Bond Valuation. Chapter 7. Example (coupon rate = r d ) Bonds, Bond Valuation, and Interest Rates. Valuing the cash flows
|
|
|
- Ruth Townsend
- 10 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bond Valuation Chapter 7 Bonds, Bond Valuation, and Interest Rates Valuing the cash flows (1) coupon payment (interest payment) = (coupon rate * principal) usually paid every 6 months (2) maturity value = principal or par value = $1000 Example (coupon rate = r d ) Five year corp. bond pay coupons at 10% rate, market rate (discount rate) (required rate of return) is 10% r d = 10% P 0 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $1,000 Example (coupon rate = r d ) Define Terms C = coupon payment = coupon rate x $1000 = 10% x $1,000 = $100 F = face amount or maturity value = $1000 n = payments to maturity = 5 r d = required rate of return = 10% P 0 = bond value =? 1
2 P 0 Example (coupon rate = r d ) = PV of coupon annuity + PV of lump sum maturity value PV of coupon annuity = $ PV of lump sum maturity value = $ P 0 = $ $ = $1, Solve with Calculator PMT = C = 100 FV = F = 1000 I/Y = r d = 10% N = 5 P 0 = PV = 1,000 In this case coupon = r d so P 0 = F This Bonds sells at PAR Example (coupon rate > r d ) Five year corp. bond pay coupons at 10% rate, market rate is 8% PMT = C = 100 FV = F = 1000 I/Y = r d = 10% N = 5 Example (coupon rate > r d ) P 0 = = $1, Calculator: PMT = C = 100 FV = F = 1000 I/Y = rd = 8% N = 5 P 0 = PV = $1,
3 Example (coupon rate > r d ) In this case coupon rate > r d so P 0 > F, we are getting more in coupon than we demand through required rate of return. Premium = $79.85 Example (coupon rate < r d ) Five year corp. bond pay coupons at 10% rate, market rate is 12% PMT = C = 100 FV = F = 1000 I/Y = r d = 12% N = 5 Example (coupon rate > r d ) P 0 = = $ Calculator: PMT = C = 100 FV = F = 1000 I/Y = rd = 12% N = 5 Example (coupon rate < r d ) In this case coupon rate < r d so P 0 < F, we are getting less in coupon than we demand through required rate of return. Discount = $72.10 P 0 = PV = $
4 A Harrah s Entertainment Inc 9 7/8 percent bond matures in ten years. Assume that the interest on these bonds is paid and compounded annually. Determine the value of a $1,000 denomination Harrah s bond as of today if the required rate of return is 7 percent. Solution PMT = 9.875% x $1,000 = FV = 1000 I/Y = 7% N = 10 PV = $1, A Harrah s Entertainment Inc 9 7/8 percent bond matures in ten years. Assume that the interest on these bonds is paid and compounded annually. Determine the value of a $1,000 denomination Harrah s bond as of today if the required rate of return is 9 percent. Solution PMT = 9.875% x $1,000 = FV = 1000 I/Y = 9% N = 10 PV = $1,
5 A Harrah s Entertainment Inc 9 7/8 percent bond matures in ten years. Assume that the interest on these bonds is paid and compounded annually. Determine the value of a $1,000 denomination Harrah s bond as of today if the required rate of return is 11 percent. Solution PMT = 9.875% x $1,000 = FV = 1000 I/Y = 11% N = 10 PV = $ Assume you purchased a Stations Casino, Inc. bond one year ago for $ when the market rate of interest was 10%. This bond matures in 19 years and is contracted to pay a annual coupons at the rate of 8%. If the current market rate of interest is 13%, what would be the percentage change in bond value from the time you purchased this bond until today? (cont) Assume you purchased a Stations Casino, Inc. bond one year ago for $ when the market rate of interest was 10%. This bond matures in 19 years and is contracted to pay a annual coupons at the rate of 8%. If the current market rate of interest is 7%, what would be the percentage change in bond value from the time you purchased this bond until today? 5
6 Bond Rules (1) coupon rate = r d, Bond sells for PAR (2) coupon rate < r d, Bond sells for a discount (3) coupon rate > r d, Bond sells for a premium (4) r d increases, Value decreases Semi-Annual Coupons Example: What is the price of a 10 year bond with a coupon rate of 10%, if it pays coupons semiannually and the market rate of interest is 8%? P 0 =?? (5) r d decreases, Value increases Answer: Semi-Annual Coupons PMT = (coupon rate*maturity Value) / m = $50 N = years to maturity * m = 10 * 2 = 20 FV = $1,000 I/Y = rd / m = 8% / 2 = 4% A MGM-Mirage Corporation bond pays a 14.5% coupon on a semi-annual basis. What is the value of this bond if it matures in 16 years and the market rate is 11%? P 0 = $1,
7 Answer PMT = (14.5% x $1,000) / 2 = $72.50 N = 16 x 2 = 32 FV = $1,000 I/Y = 11% / 2 = 5.5% What is the value of a Walt Disney Incorporated 30 year zero coupon bond if the required rate of return is 9% and a similar AA-rated Paychex Incorporated bond pays a 10% coupon? P 0 = $1, Answer PMT = (0.0% x $1,000) = $0.00 N = 30 FV = $1,000 I/Y = 9% Yield -to-maturity (YTM) Calculating the return on a Bond. Consider a bond with a 10% annual coupon rate, 15 years to maturity, and a par value of $1,000. The current price is $ What is the YTM? P 0 = $
8 Yield -to-maturity (YTM) N = 15 PV = FV = 1, PMT = 100 YTM = i = 11% YTM = ( Coupon yield ) ± (%)P 0 ) Coupon Yield = return from the coupon = annual coupon / P 0 = $100 / $ = 10.77% %)P 0 = ( P 1 -P 0 ) / P 0 = ( $ $ ) / $ = 0.23% YTM = 10.77% % = 11.00% A Microsoft, Incorporated bond has a coupon rate of 8.5%, matures in 12 years, and sells for $ (assume coupons are paid on a semi-annual basis). What is the YTM for this Microsoft, Inc. Corporate Bond? Yield -to-maturity (YTM) N = 12 x 2 = 24 PV = -$ FV = $1, PMT = (8.5% x $1,000) / 2 = $42.50 YTM = i = 5.5% x 2 = 11% 8
9 A Microsoft, Incorporated bond has a coupon rate of 8.5%, matures in 12 years, and sells for $ (assume coupons are paid on a semi-annual basis). What is the current yield for the first year on this bond? Current Yield Current or Coupon Yield is the return on a bond from the coupon only Current Yield = Annual Coupon / P 0 Current Yield = $85 / $ = 10.17% A Microsoft, Incorporated bond has a coupon rate of 8.5%, matures in 12 years, and sells for $ (assume coupons are paid on a semi-annual basis). What is the expected percentage capital gain or loss for the first year on this bond? Capital Gain or Loss Expected Percentage Capital Gain or Loss = %)P 0 = ( P 1 -P 0 ) / P 0 = ( ) / %)P % 9
10 Capital Gain or Loss YTM = ( Coupon yield ) ± (%)P 0 ) 11.0% = 10.17% ± (%)P 0 ) 11.0% = 10.17% + (%)P 0 ) %)P 0 = 11.00% % Corporate Bond Quotes FINRA Investor Information Table 7-4 on page 221 %)P 0 = 0.83% Bond Ratings Investment Quality High Grade Moody s Aaa and S&P AAA capacity to pay is extremely strong Moody s Aa and S&P AA capacity to pay is very strong Medium Grade Moody s A and S&P A capacity to pay is strong, but more susceptible to changes in circumstances Moody s Baa and S&P BBB capacity to pay is adequate, adverse conditions will have more impact on the firm s ability to pay Bond Ratings Speculative (Junk) Low Grade Moody s Ba, B, Caa and Ca; S&P BB, B, CCC, CC Considered speculative with respect to capacity to pay Very Low Grade Moody s C and S&P C income bonds with no interest being paid Moody s D and S&P D in default with principal and interest in arrears 10
11 Bond Evaluation Use bond rating - yield comparisons Also, consider maturity, liquidity, call provision, convertibility feature, collateral, other provisions Major Credit Rating Companies - Moody s, Standard and Poors (S&P), Fitch 11
Chapter 6 Valuing Bonds. (1) coupon payment - interest payment (coupon rate * principal) - usually paid every 6 months.
 Chapter 6 Valuing Bonds Bond Valuation - value the cash flows (1) coupon payment - interest payment (coupon rate * principal) - usually paid every 6 months. (2) maturity value = principal or par value
Chapter 6 Valuing Bonds Bond Valuation - value the cash flows (1) coupon payment - interest payment (coupon rate * principal) - usually paid every 6 months. (2) maturity value = principal or par value
Interest Rates and Bond Valuation
 Interest Rates and Bond Valuation Chapter 6 Key Concepts and Skills Know the important bond features and bond types Understand bond values and why they fluctuate Understand bond ratings and what they mean
Interest Rates and Bond Valuation Chapter 6 Key Concepts and Skills Know the important bond features and bond types Understand bond values and why they fluctuate Understand bond ratings and what they mean
Interest Rates and Bond Valuation
 and Bond Valuation 1 Bonds Debt Instrument Bondholders are lending the corporation money for some stated period of time. Liquid Asset Corporate Bonds can be traded in the secondary market. Price at which
and Bond Valuation 1 Bonds Debt Instrument Bondholders are lending the corporation money for some stated period of time. Liquid Asset Corporate Bonds can be traded in the secondary market. Price at which
education booklet CORPS Introduction to corporate bonds STOCKCROSS FINANCIAL SERVICES
 education booklet CORPS Introduction to corporate bonds STOCKCROSS FINANCIAL SERVICES corporate bonds Definition Corporate Bonds represent debt certificates issued by a corporation to raise funds for various
education booklet CORPS Introduction to corporate bonds STOCKCROSS FINANCIAL SERVICES corporate bonds Definition Corporate Bonds represent debt certificates issued by a corporation to raise funds for various
Chapter 5: Valuing Bonds
 FIN 302 Class Notes Chapter 5: Valuing Bonds What is a bond? A long-term debt instrument A contract where a borrower agrees to make interest and principal payments on specific dates Corporate Bond Quotations
FIN 302 Class Notes Chapter 5: Valuing Bonds What is a bond? A long-term debt instrument A contract where a borrower agrees to make interest and principal payments on specific dates Corporate Bond Quotations
Bonds and Yield to Maturity
 Bonds and Yield to Maturity Bonds A bond is a debt instrument requiring the issuer to repay to the lender/investor the amount borrowed (par or face value) plus interest over a specified period of time.
Bonds and Yield to Maturity Bonds A bond is a debt instrument requiring the issuer to repay to the lender/investor the amount borrowed (par or face value) plus interest over a specified period of time.
Topics in Chapter. Key features of bonds Bond valuation Measuring yield Assessing risk
 Bond Valuation 1 Topics in Chapter Key features of bonds Bond valuation Measuring yield Assessing risk 2 Determinants of Intrinsic Value: The Cost of Debt Net operating profit after taxes Free cash flow
Bond Valuation 1 Topics in Chapter Key features of bonds Bond valuation Measuring yield Assessing risk 2 Determinants of Intrinsic Value: The Cost of Debt Net operating profit after taxes Free cash flow
Chapter 4 Valuing Bonds
 Chapter 4 Valuing Bonds MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A 15 year, 8%, $1000 face value bond is currently trading at $958. The yield to maturity of this bond must be a. less than 8%. b. equal to 8%. c. greater than
Chapter 4 Valuing Bonds MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A 15 year, 8%, $1000 face value bond is currently trading at $958. The yield to maturity of this bond must be a. less than 8%. b. equal to 8%. c. greater than
TIME VALUE OF MONEY #6: TREASURY BOND. Professor Peter Harris Mathematics by Dr. Sharon Petrushka. Introduction
 TIME VALUE OF MONEY #6: TREASURY BOND Professor Peter Harris Mathematics by Dr. Sharon Petrushka Introduction This problem assumes that you have mastered problems 1-5, which are prerequisites. In this
TIME VALUE OF MONEY #6: TREASURY BOND Professor Peter Harris Mathematics by Dr. Sharon Petrushka Introduction This problem assumes that you have mastered problems 1-5, which are prerequisites. In this
Bonds and preferred stock. Basic definitions. Preferred(?) stock. Investing in fixed income securities
 Bonds and preferred stock Investing in fixed income securities Basic definitions Stock: share of ownership Stockholders are the owners of the firm Two types of stock: preferred and common Preferred stock:
Bonds and preferred stock Investing in fixed income securities Basic definitions Stock: share of ownership Stockholders are the owners of the firm Two types of stock: preferred and common Preferred stock:
INTERACTIVE BROKERS DISCLOSURE STATEMENT FOR BOND TRADING
 INTERACTIVE BROKERS DISCLOSURE STATEMENT FOR BOND TRADING THIS DISCLOSURE STATEMENT DISCUSSES THE CHARACTERISTICS AND RISKS OF TRADING BONDS THROUGH INTERACTIVE BROKERS (IB). BEFORE TRADING BONDS YOU SHOULD
INTERACTIVE BROKERS DISCLOSURE STATEMENT FOR BOND TRADING THIS DISCLOSURE STATEMENT DISCUSSES THE CHARACTERISTICS AND RISKS OF TRADING BONDS THROUGH INTERACTIVE BROKERS (IB). BEFORE TRADING BONDS YOU SHOULD
Bond Valuation. Capital Budgeting and Corporate Objectives
 Bond Valuation Capital Budgeting and Corporate Objectives Professor Ron Kaniel Simon School of Business University of Rochester 1 Bond Valuation An Overview Introduction to bonds and bond markets» What
Bond Valuation Capital Budgeting and Corporate Objectives Professor Ron Kaniel Simon School of Business University of Rochester 1 Bond Valuation An Overview Introduction to bonds and bond markets» What
Chapter. Investing in Bonds. 13.1 Evaluating Bonds 13.2 Buying and Selling Bonds. 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning
 Chapter 13 Investing in Bonds 13.1 Evaluating Bonds 13.2 Buying and Selling Bonds 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning Standards Standard 4.0 Investigate opportunities available for saving and investing.
Chapter 13 Investing in Bonds 13.1 Evaluating Bonds 13.2 Buying and Selling Bonds 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning Standards Standard 4.0 Investigate opportunities available for saving and investing.
Chapter Review and Self-Test Problems. Answers to Chapter Review and Self-Test Problems
 236 PART THREE Valuation of Future Cash Flows Chapter Review and Self-Test Problems 7.1 Bond Values A Microgates Industries bond has a 10 percent coupon rate and a $1,000 face value. Interest is paid semiannually,
236 PART THREE Valuation of Future Cash Flows Chapter Review and Self-Test Problems 7.1 Bond Values A Microgates Industries bond has a 10 percent coupon rate and a $1,000 face value. Interest is paid semiannually,
Bond Valuation. FINANCE 350 Global Financial Management. Professor Alon Brav Fuqua School of Business Duke University. Bond Valuation: An Overview
 Bond Valuation FINANCE 350 Global Financial Management Professor Alon Brav Fuqua School of Business Duke University 1 Bond Valuation: An Overview Bond Markets What are they? How big? How important? Valuation
Bond Valuation FINANCE 350 Global Financial Management Professor Alon Brav Fuqua School of Business Duke University 1 Bond Valuation: An Overview Bond Markets What are they? How big? How important? Valuation
Chapter 8. Step 2: Find prices of the bonds today: n i PV FV PMT Result Coupon = 4% 29.5 5? 100 4 84.74 Zero coupon 29.5 5? 100 0 23.
 Chapter 8 Bond Valuation with a Flat Term Structure 1. Suppose you want to know the price of a 10-year 7% coupon Treasury bond that pays interest annually. a. You have been told that the yield to maturity
Chapter 8 Bond Valuation with a Flat Term Structure 1. Suppose you want to know the price of a 10-year 7% coupon Treasury bond that pays interest annually. a. You have been told that the yield to maturity
Prepared by: Dalia A. Marafi Version 2.0
 Kuwait University College of Business Administration Department of Finance and Financial Institutions Using )Casio FC-200V( for Fundamentals of Financial Management (220) Prepared by: Dalia A. Marafi Version
Kuwait University College of Business Administration Department of Finance and Financial Institutions Using )Casio FC-200V( for Fundamentals of Financial Management (220) Prepared by: Dalia A. Marafi Version
How To Value Bonds
 Chapter 6 Interest Rates And Bond Valuation Learning Goals 1. Describe interest rate fundamentals, the term structure of interest rates, and risk premiums. 2. Review the legal aspects of bond financing
Chapter 6 Interest Rates And Bond Valuation Learning Goals 1. Describe interest rate fundamentals, the term structure of interest rates, and risk premiums. 2. Review the legal aspects of bond financing
Bond valuation. Present value of a bond = present value of interest payments + present value of maturity value
 Bond valuation A reading prepared by Pamela Peterson Drake O U T L I N E 1. Valuation of long-term debt securities 2. Issues 3. Summary 1. Valuation of long-term debt securities Debt securities are obligations
Bond valuation A reading prepared by Pamela Peterson Drake O U T L I N E 1. Valuation of long-term debt securities 2. Issues 3. Summary 1. Valuation of long-term debt securities Debt securities are obligations
Fixed Income: Practice Problems with Solutions
 Fixed Income: Practice Problems with Solutions Directions: Unless otherwise stated, assume semi-annual payment on bonds.. A 6.0 percent bond matures in exactly 8 years and has a par value of 000 dollars.
Fixed Income: Practice Problems with Solutions Directions: Unless otherwise stated, assume semi-annual payment on bonds.. A 6.0 percent bond matures in exactly 8 years and has a par value of 000 dollars.
Chapter 4 Bonds and Their Valuation ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS
 Chapter 4 Bonds and Their Valuation ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS 4-1 a. A bond is a promissory note issued by a business or a governmental unit. Treasury bonds, sometimes referred to as government
Chapter 4 Bonds and Their Valuation ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS 4-1 a. A bond is a promissory note issued by a business or a governmental unit. Treasury bonds, sometimes referred to as government
Bonds, in the most generic sense, are issued with three essential components.
 Page 1 of 5 Bond Basics Often considered to be one of the most conservative of all investments, bonds actually provide benefits to both conservative and more aggressive investors alike. The variety of
Page 1 of 5 Bond Basics Often considered to be one of the most conservative of all investments, bonds actually provide benefits to both conservative and more aggressive investors alike. The variety of
Math of Finance. Texas Association of Counties January 2014
 Math of Finance Texas Association of Counties January 2014 Money Market Securities Sample Treasury Bill Quote*: N Bid Ask Ask Yld 126 4.86 4.85 5.00 *(Yields do not reflect current market conditions) Bank
Math of Finance Texas Association of Counties January 2014 Money Market Securities Sample Treasury Bill Quote*: N Bid Ask Ask Yld 126 4.86 4.85 5.00 *(Yields do not reflect current market conditions) Bank
CHAPTER 9 DEBT SECURITIES. by Lee M. Dunham, PhD, CFA, and Vijay Singal, PhD, CFA
 CHAPTER 9 DEBT SECURITIES by Lee M. Dunham, PhD, CFA, and Vijay Singal, PhD, CFA LEARNING OUTCOMES After completing this chapter, you should be able to do the following: a Identify issuers of debt securities;
CHAPTER 9 DEBT SECURITIES by Lee M. Dunham, PhD, CFA, and Vijay Singal, PhD, CFA LEARNING OUTCOMES After completing this chapter, you should be able to do the following: a Identify issuers of debt securities;
- Short term notes (bonds) Maturities of 1-4 years - Medium-term notes/bonds Maturities of 5-10 years - Long-term bonds Maturities of 10-30 years
 Contents 1. What Is A Bond? 2. Who Issues Bonds? Government Bonds Corporate Bonds 3. Basic Terms of Bonds Maturity Types of Coupon (Fixed, Floating, Zero Coupon) Redemption Seniority Price Yield The Relation
Contents 1. What Is A Bond? 2. Who Issues Bonds? Government Bonds Corporate Bonds 3. Basic Terms of Bonds Maturity Types of Coupon (Fixed, Floating, Zero Coupon) Redemption Seniority Price Yield The Relation
This is Interest Rates and Bond Valuation, chapter 9 from the book Finance for Managers (index.html) (v. 0.1).
 This is Interest Rates and Bond Valuation, chapter 9 from the book Finance for Managers (index.html) (v. 0.1). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Interest Rates and Bond Valuation, chapter 9 from the book Finance for Managers (index.html) (v. 0.1). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
BOND - Security that obligates the issuer to make specified payments to the bondholder.
 Bond Valuation BOND - Security that obligates the issuer to make specified payments to the bondholder. COUPON - The interest payments paid to the bondholder. FACE VALUE - Payment at the maturity of the
Bond Valuation BOND - Security that obligates the issuer to make specified payments to the bondholder. COUPON - The interest payments paid to the bondholder. FACE VALUE - Payment at the maturity of the
Investors Chronicle Roadshow 2011. Trading Bonds on the London Stock Exchange
 Investors Chronicle Roadshow 2011 Trading Bonds on the London Stock Exchange Agenda How do bonds work? Risks associated with bonds Order book for Retail Bonds London Stock Exchange Website Tools 2 How
Investors Chronicle Roadshow 2011 Trading Bonds on the London Stock Exchange Agenda How do bonds work? Risks associated with bonds Order book for Retail Bonds London Stock Exchange Website Tools 2 How
Chapter 3 Fixed Income Securities
 Chapter 3 Fixed Income Securities Road Map Part A Introduction to finance. Part B Valuation of assets, given discount rates. Fixed-income securities. Stocks. Real assets (capital budgeting). Part C Determination
Chapter 3 Fixed Income Securities Road Map Part A Introduction to finance. Part B Valuation of assets, given discount rates. Fixed-income securities. Stocks. Real assets (capital budgeting). Part C Determination
FNCE 301, Financial Management H Guy Williams, 2006
 REVIEW We ve used the DCF method to find present value. We also know shortcut methods to solve these problems such as perpetuity present value = C/r. These tools allow us to value any cash flow including
REVIEW We ve used the DCF method to find present value. We also know shortcut methods to solve these problems such as perpetuity present value = C/r. These tools allow us to value any cash flow including
Duration and convexity
 Duration and convexity Prepared by Pamela Peterson Drake, Ph.D., CFA Contents 1. Overview... 1 A. Calculating the yield on a bond... 4 B. The yield curve... 6 C. Option-like features... 8 D. Bond ratings...
Duration and convexity Prepared by Pamela Peterson Drake, Ph.D., CFA Contents 1. Overview... 1 A. Calculating the yield on a bond... 4 B. The yield curve... 6 C. Option-like features... 8 D. Bond ratings...
Chapter 9 Bonds and Their Valuation ANSWERS TO SELECTED END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS
 Chapter 9 Bonds and Their Valuation ANSWERS TO SELECTED END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS 9-1 a. A bond is a promissory note issued by a business or a governmental unit. Treasury bonds, sometimes referred to as
Chapter 9 Bonds and Their Valuation ANSWERS TO SELECTED END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS 9-1 a. A bond is a promissory note issued by a business or a governmental unit. Treasury bonds, sometimes referred to as
Practice Set #2 and Solutions.
 FIN-672 Securities Analysis & Portfolio Management Professor Michel A. Robe Practice Set #2 and Solutions. What to do with this practice set? To help MBA students prepare for the assignment and the exams,
FIN-672 Securities Analysis & Portfolio Management Professor Michel A. Robe Practice Set #2 and Solutions. What to do with this practice set? To help MBA students prepare for the assignment and the exams,
Saving and Investing. Chapter 11 Section Main Menu
 Saving and Investing How does investing contribute to the free enterprise system? How does the financial system bring together savers and borrowers? How do financial intermediaries link savers and borrowers?
Saving and Investing How does investing contribute to the free enterprise system? How does the financial system bring together savers and borrowers? How do financial intermediaries link savers and borrowers?
You just paid $350,000 for a policy that will pay you and your heirs $12,000 a year forever. What rate of return are you earning on this policy?
 1 You estimate that you will have $24,500 in student loans by the time you graduate. The interest rate is 6.5%. If you want to have this debt paid in full within five years, how much must you pay each
1 You estimate that you will have $24,500 in student loans by the time you graduate. The interest rate is 6.5%. If you want to have this debt paid in full within five years, how much must you pay each
CHAPTER 15: THE TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATES
 CHAPTER 15: THE TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATES 1. Expectations hypothesis. The yields on long-term bonds are geometric averages of present and expected future short rates. An upward sloping curve is
CHAPTER 15: THE TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATES 1. Expectations hypothesis. The yields on long-term bonds are geometric averages of present and expected future short rates. An upward sloping curve is
Chapter 10. Fixed Income Markets. Fixed-Income Securities
 Chapter 10 Fixed-Income Securities Bond: Tradable security that promises to make a pre-specified series of payments over time. Straight bond makes fixed coupon and principal payment. Bonds are traded mainly
Chapter 10 Fixed-Income Securities Bond: Tradable security that promises to make a pre-specified series of payments over time. Straight bond makes fixed coupon and principal payment. Bonds are traded mainly
Chapter 11. Stocks and Bonds. How does this distribution work? An example. What form do the distributions to common shareholders take?
 Chapter 11. Stocks and Bonds Chapter Objectives To identify basic shareholder rights and the means by which corporations make distributions to shareholders To recognize the investment opportunities in
Chapter 11. Stocks and Bonds Chapter Objectives To identify basic shareholder rights and the means by which corporations make distributions to shareholders To recognize the investment opportunities in
High-yield bonds. Bonds that potentially reward investors for taking additional risk. High-yield bond basics
 High-yield bonds Bonds that potentially reward investors for taking additional risk Types of high-yield bonds Types of high-yield bonds include: Cash-pay bonds. Known as plain vanilla bonds, these bonds
High-yield bonds Bonds that potentially reward investors for taking additional risk Types of high-yield bonds Types of high-yield bonds include: Cash-pay bonds. Known as plain vanilla bonds, these bonds
Chapter 11. Bond Pricing - 1. Bond Valuation: Part I. Several Assumptions: To simplify the analysis, we make the following assumptions.
 Bond Pricing - 1 Chapter 11 Several Assumptions: To simplify the analysis, we make the following assumptions. 1. The coupon payments are made every six months. 2. The next coupon payment for the bond is
Bond Pricing - 1 Chapter 11 Several Assumptions: To simplify the analysis, we make the following assumptions. 1. The coupon payments are made every six months. 2. The next coupon payment for the bond is
Traditionally pension schemes invested in four main asset classes: Shares (Equities or Stocks), Bonds, Property and Cash.
 Asset Classes Traditionally pension schemes invested in four main asset classes: Shares (Equities or Stocks), Bonds, Property and Cash. Shares (also called Equities or Stocks) are shares bought in quoted
Asset Classes Traditionally pension schemes invested in four main asset classes: Shares (Equities or Stocks), Bonds, Property and Cash. Shares (also called Equities or Stocks) are shares bought in quoted
INVESTMENT CHOICES. Dr. Suzanne B. Badenhop Professor/Extension Specialist
 INVESTMENT CHOICES Dr. Suzanne B. Badenhop Professor/Extension Specialist INVESTING 101 What is your investment objective? What is your age? What is your time horizon What is your risk comfort level? What
INVESTMENT CHOICES Dr. Suzanne B. Badenhop Professor/Extension Specialist INVESTING 101 What is your investment objective? What is your age? What is your time horizon What is your risk comfort level? What
Using Financial Calculators
 Chapter 4 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation 4B-1 Appendix 4B Using Financial Calculators This appendix is intended to help you use your Hewlett-Packard or Texas Instruments BA II Plus financial calculator
Chapter 4 Discounted Cash Flow Valuation 4B-1 Appendix 4B Using Financial Calculators This appendix is intended to help you use your Hewlett-Packard or Texas Instruments BA II Plus financial calculator
A guide to investing in high-yield bonds
 A guide to investing in high-yield bonds What you should know before you buy Are high-yield bonds suitable for you? High-yield bonds are designed for investors who: Can accept additional risks of investing
A guide to investing in high-yield bonds What you should know before you buy Are high-yield bonds suitable for you? High-yield bonds are designed for investors who: Can accept additional risks of investing
Answers to Review Questions
 Answers to Review Questions 1. The real rate of interest is the rate that creates an equilibrium between the supply of savings and demand for investment funds. The nominal rate of interest is the actual
Answers to Review Questions 1. The real rate of interest is the rate that creates an equilibrium between the supply of savings and demand for investment funds. The nominal rate of interest is the actual
Lecture 2 Bond pricing. Hedging the interest rate risk
 Lecture 2 Bond pricing. Hedging the interest rate risk IMQF, Spring Semester 2011/2012 Module: Derivatives and Fixed Income Securities Course: Fixed Income Securities Lecturer: Miloš Bo ović Lecture outline
Lecture 2 Bond pricing. Hedging the interest rate risk IMQF, Spring Semester 2011/2012 Module: Derivatives and Fixed Income Securities Course: Fixed Income Securities Lecturer: Miloš Bo ović Lecture outline
Using Securities Markets for Financing and Investing Opportunities
 Chapter 19 Using Securities Markets for Financing and Investing Opportunities McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2014 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Nineteen NAME that COMPANY
Chapter 19 Using Securities Markets for Financing and Investing Opportunities McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2014 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Nineteen NAME that COMPANY
Goals. Bonds: Fixed Income Securities. Two Parts. Bond Returns
 Goals Bonds: Fixed Income Securities History Features and structure Bond ratings Economics 71a: Spring 2007 Mayo chapter 12 Lecture notes 4.3 Bond Returns Two Parts Interest and capital gains Stock comparison:
Goals Bonds: Fixed Income Securities History Features and structure Bond ratings Economics 71a: Spring 2007 Mayo chapter 12 Lecture notes 4.3 Bond Returns Two Parts Interest and capital gains Stock comparison:
Problem Set: Annuities and Perpetuities (Solutions Below)
 Problem Set: Annuities and Perpetuities (Solutions Below) 1. If you plan to save $300 annually for 10 years and the discount rate is 15%, what is the future value? 2. If you want to buy a boat in 6 years
Problem Set: Annuities and Perpetuities (Solutions Below) 1. If you plan to save $300 annually for 10 years and the discount rate is 15%, what is the future value? 2. If you want to buy a boat in 6 years
CHAPTER 15: THE TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATES
 Chapter - The Term Structure of Interest Rates CHAPTER : THE TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATES PROBLEM SETS.. In general, the forward rate can be viewed as the sum of the market s expectation of the future
Chapter - The Term Structure of Interest Rates CHAPTER : THE TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATES PROBLEM SETS.. In general, the forward rate can be viewed as the sum of the market s expectation of the future
CHAPTER 15: THE TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATES
 CHAPTER : THE TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATES CHAPTER : THE TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATES PROBLEM SETS.. In general, the forward rate can be viewed as the sum of the market s expectation of the future
CHAPTER : THE TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATES CHAPTER : THE TERM STRUCTURE OF INTEREST RATES PROBLEM SETS.. In general, the forward rate can be viewed as the sum of the market s expectation of the future
Bonds and the Term Structure of Interest Rates: Pricing, Yields, and (No) Arbitrage
 Prof. Alex Shapiro Lecture Notes 12 Bonds and the Term Structure of Interest Rates: Pricing, Yields, and (No) Arbitrage I. Readings and Suggested Practice Problems II. Bonds Prices and Yields (Revisited)
Prof. Alex Shapiro Lecture Notes 12 Bonds and the Term Structure of Interest Rates: Pricing, Yields, and (No) Arbitrage I. Readings and Suggested Practice Problems II. Bonds Prices and Yields (Revisited)
Life Insurer Financial Profile
 Life Insurer Financial Profile Company New York Life Ins Northwestern Massachusetts John Hancock Life Mutual of Omaha Lincoln National Pacific Life Ins Co Genworth Life Ins Co Long Term Care Mutual Life
Life Insurer Financial Profile Company New York Life Ins Northwestern Massachusetts John Hancock Life Mutual of Omaha Lincoln National Pacific Life Ins Co Genworth Life Ins Co Long Term Care Mutual Life
Understanding Fixed Income
 Understanding Fixed Income 2014 AMP Capital Investors Limited ABN 59 001 777 591 AFSL 232497 Understanding Fixed Income About fixed income at AMP Capital Our global presence helps us deliver outstanding
Understanding Fixed Income 2014 AMP Capital Investors Limited ABN 59 001 777 591 AFSL 232497 Understanding Fixed Income About fixed income at AMP Capital Our global presence helps us deliver outstanding
Chapter 6. Learning Objectives Principles Used in This Chapter 1. Annuities 2. Perpetuities 3. Complex Cash Flow Streams
 Chapter 6 Learning Objectives Principles Used in This Chapter 1. Annuities 2. Perpetuities 3. Complex Cash Flow Streams 1. Distinguish between an ordinary annuity and an annuity due, and calculate present
Chapter 6 Learning Objectives Principles Used in This Chapter 1. Annuities 2. Perpetuities 3. Complex Cash Flow Streams 1. Distinguish between an ordinary annuity and an annuity due, and calculate present
How to calculate present values
 How to calculate present values Back to the future Chapter 3 Discounted Cash Flow Analysis (Time Value of Money) Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis is the foundation of valuation in corporate finance
How to calculate present values Back to the future Chapter 3 Discounted Cash Flow Analysis (Time Value of Money) Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis is the foundation of valuation in corporate finance
2. Determine the appropriate discount rate based on the risk of the security
 Fixed Income Instruments III Intro to the Valuation of Debt Securities LOS 64.a Explain the steps in the bond valuation process 1. Estimate the cash flows coupons and return of principal 2. Determine the
Fixed Income Instruments III Intro to the Valuation of Debt Securities LOS 64.a Explain the steps in the bond valuation process 1. Estimate the cash flows coupons and return of principal 2. Determine the
Practice Questions for Midterm II
 Finance 333 Investments Practice Questions for Midterm II Winter 2004 Professor Yan 1. The market portfolio has a beta of a. 0. *b. 1. c. -1. d. 0.5. By definition, the beta of the market portfolio is
Finance 333 Investments Practice Questions for Midterm II Winter 2004 Professor Yan 1. The market portfolio has a beta of a. 0. *b. 1. c. -1. d. 0.5. By definition, the beta of the market portfolio is
A guide to investing in high-yield bonds
 A guide to investing in high-yield bonds What you should know before you buy Are high-yield bonds suitable for you? High-yield bonds are designed for investors who: Can accept additional risks of investing
A guide to investing in high-yield bonds What you should know before you buy Are high-yield bonds suitable for you? High-yield bonds are designed for investors who: Can accept additional risks of investing
CHAPTER 14: BOND PRICES AND YIELDS
 CHAPTER 14: BOND PRICES AND YIELDS PROBLEM SETS 1. The bond callable at 105 should sell at a lower price because the call provision is more valuable to the firm. Therefore, its yield to maturity should
CHAPTER 14: BOND PRICES AND YIELDS PROBLEM SETS 1. The bond callable at 105 should sell at a lower price because the call provision is more valuable to the firm. Therefore, its yield to maturity should
CHAPTER 14: BOND PRICES AND YIELDS
 CHAPTER 14: BOND PRICES AND YIELDS 1. a. Effective annual rate on 3-month T-bill: ( 100,000 97,645 )4 1 = 1.02412 4 1 =.10 or 10% b. Effective annual interest rate on coupon bond paying 5% semiannually:
CHAPTER 14: BOND PRICES AND YIELDS 1. a. Effective annual rate on 3-month T-bill: ( 100,000 97,645 )4 1 = 1.02412 4 1 =.10 or 10% b. Effective annual interest rate on coupon bond paying 5% semiannually:
Click Here to Buy the Tutorial
 FIN 534 Week 4 Quiz 3 (Str) Click Here to Buy the Tutorial http://www.tutorialoutlet.com/fin-534/fin-534-week-4-quiz-3- str/ For more course tutorials visit www.tutorialoutlet.com Which of the following
FIN 534 Week 4 Quiz 3 (Str) Click Here to Buy the Tutorial http://www.tutorialoutlet.com/fin-534/fin-534-week-4-quiz-3- str/ For more course tutorials visit www.tutorialoutlet.com Which of the following
Lecture Notes on MONEY, BANKING, AND FINANCIAL MARKETS. Peter N. Ireland Department of Economics Boston College. [email protected]
 Lecture Notes on MONEY, BANKING, AND FINANCIAL MARKETS Peter N. Ireland Department of Economics Boston College [email protected] http://www.bc.edu/~irelandp/ec61.html Chapter 6: The Risk and Term Structure
Lecture Notes on MONEY, BANKING, AND FINANCIAL MARKETS Peter N. Ireland Department of Economics Boston College [email protected] http://www.bc.edu/~irelandp/ec61.html Chapter 6: The Risk and Term Structure
Fin 3312 Sample Exam 1 Questions
 Fin 3312 Sample Exam 1 Questions Here are some representative type questions. This review is intended to give you an idea of the types of questions that may appear on the exam, and how the questions might
Fin 3312 Sample Exam 1 Questions Here are some representative type questions. This review is intended to give you an idea of the types of questions that may appear on the exam, and how the questions might
Basics of Investment
 Presented By Ye Yi 6718 South, 2680 East Salt Lake City, Utah 84121 1 A. Introduction of Money Value Measurement -- Present Value and Future Value Assuming that you have deposited $1,000 into a bank CD
Presented By Ye Yi 6718 South, 2680 East Salt Lake City, Utah 84121 1 A. Introduction of Money Value Measurement -- Present Value and Future Value Assuming that you have deposited $1,000 into a bank CD
Bonds. Describe Bonds. Define Key Words. Created 2007 By Michael Worthington Elizabeth City State University
 Bonds OBJECTIVES Describe bonds Define key words Explain why bond prices fluctuate Compute interest payments Calculate the price of bonds Created 2007 By Michael Worthington Elizabeth City State University
Bonds OBJECTIVES Describe bonds Define key words Explain why bond prices fluctuate Compute interest payments Calculate the price of bonds Created 2007 By Michael Worthington Elizabeth City State University
CHAPTER 10 BOND PRICES AND YIELDS
 CHAPTER 10 BOND PRICES AND YIELDS 1. a. Catastrophe bond. Typically issued by an insurance company. They are similar to an insurance policy in that the investor receives coupons and par value, but takes
CHAPTER 10 BOND PRICES AND YIELDS 1. a. Catastrophe bond. Typically issued by an insurance company. They are similar to an insurance policy in that the investor receives coupons and par value, but takes
Chapter 6 Interest rates and Bond Valuation. 2012 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 4-1
 Chapter 6 Interest rates and Bond Valuation 2012 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 4-1 Interest Rates and Required Returns: Interest Rate Fundamentals The interest rate is usually applied to
Chapter 6 Interest rates and Bond Valuation 2012 Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 4-1 Interest Rates and Required Returns: Interest Rate Fundamentals The interest rate is usually applied to
Chapter 4: Common Stocks. Chapter 5: Forwards and Futures
 15.401 Part B Valuation Chapter 3: Fixed Income Securities Chapter 4: Common Stocks Chapter 5: Forwards and Futures Chapter 6: Options Lecture Notes Introduction 15.401 Part B Valuation We have learned
15.401 Part B Valuation Chapter 3: Fixed Income Securities Chapter 4: Common Stocks Chapter 5: Forwards and Futures Chapter 6: Options Lecture Notes Introduction 15.401 Part B Valuation We have learned
Manual for SOA Exam FM/CAS Exam 2.
 Manual for SOA Exam FM/CAS Exam 2. Chapter 5. Bonds. c 2009. Miguel A. Arcones. All rights reserved. Extract from: Arcones Manual for the SOA Exam FM/CAS Exam 2, Financial Mathematics. Fall 2009 Edition,
Manual for SOA Exam FM/CAS Exam 2. Chapter 5. Bonds. c 2009. Miguel A. Arcones. All rights reserved. Extract from: Arcones Manual for the SOA Exam FM/CAS Exam 2, Financial Mathematics. Fall 2009 Edition,
Excel Financial Functions
 Excel Financial Functions PV() Effect() Nominal() FV() PMT() Payment Amortization Table Payment Array Table NPer() Rate() NPV() IRR() MIRR() Yield() Price() Accrint() Future Value How much will your money
Excel Financial Functions PV() Effect() Nominal() FV() PMT() Payment Amortization Table Payment Array Table NPer() Rate() NPV() IRR() MIRR() Yield() Price() Accrint() Future Value How much will your money
Chapter 6 Interest Rates and Bond Valuation
 Chapter 6 Interest Rates and Bond Valuation Solutions to Problems P6-1. P6-2. LG 1: Interest Rate Fundamentals: The Real Rate of Return Basic Real rate of return = 5.5% 2.0% = 3.5% LG 1: Real Rate of Interest
Chapter 6 Interest Rates and Bond Valuation Solutions to Problems P6-1. P6-2. LG 1: Interest Rate Fundamentals: The Real Rate of Return Basic Real rate of return = 5.5% 2.0% = 3.5% LG 1: Real Rate of Interest
A) 1.8% B) 1.9% C) 2.0% D) 2.1% E) 2.2%
 1 Exam FM Questions Practice Exam 1 1. Consider the following yield curve: Year Spot Rate 1 5.5% 2 5.0% 3 5.0% 4 4.5% 5 4.0% Find the four year forward rate. A) 1.8% B) 1.9% C) 2.0% D) 2.1% E) 2.2% 2.
1 Exam FM Questions Practice Exam 1 1. Consider the following yield curve: Year Spot Rate 1 5.5% 2 5.0% 3 5.0% 4 4.5% 5 4.0% Find the four year forward rate. A) 1.8% B) 1.9% C) 2.0% D) 2.1% E) 2.2% 2.
ECON 354 Money and Banking. Risk Structure of Long-Term Bonds in the United States 20. Professor Yamin Ahmad
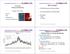 Lecture 5 Risk Term Structure Theories to explain facts ECO 354 Money and Banking Professor Yamin Ahmad Big Concepts The Risk Structure of Interest Rates The Term Structure of Interest Rates Premiums:
Lecture 5 Risk Term Structure Theories to explain facts ECO 354 Money and Banking Professor Yamin Ahmad Big Concepts The Risk Structure of Interest Rates The Term Structure of Interest Rates Premiums:
Math Workshop Algebra (Time Value of Money; TVM)
 Math Workshop Algebra (Time Value of Money; TVM) FV 1 = PV+INT 1 = PV+PV*I = PV(1+I) = $100(1+10%) = $110.00 FV 2 = FV 1 (1+I) = PV(1+I)(1+I) = PV(1+I) 2 =$100(1.10) 2 = $121.00 FV 3 = FV 2 (1+I) = PV(1
Math Workshop Algebra (Time Value of Money; TVM) FV 1 = PV+INT 1 = PV+PV*I = PV(1+I) = $100(1+10%) = $110.00 FV 2 = FV 1 (1+I) = PV(1+I)(1+I) = PV(1+I) 2 =$100(1.10) 2 = $121.00 FV 3 = FV 2 (1+I) = PV(1
USING THE SHARP EL 738 FINANCIAL CALCULATOR
 USING THE SHARP EL 738 FINANCIAL CALCULATOR Basic financial examples with financial calculator steps Prepared by Colin C Smith 2010 Some important things to consider 1. These notes cover basic financial
USING THE SHARP EL 738 FINANCIAL CALCULATOR Basic financial examples with financial calculator steps Prepared by Colin C Smith 2010 Some important things to consider 1. These notes cover basic financial
VALUATION OF DEBT CONTRACTS AND THEIR PRICE VOLATILITY CHARACTERISTICS QUESTIONS See answers below
 VALUATION OF DEBT CONTRACTS AND THEIR PRICE VOLATILITY CHARACTERISTICS QUESTIONS See answers below 1. Determine the value of the following risk-free debt instrument, which promises to make the respective
VALUATION OF DEBT CONTRACTS AND THEIR PRICE VOLATILITY CHARACTERISTICS QUESTIONS See answers below 1. Determine the value of the following risk-free debt instrument, which promises to make the respective
Bond Valuation. What is a bond?
 Lecture: III 1 What is a bond? Bond Valuation When a corporation wishes to borrow money from the public on a long-term basis, it usually does so by issuing or selling debt securities called bonds. A bond
Lecture: III 1 What is a bond? Bond Valuation When a corporation wishes to borrow money from the public on a long-term basis, it usually does so by issuing or selling debt securities called bonds. A bond
CHAPTER 8 INTEREST RATES AND BOND VALUATION
 CHAPTER 8 INTEREST RATES AND BOND VALUATION Answers to Concept Questions 1. No. As interest rates fluctuate, the value of a Treasury security will fluctuate. Long-term Treasury securities have substantial
CHAPTER 8 INTEREST RATES AND BOND VALUATION Answers to Concept Questions 1. No. As interest rates fluctuate, the value of a Treasury security will fluctuate. Long-term Treasury securities have substantial
Finance Homework Julian Vu May 28, 2008
 Finance Homework Julian Vu May 28, 2008 Assignment: p. 28-29 Problems 1-1 and 1-2 p. 145-147 Questions 4-2, 4-3, and 4-4, and Problems 4-1, 4-2, 4-3, and 4-13 P1-1 A Treasury Bond that matures in 10 years
Finance Homework Julian Vu May 28, 2008 Assignment: p. 28-29 Problems 1-1 and 1-2 p. 145-147 Questions 4-2, 4-3, and 4-4, and Problems 4-1, 4-2, 4-3, and 4-13 P1-1 A Treasury Bond that matures in 10 years
Basic financial arithmetic
 2 Basic financial arithmetic Simple interest Compound interest Nominal and effective rates Continuous discounting Conversions and comparisons Exercise Summary File: MFME2_02.xls 13 This chapter deals
2 Basic financial arithmetic Simple interest Compound interest Nominal and effective rates Continuous discounting Conversions and comparisons Exercise Summary File: MFME2_02.xls 13 This chapter deals
Module 1: Corporate Finance and the Role of Venture Capital Financing TABLE OF CONTENTS
 1.0 ALTERNATIVE SOURCES OF FINANCE Module 1: Corporate Finance and the Role of Venture Capital Financing Alternative Sources of Finance TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.1 Short-Term Debt (Short-Term Loans, Line of
1.0 ALTERNATIVE SOURCES OF FINANCE Module 1: Corporate Finance and the Role of Venture Capital Financing Alternative Sources of Finance TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.1 Short-Term Debt (Short-Term Loans, Line of
LOS 56.a: Explain steps in the bond valuation process.
 The following is a review of the Analysis of Fixed Income Investments principles designed to address the learning outcome statements set forth by CFA Institute. This topic is also covered in: Introduction
The following is a review of the Analysis of Fixed Income Investments principles designed to address the learning outcome statements set forth by CFA Institute. This topic is also covered in: Introduction
Gordon Guides For the LLQP Exam. Financial Math
 Financial Math, candidates are expected to have a high degree of understanding of time value of money principles, security valuation and basic statistics. Formulas are provided on the exam, therefore do
Financial Math, candidates are expected to have a high degree of understanding of time value of money principles, security valuation and basic statistics. Formulas are provided on the exam, therefore do
HP 12C Calculations. 2. If you are given the following set of cash flows and discount rates, can you calculate the PV? (pg.
 HP 12C Calculations This handout has examples for calculations on the HP12C: 1. Present Value (PV) 2. Present Value with cash flows and discount rate constant over time 3. Present Value with uneven cash
HP 12C Calculations This handout has examples for calculations on the HP12C: 1. Present Value (PV) 2. Present Value with cash flows and discount rate constant over time 3. Present Value with uneven cash
TIME VALUE OF MONEY PROBLEM #5: ZERO COUPON BOND
 TIME VALUE OF MONEY PROBLEM #5: ZERO COUPON BOND Professor Peter Harris Mathematics by Dr. Sharon Petrushka Introduction This assignment will focus on using the TI - 83 to calculate the price of a Zero
TIME VALUE OF MONEY PROBLEM #5: ZERO COUPON BOND Professor Peter Harris Mathematics by Dr. Sharon Petrushka Introduction This assignment will focus on using the TI - 83 to calculate the price of a Zero
Bond valuation and bond yields
 RELEVANT TO ACCA QUALIFICATION PAPER P4 AND PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES 15 AND 16 Bond valuation and bond yields Bonds and their variants such as loan notes, debentures and loan stock, are IOUs issued by governments
RELEVANT TO ACCA QUALIFICATION PAPER P4 AND PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES 15 AND 16 Bond valuation and bond yields Bonds and their variants such as loan notes, debentures and loan stock, are IOUs issued by governments
Exam 1 Morning Session
 91. A high yield bond fund states that through active management, the fund s return has outperformed an index of Treasury securities by 4% on average over the past five years. As a performance benchmark
91. A high yield bond fund states that through active management, the fund s return has outperformed an index of Treasury securities by 4% on average over the past five years. As a performance benchmark
DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW VALUATION and MULTIPLE CASH FLOWS
 Chapter 5 DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW VALUATION and MULTIPLE CASH FLOWS The basic PV and FV techniques can be extended to handle any number of cash flows. PV with multiple cash flows: Suppose you need $500 one
Chapter 5 DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW VALUATION and MULTIPLE CASH FLOWS The basic PV and FV techniques can be extended to handle any number of cash flows. PV with multiple cash flows: Suppose you need $500 one
YIELD CURVE GENERATION
 1 YIELD CURVE GENERATION Dr Philip Symes Agenda 2 I. INTRODUCTION II. YIELD CURVES III. TYPES OF YIELD CURVES IV. USES OF YIELD CURVES V. YIELD TO MATURITY VI. BOND PRICING & VALUATION Introduction 3 A
1 YIELD CURVE GENERATION Dr Philip Symes Agenda 2 I. INTRODUCTION II. YIELD CURVES III. TYPES OF YIELD CURVES IV. USES OF YIELD CURVES V. YIELD TO MATURITY VI. BOND PRICING & VALUATION Introduction 3 A
How To Value A Bond In Excel
 Financial Modeling Templates http://spreadsheetml.com/finance/bondvaluationyieldtomaturity.shtml Copyright (c) 2009-2014, ConnectCode All Rights Reserved. ConnectCode accepts no responsibility for any
Financial Modeling Templates http://spreadsheetml.com/finance/bondvaluationyieldtomaturity.shtml Copyright (c) 2009-2014, ConnectCode All Rights Reserved. ConnectCode accepts no responsibility for any
Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization Worksheets
 2 Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization Worksheets The Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization worksheets are useful in applications where the cash flows are equal, evenly spaced, and either all inflows or
2 Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization Worksheets The Time-Value-of-Money and Amortization worksheets are useful in applications where the cash flows are equal, evenly spaced, and either all inflows or
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation
 6 Formulas Discounted Cash Flow Valuation McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Outline Future and Present Values of Multiple Cash Flows Valuing
6 Formulas Discounted Cash Flow Valuation McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter Outline Future and Present Values of Multiple Cash Flows Valuing
2 The Mathematics. of Finance. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 2 The Mathematics of Finance Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.3 Annuities, Loans, and Bonds Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Annuities, Loans, and Bonds A typical defined-contribution
2 The Mathematics of Finance Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2.3 Annuities, Loans, and Bonds Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Annuities, Loans, and Bonds A typical defined-contribution
C H A P T E R Investing in Bonds 441
 Investing in Bonds C H A P T E R 16 Tom scratched his head for a moment. This was something entirely new to him. His broker was recommending a car and junk? And who were all these people that his broker
Investing in Bonds C H A P T E R 16 Tom scratched his head for a moment. This was something entirely new to him. His broker was recommending a car and junk? And who were all these people that his broker
PowerPoint. to accompany. Chapter 5. Interest Rates
 PowerPoint to accompany Chapter 5 Interest Rates 5.1 Interest Rate Quotes and Adjustments To understand interest rates, it s important to think of interest rates as a price the price of using money. When
PowerPoint to accompany Chapter 5 Interest Rates 5.1 Interest Rate Quotes and Adjustments To understand interest rates, it s important to think of interest rates as a price the price of using money. When
Bond Market Overview and Bond Pricing
 Bond Market Overview and Bond Pricing. Overview of Bond Market 2. Basics of Bond Pricing 3. Complications 4. Pricing Floater and Inverse Floater 5. Pricing Quotes and Accrued Interest What is A Bond? Bond:
Bond Market Overview and Bond Pricing. Overview of Bond Market 2. Basics of Bond Pricing 3. Complications 4. Pricing Floater and Inverse Floater 5. Pricing Quotes and Accrued Interest What is A Bond? Bond:
