Methodology for Lecture. Review of Last Demo
|
|
|
- Daisy Marsh
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Basic Geometry Setup Methodology for Lecture Make mytest1 more ambitious Sequence of steps Demo Review of Last Demo Changed floor to all white, added global for teapot and teapotloc, moved geometry to new header file Demo 0 [set DEMO to 4 all features] #include <GL/glut.h> #include shaders.h #include geometry.h int mouseoldx, mouseoldy ; // For mouse motion GLdouble eyeloc = 2.0 ; // Where to look from; initially 0-2, 2 GLfloat teapotloc = -0.5 ; // ** NEW ** where the teapot is located GLint animate = 0 ; // ** NEW ** whether to animate or not GLuint vertexshader, fragmentshader, shaderprogram ; // shaders const int DEMO = 0 ; // ** NEW ** To turn on and off features Geometry Basic Setup const int numobjects = 2 ; // number of objects for buffer const int numperobj = 3 ; const int ncolors = 4 ; GLuint buffers[numperobj*numobjects+ncolors] ; // ** NEW ** List of buffers for geometric data GLuint objects[numobjects] ; // For each object GLenum PrimType[numobjects] ; GLsizei NumElems[numobjects] ; // Floor, Cube Geometry is specified with a vertex array // The Buffer Offset Macro is from Red Book, page 103, 106 #define BUFFER_OFFSET(bytes) ((GLubyte *) NULL + (bytes)) #define NumberOf(array) (sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0])) enum {Vertices, Colors, Elements ; // For arrays for object enum {FLOOR, CUBE ; // For objects, for the floor Cube geometry (for pillars) const GLfloat wd = 0.1 ; const GLfloat ht = 0.5 ; const GLfloat _cubecol[4][3] = { {1.0, 0.0, 0.0, {0.0, 1.0, 0.0, {0.0, 0.0, 1.0, {1.0, 1.0, 0.0 ; const GLfloat cubeverts[8][3] = { {-wd, -wd, 0.0, {-wd, wd, 0.0, {wd, wd, 0.0, {wd, -wd, 0.0, {-wd, -wd, ht, {wd, -wd, ht, {wd, wd, ht, {-wd, wd, ht ; GLfloat cubecol[8][3] ; const GLubyte cubeinds[6][4] = { {0, 1, 2, 3, // BOTTOM {4, 5, 6, 7, // TOP {0, 4, 7, 1, // LEFT {0, 3, 5, 4, // FRONT {3, 2, 6, 5, // RIGHT {1, 7, 6, 2 // BACK ; 1
2 Cube Geometry (separate Color) // Simple function to set the color separately. Takes out colors void initobjectnocol(gluint object, GLfloat * vert, GLint sizevert, GLubyte * inds, GLint sizeind, GLenum type) { int offset = object * numperobj ; glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, buffers[vertices+offset]) ; glbufferdata(gl_array_buffer, sizevert, vert,gl_static_draw); glvertexpointer(3, GL_FLOAT, 0, BUFFER_OFFSET(0)) ; glenableclientstate(gl_vertex_array) ; glbindbuffer(gl_element_array_buffer,buffers[elements+offset]) ; glbufferdata(gl_element_array_buffer, sizeind, inds,gl_static_draw); PrimType[object] = type ; NumElems[object] = sizeind ; Cube Colors // Simple function to init a bunch of color buffers for the cube void initcolorscube (void) { int base = numobjects * numperobj ; for (int i = 0 ; i < ncolors ; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 8 ; j++) for (int k = 0 ; k < 3 ; k++) cubecol[j][k] = _cubecol[i][k] ; glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, buffers[base+i]) ; glbufferdata(gl_array_buffer, sizeof(cubecol), cubecol,gl_static_draw); glcolorpointer(3, GL_FLOAT, 0, BUFFER_OFFSET(0)) ; glenableclientstate(gl_color_array) ; //in init initobjectnocol(cube, (GLfloat *) cubeverts, sizeof(cubeverts), (GLubyte *) cubeinds, sizeof (cubeinds), GL_QUADS) ; Drawing with Cube Colors // And a function to draw with them, similar to drawobject but with color void drawcolor(gluint object, GLuint color) { int offset = object * numperobj ; int base = numobjects * numperobj ; glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, buffers[vertices+offset]) ; glvertexpointer(3, GL_FLOAT, 0, BUFFER_OFFSET(0)) ; glenableclientstate(gl_vertex_array) ; glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, buffers[base+color]) ; // Set color glcolorpointer(3, GL_FLOAT, 0, BUFFER_OFFSET(0)) ; glenableclientstate(gl_color_array) ; glbindbuffer(gl_element_array_buffer, buffers[elements+offset]) ; gldrawelements(primtype[object], NumElems[object], GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, BUFFER_OFFSET(0)) ; Matrix Stacks and Transforms (Draw 4 Pillars) Summary OpenGL Vertex Transforms Object coords (x y z w) t vertex Modelview matrix [Object Transforms and glm::lookat] Clip coordinates Projection matrix Eye coordinates [3D to 2D, usually (used for lighting) glm::perspective] Perspective Divide (Dehomogenization) Viewport Transform (glviewport) Window Coords Normalized Device Coordinates 2
3 Transformations Matrix Stacks Useful for hierarchically defined figures, placing pillars Old OpenGL: glpushmatrix, glpopmatrix, glload, glmultmatrixf Mytest2 uses old-style stacks. Current recommendation is STL stacks managed yourself. (You must manage the stack yourself for HW 2). Transforms Write your own translate, scale, rotate for HW 1 and HW 2 Careful of OpenGL convetion: In old-style, Right-multiply current matrix (last is first applied). glm operators follow this sometimes. Also glulookat (glm::lookat), gluperspective (glm::perspective) glulookat just matrix like any other transform, affecting modelview Must come before in code, after in action to other transforms Why not usually an issue for gluperspective? Drawing Pillars 1 (in display) glmatrixmode(gl_modelview) ; // 1st pillar gltranslatef(-0.4,-0.4,0.0) ; drawcolor(cube, 0) ; // 2nd pillar gltranslatef(0.4,-0.4,0.0) ; drawcolor(cube, 1) ; Drawing Pillars 2 // 3rd pillar gltranslatef(0.4,0.4,0.0) ; drawcolor(cube, 2) ; // 4th pillar gltranslatef(-0.4,0.4,0.0) ; drawcolor(cube, 3) ; Demo Demo 1 Does order of drawing matter? What if I move floor after pillars in code? Is this desirable? If not, what can I do about it? Depth Testing (Z-Buffering) 3
4 Double Buffering New primitives draw over (replace) old objects Can lead to jerky sensation Solution: double buffer. Render into back (off-screen) buffer. When finished, swap buffers to display entire image at once. Changes in main and display glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_DOUBLE GLUT_RGB GLUT_DEPTH); glutswapbuffers() ; glflush (); Turning on Depth test (Z-buffer) OpenGL uses a Z-buffer for depth tests For each pixel, store nearest Z value (to camera) so far If new fragment is closer, it replaces old z, color [ less than can be over-ridden in fragment program] Simple technique to get accurate visibility Changes in main fn, display to Z-buffer glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB GLUT_DEPTH); glclear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); In init function glenable(gl_depth_test) ; gldepthfunc(gl_less) ; // The default option Demo Demo 2 Does order of drawing matter any more? What if I change near plane to 0? Is this desirable? If not, what can I do about it? Animation (Moving Teapot) Demo 3 Demo Notice how teapot cycles around And that I can pause and restart animation And do everything else (zoom etc.) while teapot moves in background 4
5 Drawing Teapot (in display) // ** NEW ** Put a teapot in the middle that animates glcolor3f(0.0,1.0,1.0) ; // Deprecated command to set the color // I now transform by the teapot translation for animation */ gltranslatef(teapotloc, 0.0, 0.0) ; // The following two transforms set up and center the teapot // Remember that transforms right-multiply the stack gltranslatef(0.0,0.0,0.1) ; glrotatef(90.0,1.0,0.0,0.0) ; glutsolidteapot(0.15) ; Simple Animation routine // ** NEW ** in this assignment, is an animation of a teapot // Hitting p will pause this animation; see keyboard callback void animation(void) { teapotloc = teapotloc ; if (teapotloc > 0.5) teapotloc = -0.5 ; glutpostredisplay() ; Keyboard callback (p to pause) GLint animate = 0 ; // ** NEW ** whether to animate or not void keyboard (unsigned char key, int x, int y) { switch (key) { case 27: // Escape to quit exit(0) ; case 'p': // ** NEW ** to pause/restart animation animate =!animate ; if (animate) glutidlefunc(animation) ; else glutidlefunc(null) ; default: Texture Mapping (Wooden Floor mytest3) Display lists (extend init for pillars) Matrix stacks and transforms (draw 4 pillars) Depth testing or z-buffering Texture mapping (wooden floor) [mytest3] New globals and basic setup GLubyte woodtexture[256][256][3] ; // texture (from grsites.com) GLuint texnames[1] ; // texture buffer GLuint istex ; // blend parameter for texturing GLuint islight ; // for lighting GLint texturing = 1 ; // to turn on/off texturing GLint lighting = 1 ; // to turn on/off lighting // In Display gluniform1i(islight,0) ; // Turn off lighting (except on teapot, later) gluniform1i(istex,texturing) ; drawtexture(floor,texnames[0]) ; // Texturing floor // drawobject(floor) ; gluniform1i(istex,0) ; // Other items aren't textured 5
6 Simple Toggles for Keyboard case 't': // ** NEW ** to turn on/off texturing ; texturing =!texturing ; glutpostredisplay() ; case 's': // ** NEW ** to turn on/off shading (always smooth) ; lighting =!lighting ; glutpostredisplay() ; Adding Visual Detail Basic idea: use images instead of more polygons to represent fine scale color variation Texture Mapping Important topic: nearly all objects textured Wood grain, faces, bricks and so on Adds visual detail to scenes Can be added in a fragment shader Polygonal model With surface texture Setting up texture inittexture("wood.ppm", shaderprogram) ; // in init() // Very basic code to read a ppm file // And then set up buffers for texture coordinates void inittexture (const char * filename, GLuint program) { int i,j,k ; FILE * fp ; GLint err ; assert(fp = fopen(filename,"rb")) ; fscanf(fp,"%*s %*d %*d %*d%*c") ; for (i = 0 ; i < 256 ; i++) for (j = 0 ; j < 256 ; j++) for (k = 0 ; k < 3 ; k++) fscanf(fp,"%c",&(woodtexture[i][j][k])) ; fclose(fp) ; Texture Coordinates Each vertex must have a texture coordinate: pointer to texture. Interpolate for pixels (each fragment has st) // Set up Texture Coordinates glgentextures(1, texnames) ; glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, buffers[numobjects*numperobj+ncolors]) ; glbufferdata(gl_array_buffer, sizeof (floortex), floortex,gl_static_draw); glactivetexture(gl_texture0) ; glenable(gl_texture_2d) ; gltexcoordpointer(2,gl_float,0,buffer_offset(0)) ; glenableclientstate(gl_texture_coord_array) ; glbindtexture (GL_TEXTURE_2D, texnames[0]) ; Specifying the Texture Image glteximage2d( target, level, components, width height, border, format, type, data ) target is GL_TEXTURE_2D level is (almost always) 0 components = 3 or 4 (RGB/RGBA) width/height MUST be a power of 2 border = 0 (usually) format = GL_RGB or GL_RGBA (usually) type = GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, GL_FLOAT, etc 6
7 Texture Image and Bind to Shader glteximage2d(gl_texture_2d,0,gl_rgb, 256, 256, 0, GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, woodtexture) ; gltexparameterf(gl_texture_2d, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR) ; gltexparameterf(gl_texture_2d, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR) ; gltexparameteri(gl_texture_2d, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT) ; gltexparameteri(gl_texture_2d, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT) ; // Define a sampler. See page 709 in red book, 7th ed. GLint texsampler ; texsampler = glgetuniformlocation(program, "tex") ; gluniform1i(texsampler,0) ; // Could also be GL_TEXTURE0 istex = glgetuniformlocation(program,"istex") ; Drawing with Texture void drawtexture(gluint object, GLuint texture) { int offset = object * numperobj ; int base = numobjects * numperobj + ncolors ; glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, buffers[vertices+offset]) ; glvertexpointer(3, GL_FLOAT, 0, BUFFER_OFFSET(0)) ; glenableclientstate(gl_vertex_array) ; glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, buffers[colors+offset]) ; glcolorpointer(3, GL_FLOAT, 0, BUFFER_OFFSET(0)) ; glenableclientstate(gl_color_array) ; // Textures... Drawing with Texture void drawtexture(gluint object, GLuint texture) {... // Textures glactivetexture(gl_texture0) ; glenable(gl_texture_2d) ; glbindtexture(gl_texture_2d, texture) ; glenableclientstate(gl_texture_coord_array) ; glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, buffers[base]) ; // Texcoords gltexcoordpointer(2, GL_FLOAT, 0, BUFFER_OFFSET(0)) ; glbindbuffer(gl_element_array_buffer, buffers[elements+offset]) ; gldrawelements(primtype[object], NumElems[object], GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, BUFFER_OFFSET(0)) ; Final Steps for Drawing (+Demo) Vertex shader (just pass on texture coords) gl_texcoord[0] = gl_multitexcoord0 ; Fragment shader (can be more complex blend) uniform sampler2d tex ; uniform int istex ; void main (void) { if (istex > 0) gl_fragcolor = texture2d(tex, gl_texcoord[0].st) ; 7
Graphics Pipeline in a Nutshell
 Graphics Pipeline in a Nutshell How do we create a rendering such as this? CS334 Spring 2008 Design the scene (technical drawing in wireframe ) Apply perspective transformations to the scene geometry for
Graphics Pipeline in a Nutshell How do we create a rendering such as this? CS334 Spring 2008 Design the scene (technical drawing in wireframe ) Apply perspective transformations to the scene geometry for
OpenGL & Delphi. Max Kleiner. http://max.kleiner.com/download/openssl_opengl.pdf 1/22
 OpenGL & Delphi Max Kleiner http://max.kleiner.com/download/openssl_opengl.pdf 1/22 OpenGL http://www.opengl.org Evolution of Graphics Assembler (demo pascalspeed.exe) 2D 3D Animation, Simulation (Terrain_delphi.exe)
OpenGL & Delphi Max Kleiner http://max.kleiner.com/download/openssl_opengl.pdf 1/22 OpenGL http://www.opengl.org Evolution of Graphics Assembler (demo pascalspeed.exe) 2D 3D Animation, Simulation (Terrain_delphi.exe)
Computer Graphics Labs
 Computer Graphics Labs Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Beira Interior Portugal 2011 Copyright 2009-2011 All rights reserved. LAB. 2 1. Learning goals
Computer Graphics Labs Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Beira Interior Portugal 2011 Copyright 2009-2011 All rights reserved. LAB. 2 1. Learning goals
Image Processing and Computer Graphics. Rendering Pipeline. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Image Processing and Computer Graphics Rendering Pipeline Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction rendering pipeline vertex processing primitive processing
Image Processing and Computer Graphics Rendering Pipeline Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction rendering pipeline vertex processing primitive processing
Computer Graphics Labs
 Computer Graphics Labs Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 3 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Beira Interior Portugal 2011 Copyright 2009-2011 All rights reserved. 1. Learning goals 2. Timing
Computer Graphics Labs Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 3 Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Beira Interior Portugal 2011 Copyright 2009-2011 All rights reserved. 1. Learning goals 2. Timing
An Introduction to. Graphics Programming
 An Introduction to Graphics Programming with Tutorial and Reference Manual Toby Howard School of Computer Science University of Manchester V3.3, January 13, 2010 Contents 1 About this manual 1 1.1 How
An Introduction to Graphics Programming with Tutorial and Reference Manual Toby Howard School of Computer Science University of Manchester V3.3, January 13, 2010 Contents 1 About this manual 1 1.1 How
Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Sample Exam Questions 2007
 Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Questions 2007 INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions. Spend approximately 1 minute per mark. Question 1 30 Marks Total
Monash University Clayton s School of Information Technology CSE3313 Computer Graphics Questions 2007 INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions. Spend approximately 1 minute per mark. Question 1 30 Marks Total
How To Use An Amd Graphics Card In Greece 2.5.1 And 2.4.1 (Amd) With Greege 2.3.5 (Greege) With An Amd Greeper 2.2.
 AMD GPU Association Targeting GPUs for Load Balancing in OpenGL The contents of this document are provided in connection with Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. ( AMD ) products. THE INFORMATION IN THIS PUBLICATION
AMD GPU Association Targeting GPUs for Load Balancing in OpenGL The contents of this document are provided in connection with Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. ( AMD ) products. THE INFORMATION IN THIS PUBLICATION
Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction)
 Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction) Thilo Kielmann Fall 2008 Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam [email protected] http://www.cs.vu.nl/ graphics/ Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and
Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction) Thilo Kielmann Fall 2008 Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam [email protected] http://www.cs.vu.nl/ graphics/ Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and
Aston University. School of Engineering & Applied Science
 CS2150 Aston University School of Engineering & Applied Science CS2150: Computer Graphics January Examinations 2010 Date: XXX Time: XXX Instructions to Candidates: 1. Answer Question ONE and any other
CS2150 Aston University School of Engineering & Applied Science CS2150: Computer Graphics January Examinations 2010 Date: XXX Time: XXX Instructions to Candidates: 1. Answer Question ONE and any other
OpenGL Shading Language Course. Chapter 5 Appendix. By Jacobo Rodriguez Villar [email protected]
 OpenGL Shading Language Course Chapter 5 Appendix By Jacobo Rodriguez Villar [email protected] TyphoonLabs GLSL Course 1/1 APPENDIX INDEX Using GLSL Shaders Within OpenGL Applications 2
OpenGL Shading Language Course Chapter 5 Appendix By Jacobo Rodriguez Villar [email protected] TyphoonLabs GLSL Course 1/1 APPENDIX INDEX Using GLSL Shaders Within OpenGL Applications 2
Shadows. Shadows. Thanks to: Frédo Durand and Seth Teller MIT. Realism Depth cue
 Shadows Thanks to: Frédo Durand and Seth Teller MIT 1 Shadows Realism Depth cue 2 1 Shadows as depth cue 3 Spatial relationship between objects Michael McCool Univ of Waterloo 4 2 Spatial relationship
Shadows Thanks to: Frédo Durand and Seth Teller MIT 1 Shadows Realism Depth cue 2 1 Shadows as depth cue 3 Spatial relationship between objects Michael McCool Univ of Waterloo 4 2 Spatial relationship
4BA6 - Topic 4 Dr. Steven Collins. Chap. 5 3D Viewing and Projections
 4BA6 - Topic 4 Dr. Steven Collins Chap. 5 3D Viewing and Projections References Computer graphics: principles & practice, Fole, vandam, Feiner, Hughes, S-LEN 5.644 M23*;-6 (has a good appendix on linear
4BA6 - Topic 4 Dr. Steven Collins Chap. 5 3D Viewing and Projections References Computer graphics: principles & practice, Fole, vandam, Feiner, Hughes, S-LEN 5.644 M23*;-6 (has a good appendix on linear
Transformations in the pipeline
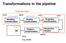 Transformations in the pipeline gltranslatef() Modeling transformation ModelView Matrix OCS WCS glulookat() VCS CCS Viewing transformation Projection transformation DCS Viewport transformation (e.g. pixels)
Transformations in the pipeline gltranslatef() Modeling transformation ModelView Matrix OCS WCS glulookat() VCS CCS Viewing transformation Projection transformation DCS Viewport transformation (e.g. pixels)
OpenGL "Hello, world!"
 OpenGL "Hello, world!" by Ian Romanick This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike (by-nc-sa) License. To view a copy of this license, (a) visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/;
OpenGL "Hello, world!" by Ian Romanick This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike (by-nc-sa) License. To view a copy of this license, (a) visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/;
OpenGL Insights. Edited by. Patrick Cozzi and Christophe Riccio
 OpenGL Insights Edited by Patrick Cozzi and Christophe Riccio Browser Graphics Analysis and Optimizations 36 Chris Dirks and Omar A. Rodriguez 36.1 Introduction Understanding performance bottlenecks in
OpenGL Insights Edited by Patrick Cozzi and Christophe Riccio Browser Graphics Analysis and Optimizations 36 Chris Dirks and Omar A. Rodriguez 36.1 Introduction Understanding performance bottlenecks in
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics 2D and 3D Transformations Doug Bowman Adapted from notes by Yong Cao Virginia Tech 1 Transformations What are they? changing something to something else via rules mathematics:
CS 4204 Computer Graphics 2D and 3D Transformations Doug Bowman Adapted from notes by Yong Cao Virginia Tech 1 Transformations What are they? changing something to something else via rules mathematics:
Chapter 1 Introduction to OpenGL
 OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 1 Introduction to OpenGL Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Appreciate in general terms
OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 1 Introduction to OpenGL Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Appreciate in general terms
Basic ios development
 Basic ios development The minimal ios appication "Keep it as small and simple as possible" - me, all the time Xcode, New Project -> Application -> Window Based Application, name it Minimal, and Save. What
Basic ios development The minimal ios appication "Keep it as small and simple as possible" - me, all the time Xcode, New Project -> Application -> Window Based Application, name it Minimal, and Save. What
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics
 A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
A Short Introduction to Computer Graphics Frédo Durand MIT Laboratory for Computer Science 1 Introduction Chapter I: Basics Although computer graphics is a vast field that encompasses almost any graphical
Introduction to Computer Graphics
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller TASC 8021 778-782-2215 [email protected] www.cs.sfu.ca/~torsten Today What is computer graphics? Contents of this course Syllabus Overview of course topics
Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller TASC 8021 778-782-2215 [email protected] www.cs.sfu.ca/~torsten Today What is computer graphics? Contents of this course Syllabus Overview of course topics
CSE 564: Visualization. GPU Programming (First Steps) GPU Generations. Klaus Mueller. Computer Science Department Stony Brook University
 GPU Generations CSE 564: Visualization GPU Programming (First Steps) Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University For the labs, 4th generation is desirable Graphics Hardware Pipeline
GPU Generations CSE 564: Visualization GPU Programming (First Steps) Klaus Mueller Computer Science Department Stony Brook University For the labs, 4th generation is desirable Graphics Hardware Pipeline
3D Graphics and Cameras
 3D Graphics and Cameras Kari Pulli Senior Director Overview OpenGL ES 1.x OpenGL ES 2.0 WebGL OpenCV FCam All examples on this session on Android OpenGL: Project vertices to camera connect them to triangles
3D Graphics and Cameras Kari Pulli Senior Director Overview OpenGL ES 1.x OpenGL ES 2.0 WebGL OpenCV FCam All examples on this session on Android OpenGL: Project vertices to camera connect them to triangles
Tutorial 9: Skeletal Animation
 Tutorial 9: Skeletal Animation Summary In the last couple of tutorials, you ve seen how to create a scene graph, and implemented a simple animating cube robot using them. You re probably wondering how
Tutorial 9: Skeletal Animation Summary In the last couple of tutorials, you ve seen how to create a scene graph, and implemented a simple animating cube robot using them. You re probably wondering how
CMSC 427 Computer Graphics 1
 CMSC 427 Computer Graphics 1 David M. Mount Department of Computer Science University of Maryland Fall 2010 1 Copyright, David M. Mount, 2010, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Maryland, College
CMSC 427 Computer Graphics 1 David M. Mount Department of Computer Science University of Maryland Fall 2010 1 Copyright, David M. Mount, 2010, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Maryland, College
Blender Notes. Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 9 The Game Engine
 Blender Notes Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 9 The Game Engine The Blender Game Engine This week we will have an introduction to the Game Engine build
Blender Notes Introduction to Digital Modelling and Animation in Design Blender Tutorial - week 9 The Game Engine The Blender Game Engine This week we will have an introduction to the Game Engine build
The mouse callback. Positioning. Working with Callbacks. Obtaining the window size. Objectives
 Objectives Working with Callbacks Learn to build interactive programs using GLUT callbacks - Mouse - Keyboard - Reshape Introduce menus in GLUT The mouse callback glutmousefunc(mymouse) void mymouse(glint
Objectives Working with Callbacks Learn to build interactive programs using GLUT callbacks - Mouse - Keyboard - Reshape Introduce menus in GLUT The mouse callback glutmousefunc(mymouse) void mymouse(glint
Android and OpenGL. Android Smartphone Programming. Matthias Keil. University of Freiburg
 Android and OpenGL Android Smartphone Programming Matthias Keil Institute for Computer Science Faculty of Engineering 16. Dezember 2013 Outline 1 OpenGL Introduction 2 Displaying Graphics 3 Interaction
Android and OpenGL Android Smartphone Programming Matthias Keil Institute for Computer Science Faculty of Engineering 16. Dezember 2013 Outline 1 OpenGL Introduction 2 Displaying Graphics 3 Interaction
Shader Model 3.0. Ashu Rege. NVIDIA Developer Technology Group
 Shader Model 3.0 Ashu Rege NVIDIA Developer Technology Group Talk Outline Quick Intro GeForce 6 Series (NV4X family) New Vertex Shader Features Vertex Texture Fetch Longer Programs and Dynamic Flow Control
Shader Model 3.0 Ashu Rege NVIDIA Developer Technology Group Talk Outline Quick Intro GeForce 6 Series (NV4X family) New Vertex Shader Features Vertex Texture Fetch Longer Programs and Dynamic Flow Control
A Tutorial for 3D Point Cloud Editor
 A Tutorial for 3D Point Cloud Editor Yue Li and Matthew Hielsberg Texas A&M University April 9, 2012 Abstract This tutorial illustrates the uses of the point cloud editor with examples. 1 Introduction
A Tutorial for 3D Point Cloud Editor Yue Li and Matthew Hielsberg Texas A&M University April 9, 2012 Abstract This tutorial illustrates the uses of the point cloud editor with examples. 1 Introduction
Input and Interaction. Project Sketchpad. Graphical Input. Physical Devices. Objectives
 Input and Interaction Project Sketchpad Objectives Introduce the basic input devices - Physical Devices - Logical Devices - Input Modes Event-driven input Introduce double buffering for smooth animations
Input and Interaction Project Sketchpad Objectives Introduce the basic input devices - Physical Devices - Logical Devices - Input Modes Event-driven input Introduce double buffering for smooth animations
Castle Modeling. In this PDF tutorial we will be modeling a simple castle as pictured above.
 Course: 3D Design Title: Castle Modeling Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig ([email protected]) May, 2012 This tutorial assumes that you already know how to: Display orthographic
Course: 3D Design Title: Castle Modeling Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig ([email protected]) May, 2012 This tutorial assumes that you already know how to: Display orthographic
INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES
 INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES 22 Mar. 212 Yanir Kleiman What is 3D Graphics? Why 3D? Draw one frame at a time Model only once X 24 frames per second Color / texture only once 15, frames for a feature
INTRODUCTION TO RENDERING TECHNIQUES 22 Mar. 212 Yanir Kleiman What is 3D Graphics? Why 3D? Draw one frame at a time Model only once X 24 frames per second Color / texture only once 15, frames for a feature
CMSC 427 Computer Graphics 1
 CMSC 427 Computer Graphics 1 David M. Mount Department of Computer Science University of Maryland Spring 2004 1 Copyright, David M. Mount, 2004, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Maryland, College
CMSC 427 Computer Graphics 1 David M. Mount Department of Computer Science University of Maryland Spring 2004 1 Copyright, David M. Mount, 2004, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Maryland, College
2: Introducing image synthesis. Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system architecture Overview of OpenGL / GLU / GLUT
 COMP27112 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 2: Introducing image synthesis [email protected] 1 Introduction In these notes we ll cover: Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system
COMP27112 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 2: Introducing image synthesis [email protected] 1 Introduction In these notes we ll cover: Some orientation how did we get here? Graphics system
4D Interactive Model Animations
 Animation Using 4D Interactive Models MVSand EVS-PRO have two distinctly different animation concepts. Our traditional animations consist of a sequence of bitmap images that have been encoded into an animation
Animation Using 4D Interactive Models MVSand EVS-PRO have two distinctly different animation concepts. Our traditional animations consist of a sequence of bitmap images that have been encoded into an animation
Tutorial: Biped Character in 3D Studio Max 7, Easy Animation
 Tutorial: Biped Character in 3D Studio Max 7, Easy Animation Written by: Ricardo Tangali 1. Introduction:... 3 2. Basic control in 3D Studio Max... 3 2.1. Navigating a scene:... 3 2.2. Hide and Unhide
Tutorial: Biped Character in 3D Studio Max 7, Easy Animation Written by: Ricardo Tangali 1. Introduction:... 3 2. Basic control in 3D Studio Max... 3 2.1. Navigating a scene:... 3 2.2. Hide and Unhide
The Rocket Steam Locomotive - Animation
 Course: 3D Design Title: Rocket Steam Locomotive - Animation Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig ([email protected]) (May 2012) The Rocket Steam Locomotive - Animation In this tutorial
Course: 3D Design Title: Rocket Steam Locomotive - Animation Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig ([email protected]) (May 2012) The Rocket Steam Locomotive - Animation In this tutorial
Keyboard Mouse and Menus
 Keyboard Mouse and Menus Reshape Callback Whenever a window is initialized, moved or resized, the window sends an event to notify us of the change When we use GLUT, the event will be handled by the function
Keyboard Mouse and Menus Reshape Callback Whenever a window is initialized, moved or resized, the window sends an event to notify us of the change When we use GLUT, the event will be handled by the function
WebCL for Hardware-Accelerated Web Applications. Won Jeon, Tasneem Brutch, and Simon Gibbs
 WebCL for Hardware-Accelerated Web Applications Won Jeon, Tasneem Brutch, and Simon Gibbs What is WebCL? WebCL is a JavaScript binding to OpenCL. WebCL enables significant acceleration of compute-intensive
WebCL for Hardware-Accelerated Web Applications Won Jeon, Tasneem Brutch, and Simon Gibbs What is WebCL? WebCL is a JavaScript binding to OpenCL. WebCL enables significant acceleration of compute-intensive
What s New V 11. Preferences: Parameters: Layout/ Modifications: Reverse mouse scroll wheel zoom direction
 What s New V 11 Preferences: Reverse mouse scroll wheel zoom direction Assign mouse scroll wheel Middle Button as Fine tune Pricing Method (Manufacturing/Design) Display- Display Long Name Parameters:
What s New V 11 Preferences: Reverse mouse scroll wheel zoom direction Assign mouse scroll wheel Middle Button as Fine tune Pricing Method (Manufacturing/Design) Display- Display Long Name Parameters:
Scan-Line Fill. Scan-Line Algorithm. Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list
 Scan-Line Fill Can also fill by maintaining a data structure of all intersections of polygons with scan lines Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list desired order Scan-Line
Scan-Line Fill Can also fill by maintaining a data structure of all intersections of polygons with scan lines Sort by scan line Fill each span vertex order generated by vertex list desired order Scan-Line
How To Teach Computer Graphics
 Computer Graphics Thilo Kielmann Lecture 1: 1 Introduction (basic administrative information) Course Overview + Examples (a.o. Pixar, Blender, ) Graphics Systems Hands-on Session General Introduction http://www.cs.vu.nl/~graphics/
Computer Graphics Thilo Kielmann Lecture 1: 1 Introduction (basic administrative information) Course Overview + Examples (a.o. Pixar, Blender, ) Graphics Systems Hands-on Session General Introduction http://www.cs.vu.nl/~graphics/
Nicolas P. Rougier PyConFr Conference 2014 Lyon, October 24 25
 GRAPHICS AND ANIMATIONS IN PYTHON USING MATPLOTLIB AND OPENGL Nicolas P. Rougier PyConFr Conference 2014 Lyon, October 24 25 Graphics and Animations in Python Where do we start? A Bit of Context The Python
GRAPHICS AND ANIMATIONS IN PYTHON USING MATPLOTLIB AND OPENGL Nicolas P. Rougier PyConFr Conference 2014 Lyon, October 24 25 Graphics and Animations in Python Where do we start? A Bit of Context The Python
Sweet Home 3D user's guide
 1 de 14 08/01/2013 13:08 Features Download Online Gallery Blog Documentation FAQ User's guide Video tutorial Developer's guides History Reviews Support 3D models Textures Translations Forum Report a bug
1 de 14 08/01/2013 13:08 Features Download Online Gallery Blog Documentation FAQ User's guide Video tutorial Developer's guides History Reviews Support 3D models Textures Translations Forum Report a bug
Computer Graphics Through OpenGL: From Theory to Experiments
 Computer Graphics Through OpenGL: From Theory to Experiments by Sumanta Guha Chapman & Hall/CRC v Experimenter Software (Prepared by Chansophea Chuon and Sumanta Guha) This file is to help you run the
Computer Graphics Through OpenGL: From Theory to Experiments by Sumanta Guha Chapman & Hall/CRC v Experimenter Software (Prepared by Chansophea Chuon and Sumanta Guha) This file is to help you run the
Adding Animation With Cinema 4D XL
 Step-by-Step Adding Animation With Cinema 4D XL This Step-by-Step Card covers the basics of using the animation features of Cinema 4D XL. Note: Before you start this Step-by-Step Card, you need to have
Step-by-Step Adding Animation With Cinema 4D XL This Step-by-Step Card covers the basics of using the animation features of Cinema 4D XL. Note: Before you start this Step-by-Step Card, you need to have
Introduction to GPGPU. Tiziano Diamanti [email protected]
 [email protected] Agenda From GPUs to GPGPUs GPGPU architecture CUDA programming model Perspective projection Vectors that connect the vanishing point to every point of the 3D model will intersecate
[email protected] Agenda From GPUs to GPGPUs GPGPU architecture CUDA programming model Perspective projection Vectors that connect the vanishing point to every point of the 3D model will intersecate
The OpenGL Framebuffer Object Extension. Simon Green. NVIDIA Corporation
 The OpenGL Framebuffer Object Extension Simon Green NVIDIA Corporation Overview Why render to texture? P-buffer / ARB render texture review Framebuffer object extension Examples Future directions Why Render
The OpenGL Framebuffer Object Extension Simon Green NVIDIA Corporation Overview Why render to texture? P-buffer / ARB render texture review Framebuffer object extension Examples Future directions Why Render
Vertex and fragment programs
 Vertex and fragment programs Jon Hjelmervik email: [email protected] 1 Fixed function transform and lighting Each vertex is treated separately Affine transformation transforms the vertex by matrix multiplication
Vertex and fragment programs Jon Hjelmervik email: [email protected] 1 Fixed function transform and lighting Each vertex is treated separately Affine transformation transforms the vertex by matrix multiplication
AMD s 10-bit Video Output Technology
 AMD s 10-bit Video Output Technology Introduction Display devices with a greater bit depth than the conventional 8-bits per color channel are rapidly gaining popularity in application areas such as medical
AMD s 10-bit Video Output Technology Introduction Display devices with a greater bit depth than the conventional 8-bits per color channel are rapidly gaining popularity in application areas such as medical
Tutorial 13: Object Animation
 Tutorial 13: Object Animation In this tutorial we will learn how to: Completion time 40 minutes Establish the number of frames for an object animation Rotate objects into desired positions Set key frames
Tutorial 13: Object Animation In this tutorial we will learn how to: Completion time 40 minutes Establish the number of frames for an object animation Rotate objects into desired positions Set key frames
Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline 1
 Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline 1 Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline Windows Embedded Compact 7 Technical Article Writers: David Franklin,
Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline 1 Silverlight for Windows Embedded Graphics and Rendering Pipeline Windows Embedded Compact 7 Technical Article Writers: David Franklin,
Lecture 3: Coordinate Systems and Transformations
 Lecture 3: Coordinate Systems and Transformations Topics: 1. Coordinate systems and frames 2. Change of frames 3. Affine transformations 4. Rotation, translation, scaling, and shear 5. Rotation about an
Lecture 3: Coordinate Systems and Transformations Topics: 1. Coordinate systems and frames 2. Change of frames 3. Affine transformations 4. Rotation, translation, scaling, and shear 5. Rotation about an
Input and Interaction
 Input and Interaction 1 Objectives Introduce basic input devices Physical Devices Logical Devices Input Modes Event-driven input Introduce double buffering for smooth animations Programming event input
Input and Interaction 1 Objectives Introduce basic input devices Physical Devices Logical Devices Input Modes Event-driven input Introduce double buffering for smooth animations Programming event input
OpenGL Insights. Edited by. Patrick Cozzi and Christophe Riccio
 OpenGL Insights Edited by Patrick Cozzi and Christophe Riccio ARB debug output: A Helping Hand for Desperate Developers 33 António Ramires Fernandes and Bruno Oliveira 33.1 Introduction Since the inception
OpenGL Insights Edited by Patrick Cozzi and Christophe Riccio ARB debug output: A Helping Hand for Desperate Developers 33 António Ramires Fernandes and Bruno Oliveira 33.1 Introduction Since the inception
SketchUp Instructions
 SketchUp Instructions Every architect needs to know how to use SketchUp! SketchUp is free from Google just Google it and download to your computer. You can do just about anything with it, but it is especially
SketchUp Instructions Every architect needs to know how to use SketchUp! SketchUp is free from Google just Google it and download to your computer. You can do just about anything with it, but it is especially
Watch Your Garden Grow
 Watch Your Garden Grow The Brinno GardenWatchCam is a low cost, light weight, weather resistant, battery operated time-lapse camera that captures the entire lifecycle of any garden season by taking photos
Watch Your Garden Grow The Brinno GardenWatchCam is a low cost, light weight, weather resistant, battery operated time-lapse camera that captures the entire lifecycle of any garden season by taking photos
How To Draw A Billiards Ball In Gta 3D With Texture Mapping (Gta 3) On A Computer Or 2D Or Gta 2D (Gt) On Your Computer Or Computer Or Your Computer (Or Your Computer)
 Pool Billiard An OpenGL-based billiard simulation Stefan HUBER Kamran SAFDAR Andreas SCHRÖCKER Fachbereich Computerwissenschaften Universität Salzburg June 10, 2009 S. Huber, K. Safdar, A. Schröcker: Pool
Pool Billiard An OpenGL-based billiard simulation Stefan HUBER Kamran SAFDAR Andreas SCHRÖCKER Fachbereich Computerwissenschaften Universität Salzburg June 10, 2009 S. Huber, K. Safdar, A. Schröcker: Pool
Pro/E Design Animation Tutorial*
 MAE 377 Product Design in CAD Environment Pro/E Design Animation Tutorial* For Pro/Engineer Wildfire 3.0 Leng-Feng Lee 08 OVERVIEW: Pro/ENGINEER Design Animation provides engineers with a simple yet powerful
MAE 377 Product Design in CAD Environment Pro/E Design Animation Tutorial* For Pro/Engineer Wildfire 3.0 Leng-Feng Lee 08 OVERVIEW: Pro/ENGINEER Design Animation provides engineers with a simple yet powerful
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Nikon TiE Deconvolution Microscope CCRB 1-220G
 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Nikon TiE Deconvolution Microscope CCRB 1-220G Conventions Through these notes bold font refers to a software button and italics refer to a hardware switch. The software makes extensive
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Nikon TiE Deconvolution Microscope CCRB 1-220G Conventions Through these notes bold font refers to a software button and italics refer to a hardware switch. The software makes extensive
The Car Tutorial Part 1 Creating a Racing Game for Unity
 The Car Tutorial Part 1 Creating a Racing Game for Unity Introduction 3 We will show 3 Prerequisites 3 We will not show 4 Part 1: Assembling the Car 5 Adding Collision 6 Shadow settings for the car model
The Car Tutorial Part 1 Creating a Racing Game for Unity Introduction 3 We will show 3 Prerequisites 3 We will not show 4 Part 1: Assembling the Car 5 Adding Collision 6 Shadow settings for the car model
COMP175: Computer Graphics. Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies
 COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su ([email protected]) TA: Matt Menke
COMP175: Computer Graphics Lecture 1 Introduction and Display Technologies Course mechanics Number: COMP 175-01, Fall 2009 Meetings: TR 1:30-2:45pm Instructor: Sara Su ([email protected]) TA: Matt Menke
Input and Interaction. CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science
 Input and Interaction CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science E. Angel and D. Shreiner : Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 1 Objectives
Input and Interaction CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science E. Angel and D. Shreiner : Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 1 Objectives
Java game programming. Game engines. Fayolle Pierre-Alain
 Java game programming Game engines 2010 Fayolle Pierre-Alain Plan Some definitions List of (Java) game engines Examples of game engines and their use A first and simple definition A game engine is a (complex)
Java game programming Game engines 2010 Fayolle Pierre-Alain Plan Some definitions List of (Java) game engines Examples of game engines and their use A first and simple definition A game engine is a (complex)
IT 386: 3D Modeling and Animation. Review Sheet. Notes from Professor Nersesian s IT 386: 3D Modeling and Animation course
 IT 386: 3D Modeling and Animation Review Sheet Sources: Notes from Professor Nersesian s IT 386: 3D Modeling and Animation course Notes from CannedMushrooms on YouTube Notes from Digital Tutors tutorial
IT 386: 3D Modeling and Animation Review Sheet Sources: Notes from Professor Nersesian s IT 386: 3D Modeling and Animation course Notes from CannedMushrooms on YouTube Notes from Digital Tutors tutorial
2013 Getting Started Guide
 2013 Getting Started Guide The contents of this guide and accompanying exercises were originally created by Nemetschek Vectorworks, Inc. Vectorworks Fundamentals Getting Started Guide Created using: Vectorworks
2013 Getting Started Guide The contents of this guide and accompanying exercises were originally created by Nemetschek Vectorworks, Inc. Vectorworks Fundamentals Getting Started Guide Created using: Vectorworks
DATA VISUALIZATION OF THE GRAPHICS PIPELINE: TRACKING STATE WITH THE STATEVIEWER
 DATA VISUALIZATION OF THE GRAPHICS PIPELINE: TRACKING STATE WITH THE STATEVIEWER RAMA HOETZLEIN, DEVELOPER TECHNOLOGY, NVIDIA Data Visualizations assist humans with data analysis by representing information
DATA VISUALIZATION OF THE GRAPHICS PIPELINE: TRACKING STATE WITH THE STATEVIEWER RAMA HOETZLEIN, DEVELOPER TECHNOLOGY, NVIDIA Data Visualizations assist humans with data analysis by representing information
3D Application and Game Development With OpenGL
 3D Application and Game Development With OpenGL java.sun.com/javaone/sf Daniel Petersen Kenneth Russell Sun Microsystems, Inc. 1 Presentation Goal Show how to build leading-edge 3D applications and games
3D Application and Game Development With OpenGL java.sun.com/javaone/sf Daniel Petersen Kenneth Russell Sun Microsystems, Inc. 1 Presentation Goal Show how to build leading-edge 3D applications and games
GPU Christmas Tree Rendering. Evan Hart [email protected]
 GPU Christmas Tree Rendering Evan Hart [email protected] February 2007 Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change 0.9 2/20/2007 Ehart Betarelease February 2007 ii Beta Release This
GPU Christmas Tree Rendering Evan Hart [email protected] February 2007 Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change 0.9 2/20/2007 Ehart Betarelease February 2007 ii Beta Release This
Compositing a 3D character over video footage in Maya Jean-Marc Gauthier, Spring 2008
 Compositing a 3D character over video footage in Maya Jean-Marc Gauthier, Spring 2008 Video footage before compositing And after compositing with an animated character This tutorial is organized as small
Compositing a 3D character over video footage in Maya Jean-Marc Gauthier, Spring 2008 Video footage before compositing And after compositing with an animated character This tutorial is organized as small
Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview
 Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview Graphics System Monitor Input devices CPU/Memory GPU Raster Graphics System Raster: An array of picture elements Based on raster-scan TV technology The screen (and
Computer Graphics Hardware An Overview Graphics System Monitor Input devices CPU/Memory GPU Raster Graphics System Raster: An array of picture elements Based on raster-scan TV technology The screen (and
GUI GRAPHICS AND USER INTERFACES. Welcome to GUI! Mechanics. Mihail Gaianu 26/02/2014 1
 Welcome to GUI! Mechanics 26/02/2014 1 Requirements Info If you don t know C++, you CAN take this class additional time investment required early on GUI Java to C++ transition tutorial on course website
Welcome to GUI! Mechanics 26/02/2014 1 Requirements Info If you don t know C++, you CAN take this class additional time investment required early on GUI Java to C++ transition tutorial on course website
Programming 3D Applications with HTML5 and WebGL
 Programming 3D Applications with HTML5 and WebGL Tony Parisi Beijing Cambridge Farnham Köln Sebastopol Tokyo Table of Contents Preface ix Part I. Foundations 1. Introduction 3 HTML5: A New Visual Medium
Programming 3D Applications with HTML5 and WebGL Tony Parisi Beijing Cambridge Farnham Köln Sebastopol Tokyo Table of Contents Preface ix Part I. Foundations 1. Introduction 3 HTML5: A New Visual Medium
Graphic Design. Background: The part of an artwork that appears to be farthest from the viewer, or in the distance of the scene.
 Graphic Design Active Layer- When you create multi layers for your images the active layer, or the only one that will be affected by your actions, is the one with a blue background in your layers palette.
Graphic Design Active Layer- When you create multi layers for your images the active layer, or the only one that will be affected by your actions, is the one with a blue background in your layers palette.
Optimizing AAA Games for Mobile Platforms
 Optimizing AAA Games for Mobile Platforms Niklas Smedberg Senior Engine Programmer, Epic Games Who Am I A.k.a. Smedis Epic Games, Unreal Engine 15 years in the industry 30 years of programming C64 demo
Optimizing AAA Games for Mobile Platforms Niklas Smedberg Senior Engine Programmer, Epic Games Who Am I A.k.a. Smedis Epic Games, Unreal Engine 15 years in the industry 30 years of programming C64 demo
Advanced Visual Effects with Direct3D
 Advanced Visual Effects with Direct3D Presenters: Mike Burrows, Sim Dietrich, David Gosselin, Kev Gee, Jeff Grills, Shawn Hargreaves, Richard Huddy, Gary McTaggart, Jason Mitchell, Ashutosh Rege and Matthias
Advanced Visual Effects with Direct3D Presenters: Mike Burrows, Sim Dietrich, David Gosselin, Kev Gee, Jeff Grills, Shawn Hargreaves, Richard Huddy, Gary McTaggart, Jason Mitchell, Ashutosh Rege and Matthias
Basic controls of Rhinoceros 3D software
 lecture 2 Basic controls of Rhinoceros 3D software After the start Rhinoceros 3D software shows basic working area compound by four viewports (show model in other positions), popup menu over, palette menu
lecture 2 Basic controls of Rhinoceros 3D software After the start Rhinoceros 3D software shows basic working area compound by four viewports (show model in other positions), popup menu over, palette menu
Computer Graphics. Introduction. Computer graphics. What is computer graphics? Yung-Yu Chuang
 Introduction Computer Graphics Instructor: Yung-Yu Chuang ( 莊 永 裕 ) E-mail: [email protected] Office: CSIE 527 Grading: a MatchMove project Computer Science ce & Information o Technolog og Yung-Yu Chuang
Introduction Computer Graphics Instructor: Yung-Yu Chuang ( 莊 永 裕 ) E-mail: [email protected] Office: CSIE 527 Grading: a MatchMove project Computer Science ce & Information o Technolog og Yung-Yu Chuang
Introduzione ad OpenGL
 Introduzione ad OpenGL Cosa è OpenGL E una interfaccia so8ware all hardware grafico, rendering API Indipendente dal sistema di windowing Indipendente dal sistema operabvo Evoluzione di OpenGL Viene gesbta
Introduzione ad OpenGL Cosa è OpenGL E una interfaccia so8ware all hardware grafico, rendering API Indipendente dal sistema di windowing Indipendente dal sistema operabvo Evoluzione di OpenGL Viene gesbta
Creating Your Own 3D Models
 14 Creating Your Own 3D Models DAZ 3D has an extensive growing library of 3D models, but there are times that you may not find what you want or you may just want to create your own model. In either case
14 Creating Your Own 3D Models DAZ 3D has an extensive growing library of 3D models, but there are times that you may not find what you want or you may just want to create your own model. In either case
Illustration 1: Diagram of program function and data flow
 The contract called for creation of a random access database of plumbing shops within the near perimeter of FIU Engineering school. The database features a rating number from 1-10 to offer a guideline
The contract called for creation of a random access database of plumbing shops within the near perimeter of FIU Engineering school. The database features a rating number from 1-10 to offer a guideline
Blender addons ESRI Shapefile import/export and georeferenced raster import
 Blender addons ESRI Shapefile import/export and georeferenced raster import This blender addon is a collection of 4 tools: ESRI Shapefile importer - Import point, pointz, polyline, polylinez, polygon,
Blender addons ESRI Shapefile import/export and georeferenced raster import This blender addon is a collection of 4 tools: ESRI Shapefile importer - Import point, pointz, polyline, polylinez, polygon,
Character Creation You can customize a character s look using Mixamo Fuse:
 Using Mixamo Fuse, Mixamo, and 3ds Max, you can create animated characters for use with FlexSim. Character Creation You can customize a character s look using Mixamo Fuse: After creating the character,
Using Mixamo Fuse, Mixamo, and 3ds Max, you can create animated characters for use with FlexSim. Character Creation You can customize a character s look using Mixamo Fuse: After creating the character,
5. Tutorial. Starting FlashCut CNC
 FlashCut CNC Section 5 Tutorial 259 5. Tutorial Starting FlashCut CNC To start FlashCut CNC, click on the Start button, select Programs, select FlashCut CNC 4, then select the FlashCut CNC 4 icon. A dialog
FlashCut CNC Section 5 Tutorial 259 5. Tutorial Starting FlashCut CNC To start FlashCut CNC, click on the Start button, select Programs, select FlashCut CNC 4, then select the FlashCut CNC 4 icon. A dialog
Graphics Input Primitives. 5. Input Devices Introduction to OpenGL. String Choice/Selection Valuator
 4ICT10 Computer Graphics and Virtual Reality 5. Input Devices Introduction to OpenGL Dr Ann McNamara String Choice/Selection Valuator Graphics Input Primitives Locator coordinate pair x,y Pick required
4ICT10 Computer Graphics and Virtual Reality 5. Input Devices Introduction to OpenGL Dr Ann McNamara String Choice/Selection Valuator Graphics Input Primitives Locator coordinate pair x,y Pick required
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 12 (Part 1) Curves. Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics CS 54 Lecture 1 (Part 1) Curves Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) So Far Dealt with straight lines and flat surfaces Real world objects include
Computer Graphics CS 54 Lecture 1 (Part 1) Curves Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) So Far Dealt with straight lines and flat surfaces Real world objects include
Beginning Android 4. Games Development. Mario Zechner. Robert Green
 Beginning Android 4 Games Development Mario Zechner Robert Green Contents Contents at a Glance About the Authors Acknowledgments Introduction iv xii xiii xiv Chapter 1: Android, the New Kid on the Block...
Beginning Android 4 Games Development Mario Zechner Robert Green Contents Contents at a Glance About the Authors Acknowledgments Introduction iv xii xiii xiv Chapter 1: Android, the New Kid on the Block...
NVFX : A NEW SCENE AND MATERIAL EFFECT FRAMEWORK FOR OPENGL AND DIRECTX. TRISTAN LORACH Senior Devtech Engineer SIGGRAPH 2013
 NVFX : A NEW SCENE AND MATERIAL EFFECT FRAMEWORK FOR OPENGL AND DIRECTX TRISTAN LORACH Senior Devtech Engineer SIGGRAPH 2013 nvfx : Plan What is an Effect New Approach and new ideas of nvfx Examples Walkthrough
NVFX : A NEW SCENE AND MATERIAL EFFECT FRAMEWORK FOR OPENGL AND DIRECTX TRISTAN LORACH Senior Devtech Engineer SIGGRAPH 2013 nvfx : Plan What is an Effect New Approach and new ideas of nvfx Examples Walkthrough
Introduction to Computer Graphics with WebGL
 Introduction to Computer Graphics with WebGL Ed Angel Professor Emeritus of Computer Science Founding Director, Arts, Research, Technology and Science Laboratory University of New Mexico 1 Programming
Introduction to Computer Graphics with WebGL Ed Angel Professor Emeritus of Computer Science Founding Director, Arts, Research, Technology and Science Laboratory University of New Mexico 1 Programming
 Edinburgh COLLEGE of ART ARCHITECTURE 3D Modelling in AutoCAD - tutorial exercise The screen The graphics area This is the part of the screen in which the drawing will be created. The command prompt area
Edinburgh COLLEGE of ART ARCHITECTURE 3D Modelling in AutoCAD - tutorial exercise The screen The graphics area This is the part of the screen in which the drawing will be created. The command prompt area
Help on the Embedded Software Block
 Help on the Embedded Software Block Powersim Inc. 1. Introduction The Embedded Software Block is a block that allows users to model embedded devices such as microcontrollers, DSP, or other devices. It
Help on the Embedded Software Block Powersim Inc. 1. Introduction The Embedded Software Block is a block that allows users to model embedded devices such as microcontrollers, DSP, or other devices. It
The main imovie window is divided into six major parts.
 The main imovie window is divided into six major parts. 1. Project Drag clips to the project area to create a timeline 2. Preview Window Displays a preview of your video 3. Toolbar Contains a variety of
The main imovie window is divided into six major parts. 1. Project Drag clips to the project area to create a timeline 2. Preview Window Displays a preview of your video 3. Toolbar Contains a variety of
Optimizing Unity Games for Mobile Platforms. Angelo Theodorou Software Engineer Unite 2013, 28 th -30 th August
 Optimizing Unity Games for Mobile Platforms Angelo Theodorou Software Engineer Unite 2013, 28 th -30 th August Agenda Introduction The author and ARM Preliminary knowledge Unity Pro, OpenGL ES 3.0 Identify
Optimizing Unity Games for Mobile Platforms Angelo Theodorou Software Engineer Unite 2013, 28 th -30 th August Agenda Introduction The author and ARM Preliminary knowledge Unity Pro, OpenGL ES 3.0 Identify
The OpenGL R Graphics System: A Specification (Version 3.3 (Core Profile) - March 11, 2010)
 The OpenGL R Graphics System: A Specification (Version 3.3 (Core Profile) - March 11, 2010) Mark Segal Kurt Akeley Editor (version 1.1): Chris Frazier Editor (versions 1.2-3.3): Jon Leech Editor (version
The OpenGL R Graphics System: A Specification (Version 3.3 (Core Profile) - March 11, 2010) Mark Segal Kurt Akeley Editor (version 1.1): Chris Frazier Editor (versions 1.2-3.3): Jon Leech Editor (version
