Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location. Controls user connection. Transmission.
|
|
|
- Morgan Stephens
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission
3 Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part of RR, not MM! $! " # $ % & %&& # # # #
4 " $ # ' # & ( $ # # " % # #
5 '(##()) $ # # ) * + * +! ', %' # # - #
6 CM MM GMSC RR HLR Trans. MS BTS BSC MSC (VLR)
7 MS BTS BSC Relay MSC Anchor MSC HLR CM MM RIL3-CC RIL3-MM MAP/D RR RIL3-RR RSM BSSMAP MAP/E TCAP SCCP SCCP SCCP LAPDm LAPD MTP MTP MTP! "! "
8 * +#,
9 BTS 2 BTS 1 BTS n - $. $ / 0 * ) 1 * ) 22+ # $ At least once every 5 minutes BSIC (from SCH) refreshed every at most 30s
10 max! C1(n) = RXLEV(n) RXLEV_ACCESS_MIN Select cell with greatest c1(n)>0: [ 0, ( MS_TXPWR_MAX_CCH P) ] # $ % &' ( ) &' # $ % * $ * + ( ) (, " $ 3 $ * # - * # *. / ) ). $ 3 $ 9 7,9 5 / ) & ' When cell parameters are the same, simply select cell with higher RXLEV!
11 "#$ & '*./ C2(n) = C1(n) + CELL_RESELECT_OFFSET TEMPORARY_OFFSET H(PENALTY_TIME 0 where H(x) = 1 x x < 0 0 T) ( ) " $ + 3 * $ 4 $ * $ $ $ * $ 4 $ 5 3 * $. $ * $ $ $ * $ 6, " 7 & ' : 2 4 ) " " & " '
12 % & BTS BTS 0()1 No need to inform BTS at all! 23# : $ ( ; $ Need to inform the network! - < = ) ( ( > ) # ) ( ) >? # ) ) # '#
13 '( ) 45)(45)( # / # 6 0. (, Based on radio link quality measurements. ( / $, $ 7# $ $ Not possible in GSM: for about ms, communication is interrupted $ Not possible in GSM; possible in UMTS
14 )'* *&'( before during after Hard handover (GSM) MSC BSS 1 BSS 2 f 1 MS MSC BSS 1 BSS 2 f 1 MS MSC BSS 1 BSS 2 MS f 2 Seamless (DECT) MSC BSS 1 BSS 2 MSC BSS 1 BSS 2 MSC BSS 1 BSS 2 f 1 MS f 1 MS f 2 MS f 2 Soft handover (UMTS) MSC BSS 1 BSS 2 f 1 MS f 1 MSC BSS 1 BSS 2 f 1 MS f 1 MSC BSS 1 BSS 2 MS f 1
15 )'( & Classification by motivation & +, *! ' 5 +", *, Classification by typology 7 ', # New radio channel in the same cell Not termed as handover but as subsequent assignment ', # ', # Under control of same BSC 23 ', # ',# Change reference BSC; may imply a location area update ',# Most complex: need to change MSC
16 &'( Switching point for all inter-msc handover Switching point for internal handover Anchor MSC: the MSC that first managed the current call A-MSC BSC Relay MSC: the MSC that currently manages the call BSC R-MSC BSC A A-bis Switching point for inter-bsc handover BTS BTS BTS BTS radio interface
17 )'(+ # ) # ) ) #!)4'68-68 / # / # # B / #,#,# $ $
18 )'( #45) ; $,/ # RXLEV_UL < L_RXLEV_UL_H ; $,/! ) # RXQUAL_UL < L_RXQUAL_UL_H * # # adaptive timing advance parameter > MAX_MS_RANGE ' 2 #) *,/ RXLEV_DL < L_RXLEV_DL_H *,/! ) RXQUAL_DL < L_RXQUAL_DL_H *,/ RXLEV_NCELL(n) > RXLEV_MIN(n) RX signal level RXLEV_0 RXLEV_1 RXLEV_2 RXLEV_3 RXLEV_62 RXLEV_63 Bit error Ratio RXQUAL_0 RXQUAL_1 RXQUAL_2 RXQUAL_3 RXQUAL_4 RXQUAL_5 RXQUAL_6 From (dbm) From (%) To (dbm) To (%) RXQUAL_
19 ' ' 2d TA TA[ bits] tbit = d = c tbit c [ mt / ms] [ ms] c tbit d TA = TA = TA TA ( ) mt 'B # ; + + ' ') B C #
20 )'( '' 5# A # $ A # $ A # $ # # provided they can support the MS. 6 $,$ D,7 8 $ 3 $ 9 8 $ RXLEV (cell A) RXLEV (cell A) Handover Handover RXLEV (cell B) RXLEV (cell B) HANDOVER ALGORITHM: operator-dependent! GSM standard SUGGESTS a simple reference algorithm, but implementation left to operator hysteresis
21 '(' 1) Handover request goes up to switching point MSC 2) Switching point prepares new path on fixed net ) Switching point sends HO command to MS 4) MS accesses new channel 5) Old channel/path torn down
22 &, '( " &'$ MS BTS-A BSC-A MSC BSC-B BTS-B MS " ( " (, & ' " (, " (, <! " ( " ( " ( " " ( ; " ( " ( "! " (
23 -, '( #3(7)0 )' : EF 5 First MSC change (basic handover) Second MSC change (subsequent handover) MSC-A MSC-R1 MSC-A MSC-R1 MSC-R2 Note the role of the Anchor MSC!
24 : ;# -<'#
25 . ( ( LA-1 LA-2 LA-3 MSC VLR LA-4 LA-n
26 ( ' =#( * ( User first access to PLMN ( ; $» Needs to send IMSI and receive TMSI Subsequent accesses to PLMN (either in old or new MSC/VLS)» Also after MS shut-down!» TMSI-based identification & ( B / ( $ $
27 ', ) 4''6 & 4''6 8-7 ( '@G B ( H Country Code (CC): 3 digits Mobile Network Code: 2 digits Location Area Code: max 5 digits
28 ./.0"($ ' MSC VLR 3 HLR 1 2 1) Obtain LAI from BCCH 2) Register MS ID into local VLR 3) Update pointer at HLR
29 . MS BSS/MSC VLR HLR AUC Loc. Upd. Request IMSI, LAI Update Loc. Area IMSI, LAI Auth. Param. Req. IMSI Auth. Info (Auth. Parameters) Auth. Info. Req. IMSI Auth. Info (Auth. Parameters) Activate ciphering authentication Start Ciphering Kc Forward new TMSI TMSI Locat. Upd. Accept Update Location IMSI, MSRN Insert Subscrib. Data IMSI, additional data Insert Subscrib. Data ACK Locat. Upd. Accept IMSI TMSI Realloc Cmd Locat. Upd. Accept TMSI Realloc ACK TMSI ACK
30 " '1.$ Authentication Request Challenge: 128 bit RAND VLR IMSI, RAND SRES, Kc HLR / AUC Ki RAND A3 SRES SRES Authentication Response Signed RESult: 32 bit SRES Equal? Ki RAND A8 Kc
31 "' $ ) - $ /. 6 )-:(->+, # # ' Along with secret key Ki B $ * 1 ) # B 1 / C Since A3,A8 run ONLY in the AUC at the home HLR Ki is NEVER transmitted away from AUC or MS!!# G# ) #. HI 9 6 G. B * H 5(# J ( '# ' / $ B * # ) #. #!
32 -"+,!# $ / / #! $ $ < 0 A D7 A < 8 K 6 I < L 7 D0 K =2,097,152 < 2,715,648 < 2 22 Frame number FN, 22 bits Kc 64 bits Frame number FN, 22 bits Kc 64 bits MS A5 A5 BTS S1 S2 S1 S2 In-clear uplink XOR enciphered uplink XOR In-clear uplink In-clear downlink XOR enciphered downlink XOR In-clear downlink
33 .0' 1. " * -$ MS BSS/MSC VLR HLR AUC Loc. Upd. Request TMSI, LAI Activate ciphering TMSI Realloc Cmd authentication Update Loc. Area TMSI, LAI Update Location IMSI, MSRN Generate New TMSI Start Ciphering Kc Insert Subscrib. Data Forward new TMSI IMSI, additional data Ins. subs. data ACK Locat. Upd. Accept Locat. Upd. Accept IMSI Locat. Upd. Accept TMSI Realloc ACK TMSI ACK Auth. Param. Req. IMSI Auth. Info B A. B * # ) # Auth. Info. Req. IMSI Auth. Info B A. B * # ) #
34 /1.. % # ) ) " " " " ) )!! + + % #
35 - 5)795#) 7 K 9 < $ 3 ( ; "'# '> J # '> > " # '> > $ '1 B ( # ' C # ' $ =& # $ ( CC Some author (Mouly-Pautet) uses the term» TIC (Temporary Identity Code) = 4 bytes» TMSI = TIC+LAI = unambiguous user identification % - # 'M ( ' $ 2 Operator may set a 6min up to 24hrs periodicity for LU (value transmitted on BCCH) IMSI_attach = a special LU in a same Location Area; IMSI_attach follows an IMSI_detach (power-down of MS)
36 .0'2'&&1. MS BSS/MSC VLR-new HLR VLR-old Loc. Upd. Request # 'M ( '( ' Activate ciphering authentication Update Loc. Area # 'M ( '( ' determine VLR-old From old LAI Send parameters (TMSI, old LAI) Update Location IMSI, MSRN Generate New TMSI Start Ciphering Kc Insert Subscrib. Data Forward new TMSI IMSI, additional data Ins. subs. data ACK IMSI response (IMSI,RAND,SRES,Kc) Locat. Upd. Accept IMSI Cancel Location IMSI Cancel Locat. ACK
37 0=& # =& -7 * 8=& A 5)7 ' $ '# ' MS Identity Request Identity Response IMSI MSC PAGING: - Normally based on TMSI - But when no valid TMSI information available (e.g. after a DB restore after crash), based on IMSI
38 ? '<
39 -BC '+, '+, 8'+8', # 5'+5', #
40 MS Mobile Terminated Call MSC Fixed party MS Mobile Originated Call! MSC Fixed party DATA DATA In ISDN ISUP: - setup = IAM (Initial Address Message); - Alerting = ACM (Address Complete Message); - Connect = ANS (Answer)
41 MS Mobile Terminated Call network MS Mobile Originated Call network Paging request Channel request Immediate Assignment Paging Response Authentication Request Authentication Response Ciphering mode command Ciphering Mode Complete Setup Call Confirmed Assignment Command Assignment Complete Alerting Connect Connect Acknowledge Channel request Immediate Assignment Service Request Authentication Request Authentication Response Ciphering mode command Ciphering Mode Complete Setup Call proceeding Assignment Command Assignment Complete Alerting Connect Connect Acknowledge
42 ' ''3' 08-')#+08-'), B $ $ 8-')#+8-'), $ $ C Best utilization of radio resource (avoids allocation if callee not available) Call drop if no TCH is available at this point =2- +=2-, ' Fastest signalling process Waste of resources VEA Non-OACSU OACSU RACH RACH RACH TCH (FACCH) SDCCH TCH (FACCH) SDCCH TCH (DATA) TCH (DATA) TCH (DATA) Connection established Callee responds
43 4 5 5 $ * / 0 9 # 7 C B / Key Pressed MS Start DTMF (w. key code) Start DTMF ACK MSC 8 # + $ / 1 $ * + # # 1 * + On FACCH) Stop DTMF
44 GMSC ISDN 1: MSISDN MSC C VLR B 5: MSRN 6: TMSI MSC B 4: MSRN 7: paging MSC A 2: MSISDN 3: MSRN HLR
45 "($ ' '' '.0 During an LU within a same VLR, MSRN is NOT signaled! MSRN retrieved on a per-call basis! (choice of solution depends on trade-offs) GMSC ISDN 1: MSISDN MSC C 7: MSRN VLR B 8: TMSI MSC B 6: MSRN 9: paging MSC A 2: MSISDN 5: MSRN HLR 3: IMSI 4: MSRN
46 + &> ; ' International Switching Center + = &> ; ' # + & ' Transit Exchange Local Exchange International Switching Center MSISDN # 7. MSRN +44.NDC & ' #
47 Call to MSISDN ISC (UK) + = &> ; ' # Call to MSISDN ISC (ITA) MSISDN # 7. MSRN +44.NDC & ' # Is the PRICE (!) to pay for simple routing and billing
48 $, ( ( Consulted by ISCs (which MUST support GSM-MAP!) )0# ( ( B M $ B * C I.e. must know the MS is roaming in the PLMN $!» Extensions tovlr or to GMSC» Details in Lin-Chlamtac
49 .-,. ' 3 bis ISC (UK) 2 % # + = &> ; ' 1 3 ISC (ITA) & '
50 ( )) $ # # * 5,,$ ' % '$ # #
51 MSC PLMN Internet, PSDN IWMSC Short Message Service Center SMS-GMSC Get routing info for terminating MS. MSC PLMN
52 MS SM-SC # $ $ ( #, ( # ( #, ( # #, MSC IW-MSC # ( #,( #, " $ & ' " $ & ' # #, # #, " $ & ' " $ & ' Quite complex signalling involved (see specific texts)
53 ) # $#3" < 8 8 < A / 2 # "# < N $ $ N $ & # B $ $ $ $
54 $ O$ P $ &# $
55 $ &' Originating network switch Donor network switch switch Recipient network Originating switch sets-up trunk to donor switch Donor switch sets-up trunk to recipient switch Simplest solution, as call forwarding is a feature available in virtually all switches
56 $% Originating network switch SS7 ISUP IAM SS7 ISUP REL Donor network switch Number Portability DataBase switch Recipient network Donor switch blocks incoming call with a release message (REL) REL carries a QoR cause value, stating that called party number is ported Originating switch then queries Number Portability database
57 $, % Originating network switch Donor network switch Number Portability DataBase switch Recipient network Originating switch queries Number Portability database for every call!! - best solution if majority of numbers are ported (no interaction with donor) - but very high DB load, as EVERY number must be looked-up!
58 ) 3# - # /!)''+ 3# ##, : $ # B C Recipient network MSC GMSC HLR Note: If path must cross GMSC: Use Intermediate Routing Number Incoming call MSRN IRN MSRN (or IRN) GMSC Signaling relay function HLR Donor network
59 " % $ Recipient network MSC GMSC Query MSRN Return MSRN HLR IRN Incoming call switch Query IRN Return IRN Number Portability DataBase
60 (' "%$ Recipient network MSC GMSC HLR Incoming call MSRN switch Query MSRN Return MSRN Signaling relay function Number Portability DataBase
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
GSM Databases. Virginia Location Area HLR Vienna Cell Virginia BSC. Virginia MSC VLR
 Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
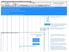 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY:
 GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM Architecture and Interfaces
 GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
Theory and Practice. IT-Security: GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.7. Mobile Communication. December 18, 2001. GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.
 Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke [email protected] Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke [email protected] Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
Mobile Services (ST 2010)
 Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE [email protected] UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE [email protected] UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing
 GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
9.1 Introduction. 9.2 Roaming
 9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
Frequency [MHz] ! " # $ %& &'( " Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.
![Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2. Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.](/thumbs/18/697237.jpg) Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
Ch 2.3.3 GSM PENN. Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98
 Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview
 The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' Giuseppe Bianchi
 !!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
GSM GPRS. Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides)
 GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley
 Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
GSM Channels. Physical & Logical Channels. Traffic and Control Mutltiframing. Frame Structure
 GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 7: GSM Network Signaling Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Nov. 2006 1 Outline
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 7: GSM Network Signaling Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Nov. 2006 1 Outline
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems
 Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
MRN 6 GSM part 1. Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione. Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone
 Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology
 Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
RELEASE NOTE. Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08. Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90
 ETSI /TC SMG Release by : ETSI /PT 12 Release date : December 1995 RELEASE NOTE Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08 Radio Sub - system Link Control Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90 New
ETSI /TC SMG Release by : ETSI /PT 12 Release date : December 1995 RELEASE NOTE Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08 Radio Sub - system Link Control Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90 New
Global System for Mobile (GSM) Global System for Mobile (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile (GSM) David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program of Telecommunications and Networking University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2720 Slides 8 Based largely on material from Jochen
Global System for Mobile (GSM) David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program of Telecommunications and Networking University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2720 Slides 8 Based largely on material from Jochen
The Network Layer Layer 3
 CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
2 System introduction
 2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
2G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系
 Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系 Mobility Management in Cellular Systems Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC cell BTS BTS BTS BTS MT BTS BTS BTS BTS HLR and VLR HLR (Home Location Register)
Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系 Mobility Management in Cellular Systems Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC cell BTS BTS BTS BTS MT BTS BTS BTS BTS HLR and VLR HLR (Home Location Register)
TELECOMMUNICATIONS REGULATORY AUTHORITY BAHRAIN. Bahrain Number Portability Implementation Routing and Charging specification
 TELECOMMUNICATIONS REGULATORY AUTHORITY BAHRAIN Bahrain Number Portability Implementation Routing and Charging specification Version: 0.4 Status: draft Date: 4-0-00 Modification History Issue Date Modification
TELECOMMUNICATIONS REGULATORY AUTHORITY BAHRAIN Bahrain Number Portability Implementation Routing and Charging specification Version: 0.4 Status: draft Date: 4-0-00 Modification History Issue Date Modification
GSM System Architecture
 Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0
 GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020508QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020508QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Cellular mobile communication is based on the. The Cellular Concept. GSM and PCNs. Moe Rahnema
 GSM and PCNs Overview Of he GSM System and Protocol Architecture We can use GSM as a basic framework to define and develop the standards for handling the mobility-specific functions of next-generation
GSM and PCNs Overview Of he GSM System and Protocol Architecture We can use GSM as a basic framework to define and develop the standards for handling the mobility-specific functions of next-generation
GSM Security Claude Castelluccia INRIA
 GSM Security Claude Castelluccia INRIA Technology behind GSM 900 MHz (or 1800 MHz) band uplink frequency band 890-915 MHz downlink frequency band is 935-960 MHz 25 MHz subdivided into 124 carrier frequency
GSM Security Claude Castelluccia INRIA Technology behind GSM 900 MHz (or 1800 MHz) band uplink frequency band 890-915 MHz downlink frequency band is 935-960 MHz 25 MHz subdivided into 124 carrier frequency
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
ETSI TS 101 043 V7.5.0 (2003-12)
 TS 101 043 V7.5.0 (2003-12) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Basic call handling (3GPP TS 03.18 version 7.5.0 1998) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
TS 101 043 V7.5.0 (2003-12) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Basic call handling (3GPP TS 03.18 version 7.5.0 1998) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
Pocket Guide for Fundamentals and GSM Testing
 Pocket Guide for Fundamentals and GSM Testing Publisher: Author: Wandel & Goltermann GmbH & Co Elektronische Meûtechnik P. O. Box 12 62 D-72795 Eningen u.a. Germany e-mail: [email protected] http://www.wg.com
Pocket Guide for Fundamentals and GSM Testing Publisher: Author: Wandel & Goltermann GmbH & Co Elektronische Meûtechnik P. O. Box 12 62 D-72795 Eningen u.a. Germany e-mail: [email protected] http://www.wg.com
1 Introduction. 2 Assumptions. Implementing roaming for OpenBTS
 Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
GSM System. Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks
 Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 10.1 GSM-IP: VoIP Service for GSM 256
Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 10.1 GSM-IP: VoIP Service for GSM 256
Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks
 Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks Thomas A. Cooper Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks Thomas A. Cooper Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
GLOSARIO. Authentication key, se usa en sistemas basados en TIA/EIA-41. Estándar de comunicación celular basado en TDMA.
 GLOSARIO A AC o AuC Ack AGCH A-key AMPS ANSI-136 ó IS-136 ARFCN ASE Authentication Center. Acknowledgement. Access Grant Channel. Authentication key, se usa en sistemas basados en TIA/EIA-41. Advanced
GLOSARIO A AC o AuC Ack AGCH A-key AMPS ANSI-136 ó IS-136 ARFCN ASE Authentication Center. Acknowledgement. Access Grant Channel. Authentication key, se usa en sistemas basados en TIA/EIA-41. Advanced
GSM Architecture Training Document
 Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
ASR 5x00 Series SGSN Authentication and PTMSI Reallocation Best Practices
 ASR 5x00 Series SGSN Authentication and PTMSI Reallocation Best Practices Document ID: 119148 Contributed by Krishna Kishore DV, Sujin Anagani, and Parthasarathy M, Cisco TAC Engineers. Jun 12, 2015 Contents
ASR 5x00 Series SGSN Authentication and PTMSI Reallocation Best Practices Document ID: 119148 Contributed by Krishna Kishore DV, Sujin Anagani, and Parthasarathy M, Cisco TAC Engineers. Jun 12, 2015 Contents
Optimization. Log File Analysis GSM
 Optimization and Log File Analysis in GSM by Somer GOKSEL January 26, 2003 2 Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...04 1.1 PURPOSE and SCOPE of OPTIMIZATION... 04 1.2 OPTIMIZATION PROCESS... 05 1.2.1 PROBLEM ANALYSIS...
Optimization and Log File Analysis in GSM by Somer GOKSEL January 26, 2003 2 Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...04 1.1 PURPOSE and SCOPE of OPTIMIZATION... 04 1.2 OPTIMIZATION PROCESS... 05 1.2.1 PROBLEM ANALYSIS...
Mobile Computing. Basic Call Calling terminal Network Called terminal 10/25/14. Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN. CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014
 Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Lecture overview. History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction. Basic architecture of GSM system. Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM
 Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Product report GSM Call Service
 Product report GSM Call Service 1DT054 Project CS Ebby Wiselyn Jeyapaul Egemen Taskin Erik Grafström Fartash M. Nejad Fredrik Pasanen Max Morén Mohammadreza Taghilu Moritz Rogalli Praveenkumar Bhadrapur
Product report GSM Call Service 1DT054 Project CS Ebby Wiselyn Jeyapaul Egemen Taskin Erik Grafström Fartash M. Nejad Fredrik Pasanen Max Morén Mohammadreza Taghilu Moritz Rogalli Praveenkumar Bhadrapur
SIP Based Architecture for Integration of 1xRTT Femtocells
 SIP Based Architecture for Integration of 1xRTT Femtocells 2007 Tatara Systems Tatara Systems grants a free, irrevocable license to 3GPP2 and its Organizational Partners to incorporate text or other copyrightable
SIP Based Architecture for Integration of 1xRTT Femtocells 2007 Tatara Systems Tatara Systems grants a free, irrevocable license to 3GPP2 and its Organizational Partners to incorporate text or other copyrightable
GPRS Overview. GPRS = General Packet Radio Service. GPRS Network
 GPRS - Overview GPRS Overview GPRS = General Packet Radio Service INTERNET/ INTRANET GPRS Network abcde X.25 Disclaimer: These overview slides are intended for informational purposes only. They have not
GPRS - Overview GPRS Overview GPRS = General Packet Radio Service INTERNET/ INTRANET GPRS Network abcde X.25 Disclaimer: These overview slides are intended for informational purposes only. They have not
ETSI TS 123 251 V6.5.0 (2005-09)
 TS 123 251 V6.5.0 (2005-09) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Network sharing; Architecture and functional description (3GPP TS 23.251 version 6.5.0 Release 6)
TS 123 251 V6.5.0 (2005-09) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Network sharing; Architecture and functional description (3GPP TS 23.251 version 6.5.0 Release 6)
Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks
 Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Wireless Mobile Telephony
 Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 [email protected] http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 [email protected] http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems. Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering
 Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Mobile Application Part Interface (MAPI) Specification
 Mobile Application Part Interface (MAPI) Specification Mobile Application Part Interface (MAPI) Specification Version 1.1 Edition 7.20141001 Updated October 25, 2014 Distributed with Package openss7-1.1.7.20141001
Mobile Application Part Interface (MAPI) Specification Mobile Application Part Interface (MAPI) Specification Version 1.1 Edition 7.20141001 Updated October 25, 2014 Distributed with Package openss7-1.1.7.20141001
Locating Mobile Phones using Signalling System #7. Tobias Engel <[email protected]> twitter: @2b_as
 Locating Mobile Phones using Signalling System #7 Tobias Engel twitter: @2b_as What is Signalling System #7? protocol suite used by most telecommunications operators throughout the world
Locating Mobile Phones using Signalling System #7 Tobias Engel twitter: @2b_as What is Signalling System #7? protocol suite used by most telecommunications operators throughout the world
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
GSM Network Structure and Network Planning. Contents: Dipl.- Ing. Reiner Stuhlfauth, ROHDE & SCHWARZ; Training Centre
 GSM Network Structure and Network Planning Dipl.- Ing. Reiner Stuhlfauth, ROHDE & SCHWARZ; Training Centre Contents: 1. Geographical structures in a GSM network 2. Methods of network planning 2.1. Principles
GSM Network Structure and Network Planning Dipl.- Ing. Reiner Stuhlfauth, ROHDE & SCHWARZ; Training Centre Contents: 1. Geographical structures in a GSM network 2. Methods of network planning 2.1. Principles
Cellular Network Organization
 Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Authentication and Secure Communication in GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Using Asymmetric Cryptography
 ISSN (Online): 1694-0784 ISSN (Print): 1694-0814 10 Authentication and Secure Communication in GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Using Asymmetric Cryptography Wilayat Khan 1 and Habib Ullah 2 1 Department of Electrical
ISSN (Online): 1694-0784 ISSN (Print): 1694-0814 10 Authentication and Secure Communication in GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Using Asymmetric Cryptography Wilayat Khan 1 and Habib Ullah 2 1 Department of Electrical
[Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2]
![[Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2] [Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2]](/thumbs/26/8506801.jpg) JP-3GA-23.054(R99) GSM PLMN (SIWF) 2 [Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2] [Remarks] [Application level of English description] [Application level]
JP-3GA-23.054(R99) GSM PLMN (SIWF) 2 [Description for the use of a Shared Inter Working Function (SIWF) in a GSM PLMN - Stage 2] [Remarks] [Application level of English description] [Application level]
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 13: VoIP Service for Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Dec. 2006
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 13: VoIP Service for Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Dec. 2006
LTE Tutorial GSM Tutorial i
 GSM Tutorial i GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS (GSM) TUTORIAL Simply Easy Learning by tutorialspoint.com tutorialspoint.co ii ABOUT THE TUTORIAL GSM Tutorial GSM is a globally accepted standard
GSM Tutorial i GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS (GSM) TUTORIAL Simply Easy Learning by tutorialspoint.com tutorialspoint.co ii ABOUT THE TUTORIAL GSM Tutorial GSM is a globally accepted standard
4th European Tcl/Tk User Meeting. Tcl used for testing in the mobile world
 4th European Tcl/Tk User Meeting Tcl used for testing in the mobile world Hans Banken, SIGOS GmbH May 2003 Klingenhofstraße 50d D-90411 Nürnberg Fon +49 911 95168-0 Fax +49 911 95 16 8-355 www.sigos.de
4th European Tcl/Tk User Meeting Tcl used for testing in the mobile world Hans Banken, SIGOS GmbH May 2003 Klingenhofstraße 50d D-90411 Nürnberg Fon +49 911 95168-0 Fax +49 911 95 16 8-355 www.sigos.de
3GPP TR 23.912 V3.1.0 (2001-12)
 TR 23.912 V3.1.0 (2001-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Technical report on Super-Charger (Release 1999) The present document
TR 23.912 V3.1.0 (2001-12) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core Network; Technical report on Super-Charger (Release 1999) The present document
Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS
 Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 2.1 Network Architectures 2.2 Concepts
Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 2.1 Network Architectures 2.2 Concepts
Using TEMS Pocket. Johan Montelius
 Using TEMS Pocket Johan Montelius Introduction In this laboration you will get acquainted with the TEMS Pocket tool. You will examine both the Monaco network and a commercial network. Since this is your
Using TEMS Pocket Johan Montelius Introduction In this laboration you will get acquainted with the TEMS Pocket tool. You will examine both the Monaco network and a commercial network. Since this is your
ETSI TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06)
 TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
GSM Network and Services
 GSM Network and Services GPRS - sharing of resources 1 What is the problem? Many data applications are very bursty in its traffic pattern: http, smtp, pop, telnet,... Why reserve physical resources at
GSM Network and Services GPRS - sharing of resources 1 What is the problem? Many data applications are very bursty in its traffic pattern: http, smtp, pop, telnet,... Why reserve physical resources at
How To Make A Cell Phone Network More Efficient
 Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Draft ETSI EN 301 716 V7.1.0 (1999-08)
 Draft EN 301 716 V7.1.0 (1999-08) European Standard (Telecommunications series) Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Support of Mobile Number Portability (MNP); Technical Realisation;
Draft EN 301 716 V7.1.0 (1999-08) European Standard (Telecommunications series) Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Support of Mobile Number Portability (MNP); Technical Realisation;
What is telecommunication? electronic communications? What is telephony?
 What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
GSM and IN Architecture
 GSM and IN Architecture a common component: TCAP [email protected] Rka S-2007 Signaling Protocols 8-1 GSM system consists of sub-systems MS = ME+SIM Radio or Air i/f Base Station Sub-system (BSS)
GSM and IN Architecture a common component: TCAP [email protected] Rka S-2007 Signaling Protocols 8-1 GSM system consists of sub-systems MS = ME+SIM Radio or Air i/f Base Station Sub-system (BSS)
Encrypted SMS, an analysis of the theoretical necessities and implementation possibilities
 Radboud University Nijmegen Bachelor Thesis Encrypted SMS, an analysis of the theoretical necessities and implementation possibilities Author: Lars Lockefeer Supervisors: Engelbert Hubbers Roel Verdult
Radboud University Nijmegen Bachelor Thesis Encrypted SMS, an analysis of the theoretical necessities and implementation possibilities Author: Lars Lockefeer Supervisors: Engelbert Hubbers Roel Verdult
What is telecommunication? electronic communications. service?
 What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
Cellular Phone Systems
 Cellular Phone Systems Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC 1 Why Cellular Mobile Telephone Systems? Operational limitations of conventional mobile
Cellular Phone Systems Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC 1 Why Cellular Mobile Telephone Systems? Operational limitations of conventional mobile
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]
![192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]](/thumbs/18/698539.jpg) 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS, UMTS. GSM as basis of current systems Satellites and
 Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
Worldwide attacks on SS7 network
 Worldwide attacks on SS7 network P1 Security Hackito Ergo Sum 26 th April 2014 Pierre-Olivier Vauboin ([email protected]) Alexandre De Oliveira ([email protected]) Agenda Overall telecom architecture Architecture
Worldwide attacks on SS7 network P1 Security Hackito Ergo Sum 26 th April 2014 Pierre-Olivier Vauboin ([email protected]) Alexandre De Oliveira ([email protected]) Agenda Overall telecom architecture Architecture
CHANGE REQUEST. 03.35 CR xx
 3GPP TSG SA WG3 #16 Document S3-000676 Sophia Antipolis (France), 28 th 30 th November, 2000 e.g. for 3GPP use the format TP-99xxx or for SMG, use the format P-99-xxx CHANGE REQUEST Please see embedded
3GPP TSG SA WG3 #16 Document S3-000676 Sophia Antipolis (France), 28 th 30 th November, 2000 e.g. for 3GPP use the format TP-99xxx or for SMG, use the format P-99-xxx CHANGE REQUEST Please see embedded
An investigation into the claims of IMSI catchers use in Oslo in late 2014. Centre for Resilient Networks and Applications Simula Research Laboratory
 An investigation into the claims of IMSI catchers use in Oslo in late 2014 Centre for Resilient Networks and Applications Simula Research Laboratory Publication date 01. July 2015 Contents 1 Introduction
An investigation into the claims of IMSI catchers use in Oslo in late 2014 Centre for Resilient Networks and Applications Simula Research Laboratory Publication date 01. July 2015 Contents 1 Introduction
GSM Networks: Protocols, Terminology, and Implementation
 GSM Networks: Protocols, Terminology, and Implementation GSM Networks: Protocols, Terminology, and Implementation Gunnar Heine Artech House Boston London Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
GSM Networks: Protocols, Terminology, and Implementation GSM Networks: Protocols, Terminology, and Implementation Gunnar Heine Artech House Boston London Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data
ETSI TS 129 119 V9.0.0 (2010-01) Technical Specification
 TS 129 119 V9.0.0 (2010-01) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) specification for Gateway Location Register (GLR) (3GPP TS 29.119
TS 129 119 V9.0.0 (2010-01) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) specification for Gateway Location Register (GLR) (3GPP TS 29.119
Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET
 Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET Vladimir Vukadinovic and Ljiljana Trajkovic School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Vancouver, BC, Canada E-mail: {vladimir, ljilja}@cs.sfu.ca
Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET Vladimir Vukadinovic and Ljiljana Trajkovic School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Vancouver, BC, Canada E-mail: {vladimir, ljilja}@cs.sfu.ca
Mobile Networking. SS7 Network Architecture. Purpose. Mobile Network Signaling
 Purpose The purpose of this white paper is to inform the reader about mobile networking technology. For further information, see. Mobile Network Signaling Telecommunications signaling is the transmission
Purpose The purpose of this white paper is to inform the reader about mobile networking technology. For further information, see. Mobile Network Signaling Telecommunications signaling is the transmission
Bölüm 8. GSM. 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar!
 Bölüm 8. GSM http://ceng.gazi.edu.tr/~ozdemir Durum 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar! * http://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/ind/d-ind-ictoi-2012-sum-pdf-e.pdf 1 Global
Bölüm 8. GSM http://ceng.gazi.edu.tr/~ozdemir Durum 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar! * http://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/ind/d-ind-ictoi-2012-sum-pdf-e.pdf 1 Global
