Advanced Topics in Statistical Process Control
|
|
|
- Bruno Carson
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advanced Topics in Statistical Process Control The Power of Shewhart s Charts Second Edition Donald J. Wheeler SPC Press Knoxville, Tennessee
2 Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface The Shewhart Catechism Chapter One Shewhart s Control Charts Shewhart s Definition of Statistical Control Shewhart s Operation of Statistical Control The Four Possibilities for Any Process Process Behavior Charts and the Probability Approach Enumerative Studies and Analytic Studies The Uses of Shewhart s Charts The Four Foundations of Shewhart s Charts Process Behavior Charts and Chaos Theory The Transformation of Data 28 Chapter Two Statistics Versus Parameters Measures of Location and Dispersion The Notion of a Probability Distribution Statistics, Parameters, and Process Behavior Chart Limits Skewness and Kurtosis 46 Chapter Three Estimating Dispersion Parameters Estimators of SD(X) and V(X) for One Subgroup of Size n Three Ways to Estimate SD(X) for k Subgroups of Size n The Second Foundation of Shewhart s Charts Within-Subgroup Estimates of Dispersion Time Series Data (Subgroups of Size One) Degrees of Freedom Summary 83 Chapter Four Process Behavior Charts for Measurements Average and Range Charts Average and Root Mean Square Deviation Charts Average and Standard Deviation Charts Average and Variance Charts So What s the Difference? Charts for Individual Values Median and Range Charts 113 viii ix x iii
3 Contents Chapter Five Three Sigma Limits Why Three-Sigma Limits? But What About the Central Limit Theorem? The Recalculation of Limits The Role of the Normal Distribution Calculating Limits With Small Amounts of Data Inadequate Measurement Units Detecting Assignable Causes Summary 140 Chapter Six Rational Sampling and Rational Subgrouping Rational Sampling Rational Subgrouping Principles for Subgrouping Three-Way Charts Summary 165 Chapter Seven The Quality of the Limits The Distribution of the Average Range Statistic The Distribution of the Average Root Mean Square Statistic The Distribution of the Average Standard Deviation Statistic The Distribution of the Pooled Variance Statistic The Distribution of the Median Range Statistic The Distribution of the Average Moving Range Degrees of Freedom Effective Degrees of Freedom Using Degrees of Freedom The Quality of Process Behavior Chart Limits Summary 186 Chapter Eight Capability Confusion Capability, Capability Ratios, and Performance Ratios The Capability of a Predictable Process Capability Measures Converting Capabilities Into Fraction Nonconforming Performance Ratios World-Class Quality Summary 204 Chapter Nine Power Functions for Process Behavior Charts The Power of Charts for Location The Formulas for the Power Functions The Average Run Length for a Procedure Summary 224 iv
4 Contents Chapter Ten Comparing Different Types of Process Behavior Charts Process Behavior Charts for Subgroup Averages Charts for Moving Averages Moving Averages or Individual Values? Contra Two-Sigma Limits Summary 250 Chapter Eleven Charts for Count Data Charts for Count Data np-charts p-charts A Problem With Binomial Counts c-charts u-charts A Problem With Poisson Counts Degrees of Freedom Process Behavior Charts for Rare Events Summary 271 Chapter Twelve Charts for Autocorrelated Data Correlation Significant Correlations Autocorrelation What Does Autocorrelation Say About the Process? The Effect of Autocorrelation Autocorrelation s Effect Upon Chart Limits So What Shall I Do With My Autocorrelated Data? 287 Chapter Thirteen The Cumulative Sum Technique Cumulative Sums for Individual Values Cumulative Sums for Subgroup Averages Average Run Lengths for Selected Cusum Procedures Summary 311 Chapter Fourteen Exponentially Weighted Moving Averages The EWMA Algorithm EWMA for Individual Values Average Run Lengths for the EWMA Then What Does an EWMA Do? Summary 327 v
5 Contents Chapter Fifteen Multivariate Charts Simple Multivariate Charts Charts for Hotelling s T 2 Statistic 334 Chapter Sixteen Miscellaneous Techniques Zone Charts Modified Control Charts PreControl Summary 354 Chapter Seventeen The Characterization of Product Characterizing the Measured Item Characterizing Product Which Has Not Been Measured The Fallacy of Acceptance Sampling Estimating the Fraction Nonconforming Summary 371 Chapter Eighteen The Analysis of Means Comparing k Treatments Using Average Charts Experimental Data vs. Production Data The Decision Limits for ANOM The Role of the Range Chart with ANOM ANOM With Multifactor Studies Interaction Effects and ANOM ANOM With Unequal Subgroup Sizes The Analysis of Mean Ranges Range-Based Analysis of Means Summary 397 Chapter Nineteen Some Differences Between Theory and Practice The Scientific Process Statistical Tests of Hypotheses Enumerative Studies Analytical Studies Shewhart on Probability Models and Processes Finding Decision Rules for Analytic Studies Conclusions 409 vi
6 Contents Appendix 411 Glossary of Symbols 412 Bibliography 414 Tables Table 1: Bias Correction Factors 416 Table 2: Bias Correction Factors for Estimating V(X) 417 Table 3: Charts for Individual Values and Moving Ranges 418 Table 4: Average and Range Charts Using the Average Range 419 Table 5: Average and Range Charts Using the Median Range 420 Table 6: Average and Range Charts Based on Sigma(X) 421 Table 7: Average and RMS Dev. Charts Using Average RMS Dev. 422 Table 8: Average and RMS Dev. Charts Using Median RMS Dev. 423 Table 9: Average and RMS Dev. Charts Based on Sigma(X) 424 Table 10: Average and Std. Dev. Charts Using Average Std. Dev. 425 Table 11: Average and Std. Dev. Charts Using Median Std. Dev. 426 Table 12: Average and Std. Dev. Charts Based on Sigma(X) 427 Table 13: Average and Std. Dev. Charts Using Pooled Variance 428 Table 14: Median and Range Charts Using the Average Range 430 Table 15: Median and Range Charts Using the Median Range 431 Table 16: Median and Range Charts Based on Sigma(X) 432 Table 17: Average and Variance Charts 433 Table 18: Moments for Range Distributions 434 Table 19: Moments for Distributions of the RMS Deviation 436 Table 20: Moments for Distributions of the Standard Deviation 438 Table 21: Degrees of Freedom for Average Ranges 442 Table 22: Degrees of Freedom for Median Ranges 444 Table 23: Degrees of Freedom for Average Moving Ranges 446 Table 24: Degrees of Freedom for Median Moving Ranges 447 Table 25: Degrees of Freedom for Average Std. Dev. and RMS Dev. 448 Table 26: Degrees of Freedom for Median Std. Dev. and RMS Dev. 450 Table 27: The Standard Normal Distribution 452 Table 28: ANOM Critical Values, H 454 Table 29: Range-Based ANOM Critical Values 458 Table 30: Range-Based ANOME Critical Values 459 Table 31: Range-Based ANOMR Critical Values 460 Table 32: Central Lines and Upper Limits for Hotelling s T Table 33: 37 Reference Tables and Figures Located Within Text 463 Table 34: Alpha Levels for Average Charts 464 Index 465 vii
7 x The Shewhart Catechism 1. What if a state of predictability is beyond the capability of our process? This cannot happen. A process is operating predictably when it is being operated as consistently as it can no more, and no less. See Sections 1.1, Is quality defined by conformance to specifications? No. Today world-class quality is defined as on-target with minimum variance. Conformance to specifications is merely the starting point, not the finish line. See Section What do capability ratios do? Capability ratios may be used to compare the Voice of the Process with the Voice of the Customer. However, it is easy to go overboard with this. Some other measures are also useful, and no numerical summary is an adequate replacement for the basic graphs of the data. See Section How do Dr. Deming s 14 Points relate to Statistical Process Control? They may be thought of as corollaries to the observation that organizations do not behave in a rational manner and therefore cannot effectively use the knowledge gained from the charts. See Section How do Shewhart s process behavior charts differ from tests of hypotheses? Shewhart s charts characterize a time series as being either predictable or unpredictable. When a test of hypotheses is applied to a time series it presumes the timeseries to be predictable, and looks for changes in parameters of the predictable timeseries. See Sections 1.3 through 1.5 and Chapter Does it matter how we calculate the limits of a process behavior chart? Yes. There are right and wrong ways of computing limits. While all of the right ways will yield essentially the same limits, the wrong ways will result in incorrect limits and faulty decisions. See Section Do we have to remove the outliers from the data before we calculate the limits? No. The correct computational procedures for process behavior chart limits are not severely affected by outliers. See Sections 3.2 and Must the data be in control prior to placing them on a process behavior chart? No. One purpose of a process behavior chart is to detect the presence or absence of a state of predictability. Therefore, you do not have to wait for pristine data, nor do you have to clean up the data prior to computing the limits. See Section 3.2 and Chapter 4
8 9. How can we calculate good limits from data which are out of control? The correct approaches to computing limits will minimize the impact of exceptional variation upon the limits. See Chapter Should we calculate limits for the Average Chart when the Range Chart is unpredictable? Yes. You will not discover anything by not calculating limits! See Sections 4.1 and Can we use two-sigma limits? No. Two-sigma limits are inappropriate for a process behavior chart. See Section Do three-sigma limits depend upon having normally distributed data? No. Three-sigma limits are sufficiently general to work with virtually any distribution. See Sections 5.1 and Are the process behavior chart constants dependent upon having normally distributed data? No. These constants are remarkably similar for a wide range of different distributions. See Section Do we have to wait until we have 25 or 30 subgroups before calculating limits? No. Limits may be calculated using small amounts of data. The degrees of freedom will characterize just how reliable the calculated limits have become. See Sections 3.6, 5.4, and What about data which display autocorrelation? Shewhart placed autocorrelated data on charts. You can too. See Chapter Do we have to use subgroups of size 5? No. The subgroup size is not the most important characteristic of the chart. Rational subgrouping is more important than the subgroup size, even if that requires subgroups of size one. See Sections 1.6, 10.1, and Chapter What is a rational subgrouping? Among other things, a rational subgrouping is one in which the measurements inside each subgroup are judged to have been obtained under essentially the same conditions. Moreover, the subgrouping must respect the structure of the data. See Section 1.2 and Chapter Does the Central Limit Theorem require charts to use subgroups of size 4 or 5? While the Central Limit Theorem is true, it is not the basis on which the process behavior chart is built. Therefore, this theorem cannot require anything of a process behavior chart. The charts will work with subgroups of size 1, and they will do so even when the data are not normally distributed. See Sections 5.2, 10.1, and 10.3 xi
9 19. Does a subgroup always consist of consecutive measurements? No. While many processes may be tracked using subgroups of consecutive measurements, this is not a requirement of the chart. Once again, it is more important that the subgrouping be rational. See Section 1.6 and Chapter What happens to a process behavior chart when the measurement units are too large to detect the variation in the data? False alarms will proliferate. This problem is easy to spot, but it must be considered if you are to avoid looking for nonexistent assignable causes. See Section Why do we use so many symbols for dispersion? There is a multiplicity of dispersion statistics as well as a plurality of dispersion parameters. A lack of a standard nomenclature here is a real source of confusion. See Sections 3.1 through Is the standard deviation statistic better than the range? Not for small subgroup sizes. See Sections 4.1, 4.3, and Appendix Tables 18, 19, and Is not the Pooled Variance a better measure of dispersion than the Average Standard Deviation or the Average Range? Yes and No. The Pooled Variance will have more degrees of freedom than the other measures, but it will be more severely affected by a lack of homogeneity than will the other measures. See Sections 3.4 and What are Degrees of Freedom? Degrees of Freedom is the name given to a characterization of the variation of a measure of dispersion. The greater the Degrees of Freedom, the smaller the variation of the measure of dispersion. See Sections 3.6, 7.7, 7.8, and How do we measure dispersion when our subgroup size is one? We must use a two-point moving range to measure dispersion when placing a time series of individual values on a process behavior chart. See Sections 3.5 and What role does the Moving Range Chart play with an Individual Value Chart? It signals that the user knows the correct way of computing limits, it identifies breaks in the original time series, and it provides those who look at the chart with the ability to easily check that the computation of the limits is correct. See Section Are unbiased estimators better than biased estimators? No. The property of being unbiased does not imply closeness to the parameter. See Section Should I be using the skewness and kurtosis values from my printout? No. You will never have enough data to make these shape statistics useful. See Section 2.4 xii
10 29. Will Chaos Theory replace process behavior charts? No. Since Dr. Shewhart s approach is holistic and empirical, it can accommodate the paradigm shift represented by the new theories of quasi-chaotic variation. See Section What about transforming the data prior to placing them on a chart? Transformations to achieve a quasi-normal histogram or transformations to achieve other statistical properties are not recommended. They introduce more complexity than they are worth. Transformations to achieve clarity of interpretation are always appropriate. See Sections 1.8, 6.1, 11.9, and Chapter Is a Moving Average Chart better than a chart for Individual Values? Only occasionally. Most times the Individual Value Chart will be the better chart. See Section What is the difference between Attribute Charts and XmR Charts? XmR Charts use empirical limits while Attribute Charts use theory to construct limits. Therefore, with Attribute Charts you must check to see if the theory is appropriate. See Chapter How can we chart rare events? Counts of rare events will result in weak charts. It is better to measure the area of opportunity between the rare events and use these measurements on the charts. See Section Is it true that the Cumulative Sum (Cusum) is better than a process behavior chart? No. The Cusum technique may be easier to program than a process behavior chart, but contrary to much of what has been written, it does not really work any better than process behavior charts. Moreover, by transforming the original data, the Cusum technique can actually obscure that which is easily seen in the running records of the process behavior charts. See Chapter Can we use an Exponentially Weighted Moving Average instead of a process behavior chart? An EWMA attempts to model a time series. Such models may be used for process monitoring. However, EWMAs are no more sensitive than a process behavior chart, they will always lag behind a chart, and they are more complex than a chart. See Chapter Can we use PreControl instead of a process behavior chart? No. PreControl is totally different from a process behavior chart, and inferior as well. See Section Are Zone Charts a valid alternative to a process behavior chart? No. Zone charts result in too many false alarms. In addition, they are actually more complex than a process behavior chart, while providing nothing more than a parody of the process behavior chart. See Section 16.1 xiii
Variables Control Charts
 MINITAB ASSISTANT WHITE PAPER This paper explains the research conducted by Minitab statisticians to develop the methods and data checks used in the Assistant in Minitab 17 Statistical Software. Variables
MINITAB ASSISTANT WHITE PAPER This paper explains the research conducted by Minitab statisticians to develop the methods and data checks used in the Assistant in Minitab 17 Statistical Software. Variables
THE CERTIFIED SIX SIGMA BLACK BELT HANDBOOK
 THE CERTIFIED SIX SIGMA BLACK BELT HANDBOOK SECOND EDITION T. M. Kubiak Donald W. Benbow ASQ Quality Press Milwaukee, Wisconsin Table of Contents list of Figures and Tables Preface to the Second Edition
THE CERTIFIED SIX SIGMA BLACK BELT HANDBOOK SECOND EDITION T. M. Kubiak Donald W. Benbow ASQ Quality Press Milwaukee, Wisconsin Table of Contents list of Figures and Tables Preface to the Second Edition
Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CT3 Probability and Mathematical Statistics
 Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CT3 Probability and Mathematical Statistics For 2015 Examinations Aim The aim of the Probability and Mathematical Statistics subject is to provide a grounding in
Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CT3 Probability and Mathematical Statistics For 2015 Examinations Aim The aim of the Probability and Mathematical Statistics subject is to provide a grounding in
TABLE OF CONTENTS. GENERAL AND HISTORICAL PREFACE iii SIXTH EDITION PREFACE v PART ONE: REVIEW AND BACKGROUND MATERIAL
 TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL AND HISTORICAL PREFACE iii SIXTH EDITION PREFACE v PART ONE: REVIEW AND BACKGROUND MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE: REVIEW OF INTEREST THEORY 3 1.1 Interest Measures 3 1.2 Level Annuity
TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL AND HISTORICAL PREFACE iii SIXTH EDITION PREFACE v PART ONE: REVIEW AND BACKGROUND MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE: REVIEW OF INTEREST THEORY 3 1.1 Interest Measures 3 1.2 Level Annuity
Statistical Process Control OPRE 6364 1
 Statistical Process Control OPRE 6364 1 Statistical QA Approaches Statistical process control (SPC) Monitors production process to prevent poor quality Acceptance sampling Inspects random sample of product
Statistical Process Control OPRE 6364 1 Statistical QA Approaches Statistical process control (SPC) Monitors production process to prevent poor quality Acceptance sampling Inspects random sample of product
Business Statistics. Successful completion of Introductory and/or Intermediate Algebra courses is recommended before taking Business Statistics.
 Business Course Text Bowerman, Bruce L., Richard T. O'Connell, J. B. Orris, and Dawn C. Porter. Essentials of Business, 2nd edition, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2008, ISBN: 978-0-07-331988-9. Required Computing
Business Course Text Bowerman, Bruce L., Richard T. O'Connell, J. B. Orris, and Dawn C. Porter. Essentials of Business, 2nd edition, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2008, ISBN: 978-0-07-331988-9. Required Computing
An Honest Gauge R&R Study
 006 ASQ/ASA Fall Technical Conference Manuscript No. 189 An Honest Gauge R&R Study Donald J. Wheeler January 009 Revision In a 1994 paper Stanley Deming reported that when he did his literature search
006 ASQ/ASA Fall Technical Conference Manuscript No. 189 An Honest Gauge R&R Study Donald J. Wheeler January 009 Revision In a 1994 paper Stanley Deming reported that when he did his literature search
Measures of Central Tendency and Variability: Summarizing your Data for Others
 Measures of Central Tendency and Variability: Summarizing your Data for Others 1 I. Measures of Central Tendency: -Allow us to summarize an entire data set with a single value (the midpoint). 1. Mode :
Measures of Central Tendency and Variability: Summarizing your Data for Others 1 I. Measures of Central Tendency: -Allow us to summarize an entire data set with a single value (the midpoint). 1. Mode :
Summary of Formulas and Concepts. Descriptive Statistics (Ch. 1-4)
 Summary of Formulas and Concepts Descriptive Statistics (Ch. 1-4) Definitions Population: The complete set of numerical information on a particular quantity in which an investigator is interested. We assume
Summary of Formulas and Concepts Descriptive Statistics (Ch. 1-4) Definitions Population: The complete set of numerical information on a particular quantity in which an investigator is interested. We assume
THE SIX SIGMA BLACK BELT PRIMER
 INTRO-1 (1) THE SIX SIGMA BLACK BELT PRIMER by Quality Council of Indiana - All rights reserved Fourth Edition - September, 2014 Quality Council of Indiana 602 West Paris Avenue West Terre Haute, IN 47885
INTRO-1 (1) THE SIX SIGMA BLACK BELT PRIMER by Quality Council of Indiana - All rights reserved Fourth Edition - September, 2014 Quality Council of Indiana 602 West Paris Avenue West Terre Haute, IN 47885
Benchmarking Student Learning Outcomes using Shewhart Control Charts
 Benchmarking Student Learning Outcomes using Shewhart Control Charts Steven J. Peterson, MBA, PE Weber State University Ogden, Utah This paper looks at how Shewhart control charts a statistical tool used
Benchmarking Student Learning Outcomes using Shewhart Control Charts Steven J. Peterson, MBA, PE Weber State University Ogden, Utah This paper looks at how Shewhart control charts a statistical tool used
Course Text. Required Computing Software. Course Description. Course Objectives. StraighterLine. Business Statistics
 Course Text Business Statistics Lind, Douglas A., Marchal, William A. and Samuel A. Wathen. Basic Statistics for Business and Economics, 7th edition, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2010, ISBN: 9780077384470 [This
Course Text Business Statistics Lind, Douglas A., Marchal, William A. and Samuel A. Wathen. Basic Statistics for Business and Economics, 7th edition, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2010, ISBN: 9780077384470 [This
Biostatistics: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS: 2, VARIABILITY
 Biostatistics: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS: 2, VARIABILITY 1. Introduction Besides arriving at an appropriate expression of an average or consensus value for observations of a population, it is important to
Biostatistics: DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS: 2, VARIABILITY 1. Introduction Besides arriving at an appropriate expression of an average or consensus value for observations of a population, it is important to
Process Capability Analysis Using MINITAB (I)
 Process Capability Analysis Using MINITAB (I) By Keith M. Bower, M.S. Abstract The use of capability indices such as C p, C pk, and Sigma values is widespread in industry. It is important to emphasize
Process Capability Analysis Using MINITAB (I) By Keith M. Bower, M.S. Abstract The use of capability indices such as C p, C pk, and Sigma values is widespread in industry. It is important to emphasize
Curriculum Map Statistics and Probability Honors (348) Saugus High School Saugus Public Schools 2009-2010
 Curriculum Map Statistics and Probability Honors (348) Saugus High School Saugus Public Schools 2009-2010 Week 1 Week 2 14.0 Students organize and describe distributions of data by using a number of different
Curriculum Map Statistics and Probability Honors (348) Saugus High School Saugus Public Schools 2009-2010 Week 1 Week 2 14.0 Students organize and describe distributions of data by using a number of different
Introduction to. Hypothesis Testing CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES. 1 Identify the four steps of hypothesis testing.
 Introduction to Hypothesis Testing CHAPTER 8 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, you should be able to: 1 Identify the four steps of hypothesis testing. 2 Define null hypothesis, alternative
Introduction to Hypothesis Testing CHAPTER 8 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, you should be able to: 1 Identify the four steps of hypothesis testing. 2 Define null hypothesis, alternative
Lesson 4 Measures of Central Tendency
 Outline Measures of a distribution s shape -modality and skewness -the normal distribution Measures of central tendency -mean, median, and mode Skewness and Central Tendency Lesson 4 Measures of Central
Outline Measures of a distribution s shape -modality and skewness -the normal distribution Measures of central tendency -mean, median, and mode Skewness and Central Tendency Lesson 4 Measures of Central
Comparative study of the performance of the CuSum and EWMA control charts
 Computers & Industrial Engineering 46 (2004) 707 724 www.elsevier.com/locate/dsw Comparative study of the performance of the CuSum and EWMA control charts Vera do Carmo C. de Vargas*, Luis Felipe Dias
Computers & Industrial Engineering 46 (2004) 707 724 www.elsevier.com/locate/dsw Comparative study of the performance of the CuSum and EWMA control charts Vera do Carmo C. de Vargas*, Luis Felipe Dias
Change-Point Analysis: A Powerful New Tool For Detecting Changes
 Change-Point Analysis: A Powerful New Tool For Detecting Changes WAYNE A. TAYLOR Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Round Lake, IL 60073 Change-point analysis is a powerful new tool for determining whether
Change-Point Analysis: A Powerful New Tool For Detecting Changes WAYNE A. TAYLOR Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Round Lake, IL 60073 Change-point analysis is a powerful new tool for determining whether
Statistics 2014 Scoring Guidelines
 AP Statistics 2014 Scoring Guidelines College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online home
AP Statistics 2014 Scoring Guidelines College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online home
Quantitative Methods for Finance
 Quantitative Methods for Finance Module 1: The Time Value of Money 1 Learning how to interpret interest rates as required rates of return, discount rates, or opportunity costs. 2 Learning how to explain
Quantitative Methods for Finance Module 1: The Time Value of Money 1 Learning how to interpret interest rates as required rates of return, discount rates, or opportunity costs. 2 Learning how to explain
Module 3: Correlation and Covariance
 Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions Module 3: Correlation and Covariance Tom Ilvento Dr. Mugdim Pašiƒ University of Delaware Sarajevo Graduate School of Business O ften our interest in data analysis
Using Statistical Data to Make Decisions Module 3: Correlation and Covariance Tom Ilvento Dr. Mugdim Pašiƒ University of Delaware Sarajevo Graduate School of Business O ften our interest in data analysis
Data Mining Techniques Chapter 5: The Lure of Statistics: Data Mining Using Familiar Tools
 Data Mining Techniques Chapter 5: The Lure of Statistics: Data Mining Using Familiar Tools Occam s razor.......................................................... 2 A look at data I.........................................................
Data Mining Techniques Chapter 5: The Lure of Statistics: Data Mining Using Familiar Tools Occam s razor.......................................................... 2 A look at data I.........................................................
 DIVISION ONE 1 Income-tax Rules, 1962 Arrangement of Rules I-1 Text of the Income-tax Rules, 1962 as amended upto date 1.1 Appendix Text of provisions of Allied Laws referred to in Income-tax Rules 1.1281
DIVISION ONE 1 Income-tax Rules, 1962 Arrangement of Rules I-1 Text of the Income-tax Rules, 1962 as amended upto date 1.1 Appendix Text of provisions of Allied Laws referred to in Income-tax Rules 1.1281
Exploratory Data Analysis. Psychology 3256
 Exploratory Data Analysis Psychology 3256 1 Introduction If you are going to find out anything about a data set you must first understand the data Basically getting a feel for you numbers Easier to find
Exploratory Data Analysis Psychology 3256 1 Introduction If you are going to find out anything about a data set you must first understand the data Basically getting a feel for you numbers Easier to find
3. What is the difference between variance and standard deviation? 5. If I add 2 to all my observations, how variance and mean will vary?
 Variance, Standard deviation Exercises: 1. What does variance measure? 2. How do we compute a variance? 3. What is the difference between variance and standard deviation? 4. What is the meaning of the
Variance, Standard deviation Exercises: 1. What does variance measure? 2. How do we compute a variance? 3. What is the difference between variance and standard deviation? 4. What is the meaning of the
Statistical Rules of Thumb
 Statistical Rules of Thumb Second Edition Gerald van Belle University of Washington Department of Biostatistics and Department of Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences Seattle, WA WILEY AJOHN
Statistical Rules of Thumb Second Edition Gerald van Belle University of Washington Department of Biostatistics and Department of Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences Seattle, WA WILEY AJOHN
Probability and Statistics Prof. Dr. Somesh Kumar Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Probability and Statistics Prof. Dr. Somesh Kumar Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module No. #01 Lecture No. #15 Special Distributions-VI Today, I am going to introduce
Probability and Statistics Prof. Dr. Somesh Kumar Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module No. #01 Lecture No. #15 Special Distributions-VI Today, I am going to introduce
Instruction Manual for SPC for MS Excel V3.0
 Frequency Business Process Improvement 281-304-9504 20314 Lakeland Falls www.spcforexcel.com Cypress, TX 77433 Instruction Manual for SPC for MS Excel V3.0 35 30 25 LSL=60 Nominal=70 Capability Analysis
Frequency Business Process Improvement 281-304-9504 20314 Lakeland Falls www.spcforexcel.com Cypress, TX 77433 Instruction Manual for SPC for MS Excel V3.0 35 30 25 LSL=60 Nominal=70 Capability Analysis
Statistical Process Control (SPC) Training Guide
 Statistical Process Control (SPC) Training Guide Rev X05, 09/2013 What is data? Data is factual information (as measurements or statistics) used as a basic for reasoning, discussion or calculation. (Merriam-Webster
Statistical Process Control (SPC) Training Guide Rev X05, 09/2013 What is data? Data is factual information (as measurements or statistics) used as a basic for reasoning, discussion or calculation. (Merriam-Webster
1) Write the following as an algebraic expression using x as the variable: Triple a number subtracted from the number
 1) Write the following as an algebraic expression using x as the variable: Triple a number subtracted from the number A. 3(x - x) B. x 3 x C. 3x - x D. x - 3x 2) Write the following as an algebraic expression
1) Write the following as an algebraic expression using x as the variable: Triple a number subtracted from the number A. 3(x - x) B. x 3 x C. 3x - x D. x - 3x 2) Write the following as an algebraic expression
Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education
 Date Adopted 1998 Dates reviewed 2007, 2011, 2013 Dates revised 2004, 2008, 2011, 2013, 2015 Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System Jefferson
Date Adopted 1998 Dates reviewed 2007, 2011, 2013 Dates revised 2004, 2008, 2011, 2013, 2015 Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education Representing Alabama s Public Two-Year College System Jefferson
II. DISTRIBUTIONS distribution normal distribution. standard scores
 Appendix D Basic Measurement And Statistics The following information was developed by Steven Rothke, PhD, Department of Psychology, Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago (RIC) and expanded by Mary F. Schmidt,
Appendix D Basic Measurement And Statistics The following information was developed by Steven Rothke, PhD, Department of Psychology, Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago (RIC) and expanded by Mary F. Schmidt,
Descriptive Statistics
 Y520 Robert S Michael Goal: Learn to calculate indicators and construct graphs that summarize and describe a large quantity of values. Using the textbook readings and other resources listed on the web
Y520 Robert S Michael Goal: Learn to calculate indicators and construct graphs that summarize and describe a large quantity of values. Using the textbook readings and other resources listed on the web
DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS. The purpose of statistics is to condense raw data to make it easier to answer specific questions; test hypotheses.
 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS The purpose of statistics is to condense raw data to make it easier to answer specific questions; test hypotheses. DESCRIPTIVE VS. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Descriptive To organize,
DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS The purpose of statistics is to condense raw data to make it easier to answer specific questions; test hypotheses. DESCRIPTIVE VS. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Descriptive To organize,
1.5 Oneway Analysis of Variance
 Statistics: Rosie Cornish. 200. 1.5 Oneway Analysis of Variance 1 Introduction Oneway analysis of variance (ANOVA) is used to compare several means. This method is often used in scientific or medical experiments
Statistics: Rosie Cornish. 200. 1.5 Oneway Analysis of Variance 1 Introduction Oneway analysis of variance (ANOVA) is used to compare several means. This method is often used in scientific or medical experiments
The right edge of the box is the third quartile, Q 3, which is the median of the data values above the median. Maximum Median
 CONDENSED LESSON 2.1 Box Plots In this lesson you will create and interpret box plots for sets of data use the interquartile range (IQR) to identify potential outliers and graph them on a modified box
CONDENSED LESSON 2.1 Box Plots In this lesson you will create and interpret box plots for sets of data use the interquartile range (IQR) to identify potential outliers and graph them on a modified box
A Better Statistical Method for A/B Testing in Marketing Campaigns
 A Better Statistical Method for A/B Testing in Marketing Campaigns Scott Burk Marketers are always looking for an advantage, a way to win customers, improve market share, profitability and demonstrate
A Better Statistical Method for A/B Testing in Marketing Campaigns Scott Burk Marketers are always looking for an advantage, a way to win customers, improve market share, profitability and demonstrate
Descriptive Statistics
 Descriptive Statistics Primer Descriptive statistics Central tendency Variation Relative position Relationships Calculating descriptive statistics Descriptive Statistics Purpose to describe or summarize
Descriptive Statistics Primer Descriptive statistics Central tendency Variation Relative position Relationships Calculating descriptive statistics Descriptive Statistics Purpose to describe or summarize
business statistics using Excel OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Glyn Davis & Branko Pecar
 business statistics using Excel Glyn Davis & Branko Pecar OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Detailed contents Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2003 Overview Learning Objectives 1.1 Introduction to Microsoft Excel
business statistics using Excel Glyn Davis & Branko Pecar OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Detailed contents Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2003 Overview Learning Objectives 1.1 Introduction to Microsoft Excel
118 One hundred Eighteen
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ten 11 Eleven 12 Twelve 13 Thirteen 14 Fourteen 15 Fifteen 16 Sixteen 17 Seventeen 18 Eighteen 19 Nineteen 20 Twenty 21 Twenty 22 Twenty 23 Twenty 24 Twenty 25 Twenty 26 Twenty 27
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ten 11 Eleven 12 Twelve 13 Thirteen 14 Fourteen 15 Fifteen 16 Sixteen 17 Seventeen 18 Eighteen 19 Nineteen 20 Twenty 21 Twenty 22 Twenty 23 Twenty 24 Twenty 25 Twenty 26 Twenty 27
Good luck! BUSINESS STATISTICS FINAL EXAM INSTRUCTIONS. Name:
 Glo bal Leadership M BA BUSINESS STATISTICS FINAL EXAM Name: INSTRUCTIONS 1. Do not open this exam until instructed to do so. 2. Be sure to fill in your name before starting the exam. 3. You have two hours
Glo bal Leadership M BA BUSINESS STATISTICS FINAL EXAM Name: INSTRUCTIONS 1. Do not open this exam until instructed to do so. 2. Be sure to fill in your name before starting the exam. 3. You have two hours
Description. Textbook. Grading. Objective
 EC151.02 Statistics for Business and Economics (MWF 8:00-8:50) Instructor: Chiu Yu Ko Office: 462D, 21 Campenalla Way Phone: 2-6093 Email: [email protected] Office Hours: by appointment Description This course
EC151.02 Statistics for Business and Economics (MWF 8:00-8:50) Instructor: Chiu Yu Ko Office: 462D, 21 Campenalla Way Phone: 2-6093 Email: [email protected] Office Hours: by appointment Description This course
MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF STATISTICS
 MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF STATISTICS By HARALD CRAMER TROFESSOK IN THE UNIVERSITY OF STOCKHOLM Princeton PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PRESS 1946 TABLE OF CONTENTS. First Part. MATHEMATICAL INTRODUCTION. CHAPTERS
MATHEMATICAL METHODS OF STATISTICS By HARALD CRAMER TROFESSOK IN THE UNIVERSITY OF STOCKHOLM Princeton PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PRESS 1946 TABLE OF CONTENTS. First Part. MATHEMATICAL INTRODUCTION. CHAPTERS
Financial Assets Behaving Badly The Case of High Yield Bonds. Chris Kantos Newport Seminar June 2013
 Financial Assets Behaving Badly The Case of High Yield Bonds Chris Kantos Newport Seminar June 2013 Main Concepts for Today The most common metric of financial asset risk is the volatility or standard
Financial Assets Behaving Badly The Case of High Yield Bonds Chris Kantos Newport Seminar June 2013 Main Concepts for Today The most common metric of financial asset risk is the volatility or standard
USING TIME SERIES CHARTS TO ANALYZE FINANCIAL DATA (Presented at 2002 Annual Quality Conference)
 USING TIME SERIES CHARTS TO ANALYZE FINANCIAL DATA (Presented at 2002 Annual Quality Conference) William McNeese Walt Wilson Business Process Improvement Mayer Electric Company, Inc. 77429 Birmingham,
USING TIME SERIES CHARTS TO ANALYZE FINANCIAL DATA (Presented at 2002 Annual Quality Conference) William McNeese Walt Wilson Business Process Improvement Mayer Electric Company, Inc. 77429 Birmingham,
Additional sources Compilation of sources: http://lrs.ed.uiuc.edu/tseportal/datacollectionmethodologies/jin-tselink/tselink.htm
 Mgt 540 Research Methods Data Analysis 1 Additional sources Compilation of sources: http://lrs.ed.uiuc.edu/tseportal/datacollectionmethodologies/jin-tselink/tselink.htm http://web.utk.edu/~dap/random/order/start.htm
Mgt 540 Research Methods Data Analysis 1 Additional sources Compilation of sources: http://lrs.ed.uiuc.edu/tseportal/datacollectionmethodologies/jin-tselink/tselink.htm http://web.utk.edu/~dap/random/order/start.htm
individualdifferences
 1 Simple ANalysis Of Variance (ANOVA) Oftentimes we have more than two groups that we want to compare. The purpose of ANOVA is to allow us to compare group means from several independent samples. In general,
1 Simple ANalysis Of Variance (ANOVA) Oftentimes we have more than two groups that we want to compare. The purpose of ANOVA is to allow us to compare group means from several independent samples. In general,
Study Guide for the Final Exam
 Study Guide for the Final Exam When studying, remember that the computational portion of the exam will only involve new material (covered after the second midterm), that material from Exam 1 will make
Study Guide for the Final Exam When studying, remember that the computational portion of the exam will only involve new material (covered after the second midterm), that material from Exam 1 will make
Control Charts for Variables. Control Chart for X and R
 Control Charts for Variables X-R, X-S charts, non-random patterns, process capability estimation. 1 Control Chart for X and R Often, there are two things that might go wrong in a process; its mean or its
Control Charts for Variables X-R, X-S charts, non-random patterns, process capability estimation. 1 Control Chart for X and R Often, there are two things that might go wrong in a process; its mean or its
Randomized Block Analysis of Variance
 Chapter 565 Randomized Block Analysis of Variance Introduction This module analyzes a randomized block analysis of variance with up to two treatment factors and their interaction. It provides tables of
Chapter 565 Randomized Block Analysis of Variance Introduction This module analyzes a randomized block analysis of variance with up to two treatment factors and their interaction. It provides tables of
Common Tools for Displaying and Communicating Data for Process Improvement
 Common Tools for Displaying and Communicating Data for Process Improvement Packet includes: Tool Use Page # Box and Whisker Plot Check Sheet Control Chart Histogram Pareto Diagram Run Chart Scatter Plot
Common Tools for Displaying and Communicating Data for Process Improvement Packet includes: Tool Use Page # Box and Whisker Plot Check Sheet Control Chart Histogram Pareto Diagram Run Chart Scatter Plot
Global Medical Power Supply Equipment Industry 2015. Market Research Report
 Global Medical Power Supply Equipment Industry 2015 Market Research Report 2015 Global Medical Power Supply Equipment Industry Report is a professional and indepth research report on the world s major
Global Medical Power Supply Equipment Industry 2015 Market Research Report 2015 Global Medical Power Supply Equipment Industry Report is a professional and indepth research report on the world s major
Permutation Tests for Comparing Two Populations
 Permutation Tests for Comparing Two Populations Ferry Butar Butar, Ph.D. Jae-Wan Park Abstract Permutation tests for comparing two populations could be widely used in practice because of flexibility of
Permutation Tests for Comparing Two Populations Ferry Butar Butar, Ph.D. Jae-Wan Park Abstract Permutation tests for comparing two populations could be widely used in practice because of flexibility of
The G Chart in Minitab Statistical Software
 The G Chart in Minitab Statistical Software Background Developed by James Benneyan in 1991, the g chart (or G chart in Minitab) is a control chart that is based on the geometric distribution. Benneyan
The G Chart in Minitab Statistical Software Background Developed by James Benneyan in 1991, the g chart (or G chart in Minitab) is a control chart that is based on the geometric distribution. Benneyan
Use and interpretation of statistical quality control charts
 International Journal for Quality in Health Care 1998; Volume 10, Number I: pp. 69-73 Methodology matters VIII 'Methodology Matters' is a series of intermittently appearing articles on methodology. Suggestions
International Journal for Quality in Health Care 1998; Volume 10, Number I: pp. 69-73 Methodology matters VIII 'Methodology Matters' is a series of intermittently appearing articles on methodology. Suggestions
2 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION TECHNIQUES
 2 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION TECHNIQUES 2.1 INTRODUCTION Graphical representation of any process is always better and more meaningful than its representation in words. Moreover, it is very difficult to arrange
2 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION TECHNIQUES 2.1 INTRODUCTION Graphical representation of any process is always better and more meaningful than its representation in words. Moreover, it is very difficult to arrange
Introduction to Statistics for Psychology. Quantitative Methods for Human Sciences
 Introduction to Statistics for Psychology and Quantitative Methods for Human Sciences Jonathan Marchini Course Information There is website devoted to the course at http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/ marchini/phs.html
Introduction to Statistics for Psychology and Quantitative Methods for Human Sciences Jonathan Marchini Course Information There is website devoted to the course at http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/ marchini/phs.html
Glencoe. correlated to SOUTH CAROLINA MATH CURRICULUM STANDARDS GRADE 6 3-3, 5-8 8-4, 8-7 1-6, 4-9
 Glencoe correlated to SOUTH CAROLINA MATH CURRICULUM STANDARDS GRADE 6 STANDARDS 6-8 Number and Operations (NO) Standard I. Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers,
Glencoe correlated to SOUTH CAROLINA MATH CURRICULUM STANDARDS GRADE 6 STANDARDS 6-8 Number and Operations (NO) Standard I. Understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers,
Week 3&4: Z tables and the Sampling Distribution of X
 Week 3&4: Z tables and the Sampling Distribution of X 2 / 36 The Standard Normal Distribution, or Z Distribution, is the distribution of a random variable, Z N(0, 1 2 ). The distribution of any other normal
Week 3&4: Z tables and the Sampling Distribution of X 2 / 36 The Standard Normal Distribution, or Z Distribution, is the distribution of a random variable, Z N(0, 1 2 ). The distribution of any other normal
NCSS Statistical Software
 Chapter 06 Introduction This procedure provides several reports for the comparison of two distributions, including confidence intervals for the difference in means, two-sample t-tests, the z-test, the
Chapter 06 Introduction This procedure provides several reports for the comparison of two distributions, including confidence intervals for the difference in means, two-sample t-tests, the z-test, the
LONDON SCHOOL OF HYGIENE & TROPICAL MEDICINE
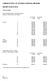 Clinical Staff Staff not holding honorary consultant contracts (lecturers, senior lecturers and readers) 01.04.2012 01.04.2013 scales scales Lecturer 1 33,265 33,597 2 34,799 35,146 3 36,334 36,697 4 37,869
Clinical Staff Staff not holding honorary consultant contracts (lecturers, senior lecturers and readers) 01.04.2012 01.04.2013 scales scales Lecturer 1 33,265 33,597 2 34,799 35,146 3 36,334 36,697 4 37,869
An introduction to using Microsoft Excel for quantitative data analysis
 Contents An introduction to using Microsoft Excel for quantitative data analysis 1 Introduction... 1 2 Why use Excel?... 2 3 Quantitative data analysis tools in Excel... 3 4 Entering your data... 6 5 Preparing
Contents An introduction to using Microsoft Excel for quantitative data analysis 1 Introduction... 1 2 Why use Excel?... 2 3 Quantitative data analysis tools in Excel... 3 4 Entering your data... 6 5 Preparing
Statistics I for QBIC. Contents and Objectives. Chapters 1 7. Revised: August 2013
 Statistics I for QBIC Text Book: Biostatistics, 10 th edition, by Daniel & Cross Contents and Objectives Chapters 1 7 Revised: August 2013 Chapter 1: Nature of Statistics (sections 1.1-1.6) Objectives
Statistics I for QBIC Text Book: Biostatistics, 10 th edition, by Daniel & Cross Contents and Objectives Chapters 1 7 Revised: August 2013 Chapter 1: Nature of Statistics (sections 1.1-1.6) Objectives
2. Filling Data Gaps, Data validation & Descriptive Statistics
 2. Filling Data Gaps, Data validation & Descriptive Statistics Dr. Prasad Modak Background Data collected from field may suffer from these problems Data may contain gaps ( = no readings during this period)
2. Filling Data Gaps, Data validation & Descriptive Statistics Dr. Prasad Modak Background Data collected from field may suffer from these problems Data may contain gaps ( = no readings during this period)
Global Personal Care Packaging Industry 2016 Market. Research Report
 Global Personal Care Packaging Industry 2016 Market Research Report 2016 Global Personal Care Packaging Industry Report is a professional and in-depth research report on the world s major regional market
Global Personal Care Packaging Industry 2016 Market Research Report 2016 Global Personal Care Packaging Industry Report is a professional and in-depth research report on the world s major regional market
4.1 Exploratory Analysis: Once the data is collected and entered, the first question is: "What do the data look like?"
 Data Analysis Plan The appropriate methods of data analysis are determined by your data types and variables of interest, the actual distribution of the variables, and the number of cases. Different analyses
Data Analysis Plan The appropriate methods of data analysis are determined by your data types and variables of interest, the actual distribution of the variables, and the number of cases. Different analyses
CALCULATIONS & STATISTICS
 CALCULATIONS & STATISTICS CALCULATION OF SCORES Conversion of 1-5 scale to 0-100 scores When you look at your report, you will notice that the scores are reported on a 0-100 scale, even though respondents
CALCULATIONS & STATISTICS CALCULATION OF SCORES Conversion of 1-5 scale to 0-100 scores When you look at your report, you will notice that the scores are reported on a 0-100 scale, even though respondents
Schneps, Leila; Colmez, Coralie. Math on Trial : How Numbers Get Used and Abused in the Courtroom. New York, NY, USA: Basic Books, 2013. p i.
 New York, NY, USA: Basic Books, 2013. p i. http://site.ebrary.com/lib/mcgill/doc?id=10665296&ppg=2 New York, NY, USA: Basic Books, 2013. p ii. http://site.ebrary.com/lib/mcgill/doc?id=10665296&ppg=3 New
New York, NY, USA: Basic Books, 2013. p i. http://site.ebrary.com/lib/mcgill/doc?id=10665296&ppg=2 New York, NY, USA: Basic Books, 2013. p ii. http://site.ebrary.com/lib/mcgill/doc?id=10665296&ppg=3 New
Why Taking This Course? Course Introduction, Descriptive Statistics and Data Visualization. Learning Goals. GENOME 560, Spring 2012
 Why Taking This Course? Course Introduction, Descriptive Statistics and Data Visualization GENOME 560, Spring 2012 Data are interesting because they help us understand the world Genomics: Massive Amounts
Why Taking This Course? Course Introduction, Descriptive Statistics and Data Visualization GENOME 560, Spring 2012 Data are interesting because they help us understand the world Genomics: Massive Amounts
Methods for Meta-analysis in Medical Research
 Methods for Meta-analysis in Medical Research Alex J. Sutton University of Leicester, UK Keith R. Abrams University of Leicester, UK David R. Jones University of Leicester, UK Trevor A. Sheldon University
Methods for Meta-analysis in Medical Research Alex J. Sutton University of Leicester, UK Keith R. Abrams University of Leicester, UK David R. Jones University of Leicester, UK Trevor A. Sheldon University
MEASURES OF VARIATION
 NORMAL DISTRIBTIONS MEASURES OF VARIATION In statistics, it is important to measure the spread of data. A simple way to measure spread is to find the range. But statisticians want to know if the data are
NORMAL DISTRIBTIONS MEASURES OF VARIATION In statistics, it is important to measure the spread of data. A simple way to measure spread is to find the range. But statisticians want to know if the data are
Accuplacer Arithmetic Study Guide
 Accuplacer Arithmetic Study Guide Section One: Terms Numerator: The number on top of a fraction which tells how many parts you have. Denominator: The number on the bottom of a fraction which tells how
Accuplacer Arithmetic Study Guide Section One: Terms Numerator: The number on top of a fraction which tells how many parts you have. Denominator: The number on the bottom of a fraction which tells how
How To Write A Data Analysis
 Mathematics Probability and Statistics Curriculum Guide Revised 2010 This page is intentionally left blank. Introduction The Mathematics Curriculum Guide serves as a guide for teachers when planning instruction
Mathematics Probability and Statistics Curriculum Guide Revised 2010 This page is intentionally left blank. Introduction The Mathematics Curriculum Guide serves as a guide for teachers when planning instruction
Descriptive statistics Statistical inference statistical inference, statistical induction and inferential statistics
 Descriptive statistics is the discipline of quantitatively describing the main features of a collection of data. Descriptive statistics are distinguished from inferential statistics (or inductive statistics),
Descriptive statistics is the discipline of quantitatively describing the main features of a collection of data. Descriptive statistics are distinguished from inferential statistics (or inductive statistics),
LAB : THE CHI-SQUARE TEST. Probability, Random Chance, and Genetics
 Period Date LAB : THE CHI-SQUARE TEST Probability, Random Chance, and Genetics Why do we study random chance and probability at the beginning of a unit on genetics? Genetics is the study of inheritance,
Period Date LAB : THE CHI-SQUARE TEST Probability, Random Chance, and Genetics Why do we study random chance and probability at the beginning of a unit on genetics? Genetics is the study of inheritance,
SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SCIENCES DON T FORGET TO RECODE YOUR MISSING VALUES
 SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SCIENCES Using SPSS Topics addressed today: 1. Differences between groups 2. Graphing Use the s4data.sav file for the first part of this session. DON T FORGET TO RECODE YOUR
SCHOOL OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SCIENCES Using SPSS Topics addressed today: 1. Differences between groups 2. Graphing Use the s4data.sav file for the first part of this session. DON T FORGET TO RECODE YOUR
The Management and Control of Quality
 The Management and Control of Quality JAMES R. EVANS University of Cincinnati WILLIAM M. LINDSAY Northern Kentucky University TfCHNISCHE HOCHSCHULE DARMSTADT Fochbcroic'n 1 G e 8o m t b i b I i o t h e
The Management and Control of Quality JAMES R. EVANS University of Cincinnati WILLIAM M. LINDSAY Northern Kentucky University TfCHNISCHE HOCHSCHULE DARMSTADT Fochbcroic'n 1 G e 8o m t b i b I i o t h e
Global Packaging Films Industry 2015 Market Research. Report
 Global Packaging Films Industry 2015 Market Research Report 2015 Global Packaging Films Industry Report is a professional and in-depth research report on the world s major regional market conditions of
Global Packaging Films Industry 2015 Market Research Report 2015 Global Packaging Films Industry Report is a professional and in-depth research report on the world s major regional market conditions of
Global Packaging Films Industry 2015 Market Research. Report
 Global Packaging Films Industry 2015 Market Research Report 2015 Global Packaging Films Industry Report is a professional and in-depth research report on the world s major regional market conditions of
Global Packaging Films Industry 2015 Market Research Report 2015 Global Packaging Films Industry Report is a professional and in-depth research report on the world s major regional market conditions of
Simple Regression Theory II 2010 Samuel L. Baker
 SIMPLE REGRESSION THEORY II 1 Simple Regression Theory II 2010 Samuel L. Baker Assessing how good the regression equation is likely to be Assignment 1A gets into drawing inferences about how close the
SIMPLE REGRESSION THEORY II 1 Simple Regression Theory II 2010 Samuel L. Baker Assessing how good the regression equation is likely to be Assignment 1A gets into drawing inferences about how close the
NCSS Statistical Software Principal Components Regression. In ordinary least squares, the regression coefficients are estimated using the formula ( )
 Chapter 340 Principal Components Regression Introduction is a technique for analyzing multiple regression data that suffer from multicollinearity. When multicollinearity occurs, least squares estimates
Chapter 340 Principal Components Regression Introduction is a technique for analyzing multiple regression data that suffer from multicollinearity. When multicollinearity occurs, least squares estimates
Global Passenger Information System Industry 2015. Market Research Report
 Global Passenger Information System Industry 2015 Market Research Report 2015 Global Passenger Information System Industry Report is a professional and in-depth research report on the world s major regional
Global Passenger Information System Industry 2015 Market Research Report 2015 Global Passenger Information System Industry Report is a professional and in-depth research report on the world s major regional
Content Sheet 7-1: Overview of Quality Control for Quantitative Tests
 Content Sheet 7-1: Overview of Quality Control for Quantitative Tests Role in quality management system Quality Control (QC) is a component of process control, and is a major element of the quality management
Content Sheet 7-1: Overview of Quality Control for Quantitative Tests Role in quality management system Quality Control (QC) is a component of process control, and is a major element of the quality management
SPC Data Visualization of Seasonal and Financial Data Using JMP WHITE PAPER
 SPC Data Visualization of Seasonal and Financial Data Using JMP WHITE PAPER SAS White Paper Table of Contents Abstract.... 1 Background.... 1 Example 1: Telescope Company Monitors Revenue.... 3 Example
SPC Data Visualization of Seasonal and Financial Data Using JMP WHITE PAPER SAS White Paper Table of Contents Abstract.... 1 Background.... 1 Example 1: Telescope Company Monitors Revenue.... 3 Example
Lecture 2: Descriptive Statistics and Exploratory Data Analysis
 Lecture 2: Descriptive Statistics and Exploratory Data Analysis Further Thoughts on Experimental Design 16 Individuals (8 each from two populations) with replicates Pop 1 Pop 2 Randomly sample 4 individuals
Lecture 2: Descriptive Statistics and Exploratory Data Analysis Further Thoughts on Experimental Design 16 Individuals (8 each from two populations) with replicates Pop 1 Pop 2 Randomly sample 4 individuals
Selecting SPC Software for Batch and Specialty Chemicals Processing
 WHITE PAPER Selecting SPC Software for Batch and Specialty Chemicals Processing Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a necessary part of modern chemical processing. The software chosen to collect quality
WHITE PAPER Selecting SPC Software for Batch and Specialty Chemicals Processing Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a necessary part of modern chemical processing. The software chosen to collect quality
Descriptive Statistics. Purpose of descriptive statistics Frequency distributions Measures of central tendency Measures of dispersion
 Descriptive Statistics Purpose of descriptive statistics Frequency distributions Measures of central tendency Measures of dispersion Statistics as a Tool for LIS Research Importance of statistics in research
Descriptive Statistics Purpose of descriptive statistics Frequency distributions Measures of central tendency Measures of dispersion Statistics as a Tool for LIS Research Importance of statistics in research
Investment Statistics: Definitions & Formulas
 Investment Statistics: Definitions & Formulas The following are brief descriptions and formulas for the various statistics and calculations available within the ease Analytics system. Unless stated otherwise,
Investment Statistics: Definitions & Formulas The following are brief descriptions and formulas for the various statistics and calculations available within the ease Analytics system. Unless stated otherwise,
Global Benchmarking Mining Equipment Industry 2015. Market Research Report
 Global Benchmarking Mining Equipment Industry 2015 Market Research Report 2015 Global Benchmarking Mining Equipment Industry Report is a professional and in-depth research report on the world s major regional
Global Benchmarking Mining Equipment Industry 2015 Market Research Report 2015 Global Benchmarking Mining Equipment Industry Report is a professional and in-depth research report on the world s major regional
Introduction to Quantitative Methods
 Introduction to Quantitative Methods October 15, 2009 Contents 1 Definition of Key Terms 2 2 Descriptive Statistics 3 2.1 Frequency Tables......................... 4 2.2 Measures of Central Tendencies.................
Introduction to Quantitative Methods October 15, 2009 Contents 1 Definition of Key Terms 2 2 Descriptive Statistics 3 2.1 Frequency Tables......................... 4 2.2 Measures of Central Tendencies.................
Confidence Intervals for the Difference Between Two Means
 Chapter 47 Confidence Intervals for the Difference Between Two Means Introduction This procedure calculates the sample size necessary to achieve a specified distance from the difference in sample means
Chapter 47 Confidence Intervals for the Difference Between Two Means Introduction This procedure calculates the sample size necessary to achieve a specified distance from the difference in sample means
Global IP VIDEO SURVEILLANCE SOFTWARE Industry 2015. Market Research Report
 Global IP VIDEO SURVEILLANCE SOFTWARE Industry 2015 Market Research Report 2015 Global IP VIDEO SURVEILLANCE SOFTWARE Industry Report is a professional and in-depth research report on the world s major
Global IP VIDEO SURVEILLANCE SOFTWARE Industry 2015 Market Research Report 2015 Global IP VIDEO SURVEILLANCE SOFTWARE Industry Report is a professional and in-depth research report on the world s major
E3: PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS lecture notes
 E3: PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS lecture notes 2 Contents 1 PROBABILITY THEORY 7 1.1 Experiments and random events............................ 7 1.2 Certain event. Impossible event............................
E3: PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS lecture notes 2 Contents 1 PROBABILITY THEORY 7 1.1 Experiments and random events............................ 7 1.2 Certain event. Impossible event............................
Session 7 Bivariate Data and Analysis
 Session 7 Bivariate Data and Analysis Key Terms for This Session Previously Introduced mean standard deviation New in This Session association bivariate analysis contingency table co-variation least squares
Session 7 Bivariate Data and Analysis Key Terms for This Session Previously Introduced mean standard deviation New in This Session association bivariate analysis contingency table co-variation least squares
