Theory and Practice. IT-Security: GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.7. Mobile Communication. December 18, GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.
|
|
|
- Joel Lawrence
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke Lecture Homepage: Uwe Jendricke, 11/2001 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 1 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 2 Location Retrieval starting... Location Retrieval locked Area: Hamburg Mapping... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 3 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 4
2 Location Retrieval locked Area: Hamburg Map: zooming Location: Participant Hack in City: Hamburg Location Retrieval locked Area: Hamburg Map: zooming Location: Participant Hack in City: Hamburg Area: Inner City IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 5 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 6 Participant: Hack arrested Location Retrieval locked Area: Hamburg Map: zooming Location: Participant Hack in City: Hamburg Area: Jungfernstieg/ Neuer Wall LAI: 1837HH483NJ MSISDN: Aus dem Film `Blues Brothers` IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 7 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 8
3 Characteristics of Mobile Communication Security aspects Moving participants and devices Limited power (HF, CPU, display, etc) of devices Devices change networks (roaming) Radio transmission: - Air interface (broadcast) - Interferences - Limited bandwidth More risks than in fixed networks Location retrieval Movement profiles Adversarial environment Misuse by third parties Wireless interface Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 9 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 10 Example: GSM Cell Structure of GSM Global System for Mobile Communication High mobility, even internationally (roaming) Size depending on local conditions and # of users High reachability with only one call number High capacity High availability Integrated security mechanisms: Picocell Mikrocell Makrocell Hypercell Overlaycell d < 100m d < 1 km d < 20 km d < 60 km d < 400 km Encryption of transmitted data Authentification (PIN, Smart Card) Base station for >= 1 cells Temporary identification (pseudonyms) IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 11 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 12
4 Frequency Usage Architecture (1/2) Efficiency Problems with over range Efficiency decreases with cell size Downsizing cells: Precise location determination More confidentiality Lower transmission power Four subsystems of GSM Mobile Station (= Mobile Equipment + Subscriber Identity Module) Base Station Sub-System Network Sub-System Mobile Switching Center Home Location Register Visitor Location Register Authentication Center Equipment Identity Register Network Management Center Operation and Maintenance Center IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 13 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 14 Architecture (2/2) AUC Authentication Center EIR Equipment Identity Register BS Base Station GMSC Gateway MSC MS Mobile Station PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network Example: Calling from fixed network Caller Guest MSC Home MSC Routing to GMSC Connecting to home-msc Reading of HLR VLR-address Guest-MSC address IMSI Connecting to guest-msc Reading from VLR (IMSI -> TMSI) Connecting to MS (with TMSI) Authentication of the MS by challenge-response (with AuC) Call setup Location Areas IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 15 Location AuC Authentication Center BS Base Station EIR Equipment Identity Register GMSC Gateway Mobile Switching Center Location Areas TMSITemporary Mobile Subscriber Number IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication Subscriber Identity Module 16
5 Subscriber Identity Module Smart Card in Mobile Station (Mobile Phone) Stores private user data Splitting device- and user mobility K i (user specific, symmetric key) Algorithm A3 for challenge-response-authentication Algorithm A8 for generation of K c LAI PIN IMSI TMSI user specific symmetric session key MS Mobile Station PIN Personal Identification Number TMSI Temporary Mobile Subscriber Number LAI Location Area Identification Home Location Register HLR HLR stores data of the user IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Number) MSISDN (Mobile Subscriber International ISDN Number) Personal data (name, address, bank account, etc.) Service profile (priorities, call forwarding, restrictions) VLR-address, guest-msc-address Billing data Security conflict: Reachability location information MSISDN Mobile Subscriber International ISDN Number TMSI Temporary Mobile Subscriber Number IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 17 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 18 Visitor Location Register VLR VLR stores data of the user used at the MSC IMSI, MSISDN TMSI (Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) MSRN (Mobile Station Roaming Number) LAI (Location Area Identification) Home-MSC-address, HLR-address Billing data TMSI Temporary Mobile Subscriber Number MSISDN Mobile Subscriber International ISDN Number Authentication Center AuC Stores user key K i Generates session key K c from K i and random number Authentication with challenge-response AuC sends random number to mobile AuC receives response (generated on the by A3 (with challenge as input)) AuC compares response to self generated value Algorithm A3 Not standardized Defined by telecommunication company (telco) Secret algorithm: security by obscurity Subscriber Identity Module symmetric user key, in and in AuC IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 19 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 20
6 Repeat: Call from fixed network Guest MSC Location Caller Home MSC Location Areas Routing to the GMSC Connecting to home-msc Reading from HLR VLR-address Guest-MSC address IMSI Connecting to guest-msc Reading from VLR (IMSI -> TMSI) Connecting to MS (with TMSI) Authentication of MS by challengeresponse (with AuC) Call setup AUC Authentication Center BS Base Station EIR Equipment Identity Register TMSITemporary Mobile Subscriber Number Subscriber Identity Module User Authentification Mobile Station A3 Initiated at: Location registration Location update with VLR-switching Call setup (in both directions) Activation of additional services Short Message Service (SMS) Authentication Request RAND Unilateral Authentication! AuC RandomGenerator A3 Authentication Response SRES 32 bit = True? 32 bit A3 secret algorithm AuC Authentication Center user specific symmetric key Subscriber Identity Module IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 21 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 22 Pseudonymization of the user Mobile Station TMSI old IMSI TMSI new (Message with TMSI) old LAI, old TMSI When TMSI not known: identity request identity response(imsi) TMSI reallocation command {new TMSI} TMSI reallocation complete TMSI (Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) No linkability of user s actions Algorithm for generation: by telco Transmission of IMSI at first login or after error (attack: IMSI-Catcher) Network VLR: relation TMSI - IMSI VLR: generation of TMSI VLR: storing TMSI BSC:encryption with Deleting old TMSI BSC Base Station Controller user specific symmetric session key LAI Location Area Identification Subscriber Identity Module TMSITemporary Mobile Subscriber Number Link Encryption (1/2) Mobile Station A8 stored in used in MS Key generation Authentication Request RAND AuC RandomGenerator A8 64 bit 64 bit is session key Algorithm A8 In and in authentication center AuC parameterized one way function Standardized interfaces, non-standardized algorithm A3/A8 known as COMP128 stored in HLR used in BSC AuC Authentication Center BSC Base Station Controller user specific symmetric session key MS Mobile Station Subscriber Identity Module IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 23 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 24
7 Link Encryption (2/2) 64 bit Mobile Station 114 bit bit Cleartext xor block Cleartextblock TDMA- Frame Number Key block 22 bit Transmission Ciphering Mode Command (Encryption Mode) Encrypted text (Ciphering Mode Complete) Algorithm In the mobile station, not in! Worldwide standardization Weak algorithm * or /2 in some countries Netz TDMA- Frame- Number 22 bit 114 bit + xor 64 bit AuC Authentication Center BSC Base Station Controller user specific symmetric session key MS Mobile Station Subscriber Identity Module TDMA Time Division Multiple Access Security in GSM: Overview Mobile Station Base Station (BS) Guest-MSC Home-MSC A3 A8 Encrypted radio transmission BS-Controller RAND SRES Non-encrypted directed radio transmission VLR generatestmsi AuC RandomGenerator = IMSI A3 A8 Non-encrypted transmission by wire HLR IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 25 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 26 Security Relevant Functionality for access control (PIN) and authentication Unilateral authentication (MS network) by challenge-response Pseudonymization of the participants on the air interface (TMSI) Link encryption on the air interface Security Problems in GSM Confidentiality of location information only against outsider Radio-bearing of MS possible No bit transparency no end-to-end encryption possible No end-to-end authentication Some secret crypto algorithms Only symmetric crypto algorithms Key management without user control No anonymous activity possible Users must trust the billing data IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 27 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 28
8 Protection of location information Further Information Hannes Federrath: Mobile Communication Database request Database request GSM Security and Links Distribution service Hack by german Chaos Computer Club (in german) Trusted Area Personal Trusted Area Exercise on Thursday, in Building 051, SR Source: Hannes Federrath IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 29 IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication 30
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology
 Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE [email protected] UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE [email protected] UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
GSM Databases. Virginia Location Area HLR Vienna Cell Virginia BSC. Virginia MSC VLR
 Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
2 System introduction
 2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
2 System introduction Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to describe the different nodes in a GSM network. be able to describe geographical subdivision of a GSM network. be able to
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
GSM and UMTS security
 2007 Levente Buttyán Why is security more of a concern in wireless? no inherent physical protection physical connections between devices are replaced by logical associations sending and receiving messages
2007 Levente Buttyán Why is security more of a concern in wireless? no inherent physical protection physical connections between devices are replaced by logical associations sending and receiving messages
Authentication and Secure Communication in GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Using Asymmetric Cryptography
 ISSN (Online): 1694-0784 ISSN (Print): 1694-0814 10 Authentication and Secure Communication in GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Using Asymmetric Cryptography Wilayat Khan 1 and Habib Ullah 2 1 Department of Electrical
ISSN (Online): 1694-0784 ISSN (Print): 1694-0814 10 Authentication and Secure Communication in GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Using Asymmetric Cryptography Wilayat Khan 1 and Habib Ullah 2 1 Department of Electrical
GSM Research. Chair in Communication Systems Department of Applied Sciences University of Freiburg 2010
 Chair in Communication Systems Department of Applied Sciences University of Freiburg 2010 Dennis Wehrle, Konrad Meier, Dirk von Suchodoletz, Klaus Rechert, Gerhard Schneider Overview 1. GSM Infrastructure
Chair in Communication Systems Department of Applied Sciences University of Freiburg 2010 Dennis Wehrle, Konrad Meier, Dirk von Suchodoletz, Klaus Rechert, Gerhard Schneider Overview 1. GSM Infrastructure
Ch 2.3.3 GSM PENN. Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98
 Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Lecture overview. History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction. Basic architecture of GSM system. Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM
 Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G
 Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location. Controls user connection. Transmission.
 Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
Mobile Office Security Requirements for the Mobile Office
 Mobile Office Security Requirements for the Mobile Office [email protected] Alcatel SEL AG 20./21.06.2001 Overview Security Concepts in Mobile Networks Applications in Mobile Networks Mobile Terminal used
Mobile Office Security Requirements for the Mobile Office [email protected] Alcatel SEL AG 20./21.06.2001 Overview Security Concepts in Mobile Networks Applications in Mobile Networks Mobile Terminal used
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
9.1 Introduction. 9.2 Roaming
 9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
GSM System Architecture
 Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
Wireless Mobile Telephony
 Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 [email protected] http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 [email protected] http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Mobile Services (ST 2010)
 Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY:
 GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
2G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
GSM Architecture Training Document
 Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (20) The information in this document is subject to change without notice and describes only the product defined in the introduction of this documentation.
Security in the GSM Network
 Security in the GSM Network Ammar Yasir Korkusuz 2012 Bogazici University, Electrical-Electronics Engineering Department, MSc. Student EE 588 NETWORK SECURITY TERM PROJECT Abstract: GSM is the biggest
Security in the GSM Network Ammar Yasir Korkusuz 2012 Bogazici University, Electrical-Electronics Engineering Department, MSc. Student EE 588 NETWORK SECURITY TERM PROJECT Abstract: GSM is the biggest
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 13: VoIP Service for Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Dec. 2006
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 13: VoIP Service for Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Dec. 2006
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview
 The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
UMTS security. Helsinki University of Technology S-38.153 Security of Communication Protocols [email protected] 15.4.2003
 UMTS security Helsinki University of Technology S-38.153 Security of Communication Protocols [email protected] 15.4.2003 Contents UMTS Security objectives Problems with GSM security UMTS security mechanisms
UMTS security Helsinki University of Technology S-38.153 Security of Communication Protocols [email protected] 15.4.2003 Contents UMTS Security objectives Problems with GSM security UMTS security mechanisms
What is telecommunication? electronic communications? What is telephony?
 What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS, UMTS. GSM as basis of current systems Satellites and
 Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' Giuseppe Bianchi
 !!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
Mobile Phone Security. Hoang Vo Billy Ngo
 Mobile Phone Security Hoang Vo Billy Ngo Table of Content 1. Introduction Page 2 1.1 Analog Network Page 2 1.2 Digital Network Page 2 2. Security Protocols Page 4 2.1 Analog Page 4 2.2 Digital Page 5 3.
Mobile Phone Security Hoang Vo Billy Ngo Table of Content 1. Introduction Page 2 1.1 Analog Network Page 2 1.2 Digital Network Page 2 2. Security Protocols Page 4 2.1 Analog Page 4 2.2 Digital Page 5 3.
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 7: GSM Network Signaling Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Nov. 2006 1 Outline
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 7: GSM Network Signaling Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Nov. 2006 1 Outline
What is telecommunication? electronic communications. service?
 What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
What is telecommunication? Telecommunication: Any transmission, emission or reception of signs, signals, writing, images and sounds or intelligence of any nature by wire, radio, optical or other electromagnetic
Cellular Network Organization
 Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Cellular Network Organization. Cellular Wireless Networks. Approaches to Cope with Increasing Capacity. Frequency Reuse
 Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Network Security. Chapter 14. Security Aspects of Mobile Communications
 Network Security Chapter 14 Security Aspects of Mobile Communications Network Security (WS 2002): 14 Security Aspects of Mobile Communications 1 Security Aspects of Mobile Communication Mobile communication
Network Security Chapter 14 Security Aspects of Mobile Communications Network Security (WS 2002): 14 Security Aspects of Mobile Communications 1 Security Aspects of Mobile Communication Mobile communication
Mobile Computing. Basic Call Calling terminal Network Called terminal 10/25/14. Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN. CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014
 Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Definition Global system for mobile communication (GSM) is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communication. GSM is the name of a standardization
Mobile Wireless Overview
 Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
IMSI Catcher. Daehyun Strobel. 13.Juli 2007. Seminararbeit Ruhr-Universität Bochum. Chair for Communication Security Prof. Dr.-Ing.
 IMSI Catcher Daehyun Strobel 13.Juli 2007 Seminararbeit Ruhr-Universität Bochum Chair for Communication Security Prof. Dr.-Ing. Christof Paar Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 GSM (Global System for Mobile
IMSI Catcher Daehyun Strobel 13.Juli 2007 Seminararbeit Ruhr-Universität Bochum Chair for Communication Security Prof. Dr.-Ing. Christof Paar Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 GSM (Global System for Mobile
Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系
 Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系 Mobility Management in Cellular Systems Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC cell BTS BTS BTS BTS MT BTS BTS BTS BTS HLR and VLR HLR (Home Location Register)
Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系 Mobility Management in Cellular Systems Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC cell BTS BTS BTS BTS MT BTS BTS BTS BTS HLR and VLR HLR (Home Location Register)
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
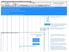 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
Encrypted SMS, an analysis of the theoretical necessities and implementation possibilities
 Radboud University Nijmegen Bachelor Thesis Encrypted SMS, an analysis of the theoretical necessities and implementation possibilities Author: Lars Lockefeer Supervisors: Engelbert Hubbers Roel Verdult
Radboud University Nijmegen Bachelor Thesis Encrypted SMS, an analysis of the theoretical necessities and implementation possibilities Author: Lars Lockefeer Supervisors: Engelbert Hubbers Roel Verdult
Development of Wireless Networks
 Development of Wireless Networks Cellular Revolution In 1990 mobile phone users populate 11 million. By 2004 the figure will become 1 billion Phones are most obvious sign of the success of wireless technology.
Development of Wireless Networks Cellular Revolution In 1990 mobile phone users populate 11 million. By 2004 the figure will become 1 billion Phones are most obvious sign of the success of wireless technology.
An Example of Mobile Forensics
 An Example of Mobile Forensics Kelvin Hilton K319 kchilton@staffsacuk [email protected] www.soc.staffs.ac.uk/kch1 Objectives The sources of evidence The subscriber The mobile station The network
An Example of Mobile Forensics Kelvin Hilton K319 kchilton@staffsacuk [email protected] www.soc.staffs.ac.uk/kch1 Objectives The sources of evidence The subscriber The mobile station The network
Communication Infrastructure: GSM Communication
 Communication Infrastructure: GSM Communication Andreas Schöffl and Michael Irger Abstract. In this Paper we describe the GSM Standard of Mobile Phones. The Global System for Mobile communications is the
Communication Infrastructure: GSM Communication Andreas Schöffl and Michael Irger Abstract. In this Paper we describe the GSM Standard of Mobile Phones. The Global System for Mobile communications is the
GSM Architecture and Interfaces
 GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL THESIS
 NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA THESIS SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE (SMS) SECURITY SOLUTION FOR MOBILE DEVICES by Yu Loon Ng December 2006 Thesis Advisor: Co-Advisor: Gurminder Singh John Gibson
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA THESIS SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE (SMS) SECURITY SOLUTION FOR MOBILE DEVICES by Yu Loon Ng December 2006 Thesis Advisor: Co-Advisor: Gurminder Singh John Gibson
GSM GPRS. Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides)
 GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
Cellular Phone Systems
 Cellular Phone Systems Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC 1 Why Cellular Mobile Telephone Systems? Operational limitations of conventional mobile
Cellular Phone Systems Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC 1 Why Cellular Mobile Telephone Systems? Operational limitations of conventional mobile
GSM Security Claude Castelluccia INRIA
 GSM Security Claude Castelluccia INRIA Technology behind GSM 900 MHz (or 1800 MHz) band uplink frequency band 890-915 MHz downlink frequency band is 935-960 MHz 25 MHz subdivided into 124 carrier frequency
GSM Security Claude Castelluccia INRIA Technology behind GSM 900 MHz (or 1800 MHz) band uplink frequency band 890-915 MHz downlink frequency band is 935-960 MHz 25 MHz subdivided into 124 carrier frequency
In this Lecture" Access method CDMA" Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
GSM System. Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM Network Structure and Network Planning. Contents: Dipl.- Ing. Reiner Stuhlfauth, ROHDE & SCHWARZ; Training Centre
 GSM Network Structure and Network Planning Dipl.- Ing. Reiner Stuhlfauth, ROHDE & SCHWARZ; Training Centre Contents: 1. Geographical structures in a GSM network 2. Methods of network planning 2.1. Principles
GSM Network Structure and Network Planning Dipl.- Ing. Reiner Stuhlfauth, ROHDE & SCHWARZ; Training Centre Contents: 1. Geographical structures in a GSM network 2. Methods of network planning 2.1. Principles
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Mobility and cellular networks
 Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems. Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering
 Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
MRN 6 GSM part 1. Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione. Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone
 Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server
 Application Note EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server Introduction The demand for wireless LAN (WLAN) access to the public IP network is growing rapidly. It is only
Application Note EAP-SIM Authentication using Interlink Networks RAD-Series RADIUS Server Introduction The demand for wireless LAN (WLAN) access to the public IP network is growing rapidly. It is only
Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS
 Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 2.1 Network Architectures 2.2 Concepts
Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 2.1 Network Architectures 2.2 Concepts
Locating Mobile Phones using Signalling System #7. Tobias Engel <[email protected]> twitter: @2b_as
 Locating Mobile Phones using Signalling System #7 Tobias Engel twitter: @2b_as What is Signalling System #7? protocol suite used by most telecommunications operators throughout the world
Locating Mobile Phones using Signalling System #7 Tobias Engel twitter: @2b_as What is Signalling System #7? protocol suite used by most telecommunications operators throughout the world
1 Introduction. 2 Assumptions. Implementing roaming for OpenBTS
 Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
Implementing roaming for OpenBTS 1 Introduction One of the main advantages of OpenBTS TM system architecture is absence of a legacy GSM core network. SIP is used for registering, call control and messaging.
How To Understand The Performance Of A Cell Phone Network
 Survivability Analysis for Mobile Cellular Networks David W. Tipper *, Chalermpol Charnsripinyo *, Hyundoo Shin * Teresa A. Dahlberg ** * Department of Information Science and Telecommunications, University
Survivability Analysis for Mobile Cellular Networks David W. Tipper *, Chalermpol Charnsripinyo *, Hyundoo Shin * Teresa A. Dahlberg ** * Department of Information Science and Telecommunications, University
1. Introduction: The Evolution of Mobile Telephone Systems
 IEC: The Global System for Mobile Communication Tutorial: Index Page 1 of 14 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Tutorial Definition Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) is a globally
IEC: The Global System for Mobile Communication Tutorial: Index Page 1 of 14 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Tutorial Definition Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) is a globally
Formal Analysis of A Novel Mutual Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol
 Formal Analysis of A Novel Mutual Authentication and ey Agreement Protocol Ja'afer M. AL-Saraireh Applied Science University Amman 11961, Jordan Saleh S. Saraireh Philadelphia University Amman 11961, Jordan
Formal Analysis of A Novel Mutual Authentication and ey Agreement Protocol Ja'afer M. AL-Saraireh Applied Science University Amman 11961, Jordan Saleh S. Saraireh Philadelphia University Amman 11961, Jordan
Bölüm 8. GSM. 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar!
 Bölüm 8. GSM http://ceng.gazi.edu.tr/~ozdemir Durum 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar! * http://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/ind/d-ind-ictoi-2012-sum-pdf-e.pdf 1 Global
Bölüm 8. GSM http://ceng.gazi.edu.tr/~ozdemir Durum 6 Milyar mobil telefon kullanıcısı (2011 sonu)* Dünya nüfusu 7 Milyar! * http://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/ind/d-ind-ictoi-2012-sum-pdf-e.pdf 1 Global
ETSI ETR 363 TECHNICAL January 1997 REPORT
 ETSI ETR 363 TECHNICAL January 1997 REPORT Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: DTR/SMG-101020Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile communications (GSM)
ETSI ETR 363 TECHNICAL January 1997 REPORT Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: DTR/SMG-101020Q ICS: 33.020 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile communications (GSM)
Module 5. Broadcast Communication Networks. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
Toolkit for vulnerability assessment in 3G networks. Kameswari Kotapati The Pennsylvania State University University Park PA 16802
 Toolkit for vulnerability assessment in 3G networks Kameswari Kotapati The Pennsylvania State University University Park PA 16802 Contents Motivation Solution Overview Methodology Overview 3G Attack Graph
Toolkit for vulnerability assessment in 3G networks Kameswari Kotapati The Pennsylvania State University University Park PA 16802 Contents Motivation Solution Overview Methodology Overview 3G Attack Graph
29.09.2015. Digital Communications Exploring SS7 signaling fraud that threatens mobile network security and subscriber privacy
 29.09.2015 Digital Communications Exploring SS7 signaling fraud that threatens mobile Mobile communications is a prime target for hackers who desire to penetrate critical infrastructures and businesses
29.09.2015 Digital Communications Exploring SS7 signaling fraud that threatens mobile Mobile communications is a prime target for hackers who desire to penetrate critical infrastructures and businesses
Mobile Security. Practical attacks using cheap equipment. Business France. Presented the 07/06/2016. For. By Sébastien Dudek
 Mobile Security Practical attacks using cheap equipment Presented the 07/06/2016 Business France By Sébastien Dudek For Content Security measures Recent publications in the hacking community Practical
Mobile Security Practical attacks using cheap equipment Presented the 07/06/2016 Business France By Sébastien Dudek For Content Security measures Recent publications in the hacking community Practical
ETSI TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06)
 TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
TR 101 643 V8.0.0 (2000-06) Technical Report Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); General network interworking scenarios (GSM 09.01 version 8.0.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE
ETSI TS 123 251 V6.5.0 (2005-09)
 TS 123 251 V6.5.0 (2005-09) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Network sharing; Architecture and functional description (3GPP TS 23.251 version 6.5.0 Release 6)
TS 123 251 V6.5.0 (2005-09) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Network sharing; Architecture and functional description (3GPP TS 23.251 version 6.5.0 Release 6)
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley
 Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
International Journal of Computing and Business Research (IJCBR)
 AN INVESTIGATION OF GSM ARCHITECTURE AND OVERLAYING WITH EFFICIENT SECURITY PROTOCOL Karun Madan, Surya World Institute of Engg. & Technology, Rajpura, Punjab ABSTRACT The Global System for Mobile Communications
AN INVESTIGATION OF GSM ARCHITECTURE AND OVERLAYING WITH EFFICIENT SECURITY PROTOCOL Karun Madan, Surya World Institute of Engg. & Technology, Rajpura, Punjab ABSTRACT The Global System for Mobile Communications
Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks
 Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 10.1 GSM-IP: VoIP Service for GSM 256
Chapter 10 VoIP for the Non-All-IP Mobile Networks Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 10.1 GSM-IP: VoIP Service for GSM 256
The GSM Standard (An overview of its security)
 Interested in learning more about security? SANS Institute InfoSec Reading Room This paper is from the SANS Institute Reading Room site. Reposting is not permitted without express written permission. The
Interested in learning more about security? SANS Institute InfoSec Reading Room This paper is from the SANS Institute Reading Room site. Reposting is not permitted without express written permission. The
Chapter 3: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks
 Chapter 3: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks IEEE Wireless Communication, Oct. 2002 Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National
Chapter 3: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks IEEE Wireless Communication, Oct. 2002 Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National
Security Evaluation of CDMA2000
 Security Evaluation of CDMA2000 L. Ertaul 1, S. Natte 2, and G. Saldamli 3 1 Mathematics and Computer Science, CSU East Bay, Hayward, CA, USA 2 Mathematics and Computer Science, CSU East Bay, Hayward,
Security Evaluation of CDMA2000 L. Ertaul 1, S. Natte 2, and G. Saldamli 3 1 Mathematics and Computer Science, CSU East Bay, Hayward, CA, USA 2 Mathematics and Computer Science, CSU East Bay, Hayward,
Evolution of the SIM to esim
 Evolution of the SIM to esim Elaheh Vahidian Master of Telematics - Communication Networks and Networked Services (2 Submission date: Januar 2013 Supervisor: Van Thanh Do, ITEM Norwegian University of
Evolution of the SIM to esim Elaheh Vahidian Master of Telematics - Communication Networks and Networked Services (2 Submission date: Januar 2013 Supervisor: Van Thanh Do, ITEM Norwegian University of
Mobile SCTP Transport Layer Mobility Management for the Internet
 Mobile SCTP Transport Layer Mobility Management for the Maximilian Riegel Siemens AG, Munich, Germany E-mail: [email protected] Dr. Michael Tüxen Siemens AG, Munich, Germany E-mail: [email protected]
Mobile SCTP Transport Layer Mobility Management for the Maximilian Riegel Siemens AG, Munich, Germany E-mail: [email protected] Dr. Michael Tüxen Siemens AG, Munich, Germany E-mail: [email protected]
