GSM GPRS. Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides)
|
|
|
- Hugo Chambers
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating in several frequency bands (GSM 900, GSM 1800 = DCS 1800, GSM 1900 = PCS 900) ETSI Specifications ( ) Future evolution?
2 GSM Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides) GPRS Course requirements: GPRS: Architecture, Protocols, and Air Interface article available at If you have problems obtaining this article, please contact the course assistant (Mika Nupponen)
3 Digital PLMN systems (status 2000) 2 nd Generation 3 rd Generation 4 th Generation GSM IS-136 IS-95 GPRS USA EDGE IMT-2000 UMTS W- CDMA TDD CDMA 2000
4 Digital PLMN systems GSM Global System for Mobile communications: (FDMA/)TDMA-based system specified by ETSI Several evolution steps towards 3 rd generation systems: HSCSD High Speed Circuit Switched Data (possibility of combining up to 4 time slots for a data connection) GPRS General Packet Radio Service (packet switching overlay on TDMA radio access network) EDGE Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (change at the air interface: 8 PSK modulation as in UMTS) IS-95 American CDMA system IS-136 American TDMA system
5 UMTS Universal Mobile Telecommunications System UTRA FDD mode (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access, Frequency Division Duplex mode) W-CDMA UTRA TDD mode CDMA2000 American 3 rd Generation CDMA system IMT-2000 International Mobile Telecommunications (ITU) Other wireless systems & networks: DECT (no roaming), TETRA (not public), HIPERLAN et al., UPT concept, GPS, mobile satellite systems
6 GSM system architecture BSS NSS SIM BTS BSC C VLR N GC HLR BTS OMC database AC EIR
7 GSM: circuit switched connections BSS NSS BSC C VLR GC HLR BTS AC EIR
8 GPRS: packet switched connections BSS NSS BSC PCU C VLR GC HLR BTS SGSN GGSN AC EIR
9 UMTS network architecture Uu Radio access network UTRAN RNC BS Iur Core network (GSM/GPRS-based) Iu CS GC C VLR BS Iub RNC Iu PS SGSN HLR AC Gn GGSN EIR
10 IMT-2000 / UMTS: RNS (access network) Core network (GSM-based) BS RNC C VLR GC BS RNC SGSN GGSN HLR AC EIR
11 Radio interface aspects Radio access techniques (FDMA / TDMA / CDMA) Physical / logical channel structure / GSM burst Modulation method (GK, 8-PSK) Source coding / channel coding / interleaving Radio channel estimation & equalization techniques (constructive use of the multipath channel) Diversity techniques Circuit vs. packet switched access Protocols: random access, power control, handover (with associated measurement procedures)
12 Radio interface access techniques frequency Time division time code nr. Frequency division Code division
13 Radio interface - physical channels Carrier 0 Carrier 1 Carrier 2 Carrier 3 TS0 Typically used for signaling TS1 T S S T T T T T T S S T T T T T T T T T T T T T TS2 TS2 T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T T Frame of length 8 time slots
14 Radio interface logical channels Traffic channels Control channels (for signaling) TCH/F Broadcast Common control Dedicated TCH/H SCH PCH SDCCH bidirectional downlink uplink FCCH BCCH AGCH RACH SACCH FACCH
15 GPRS channel structure Carrier 0 TS0 Used for GSM signaling TS1 T S S T T T T T T S S T Carrier 1 Carrier 2 T T T T T T T PDCH:s for GPRS use (for example) T T T T T T T PBCCH Packet Broadcast Control Channel (optional) PCCCH Packet Common Control Channel (optional) PDTCH Packet Data Traffic Channel Also, PACCH and PTCCH possible
16 GSM/GPRS channel allocation example TS7 Only for GPRS TS0 Dynamical allocation (circuit switched GSM channels are given higher priority) time (observation intervals) Allocation schemes are network operator dependent
17 GSM radio interface GSM normal burst: bits (0.577 ms) 3 57 encrypted bits 1 26 training bits 1 57 encrypted bits TDMA frame (4.615 ms): TS7 TS0 TS1 TS2 TS3 TS4 TS5 TS6 TS7 TS0 TS1 TDMA multiframe: SACCH = 26 TDMA frames / 51 TDMA frames Idle
18 GSM speech encoding Voice coding: 260 bits in 20 ms blocks (13 kbit/s) - BSC 260 bits 260 bits Channel coding: 456 coded bits (22.8 kbit/s) - BTS 456 bits Interleaving: 8 x 57 bits (22.8 kbit/s) bits 4, 12, 20, 28, 36, 44, etc. from the 456 bit frame 57 bits 57 bits 57 bits
19 GSM signaling message encoding Signalling message in (split into) block(s) of 184 bits: 184 bits Each block is coded into 456 bits (22.8 kbit/s) 456 bits Interleaving: 8 x 57 bits (22.8 kbit/s) bits 4, 12, 20, 28, 36, 44, etc. from the 456 bit frame 57 bits 57 bits 57 bits
20 GPRS packet encoding FH For instance, segment of IP packet FCS LLC frame Segment Segment Segment. Segment BH Info BCS T RLC block Convolutional encoding into 456 bits Interleaving: 8 x 57 bits (22.8 kbit/s) bits 4, 12, 20, 28, 36, 44, etc. from the 456 bit frame 57 bits 57 bits 57 bits
21 GSM protocols ( C) U m A bis A CM CM MM DTAP RR LAPDm RR LAPDm BTSM LAPD RR BTSM LAPD MM BSSMAP BSSAP BSSAP SCCP MTP SCCP MTP Radio Radio 64 kb/s 64 kb/s 64 kb/s 64 kb/s BTS BSC C
22 GPRS protocols (user plane) U m G b G n IP/X.25 IP/X.25 SNDCP SNDCP GTP GTP LLC LLC TCP TCP RLC RLC BSSGP BSSGP IP IP MAC MAC NS NS L2 L2 Radio Radio L1bis L1bis L1 L1 BSS SGSN GGSN
23 GSM signaling at layer 3 RR (Radio Resource management) Access and initial assignment (reserving a SDCCH) Handover management MM (Mobility Management) Registration ( power switch on) Location updating ( moves to another location area) Authentication CM (Call control Management) Signaling for setting up and releasing circuit switched connections (very similar to DSS 1 in N-ISDN)
24 Connectivity modes in GSM and GPRS GSM: Disconnected Idle Connected GPRS: Idle Standby Ready is switched off (circuit mode) location updates are performed handovers in c.s. connection is switched off (packet mode) location updates on a larger basis location updates on cell-by-cell basis
25 Random access in GSM / GPRS No communication between and network can be started without first using the random access procedure in network originated activity (paging, e.g. for MTC) originated activity (MOC, location updating, registration, de-registration at power switch-off) 1) sends a short access burst over the RACH (uplink), (Slotted Aloha, collision possibility retransmission) 2) Network (BSC) returns permission message including: - allocated channel (frequency, time slot) - timing advance for correct time slot alignment
26 Important identifiers in GSM II International Mobile Subscriber Identity (global) TI Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity (local and temporary) Location Area Identity (global) ISDN Mobile Subscriber ISDN number (address of subscriber HLR database) PIN Personal Identification Number (only within ) IMEI International Mobile Equipment Identity (global) Temporary, local numbers for routing (RN, HON )
27 Case study: location updating (1) SIM TI VLR 1 TI II HLR II => VLR 1 VLR 2 Last and TI stored in SIM. monitors broadcast. matching => everything ok!
28 Case study: location updating (2) SIM TI VLR 1 TI II HLR II => VLR 1 VLR 2 different => location update needed!
29 Case study: location updating (3) SIM TI VLR 1 TI II HLR II => VLR 1 VLR 2 TI SIM sends old and TI to VLR 2 But, VLR 2 does not know II!
30 Case study: location updating (4) SIM TI VLR 2 TI VLR 1 TI II => VLR 2 HLR II => VLR 1 => VLR 2 TI VLR 2 sends new to VLR 1 which in turn updates the HLR
31 Case study: location updating (5) SIM TI VLR 1 HLR II => VLR 2 VLR 2 TI II HLR sends II to VLR 2 and cancels subscriber data in VLR 1
32 Case study: location updating (6) VLR 1 SIM TI HLR II VLR 2 Important information for MTC (see below) VLR 2 TI II VLR 2 sends new TI to (SIM). also updates. Compare with slide (1). Location update successful!
33 Case study: mobile terminated call (1) (mobile terminated call = MTC) SIM TI C VLR 2 TI => II HLR GC ISDN => II => VLR 2 ISDN MTC directed through PSTN to GC using ISDN. GC contacts HLR (ISDN is in fact the address of the register location of the subscriber with given II)
34 Case study: mobile terminated call (2) SIM TI C VLR 2 TI => II HLR GC ISDN => II => VLR 2 ISDN => VLR 2 HLR returns to GC the current of called mobile subscriber. The GC can now route the call to the C serving the subscriber
35 Case study: mobile terminated call (3) SIM TI C VLR 2 TI => II HLR II => VLR 2 GC The C broadcasts a paging message (including TI) within the location area defined by
36 Case study: mobile terminated call (4) SIM TI C VLR 2 TI => II HLR II => VLR 2 GC Only the mobile subscriber with the correct TI reacts to the paging. A connection between and C is established and the call set-up is completed.
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 Integrated Communication Systems Group Ilmenau University of Technology Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung GSM System Architecture Um (ME/SIM) C E C PSTN, ISDN, PSPDN, CSPDN A-bis A F A-bis C B BTS BSS BSC HLR VLR EIR
GSM Network and Services
 GSM Network and Services GPRS - sharing of resources 1 What is the problem? Many data applications are very bursty in its traffic pattern: http, smtp, pop, telnet,... Why reserve physical resources at
GSM Network and Services GPRS - sharing of resources 1 What is the problem? Many data applications are very bursty in its traffic pattern: http, smtp, pop, telnet,... Why reserve physical resources at
How To Understand The Gsm And Mts Mobile Network Evolution
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components GPRS DECT Not a part if this course! TETRA Not a part if this course! w-cdma (rel
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)
 General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) What is GPRS? GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) a packet oriented data service for IP and X.25 over GSM networks enables packet-switched services on the resources
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) What is GPRS? GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) a packet oriented data service for IP and X.25 over GSM networks enables packet-switched services on the resources
GSM System. Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
GSM System Global System for Mobile Communications Introduced in 1991. Settings of standards under ETSI (European Telecommunication Standards Institute) Services - Telephone services - Data services -
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]
![192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking. Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4]](/thumbs/18/698539.jpg) 192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
192620010 Mobile & Wireless Networking Lecture 5: Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) [Schiller, Section 4.4] Geert Heijenk Outline of Lecture 5 Cellular Systems (UMTS / LTE) (1/2) q Evolution of cellular
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: GSM - In Detail Professor Patrick Traynor 9/27/12 Cellular Telecommunications Architecture Background Air Interfaces Network Protocols Application: Messaging
Mobile Wireless Overview
 Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Mobile Wireless Overview A fast-paced technological transition is occurring today in the world of internetworking. This transition is marked by the convergence of the telecommunications infrastructure
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems. Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering
 Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
Handoff in GSM/GPRS Cellular Systems Avi Freedman Hexagon System Engineering Outline GSM and GSM referemce model GPRS basics Handoffs GSM GPRS Location and Mobility Management Re-selection and routing
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications
 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN MS HLR 1) Overview of GSM architecture 2) GSM channel structure 05-1 GSM - Global System for Mobile Communications VLR BTS BSC GMSC PSTN
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu
 Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systems slides by Jochen Schiller with modifications by Emmanuel Agu Market GSM Overview Services Sub-systems Components Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen
Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G
 CMPE 477 Wireless and Mobile Networks Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G New Data Services for GSM CMPE 477 HSCSD GPRS 3G UMTS IMT2000 UMTS Architecture UTRAN Architecture Data services in GSM I Data transmission
CMPE 477 Wireless and Mobile Networks Evolution of GSM in to 2.5G and 3G New Data Services for GSM CMPE 477 HSCSD GPRS 3G UMTS IMT2000 UMTS Architecture UTRAN Architecture Data services in GSM I Data transmission
GSM Channels. Physical & Logical Channels. Traffic and Control Mutltiframing. Frame Structure
 GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
GSM Channels Physical & Logical Channels Traffic and Control Mutltiframing Frame Structure Engr. Mian Shahzad Iqbal Lecturer Department of Telecommunication Engineering Radio Interface The radio interface
GSM Architecture and Interfaces
 GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
GSM.05 Page 71 Monday, November 30, 1998 2:07 PM C H A P T E R 5 GSM Architecture and Interfaces 5.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter we present an overview of the GSM as described in ETSI s recommendations.
PDF vytvořeno zkušební verzí pdffactory www.fineprint.cz UMTS
 UMTS Generations of mobile systems Generation 1 (1980-1995) 2 (1992-2000) 2,5 (1999-2010) 3 (2004-20?) Names NMT (Nordic Mobile Telephone); 450 MHz, 900 MHz AMPS (Advance Mobile Telephone System); USA
UMTS Generations of mobile systems Generation 1 (1980-1995) 2 (1992-2000) 2,5 (1999-2010) 3 (2004-20?) Names NMT (Nordic Mobile Telephone); 450 MHz, 900 MHz AMPS (Advance Mobile Telephone System); USA
Frequency [MHz] ! " # $ %& &'( " Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.
![Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2. Frequency [MHz] ! # $ %& &'( Use top & bottom as additional guard. guard band. Giuseppe Bianchi DOWNLINK BS MS 890.4 UPLINK MS BS 890.2.](/thumbs/18/697237.jpg) Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
Frequency [MHz] 960 DOWNLINK BS MS 935 915 UPLINK MS BS 890 890.4 890.2 guard band Use top & bottom as additional guard! " # $ %& &'( " 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 F F uplink dwlink ( n) = [ 890.2 + 0.2( n 1) ] (
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
GSM: PHYSICAL & LOGICAL CHANNELS AN OVERVIEW Prepared by Learntelecom.com 1. GSM: PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL CHANNELS GSM uses a mix of Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) and Time Division Multiple Access
Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS
 Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 2.1 Network Architectures 2.2 Concepts
Chapter 2 Mobility Management for GPRS and UMTS Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Outline 2.1 Network Architectures 2.2 Concepts
MRN 6 GSM part 1. Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione. Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone
 Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 6 GSM part 1 Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone A. Capone: Mobile Radio Networks 1 General characteristics of the system A. Capone:
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY:
 GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
GSM BASICS GSM HISTORY: In 1982 the Nordic PTTs sent a proposal to CEPT (Conference of European Postal & telegraph Administration) to study and to improve digital cellular technology by forming a team
2G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing
 GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
GSM Network Architecture, Channelisation, Signalling and Call Processing Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi Professor Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Dr Bhaskar Ramamurthi GSM 1 Call Routing in Wireline
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G
 Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Wireless Cellular Networks: 1G and 2G Raj Jain Professor of Computer Science and Engineering Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available
Performance Issues of TCP and MPEG-4 4 over UMTS
 Performance Issues of TCP and MPEG-4 4 over UMTS Anthony Lo [email protected] 1 Wiskunde end Informatica Outline UMTS Overview TCP and MPEG-4 Performance Summary 2 1 Universal Mobile Telecommunications
Performance Issues of TCP and MPEG-4 4 over UMTS Anthony Lo [email protected] 1 Wiskunde end Informatica Outline UMTS Overview TCP and MPEG-4 Performance Summary 2 1 Universal Mobile Telecommunications
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301
 The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
The GSM and GPRS network T-110.300/301 History The successful analog 1:st generation mobile telephone systems proved that there is a market for mobile telephones ARP (AutoRadioPuhelin) in Finland NMT (Nordic
Wireless Access of GSM
 Wireless Access of GSM Project Report FALL, 1999 Wireless Access of GSM Abstract: Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) started to be developed by Europeans when the removal of many European trade
Wireless Access of GSM Project Report FALL, 1999 Wireless Access of GSM Abstract: Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) started to be developed by Europeans when the removal of many European trade
Mobile Communications
 October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
October 21, 2009 Agenda Topic 2: Case Study: The GSM Network 1 GSM System General Architecture 2 GSM Access network. 3 Traffic Models for the Air interface 4 Models for the BSS design. 5 UMTS and the path
1G to 4G. Overview. Presentation By Rajeev Bansal Director(Mobile-1) Telecommunication Engineering Centre
 1G to 4G Overview Presentation By Rajeev Bansal Director(Mobile-1) Telecommunication Engineering Centre Mobile Networks differentiated from each other by the word Generation 1G, 2G, 2.5G, 2.75G, 3G milestones
1G to 4G Overview Presentation By Rajeev Bansal Director(Mobile-1) Telecommunication Engineering Centre Mobile Networks differentiated from each other by the word Generation 1G, 2G, 2.5G, 2.75G, 3G milestones
GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS
 GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS There are two types of GSM logical channels 1. Traffic Channels (TCHs) 2. Control Channels (CCHs) Traffic channels carry digitally encoded user speech or user data and have identical
GSM LOGICAL CHANNELS There are two types of GSM logical channels 1. Traffic Channels (TCHs) 2. Control Channels (CCHs) Traffic channels carry digitally encoded user speech or user data and have identical
9.1 Introduction. 9.2 Roaming
 9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
9 Location Updating Objectives After this chapter the student will: be able to define the concepts of roaming and location updating. be able to name the different types of location updating and why they
UMTS/GPRS system overview from an IP addressing perspective. David Kessens Jonne Soininen
 UMTS/GPRS system overview from an IP addressing perspective David Kessens Jonne Soininen Introduction 1) Introduction to 3GPP networks (GPRS, UMTS) Technical overview and concepts for 3GPP networks Mobility
UMTS/GPRS system overview from an IP addressing perspective David Kessens Jonne Soininen Introduction 1) Introduction to 3GPP networks (GPRS, UMTS) Technical overview and concepts for 3GPP networks Mobility
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE [email protected] UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) Nguyen Thi Mai Trang LIP6/PHARE [email protected] UPMC/PUF - M2 Networks - PTEL 1 Outline Principles of cellular networks GSM architecture Security
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview
 The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
The Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) Overview GSM D-AMPS Japan Digital PCS 1900 DCS 1800 CDMA Digital Cellular Systems World-wide Multiple Access Techniques In the GSM/DCS mobile system each
GPRS Systems Performance Analysis
 GPRS Systems Performance Analysis Fátima de Lima Procópio Duarte, Antonio A.F. Loureiro, Leonardo Barbosa e Oliveira, Cláudio Márcio de Souza Vicente Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte,
GPRS Systems Performance Analysis Fátima de Lima Procópio Duarte, Antonio A.F. Loureiro, Leonardo Barbosa e Oliveira, Cláudio Márcio de Souza Vicente Federal University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte,
Ch 2.3.3 GSM PENN. Magda El Zarki - Tcom 510 - Spring 98
 Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Ch 2.3.3 GSM In the early 80 s the European community decided to work together to define a cellular system that would permit full roaming in all countries and give the network providers freedom to provide
Pradipta Biswas Roll No. 04IT6007 M. Tech. (IT) School of Information Technology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Pradipta Biswas Roll No. 04IT6007 M. Tech. (IT) School of Information Technology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur ABSTRACT W-CDMA (Wideband Code-Division Multiple Access), an ITU standard derived
Pradipta Biswas Roll No. 04IT6007 M. Tech. (IT) School of Information Technology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur ABSTRACT W-CDMA (Wideband Code-Division Multiple Access), an ITU standard derived
Mobile Communication GSM, GPRS, EDGE, UMTS and beyond
 Mobile Communication GSM, GPRS, EDGE, UMTS and beyond Ralf Keller Ericsson Research, Corporate Unit Ericsson Eurolab Deutschland GmbH [email protected] 1 Overview Services GSM GPRS & EDGE UMTS Beyond
Mobile Communication GSM, GPRS, EDGE, UMTS and beyond Ralf Keller Ericsson Research, Corporate Unit Ericsson Eurolab Deutschland GmbH [email protected] 1 Overview Services GSM GPRS & EDGE UMTS Beyond
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley
 Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
Telecommunication Systems (GSM) Mobile Communications (Ch 4) John Schiller, Addison-Wesley 1 Telecommunication System Wireless extension of traditional PSTN Telephony architecture (NOT computer net) Many
Mobile Networking Concepts and Protocols CNT 5517
 Mobile Networking Concepts and Protocols CNT 5517 Some slides are adapted from Dr. Dave Johnson Notes Dr. Sumi Helal, Ph.D. Professor Computer & Information Science & Engineering Department University
Mobile Networking Concepts and Protocols CNT 5517 Some slides are adapted from Dr. Dave Johnson Notes Dr. Sumi Helal, Ph.D. Professor Computer & Information Science & Engineering Department University
Lecture overview. History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction. Basic architecture of GSM system. Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM
 Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
Lecture overview History of cellular systems (1G) GSM introduction Basic architecture of GSM system Basic radio transmission parameters of GSM Analogue cellular systems 70 s In the early 70 s radio frequencies
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface
 CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface Hank Carter Professor Patrick Traynor 10/4/2012 UMTS and CDMA 3G technology - major change from GSM (TDMA) Based on techniques originally
CS 8803 - Cellular and Mobile Network Security: CDMA/UMTS Air Interface Hank Carter Professor Patrick Traynor 10/4/2012 UMTS and CDMA 3G technology - major change from GSM (TDMA) Based on techniques originally
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' Giuseppe Bianchi
 !!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
!!! "# $ % & & # ' (! ) * +, -!!. / " 0! 1 (!!! ' &! & & & ' ( 2 3 0-4 ' 3 ' "#$!!% "&'! #&'!%! () *+,, 3 & 5 &,! #-!*! ' & '.! #%!* //!! & (0)/!&/, 6 5 /, "! First system: NMT-450 (Nordic Mobile Telephone)
Wireless Mobile Telephony
 Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 [email protected] http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Wireless Mobile Telephony The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 [email protected] http://www.cis.ohio-state.edu/~durresi/ 1 Overview Why wireless mobile telephony? First Generation, Analog
Global System for Mobile (GSM) Global System for Mobile (GSM)
 Global System for Mobile (GSM) David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program of Telecommunications and Networking University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2720 Slides 8 Based largely on material from Jochen
Global System for Mobile (GSM) David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Program of Telecommunications and Networking University of Pittsburgh Telcom 2720 Slides 8 Based largely on material from Jochen
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology
 Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division DHS - FLETC GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special
GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0
 GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020501Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
GSM GSM 05.01 TECHNICAL May 1996 SPECIFICATION Version 5.0.0 Source: ETSI TC-SMG Reference: TS/SMG-020501Q ICS: 33.060.50 Key words: Digital cellular telecommunications system, Global System for Mobile
How To Make A Cell Phone Network More Efficient
 Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part V: GSM Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 18.1.2008 GSM Briefly 2 General GSM was the first digital cellular system. GSM was
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems
 Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
Chapter 10 ( PART-1) Existing Wireless Systems 1 Outline AMPS IS-41 GSM PCS 2 AMPS 3 AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone System) Design goals of AMPS Characteristics of AMPS Channel usage in AMPS AMPS frequency
Mobile Computing. Basic Call Calling terminal Network Called terminal 10/25/14. Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN. CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014
 Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Mobile Computing CSE 40814/60814 Fall 2014 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Copyright. GSM - Phase 2+ From GSM to GPRS. From GSM to GPRS. Motivations. General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) HSCSD EDGE GPRS
 Copyright HSCSD EDGE GPRS GSM - Phase 2+ Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs-NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/nd-nc/1.0/
Copyright HSCSD EDGE GPRS GSM - Phase 2+ Quest opera è protetta dalla licenza Creative Commons NoDerivs-NonCommercial. Per vedere una copia di questa licenza, consultare: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/nd-nc/1.0/
Chapter 3: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks
 Chapter 3: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks IEEE Wireless Communication, Oct. 2002 Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National
Chapter 3: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks IEEE Wireless Communication, Oct. 2002 Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National
3GPP Wireless Standard
 3GPP Wireless Standard Shishir Pandey School of Technology and Computer Science TIFR, Mumbai April 10, 2009 Shishir Pandey (TIFR) 3GPP Wireless Standard April 10, 2009 1 / 23 3GPP Overview 3GPP : 3rd Generation
3GPP Wireless Standard Shishir Pandey School of Technology and Computer Science TIFR, Mumbai April 10, 2009 Shishir Pandey (TIFR) 3GPP Wireless Standard April 10, 2009 1 / 23 3GPP Overview 3GPP : 3rd Generation
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving
 GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 07 GSM Radio Interface, Data bursts and Interleaving 1 Space Division Multiple Access of the signals from the MSs A BTS with n directed antennae covers mobile stations
Wireless Cellular Networks: 3G
 Wireless Cellular Networks: 3G Raj Jain Washington University Saint Louis, MO 63131 [email protected] These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-06/ 7-1 Overview Wireless
Wireless Cellular Networks: 3G Raj Jain Washington University Saint Louis, MO 63131 [email protected] These slides are available on-line at: http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse574-06/ 7-1 Overview Wireless
In this Lecture" Access method CDMA" Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Layer and Telecommunications Dr. Cecilia Mascolo In this Lecture In this lecture we will discuss aspects related to the MAC Layer of wireless
GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies
 GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies Introduction Aeris provides network and data analytics services for Machine-to- Machine ( M2M ) and Internet of Things ( IoT ) applications using multiple
GSM v. CDMA: Technical Comparison of M2M Technologies Introduction Aeris provides network and data analytics services for Machine-to- Machine ( M2M ) and Internet of Things ( IoT ) applications using multiple
GSM Air Interface & Network Planning
 GSM Air Interface & Network Planning Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (40) GSM Air Interface & Network Planning The information in this document is subject to change without notice and
GSM Air Interface & Network Planning Training Document TC Finland Nokia Networks Oy 1 (40) GSM Air Interface & Network Planning The information in this document is subject to change without notice and
Cellular Network Organization. Cellular Wireless Networks. Approaches to Cope with Increasing Capacity. Frequency Reuse
 Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Cellular Network Organization Cellular Wireless Networks Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells Each served by its own antenna Served by base station consisting of
Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS, UMTS. GSM as basis of current systems Satellites and
 Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
Chapter 2 Technical Basics: Layer 1 Methods for Medium Access: Layer 2 Chapter 3 Wireless Networks: Bluetooth, WLAN, WirelessMAN, WirelessWAN Mobile Networks: Wireless Telecommunication Systems GSM, GPRS,
Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET
 Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET Vladimir Vukadinovic and Ljiljana Trajkovic School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Vancouver, BC, Canada E-mail: {vladimir, ljilja}@cs.sfu.ca
Mobile Application Part protocol implementation in OPNET Vladimir Vukadinovic and Ljiljana Trajkovic School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University Vancouver, BC, Canada E-mail: {vladimir, ljilja}@cs.sfu.ca
LTE Overview October 6, 2011
 LTE Overview October 6, 2011 Robert Barringer Enterprise Architect AT&T Proprietary (Internal Use Only) Not for use or disclosure outside the AT&T companies except under written agreement LTE Long Term
LTE Overview October 6, 2011 Robert Barringer Enterprise Architect AT&T Proprietary (Internal Use Only) Not for use or disclosure outside the AT&T companies except under written agreement LTE Long Term
Data Services in GSM HSCSD GPRS. GPRS Infrastructure Components
 4 4 Data Services in Data transmission in with only 9.6 kbit/s Advanced channel coding allows 14.4 kbit/s Still not enough for Internet access or even multimedia applications Thus: UMTS as 3G network :
4 4 Data Services in Data transmission in with only 9.6 kbit/s Advanced channel coding allows 14.4 kbit/s Still not enough for Internet access or even multimedia applications Thus: UMTS as 3G network :
GSM Phase 2+ General Packet Radio Service GPRS: Architecture, Protocols, and Air Interface
 Copyright 1999 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for
Copyright 1999 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for
A Performance Evaluation of Internet Access via the General Packet Radio Service of GSM
 A Performance Evaluation of Internet Access via the General Packet Radio Service of GSM Simon Hoff, Michael Meyer, Andreas Schieder Ericsson Eurolab Deutschland Ericsson Allee 1, 52134 Herzogenrath, Germany
A Performance Evaluation of Internet Access via the General Packet Radio Service of GSM Simon Hoff, Michael Meyer, Andreas Schieder Ericsson Eurolab Deutschland Ericsson Allee 1, 52134 Herzogenrath, Germany
The Network Layer Layer 3
 CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
CHAPTER 7 The Network Layer Layer 3 Now it is time to hijack the GSM freight train, to see what is inside, to break into the time-slotted boxcars and spill the drums of unknown acids and solvents on the
EETS 8316 Wireless Networks Fall 2013
 EETS 8316 Wireless Networks Fall 2013 Lecture: Cellular Overview: 3G and 4G http://lyle.smu.edu/~skangude/eets8316.html Dr. Shantanu Kangude [email protected] Third Generation Systems High-speed wireless
EETS 8316 Wireless Networks Fall 2013 Lecture: Cellular Overview: 3G and 4G http://lyle.smu.edu/~skangude/eets8316.html Dr. Shantanu Kangude [email protected] Third Generation Systems High-speed wireless
IMT-2000 Network Architecture
 IMT-2000 Network Architecture vtoshio Shimoe vtakamichi Sano (Manuscript received May 31, 2002) International Mobile Telecommunication-2000 (IMT-2000) is a third-generation mobile communication system.
IMT-2000 Network Architecture vtoshio Shimoe vtakamichi Sano (Manuscript received May 31, 2002) International Mobile Telecommunication-2000 (IMT-2000) is a third-generation mobile communication system.
Cellular Network Organization
 Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Cellular Networks Cellular Network Organization Use multiple low-power transmitters (100 W or less) Areas divided into cells o Each served by its own antenna o Served by base station consisting of transmitter,
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks
 Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations;
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks A note on the use of these ppt slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations;
2G Cellular Data Networks
 1 2 General Mobility Issues 2G Cellular Data Networks Registration and Authentication User Locate local service provider access point Obtain network access Service provider Locate mobile user within network
1 2 General Mobility Issues 2G Cellular Data Networks Registration and Authentication User Locate local service provider access point Obtain network access Service provider Locate mobile user within network
Mobile Communication Systems: DECT Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunication
 Mobile ommunication Systems: DET Digital Enhanced ordless Telecommunication Mobile ommunication: Telecommunication Systems - Jochen Schiller http://www.jochenschiller.de 1 Overview DET (Digital European
Mobile ommunication Systems: DET Digital Enhanced ordless Telecommunication Mobile ommunication: Telecommunication Systems - Jochen Schiller http://www.jochenschiller.de 1 Overview DET (Digital European
Role and Evolution of Radio Network Controllers
 01001000100000110000001000001100 010010001000 Role and Evolution of Radio Network Controllers Pekka Varis SPRP501 Senior R&D Manager / Senior Specialist Nokia [email protected] Agenda Radio Network
01001000100000110000001000001100 010010001000 Role and Evolution of Radio Network Controllers Pekka Varis SPRP501 Senior R&D Manager / Senior Specialist Nokia [email protected] Agenda Radio Network
Pocket Guide for Fundamentals and GSM Testing
 Pocket Guide for Fundamentals and GSM Testing Publisher: Author: Wandel & Goltermann GmbH & Co Elektronische Meûtechnik P. O. Box 12 62 D-72795 Eningen u.a. Germany e-mail: [email protected] http://www.wg.com
Pocket Guide for Fundamentals and GSM Testing Publisher: Author: Wandel & Goltermann GmbH & Co Elektronische Meûtechnik P. O. Box 12 62 D-72795 Eningen u.a. Germany e-mail: [email protected] http://www.wg.com
Mobility and cellular networks
 Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
Mobility and cellular s Wireless WANs Cellular radio and PCS s Wireless data s Satellite links and s Mobility, etc.- 2 Cellular s First generation: initially debuted in Japan in 1979, analog transmission
EDGE: The Introduction of High Speed Data in GSM / GPRS Networks
 10 September 2003 EDGE: The Introduction of High Speed Data in GSM / GPRS Networks Wendy Florence Ericsson South Africa Rev A 10 September 2003 1 Agenda What is EDGE? Implementing EDGE Network and transmission
10 September 2003 EDGE: The Introduction of High Speed Data in GSM / GPRS Networks Wendy Florence Ericsson South Africa Rev A 10 September 2003 1 Agenda What is EDGE? Implementing EDGE Network and transmission
Introduction to EDGE. 2.1 What Is EDGE?
 2 Introduction to EDGE This chapter is the first of a series dedicated to EDGE. It introduces the different EDGE concepts from a global point of view, explaining how they have been introduced into the
2 Introduction to EDGE This chapter is the first of a series dedicated to EDGE. It introduces the different EDGE concepts from a global point of view, explaining how they have been introduced into the
Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks
 Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
Case Study: Dimensioning and Deployment of GSM Networks Acknowledgement: some of these slides are based on originals and information kindly provided by Ian O Shea of Altobridge Ltd. 2011 1 GSM System Architecture
GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure
 GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure 1 FREQUENCY BANDS AND CHANNELS...2 2 GSM TDMA...4 3 TDMA FRAME HIERARCHY...6 4 BURST STRUCTURE...7 5 TDMA MULTIFRAME STRUCTURE...9 5.1 Traffic Multiframe (26-Multiframe)...10
GSM Radio Part 1: Physical Channel Structure 1 FREQUENCY BANDS AND CHANNELS...2 2 GSM TDMA...4 3 TDMA FRAME HIERARCHY...6 4 BURST STRUCTURE...7 5 TDMA MULTIFRAME STRUCTURE...9 5.1 Traffic Multiframe (26-Multiframe)...10
Nokia Networks Oy 1 (48)
 1 (48) GPRS Architecture: Interfaces and Protocols Training Document GPRS System Course 2 (48) 3 (48) GPRS Architecture: Interfaces and Protocols The information in this document is subject to change without
1 (48) GPRS Architecture: Interfaces and Protocols Training Document GPRS System Course 2 (48) 3 (48) GPRS Architecture: Interfaces and Protocols The information in this document is subject to change without
Mobile Communications TCS 455
 Mobile Communications TCS 455 Dr. Prapun Suksompong [email protected] Lecture 26 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 Announcements Read the following from the SIIT online
Mobile Communications TCS 455 Dr. Prapun Suksompong [email protected] Lecture 26 1 Office Hours: BKD 3601-7 Tuesday 14:00-16:00 Thursday 9:30-11:30 Announcements Read the following from the SIIT online
Cellular Technology Sections 6.4 & 6.7
 Overview Cellular Technology Sections 6. & 6.7 CSC 9 December, 0 Cellular architecture evolution Cellular telephony and internet terminology Mobility for cellular mobiles 6- Components of cellular architecture
Overview Cellular Technology Sections 6. & 6.7 CSC 9 December, 0 Cellular architecture evolution Cellular telephony and internet terminology Mobility for cellular mobiles 6- Components of cellular architecture
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location. Controls user connection. Transmission.
 Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
Provides a communication link between MS and MSC; Manages DB for MS location Controls user connection CM MM RR Transmission Several RR functions considered in previous part!"# Surprise! handover is part
How To Improve Data Rates For Global Evolution (Edge)
 EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution SIDDARTH WANDRE ID: 999-29-3194 CS 548: Broadband Networks ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Abstract:- This paper gives an overview of the EDGE concept. It gives
EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution SIDDARTH WANDRE ID: 999-29-3194 CS 548: Broadband Networks ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Abstract:- This paper gives an overview of the EDGE concept. It gives
EE 4105 Communication Engg-II Dr. Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury Slide # 1
 EE 4105 Communication Engg-II Dr. Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury Slide # 1 1 Circuit-Switched Systems In a circuit-switched system, each traffic channel is dedicated to a user until its cell is terminated. Circuit
EE 4105 Communication Engg-II Dr. Mostafa Zaman Chowdhury Slide # 1 1 Circuit-Switched Systems In a circuit-switched system, each traffic channel is dedicated to a user until its cell is terminated. Circuit
GPRS Overview. GPRS = General Packet Radio Service. GPRS Network
 GPRS - Overview GPRS Overview GPRS = General Packet Radio Service INTERNET/ INTRANET GPRS Network abcde X.25 Disclaimer: These overview slides are intended for informational purposes only. They have not
GPRS - Overview GPRS Overview GPRS = General Packet Radio Service INTERNET/ INTRANET GPRS Network abcde X.25 Disclaimer: These overview slides are intended for informational purposes only. They have not
IP-based Mobility Management for a Distributed Radio Access Network Architecture. [email protected]
 IP-based Mobility Management for a Distributed Radio Access Network Architecture [email protected] Outline - Definition IP-based Mobility Management for a Distributed RAN Architecture Page 2 Siemens
IP-based Mobility Management for a Distributed Radio Access Network Architecture [email protected] Outline - Definition IP-based Mobility Management for a Distributed RAN Architecture Page 2 Siemens
MAP/C SEND ROUTING INFO FOR SM. Destination Mobile Number. Obtain the SS7 address of the MSC VLR currently serving the specified Mobile Number
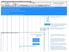 In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
In this call flow we will look at how a terminating SMS is handled in GSM. Setting up a terminating SMS session is a multi-step process. (1) Interrogate the MSC to locate the subscriber (2)Setting SMS
Product Description. HiLink E3531 HSPA+ USB Stick V100R001 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Issue 01. Date 2013-6-13
 HiLink E3531 HSPA+ USB Stick V100R001 Issue 01 Date 2013-6-13 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. provides customers with comprehensive technical support and service. Please feel
HiLink E3531 HSPA+ USB Stick V100R001 Issue 01 Date 2013-6-13 HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. provides customers with comprehensive technical support and service. Please feel
RESOURCE ALLOCATION FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC CLASS OVER GPRS
 RESOURCE ALLOCATION FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC CLASS OVER GPRS Edward Nowicki and John Murphy 1 ABSTRACT The General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a new bearer service for GSM that greatly simplify wireless
RESOURCE ALLOCATION FOR INTERACTIVE TRAFFIC CLASS OVER GPRS Edward Nowicki and John Murphy 1 ABSTRACT The General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a new bearer service for GSM that greatly simplify wireless
Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks
 Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks Thomas A. Cooper Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Integration of Open-Source GSM Networks Thomas A. Cooper Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Development of Wireless Networks
 Development of Wireless Networks Cellular Revolution In 1990 mobile phone users populate 11 million. By 2004 the figure will become 1 billion Phones are most obvious sign of the success of wireless technology.
Development of Wireless Networks Cellular Revolution In 1990 mobile phone users populate 11 million. By 2004 the figure will become 1 billion Phones are most obvious sign of the success of wireless technology.
Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04. Simon Sörman
 Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04 Simon Sörman Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Channels... 2 2.1 Physical channels... 2 2.1.1 FDMA/TDMA... 2 2.1.2 Bursts... 3 2.2 Logical channels... 3 2.3 Mapping of logical
Wireless systems GSM 2015-05-04 Simon Sörman Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Channels... 2 2.1 Physical channels... 2 2.1.1 FDMA/TDMA... 2 2.1.2 Bursts... 3 2.2 Logical channels... 3 2.3 Mapping of logical
Cellular Phone Systems
 Cellular Phone Systems Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC 1 Why Cellular Mobile Telephone Systems? Operational limitations of conventional mobile
Cellular Phone Systems Li-Hsing Yen National University of Kaohsiung Cellular System HLR PSTN MSC MSC VLR BSC BSC BSC 1 Why Cellular Mobile Telephone Systems? Operational limitations of conventional mobile
