Describing Sound Waves. Period. Frequency. Parameters used to completely characterize a sound wave. Chapter 3. Period Frequency Amplitude Power
|
|
|
- Basil Boyd
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Parameters used to completely characterize a sound wave Describing Sound Waves Chapter 3 Period Frequency Amplitude Power Intensity Speed Wave Length Period Defined as the time it take one wave vibrate a single cycle. The start of one cycle to the start of the next cycle Measured in units of time. ex. Milliseconds, seconds. Determined by the source only and not the medium It is not adjustable by the sonographer Frequency As pertains to the ultrasound wave Defined as the number of complete cycles in one second. The unit of measure is the hertz. ex 1 cycle in 1 second = 1 hertz Typical clinical values range from 2 to 15MHz Determined by the source and not the medium not adjustable with some ultrasound systems and transducer combinations 1
2 Source and Medium The source of a sound wave is the ultrasound system and transducer combination. The sonographer can adjust some of the system parameters while others are fixed. The material or tissue through which the sound travels is refereed to as the medium. Where did the term ultrasound come from The human ear can only hear sound when it is within an audible range. 20 Hz to 20 khz sound that has a frequency below 20 Hz is referred to as infrasound Sound that is greater than 20 khz is referred to as ultrasound Frequency is important to the very essence of ultrasound imaging. It has pronounced effects on both image quality and depth of penetration Period and frequency are inversely related to each other. As frequency increases the period will decrease As frequency decreases the period will increase. Period and frequency also have a reciprocal relationship When the two parameters are multiplied together the result is 1 If a wave takes 1 / 5 of a second to complete one cycle the period is 1 / 5 second and the frequency is 5 per second. 1 / 5 x 5 = 1 The frequency of this wave is 8Hz and the period is 1/8 of a second 2
3 Parameters that describe the magnitude of a sound wave are: amplitude power intensity Amplitude Defined as the of a given wave either above the baseline or below the baseline The unit of measure is variable and includes pressure - pascals density -g/cm 3 particle motion - cm, inches - any distance Amplitude can also be expressed in decibels (db) Peak to peak amplitude Amplitude continued Typically in clinical imaging pressure amplitude ranges from 1 million pascals (1MPa) to 3 million pascals (MPa). Determined only by the source the amplitude however does decrease as it propagates through the body and is also affected by the density of the medium as well Adjustable with a control on ultrasound systems allowing the sonographer to alter the initial amplitude Power Is the rate of energy transfer, or the rate at which work is done The unit of measure is watts Typical clinical imaging values range from to watts also expressed as 4 to 90 milliwatts Determined by the source and not the medium not adjustable with some ultrasound systems and transducer combinations 3
4 Power continued Determined by the source and not the medium However power does decrease as it propagates through the body and is also affected by the density of the medium as well It is adjustable with a control on the ultrasound systems allowing the sonographer to alter the initial power of the wave Power continued When power increase amplitude increases and when power decreases amplitude decreases. Power is proportional to amplitude 2 as you increase the amplitude of a wave by a factor of 4 you have increased the power by 16. 4x4=16 as you decrease the amplitude of a wave to ½ of the original value you have changed to power to ¼ its original value, ½ x ½ = ¼ Intensity Defined as the concentration of energy in a sound beam. Calculated by dividing the beams power by the beams cross-sectional area The units of intensity are watts/square centimeter (W/cm 2 ) watts from the power and cm 2 from the beam area intensity (W/cm2) = power (w) area (cm 2 ) It depends on the power of the beam and over how big an areas it is spread out on Intensity continued Typical clinical intensity values range from 0.01 to 300 W/cm 2 Determined by the source initially but its characteristics changes as it propagates through the medium and if one adjusts the beam shape. It is adjustable with ultrasound systems allowing the sonographer to either increase or decrease the initial intensity wave. Intensity continued Relationship between intensity and power Intensity is proportional to power if a the power of a wave doubles the intensity also doubles if the power of a wave is cut in half so too the intensity is cut in half Intensity continued Relationship between intensity and amplitude Intensity is proportional to the amplitude of the wave squared. if the wave s intensity is doubled the amplitude is increased four times 4
5 Wavelength Wavelength The distance or length of one complete cycle Units of measurements include but not limited to mm, meters In diagnostic imaging the wavelength in soft tissue range form 0.15 to 0.8 mm Is determined by both the source and medium The sonographer cannot adjust the wavelength of a particular transducer. (even a multihertz transducer has fixed wavelengths) Wavelength continued Wavelength is inversely related to frequency In soft tissue sound with a frequency of 1 MHz has a wavelength of 1.54mm This can be converted into a formula to calculate the wavelength of may MHz transducer wavelength (mm) = 1.54 mm/us frequency (MHz) Wavelength continued Wavelength plays an intricate role in role in ultrasound imaging The higher the frequency the shorter the wavelength and the higher the image quality The lower the frequency the longer the wavelength and the lower the image quality Wave length of 3 different frequencies Propagation speed Defined as the distance a sound wave travels in 1 second through a medium Speed is measured in meters per second, mm/μs, or distance divided by time Depending on the type of tissue the sound is traveling through the typical speed ranges from 500 m/s to 4000m/s 5
6 Propagation speed continued Speed is affected only by the medium through which it travels Irrespective of the frequency all sound travels at the same speed through the same medium Speed changes only when it travels form one medium to another medium of different density Propagation speed continued The average speed of sound in soft tissue is 1,540 m/s or 1.54 mm/μs or 1/54 km/s Sound travels fastest in solids slower in liquids and the slowest is gasses Speed(m/s) = frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m) Propagation speed continued Propagation speed continued Tissue Type Lung Fat Speed (m/s) 500 1,450 Material Air Speed (m/s 330 Soft Tissue (average) Liver 1,540 1,560 Water 1,480 Blood Muscle 1,560 1,600 Metals 2,000 to 7,000 Tendon 1,700 Bone 3,500 Characteristics of a medium Stiffness is the ability of an object to resist compression ex. a golf ball is stiff and Jell-O is not Stiffness and speed are directly related If you stiffness you speed Elasticity and compressibility are terms used to describe a type of stiffness The skin is elastic The appendix is compressible Characteristics of a medium continued Density is the weight of a material When equal volumes of material are compared the dense material will weight the most Ex bone is more dense than muscle Density and speed are inversely related As density speed will 6
A pulse is a collection of cycles that travel together. the cycles ( on or transmit time), and. the dead time ( off or receive time)
 chapter 2 Pulsed Ultrasound In diagnostic ultrasound imaging, short bursts, or pulses, of acoustic energy are used to create anatomic images. Continuous wave sound cannot create anatomic images. Analogy
chapter 2 Pulsed Ultrasound In diagnostic ultrasound imaging, short bursts, or pulses, of acoustic energy are used to create anatomic images. Continuous wave sound cannot create anatomic images. Analogy
BIOMEDICAL ULTRASOUND
 BIOMEDICAL ULTRASOUND Goals: To become familiar with: Ultrasound wave Wave propagation and Scattering Mechanisms of Tissue Damage Biomedical Ultrasound Transducers Biomedical Ultrasound Imaging Ultrasonic
BIOMEDICAL ULTRASOUND Goals: To become familiar with: Ultrasound wave Wave propagation and Scattering Mechanisms of Tissue Damage Biomedical Ultrasound Transducers Biomedical Ultrasound Imaging Ultrasonic
FXA 2008. UNIT G485 Module 4 5.4.3 Ultrasound. Candidates should be able to :
 1 Candidates should be able to : ULTRASOUND Describe the properties of ultrasound. ULTRASOUND is any sound wave having a frequency greater than the upper frequency limit of human hearing (20 khz). Describe
1 Candidates should be able to : ULTRASOUND Describe the properties of ultrasound. ULTRASOUND is any sound wave having a frequency greater than the upper frequency limit of human hearing (20 khz). Describe
Hunting Bats. Diagnostic Ultrasound. Ultrasound Real-time modality
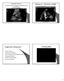 Diagnostik Ultrasound Basic physics, image reconstruction and signal processing Per Åke Olofsson Dpt of Biomedical Engineering, Malmö University Hospital, Sweden Ultrasound Real-time modality 17-WEEK FETAL
Diagnostik Ultrasound Basic physics, image reconstruction and signal processing Per Åke Olofsson Dpt of Biomedical Engineering, Malmö University Hospital, Sweden Ultrasound Real-time modality 17-WEEK FETAL
Doppler. Doppler. Doppler shift. Doppler Frequency. Doppler shift. Doppler shift. Chapter 19
 Doppler Doppler Chapter 19 A moving train with a trumpet player holding the same tone for a very long time travels from your left to your right. The tone changes relative the motion of you (receiver) and
Doppler Doppler Chapter 19 A moving train with a trumpet player holding the same tone for a very long time travels from your left to your right. The tone changes relative the motion of you (receiver) and
Energy. Mechanical Energy
 Principles of Imaging Science I (RAD119) Electromagnetic Radiation Energy Definition of energy Ability to do work Physicist s definition of work Work = force x distance Force acting upon object over distance
Principles of Imaging Science I (RAD119) Electromagnetic Radiation Energy Definition of energy Ability to do work Physicist s definition of work Work = force x distance Force acting upon object over distance
Waves and Sound. AP Physics B
 Waves and Sound AP Physics B What is a wave A WAVE is a vibration or disturbance in space. A MEDIUM is the substance that all SOUND WAVES travel through and need to have in order to move. Two types of
Waves and Sound AP Physics B What is a wave A WAVE is a vibration or disturbance in space. A MEDIUM is the substance that all SOUND WAVES travel through and need to have in order to move. Two types of
Acoustics: the study of sound waves
 Acoustics: the study of sound waves Sound is the phenomenon we experience when our ears are excited by vibrations in the gas that surrounds us. As an object vibrates, it sets the surrounding air in motion,
Acoustics: the study of sound waves Sound is the phenomenon we experience when our ears are excited by vibrations in the gas that surrounds us. As an object vibrates, it sets the surrounding air in motion,
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley.
 Chapter 20. Traveling Waves You may not realize it, but you are surrounded by waves. The waviness of a water wave is readily apparent, from the ripples on a pond to ocean waves large enough to surf. It
Chapter 20. Traveling Waves You may not realize it, but you are surrounded by waves. The waviness of a water wave is readily apparent, from the ripples on a pond to ocean waves large enough to surf. It
Waves-Wave Characteristics
 1. What is the wavelength of a 256-hertz sound wave in air at STP? 1. 1.17 10 6 m 2. 1.29 m 3. 0.773 m 4. 8.53 10-7 m 2. The graph below represents the relationship between wavelength and frequency of
1. What is the wavelength of a 256-hertz sound wave in air at STP? 1. 1.17 10 6 m 2. 1.29 m 3. 0.773 m 4. 8.53 10-7 m 2. The graph below represents the relationship between wavelength and frequency of
Various Technics of Liquids and Solids Level Measurements. (Part 3)
 (Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
(Part 3) In part one of this series of articles, level measurement using a floating system was discusses and the instruments were recommended for each application. In the second part of these articles,
Ultrasound Physics. ASCeXAM Review- 2011. Sidney K. Edelman, Ph.D. Director, ESP Ultrasound [email protected] 281-292-9400 www.esp-inc.
 chapter 1 Ultrasound Physics ASCeXAM Review- 2011 Sidney K. Edelman, Ph.D. Director, ESP Ultrasound [email protected] 281-292-9400 www.esp-inc.com Definitions Sound A type of wave that carries energy
chapter 1 Ultrasound Physics ASCeXAM Review- 2011 Sidney K. Edelman, Ph.D. Director, ESP Ultrasound [email protected] 281-292-9400 www.esp-inc.com Definitions Sound A type of wave that carries energy
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST. PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON. (THANK YOU FOR SAVING A TREE.)
 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST. PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON. (THANK YOU FOR SAVING A TREE.) Sound Waves Test -- each multiple choice question is worth 3 points. 1. Sound waves are
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THE TEST. PLACE ALL MULTIPLE CHOICE ANSWERS ON THE SCANTRON. (THANK YOU FOR SAVING A TREE.) Sound Waves Test -- each multiple choice question is worth 3 points. 1. Sound waves are
Basics of Ultrasound Imaging
 2 Basics of Ultrasound Imaging Vincent Chan and Anahi Perlas Introduction... Basic Principles of B-Mode US... Generation of Ultrasound Pulses... Ultrasound Wavelength and Frequency... Ultrasound Tissue
2 Basics of Ultrasound Imaging Vincent Chan and Anahi Perlas Introduction... Basic Principles of B-Mode US... Generation of Ultrasound Pulses... Ultrasound Wavelength and Frequency... Ultrasound Tissue
APPLICATION NOTE ULTRASONIC CERAMIC TRANSDUCERS
 APPLICATION NOTE ULTRASONIC CERAMIC TRANSDUCERS Selection and use of Ultrasonic Ceramic Transducers The purpose of this application note is to aid the user in the selection and application of the Ultrasonic
APPLICATION NOTE ULTRASONIC CERAMIC TRANSDUCERS Selection and use of Ultrasonic Ceramic Transducers The purpose of this application note is to aid the user in the selection and application of the Ultrasonic
RICHARD T ELL ASSOCIATES,INC.
 RICHARD T ELL ASSOCIATES,INC. An Evaluation of Test Measurement Data Obtained on the KW-Gard RF Protective Suit March 30, 1998 Prepared for Euclid Garment Manufacturing Company 333 Martinel Drive Kent,
RICHARD T ELL ASSOCIATES,INC. An Evaluation of Test Measurement Data Obtained on the KW-Gard RF Protective Suit March 30, 1998 Prepared for Euclid Garment Manufacturing Company 333 Martinel Drive Kent,
Waves - Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
 Waves - Transverse and Longitudinal Waves wave may be defined as a periodic disturbance in a medium that carries energy from one point to another. ll waves require a source and a medium of propagation.
Waves - Transverse and Longitudinal Waves wave may be defined as a periodic disturbance in a medium that carries energy from one point to another. ll waves require a source and a medium of propagation.
Introduction to acoustic imaging
 Introduction to acoustic imaging Contents 1 Propagation of acoustic waves 3 1.1 Wave types.......................................... 3 1.2 Mathematical formulation.................................. 4 1.3
Introduction to acoustic imaging Contents 1 Propagation of acoustic waves 3 1.1 Wave types.......................................... 3 1.2 Mathematical formulation.................................. 4 1.3
UNIT 1: mechanical waves / sound
 1. waves/intro 2. wave on a string 3. sound waves UNIT 1: mechanical waves / sound Chapter 16 in Cutnell, Johnson: Physics, 8th Edition Properties of waves, example of waves (sound. Light, seismic), Reflection,
1. waves/intro 2. wave on a string 3. sound waves UNIT 1: mechanical waves / sound Chapter 16 in Cutnell, Johnson: Physics, 8th Edition Properties of waves, example of waves (sound. Light, seismic), Reflection,
Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect
 Objectives: PS-7.1 Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect Illustrate ways that the energy of waves is transferred by interaction with
Objectives: PS-7.1 Physical Science Study Guide Unit 7 Wave properties and behaviors, electromagnetic spectrum, Doppler Effect Illustrate ways that the energy of waves is transferred by interaction with
APPLICATION NOTE AP050830
 APPLICATION NOTE AP050830 Selection and use of Ultrasonic Ceramic Transducers Pro-Wave Electronics Corp. E-mail: [email protected] URL: http://www.prowave.com.tw The purpose of this application note
APPLICATION NOTE AP050830 Selection and use of Ultrasonic Ceramic Transducers Pro-Wave Electronics Corp. E-mail: [email protected] URL: http://www.prowave.com.tw The purpose of this application note
Noise. CIH Review PDC March 2012
 Noise CIH Review PDC March 2012 Learning Objectives Understand the concept of the decibel, decibel determination, decibel addition, and weighting Know the characteristics of frequency that are relevant
Noise CIH Review PDC March 2012 Learning Objectives Understand the concept of the decibel, decibel determination, decibel addition, and weighting Know the characteristics of frequency that are relevant
Giant Slinky: Quantitative Exhibit Activity
 Name: Giant Slinky: Quantitative Exhibit Activity Materials: Tape Measure, Stopwatch, & Calculator. In this activity, we will explore wave properties using the Giant Slinky. Let s start by describing the
Name: Giant Slinky: Quantitative Exhibit Activity Materials: Tape Measure, Stopwatch, & Calculator. In this activity, we will explore wave properties using the Giant Slinky. Let s start by describing the
physics 1/12/2016 Chapter 20 Lecture Chapter 20 Traveling Waves
 Chapter 20 Lecture physics FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS a strategic approach THIRD EDITION randall d. knight Chapter 20 Traveling Waves Chapter Goal: To learn the basic properties of traveling waves. Slide
Chapter 20 Lecture physics FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS a strategic approach THIRD EDITION randall d. knight Chapter 20 Traveling Waves Chapter Goal: To learn the basic properties of traveling waves. Slide
Waves: Recording Sound Waves and Sound Wave Interference (Teacher s Guide)
 Waves: Recording Sound Waves and Sound Wave Interference (Teacher s Guide) OVERVIEW Students will measure a sound wave by placing the Ward s DataHub microphone near one tuning fork A440 (f=440hz). Then
Waves: Recording Sound Waves and Sound Wave Interference (Teacher s Guide) OVERVIEW Students will measure a sound wave by placing the Ward s DataHub microphone near one tuning fork A440 (f=440hz). Then
Experiment 1: SOUND. The equation used to describe a simple sinusoidal function that propagates in space is given by Y = A o sin(k(x v t))
 Experiment 1: SOUND Introduction Sound is classified under the topic of mechanical waves. A mechanical wave is a term which refers to a displacement of elements in a medium from their equilibrium state,
Experiment 1: SOUND Introduction Sound is classified under the topic of mechanical waves. A mechanical wave is a term which refers to a displacement of elements in a medium from their equilibrium state,
The Effects of Ultrasonic Sound Generated by Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems on Human Hearing and Physiology
 The Effects of Ultrasonic Sound Generated by Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems on Human Hearing and Physiology Questions about the effects of ultrasonic energy on hearing and other human physiology arise from
The Effects of Ultrasonic Sound Generated by Ultrasonic Cleaning Systems on Human Hearing and Physiology Questions about the effects of ultrasonic energy on hearing and other human physiology arise from
Waves Sound and Light
 Waves Sound and Light r2 c:\files\courses\1710\spr12\wavetrans.doc Ron Robertson The Nature of Waves Waves are a type of energy transmission that results from a periodic disturbance (vibration). They are
Waves Sound and Light r2 c:\files\courses\1710\spr12\wavetrans.doc Ron Robertson The Nature of Waves Waves are a type of energy transmission that results from a periodic disturbance (vibration). They are
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy Training
 Scanning Acoustic Microscopy Training This presentation and images are copyrighted by Sonix, Inc. They may not be copied, reproduced, modified, published, uploaded, posted, transmitted, or distributed
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy Training This presentation and images are copyrighted by Sonix, Inc. They may not be copied, reproduced, modified, published, uploaded, posted, transmitted, or distributed
INTERFERENCE OF SOUND WAVES
 1/2016 Sound 1/8 INTERFERENCE OF SOUND WAVES PURPOSE: To measure the wavelength, frequency, and propagation speed of ultrasonic sound waves and to observe interference phenomena with ultrasonic sound waves.
1/2016 Sound 1/8 INTERFERENCE OF SOUND WAVES PURPOSE: To measure the wavelength, frequency, and propagation speed of ultrasonic sound waves and to observe interference phenomena with ultrasonic sound waves.
Antonio Rampoldi Struttura Complessa di Radiologia Interventistica Azienda Ospedale Niguarda Ca Granda, Milano. Terminology
 Biophysical principles and clinical applications of MRgFUS Alberto Torresin Struttura Complessa di Fisica Sanitaria Azienda, Milano Università degli Studi di Milano Dip. di Fisica Antonio Rampoldi Struttura
Biophysical principles and clinical applications of MRgFUS Alberto Torresin Struttura Complessa di Fisica Sanitaria Azienda, Milano Università degli Studi di Milano Dip. di Fisica Antonio Rampoldi Struttura
Selected Radio Frequency Exposure Limits
 ENVIRONMENT, SAFETY & HEALTH DIVISION Chapter 50: Non-ionizing Radiation Selected Radio Frequency Exposure Limits Product ID: 94 Revision ID: 1736 Date published: 30 June 2015 Date effective: 30 June 2015
ENVIRONMENT, SAFETY & HEALTH DIVISION Chapter 50: Non-ionizing Radiation Selected Radio Frequency Exposure Limits Product ID: 94 Revision ID: 1736 Date published: 30 June 2015 Date effective: 30 June 2015
Understanding Range for RF Devices
 Understanding Range for RF Devices October 2012 White Paper Understanding how environmental factors can affect range is one of the key aspects to deploying a radio frequency (RF) solution. This paper will
Understanding Range for RF Devices October 2012 White Paper Understanding how environmental factors can affect range is one of the key aspects to deploying a radio frequency (RF) solution. This paper will
E190Q Lecture 5 Autonomous Robot Navigation
 E190Q Lecture 5 Autonomous Robot Navigation Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Spring 2014 1 Figures courtesy of Siegwart & Nourbakhsh Control Structures Planning Based Control Prior Knowledge Operator
E190Q Lecture 5 Autonomous Robot Navigation Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Spring 2014 1 Figures courtesy of Siegwart & Nourbakhsh Control Structures Planning Based Control Prior Knowledge Operator
Chapter Test B. Chapter: Measurements and Calculations
 Assessment Chapter Test B Chapter: Measurements and Calculations PART I In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1.
Assessment Chapter Test B Chapter: Measurements and Calculations PART I In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1.
The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking
 The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking EQUIPMENT Pasco sonometers (pick up 5 from teaching lab) and 5 kits to go with them BK Precision function generators and Tenma oscilloscopes
The Sonometer The Resonant String and Timbre Change after plucking EQUIPMENT Pasco sonometers (pick up 5 from teaching lab) and 5 kits to go with them BK Precision function generators and Tenma oscilloscopes
Laminar and Turbulent flow. Flow Sensors. Reynolds Number. Thermal flow Sensor. Flow and Flow rate. R = Mass Flow controllers
 Flow and Flow rate. Laminar and Turbulent flow Laminar flow: smooth, orderly and regular Mechanical sensors have inertia, which can integrate out small variations due to turbulence Turbulent flow: chaotic
Flow and Flow rate. Laminar and Turbulent flow Laminar flow: smooth, orderly and regular Mechanical sensors have inertia, which can integrate out small variations due to turbulence Turbulent flow: chaotic
XI / PHYSICS FLUIDS IN MOTION 11/PA
 Viscosity It is the property of a liquid due to which it flows in the form of layers and each layer opposes the motion of its adjacent layer. Cause of viscosity Consider two neighboring liquid layers A
Viscosity It is the property of a liquid due to which it flows in the form of layers and each layer opposes the motion of its adjacent layer. Cause of viscosity Consider two neighboring liquid layers A
THE IMPOSSIBLE DOSE HOW CAN SOMETHING SIMPLE BE SO COMPLEX? Lars Hode
 THE IMPOSSIBLE DOSE HOW CAN SOMETHING SIMPLE BE SO COMPLEX? Lars Hode Swedish Laser-Medical Society The dose is the most important parameter in laser phototherapy. At a first glance, the dose seem very
THE IMPOSSIBLE DOSE HOW CAN SOMETHING SIMPLE BE SO COMPLEX? Lars Hode Swedish Laser-Medical Society The dose is the most important parameter in laser phototherapy. At a first glance, the dose seem very
AP1 Waves. (A) frequency (B) wavelength (C) speed (D) intensity. Answer: (A) and (D) frequency and intensity.
 1. A fire truck is moving at a fairly high speed, with its siren emitting sound at a specific pitch. As the fire truck recedes from you which of the following characteristics of the sound wave from the
1. A fire truck is moving at a fairly high speed, with its siren emitting sound at a specific pitch. As the fire truck recedes from you which of the following characteristics of the sound wave from the
Sound and stringed instruments
 Sound and stringed instruments Lecture 14: Sound and strings Reminders/Updates: HW 6 due Monday, 10pm. Exam 2, a week today! 1 Sound so far: Sound is a pressure or density fluctuation carried (usually)
Sound and stringed instruments Lecture 14: Sound and strings Reminders/Updates: HW 6 due Monday, 10pm. Exam 2, a week today! 1 Sound so far: Sound is a pressure or density fluctuation carried (usually)
Electromagnetic (EM) waves. Electric and Magnetic Fields. L 30 Electricity and Magnetism [7] James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879)
![Electromagnetic (EM) waves. Electric and Magnetic Fields. L 30 Electricity and Magnetism [7] James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Electromagnetic (EM) waves. Electric and Magnetic Fields. L 30 Electricity and Magnetism [7] James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879)](/thumbs/40/20813653.jpg) L 30 Electricity and Magnetism [7] ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Faraday laid the groundwork with his discovery of electromagnetic induction Maxwell added the last piece of the puzzle Heinrich Hertz made the experimental
L 30 Electricity and Magnetism [7] ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Faraday laid the groundwork with his discovery of electromagnetic induction Maxwell added the last piece of the puzzle Heinrich Hertz made the experimental
Engineering with Sound Lesson Plan
 Type of lesson: Challenge Teaching Plan: Engineering with Sound Lesson Plan Goal The goal of this lesson is to introduce the students to sound and its properties and have them apply what they learn to
Type of lesson: Challenge Teaching Plan: Engineering with Sound Lesson Plan Goal The goal of this lesson is to introduce the students to sound and its properties and have them apply what they learn to
Answer the following questions during or after your study of Wave Properties. 4. How are refraction and the speed of wave in different media related?
 Wave Properties Student Worksheet Answer the following questions during or after your study of Wave Properties. 1. A person standing 385 m from a cliff claps her hands loudly, only to hear the sound return
Wave Properties Student Worksheet Answer the following questions during or after your study of Wave Properties. 1. A person standing 385 m from a cliff claps her hands loudly, only to hear the sound return
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT
 UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION BMMC (2011 Admission) V SEMESTER CORE COURSE AUDIO RECORDING & EDITING QUESTION BANK 1. Sound measurement a) Decibel b) frequency c) Wave 2. Acoustics
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION BMMC (2011 Admission) V SEMESTER CORE COURSE AUDIO RECORDING & EDITING QUESTION BANK 1. Sound measurement a) Decibel b) frequency c) Wave 2. Acoustics
Acceleration levels of dropped objects
 Acceleration levels of dropped objects cmyk Acceleration levels of dropped objects Introduction his paper is intended to provide an overview of drop shock testing, which is defined as the acceleration
Acceleration levels of dropped objects cmyk Acceleration levels of dropped objects Introduction his paper is intended to provide an overview of drop shock testing, which is defined as the acceleration
Ultrasound Condition Monitoring
 Ultrasound Condition Monitoring Whitepaper Alan Bandes UE Systems, Inc. Abstract: Instruments based on airborne/structure borne ultrasound technology offer many opportunities for reducing energy waste
Ultrasound Condition Monitoring Whitepaper Alan Bandes UE Systems, Inc. Abstract: Instruments based on airborne/structure borne ultrasound technology offer many opportunities for reducing energy waste
Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control
 EVERYONE'S RESPONSIBILITY Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control February 2007 Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Workplace Safety & Health Division 200 401 York Avenue
EVERYONE'S RESPONSIBILITY Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control February 2007 Guideline for Hearing Conservation and Noise Control Workplace Safety & Health Division 200 401 York Avenue
v = λ f this is the Golden Rule for waves transverse & longitudinal waves Harmonic waves The golden rule for waves Example: wave on a string Review
 L 23 Vibrations and Waves [3] resonance clocks pendulum springs harmonic motion mechanical waves sound waves golden rule for waves musical instruments The Doppler effect Doppler radar radar guns Review
L 23 Vibrations and Waves [3] resonance clocks pendulum springs harmonic motion mechanical waves sound waves golden rule for waves musical instruments The Doppler effect Doppler radar radar guns Review
Indiana's Academic Standards 2010 ICP Indiana's Academic Standards 2016 ICP. map) that describe the relationship acceleration, velocity and distance.
 .1.1 Measure the motion of objects to understand.1.1 Develop graphical, the relationships among distance, velocity and mathematical, and pictorial acceleration. Develop deeper understanding through representations
.1.1 Measure the motion of objects to understand.1.1 Develop graphical, the relationships among distance, velocity and mathematical, and pictorial acceleration. Develop deeper understanding through representations
Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Review
 Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Review Presented by: Sami El-Ali 1 1. Introduction Ultrasonic refers to any study or application of sound waves that are higher frequency than the human audible range. Ultrasonic
Ultrasonic Wave Propagation Review Presented by: Sami El-Ali 1 1. Introduction Ultrasonic refers to any study or application of sound waves that are higher frequency than the human audible range. Ultrasonic
Acoustic Terms, Definitions and General Information
 Acoustic Terms, Definitions and General Information Authored by: Daniel Ziobroski Acoustic Engineer Environmental and Acoustic Engineering GE Energy Charles Powers Program Manager Environmental and Acoustic
Acoustic Terms, Definitions and General Information Authored by: Daniel Ziobroski Acoustic Engineer Environmental and Acoustic Engineering GE Energy Charles Powers Program Manager Environmental and Acoustic
Objective: Work Done by a Variable Force Work Done by a Spring. Homework: Assignment (1-25) Do PROBS # (64, 65) Ch. 6, + Do AP 1986 # 2 (handout)
 Double Date: Objective: Work Done by a Variable Force Work Done by a Spring Homework: Assignment (1-25) Do PROBS # (64, 65) Ch. 6, + Do AP 1986 # 2 (handout) AP Physics B Mr. Mirro Work Done by a Variable
Double Date: Objective: Work Done by a Variable Force Work Done by a Spring Homework: Assignment (1-25) Do PROBS # (64, 65) Ch. 6, + Do AP 1986 # 2 (handout) AP Physics B Mr. Mirro Work Done by a Variable
Testing thermo-acoustic sound generation in water with proton and laser beams
 International ARENA Workshop DESY, Zeuthen 17th 19th of May 25 Testing thermo-acoustic sound generation in water with proton and laser beams Kay Graf Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg Physikalisches Institut
International ARENA Workshop DESY, Zeuthen 17th 19th of May 25 Testing thermo-acoustic sound generation in water with proton and laser beams Kay Graf Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg Physikalisches Institut
226 Chapter 15: OSCILLATIONS
 Chapter 15: OSCILLATIONS 1. In simple harmonic motion, the restoring force must be proportional to the: A. amplitude B. frequency C. velocity D. displacement E. displacement squared 2. An oscillatory motion
Chapter 15: OSCILLATIONS 1. In simple harmonic motion, the restoring force must be proportional to the: A. amplitude B. frequency C. velocity D. displacement E. displacement squared 2. An oscillatory motion
T = 1 f. Phase. Measure of relative position in time within a single period of a signal For a periodic signal f(t), phase is fractional part t p
 Data Transmission Concepts and terminology Transmission terminology Transmission from transmitter to receiver goes over some transmission medium using electromagnetic waves Guided media. Waves are guided
Data Transmission Concepts and terminology Transmission terminology Transmission from transmitter to receiver goes over some transmission medium using electromagnetic waves Guided media. Waves are guided
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING PHYSICS. Friday, June 20, 2014 1:15 to 4:15 p.m.
 P.S./PHYSICS The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING PHYSICS Friday, June 20, 2014 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only The possession or use of any communications device
P.S./PHYSICS The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING PHYSICS Friday, June 20, 2014 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only The possession or use of any communications device
AP PHYSICS C Mechanics - SUMMER ASSIGNMENT FOR 2016-2017
 AP PHYSICS C Mechanics - SUMMER ASSIGNMENT FOR 2016-2017 Dear Student: The AP physics course you have signed up for is designed to prepare you for a superior performance on the AP test. To complete material
AP PHYSICS C Mechanics - SUMMER ASSIGNMENT FOR 2016-2017 Dear Student: The AP physics course you have signed up for is designed to prepare you for a superior performance on the AP test. To complete material
Data Transmission. Data Communications Model. CSE 3461 / 5461: Computer Networking & Internet Technologies. Presentation B
 CSE 3461 / 5461: Computer Networking & Internet Technologies Data Transmission Presentation B Kannan Srinivasan 08/30/2012 Data Communications Model Figure 1.2 Studying Assignment: 3.1-3.4, 4.1 Presentation
CSE 3461 / 5461: Computer Networking & Internet Technologies Data Transmission Presentation B Kannan Srinivasan 08/30/2012 Data Communications Model Figure 1.2 Studying Assignment: 3.1-3.4, 4.1 Presentation
Nano Meter Stepping Drive of Surface Acoustic Wave Motor
 Proc. of 1st IEEE Conf. on Nanotechnology, Oct. 28-3, pp. 495-5, (21) Maui, Hawaii Nano Meter Stepping Drive of Surface Acoustic Wave Motor Takashi Shigematsu*, Minoru Kuribayashi Kurosawa*, and Katsuhiko
Proc. of 1st IEEE Conf. on Nanotechnology, Oct. 28-3, pp. 495-5, (21) Maui, Hawaii Nano Meter Stepping Drive of Surface Acoustic Wave Motor Takashi Shigematsu*, Minoru Kuribayashi Kurosawa*, and Katsuhiko
Audible Alarm Basics Everything you wanted to know, but were afraid to ask by Dan O Brien, Sales Engineer, Mallory Sonalert Products, Inc.
 Audible Alarm Basics Everything you wanted to know, but were afraid to ask by Dan O Brien, Sales Engineer, Mallory Sonalert Products, Inc. From smoke detectors to automobiles, audible alarms (also known
Audible Alarm Basics Everything you wanted to know, but were afraid to ask by Dan O Brien, Sales Engineer, Mallory Sonalert Products, Inc. From smoke detectors to automobiles, audible alarms (also known
Technician Licensing Class. Lesson 1. presented by the Arlington Radio Public Service Club Arlington County, Virginia
 Technician Licensing Class Lesson 1 presented by the Arlington Radio Public Service Club Arlington County, Virginia 1 FCC Rules Sub element T1 2 Why Amateur Radio? The basis & purpose of the amateur service
Technician Licensing Class Lesson 1 presented by the Arlington Radio Public Service Club Arlington County, Virginia 1 FCC Rules Sub element T1 2 Why Amateur Radio? The basis & purpose of the amateur service
Building Design for Advanced Technology Instruments Sensitive to Acoustical Noise
 Building Design for Advanced Technology Instruments Sensitive to Acoustic Noise Michael Gendreau Colin Gordon & Associates Presentation Outline! High technology research and manufacturing instruments respond
Building Design for Advanced Technology Instruments Sensitive to Acoustic Noise Michael Gendreau Colin Gordon & Associates Presentation Outline! High technology research and manufacturing instruments respond
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING PHYSICS. Wednesday, June 17, 2015 1:15 to 4:15 p.m.
 P.S./PHYSICS The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING PHYSICS Wednesday, June 17, 2015 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only The possession or use of any communications
P.S./PHYSICS The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING PHYSICS Wednesday, June 17, 2015 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only The possession or use of any communications
Review of Chapter 25. Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review of Chapter 25 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The time needed for a wave to make one complete cycle is its b. velocity.
Review of Chapter 25 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The time needed for a wave to make one complete cycle is its b. velocity.
ITRAINONLINE MMTK BASIC RADIO PHYSICS HANDOUT
 ITRAINONLINE MMTK BASIC RADIO PHYSICS HANDOUT Developed by: Sebastian Buettrich, wire.less.dk Edited by: Alberto Escudero Pascual, IT +46 Table of Contents 1. About this document...1 1.1 Copyright information...2
ITRAINONLINE MMTK BASIC RADIO PHYSICS HANDOUT Developed by: Sebastian Buettrich, wire.less.dk Edited by: Alberto Escudero Pascual, IT +46 Table of Contents 1. About this document...1 1.1 Copyright information...2
SOLUTIONS TO CONCEPTS CHAPTER 15
 SOLUTIONS TO CONCEPTS CHAPTER 15 1. v = 40 cm/sec As velocity of a wave is constant location of maximum after 5 sec = 40 5 = 00 cm along negative x-axis. [(x / a) (t / T)]. Given y = Ae a) [A] = [M 0 L
SOLUTIONS TO CONCEPTS CHAPTER 15 1. v = 40 cm/sec As velocity of a wave is constant location of maximum after 5 sec = 40 5 = 00 cm along negative x-axis. [(x / a) (t / T)]. Given y = Ae a) [A] = [M 0 L
18 Q0 a speed of 45.0 m/s away from a moving car. If the car is 8 Q0 moving towards the ambulance with a speed of 15.0 m/s, what Q0 frequency does a
 First Major T-042 1 A transverse sinusoidal wave is traveling on a string with a 17 speed of 300 m/s. If the wave has a frequency of 100 Hz, what 9 is the phase difference between two particles on the
First Major T-042 1 A transverse sinusoidal wave is traveling on a string with a 17 speed of 300 m/s. If the wave has a frequency of 100 Hz, what 9 is the phase difference between two particles on the
Noise. Patrick N. Breysse, PhD, CIH Peter S.J. Lees, PhD, CIH. Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING PHYSICS
 PS/PHYSICS The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING PHYSICS Wednesday, June 24, 2009 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only The answer sheet for Part A and Part B
PS/PHYSICS The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION PHYSICAL SETTING PHYSICS Wednesday, June 24, 2009 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only The answer sheet for Part A and Part B
Yerkes Summer Institute 2002
 Before we begin our investigations into radio waves you should review the following material on your trip up to Yerkes. For some of you this will be a refresher, but others may want to spend more time
Before we begin our investigations into radio waves you should review the following material on your trip up to Yerkes. For some of you this will be a refresher, but others may want to spend more time
The Physics of Guitar Strings
 The Physics of Guitar Strings R. R. McNeil 1. Introduction The guitar makes a wonderful device to demonstrate the physics of waves on a stretched string. This is because almost every student has seen a
The Physics of Guitar Strings R. R. McNeil 1. Introduction The guitar makes a wonderful device to demonstrate the physics of waves on a stretched string. This is because almost every student has seen a
Ch 25 Chapter Review Q & A s
 Ch 25 Chapter Review Q & A s a. a wiggle in time is called? b. a wiggle in space & time is called? a. vibration b. wave What is the period of a pendulum? The period is the time for 1 cycle (back & forth)
Ch 25 Chapter Review Q & A s a. a wiggle in time is called? b. a wiggle in space & time is called? a. vibration b. wave What is the period of a pendulum? The period is the time for 1 cycle (back & forth)
Solution Derivations for Capa #13
 Solution Derivations for Capa #13 1 Identify the following waves as T-Transverse, or L-Longitudinal. If the first is T and the rets L, enter TLLL. QUESTION: A The WAVE made by fans at sports events. B
Solution Derivations for Capa #13 1 Identify the following waves as T-Transverse, or L-Longitudinal. If the first is T and the rets L, enter TLLL. QUESTION: A The WAVE made by fans at sports events. B
Basic Acoustics and Acoustic Filters
 Basic CHAPTER Acoustics and Acoustic Filters 1 3 Basic Acoustics and Acoustic Filters 1.1 The sensation of sound Several types of events in the world produce the sensation of sound. Examples include doors
Basic CHAPTER Acoustics and Acoustic Filters 1 3 Basic Acoustics and Acoustic Filters 1.1 The sensation of sound Several types of events in the world produce the sensation of sound. Examples include doors
1) The time for one cycle of a periodic process is called the A) wavelength. B) period. C) frequency. D) amplitude.
 practice wave test.. Name Use the text to make use of any equations you might need (e.g., to determine the velocity of waves in a given material) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
practice wave test.. Name Use the text to make use of any equations you might need (e.g., to determine the velocity of waves in a given material) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine
 Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
Physiological Basis of Hearing Tests By Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Introduction Def: Hearing is the ability to perceive certain pressure vibrations in the
EECC694 - Shaaban. Transmission Channel
 The Physical Layer: Data Transmission Basics Encode data as energy at the data (information) source and transmit the encoded energy using transmitter hardware: Possible Energy Forms: Electrical, light,
The Physical Layer: Data Transmission Basics Encode data as energy at the data (information) source and transmit the encoded energy using transmitter hardware: Possible Energy Forms: Electrical, light,
Amplification of the Radiation from Two Collocated Cellular System Antennas by the Ground Wave of an AM Broadcast Station
 Amplification of the Radiation from Two Collocated Cellular System Antennas by the Ground Wave of an AM Broadcast Station Dr. Bill P. Curry EMSciTek Consulting Co., W101 McCarron Road Glen Ellyn, IL 60137,
Amplification of the Radiation from Two Collocated Cellular System Antennas by the Ground Wave of an AM Broadcast Station Dr. Bill P. Curry EMSciTek Consulting Co., W101 McCarron Road Glen Ellyn, IL 60137,
The Regulation is established pursuant to 3 (4) and 6 (6) of the Occupational Health and Safety Act. Chapter 1 GENERAL PROVISIONS
 Health and Safety Requirements for the Working Environments Affected by Noise, Maximum Noise Limits for the Working Environments and the Noise Measurement Procedure 1 Government of the Republic Regulation
Health and Safety Requirements for the Working Environments Affected by Noise, Maximum Noise Limits for the Working Environments and the Noise Measurement Procedure 1 Government of the Republic Regulation
Mathematical Harmonies Mark Petersen
 1 Mathematical Harmonies Mark Petersen What is music? When you hear a flutist, a signal is sent from her fingers to your ears. As the flute is played, it vibrates. The vibrations travel through the air
1 Mathematical Harmonies Mark Petersen What is music? When you hear a flutist, a signal is sent from her fingers to your ears. As the flute is played, it vibrates. The vibrations travel through the air
PHYS 101-4M, Fall 2005 Exam #3. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 PHYS 101-4M, Fall 2005 Exam #3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A bicycle wheel rotates uniformly through 2.0 revolutions in
PHYS 101-4M, Fall 2005 Exam #3 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A bicycle wheel rotates uniformly through 2.0 revolutions in
Basic Concepts of Sound. Contents: Definitions db Conversion Sound Fields db ± db
 Basic Concepts of Sound Contents: Definitions db Conversion Sound Fields db ± db BA 7666-11, 1 Abstract This lecture introduces sound and sound measurements by describing sound pressure, sound level and
Basic Concepts of Sound Contents: Definitions db Conversion Sound Fields db ± db BA 7666-11, 1 Abstract This lecture introduces sound and sound measurements by describing sound pressure, sound level and
Spectrum Level and Band Level
 Spectrum Level and Band Level ntensity, ntensity Level, and ntensity Spectrum Level As a review, earlier we talked about the intensity of a sound wave. We related the intensity of a sound wave to the acoustic
Spectrum Level and Band Level ntensity, ntensity Level, and ntensity Spectrum Level As a review, earlier we talked about the intensity of a sound wave. We related the intensity of a sound wave to the acoustic
Sound Attenuation INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION In the broadest sense, a sound wave is any disturbance that is propagated in an elastic medium, which may be a gas, a liquid, or a solid. Noise is defined as any unwanted sound perceived by
INTRODUCTION In the broadest sense, a sound wave is any disturbance that is propagated in an elastic medium, which may be a gas, a liquid, or a solid. Noise is defined as any unwanted sound perceived by
Electromagnetic Field Safety
 SAR A Basic Restriction for Electromagnetic Field Safety David Baron, PE Consulting Engineer Electromagnetic Field Safety [email protected] NOTE. CENAM is not responsible for the content of this document.
SAR A Basic Restriction for Electromagnetic Field Safety David Baron, PE Consulting Engineer Electromagnetic Field Safety [email protected] NOTE. CENAM is not responsible for the content of this document.
VOLUME of Rectangular Prisms Volume is the measure of occupied by a solid region.
 Math 6 NOTES 7.5 Name VOLUME of Rectangular Prisms Volume is the measure of occupied by a solid region. **The formula for the volume of a rectangular prism is:** l = length w = width h = height Study Tip:
Math 6 NOTES 7.5 Name VOLUME of Rectangular Prisms Volume is the measure of occupied by a solid region. **The formula for the volume of a rectangular prism is:** l = length w = width h = height Study Tip:
Chapter 4 Physiological Therapeutics. 3 Therapeutic Ultrasound
 Chapter 4 Physiological Therapeutics 3 Therapeutic Ultrasound Therapeutic Ultrasound PHYSIOLOGIC EFFECTS OF ULTRASOUND 1. Increased collagen extensibility 5. Increased nerve conduction velocities 2. Increased
Chapter 4 Physiological Therapeutics 3 Therapeutic Ultrasound Therapeutic Ultrasound PHYSIOLOGIC EFFECTS OF ULTRASOUND 1. Increased collagen extensibility 5. Increased nerve conduction velocities 2. Increased
Robot Perception Continued
 Robot Perception Continued 1 Visual Perception Visual Odometry Reconstruction Recognition CS 685 11 Range Sensing strategies Active range sensors Ultrasound Laser range sensor Slides adopted from Siegwart
Robot Perception Continued 1 Visual Perception Visual Odometry Reconstruction Recognition CS 685 11 Range Sensing strategies Active range sensors Ultrasound Laser range sensor Slides adopted from Siegwart
Fundamentals of Electromagnetic Fields and Waves: I
 Fundamentals of Electromagnetic Fields and Waves: I Fall 2007, EE 30348, Electrical Engineering, University of Notre Dame Mid Term II: Solutions Please show your steps clearly and sketch figures wherever
Fundamentals of Electromagnetic Fields and Waves: I Fall 2007, EE 30348, Electrical Engineering, University of Notre Dame Mid Term II: Solutions Please show your steps clearly and sketch figures wherever
Finite Element Analysis for Acoustic Behavior of a Refrigeration Compressor
 Finite Element Analysis for Acoustic Behavior of a Refrigeration Compressor Swapan Kumar Nandi Tata Consultancy Services GEDC, 185 LR, Chennai 600086, India Abstract When structures in contact with a fluid
Finite Element Analysis for Acoustic Behavior of a Refrigeration Compressor Swapan Kumar Nandi Tata Consultancy Services GEDC, 185 LR, Chennai 600086, India Abstract When structures in contact with a fluid
Iron Powder Cores for Switchmode Power Supply Inductors. by: Jim Cox
 HOME APPLICATION NOTES Iron Powder Cores for Switchmode Power Supply Inductors by: Jim Cox Purpose: The purpose of this application note is to cover the properties of iron powder as a magnetic core material
HOME APPLICATION NOTES Iron Powder Cores for Switchmode Power Supply Inductors by: Jim Cox Purpose: The purpose of this application note is to cover the properties of iron powder as a magnetic core material
Level 3 Science, 2008
 90732 3 907320 For Supervisor s Level 3 Science, 2008 90732 Describe selected properties and applications of EMR, radioactive decay, sound and ultrasound Credits: Four 2.00 pm Thursday 20 November 2008
90732 3 907320 For Supervisor s Level 3 Science, 2008 90732 Describe selected properties and applications of EMR, radioactive decay, sound and ultrasound Credits: Four 2.00 pm Thursday 20 November 2008
Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005
 EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
EE516 Computer Speech Processing Winter 2005 Lecture 4: Jan 12, 2005 Lecturer: Prof: J. Bilmes University of Washington Dept. of Electrical Engineering Scribe: Scott Philips
Impact Echo Scanning Technology for Internal Grout Condition Evaluation in Post-Tensioned Bridge Ducts
 Impact Echo Scanning Technology for Internal Grout Condition Evaluation in Post-Tensioned Bridge Ducts Yajai Tinkey, Ph.D. Olson Engineering, Wheat Ridge, Colorado Larry D. Olson, P.E. Olson Engineering,
Impact Echo Scanning Technology for Internal Grout Condition Evaluation in Post-Tensioned Bridge Ducts Yajai Tinkey, Ph.D. Olson Engineering, Wheat Ridge, Colorado Larry D. Olson, P.E. Olson Engineering,
Chapter 21 Study Questions Name: Class:
 Chapter 21 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a fire engine is traveling toward you, the Doppler
Chapter 21 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. If a fire engine is traveling toward you, the Doppler
Coach and Kilowatt Ours Post FCAT Exam
 Coach and Kilowatt Ours Post FCAT Exam Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Why is it important to include units when making measurements? A
Coach and Kilowatt Ours Post FCAT Exam Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Why is it important to include units when making measurements? A
2. Complete the table to identify the effect tripling the radius of a cylinder s base has on its volume. Cylinder Height (cm) h
 Name: Period: Date: K. Williams ID: A 8th Grade Chapter 14 TEST REVIEW 1. Determine the volume of the cylinder. Use 3.14 for. 2. Complete the table to identify the effect tripling the radius of a cylinder
Name: Period: Date: K. Williams ID: A 8th Grade Chapter 14 TEST REVIEW 1. Determine the volume of the cylinder. Use 3.14 for. 2. Complete the table to identify the effect tripling the radius of a cylinder

