CS Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail
|
|
|
- Ernest Powell
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12
2 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging Research 2
3 GSM The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is the de facto standard for wireless communications with well over 5 billion users. As a comparison, there are approximately 1.5 billion Internet users. The architectures of other network are similar, so knowing how to speak GSM will get you a long way in this space. 3
4 Wireless Signaling and Control in GSM Common Control Channel Structure Broadcast Channels Channel Access from Mobile Procedures and Messages for Call Control Traffic Channel Structure Handoffs 4
5 GSM Control Functions Read System Parameters Register Receive and Originate Calls Manage Handoffs 5
6 GSM Structure Traffic Channel (per user in a call) Common Control Channel (CCCH) TCH (13 KBps) Common Control Channel (CCCH) Used for control information: registration, paging, call origination/termination. Traffic Channel (TCH) Information transfer in-call control (fast/slow associated control channels) 6
7 GSM TDMA Frames TDMA Frame: Slot 0 Slot 1 Slot 2 Slot 3 Slot 4 Slot 5 Slot 6 Slot 7 Frame: msec Frame 0 Frame 1 Frame 2... Frame Multiframe: msec 7
8 From Frames to Channels 26 Multiframe: ms }Frame: 4.615ms 8
9 GSM CCCH Reverse (MS BS) Forward (BS MS) Forward (BS MS) Forward (BS MS) Forward (BS MS) Random Access Control Channel (RACH) Paging and Access Grant Channel (PAGCH) PCH Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH) Synchronization Channel (SCH) Frequency Correction Channel (FCCH) AGCH 9
10 GSM CCCH Structure TDMA Frame: Slot 0 Slot 1 Slot 2 Slot 3 Slot 4 Slot 5 Slot 6 Slot 7 Frame: msec Frame 0 Frame 1 Frame 2... Frame Multiframe: msec Uplink: Channel Name (Frame #) FCCH (0) SCH (1) BCCH (2-5) PAGCH (6-9) Downlink RACH (0)... RACH (50) FCCH (10) SCH (11) PAGCH (12-19) FCCH (20) SCH (21) PAGCH (22-29) PAGCH (11) FCCH (30) SCH (31) PAGCH (32-39) FCCH (40) SCH (41) PAGCH (42-49) I (50) CCCH/RACH always uses Slot 0 of each frame; other seven slots for TCH TCH: 26 multi-frame repeats every 120 msec (13th and 16th frames are used by Slow Associated Control Channel (SACCH) or is idle 10
11 GSM: BCCH Broadcast to all users on the CCCH No addressing Used to acquire system parameters, so mobile may operate with the system. Key parameters (contained in RR SYSTEM INFORMATION MESSAGES): RACH control parameters cell channel descriptions (frequencies) neighbor cells (frequencies) cell id Location Area ID (LAI) Control Channel description 11
12 GSM: FCCH and SCH Keeps system synchronization What do you mean, synchronization? Broadcasts Basestation ID Why is this useful information? 12
13 GSM: Mobile Channel Access Procedures (RACH) MS Communicates with BS over RACH Only initially and must compete for this shared resource. Feedback provided with AGCH Points the user to a dedicated channel for real exchanges. Functions: Responses to paging messages Location update (registration) Call Origination 13
14 GSM: Paging Channel (PCH) Used to send pages to mobile devices. Notifications of incoming services (e.g., voice, data, SMS) Done at regular intervals Mobiles belong to a paging class Allows the device to sleep, conserve power More than 1 mobile paged at a time. 14
15 GSM: RACH and Slotted ALOHA (Layer 2) Assumptions all frames same size time is divided into equal size slots, time to transmit 1 frame nodes start to transmit frames only at beginning of slots Operation when node obtains fresh frame, it transmits in next slot no collision, node successfully transmitted the frame if collision, node retransmits frame in each subsequent slot with prob. p until success clocks are synchronized if 2 or more nodes transmit in slot, all nodes detect collision 15
16 GSM: More Slotted ALOHA Pros single active node can continuously transmit at full rate of channel highly decentralized: only slots in nodes need to be in sync simple Cons collisions, wasting slots idle slots nodes may be able to detect collision in less than time to transmit packet clock synchronization 16
17 GSM: Slotted ALOHA Efficiency Efficiency is the long-run fraction of successful slots when there are many nodes, each with many frames to send Suppose N nodes with many frames to send, each transmits in slot with probability p prob that node 1 has success in a slot = p(1-p) N-1 prob that any node has a success = Np(1-p) N-1 For max efficiency with N nodes, find p* that maximizes Np(1-p) N-1 For many nodes, take limit of Np*(1-p*) N-1 as N goes to infinity, gives 1/e =.37 At best: channel has maximum throughput of 37%! 17
18 GSM: RACH Procedures (Layer 2) Mobile sends assignment request with information Basestation sends back assignment with information echoed Creates Radio Resource (RR) connection Standalone Dedicated Control Channel May be a physical channel May be a traffic channel in signaling-only mode May eventually be bandwidth stolen from TCH (associated control channel). 18
19 Basic Flow on Air Interface Alert phone of incoming activity Request dedicated signaling channel Signal Release signaling channel 19
20 GSM Signaling Signaling in GSM occurs over the Radio Interface Layer 3 (RIL-3). Technically layer 3, but debatable from OSI perspective as application-esque things happen here. Control messages are handled by protocol control processes and include Call Control (CC), Mobility Management (MM), Radio Resource management (RR), Short Messaging Service management (SMS) and Supplementary Services management (SS). 20
21 Time Out: Privacy? With all of this signaling going over well-known channels, isn t there a risk of user tracking/profiling? Think about the PCH... what is transmitted here? 21
22 GSM Registration Types Power up and down Location Area changes (mobility) Periodic User Privacy Mobile device may transmit real address: International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) Get back temporary id (TMSI) Unique to a local area Subsequent registrations use TMSI 22
23 GSM: Registration, High Level Get SDCCH RR connection established Authenticate Cipher UpdateLocation Release RR connection 23
24 GSM Registration: Gory Details Get SDCCH RR connection established LOC UPD RQST Authentication Request (RAND) Authentication Response (SRES) Cipher Mode Cipher Mode Complete LOC UPD ACC (TMSI Assigned) TMSI RE-ALLOC Complete Release RR connection More details on this authentication procedure soon... 24
25 GSM: Call Termination (Receive a Call) RR connection established Page Request (TMSI) Channel Request Channel Assignment SABM(Page Response) UA(Page Response) Authentication and Ciphering SETUP Call Confirmed Alert Assignment Command Assignment Complete Connect Connect ACK Get SDCCH 25
26 GSM: Call Origination RR connection established RR connection release Channel Request Channel Assignment SABM(CM Service Req - Call Orig) UA(CM Service Request - Call Orig) Authentication and Ciphering SETUP Call Proceeding Alert Assignment Command Assignment Complete Connect Connect ACK Get SDCCH 26
27 GSM: Mobile Assisted Handoff (MAHO) MSC Old BS New BS Measurement Report Measurement Report Measurement Report Measurement Report Handoff Order Handoff Access Handoff Access Handoff Complete 27
28 Measuring Mobility-Generated Load How do we estimate the traffic load caused by handoffs? Simplest mobility model - assume conservation of flow and random movements at constant velosity. Rate of boundary crossings = vl = density of users, v = velocity and L is perimeter 28
29 Practice VLR Calculate the load at the VLR per second if each mobile creates an Update LA and creates a Reg Cancel. Assume: L = 80 miles =150 users/mi 2 v = 45 miles/hour 29
30 Example Boundary crossing rate: hour 3600 secs = 48 crossings/sec Load on VLR from mobility is 144 operations/sec: updates (3): Update LA, Reg Cancel, Auth Info 30
31 Example, cont Assume 3 calls/user/hour (1.5 in, 1.5 out on average) for each incoming call there is one database query (MSRN) = 150 users/mi 2, L = 80 miles each area contains 150 x (80/4) 2 = 60,000 users = 25 calls/second Total Load 25 queries/second (call related) 144 updates/second (mobility related) Conclusion mobility substantially dominates the database load 31
32 GSM: Short Messaging Service Bi-directional Acknowledged Service Store-and-Forward Service 140 octets/160 characters (concatenation possible) Uses SDCCH signaling channel Two services - cell broadcast and point to point Cell broadcast exists in the standards only at this time. Three types - user specific, ME-specific, SIM-specific 32
33 GSM: SMS Examples - Mobile Termination Page Page Response SMS Delivery 33
34 GSM: SMS Examples - Mobile Termination Page Page Response CP-Data (RP-Data (SMS Delivery)) CP-ACK CP-Data (RP-ACK) CP-ACK 34
35 Other Air Interfaces IS-54/IS-136/D-AMPS digital, TDMA IS-95 digital, CDMA CDMA2000 3G UMTS W-CDMA 3G 35
36 IS-54/IS-136 First North American standards Converted traffic channels (IS-54) and control channels (IS-136) to digital. Phones could gracefully degrade to AMPS if neither of these networks were available. IS-54 was the first to consider security. Used the Cellular Message Encryption Algorithm (CMEA) to protect the control channel and Cellular Authentication, Voice Privacy and Encryption (CAVE) to protect voice. Both algorithms later shown to be weak. 36
37 IS-95 Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Transmission Similar call processing to GSM and IS MHz carriers, each with 65 sub-code channels Operates in similar bands as AMPS/IS
38 Network Architecture: IS-95/CDMA2000 BS BSC RNC/ PCF VLR MSC PDSN PSTN HLR AAA BS RNC/PCF Performs frame-selection/power control Terminates Radio Link Protocol w/ mobiles Performs packet and burst control functions PDSN terminates PPP with clients provides FA support for MIP-enabled Clients AAA Provides Authentication, Authorization and Accounting for Data users HA BSC Coordinates handoff for voice users Internet performs frame-selection/power control MSC call control and mobility management interfaces to the PSTN for voice users AAA provides location management and AAA functions for voice users. 38
GSM Channels. Physical & Logical Channels. Traffic and Control Mutltiframing. Frame Structure
 GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
Ch 2.3.3 GSM PENN. Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98
 Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
9.1 Introduction. 9.2 Roaming
 9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
Frequency [MHz] ! " # $ %& &'( " Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.
![Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2. Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.](/thumbs/18/697237.jpg) Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS There are two types of GSM logical channels 1. Traffic Channels (TCHs) 2. Control Channels (CCHs) Traffic channels carry digitally encoded user speech or user data and have identical
GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS There are two types of GSM logical channels 1. Traffic Channels (TCHs) 2. Control Channels (CCHs) Traffic channels carry digitally encoded user speech or user data and have identical
GSM GPRS. Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides)
 GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface Hank Carter Professor Patrick Traynor 10/4/2012 UMTS and CDMA 3G technology - major change from GSM (TDMA) Based on techniques originally
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface Hank Carter Professor Patrick Traynor 10/4/2012 UMTS and CDMA 3G technology - major change from GSM (TDMA) Based on techniques originally
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
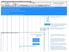 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
GSM System. Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE [email protected] UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE [email protected] UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location. Controls user connection. Transmission.
 Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY:
 GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology
 Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
GSM Databases. Virginia Location Area HLR Vienna Cell Virginia BSC. Virginia MSC VLR
 Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
Update ( Update Procedure) Network Mobiles Maryland Maryland Other Rockville Bethesda Maryland Mobile Mobile Cell Cell HLR Vienna Cell 12-Jun-14 22:48 (Page 1) This sequence diagram was generated with
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G
 Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure
 GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure 1 FREQUENCY BANDS AND CHANNELS...2 2 GSM TDMA...4 3 TDMA FRAME HIERARCHY...6 4 BURST STRUCTURE...7 5 TDMA MULTIFRAME STRUCTURE...9 5.1 Traffic Multiframe (26-Multiframe)...10
GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure 1 FREQUENCY BANDS AND CHANNELS...2 2 GSM TDMA...4 3 TDMA FRAME HIERARCHY...6 4 BURST STRUCTURE...7 5 TDMA MULTIFRAME STRUCTURE...9 5.1 Traffic Multiframe (26-Multiframe)...10
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing
 GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
Theory and Practice. IT-Security: GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.7. Mobile Communication. December 18, 2001. GSM Location System Syslog XP 3.
 Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke [email protected] Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
Participant: Hack contacting... IT-Security: Theory and Practice Mobile Communication December 18, 2001 Uwe Jendricke [email protected] Lecture Homepage: http://www.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/~softech/teaching/ws01/itsec/
GSM Architecture and Interfaces
 GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley
 Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 4: Medium Access Control October 5, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Medium Access Control Schemes: FDMA TDMA
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 4: Medium Access Control October 5, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Medium Access Control Schemes: FDMA TDMA
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving
 GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
MRN 6 GSM part 1. Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione. Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone
 Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview
 The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems. Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering
 Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
Mobile Wireless Overview
 Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Wireless Mobile Telephony
 Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 [email protected] http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 [email protected] http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Mobile Services (ST 2010)
 Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
Mobile Services (ST 2010) Chapter 3: Mobility Management Axel Küpper Service-centric Networking Deutsche Telekom Laboratories, TU Berlin 1 Mobile Services Summer Term 2010 3 Mobility Management 3.1 Handover
Lecture overview. History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction. Basic architecture of GSM system. Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM
 Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Global System for Mobile (GSM) Global System for Mobile (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile (GSM) David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program of Telecommunications and Networking University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2720 Slides 8 Based largely on material from Jochen
Global System for Mobile (GSM) David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program of Telecommunications and Networking University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2720 Slides 8 Based largely on material from Jochen
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: Cellular Networking
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: Cellular Networking Professor Patrick Traynor 9/13/2012 The Big Picture Details create the big picture. -Sanford I. Weill 2 Overview Evolution Architecture
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: Cellular Networking Professor Patrick Traynor 9/13/2012 The Big Picture Details create the big picture. -Sanford I. Weill 2 Overview Evolution Architecture
GSM Network and Services
 GSM Network and Services GPRS - sharing of resources 1 What is the problem? Many data applications are very bursty in its traffic pattern: http, smtp, pop, telnet,... Why reserve physical resources at
GSM Network and Services GPRS - sharing of resources 1 What is the problem? Many data applications are very bursty in its traffic pattern: http, smtp, pop, telnet,... Why reserve physical resources at
GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020501Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020501Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
How To Make A Multi-User Communication Efficient
 Multiple Access Techniques PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 2011/12/8 Multiple Access Scheme Allow many users to share simultaneously a finite amount of radio spectrum Need to be done without severe degradation of the
Multiple Access Techniques PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 2011/12/8 Multiple Access Scheme Allow many users to share simultaneously a finite amount of radio spectrum Need to be done without severe degradation of the
Using TEMS Pocket. Johan Montelius
 Using TEMS Pocket Johan Montelius Introduction In this laboration you will get acquainted with the TEMS Pocket tool. You will examine both the Monaco network and a commercial network. Since this is your
Using TEMS Pocket Johan Montelius Introduction In this laboration you will get acquainted with the TEMS Pocket tool. You will examine both the Monaco network and a commercial network. Since this is your
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems
 Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04. Simon Sörman
 Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04 Simon Sörman Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Channels... 2 2.1 Physical channels... 2 2.1.1 FDMA/TDMA... 2 2.1.2 Bursts... 3 2.2 Logical channels... 3 2.3 Mapping of logical
Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04 Simon Sörman Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Channels... 2 2.1 Physical channels... 2 2.1.1 FDMA/TDMA... 2 2.1.2 Bursts... 3 2.2 Logical channels... 3 2.3 Mapping of logical
Mobile Computing. Basic Call Calling terminal Network Called terminal 10/25/14. Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN. CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014
 Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Random Access Protocols
 Lecture Today slotted vs unslotted ALOHA Carrier sensing multiple access Ethernet DataLink Layer 1 Random Access Protocols When node has packet to send transmit at full channel data rate R. no a priori
Lecture Today slotted vs unslotted ALOHA Carrier sensing multiple access Ethernet DataLink Layer 1 Random Access Protocols When node has packet to send transmit at full channel data rate R. no a priori
EPL 657 Wireless Networks
 EPL 657 Wireless Networks Some fundamentals: Multiplexing / Multiple Access / Duplex Infrastructure vs Infrastructureless Panayiotis Kolios Recall: The big picture... Modulations: some basics 2 Multiplexing
EPL 657 Wireless Networks Some fundamentals: Multiplexing / Multiple Access / Duplex Infrastructure vs Infrastructureless Panayiotis Kolios Recall: The big picture... Modulations: some basics 2 Multiplexing
2G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
How To Test Gsm Cell Phone Network On A Cell Phone
 G S M C E L L B R O A D C A S T S E RV I C E S E C U R I T Y A N A LY S I S arturo cedillo torres Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Eindhoven University of Technology Supervisors: Nicola Zannone
G S M C E L L B R O A D C A S T S E RV I C E S E C U R I T Y A N A LY S I S arturo cedillo torres Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Eindhoven University of Technology Supervisors: Nicola Zannone
GSM System Architecture
 Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
Intersystem Operation and Mobility Management David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program in Telecommunications and Networking University it of Pittsburgh Telcom 2700 Slides 6 http://www.tele.pitt.edu/tipper.html
Yu.M. Tulyakov, D.Ye. Shakarov, A.A. Kalashnikov. Keywords: Data broadcasting, cellular mobile systems, WCDMA, GSM.
 Аnalysis of data broadcasting in modern cellular mobile systems of ground radio communications Yu.M. Tulyakov, D.Ye. Shakarov, A.A. Kalashnikov At the analysis of channel formation in WCDMA networks the
Аnalysis of data broadcasting in modern cellular mobile systems of ground radio communications Yu.M. Tulyakov, D.Ye. Shakarov, A.A. Kalashnikov At the analysis of channel formation in WCDMA networks the
Attenuation (amplitude of the wave loses strength thereby the signal power) Refraction Reflection Shadowing Scattering Diffraction
 Wireless Physical Layer Q1. Is it possible to transmit a digital signal, e.g., coded as square wave as used inside a computer, using radio transmission without any loss? Why? It is not possible to transmit
Wireless Physical Layer Q1. Is it possible to transmit a digital signal, e.g., coded as square wave as used inside a computer, using radio transmission without any loss? Why? It is not possible to transmit
Module 5. Broadcast Communication Networks. Version 2 CSE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
Module 5 Broadcast Communication Networks Lesson 9 Cellular Telephone Networks Specific Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain the operation of Cellular
How To Make A Cell Phone Network More Efficient
 Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Wireless Phone GSM tracking. Denis Foo Kune, John Koelndorfer, Nick Hopper, Yongdae Kim
 Wireless Phone GSM tracking Denis Foo Kune, John Koelndorfer, Nick Hopper, Yongdae Kim Can someone track your phone? GPS Need access to phone Cell network trilateration/triangulation Multiple base stations
Wireless Phone GSM tracking Denis Foo Kune, John Koelndorfer, Nick Hopper, Yongdae Kim Can someone track your phone? GPS Need access to phone Cell network trilateration/triangulation Multiple base stations
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
Abis interface Technical Specification for cdma2000 Spread Spectrum Systems. (A.S0003 : BSC to BTS Interoperability specification (Abis))
 GPP A.S000 Version 1.0.0 Date: March 1, 000 Abis interface Technical Specification for cdma000 Spread Spectrum Systems (A.S000 : BSC to BTS Interoperability specification (Abis)) COPYRIGHT GPP and its
GPP A.S000 Version 1.0.0 Date: March 1, 000 Abis interface Technical Specification for cdma000 Spread Spectrum Systems (A.S000 : BSC to BTS Interoperability specification (Abis)) COPYRIGHT GPP and its
GSM Air Interface & Network Planning
 GSM Air Interface & Network Planning Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (40) GSM Air Interface & Network Planning The information in this document is subject to change without notice and
GSM Air Interface & Network Planning Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (40) GSM Air Interface & Network Planning The information in this document is subject to change without notice and
Cellular Networks: Background and Classical Vulnerabilities
 Cellular Networks: Background and Classical Vulnerabilities Patrick Traynor CSE 545 1 Cellular Networks Provide communications infrastructure for an estimated 2.6 billion users daily. The Internet connects
Cellular Networks: Background and Classical Vulnerabilities Patrick Traynor CSE 545 1 Cellular Networks Provide communications infrastructure for an estimated 2.6 billion users daily. The Internet connects
How To Understand The Performance Of A Cell Phone Network
 Survivability Analysis for Mobile Cellular Networks David W. Tipper *, Chalermpol Charnsripinyo *, Hyundoo Shin * Teresa A. Dahlberg ** * Department of Information Science and Telecommunications, University
Survivability Analysis for Mobile Cellular Networks David W. Tipper *, Chalermpol Charnsripinyo *, Hyundoo Shin * Teresa A. Dahlberg ** * Department of Information Science and Telecommunications, University
Cellular Network Organization. Cellular Wireless Networks. Approaches to Cope with Increasing Capacity. Frequency Reuse
 Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Cellular Network Organization
 Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
RELEASE NOTE. Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08. Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90
 ETSI /TC SMG Release by : ETSI /PT 12 Release date : December 1995 RELEASE NOTE Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08 Radio Sub - system Link Control Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90 New
ETSI /TC SMG Release by : ETSI /PT 12 Release date : December 1995 RELEASE NOTE Recc)mmendation GSM 05.08 Radio Sub - system Link Control Previously distributed version :3.7.0 ( Updated Release 1/90 New
TCOM 370 NOTES 99-12 LOCAL AREA NETWORKS AND THE ALOHA PROTOCOL
 1. Local Area Networks TCOM 370 NOTES 99-12 LOCAL AREA NETWORKS AND THE ALOHA PROTOCOL These are networks spanning relatively short distances (e.g. within one building) for local point-to-point and point-to-multipoint
1. Local Area Networks TCOM 370 NOTES 99-12 LOCAL AREA NETWORKS AND THE ALOHA PROTOCOL These are networks spanning relatively short distances (e.g. within one building) for local point-to-point and point-to-multipoint
The Network Layer Layer 3
 CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0
 GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020508QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.08 TECHNICAL July 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.1.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020508QR ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
Long-Term Evolution. Mobile Telecommunications Networks WMNet Lab
 Long-Term Evolution Mobile Telecommunications Networks WMNet Lab Background Long-Term Evolution Define a new packet-only wideband radio with flat architecture as part of 3GPP radio technology family 2004:
Long-Term Evolution Mobile Telecommunications Networks WMNet Lab Background Long-Term Evolution Define a new packet-only wideband radio with flat architecture as part of 3GPP radio technology family 2004:
ASR 5x00 Series SGSN Authentication and PTMSI Reallocation Best Practices
 ASR 5x00 Series SGSN Authentication and PTMSI Reallocation Best Practices Document ID: 119148 Contributed by Krishna Kishore DV, Sujin Anagani, and Parthasarathy M, Cisco TAC Engineers. Jun 12, 2015 Contents
ASR 5x00 Series SGSN Authentication and PTMSI Reallocation Best Practices Document ID: 119148 Contributed by Krishna Kishore DV, Sujin Anagani, and Parthasarathy M, Cisco TAC Engineers. Jun 12, 2015 Contents
Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM
 Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM Comp.Eng. Serkan Kayacan (*), Prof. Levent Toker (**) (*): Ege University, The Institute of Science, Computer Engineering, M.S. Student
Implementation of Mobile Measurement-based Frequency Planning in GSM Comp.Eng. Serkan Kayacan (*), Prof. Levent Toker (**) (*): Ege University, The Institute of Science, Computer Engineering, M.S. Student
Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS
 Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 2.1 Network Architectures 2.2 Concepts
Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 2.1 Network Architectures 2.2 Concepts
Wireless Access of GSM
 Wireless Access of GSM Project Report FALL, 1999 Wireless Access of GSM Abstract: Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) started to be developed by Europeans when the removal of many European trade
Wireless Access of GSM Project Report FALL, 1999 Wireless Access of GSM Abstract: Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) started to be developed by Europeans when the removal of many European trade
CHAPTER - 4 CHANNEL ALLOCATION BASED WIMAX TOPOLOGY
 CHAPTER - 4 CHANNEL ALLOCATION BASED WIMAX TOPOLOGY 4.1. INTRODUCTION In recent years, the rapid growth of wireless communication technology has improved the transmission data rate and communication distance.
CHAPTER - 4 CHANNEL ALLOCATION BASED WIMAX TOPOLOGY 4.1. INTRODUCTION In recent years, the rapid growth of wireless communication technology has improved the transmission data rate and communication distance.
RESOURCE ALLOCATION FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC CLASS OVER GPRS
 RESOURCE ALLOCATION FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC CLASS OVER GPRS Edward Nowicki and John Murphy 1 ABSTRACT The General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a new bearer service for GSM that greatly simplify wireless
RESOURCE ALLOCATION FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC CLASS OVER GPRS Edward Nowicki and John Murphy 1 ABSTRACT The General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a new bearer service for GSM that greatly simplify wireless
GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies
 GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies Introduction Aeris provides network and data analytics services for Machine-to- Machine ( M2M ) and Internet of Things ( IoT ) applications using multiple
GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies Introduction Aeris provides network and data analytics services for Machine-to- Machine ( M2M ) and Internet of Things ( IoT ) applications using multiple
Location management Need Frequency Location updating
 Lecture-16 Mobility Management Location management Need Frequency Location updating Fig 3.10 Location management in cellular network Mobility Management Paging messages Different paging schemes Transmission
Lecture-16 Mobility Management Location management Need Frequency Location updating Fig 3.10 Location management in cellular network Mobility Management Paging messages Different paging schemes Transmission
Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks
 Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. Lecture 2.1: Voice in GSM
 Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. Lecture.: Voice in GSM GSM Specified by ETSI Frequency Division Duplex TDMA system Originally at 900MHz, but today also at 800, 800,
Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. Lecture.: Voice in GSM GSM Specified by ETSI Frequency Division Duplex TDMA system Originally at 900MHz, but today also at 800, 800,
Mobile Communication Systems: DECT Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunication
 Mobile ommunication Systems: DET Digital Enhanced ordless Telecommunication Mobile ommunication: Telecommunication Systems - Jochen Schiller http://www.jochenschiller.de 1 Overview DET (Digital European
Mobile ommunication Systems: DET Digital Enhanced ordless Telecommunication Mobile ommunication: Telecommunication Systems - Jochen Schiller http://www.jochenschiller.de 1 Overview DET (Digital European
EETS 8316 Wireless Networks Fall 2013
 EETS 8316 Wireless Networks Fall 2013 Lecture: Cellular Overview: 3G and 4G http://lyle.smu.edu/~skangude/eets8316.html Dr. Shantanu Kangude [email protected] Third Generation Systems High-speed wireless
EETS 8316 Wireless Networks Fall 2013 Lecture: Cellular Overview: 3G and 4G http://lyle.smu.edu/~skangude/eets8316.html Dr. Shantanu Kangude [email protected] Third Generation Systems High-speed wireless
FIGURE 12-1 Original Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) frequency spectrum
 FIGURE 12-1 Original Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) frequency spectrum FIGURE 12-2 Complete Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) frequency spectrum TABLE 12-1 AMPS Frequency Allocation TABLE 12-2
FIGURE 12-1 Original Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) frequency spectrum FIGURE 12-2 Complete Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) frequency spectrum TABLE 12-1 AMPS Frequency Allocation TABLE 12-2
Cellular Phone Systems
 Cellular Phone Systems Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC 1 Why Cellular Mobile Telephone Systems? Operational limitations of conventional mobile
Cellular Phone Systems Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC 1 Why Cellular Mobile Telephone Systems? Operational limitations of conventional mobile
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]
![192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]](/thumbs/18/698539.jpg) 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
3GPP Wireless Standard
 3GPP Wireless Standard Shishir Pandey School of Technology and Computer Science TIFR, Mumbai April 10, 2009 Shishir Pandey (TIFR) 3GPP Wireless Standard April 10, 2009 1 / 23 3GPP Overview 3GPP : 3rd Generation
3GPP Wireless Standard Shishir Pandey School of Technology and Computer Science TIFR, Mumbai April 10, 2009 Shishir Pandey (TIFR) 3GPP Wireless Standard April 10, 2009 1 / 23 3GPP Overview 3GPP : 3rd Generation
Mobility and cellular networks
 Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
Figure 1: cellular system architecture
 Question 1: (30 marks) Consider a FDM cellular system with 120 cites, a frequency reuse factor of N=12, and 900 overall two-way channels. Omni-directional antennas are used: Figure 1 shows some of the
Question 1: (30 marks) Consider a FDM cellular system with 120 cites, a frequency reuse factor of N=12, and 900 overall two-way channels. Omni-directional antennas are used: Figure 1 shows some of the
Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系
 Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系 Mobility Management in Cellular Systems Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC cell BTS BTS BTS BTS MT BTS BTS BTS BTS HLR and VLR HLR (Home Location Register)
Mobility Management 嚴 力 行 高 雄 大 學 資 工 系 Mobility Management in Cellular Systems Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC cell BTS BTS BTS BTS MT BTS BTS BTS BTS HLR and VLR HLR (Home Location Register)
EE 4105 Communication Engg-II Dr. Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury Slide # 1
 EE 4105 Communication Engg-II Dr. Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury Slide # 1 1 Circuit-Switched Systems In a circuit-switched system, each traffic channel is dedicated to a user until its cell is terminated. Circuit
EE 4105 Communication Engg-II Dr. Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury Slide # 1 1 Circuit-Switched Systems In a circuit-switched system, each traffic channel is dedicated to a user until its cell is terminated. Circuit
Lecture 7 Multiple Access Protocols and Wireless
 Lecture 7 Multiple Access Protocols and Wireless Networks and Security Jacob Aae Mikkelsen IMADA November 11, 2013 November 11, 2013 1 / 57 Lecture 6 Review What is the responsibility of the link layer?
Lecture 7 Multiple Access Protocols and Wireless Networks and Security Jacob Aae Mikkelsen IMADA November 11, 2013 November 11, 2013 1 / 57 Lecture 6 Review What is the responsibility of the link layer?
Mobile Communications TCS 455
 Mobile Communications TCS 455 Dr. Prapun Suksompong [email protected] Lecture 26 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 Announcements Read the following from the SIIT online
Mobile Communications TCS 455 Dr. Prapun Suksompong [email protected] Lecture 26 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 Announcements Read the following from the SIIT online
Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE
 Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 1. The Market for Voice and SMS! 2. Third Party Voice over IP! 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem! 4. Circuit Switched Fallback! 5. VoLGA LTE was designed as a
Delivery of Voice and Text Messages over LTE 1. The Market for Voice and SMS! 2. Third Party Voice over IP! 3. The IP Multimedia Subsystem! 4. Circuit Switched Fallback! 5. VoLGA LTE was designed as a
Mobile Networking Concepts and Protocols CNT 5517
 Mobile Networking Concepts and Protocols CNT 5517 Some slides are adapted from Dr. Dave Johnson Notes Dr. Sumi Helal, Ph.D. Professor Computer & Information Science & Engineering Department University
Mobile Networking Concepts and Protocols CNT 5517 Some slides are adapted from Dr. Dave Johnson Notes Dr. Sumi Helal, Ph.D. Professor Computer & Information Science & Engineering Department University
Hello viewers, welcome to today s lecture on cellular telephone systems.
 Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture minus 31 Cellular Telephone Systems Hello viewers, welcome to today s lecture
Data Communications Prof. A. Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture minus 31 Cellular Telephone Systems Hello viewers, welcome to today s lecture
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' Giuseppe Bianchi
 !!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
Index. Common Packet Channel (CPCH) 25 Compression 265, 279 82, 288 header compression 284
 bindex.fm Page 296 Tuesday, March 22, 2005 7:17 AM Index 2G, 2.5G, 3G 13 3GPP 118 Release 5 (Rel 5) 124 Release 6 (Rel 6) 125 Release 97/98 (Rel 97/98) 119 Release 99 (Rel 99) 120 4 3GPP2 129 4G 13, 44
bindex.fm Page 296 Tuesday, March 22, 2005 7:17 AM Index 2G, 2.5G, 3G 13 3GPP 118 Release 5 (Rel 5) 124 Release 6 (Rel 6) 125 Release 97/98 (Rel 97/98) 119 Release 99 (Rel 99) 120 4 3GPP2 129 4G 13, 44
Cellular mobile communication is based on the. The Cellular Concept. GSM and PCNs. Moe Rahnema
 GSM and PCNs Overview Of he GSM System and Protocol Architecture We can use GSM as a basic framework to define and develop the standards for handling the mobility-specific functions of next-generation
GSM and PCNs Overview Of he GSM System and Protocol Architecture We can use GSM as a basic framework to define and develop the standards for handling the mobility-specific functions of next-generation
In this Lecture" Access method CDMA" Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
