GPGPU architecture CUDA programming model Perspective projection Vectors that connect the vanishing point to every point of the 3D model will intersecate
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics
 A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
Computer Graphics on Mobile Devices VL SS2010 3.0 ECTS
 Computer Graphics on Mobile Devices VL SS2010 3.0 ECTS Peter Rautek Rückblick Motivation Vorbesprechung Spiel VL Framework Ablauf Android Basics Android Specifics Activity, Layouts, Service, Intent, Permission,
Computer Graphics on Mobile Devices VL SS2010 3.0 ECTS Peter Rautek Rückblick Motivation Vorbesprechung Spiel VL Framework Ablauf Android Basics Android Specifics Activity, Layouts, Service, Intent, Permission,
H.Calculating Normal Vectors
 Appendix H H.Calculating Normal Vectors This appendix describes how to calculate normal vectors for surfaces. You need to define normals to use the OpenGL lighting facility, which is described in Chapter
Appendix H H.Calculating Normal Vectors This appendix describes how to calculate normal vectors for surfaces. You need to define normals to use the OpenGL lighting facility, which is described in Chapter
Blender Notes. Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 9 The Game Engine
 Blender Notes Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 9 The Game Engine The Blender Game Engine This week we will have an introduction to the Game Engine build
Blender Notes Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 9 The Game Engine The Blender Game Engine This week we will have an introduction to the Game Engine build
Keyboard Mouse and Menus
 Keyboard Mouse and Menus Reshape Callback Whenever a window is initialized, moved or resized, the window sends an event to notify us of the change When we use GLUT, the event will be handled by the function
Keyboard Mouse and Menus Reshape Callback Whenever a window is initialized, moved or resized, the window sends an event to notify us of the change When we use GLUT, the event will be handled by the function
Einführung Computergraphik (WS 2014/15)
 Einführung Computergraphik (WS 2014/15) Martin Held FB Computerwissenschaften Universität Salzburg A-5020 Salzburg, Austria [email protected] 28. Juli 2015 UNIVERSITÄT SALZBURG Computational Geometry
Einführung Computergraphik (WS 2014/15) Martin Held FB Computerwissenschaften Universität Salzburg A-5020 Salzburg, Austria [email protected] 28. Juli 2015 UNIVERSITÄT SALZBURG Computational Geometry
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics 3D views and projection Adapted from notes by Yong Cao 1 Overview of 3D rendering Modeling: *Define object in local coordinates *Place object in world coordinates (modeling transformation)
CS 4204 Computer Graphics 3D views and projection Adapted from notes by Yong Cao 1 Overview of 3D rendering Modeling: *Define object in local coordinates *Place object in world coordinates (modeling transformation)
Lecture Notes, CEng 477
 Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make
Computer Graphics Hardware and Software Lecture Notes, CEng 477 What is Computer Graphics? Different things in different contexts: pictures, scenes that are generated by a computer. tools used to make
Lezione 4: Grafica 3D*(II)
 Lezione 4: Grafica 3D*(II) Informatica Multimediale Docente: Umberto Castellani *I lucidi sono tratti da una lezione di Maura Melotti ([email protected]) RENDERING Rendering What is rendering? Rendering
Lezione 4: Grafica 3D*(II) Informatica Multimediale Docente: Umberto Castellani *I lucidi sono tratti da una lezione di Maura Melotti ([email protected]) RENDERING Rendering What is rendering? Rendering
Lecture 3: Coordinate Systems and Transformations
 Lecture 3: Coordinate Systems and Transformations Topics: 1. Coordinate systems and frames 2. Change of frames 3. Affine transformations 4. Rotation, translation, scaling, and shear 5. Rotation about an
Lecture 3: Coordinate Systems and Transformations Topics: 1. Coordinate systems and frames 2. Change of frames 3. Affine transformations 4. Rotation, translation, scaling, and shear 5. Rotation about an
COMP175: Computer Graphics. Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies
 COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su ([email protected]) TA: Matt Menke
COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su ([email protected]) TA: Matt Menke
Vector Math Computer Graphics Scott D. Anderson
 Vector Math Computer Graphics Scott D. Anderson 1 Dot Product The notation v w means the dot product or scalar product or inner product of two vectors, v and w. In abstract mathematics, we can talk about
Vector Math Computer Graphics Scott D. Anderson 1 Dot Product The notation v w means the dot product or scalar product or inner product of two vectors, v and w. In abstract mathematics, we can talk about
Univers Virtuels. OpenGL : Modélisation / Visualisation. Alexis NEDELEC. Centre Européen de Réalité Virtuelle Ecole Nationale d Ingénieurs de Brest
 Informatique S9 module REV Univers Virtuels OpenGL : Modélisation / Visualisation Alexis NEDELEC Centre Européen de Réalité Virtuelle Ecole Nationale d Ingénieurs de Brest enib c 2012 [email protected] (ENIB-CERV)
Informatique S9 module REV Univers Virtuels OpenGL : Modélisation / Visualisation Alexis NEDELEC Centre Européen de Réalité Virtuelle Ecole Nationale d Ingénieurs de Brest enib c 2012 [email protected] (ENIB-CERV)
Visualization of 2D Domains
 Visualization of 2D Domains This part of the visualization package is intended to supply a simple graphical interface for 2- dimensional finite element data structures. Furthermore, it is used as the low
Visualization of 2D Domains This part of the visualization package is intended to supply a simple graphical interface for 2- dimensional finite element data structures. Furthermore, it is used as the low
Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline 1
 Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline 1 Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline Windows Embedded Compact 7 Technical Article Writers: David Franklin,
Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline 1 Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline Windows Embedded Compact 7 Technical Article Writers: David Franklin,
CSE 564: Visualization. GPU Programming (First Steps) GPU Generations. Klaus Mueller. Computer Science Department Stony Brook University
 GPU Generations CSE 564: Visualization GPU Programming (First Steps) Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University For the labs, 4th generation is desirable Graphics Hardware Pipeline
GPU Generations CSE 564: Visualization GPU Programming (First Steps) Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University For the labs, 4th generation is desirable Graphics Hardware Pipeline
Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE. M.Sc. in Advanced Computer Science. Friday 18 th January 2008.
 COMP60321 Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE M.Sc. in Advanced Computer Science Computer Animation Friday 18 th January 2008 Time: 09:45 11:45 Please answer any THREE Questions
COMP60321 Two hours UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE M.Sc. in Advanced Computer Science Computer Animation Friday 18 th January 2008 Time: 09:45 11:45 Please answer any THREE Questions
Visualizing Data: Scalable Interactivity
 Visualizing Data: Scalable Interactivity The best data visualizations illustrate hidden information and structure contained in a data set. As access to large data sets has grown, so has the need for interactive
Visualizing Data: Scalable Interactivity The best data visualizations illustrate hidden information and structure contained in a data set. As access to large data sets has grown, so has the need for interactive
SOEM 024: Computer Aided Design. E. Rozos
 SOEM 024: Computer Aided Design E. Rozos 3D Design with AutoCAD 2002 Isometric Drawings 3D coordinates, views Wire-frame 3D modelling, extruding Primitive objects Boolean operators Terminology Boolean
SOEM 024: Computer Aided Design E. Rozos 3D Design with AutoCAD 2002 Isometric Drawings 3D coordinates, views Wire-frame 3D modelling, extruding Primitive objects Boolean operators Terminology Boolean
GeoGebra. 10 lessons. Gerrit Stols
 GeoGebra in 10 lessons Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source (free) software for learning and teaching mathematics in schools. It was developed by Markus Hohenwarter
GeoGebra in 10 lessons Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source (free) software for learning and teaching mathematics in schools. It was developed by Markus Hohenwarter
Scan-Line Fill. Scan-Line Algorithm. Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list
 Scan-Line Fill Can also fill by maintaining a data structure of all intersections of polygons with scan lines Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list desired order Scan-Line
Scan-Line Fill Can also fill by maintaining a data structure of all intersections of polygons with scan lines Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list desired order Scan-Line
Blender addons ESRI Shapefile import/export and georeferenced raster import
 Blender addons ESRI Shapefile import/export and georeferenced raster import This blender addon is a collection of 4 tools: ESRI Shapefile importer - Import point, pointz, polyline, polylinez, polygon,
Blender addons ESRI Shapefile import/export and georeferenced raster import This blender addon is a collection of 4 tools: ESRI Shapefile importer - Import point, pointz, polyline, polylinez, polygon,
1 CHORD LENGTH OR UNIFORM PARAMETERIZATION
 1 CHORD LENGTH OR UNIFORM PARAMETERIZATION All of the better high end packages that implement Nurbs Modeling tools will offer the choice of constructing curves using either Uniform or Chord Length parameterization.
1 CHORD LENGTH OR UNIFORM PARAMETERIZATION All of the better high end packages that implement Nurbs Modeling tools will offer the choice of constructing curves using either Uniform or Chord Length parameterization.
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 12 (Part 1) Curves. Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics CS 54 Lecture 1 (Part 1) Curves Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) So Far Dealt with straight lines and flat surfaces Real world objects include
Computer Graphics CS 54 Lecture 1 (Part 1) Curves Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) So Far Dealt with straight lines and flat surfaces Real world objects include
Nicolas P. Rougier PyConFr Conference 2014 Lyon, October 24 25
 GRAPHICS AND ANIMATIONS IN PYTHON USING MATPLOTLIB AND OPENGL Nicolas P. Rougier PyConFr Conference 2014 Lyon, October 24 25 Graphics and Animations in Python Where do we start? A Bit of Context The Python
GRAPHICS AND ANIMATIONS IN PYTHON USING MATPLOTLIB AND OPENGL Nicolas P. Rougier PyConFr Conference 2014 Lyon, October 24 25 Graphics and Animations in Python Where do we start? A Bit of Context The Python
Tegra Android Accelerometer Whitepaper
 Tegra Android Accelerometer Whitepaper Version 5-1 - Contents INTRODUCTION 3 COORDINATE SPACE GLOSSARY 4 ACCELEROMETER CANONICAL AXES 6 WORKING WITH ACCELEROMETER DATA 7 POWER CONSERVATION 10 SUPPORTING
Tegra Android Accelerometer Whitepaper Version 5-1 - Contents INTRODUCTION 3 COORDINATE SPACE GLOSSARY 4 ACCELEROMETER CANONICAL AXES 6 WORKING WITH ACCELEROMETER DATA 7 POWER CONSERVATION 10 SUPPORTING
Introduction to 2D and 3D Computer Graphics Mastering 2D & 3D Computer Graphics Pipelines
 Introduction to 2D and 3D Computer Graphics Mastering 2D & 3D Computer Graphics Pipelines CS447 3-1 Mastering 2D & 3D Graphics Overview of 2D & 3D Pipelines What are pipelines? What are the fundamental
Introduction to 2D and 3D Computer Graphics Mastering 2D & 3D Computer Graphics Pipelines CS447 3-1 Mastering 2D & 3D Graphics Overview of 2D & 3D Pipelines What are pipelines? What are the fundamental
2013 Getting Started Guide
 2013 Getting Started Guide The contents of this guide and accompanying exercises were originally created by Nemetschek Vectorworks, Inc. Vectorworks Fundamentals Getting Started Guide Created using: Vectorworks
2013 Getting Started Guide The contents of this guide and accompanying exercises were originally created by Nemetschek Vectorworks, Inc. Vectorworks Fundamentals Getting Started Guide Created using: Vectorworks
C.S.E. Nodi Tipici Parametrizzati al 15-4-2015. 14/04/2015 Copyright (c) 2015 - Castalia srl
 C.S.E. Nodi Tipici Parametrizzati al 15-4-2015 14/04/2015 Copyright (c) 2015 - Castalia srl 1 Avvertenze (1) Ci sono tre sezioni in questo documento: 1. Nodi in tutte le versioni (background azzurro):
C.S.E. Nodi Tipici Parametrizzati al 15-4-2015 14/04/2015 Copyright (c) 2015 - Castalia srl 1 Avvertenze (1) Ci sono tre sezioni in questo documento: 1. Nodi in tutte le versioni (background azzurro):
11.1. Objectives. Component Form of a Vector. Component Form of a Vector. Component Form of a Vector. Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 11 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 11.1 Vectors in the Plane Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives! Write the component form of
11 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 11.1 Vectors in the Plane Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2 Objectives! Write the component form of
Adobe Illustrator CS5 Part 1: Introduction to Illustrator
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Adobe Illustrator CS5 Part 1: Introduction to Illustrator Summer 2011, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Downloading
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, LOS ANGELES INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES Adobe Illustrator CS5 Part 1: Introduction to Illustrator Summer 2011, Version 1.0 Table of Contents Introduction...2 Downloading
Practical Data Visualization and Virtual Reality. Virtual Reality VR Software and Programming. Karljohan Lundin Palmerius
 Practical Data Visualization and Virtual Reality Virtual Reality VR Software and Programming Karljohan Lundin Palmerius Synopsis Scene graphs Event systems Multi screen output and synchronization VR software
Practical Data Visualization and Virtual Reality Virtual Reality VR Software and Programming Karljohan Lundin Palmerius Synopsis Scene graphs Event systems Multi screen output and synchronization VR software
Bedford, Fowler: Statics. Chapter 4: System of Forces and Moments, Examples via TK Solver
 System of Forces and Moments Introduction The moment vector of a force vector,, with respect to a point has a magnitude equal to the product of the force magnitude, F, and the perpendicular distance from
System of Forces and Moments Introduction The moment vector of a force vector,, with respect to a point has a magnitude equal to the product of the force magnitude, F, and the perpendicular distance from
OpenGL Insights. Edited by. Patrick Cozzi and Christophe Riccio
 OpenGL Insights Edited by Patrick Cozzi and Christophe Riccio ARB debug output: A Helping Hand for Desperate Developers 33 António Ramires Fernandes and Bruno Oliveira 33.1 Introduction Since the inception
OpenGL Insights Edited by Patrick Cozzi and Christophe Riccio ARB debug output: A Helping Hand for Desperate Developers 33 António Ramires Fernandes and Bruno Oliveira 33.1 Introduction Since the inception
Computer Graphics Through OpenGL: From Theory to Experiments
 Computer Graphics Through OpenGL: From Theory to Experiments by Sumanta Guha Chapman & Hall/CRC v Experimenter Software (Prepared by Chansophea Chuon and Sumanta Guha) This file is to help you run the
Computer Graphics Through OpenGL: From Theory to Experiments by Sumanta Guha Chapman & Hall/CRC v Experimenter Software (Prepared by Chansophea Chuon and Sumanta Guha) This file is to help you run the
Game Development in Android Disgruntled Rats LLC. Sean Godinez Brian Morgan Michael Boldischar
 Game Development in Android Disgruntled Rats LLC Sean Godinez Brian Morgan Michael Boldischar Overview Introduction Android Tools Game Development OpenGL ES Marketing Summary Questions Introduction Disgruntled
Game Development in Android Disgruntled Rats LLC Sean Godinez Brian Morgan Michael Boldischar Overview Introduction Android Tools Game Development OpenGL ES Marketing Summary Questions Introduction Disgruntled
COMP-557: Fundamentals of Computer Graphics McGill University, Fall 2010
 COMP-557: Fundamentals of Computer Graphics McGill University, Fall 2010 Class times 2:25 PM - 3:55 PM Mondays and Wednesdays Lecture room Trottier Building 2120 Instructor Paul Kry, [email protected] Course
COMP-557: Fundamentals of Computer Graphics McGill University, Fall 2010 Class times 2:25 PM - 3:55 PM Mondays and Wednesdays Lecture room Trottier Building 2120 Instructor Paul Kry, [email protected] Course
The Essentials of CAGD
 The Essentials of CAGD Chapter 2: Lines and Planes Gerald Farin & Dianne Hansford CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, An A K Peters Book www.farinhansford.com/books/essentials-cagd c 2000 Farin & Hansford
The Essentials of CAGD Chapter 2: Lines and Planes Gerald Farin & Dianne Hansford CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, An A K Peters Book www.farinhansford.com/books/essentials-cagd c 2000 Farin & Hansford
A. OPENING POINT CLOUDS. (Notepad++ Text editor) (Cloud Compare Point cloud and mesh editor) (MeshLab Point cloud and mesh editor)
 MeshLAB tutorial 1 A. OPENING POINT CLOUDS (Notepad++ Text editor) (Cloud Compare Point cloud and mesh editor) (MeshLab Point cloud and mesh editor) 2 OPENING POINT CLOUDS IN NOTEPAD ++ Let us understand
MeshLAB tutorial 1 A. OPENING POINT CLOUDS (Notepad++ Text editor) (Cloud Compare Point cloud and mesh editor) (MeshLab Point cloud and mesh editor) 2 OPENING POINT CLOUDS IN NOTEPAD ++ Let us understand
Shader Model 3.0. Ashu Rege. NVIDIA Developer Technology Group
 Shader Model 3.0 Ashu Rege NVIDIA Developer Technology Group Talk Outline Quick Intro GeForce 6 Series (NV4X family) New Vertex Shader Features Vertex Texture Fetch Longer Programs and Dynamic Flow Control
Shader Model 3.0 Ashu Rege NVIDIA Developer Technology Group Talk Outline Quick Intro GeForce 6 Series (NV4X family) New Vertex Shader Features Vertex Texture Fetch Longer Programs and Dynamic Flow Control
We can display an object on a monitor screen in three different computer-model forms: Wireframe model Surface Model Solid model
 CHAPTER 4 CURVES 4.1 Introduction In order to understand the significance of curves, we should look into the types of model representations that are used in geometric modeling. Curves play a very significant
CHAPTER 4 CURVES 4.1 Introduction In order to understand the significance of curves, we should look into the types of model representations that are used in geometric modeling. Curves play a very significant
An introduction to 3D draughting & solid modelling using AutoCAD
 An introduction to 3D draughting & solid modelling using AutoCAD Faculty of Technology University of Plymouth Drake Circus Plymouth PL4 8AA These notes are to be used in conjunction with the AutoCAD software
An introduction to 3D draughting & solid modelling using AutoCAD Faculty of Technology University of Plymouth Drake Circus Plymouth PL4 8AA These notes are to be used in conjunction with the AutoCAD software
How To Test An Electronic Board With A Flying Probe Tester
 REVERSE ENGINEERING PER LA RIPARAZIONE DI SCHEDE ELETTRONICHE Luca Corli Key Account Manager Seica S.p.A. Nell'industria elettronica si definisce normalmente con reverse engineering "il processo di ricostruzione
REVERSE ENGINEERING PER LA RIPARAZIONE DI SCHEDE ELETTRONICHE Luca Corli Key Account Manager Seica S.p.A. Nell'industria elettronica si definisce normalmente con reverse engineering "il processo di ricostruzione
B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS. NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions.
 B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER
B2.53-R3: COMPUTER GRAPHICS NOTE: 1. There are TWO PARTS in this Module/Paper. PART ONE contains FOUR questions and PART TWO contains FIVE questions. 2. PART ONE is to be answered in the TEAR-OFF ANSWER
Vector Notation: AB represents the vector from point A to point B on a graph. The vector can be computed by B A.
 1 Linear Transformations Prepared by: Robin Michelle King A transformation of an object is a change in position or dimension (or both) of the object. The resulting object after the transformation is called
1 Linear Transformations Prepared by: Robin Michelle King A transformation of an object is a change in position or dimension (or both) of the object. The resulting object after the transformation is called
Adding vectors We can do arithmetic with vectors. We ll start with vector addition and related operations. Suppose you have two vectors
 1 Chapter 13. VECTORS IN THREE DIMENSIONAL SPACE Let s begin with some names and notation for things: R is the set (collection) of real numbers. We write x R to mean that x is a real number. A real number
1 Chapter 13. VECTORS IN THREE DIMENSIONAL SPACE Let s begin with some names and notation for things: R is the set (collection) of real numbers. We write x R to mean that x is a real number. A real number
Algebra Geometry Glossary. 90 angle
 lgebra Geometry Glossary 1) acute angle an angle less than 90 acute angle 90 angle 2) acute triangle a triangle where all angles are less than 90 3) adjacent angles angles that share a common leg Example:
lgebra Geometry Glossary 1) acute angle an angle less than 90 acute angle 90 angle 2) acute triangle a triangle where all angles are less than 90 3) adjacent angles angles that share a common leg Example:
Interactive Computer Graphics
 Interactive Computer Graphics A Top-Down Approach Using OpenGL FIFTH EDITION EDWARD ANGEL UNIVERSITY OF NEW MEXICO PEARSON Addison Wesley Boston San Francisco New York London Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore
Interactive Computer Graphics A Top-Down Approach Using OpenGL FIFTH EDITION EDWARD ANGEL UNIVERSITY OF NEW MEXICO PEARSON Addison Wesley Boston San Francisco New York London Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore
Chapter 2 - Graphics Programming with JOGL
 Chapter 2 - Graphics Programming with JOGL Graphics Software: Classification and History JOGL Hello World Program 2D Coordinate Systems in JOGL Dealing with Window Reshaping 3D Coordinate Systems in JOGL
Chapter 2 - Graphics Programming with JOGL Graphics Software: Classification and History JOGL Hello World Program 2D Coordinate Systems in JOGL Dealing with Window Reshaping 3D Coordinate Systems in JOGL
Number Sense and Operations
 Number Sense and Operations representing as they: 6.N.1 6.N.2 6.N.3 6.N.4 6.N.5 6.N.6 6.N.7 6.N.8 6.N.9 6.N.10 6.N.11 6.N.12 6.N.13. 6.N.14 6.N.15 Demonstrate an understanding of positive integer exponents
Number Sense and Operations representing as they: 6.N.1 6.N.2 6.N.3 6.N.4 6.N.5 6.N.6 6.N.7 6.N.8 6.N.9 6.N.10 6.N.11 6.N.12 6.N.13. 6.N.14 6.N.15 Demonstrate an understanding of positive integer exponents
Geometry of Vectors. 1 Cartesian Coordinates. Carlo Tomasi
 Geometry of Vectors Carlo Tomasi This note explores the geometric meaning of norm, inner product, orthogonality, and projection for vectors. For vectors in three-dimensional space, we also examine the
Geometry of Vectors Carlo Tomasi This note explores the geometric meaning of norm, inner product, orthogonality, and projection for vectors. For vectors in three-dimensional space, we also examine the
PROGRAMMA CORSO DI LOGIC PRO 9
 PROGRAMMA CORSO DI LOGIC PRO 9 1-VIDEO ANTEPRIMA Durata: 4 27 2-VIDEO n.1 Durata: 1 07 - APRIRE UNA NUOVA SESSIONE 3-VIDEO n.2 Durata: 3 36 - CREARE UNA NUOVA TRACCIA - SOFTWARE INSTRUMENT : - Aprire una
PROGRAMMA CORSO DI LOGIC PRO 9 1-VIDEO ANTEPRIMA Durata: 4 27 2-VIDEO n.1 Durata: 1 07 - APRIRE UNA NUOVA SESSIONE 3-VIDEO n.2 Durata: 3 36 - CREARE UNA NUOVA TRACCIA - SOFTWARE INSTRUMENT : - Aprire una
w = COI EYE view direction vector u = w ( 010,, ) cross product with y-axis v = w u up vector
 . w COI EYE view direction vector u w ( 00,, ) cross product with -ais v w u up vector (EQ ) Computer Animation: Algorithms and Techniques 29 up vector view vector observer center of interest 30 Computer
. w COI EYE view direction vector u w ( 00,, ) cross product with -ais v w u up vector (EQ ) Computer Animation: Algorithms and Techniques 29 up vector view vector observer center of interest 30 Computer
OpenGL Shading Language Course. Chapter 5 Appendix. By Jacobo Rodriguez Villar [email protected]
 OpenGL Shading Language Course Chapter 5 Appendix By Jacobo Rodriguez Villar [email protected] TyphoonLabs GLSL Course 1/1 APPENDIX INDEX Using GLSL Shaders Within OpenGL Applications 2
OpenGL Shading Language Course Chapter 5 Appendix By Jacobo Rodriguez Villar [email protected] TyphoonLabs GLSL Course 1/1 APPENDIX INDEX Using GLSL Shaders Within OpenGL Applications 2
TWO-DIMENSIONAL TRANSFORMATION
 CHAPTER 2 TWO-DIMENSIONAL TRANSFORMATION 2.1 Introduction As stated earlier, Computer Aided Design consists of three components, namely, Design (Geometric Modeling), Analysis (FEA, etc), and Visualization
CHAPTER 2 TWO-DIMENSIONAL TRANSFORMATION 2.1 Introduction As stated earlier, Computer Aided Design consists of three components, namely, Design (Geometric Modeling), Analysis (FEA, etc), and Visualization
Volume visualization I Elvins
 Volume visualization I Elvins 1 surface fitting algorithms marching cubes dividing cubes direct volume rendering algorithms ray casting, integration methods voxel projection, projected tetrahedra, splatting
Volume visualization I Elvins 1 surface fitting algorithms marching cubes dividing cubes direct volume rendering algorithms ray casting, integration methods voxel projection, projected tetrahedra, splatting
Section 1.1. Introduction to R n
 The Calculus of Functions of Several Variables Section. Introduction to R n Calculus is the study of functional relationships and how related quantities change with each other. In your first exposure to
The Calculus of Functions of Several Variables Section. Introduction to R n Calculus is the study of functional relationships and how related quantities change with each other. In your first exposure to
ipratico POS Quick Start Guide v. 1.0
 ipratico POS Quick Start Guide v. 1.0 Version History Version Pages Comment Date Author 1.0 First Release 5/Marzo/2012 Luigi Riva 2 SUMMARY 1 GETTING STARTED 4 1.1 What do you need? 4 1.2 ipad 5 1.3 Antenna
ipratico POS Quick Start Guide v. 1.0 Version History Version Pages Comment Date Author 1.0 First Release 5/Marzo/2012 Luigi Riva 2 SUMMARY 1 GETTING STARTED 4 1.1 What do you need? 4 1.2 ipad 5 1.3 Antenna
