GSM Channels. Physical & Logical Channels. Traffic and Control Mutltiframing. Frame Structure
|
|
|
- Franklin Stephen McCoy
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering
2 Radio Interface The radio interface is the general name of the connection between the mobile (MS) and the base transceiver station (BTS). It utilizes the TDMA concept with one TDMAframe per carrier frequency. Each frame consists of eight time slots (TS). The direction from BTS to MS is defined as the downlink and the opposite direction as the uplink.
3 Physical channels When an MS and a BTS communicate, they do so on a specific pair of radio frequency (RF) carriers, one for the up-link and the other for the down-link transmissions, and within a given time slot. This combination of time slot and carrier frequency forms what is termed a physical channel. One RF channel will support eight physical channels in time slots zero through seven.
4 Logical Channels The data, whether user traffic or signaling information, are mapped onto the physical channels by defining a number of logical channels. A logical channel will carry information of a specific type and a number of these channels may be combined before being mapped onto the same physical channel. For example speech is sent on the logical channel Traffic channel which during the transmission is allocated a certain physical channel, say TS 6 on carrier 0. The logical channels are divided into two groups; control channels and traffic channels.
5 From Physical Channel to Logical Time Slot LOGICAL TDMA Frame LOGICAL Logical CHANNELS = ms channels SCH FCCH multiplexing TCH TCH SCH FACCH FACCH SACCH SACCH SDCCH SDCCH CBCH CBCH AGCH AGCH PCH TS = 577 μs BCCH PCH BCCH RACH RACH MESSAGE TYPE different message types Physical Channel = Logical Channel Logical Channel different logical channels
6 LOGICAL CHANNELS TRAFFIC SIGNALLING FULL RATE HALF RATE (TCH/F) (TCH/H) 22.8 Kb/S 11.4 Kb/S BROADCAST COMMON CONTROL DEDICATED CONTROL FCCH SCH BCCH PCH RACH AGCH FCCH -- FREQUENCY CORRECTION CHANNEL SCH -- SYNCHRONISATION CHANNEL BCCH -- BROADCAST CONTROL CHANNEL PCH -- PAGING CHANNEL RACH -- RANDOM ACCESS CHANNEL SDCCH SACCH FACCH AGCH -- ACCESS GRANTED CHANNEL SDCCH -- STAND ALONE DEDICATED CONTROL CHANNEL DOWN LINK ONLY SACCH -- SLOW ASSOCIATED CONTROL CHANNEL BOTH UP & UPLINK ONLY DOWNLINKS FACCH -- FAST ASSOCIATED CONTROL CHANNEL
7 Channel Types Traffic channels (TCHs) The traffic channels are intended to carry encoded speech or user data. Control Channels (CCHs) The control channels are intended to carry signaling and Synchronization data between the base station and the Mobile station. Logical are used by the system and the MS for different purposes
8 Traffic Channels Traffic channels are intended to carry encoded speech and user data. -Full rate traffic channels at a net bit rate of 22.8 Kb/s (TCH/F) -Half rate traffic channels at a net bit rate of 11.4 Kb/s (TCH/H) Speech Channels Speech channels are defined for both full rate and half rate traffic channels. Data Channels Data channels support a variety of data rates (2.4, 4.8 and 9.6 Kb/s) on both half and full rate traffic channels. The 9.6 Kb/s data rate is only for full rate application
9 Control Channels Control channels carry signaling information between an MS and a BTS. There are several forms of control channels in GSM, and they can generally be divided into three categories according to the manner in which they are supported on the radio interface and the type of signaling information they carry. 1. Broadcast control channel 2. Common control channel 3. Dedicated control channel
10 Broadcast control channels Broadcast control channels are transmitted in downlink direction only i.e. only transmitted by BTS. The broadcast channels are used to broadcast synchronization and general network information to all the MSs within a cell. Such as Location Area Identity (LAI) and maximum output power. It has three types 1. FCCH FREQUENCY CORRECTION CHANNEL 2. SCH SYNCHRONISATION CHANNEL 3 BCCH BROADCAST CONTROL CHANNEL
11 FCCH Frequency Correction Channel (FCCH) - Used for the frequency correction / synchronization of a mobile station. - The repeated (every 10 sec) transmission of Freq Bursts is called FCCH. This serves two purposes; one is to make sure this is the BCCH-carrier, the other is to allow the MS to synchronize to the frequency. FCCH is transmitted on the downlink, point-to-multipoint. - Frequency Correction Burst
12 SCH - Synchronization Channel (SCH) - Allows the mobile station to synchronize time wise with the BTS. - Repeated broadcast (every 10 frames) of Synchronization Bursts is called (SCH) - The MS receives the TDMA frame number and also the Base Station Identity Code,BSIC, of the chosen base station. BSIC can only be decoded if the base station belongs to the GSM network. SCH is transmitted on the downlink, point to multipoint. - Synchronization Burst
13 BCCH The broadcast control channel(bcch) is used to broadcast control information to every MS within a cell. This information includes details of the control channel configuration used at the BTS, a list of the BCCH carrier frequencies used at the neighboring BTSs and a number of parameters that are used by the MS when accessing the BTS. Use normal burst. Broadcast Control channel, BCCH include the Location Area Identity (LAI), maximum output power allowed in the cell and the BCCH-carriers for the neighboring cells, on which the MS will perform measurements. BCCH is transmitted On the downlink, point-to-multipoint.
14 BCCH (Contd) Now the MS is tuned to a base station and synchronized with the frame structure in this cell. The base stations are not synchronized to each other, so every time the MS decides to camp on another cell, its FCCH, SCH and BCCH have to be read.
15 Common Control Channels The common control channels are used by an MS during the paging and access procedures. Common control channels are of three types. 1. PCH PAGING CHANNEL 2. RACH RANDOM ACCESS CHANNEL 3. AGCH ACCESS GRANTED CHANNEL
16 PCH Within certain time intervals the MS will listen to the Paging channel, PCH, to see if the network wants to get in contact with the MS. The reason could be an incoming call or an incoming Short Message. The information on PCH is a paging message, including the MS s identity number (IMSI) or a temporary number (TMSI). PCH is transmitted on the downlink, point-to-point. Use normal burst.
17 RACH If listening to the PCH, the MS will realize it is being paged. The MS answers, requesting a signalling channel, on the Random Access channel, RACH. RACH can also be used if the MS wants to get in contact with the network, e.g. when setting up a mobile originated call. RACH is transmitted on the uplink, pointto-point. It is termed random because there is no mechanism to ensure that no more than one MS transmits in each RACH time slot and there is a finite probability that two mobiles could attempt to access the same RACH at the same time. Use Access Burst.
18 AGCH The access grant channel (AGCH) is carried data which instructs the mobile to operate in a particular physical channel (Time slot or ARFCN). The AGCH is used by the network to grant, or deny, an MS access to the network by supplying it with details of a dedicated channel, i.e. TCH or SDCCH, to be used for subsequent communications. The AGCH is a down-link only channel. Use normal burst.
19 Dedicated Control Channels Signaling information is carried between an MS and a BTS using associated and dedicated control channels during or not during a call, They are of three types. 1. SACCH SLOW ASSOCIATED CONTROL CHANNEL 2. FACCH FAST ASSOCIATED CONTROL CHANNEL 3. SDCCH STAND ALONE DEDICATED CONTROL CHANNEL
20 SACCH Non-urgent information, e.g. transmitter power control, is transmitted using the slow associated control channel (SACCH). On the uplink MS sends averaged measurements on own base station (signal strength and quality) and neighboring base stations (signal strength). On the downlink the MS receives system information, which transmitting power and what timing advance to use. It is transmitted at 13 th Frame of TCH. As seen, SACCH is transmitted on both up- and downlink, point-to-point. This channel is always present when a dedicated link is active between the MS and BTS, and it occupies one timeslot in every 26. SACCH messages may be sent once every 480ms, i.e. approximately every 2 s. Use normal burst.
21 FACCH More urgent information, e.g. a handover command, is sent using time slots that are stolen from the traffic channel. If, suddenly, during the conversation a handover must be performed the Fast Associated Control channel, FACCH, is used. FACCH works in stealing mode, meaning that one 20 ms segment of speech is exchanged for signalling information necessary for the handover. The subscriber will not recognize this interruption in speech since the speech coder will repeat the previous speech block. This channel is known as the fast associated control channel (FACCH) because of its ability to transfer information between the BTS and MS more quickly than the SACCH. a complete FACCH message may be sent once in every 20 ms. Use normal burst.
22 SDCCH In some situations, signaling information must flow between a network and an MS when a call is not in progress, e.g. during a location update. This could be accommodated by allocating either a fullrate or half-rate TCH and by using either the SACCH or FACCH to carry the information. This would, however, be a waste of the limited radio resources. So a low data rate channel about 1/8 of TCH/F is defined. Also used in call setup process. The channel is termed stand-alone because it may exist independently of any TCH. - SDCCH is transmitted on both up- and downlink, point-to-point. -The MS is on the SDCCH informed about which physical channel (frequency and time slot) to use for traffic (TCH). Use normal burst.
23 Channel Mapping 1. When the MS is turned on it will listen to the FCCH in order to syn to the carrier frequency 2. Then the MS listen to the SCH to get info on the TDMA frame structure 3. The MS will then listen to the BCCH to get info such as location area, Max allowed O/P power & neighboring cells 4. The MS will periodically listen to the PCH to determine if someone is trying to call it. 5. If the MS hears a page it will use the RACH to ask for access to the system in order to respond to the incoming call
24 Channel Mapping 6. The sys will give access using the AGCH 7. The sys uses the AGCH to tell the MS which SDCCH to use for complete the Call Setup. 8. When the MS gets the SDCCH, it also gets a SACCH. Which the system uses to regulates the O/P power of the MS & gives it timing advance info. 9. The MS is given a TCH to use by the SDCCH. The MS tunes to it during the call. 10. During a call if a handover is required to a neighboring cell, the FACCH will be used to exchange the necessary info.
25 GSM Uses Paired Radio Channels Case of GSM 900 Uplink Downlink BTS 890 MHz Frequency 915 MHz 935 MHz Frequency 960 MHz 0 channel # channel # 124 Example: Channel 48 Duplex spacing = 45 MHz Frequency band spectrum = 2 x 25 MHz Channel spacing = 200 khz
26 GSM FDM
27 GSM delays uplink TDMA frames The start of the uplink TDMA is delayed of three time slots TDMA frame (4.615 ms) Downlink TDMA F1MHz R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 R8 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 Uplink TDMA Frame F1 + 45MHz R T R T Fixed transmit Delay of three time-slots
28 GSM - TDMA/FDMA MHz 124 channels (200 khz) downlink GSM TDMA frame MHz 124 channels (200 khz) uplink higher GSM frame structures time Data rate =2X57 bits every 4.615ms: 24.7kbps ms guard space GSM time-slot (normal burst) tail user data S Training S user data tail 3 bits 57 bits 1 26 bits 1 57 bits 3 guard space µs bits 577 µs
29 GSM Frame Structure Superframe 6.12 sec 120 msec msec Multiframe 26 Frames 8 Multiframe Coded data Midamble msec bits Tail bit Stealing Flag Guard period
30 Frame Types There There are two types of multiframe 26 TDMA-frame multiframe is used to carry TCH, SACCH and FACCH 51 TDMA-frame multiframe is used to carry BCCH, CCH, SDCCH and SACCH
31 HIERARCHY OF FRAMES 1 HYPER FRAME = 2048 SUPERFRAMES = TDMA FRAMES ( 3 H 28 MIN 53 S 760 MS ) TRAFFIC CHANNELS 1 SUPER FRAME = 1326 TDMA FRAMES ( 6.12 S ) 1 SUPER FRAME = 51 MULTI FRAMES LEFT (OR) RIGHT SIGNALLING CHANNELS 1 SUPER FRAME = 26 MULTI FRAMES MULTIFRAME = 26 TDMA FRAMES ( 120 ms ) MULTI FRAME = 51 TDMA FRAMES (235.4 ms ) (4.615ms) TDMA FRAME NO TIME SLOT = BITS ( ms) (4.615 ms) bit =36.9 micro sec
32 Traffic and Control Multi-Framing Traffic channel Frame ms Control channel TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS TS traffic frames = 120 ms 51 control frame = ms x 26 traffic frames = 6.12 s Super frames 26 x 51 control frames = 6.12 s Hyperframe = 2,715,648 frames= 3h 28 min. 53 s 760 ms
33 Location update from the mobile Mobile looks for BCCH after switching on RACH send channel request AGCH receive SDCCH SDCCH request for location updating SDCCH authenticate SDCCH authenticate response SDCCH switch to cipher mode SDCCH cipher mode acknowledge SDCCH allocate TMSI SDCCH acknowledge new TMSI SDCCH switch idle update mode Temporary mobile subscriber identity
34 Call establishment from a mobile Mobile looks for BCCH after switching on RACH send channel request AGCH receive SDCCH SDCCH send call establishment request SDCCH do the authentication and TMSI allocation SDCCH send the setup message and desired number SDCCH require traffic channel assignment FACCH switch to traffic channel and send ack (steal bits) FACCH receive alert signal ringing sound FACCH receive connect message FACCH acknowledge connect message and use TCH TCH conversation continues
35 Call establishment to a mobile Mobile looks for BCCH after switching on Mobile receives paging message on PCH Generate Channel Request on RACH Receive signaling channel SDCCH on AGCH Answer paging message on SDCCH Receive authentication request on SDCCH Authenticate on SDCCH Receive setup message on SDCCH Receive traffic channel assignment on SDCCH FACCH switch to traffic channel and send ack (steal bits) Receive alert signal and generate ringing on FACCH Receive connect message on FACCH FACCH acknowledge connect message and switch to TCH
36 PROPAGATION DELAYS MS2 d2 d1>>d2 MS1 BTS Frame reference TS0 TS1 TS2 TS3 TS4 TS5 TS6 TS7 Propagation Delay τp Bits Overlapping MSs transmit
37 Traffic Channels Combination Logical Channel Mapping (1/4) TCH/SACCH One Full Rate Channel- Downlink & Uplink 26 frames = 120 ms 26 frames Multi frame T T T T T T T T T T T T T A time Two Half Rate Channel- Downlink & Uplink 26 frames = 120 ms T0 T 1 T0 T 1 T0 T 1 T0 T 1 T0 T 1 T0 T 1 A0 T 1 T0 T 1 T0 T 1 T0 T 1 T0 T 1 T0 T 1 T0 A1 time : SACCH T : TCH A : SACCH sub-channel n Ti : TCHsub-channel n Ai i i : IDLE
38 Physical Chs and Logical Chs Common Channels Combination Multiframe m Multiframe Multiframe m-1 51 frames = ms m+1 C FS B C FS C C FS C C FS C C FS C C FS B Frames repeat continuously BCCHs+CCCHs (B4 combination) time PCH/AGCH BTS Physical Channel MS SCH BCCH ARFCN (n) TS (s) FCCH Absolute radio frequency channel number Logical Channels F : FCCH S : SCH B C : BCCH : PCH/AGCH : IDLE
39 Dedicated Signaling CHs Combination Logical Channel Mapping (2/4) Downlink 51 frames = 235 ms 51 frames multiframe D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 A0 A1 A2 A3 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 A4 A5 A6 A7 SDCCH + SACCH (B7 Uplink Combination) 51 frames = 235 ms time A5 A6 A7 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 A0 A1 A2 A3 D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 A4 time A : SACCH D : SDCCH : IDLE
40 Common Channels Combination Logical Channel Mapping (3/4) BCCH/CCCH Downlink 51 frames = 235 ms FS B C F S C C FS C C F S C C F S C C time Uplink 51 frames = 235 ms BCCHs+CCCHs (B4 combination) R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R time : AGCH F : FCCH S : SCH B : BCCH C R : RACH : IDLE /PCH
41 BCCH Combined Logical Channel Mapping (4/4) Downlink BCCHs+CCCHs+SDCCH+SACCH (B5 combination) 51 frames = 235 ms FS B C FS C C FS FS FS D0 D1 D2 D3 A0 A1 FS B C FS C C FS FS FS D0 D1 D2 D3 A2 A3 Uplink 51 frames = 235 ms R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R D2 D3 A2 A3 D0 D1 time R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R D3 A0 A1 D0 D1 D2 time : AGCH F : FCCH S : SCH B : BCCH C R : RACH A : SACCH D : SDCCH : IDLE /PCH
42 Burst and Frames The information contained in one time slot on the TDMA frame is call a burst. Five Five types of burst Normal Burst (NB) Frequency Correction Burst (FB) Synchronization Burst (SB) Access Burst (AB) Dummy Burst
43 Normal Burst - It is used to transmit both information and control bits - T trail bits are used as guard time in achieving power level. - Training is used to estimate channel characteristics. - SF stealing flags tells whether data or signalling is being transmitted. Normally for FACCH T Data SF Training SF Data T GP
44 Access Burst used to send the Random Access Channel (RACH) information - RACH contains the first message from MS to BTS - it has a long guard period to allow BTS to calculate the MS distance from the BTS and to provide timing advance information to MS Training Tail Sequence Data Tail Guard Period 8 bits 41 synch bits 36 encrypted bits 3 bits bits bits (0.577 ms)
45 Frequency Correction Burst used just to transmit Frequency Correction Channel (FCCH) 142 bits are set to 0 in the known time slots. Frequency Correction Burst (FCCH) Guard Tail Data Tail Period 3 bits 142 fixed bits (0) 3 bits 8.25 bits bits (0.577 ms)
46 Synchronization Burst used to transmit synchronization information the training sequence includes a well known sequence of bits Also contains the running number of TDMA frame. Synchronization Burst (SCH) Guard Tail Data Extended Training Sequence Data Tail Period 3 bits 39 encrypted bits 64 synchronization bits 39 bits 3 bits 8.25 bits bits (0.577 ms)
47 Dummy Burst It is transmitted when no other bursts are to be transmitted Uses same frequency channel which is used for BCCH to ensure if BCCH transmits burst in each time slot Quality monitoring Guard Tail Dummy Sequence Training Sequence Dummy SequenceTail Period 3 bits 58 mixed bits 28 midamble bits 58 mixed bits 3 bits 8.25 bits bits (0.577 ms)
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS There are two types of GSM logical channels 1. Traffic Channels (TCHs) 2. Control Channels (CCHs) Traffic channels carry digitally encoded user speech or user data and have identical
GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS There are two types of GSM logical channels 1. Traffic Channels (TCHs) 2. Control Channels (CCHs) Traffic channels carry digitally encoded user speech or user data and have identical
GSM System. Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Frequency [MHz] ! " # $ %& &'( " Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.
![Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2. Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.](/thumbs/18/697237.jpg) Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure
 GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure 1 FREQUENCY BANDS AND CHANNELS...2 2 GSM TDMA...4 3 TDMA FRAME HIERARCHY...6 4 BURST STRUCTURE...7 5 TDMA MULTIFRAME STRUCTURE...9 5.1 Traffic Multiframe (26-Multiframe)...10
GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure 1 FREQUENCY BANDS AND CHANNELS...2 2 GSM TDMA...4 3 TDMA FRAME HIERARCHY...6 4 BURST STRUCTURE...7 5 TDMA MULTIFRAME STRUCTURE...9 5.1 Traffic Multiframe (26-Multiframe)...10
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020501Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020501Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving
 GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
GSM Air Interface & Network Planning
 GSM Air Interface & Network Planning Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (40) GSM Air Interface & Network Planning The information in this document is subject to change without notice and
GSM Air Interface & Network Planning Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (40) GSM Air Interface & Network Planning The information in this document is subject to change without notice and
9.1 Introduction. 9.2 Roaming
 9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04. Simon Sörman
 Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04 Simon Sörman Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Channels... 2 2.1 Physical channels... 2 2.1.1 FDMA/TDMA... 2 2.1.2 Bursts... 3 2.2 Logical channels... 3 2.3 Mapping of logical
Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04 Simon Sörman Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Channels... 2 2.1 Physical channels... 2 2.1.1 FDMA/TDMA... 2 2.1.2 Bursts... 3 2.2 Logical channels... 3 2.3 Mapping of logical
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY:
 GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM GSM 05.02 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 05.02 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020502Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.02 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020502Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE Thi-Mai-Trang.Nguyen@lip6.fr UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE Thi-Mai-Trang.Nguyen@lip6.fr UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing
 GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
Ch 2.3.3 GSM PENN. Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98
 Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
MRN 6 GSM part 1. Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione. Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone
 Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0
 GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020508QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020508QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview
 The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
Using TEMS Pocket. Johan Montelius
 Using TEMS Pocket Johan Montelius Introduction In this laboration you will get acquainted with the TEMS Pocket tool. You will examine both the Monaco network and a commercial network. Since this is your
Using TEMS Pocket Johan Montelius Introduction In this laboration you will get acquainted with the TEMS Pocket tool. You will examine both the Monaco network and a commercial network. Since this is your
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
Global System for Mobile (GSM) Global System for Mobile (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile (GSM) David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program of Telecommunications and Networking University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2720 Slides 8 Based largely on material from Jochen
Global System for Mobile (GSM) David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program of Telecommunications and Networking University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2720 Slides 8 Based largely on material from Jochen
-The equipment was limited to operate only within the boundaries of each country. -The market for each mo bile equipment was limited.
 1 History of GSM During the early 1980s, analog cellular telephone systems were experienced a very fast growth in Europe, particularly in Scandinavia and the United Kingdom, but also in France and Germany.
1 History of GSM During the early 1980s, analog cellular telephone systems were experienced a very fast growth in Europe, particularly in Scandinavia and the United Kingdom, but also in France and Germany.
How To Make A Cell Phone Network More Efficient
 Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM
 Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM Comp.Eng. Serkan Kayacan (*), Prof. Levent Toker (**) (*): Ege University, The Institute of Science, Computer Engineering, M.S. Student
Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM Comp.Eng. Serkan Kayacan (*), Prof. Levent Toker (**) (*): Ege University, The Institute of Science, Computer Engineering, M.S. Student
RELEASE NOTE. Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08. Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90
 ETSI /TC SMG Release by : ETSI /PT 12 Release date : December 1995 RELEASE NOTE Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08 Radio Sub - system Link Control Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90 New
ETSI /TC SMG Release by : ETSI /PT 12 Release date : December 1995 RELEASE NOTE Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08 Radio Sub - system Link Control Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90 New
PART 4 GSM Radio Interface
 PRT 4 GSM Radio Interface Lecture 4. Physical channels Frequency [MHz] 960 OWNLINK BS MS 95 95 UPLINK MS BS 890 GSM Radio Spectrum 890.4 890.2 guard band 2 x 25 Mhz band uplex spacing: 45 MHz 24 carriers
PRT 4 GSM Radio Interface Lecture 4. Physical channels Frequency [MHz] 960 OWNLINK BS MS 95 95 UPLINK MS BS 890 GSM Radio Spectrum 890.4 890.2 guard band 2 x 25 Mhz band uplex spacing: 45 MHz 24 carriers
GSM GPRS. Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides)
 GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley
 Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G
 Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Appendix C GSM System and Modulation Description
 C1 Appendix C GSM System and Modulation Description C1. Parameters included in the modelling In the modelling the number of mobiles and their positioning with respect to the wired device needs to be taken
C1 Appendix C GSM System and Modulation Description C1. Parameters included in the modelling In the modelling the number of mobiles and their positioning with respect to the wired device needs to be taken
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 4: Medium Access Control October 5, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Medium Access Control Schemes: FDMA TDMA
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 4: Medium Access Control October 5, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Medium Access Control Schemes: FDMA TDMA
PW1 Monitoring a GSM network with a trace mobile
 LPRO WireLess Network and security PW1 Monitoring a GSM network with a trace mobile Module GSM MOBILE LPRO 2012-13 Experimental set-up: 1. SAGEM OT230/OT260 Trace Mobile and charger 2. GSM antenna and
LPRO WireLess Network and security PW1 Monitoring a GSM network with a trace mobile Module GSM MOBILE LPRO 2012-13 Experimental set-up: 1. SAGEM OT230/OT260 Trace Mobile and charger 2. GSM antenna and
How To Test Gsm Cell Phone Network On A Cell Phone
 G S M C E L L B R O A D C A S T S E RV I C E S E C U R I T Y A N A LY S I S arturo cedillo torres Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Eindhoven University of Technology Supervisors: Nicola Zannone
G S M C E L L B R O A D C A S T S E RV I C E S E C U R I T Y A N A LY S I S arturo cedillo torres Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Eindhoven University of Technology Supervisors: Nicola Zannone
Lecture overview. History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction. Basic architecture of GSM system. Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM
 Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Evaluating GSM A5/1 security on hopping channels
 Evaluating GSM A5/1 security on hopping channels Bogdan Diaconescu v1.0 This paper is a practical approach on evaluating A5/1 stream cipher on a GSM hopping network air interface called Um. The end goal
Evaluating GSM A5/1 security on hopping channels Bogdan Diaconescu v1.0 This paper is a practical approach on evaluating A5/1 stream cipher on a GSM hopping network air interface called Um. The end goal
GSM Architecture and Interfaces
 GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
Positioning in GSM. Date: 14th March 2003
 Positioning in GSM Date: 14th March 2003 Overview of seminar Potential applications in cellular network Review of localization system and techniques Localization in GSM system Progress of the project with
Positioning in GSM Date: 14th March 2003 Overview of seminar Potential applications in cellular network Review of localization system and techniques Localization in GSM system Progress of the project with
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface Hank Carter Professor Patrick Traynor 10/4/2012 UMTS and CDMA 3G technology - major change from GSM (TDMA) Based on techniques originally
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface Hank Carter Professor Patrick Traynor 10/4/2012 UMTS and CDMA 3G technology - major change from GSM (TDMA) Based on techniques originally
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems
 Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks
 Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks Thomas A. Cooper Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks Thomas A. Cooper Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
GSM VOICE CAPACITY EVOLUTION WITH VAMOS Strategic White Paper
 GSM VOICE CAPACITY EVOLUTION WITH VAMOS Strategic White Paper Table of contents VAMOS increases your GSM voice capacity at minimum investment / 1 Take the full benefit of VAMOS / 1 Standard aspects / 1
GSM VOICE CAPACITY EVOLUTION WITH VAMOS Strategic White Paper Table of contents VAMOS increases your GSM voice capacity at minimum investment / 1 Take the full benefit of VAMOS / 1 Standard aspects / 1
Roadmap for Establishing Interoperability of Heterogeneous Cellular Network Technologies -3-
 Roadmap for Establishing Interoperability of Heterogeneous Cellular Network Technologies -3- Hasni Neji Innov COM Lab, Higher School of Communications of Tunis, Sup Com University of Carthage, Tunis, Tunisia
Roadmap for Establishing Interoperability of Heterogeneous Cellular Network Technologies -3- Hasni Neji Innov COM Lab, Higher School of Communications of Tunis, Sup Com University of Carthage, Tunis, Tunisia
How To Understand The Power Of A Cell Phone Network
 TS 25.225 V3.12.0 (2003-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Physical layer Measurements (TDD) (Release 1999) The present
TS 25.225 V3.12.0 (2003-06) Technical Specification 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio Access Network; Physical layer Measurements (TDD) (Release 1999) The present
ETSI TS 100 912 V8.4.0 (2000-08)
 TS 100 912 V8.4.0 (2000-08) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Radio subsystem synchronization (GSM 05.10 version 8.4.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
TS 100 912 V8.4.0 (2000-08) Technical Specification Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Radio subsystem synchronization (GSM 05.10 version 8.4.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
The Network Layer Layer 3
 CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
Cellular Network Organization. Cellular Wireless Networks. Approaches to Cope with Increasing Capacity. Frequency Reuse
 Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
How To Make A Multi-User Communication Efficient
 Multiple Access Techniques PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 2011/12/8 Multiple Access Scheme Allow many users to share simultaneously a finite amount of radio spectrum Need to be done without severe degradation of the
Multiple Access Techniques PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 2011/12/8 Multiple Access Scheme Allow many users to share simultaneously a finite amount of radio spectrum Need to be done without severe degradation of the
3GPP Wireless Standard
 3GPP Wireless Standard Shishir Pandey School of Technology and Computer Science TIFR, Mumbai April 10, 2009 Shishir Pandey (TIFR) 3GPP Wireless Standard April 10, 2009 1 / 23 3GPP Overview 3GPP : 3rd Generation
3GPP Wireless Standard Shishir Pandey School of Technology and Computer Science TIFR, Mumbai April 10, 2009 Shishir Pandey (TIFR) 3GPP Wireless Standard April 10, 2009 1 / 23 3GPP Overview 3GPP : 3rd Generation
Agilent GSM/EDGE Self-Guided Demonstration for the E4438C ESG Vector Signal Generator and PSA Series Spectrum Analyzers
 Agilent GSM/EDGE Self-Guided Demonstration for the E4438C ESG Vector Signal Generator and PSA Series Spectrum Analyzers Product Note Striving to meet all your test needs Agilent knows that the time you
Agilent GSM/EDGE Self-Guided Demonstration for the E4438C ESG Vector Signal Generator and PSA Series Spectrum Analyzers Product Note Striving to meet all your test needs Agilent knows that the time you
Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. Lecture 2.1: Voice in GSM
 Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. Lecture.: Voice in GSM GSM Specified by ETSI Frequency Division Duplex TDMA system Originally at 900MHz, but today also at 800, 800,
Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. Lecture.: Voice in GSM GSM Specified by ETSI Frequency Division Duplex TDMA system Originally at 900MHz, but today also at 800, 800,
2G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
Exercise 2 Common Fundamentals: Multiple Access
 Exercise 2 Common Fundamentals: Multiple Access Problem 1: TDMA, guard time. To set up a GSM-connection, the base station (BTS) and the mobile station (MS) use the following short access burst in a TDMA-slot
Exercise 2 Common Fundamentals: Multiple Access Problem 1: TDMA, guard time. To set up a GSM-connection, the base station (BTS) and the mobile station (MS) use the following short access burst in a TDMA-slot
GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030852Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 08.52 TECHNICAL December 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-030852Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
Module 5. Broadcast Communication Networks. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
Optimization. Log File Analysis GSM
 Optimization and Log File Analysis in GSM by Somer GOKSEL January 26, 2003 2 Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...04 1.1 PURPOSE and SCOPE of OPTIMIZATION... 04 1.2 OPTIMIZATION PROCESS... 05 1.2.1 PROBLEM ANALYSIS...
Optimization and Log File Analysis in GSM by Somer GOKSEL January 26, 2003 2 Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...04 1.1 PURPOSE and SCOPE of OPTIMIZATION... 04 1.2 OPTIMIZATION PROCESS... 05 1.2.1 PROBLEM ANALYSIS...
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Monitoring for Handover from TDD to GSM
 Agenda Item: Source: Title: Document for: Siemens Monitoring for Handover from TDD to GSM Handover Preparation Monitoring for Handover from TDD to GSM The intention of this document is an explanation of
Agenda Item: Source: Title: Document for: Siemens Monitoring for Handover from TDD to GSM Handover Preparation Monitoring for Handover from TDD to GSM The intention of this document is an explanation of
Attenuation (amplitude of the wave loses strength thereby the signal power) Refraction Reflection Shadowing Scattering Diffraction
 Wireless Physical Layer Q1. Is it possible to transmit a digital signal, e.g., coded as square wave as used inside a computer, using radio transmission without any loss? Why? It is not possible to transmit
Wireless Physical Layer Q1. Is it possible to transmit a digital signal, e.g., coded as square wave as used inside a computer, using radio transmission without any loss? Why? It is not possible to transmit
Keysight E1968A GSM/GPRS/EGPRS Test Application
 Keysight E1968A GSM/GPRS/EGPRS Test Application For the E5515C/E wireless communications test set and the E1987A fast switching test application Technical Overview Accelerate production of high volume
Keysight E1968A GSM/GPRS/EGPRS Test Application For the E5515C/E wireless communications test set and the E1987A fast switching test application Technical Overview Accelerate production of high volume
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL THESIS
 NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA THESIS SOFTWARE-DEFINED RADIO GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS TRANSMITTER DEVELOPMENT FOR HETEROGENEOUS NETWORK VULNERABILITY TESTING by Carson C.
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA THESIS SOFTWARE-DEFINED RADIO GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS TRANSMITTER DEVELOPMENT FOR HETEROGENEOUS NETWORK VULNERABILITY TESTING by Carson C.
PXI. www.aeroflex.com. GSM/EDGE Measurement Suite
 PXI GSM/EDGE Measurement Suite The GSM/EDGE measurement suite is a collection of software tools for use with Aeroflex PXI 3000 Series RF modular instruments for characterising the performance of GSM/HSCSD/GPRS
PXI GSM/EDGE Measurement Suite The GSM/EDGE measurement suite is a collection of software tools for use with Aeroflex PXI 3000 Series RF modular instruments for characterising the performance of GSM/HSCSD/GPRS
Yu.M. Tulyakov, D.Ye. Shakarov, A.A. Kalashnikov. Keywords: Data broadcasting, cellular mobile systems, WCDMA, GSM.
 Аnalysis of data broadcasting in modern cellular mobile systems of ground radio communications Yu.M. Tulyakov, D.Ye. Shakarov, A.A. Kalashnikov At the analysis of channel formation in WCDMA networks the
Аnalysis of data broadcasting in modern cellular mobile systems of ground radio communications Yu.M. Tulyakov, D.Ye. Shakarov, A.A. Kalashnikov At the analysis of channel formation in WCDMA networks the
TSG-RAN Meeting #7 Madrid, Spain, 13 15 March 2000 RP-000034. Title: Agreed CRs to TS 25.301. Agenda item: 6.3.3
 TSG-RAN Meeting #7 Madrid, Spain, 13 15 March 2000 RP-000034 Title: Agreed CRs to TS 25.301 Source: TSG-RAN WG2 Agenda item: 6.3.3 Doc-1st- Spec CR Rev Subject Cat Version Versio R2-000213 25.301 032 Correction
TSG-RAN Meeting #7 Madrid, Spain, 13 15 March 2000 RP-000034 Title: Agreed CRs to TS 25.301 Source: TSG-RAN WG2 Agenda item: 6.3.3 Doc-1st- Spec CR Rev Subject Cat Version Versio R2-000213 25.301 032 Correction
Revision of Lecture Eighteen
 Revision of Lecture Eighteen Previous lecture has discussed equalisation using Viterbi algorithm: Note similarity with channel decoding using maximum likelihood sequence estimation principle It also discusses
Revision of Lecture Eighteen Previous lecture has discussed equalisation using Viterbi algorithm: Note similarity with channel decoding using maximum likelihood sequence estimation principle It also discusses
GSM GSM 05.05 TECHNICAL March 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 05.05 TECHNICAL March 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020505Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.05 TECHNICAL March 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020505Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
EPL 657 Wireless Networks
 EPL 657 Wireless Networks Some fundamentals: Multiplexing / Multiple Access / Duplex Infrastructure vs Infrastructureless Panayiotis Kolios Recall: The big picture... Modulations: some basics 2 Multiplexing
EPL 657 Wireless Networks Some fundamentals: Multiplexing / Multiple Access / Duplex Infrastructure vs Infrastructureless Panayiotis Kolios Recall: The big picture... Modulations: some basics 2 Multiplexing
RADIUS. Brief brochure. Product Purpose
 Product Purpose The Product is designed for searching, intercepting, registering and analyzing of communication sessions as well as service information circulating in cellular GSM networks without encryption
Product Purpose The Product is designed for searching, intercepting, registering and analyzing of communication sessions as well as service information circulating in cellular GSM networks without encryption
RESOURCE ALLOCATION FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC CLASS OVER GPRS
 RESOURCE ALLOCATION FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC CLASS OVER GPRS Edward Nowicki and John Murphy 1 ABSTRACT The General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a new bearer service for GSM that greatly simplify wireless
RESOURCE ALLOCATION FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC CLASS OVER GPRS Edward Nowicki and John Murphy 1 ABSTRACT The General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a new bearer service for GSM that greatly simplify wireless
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location. Controls user connection. Transmission.
 Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
VAMOS Technology Introduction Application Note
 VAMOS Technology Introduction Application Note R&S SMU200A R&S SMBV100A R&S AMU200A R&S CMW500 R&S FSQ R&S FSG R&S FSV R&S FSVR Existing GSM mobile communication systems have the potential to double voice
VAMOS Technology Introduction Application Note R&S SMU200A R&S SMBV100A R&S AMU200A R&S CMW500 R&S FSQ R&S FSG R&S FSV R&S FSVR Existing GSM mobile communication systems have the potential to double voice
INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA
 COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/6/2014 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/6/2014 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
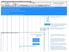 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
How To Understand The Theory Of Time Division Duplexing
 Multiple Access Techniques Dr. Francis LAU Dr. Francis CM Lau, Associate Professor, EIE, PolyU Content Introduction Frequency Division Multiple Access Time Division Multiple Access Code Division Multiple
Multiple Access Techniques Dr. Francis LAU Dr. Francis CM Lau, Associate Professor, EIE, PolyU Content Introduction Frequency Division Multiple Access Time Division Multiple Access Code Division Multiple
FIGURE 12-1 Original Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) frequency spectrum
 FIGURE 12-1 Original Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) frequency spectrum FIGURE 12-2 Complete Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) frequency spectrum TABLE 12-1 AMPS Frequency Allocation TABLE 12-2
FIGURE 12-1 Original Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) frequency spectrum FIGURE 12-2 Complete Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) frequency spectrum TABLE 12-1 AMPS Frequency Allocation TABLE 12-2
Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS, UMTS. GSM as basis of current systems Satellites and
 Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
GSM Network and Services
 GSM Network and Services Cellular networks GSM Network and Services 2G1723 Johan Montelius 1 The name of the game The number one priority for mobile/cellular networks is to implement full-duplex voice
GSM Network and Services Cellular networks GSM Network and Services 2G1723 Johan Montelius 1 The name of the game The number one priority for mobile/cellular networks is to implement full-duplex voice
Chapter 6 Bandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spreading 6.1
 Chapter 6 Bandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spreading 6.1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Note Bandwidth utilization is the wise use of
Chapter 6 Bandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spreading 6.1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Note Bandwidth utilization is the wise use of
Coverage measurement systems. Radio Network Analyzer R&S TSMU. Interferences a frequent impairment in radio networks
 MOBILE RADIO Coverage measurement systems 44820/2 FIG 1 The R&S TSMU automatically detects, analyzes and displays the results of co-channel and adjacent-channel interferences in GSM networks during a drive
MOBILE RADIO Coverage measurement systems 44820/2 FIG 1 The R&S TSMU automatically detects, analyzes and displays the results of co-channel and adjacent-channel interferences in GSM networks during a drive
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]
![192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]](/thumbs/18/698539.jpg) 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
Base Station Adjacent Time Slot Rejection Measurement with CMD and SME
 Base Station Adjacent Time Slot Rejection Measurement with CMD and SME Application Note 1GPAN26E 1CMP F.Körber, 1GPP M. Leutiger Products: Signal Generator SME Radio Communication Tester CMD54/57 General
Base Station Adjacent Time Slot Rejection Measurement with CMD and SME Application Note 1GPAN26E 1CMP F.Körber, 1GPP M. Leutiger Products: Signal Generator SME Radio Communication Tester CMD54/57 General
# DEFINITIONS TERMS. A standard cellular telephone service (CTS) initially placed into operation on Oct. 13, 1983.
 CHAPTER 20 CELLULAR TELEPHONE SYSTEM # DEFINITIONS TERMS 1) Stands for Standard Cellular Telephone Service CTS 2) An acronym for Personal Communications System. PCS 3) Stands for Personal Communications
CHAPTER 20 CELLULAR TELEPHONE SYSTEM # DEFINITIONS TERMS 1) Stands for Standard Cellular Telephone Service CTS 2) An acronym for Personal Communications System. PCS 3) Stands for Personal Communications
Multiplexing on Wireline Telephone Systems
 Multiplexing on Wireline Telephone Systems Isha Batra, Divya Raheja Information Technology, Dronacharya College of Engineering Farrukh Nagar, Gurgaon, India ABSTRACT- This Paper Outlines a research multiplexing
Multiplexing on Wireline Telephone Systems Isha Batra, Divya Raheja Information Technology, Dronacharya College of Engineering Farrukh Nagar, Gurgaon, India ABSTRACT- This Paper Outlines a research multiplexing
CMU200: 2 2,5 Generation of Mobile Communication Systems GSM / GPRS / EGPRS. 2 MAR Re 1 1 CMU 200 GSM / GPRS / EGPRS
 CMU200: 2 2,5 Generation of Mobile Communication Systems GSM / GPRS / EGPRS 2 MAR Re 1 1 08/00 of GSM, GPRS and EGPRS Basic Information about: u Physical Resource u GMSK and 8PSK u Mapping u Coding Schemes
CMU200: 2 2,5 Generation of Mobile Communication Systems GSM / GPRS / EGPRS 2 MAR Re 1 1 08/00 of GSM, GPRS and EGPRS Basic Information about: u Physical Resource u GMSK and 8PSK u Mapping u Coding Schemes
NETWORK AND RF PLANNING
 NETWORK AND RF PLANNING Introduction Achieving maximum capacity while maintaining an acceptable grade of service and good speech quality is the main issue for the network planning. Planning an immature
NETWORK AND RF PLANNING Introduction Achieving maximum capacity while maintaining an acceptable grade of service and good speech quality is the main issue for the network planning. Planning an immature
Hello viewers, welcome to today s lecture on cellular telephone systems.
 Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture minus 31 Cellular Telephone Systems Hello viewers, welcome to today s lecture
Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture minus 31 Cellular Telephone Systems Hello viewers, welcome to today s lecture
CDMA Network Planning
 CDMA Network Planning by AWE Communications GmbH www.awe-com.com Contents Motivation Overview Network Planning Module Air Interface Cell Load Interference Network Simulation Simulation Results by AWE Communications
CDMA Network Planning by AWE Communications GmbH www.awe-com.com Contents Motivation Overview Network Planning Module Air Interface Cell Load Interference Network Simulation Simulation Results by AWE Communications
Mobile Computing. Basic Call Calling terminal Network Called terminal 10/25/14. Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN. CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014
 Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
How To Improve Data Rates For Global Evolution (Edge)
 EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution SIDDARTH WANDRE ID: 999-29-3194 CS 548: Broadband Networks ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Abstract:- This paper gives an overview of the EDGE concept. It gives
EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution SIDDARTH WANDRE ID: 999-29-3194 CS 548: Broadband Networks ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Abstract:- This paper gives an overview of the EDGE concept. It gives
Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks
 Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Vehicle Theft Intimation Using GSM
 ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Vol, 04 Issue, 8 August 2014 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Vehicle Theft Intimation Using GSM 1, Minakshi Kumari, 2, Prof. Manoj Singh 1, 2, Computer
ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Vol, 04 Issue, 8 August 2014 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Vehicle Theft Intimation Using GSM 1, Minakshi Kumari, 2, Prof. Manoj Singh 1, 2, Computer
MicroNet dual band IMSI and IMEI catcher
 MicroNet dual band IMSI and IMEI catcher Datasheet Models: MNG-300-01 (GSM 900, 1800) MNG-300-02 (GSM 850, 1900) Document Nr OTK-012010 Date: 10-09-2012, revision B Table of contents 1. Acronyms and abbreviations
MicroNet dual band IMSI and IMEI catcher Datasheet Models: MNG-300-01 (GSM 900, 1800) MNG-300-02 (GSM 850, 1900) Document Nr OTK-012010 Date: 10-09-2012, revision B Table of contents 1. Acronyms and abbreviations
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
Scanning with Sony Ericsson TEMS Phones. Technical Paper
 Scanning with Sony Ericsson TEMS Phones Technical Paper Scanning with Sony Ericsson TEMS Phones 2009-05-13 Ascom 2009. All rights reserved. TEMS is a trademark of Ascom. All other trademarks are the property
Scanning with Sony Ericsson TEMS Phones Technical Paper Scanning with Sony Ericsson TEMS Phones 2009-05-13 Ascom 2009. All rights reserved. TEMS is a trademark of Ascom. All other trademarks are the property
