HYDRONMR and Fast-HYDRONMR
|
|
|
- Sharlene Ross
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 File:hydronmr7c-pub.doc HYDRONMR and Fast-HYDRONMR Index 1. Introduction to HYDRONMR 2. Literature 3. Running HYDRONMR. Input data file 4. Output files 5. Notes and hints 7. Release notes Version 7c, September Introduction to HYDRONMR and Fast-HYDRONMR HYDRONMR is a computer program intended for the calculation of NMR relaxation of small, quasirigid macromolecules whose structure, with atomic resolution, is taken from a PDB file of atomic coordintes. For this purpose, the basic hydrodynamic quantities that are involved in dynamic NMR are evaluated in the same fashion as in the closely related HYDROPRO program. Then, HYDRONMR calculates NMR quantities like T1, T2, NOE, etc. for each residue of a globular protein (the 15N-H and 13Cα-H vectors are calculated by the program itself. Alternatively, an user-supplied list of vectors can be given. HYDRONMR also reports the translational diffusion coefficient, which is available, among other sources, from some NMR experiments. Fast-HYDRONMR is a version of the same program which employs an approximate, but much faster hydrodynamic treatment. With the cost of a small loss in accuracy, the Fast-HYDRONMR is much faster: less that one second of CPU time, compared with about 3 minutes with HYDRONMR. If CPU times of the order of minutes are acceptable for you (as we expect to be the case for most users), we advise to employ HYDRONMR. The use of Fast-HYDRONMR can be advantageous in situations where calculations have to be done for many structures. We recall that the T1/T2 values obtained with the two programs may be slightly different; however the two procedures give practically the same results for values of the residues. 2. Literature The primary reference for HYDRONMR is: 1
2 J. García de la Torre, M.L. Huertas y B. Carrasco. HYDRONMR: Prediction of NMR relaxation of globular proteins from atomic-level structures and hydrodynamic calculations, Journal of Magnetic Resonance B, 147, (2000). If you employ Fast-HYDRONMR, in addition to the primary reference you also should cite: A. Ortega and J. García de la Torre, Efficient, accurate calculation of rotational difussion and NMR relaxation of globular proteins from atomic-level structures and approximate hydrodynamic calculations, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, (2005). If you wish to cite also the theoretical work on which the bead modeling procedure is based, a proper cite is our 1981 review in Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics. In our 1999 paper in Biophysical Journal, you can find an update of the theory, and a discussion on bead and shell modeling methodologies: J. Garcia de la Torre and V.A. Bloomfield, Hydrodynamic properties of complex, rigid, biological macromolecules. Theory and applications. Q. Rev. Biophy., 14, (1981) B. Carrasco and J. Garcia de la Torre, Hydrodynamic properties of rigid particles. Comparison of different modeling and computational strategies. Biophys. J. 76, (1999). IMPORTANT: HYDRONMR vs. Fast-HYDRONMR The procedures to run both programs are identical. Thus, hereafter we mention just HYDRONMR. The clever corrections that make the approximate hydrodynamics in Fast- HYDRONMR quite accurate are not valid for translational diffusion. Thus, although the present version of the program still report the translational diffusion tensor and coefficient, these results must be ignored. For the calculation of the translational diffusion, please use HYDRONMR or, if you just want translational diffusion, you may simply employ HYDROPRO. 3. Running HYDRONMR. Input data files IMPORTANT: HYDRONMR and Fast-HYDRONMR are used identically. Hereafter we mention just HYDRONMR. As in all the HYDRO family of programs, you will have to supply two input data files: (a) the main input data file, which will specify primary data such as temperature, solvent density, etc.; and (b) a structural data file, which will contain the information about the structure or geometry of the macromolecule or particle that you are considering. In the case of HYDRONMR, the structural file is just the PDB file containing the atomic 2
3 coordinates. The name of the structural file will be one of the data in the main input data file. The name of the main input data file for HYDRONMR will be hydronmr.dat, and it will contain the following lines: 3.a. First part of the input file. Basically this part provides the information on the structure of the macromolecule. It contains the following lines (the FORTRAN types are specified): TITLE(CHARACTER*20) Title of the calculation FILENAME (CHARACTER*30)Name to be used for the various output files corresponding to each subcase in a many-cases execution. The various files produced will have names of the form filename.xxx, where xxx is an extension depending on the file type (see section 4 below). This name would eventually include the path for the files. INPUT (CHARACTER*30) Name of the PDB file with the atomic coordinates, eventually including its path. AER (REAL) Effective radius (angstroms) of the atomic elements [a], [b] HYDRONMR employs the shell-model methodology. The primary hydrodynamic model is not used in the hydrodynamic calculations. Instead, a shell model, composed of minibeads of radius sigma is derived from it, and extrapolation to the shell model limit of sigma=0 is carried out. For this purpose, the following information has to be supplied next in the main input data file NSIG (INTEGER) Number of values of the radius of the minibead. It must be greater than 2 (typically 5 to 8). The radius will range from SIGMIN to SIGMAX.. There is also the possibility of letting to the program the task of estimating the two extreme values of sigma; this will be indicated giving the value 1 for NSIG, and in this case you will omit the two following lines with the values of SIGMIN and SIGMAX. SIGMIN (REAL) Lowest value of sigma, the minibead radius SIGMAX (REAL) Highest value of sigma, the minibead radius The smaller the size of the minibeads, the larger the number of them needed to cover the surface of the particle. The present version of the program works with a maximum of 2000 minibeads. If SIGMIN is too small, an error message will be obtained and the program will stop. The value of SIGMAX should be taken such that the number of minibeads is not too small, say in the range b. Second part of the input file. 3
4 This part provides information on some basic properties of macromolecule and solvent. It contains the following lines: T (REAL) Temperature, Kelvin ETA (REAL) Solvent viscosity, poises 3.c. Third part of the input file. This part is specifically intended for calculation of NMR-related quantities. Presently, this includes: (1) anisotropy of rotational diffusion ; (2) spectral densities and relaxation times for specific dipoles. The first line is: IFLAG (INTEGER) Flag that indicates the source of the vectors (dipoles) for which NMR relaxation parameters and dipolar couplings will be calculated. The possibilities are: * = 0 No calculations for dipoles; only anisotropy of rotational diffusion [c]. *= 1 N-H bonds, implicit hydrogens, not given in pdb [d]. *= 2 N-H bonds, explicit hydrogens, given in pdb. *= 3 C-H bonds, implicit hydrogens, not given in pdb [d]. *= 4 C-H bonds, explicit hydrogens, given in pdb *= 9 Dipoles taken from an user-supplied file If IFLAG=0 the following lines will be omitted. Go to section 3.d. (Only when IFLAG=9) (CHARACTER*30) Name of a (separate) file containing the vectors. The first line will contain NDIP, the number of dipoles (INTEGER, I3). The following NDIP lines will contain the three components of the unitary vectors (REAL, space or comma-separated) GAMMAX (REAL) Gyromagnetic ratio of the X nucleus. RHX (REAL) Distance X-H in angstroms. DIFSIG (REAL) Chemical shift anisotropy, in p.p.m. NFIELD (INTEGER) Number of values of the magnetic field. This line fill be followed by a number of lines equal to NFIEDL, containing: FIELD (REAL) magnetic field, in Teslas 3.D. End of calculation or next case Next or final line: If this case is the only or the final one, in the next line you will put an asterisk followed by 19 spaces. 4
5 4. Output files Several files are produced at execution time. There will be a set of files for each case included in a single run. All these files will have a common name, given by the filename specified for each case in the input file, and a different extension. The extensions correspond to:.res Output file containing the mains results, with the name specified in the input file.t12 Output file containing only the values of T1/T2 and Nabla, ready to be read or imported by other program. Contents is : 1 st line: title; 2 nd line: AER; next line: FIELD; following lines, for each residue, residue number, T1/T2 and ; next line, eventually, another FIELD; and so on. -pri.bea is a pdb-formatted file representing the primary hydrodynamic model, that can be viewed with RASMOL -pri.vrml is a VRML-formatted file containing the coordinates of primary hydrodynamic model, that can be viewed with a VRML viewer, like Cortona(for models with only subunits, without additional spheres). See our separate VisualBeads user Guide. Other files are: NOTE: Do not forget to specify: Display / SpaceFill in the RasMol menu to see the the visualization files. 5. Hints and notes. [a] At the present time a value of 3.2 Angstroms is recommended. [b] The program will take into account all non-hydrogen atoms contained in the ATOM records of the PDB file, including non-protein atoms (HETATM records) except water oxigens. [c] The option IFLAG=0 still produces a complete analysis of the fully anisotropic rotational diffusion tensor, reporting its components, eigenvalues and eigenvectors, etc. [d] In the case of implicit hydrogens, the program will read the coordinates of either the alpha carbon (CA) or the amide nitrogens (N), and their two neighboring atoms in the polypeptide chain. Thus the coordinates of the missing hydrogen will be calculated, and from them the components of the CH or NH vector. 6. Release notes 5
6 The previous released version of HYDRONMR was hydronmr5a-xxx.exe. The main changes in this new version are:.t12 and -pri.vrml files The previous version worked with the so-called estimated extrapolation method for the shell model calculation, intended for a bit faster calculation, which was activated with NSIG=1. Presently, this procedure is being reconsidered. Indeed, Fast- HYDRONMR provides now a much faster procedure.then the estimated extrapolation is not present in this version. However, both HYDRONMR and Fast-HYDRONMR have we also include the convenient special case of automatic estimate of sigmas. (particular case with NSIG=-1). The number of dipoles (C-H or N-H vectors has been redimensioned to 2000). We recall, as noted in Section 2, that Fast-HYDRONMR is not adequate for translational diffusion. The program still reports translational diffusion tensor and coefficient, just because we have not removed the corresponding instructions. If you need translational diffusion, you must use HYDRONMR or HYDROPRO. This program has been developed in a Windows PC. The MS DOS/Windows executable can be started from Windows, but we advise to open a MS DOS session in a window for program execution, while doing the other tasks (editing, visualization, etc) as usually in Windows. Executables of this program will be available for other platforms; please consult our web pages 6
Experiment 13 Molecular Models on a Computer
 Experiment 13 Models on a Computer PRE-LABORATORY QUESTIONS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to laboratory. They are intended to introduce you to several ideas that
Experiment 13 Models on a Computer PRE-LABORATORY QUESTIONS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to laboratory. They are intended to introduce you to several ideas that
Molecular Dynamics Simulations
 Molecular Dynamics Simulations Yaoquan Tu Division of Theoretical Chemistry and Biology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) 2011-06 1 Outline I. Introduction II. Molecular Mechanics Force Field III. Molecular
Molecular Dynamics Simulations Yaoquan Tu Division of Theoretical Chemistry and Biology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) 2011-06 1 Outline I. Introduction II. Molecular Mechanics Force Field III. Molecular
8.1 Relaxation in NMR Spectroscopy
 8.1 Relaxation in NMR Spectroscopy Copyright ans J. Reich 2010 All Rights Reserved University of Wisconsin An understanding of relaxation processes is important for the proper measurement and interpretation
8.1 Relaxation in NMR Spectroscopy Copyright ans J. Reich 2010 All Rights Reserved University of Wisconsin An understanding of relaxation processes is important for the proper measurement and interpretation
NMR - Basic principles
 NMR - Basic principles Subatomic particles like electrons, protons and neutrons are associated with spin - a fundamental property like charge or mass. In the case of nuclei with even number of protons
NMR - Basic principles Subatomic particles like electrons, protons and neutrons are associated with spin - a fundamental property like charge or mass. In the case of nuclei with even number of protons
NMR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
 NMR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is an effect whereby magnetic nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic (EM) energy. This energy is at a specific resonance
NMR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is an effect whereby magnetic nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic (EM) energy. This energy is at a specific resonance
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Introduction: The NMR Spectrum serves as a great resource in determining the structure of an organic compound by revealing the hydrogen and carbon skeleton.
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Introduction: The NMR Spectrum serves as a great resource in determining the structure of an organic compound by revealing the hydrogen and carbon skeleton.
Molecular Visualization. Introduction
 Molecular Visualization Jeffry D. Madura Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry Center for Computational Sciences Duquesne University Introduction Assessments of change, dynamics, and cause and effect
Molecular Visualization Jeffry D. Madura Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry Center for Computational Sciences Duquesne University Introduction Assessments of change, dynamics, and cause and effect
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance ( 1 H-NMR) Spectroscopy
 Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance ( 1 H-NMR) Spectroscopy Theory behind NMR: In the late 1940 s, physical chemists originally developed NMR spectroscopy to study different properties of atomic nuclei,
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance ( 1 H-NMR) Spectroscopy Theory behind NMR: In the late 1940 s, physical chemists originally developed NMR spectroscopy to study different properties of atomic nuclei,
NMR and IR spectra & vibrational analysis
 Lab 5: NMR and IR spectra & vibrational analysis A brief theoretical background 1 Some of the available chemical quantum methods for calculating NMR chemical shifts are based on the Hartree-Fock self-consistent
Lab 5: NMR and IR spectra & vibrational analysis A brief theoretical background 1 Some of the available chemical quantum methods for calculating NMR chemical shifts are based on the Hartree-Fock self-consistent
Spin-Lattice Relaxation Times
 Spin-Lattice Relaxation Times Reading Assignment: T. D. W. Claridge, High Resolution NMR Techniques in Organic Chemistry, Chapter 2; E. Breitmaier, W. Voelter, Carbon 13 NMR Spectroscopy,3rd Ed., 3.3.2.
Spin-Lattice Relaxation Times Reading Assignment: T. D. W. Claridge, High Resolution NMR Techniques in Organic Chemistry, Chapter 2; E. Breitmaier, W. Voelter, Carbon 13 NMR Spectroscopy,3rd Ed., 3.3.2.
Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain.
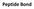 Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Peptide Bond Peptide Bond Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form polypepetide chain. + H 2 O 2 Peptide bonds are strong and not broken by conditions that denature proteins, such as heating.
Section I Using Jmol as a Computer Visualization Tool
 Section I Using Jmol as a Computer Visualization Tool Jmol is a free open source molecular visualization program used by students, teachers, professors, and scientists to explore protein structures. Section
Section I Using Jmol as a Computer Visualization Tool Jmol is a free open source molecular visualization program used by students, teachers, professors, and scientists to explore protein structures. Section
This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are
 This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are put together. 1 A more detailed view of a single protein
This class deals with the fundamental structural features of proteins, which one can understand from the structure of amino acids, and how they are put together. 1 A more detailed view of a single protein
Molar Mass of Polyvinyl Alcohol by Viscosity
 Molar Mass of Polyvinyl Alcohol by Viscosity Introduction Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVOH) is a linear polymer (i. e., it has little branching) of Ethanol monomer units: -CH 2 -CHOH- Unlike most high molar mass
Molar Mass of Polyvinyl Alcohol by Viscosity Introduction Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVOH) is a linear polymer (i. e., it has little branching) of Ethanol monomer units: -CH 2 -CHOH- Unlike most high molar mass
1 Peptide bond rotation
 1 Peptide bond rotation We now consider an application of data mining that has yielded a result that links the quantum scale with the continnum level electrostatic field. In other cases, we have considered
1 Peptide bond rotation We now consider an application of data mining that has yielded a result that links the quantum scale with the continnum level electrostatic field. In other cases, we have considered
Hydrogen Bonds The electrostatic nature of hydrogen bonds
 Hydrogen Bonds Hydrogen bonds have played an incredibly important role in the history of structural biology. Both the structure of DNA and of protein a-helices and b-sheets were predicted based largely
Hydrogen Bonds Hydrogen bonds have played an incredibly important role in the history of structural biology. Both the structure of DNA and of protein a-helices and b-sheets were predicted based largely
PROTON NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY (H-NMR)
 PROTON NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY (H-NMR) WHAT IS H-NMR SPECTROSCOPY? References: Bruice 14.1, 14.2 Introduction NMR or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a technique used to determine
PROTON NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY (H-NMR) WHAT IS H-NMR SPECTROSCOPY? References: Bruice 14.1, 14.2 Introduction NMR or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a technique used to determine
The Experiment Some nuclei have nuclear magnetic moments; just as importantly, some do not
 Chemistry 2600 Lecture Notes Chapter 15 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Page 1 of 23 Structure Determination in Organic Chemistry: NMR Spectroscopy Three main techniques are used to determine the
Chemistry 2600 Lecture Notes Chapter 15 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Page 1 of 23 Structure Determination in Organic Chemistry: NMR Spectroscopy Three main techniques are used to determine the
Viscoelasticity of Polymer Fluids.
 Viscoelasticity of Polymer Fluids. Main Properties of Polymer Fluids. Entangled polymer fluids are polymer melts and concentrated or semidilute (above the concentration c) solutions. In these systems polymer
Viscoelasticity of Polymer Fluids. Main Properties of Polymer Fluids. Entangled polymer fluids are polymer melts and concentrated or semidilute (above the concentration c) solutions. In these systems polymer
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview
 18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
18.2 Protein Structure and Function: An Overview Protein: A large biological molecule made of many amino acids linked together through peptide bonds. Alpha-amino acid: Compound with an amino group bonded
Sizes, shapes and interactions of molecules in solution
 Sizes, shapes and interactions of molecules in solution Light Scattering Analytical Viscometry Ultracentrifugation Steve Harding, NCMH University of Nottingham 1. Molecular weight distribution analysis
Sizes, shapes and interactions of molecules in solution Light Scattering Analytical Viscometry Ultracentrifugation Steve Harding, NCMH University of Nottingham 1. Molecular weight distribution analysis
Visualizing molecular simulations
 Visualizing molecular simulations ChE210D Overview Visualization plays a very important role in molecular simulations: it enables us to develop physical intuition about the behavior of a system that is
Visualizing molecular simulations ChE210D Overview Visualization plays a very important role in molecular simulations: it enables us to develop physical intuition about the behavior of a system that is
Molecular Spectroscopy
 Molecular Spectroscopy UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Some Common Chromophores UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds UV-Vis Spectroscopy Effect of extended
Molecular Spectroscopy UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Some Common Chromophores UV-Vis Spectroscopy Absorption Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds UV-Vis Spectroscopy Effect of extended
NMR for Physical and Biological Scientists Thomas C. Pochapsky and Susan Sondej Pochapsky Table of Contents
 Preface Symbols and fundamental constants 1. What is spectroscopy? A semiclassical description of spectroscopy Damped harmonics Quantum oscillators The spectroscopic experiment Ensembles and coherence
Preface Symbols and fundamental constants 1. What is spectroscopy? A semiclassical description of spectroscopy Damped harmonics Quantum oscillators The spectroscopic experiment Ensembles and coherence
Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture
 CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
CPS260/BGT204.1 Algorithms in Computational Biology November 04, 2003 Lecture 19: Proteins, Primary Struture Lecturer: Pankaj K. Agarwal Scribe: Qiuhua Liu 19.1 The Building Blocks of Protein [1] Proteins
Lecture #7 (2D NMR) Utility of Resonance Assignments
 Lecture #7 (2D NMR) Basics of multidimensional NMR (2D NMR) 2D NOESY, COSY and TOCSY 2/23/15 Utility of Resonance Assignments Resonance Assignments: Assignment of frequency positions of resonances (peaks)
Lecture #7 (2D NMR) Basics of multidimensional NMR (2D NMR) 2D NOESY, COSY and TOCSY 2/23/15 Utility of Resonance Assignments Resonance Assignments: Assignment of frequency positions of resonances (peaks)
Structure Determination
 5 Structure Determination Most of the protein structures described and discussed in this book have been determined either by X-ray crystallography or by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Although
5 Structure Determination Most of the protein structures described and discussed in this book have been determined either by X-ray crystallography or by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Although
Predicting Magnetic Properties with ChemDraw and Gaussian
 Predicting Magnetic Properties with ChemDraw and Gaussian By James R. Cheeseman and Æleen Frisch Introduction NMR chemical shifts are an important tool in characterizing molecular systems and structures.
Predicting Magnetic Properties with ChemDraw and Gaussian By James R. Cheeseman and Æleen Frisch Introduction NMR chemical shifts are an important tool in characterizing molecular systems and structures.
Structure Tools and Visualization
 Structure Tools and Visualization Gary Van Domselaar University of Alberta [email protected] Slides Adapted from Michel Dumontier, Blueprint Initiative 1 Visualization & Communication Visualization
Structure Tools and Visualization Gary Van Domselaar University of Alberta [email protected] Slides Adapted from Michel Dumontier, Blueprint Initiative 1 Visualization & Communication Visualization
Chemical Bonds and Groups - Part 1
 hemical Bonds and Groups - Part 1 ARB SKELETS arbon has a unique role in the cell because of its ability to form strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Thus carbon atoms can join to form chains.
hemical Bonds and Groups - Part 1 ARB SKELETS arbon has a unique role in the cell because of its ability to form strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Thus carbon atoms can join to form chains.
Carbon-organic Compounds
 Elements in Cells The living substance of cells is made up of cytoplasm and the structures within it. About 96% of cytoplasm and its included structures are composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
Elements in Cells The living substance of cells is made up of cytoplasm and the structures within it. About 96% of cytoplasm and its included structures are composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,
Determination of Equilibrium Constants using NMR Spectroscopy
 CHEM 331L Physical Chemistry Laboratory Revision 2.1 Determination of Equilibrium Constants using NMR Spectroscopy In this laboratory exercise we will measure the equilibrium constant for the cis-trans
CHEM 331L Physical Chemistry Laboratory Revision 2.1 Determination of Equilibrium Constants using NMR Spectroscopy In this laboratory exercise we will measure the equilibrium constant for the cis-trans
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 CHEM 334L Organic Chemistry Laboratory Revision 2.0 Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy In this laboratory exercise we will learn how to use the Chemistry Department's Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
CHEM 334L Organic Chemistry Laboratory Revision 2.0 Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy In this laboratory exercise we will learn how to use the Chemistry Department's Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
NMR Spectroscopy in Notre Dame
 NMR Spectroscopy in Notre Dame University of Notre Dame College of Science Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Facility http://www.nd.edu/~nmr Reservation system for spectrometers
NMR Spectroscopy in Notre Dame University of Notre Dame College of Science Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Facility http://www.nd.edu/~nmr Reservation system for spectrometers
Natively Disordered Proteins
 Natively Disordered Proteins 1 Gary W. Daughdrill, 2 Gary J. Pielak, 3 Vladimir N. Uversky, 4 Marc S. Cortese, and 4 A. Keith Dunker 1 Department of Microbiology, Molecular Biology, and Biochemistry, University
Natively Disordered Proteins 1 Gary W. Daughdrill, 2 Gary J. Pielak, 3 Vladimir N. Uversky, 4 Marc S. Cortese, and 4 A. Keith Dunker 1 Department of Microbiology, Molecular Biology, and Biochemistry, University
Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction
 Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction The function and chemical properties of proteins are determined by its three-dimensional structure. The final architecture of the protein
Role of Hydrogen Bonding on Protein Secondary Structure Introduction The function and chemical properties of proteins are determined by its three-dimensional structure. The final architecture of the protein
FTIR Analysis of Protein Structure
 FTIR Analysis of Protein Structure Warren Gallagher A. Introduction to protein structure The first structures of proteins at an atomic resolution were determined in the late 1950 s. 1 From that time to
FTIR Analysis of Protein Structure Warren Gallagher A. Introduction to protein structure The first structures of proteins at an atomic resolution were determined in the late 1950 s. 1 From that time to
Structures of Proteins. Primary structure - amino acid sequence
 Structures of Proteins Primary structure - amino acid sequence Secondary structure chain of covalently linked amino acids folds into regularly repeating structures. Secondary structure is the result of
Structures of Proteins Primary structure - amino acid sequence Secondary structure chain of covalently linked amino acids folds into regularly repeating structures. Secondary structure is the result of
Communicated March 31, 1951 CHR CHR CHR. *H* zz '" *H _ 0.-...H / k C,.. CHR CNR CHR CHR CHR *HN/' N 'H_N/' H_./ - H-(H.
 VOL. 37, 1951 CHEMISTR Y: PA ULING AND COREY 251 THE PLEATED SHEET, A NEW LAYER CONFIGURATION OF POL YPEPTIDE CHAINS BY LINUS PAULING AND ROBERT B. COREY GATES AND CRELLIN LABORATORIES OF CHEMISTRY,* CALIFORNIA
VOL. 37, 1951 CHEMISTR Y: PA ULING AND COREY 251 THE PLEATED SHEET, A NEW LAYER CONFIGURATION OF POL YPEPTIDE CHAINS BY LINUS PAULING AND ROBERT B. COREY GATES AND CRELLIN LABORATORIES OF CHEMISTRY,* CALIFORNIA
Determination of Equilibrium Constants using NMR Spectrscopy
 CHEM 331L Physical Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.0 Determination of Equilibrium Constants using NMR Spectrscopy In this laboratory exercise we will measure a chemical equilibrium constant using key proton
CHEM 331L Physical Chemistry Laboratory Revision 1.0 Determination of Equilibrium Constants using NMR Spectrscopy In this laboratory exercise we will measure a chemical equilibrium constant using key proton
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
 INTERMOLECULAR FORCES Intermolecular forces- forces of attraction and repulsion between molecules that hold molecules, ions, and atoms together. Intramolecular - forces of chemical bonds within a molecule
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES Intermolecular forces- forces of attraction and repulsion between molecules that hold molecules, ions, and atoms together. Intramolecular - forces of chemical bonds within a molecule
Proton NMR. One Dimensional H-NMR. Cl S. Common types of NMR experiments: 1-H NMR
 Common types of NMR experiments: 1- NMR Proton NMR ne Dimensional -NMR a. Experiment igh field proton NMR (400Mz). single-pulse experiment. b. Spectral nterpretation i. Number of multiplets gives the different
Common types of NMR experiments: 1- NMR Proton NMR ne Dimensional -NMR a. Experiment igh field proton NMR (400Mz). single-pulse experiment. b. Spectral nterpretation i. Number of multiplets gives the different
Spin-lattice and spin-spin relaxation
 Spin-lattice and spin-spin relaation Sequence of events in the NMR eperiment: (i) application of a 90 pulse alters the population ratios, and creates transverse magnetic field components (M () ); (ii)
Spin-lattice and spin-spin relaation Sequence of events in the NMR eperiment: (i) application of a 90 pulse alters the population ratios, and creates transverse magnetic field components (M () ); (ii)
HOW TO MAKE YOUR WEBSITE
 HOW TO MAKE YOUR WEBSITE Use Netscape Composer to make your web page presentation of a 3D structure of your choosing. You will need to download a few template web pages from the biochemistry website, and
HOW TO MAKE YOUR WEBSITE Use Netscape Composer to make your web page presentation of a 3D structure of your choosing. You will need to download a few template web pages from the biochemistry website, and
13C NMR Spectroscopy
 13 C NMR Spectroscopy Introduction Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the most powerful tool available for structural determination. A nucleus with an odd number of protons, an odd number
13 C NMR Spectroscopy Introduction Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the most powerful tool available for structural determination. A nucleus with an odd number of protons, an odd number
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR is probably the most useful and powerful technique for identifying and characterizing organic compounds. Felix Bloch and Edward Mills Purcell were awarded the 1952 Nobel
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR is probably the most useful and powerful technique for identifying and characterizing organic compounds. Felix Bloch and Edward Mills Purcell were awarded the 1952 Nobel
Amino Acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain. Alpha Carbon. Carboxyl. Group.
 Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Protein Structure Amino Acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA s have the same basic structure: Side Chain Alpha Carbon Amino Group Carboxyl Group Amino Acid Properties There are
Chapter 13 - LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS
 Chapter 13 - LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Problems to try at end of chapter: Answers in Appendix I: 1,3,5,7b,9b,15,17,23,25,29,31,33,45,49,51,53,61 13.1 Properties of Liquids 1. Liquids take the shape of their container,
Chapter 13 - LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Problems to try at end of chapter: Answers in Appendix I: 1,3,5,7b,9b,15,17,23,25,29,31,33,45,49,51,53,61 13.1 Properties of Liquids 1. Liquids take the shape of their container,
Protein Dynamics by NMR. Why NMR is the best!
 Protein Dynamics by NMR Why NMR is the best! Key Points NMR dynamics divided into 2 regimes: fast and slow. How protein mobons affect NMR parameters depend on whether they are faster or slower than the
Protein Dynamics by NMR Why NMR is the best! Key Points NMR dynamics divided into 2 regimes: fast and slow. How protein mobons affect NMR parameters depend on whether they are faster or slower than the
Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson
 Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\00bondingtrans.doc The Nature of Bonding Types 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic 4. Coordinate covalent Driving
Bonding & Molecular Shape Ron Robertson r2 n:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 possible slides for web\00bondingtrans.doc The Nature of Bonding Types 1. Ionic 2. Covalent 3. Metallic 4. Coordinate covalent Driving
NMR practice times. Mo 2---8 pm Jim 2-4:30 Ning 4:30-7. Tues 2--- 8 pm Jianing 2-4:30 Ting 4:30-7. Fri 10- --- 7 Donia 10-12:00 Ilya 2-4
 NMR practice times 1 Mo 2---8 pm Jim 2-4:30 Ning 4:30-7 Tues 2--- 8 pm Jianing 2-4:30 Ting 4:30-7 Wed 4:30---8 John 5:00-7:30 Fri 10- --- 7 Donia 10-12:00 Ilya 2-4 Samples are listed in the homework along
NMR practice times 1 Mo 2---8 pm Jim 2-4:30 Ning 4:30-7 Tues 2--- 8 pm Jianing 2-4:30 Ting 4:30-7 Wed 4:30---8 John 5:00-7:30 Fri 10- --- 7 Donia 10-12:00 Ilya 2-4 Samples are listed in the homework along
PROTEINS THE PEPTIDE BOND. The peptide bond, shown above enclosed in the blue curves, generates the basic structural unit for proteins.
 Ca 2+ The contents of this module were developed under grant award # P116B-001338 from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), United States Department of Education. However, those
Ca 2+ The contents of this module were developed under grant award # P116B-001338 from the Fund for the Improvement of Postsecondary Education (FIPSE), United States Department of Education. However, those
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION General.. 1 1 HNMR titration fitplots.. 2 1 HNMR titration Job plots... 2 1 HNMR spectra of 1 + TBAacetate. 3 Isothermal Titration Calorimetry.. 3 High Resolution Mass
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION General.. 1 1 HNMR titration fitplots.. 2 1 HNMR titration Job plots... 2 1 HNMR spectra of 1 + TBAacetate. 3 Isothermal Titration Calorimetry.. 3 High Resolution Mass
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Two Forms of Energy
 Module 2D - Energy and Metabolism Objective # 19 All living organisms require energy for survival. In this module we will examine some general principles about chemical reactions and energy usage within
Module 2D - Energy and Metabolism Objective # 19 All living organisms require energy for survival. In this module we will examine some general principles about chemical reactions and energy usage within
file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/terry/Desktop/DOCK%20website/terry/Old%20Versions/dock4.0_faq.txt
 -- X. Zou, 6/28/1999 -- Questions on installation of DOCK4.0.1: ======================================= Q. Can I run DOCK on platforms other than SGI (e.g., SparcStations, DEC Stations, Pentium, etc.)?
-- X. Zou, 6/28/1999 -- Questions on installation of DOCK4.0.1: ======================================= Q. Can I run DOCK on platforms other than SGI (e.g., SparcStations, DEC Stations, Pentium, etc.)?
Effects of Temperature, Pressure and Water Vapor on Gas Phase Infrared Absorption by CO 2
 Effects of Temperature, Pressure and Water Vapor on Gas Phase Infrared Absorption by CO 2 D. K. McDermitt, J. M. Welles, and R. D. Eckles - LI-COR, inc. Lincoln, NE 68504 USA Introduction Infrared analysis
Effects of Temperature, Pressure and Water Vapor on Gas Phase Infrared Absorption by CO 2 D. K. McDermitt, J. M. Welles, and R. D. Eckles - LI-COR, inc. Lincoln, NE 68504 USA Introduction Infrared analysis
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2
 Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
Chemical Basis of Life Module A Anchor 2 Key Concepts: - Water is a polar molecule. Therefore, it is able to form multiple hydrogen bonds, which account for many of its special properties. - Water s polarity
The Four Questions to Ask While Interpreting Spectra. 1. How many different environments are there?
 1 H NMR Spectroscopy (#1c) The technique of 1 H NMR spectroscopy is central to organic chemistry and other fields involving analysis of organic chemicals, such as forensics and environmental science. It
1 H NMR Spectroscopy (#1c) The technique of 1 H NMR spectroscopy is central to organic chemistry and other fields involving analysis of organic chemicals, such as forensics and environmental science. It
DO PHYSICS ONLINE FROM QUANTA TO QUARKS QUANTUM (WAVE) MECHANICS
 DO PHYSICS ONLINE FROM QUANTA TO QUARKS QUANTUM (WAVE) MECHANICS Quantum Mechanics or wave mechanics is the best mathematical theory used today to describe and predict the behaviour of particles and waves.
DO PHYSICS ONLINE FROM QUANTA TO QUARKS QUANTUM (WAVE) MECHANICS Quantum Mechanics or wave mechanics is the best mathematical theory used today to describe and predict the behaviour of particles and waves.
Chem 112 Intermolecular Forces Chang From the book (10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20,84,92,94,102,104, 108, 112, 114, 118 and 134)
 Chem 112 Intermolecular Forces Chang From the book (10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20,84,92,94,102,104, 108, 112, 114, 118 and 134) 1. Helium atoms do not combine to form He 2 molecules, What is the strongest attractive
Chem 112 Intermolecular Forces Chang From the book (10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20,84,92,94,102,104, 108, 112, 114, 118 and 134) 1. Helium atoms do not combine to form He 2 molecules, What is the strongest attractive
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Experimental Methods for Macromolecular Structure Determination
 Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Experimental Methods for Macromolecular Structure Determination Introduction Knowing the exact 3D-structure of bio-molecules is essential for any attempt to understand
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Experimental Methods for Macromolecular Structure Determination Introduction Knowing the exact 3D-structure of bio-molecules is essential for any attempt to understand
VMD - High Resolution Graphics
 Biochem 660 2008 131 VMD - High Resolution Graphics VMD (http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/research/vmd/) is a free program developed at the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group at the University of Illinois
Biochem 660 2008 131 VMD - High Resolution Graphics VMD (http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/research/vmd/) is a free program developed at the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group at the University of Illinois
INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE
 Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
Name Class: Partner, if any: INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PRIMARY STRUCTURE: 1. Write the complete structural formula of the tripeptide shown (frame 10). Circle and label the three sidechains which
Symmetric Stretch: allows molecule to move through space
 BACKGROUND INFORMATION Infrared Spectroscopy Before introducing the subject of IR spectroscopy, we must first review some aspects of the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is composed
BACKGROUND INFORMATION Infrared Spectroscopy Before introducing the subject of IR spectroscopy, we must first review some aspects of the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is composed
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR)
 INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR) Theory and Interpretation of IR spectra ASSIGNED READINGS Introduction to technique 25 (p. 833-834 in lab textbook) Uses of the Infrared Spectrum (p. 847-853) Look over pages
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR) Theory and Interpretation of IR spectra ASSIGNED READINGS Introduction to technique 25 (p. 833-834 in lab textbook) Uses of the Infrared Spectrum (p. 847-853) Look over pages
For example: (Example is from page 50 of the Thinkbook)
 SOLVING COMBINED SPECTROSCOPY PROBLEMS: Lecture Supplement: page 50-53 in Thinkbook CFQ s and PP s: page 216 241 in Thinkbook Introduction: The structure of an unknown molecule can be determined using
SOLVING COMBINED SPECTROSCOPY PROBLEMS: Lecture Supplement: page 50-53 in Thinkbook CFQ s and PP s: page 216 241 in Thinkbook Introduction: The structure of an unknown molecule can be determined using
SIZE OF A MOLECULE FROM A VISCOSITY MEASUREMENT
 Experiment 8, page 1 Version of April 25, 216 Experiment 446.8 SIZE OF A MOLECULE FROM A VISCOSITY MEASUREMENT Theory Viscous Flow. Fluids attempt to minimize flow gradients by exerting a frictional force,
Experiment 8, page 1 Version of April 25, 216 Experiment 446.8 SIZE OF A MOLECULE FROM A VISCOSITY MEASUREMENT Theory Viscous Flow. Fluids attempt to minimize flow gradients by exerting a frictional force,
Center of Gravity. We touched on this briefly in chapter 7! x 2
 Center of Gravity We touched on this briefly in chapter 7! x 1 x 2 cm m 1 m 2 This was for what is known as discrete objects. Discrete refers to the fact that the two objects separated and individual.
Center of Gravity We touched on this briefly in chapter 7! x 1 x 2 cm m 1 m 2 This was for what is known as discrete objects. Discrete refers to the fact that the two objects separated and individual.
Peptide Bonds: Structure
 Peptide Bonds: Structure Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence, from - to C-terminus, determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide
Peptide Bonds: Structure Peptide primary structure The amino acid sequence, from - to C-terminus, determines the primary structure of a peptide or protein. The amino acids are linked through amide or peptide
Chapter 5 Student Reading
 Chapter 5 Student Reading THE POLARITY OF THE WATER MOLECULE Wonderful water Water is an amazing substance. We drink it, cook and wash with it, swim and play in it, and use it for lots of other purposes.
Chapter 5 Student Reading THE POLARITY OF THE WATER MOLECULE Wonderful water Water is an amazing substance. We drink it, cook and wash with it, swim and play in it, and use it for lots of other purposes.
Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Dr. Dean L. Olson, NMR Lab Director School of Chemical Sciences University of Illinois Called figures, equations, and tables are from Principles
Introduction to Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Dr. Dean L. Olson, NMR Lab Director School of Chemical Sciences University of Illinois Called figures, equations, and tables are from Principles
NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds (#1e)
 NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds (#1e) 1 H NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds Erich Hückel s study of aromaticity in the 1930s produced a set of rules for determining whether a compound is aromatic.
NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds (#1e) 1 H NMR Spectroscopy of Aromatic Compounds Erich Hückel s study of aromaticity in the 1930s produced a set of rules for determining whether a compound is aromatic.
The Role of Electric Polarization in Nonlinear optics
 The Role of Electric Polarization in Nonlinear optics Sumith Doluweera Department of Physics University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, Ohio 45221 Abstract Nonlinear optics became a very active field of research
The Role of Electric Polarization in Nonlinear optics Sumith Doluweera Department of Physics University of Cincinnati Cincinnati, Ohio 45221 Abstract Nonlinear optics became a very active field of research
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING
 CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
CHEMISTRY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING Essential Standard: STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE PROPERTIES OF MATTER AND THEIR INTERACTIONS ARE A CONSEQUENCE OF THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER,
Molecular Models in Biology
 Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
Molecular Models in Biology Objectives: After this lab a student will be able to: 1) Understand the properties of atoms that give rise to bonds. 2) Understand how and why atoms form ions. 3) Model covalent,
Organic Chemistry Tenth Edition
 Organic Chemistry Tenth Edition T. W. Graham Solomons Craig B. Fryhle Welcome to CHM 22 Organic Chemisty II Chapters 2 (IR), 9, 3-20. Chapter 2 and Chapter 9 Spectroscopy (interaction of molecule with
Organic Chemistry Tenth Edition T. W. Graham Solomons Craig B. Fryhle Welcome to CHM 22 Organic Chemisty II Chapters 2 (IR), 9, 3-20. Chapter 2 and Chapter 9 Spectroscopy (interaction of molecule with
How do we determine which molecule is more basic?
 How do we determine which molecule is more basic? One way to determine is by considering molecules structure, because structure can affect basicity of a molecule. Let s start with this concept. Higher
How do we determine which molecule is more basic? One way to determine is by considering molecules structure, because structure can affect basicity of a molecule. Let s start with this concept. Higher
Lecture 24 - Surface tension, viscous flow, thermodynamics
 Lecture 24 - Surface tension, viscous flow, thermodynamics Surface tension, surface energy The atoms at the surface of a solid or liquid are not happy. Their bonding is less ideal than the bonding of atoms
Lecture 24 - Surface tension, viscous flow, thermodynamics Surface tension, surface energy The atoms at the surface of a solid or liquid are not happy. Their bonding is less ideal than the bonding of atoms
How to Quickly Solve Spectrometry Problems
 How to Quickly Solve Spectrometry Problems You should be looking for: Mass Spectrometry (MS) Chemical Formula DBE Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) Important Functional Groups o Alcohol O-H o Carboxylic Acid
How to Quickly Solve Spectrometry Problems You should be looking for: Mass Spectrometry (MS) Chemical Formula DBE Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) Important Functional Groups o Alcohol O-H o Carboxylic Acid
C has 4 valence electrons, O has six electrons. The total number of electrons is 4 + 2(6) = 16.
 129 Lewis Structures G. N. Lewis hypothesized that electron pair bonds between unlike elements in the second (and sometimes the third) row occurred in a way that electrons were shared such that each element
129 Lewis Structures G. N. Lewis hypothesized that electron pair bonds between unlike elements in the second (and sometimes the third) row occurred in a way that electrons were shared such that each element
EXPERIMENT 9 Dot Structures and Geometries of Molecules
 EXPERIMENT 9 Dot Structures and Geometries of Molecules INTRODUCTION Lewis dot structures are our first tier in drawing molecules and representing bonds between the atoms. The method was first published
EXPERIMENT 9 Dot Structures and Geometries of Molecules INTRODUCTION Lewis dot structures are our first tier in drawing molecules and representing bonds between the atoms. The method was first published
Solving Spectroscopy Problems
 Solving Spectroscopy Problems The following is a detailed summary on how to solve spectroscopy problems, key terms are highlighted in bold and the definitions are from the illustrated glossary on Dr. Hardinger
Solving Spectroscopy Problems The following is a detailed summary on how to solve spectroscopy problems, key terms are highlighted in bold and the definitions are from the illustrated glossary on Dr. Hardinger
Structure of proteins
 Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
Structure of proteins Primary structure: is amino acids sequence or the covalent structure (50-2500) amino acids M.Wt. of amino acid=110 Dalton (56 110=5610 Dalton). Single chain or more than one polypeptide
Prof.M.Perucca CORSO DI APPROFONDIMENTO DI FISICA ATOMICA: (III-INCONTRO) RISONANZA MAGNETICA NUCLEARE
 Prof.M.Perucca CORSO DI APPROFONDIMENTO DI FISICA ATOMICA: (III-INCONTRO) RISONANZA MAGNETICA NUCLEARE SUMMARY (I/II) Angular momentum and the spinning gyroscope stationary state equation Magnetic dipole
Prof.M.Perucca CORSO DI APPROFONDIMENTO DI FISICA ATOMICA: (III-INCONTRO) RISONANZA MAGNETICA NUCLEARE SUMMARY (I/II) Angular momentum and the spinning gyroscope stationary state equation Magnetic dipole
The Mole Concept. The Mole. Masses of molecules
 The Mole Concept Ron Robertson r2 c:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 final slides for web\mole concept.docx The Mole The mole is a unit of measurement equal to 6.022 x 10 23 things (to 4 sf) just like there
The Mole Concept Ron Robertson r2 c:\files\courses\1110-20\2010 final slides for web\mole concept.docx The Mole The mole is a unit of measurement equal to 6.022 x 10 23 things (to 4 sf) just like there
Examination of Proton NMR Spectra
 Examination of Proton NMR Spectra What to Look For 1) Number of Signals --- indicates how many "different kinds" of protons are present. 2) Positions of the Signals --- indicates something about magnetic
Examination of Proton NMR Spectra What to Look For 1) Number of Signals --- indicates how many "different kinds" of protons are present. 2) Positions of the Signals --- indicates something about magnetic
Infrared Spectroscopy: Theory
 u Chapter 15 Infrared Spectroscopy: Theory An important tool of the organic chemist is Infrared Spectroscopy, or IR. IR spectra are acquired on a special instrument, called an IR spectrometer. IR is used
u Chapter 15 Infrared Spectroscopy: Theory An important tool of the organic chemist is Infrared Spectroscopy, or IR. IR spectra are acquired on a special instrument, called an IR spectrometer. IR is used
Lecture Overview. Hydrogen Bonds. Special Properties of Water Molecules. Universal Solvent. ph Scale Illustrated. special properties of water
 Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Lecture Overview special properties of water > water as a solvent > ph molecules of the cell > properties of carbon > carbohydrates > lipids > proteins > nucleic acids Hydrogen Bonds polarity of water
Shielding vs. Deshielding:
 Shielding vs. Deshielding: Pre-tutorial: Things we need to know before we start the topic: What does the NMR Chemical shift do? The chemical shift is telling us the strength of the magnetic field that
Shielding vs. Deshielding: Pre-tutorial: Things we need to know before we start the topic: What does the NMR Chemical shift do? The chemical shift is telling us the strength of the magnetic field that
4. It is possible to excite, or flip the nuclear magnetic vector from the α-state to the β-state by bridging the energy gap between the two. This is a
 BASIC PRINCIPLES INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (NMR) 1. The nuclei of certain atoms with odd atomic number, and/or odd mass behave as spinning charges. The nucleus is the center of positive
BASIC PRINCIPLES INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (NMR) 1. The nuclei of certain atoms with odd atomic number, and/or odd mass behave as spinning charges. The nucleus is the center of positive
7. 1.00 atm = 760 torr = 760 mm Hg = 101.325 kpa = 14.70 psi. = 0.446 atm. = 0.993 atm. = 107 kpa 760 torr 1 atm 760 mm Hg = 790.
 CHATER 3. The atmosphere is a homogeneous mixture (a solution) of gases.. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. have volumes that depend on their conditions,
CHATER 3. The atmosphere is a homogeneous mixture (a solution) of gases.. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. have volumes that depend on their conditions,
= 1.038 atm. 760 mm Hg. = 0.989 atm. d. 767 torr = 767 mm Hg. = 1.01 atm
 Chapter 13 Gases 1. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. Gases have volumes that depend on their conditions, and can be compressed or expanded by
Chapter 13 Gases 1. Solids and liquids have essentially fixed volumes and are not able to be compressed easily. Gases have volumes that depend on their conditions, and can be compressed or expanded by
7-5.5. Translate chemical symbols and the chemical formulas of common substances to show the component parts of the substances including:
 7-5.5 Translate chemical symbols and the chemical formulas of common substances to show the component parts of the substances including: NaCl [salt], H 2 O [water], C 6 H 12 O 6 [simple sugar], O 2 [oxygen
7-5.5 Translate chemical symbols and the chemical formulas of common substances to show the component parts of the substances including: NaCl [salt], H 2 O [water], C 6 H 12 O 6 [simple sugar], O 2 [oxygen
Health Science Chemistry I CHEM-1180 Experiment No. 15 Molecular Models (Revised 05/22/2015)
 (Revised 05/22/2015) Introduction In the early 1900s, the chemist G. N. Lewis proposed that bonds between atoms consist of two electrons apiece and that most atoms are able to accommodate eight electrons
(Revised 05/22/2015) Introduction In the early 1900s, the chemist G. N. Lewis proposed that bonds between atoms consist of two electrons apiece and that most atoms are able to accommodate eight electrons
CHEMISTRY GAS LAW S WORKSHEET
 Boyle s Law Charles Law Guy-Lassac's Law Combined Gas Law For a given mass of gas at constant temperature, the volume of a gas varies inversely with pressure PV = k The volume of a fixed mass of gas is
Boyle s Law Charles Law Guy-Lassac's Law Combined Gas Law For a given mass of gas at constant temperature, the volume of a gas varies inversely with pressure PV = k The volume of a fixed mass of gas is
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Introduction NMR is the most powerful tool available for organic structure determination. It is used to study a wide variety of nuclei: 1 H 13 C 15 N 19 F 31 P 2
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Introduction NMR is the most powerful tool available for organic structure determination. It is used to study a wide variety of nuclei: 1 H 13 C 15 N 19 F 31 P 2
Analysis, post-processing and visualization tools
 Analysis, post-processing and visualization tools Javier Junquera Andrei Postnikov Summary of different tools for post-processing and visualization DENCHAR PLRHO DOS, PDOS DOS and PDOS total Fe, d MACROAVE
Analysis, post-processing and visualization tools Javier Junquera Andrei Postnikov Summary of different tools for post-processing and visualization DENCHAR PLRHO DOS, PDOS DOS and PDOS total Fe, d MACROAVE
Molecular Models Experiment #1
 Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
Molecular Models Experiment #1 Objective: To become familiar with the 3-dimensional structure of organic molecules, especially the tetrahedral structure of alkyl carbon atoms and the planar structure of
