Responses to Static (Isometric) Exercise
|
|
|
- Rosalind Casey
- 9 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Responses to Static (Isometric) Exercise Suggestions for Teachers Background Static exercise involves the contraction of skeletal muscle without a change in muscle length, hence the alternative term, isometric (iso = same, meter = length) exercise. Static exercise produces a cardiovascular response that differs significantly from that observed during dynamic exercise. Typical examples of static exercise include athletic events such as weight lifting, shot put, hammer throw, and everyday activities such as lifting heavy boxes or carrying a heavy briefcase. Prolonged continuous contraction of skeletal muscles inhibits regional blood flow as muscle fibers compress blood vessels. The decrease in blood flow is partially offset by local arterial vasodilation, however if the muscle is contracted to 70% of its maximal voluntary contraction, blood flow may be completely occluded. This reduction in blood flow allows the accumulation of acidic metabolic byproducts that stimulate chemoreceptors within the muscle itself. In combination with mechanoreceptors, these ascending afferents provide feedback to cardiovascular control areas in the brainstem. A second system also serves to regulate cardiac response to static exercise. This central neural mechanism originates in higher centers in the CNS and responds to increased motor output by activating cardiovascular and respiratory control areas. The combined action of this central neural mechanism and the feedback mechanism described above both serve to increase heart rate. However, this system does not result in a concomitant increase in stroke volume as is exhibited in dynamic exercise, and any increase in cardiac output is due almost entirely to increases in heart rate. In addition, as muscular exertion is relatively localized with static exercise, there is little systemic vasodilation, hence increased stroke volume is not compensated in the peripheral circulation as during dynamic exercise. This condition leads to increases in mean arterial pressures proportional to increases in cardiac output. In this activity volunteers will perform a prolonged static contraction using a grip dynamometer (or other device) as blood pressure and heart rate are monitored over a period of time. A second blood pressure cuff will then be used on the exercised arm to demonstrate the effects of the two separate neural components of the response. Materials Grip dynamometer or grip exerciser, spring clamp (available at hardware stores), or rubber ball Stopwatch or clock 2 blood pressure cuffs Stethoscope 1
2 Procedure 1. You will need groups of at least four students, five is better. 2. This works best if students have experience taking blood pressure. Groups should choose the person with the best technique to monitor blood pressure during this activity. 3. A few dry runs are suggested before beginning, as all members of the group must work closely under time constraints to gather data. 4. As with the first part of this module, quiet in the classroom is essential. 5. The subject should try to maintain about 30% of their full grip strength during a full three minutes. Choose subjects carefully, as this activity will be fatiguing and somewhat uncomfortable. Safety 1. Students should be careful to not leave the blood pressure cuff on any longer than necessary. Dry runs should only mock the occlusion at the end of the activity. 2. Group members should change roles if this activity becomes too uncomfortable for the participant. 3. Students should be warned to not drop the dynamometer. Suggestions for Assessment Students can answer analysis questions or make this a part of a full lab report along with the first part of this module. 2
3 Responses to Static (Isometric) Exercise Student Activity Background Static exercise occurs when muscles exert a force, but do not change in length. As we saw in the previous activity, a number of changes take place in the cardiovascular system to compensate for increased demands of exercising muscles. However, the response to static exercise is somewhat different than it is to dynamic exercise. In static exercise there is very little vasodilation that takes place in the periphery, hence the heart must work harder to pump blood than during dynamic exercise. In this activity you will investigate the effects of static exercise on cardiovascular response and relate this response to the underlying neural mechanisms at work. There are (at least) two neural systems at work when muscles are exercised. The first, the Central Command, is located in the higher centers in the brain. It monitors the nerve signals sent out to the muscles and responds by stimulating areas in the brainstem responsible for heart rate and strength of contraction. The second is a feedback system that detects work in the muscle by monitoring contraction and the buildup of cellular wastes. It then signals the brainstem to increase cardiac output to compensate for increased muscular activity. This activity has two components. In the first, you will measure the blood pressure of a volunteer who is performing static (isometric) exercise over a three-minute period. Then you will use a second cuff to block blood flow to the exercising arm as the volunteer stops exercising and continue to monitor blood pressure. Materials Grip dynamometer (or grip exerciser, spring clamp, or rubber ball) Stopwatch or clock 2 blood pressure cuffs Stethoscope Procedure 1. This activity works best with a group of 5 students. Choose one person for each of the following jobs: subject, blood pressure monitor, pulse monitor, timer/recorder, and someone to inflate second (occlusion) cuff. 2. Read over the entire procedure, making note of the timing of the measurements. Practice the procedure at least once with all participants. Do not inflate the occlusion cuff during practice runs. 1
4 3. Have the volunteer sit in a chair. If a grip dynamometer is available, determine the maximum force that the volunteer can exert with their dominant hand. Their target force for this activity will be about 30% of that value. If a rubber ball or spring exerciser is used, the subject should try to estimate the grip force to be in this range. 4. Place the blood pressure cuff on the other arm. Take an initial reading. Record the systolic and diastolic pressures in the data table. Leave the cuff on the volunteer s arm. 5. Determine the volunteer s resting heart rate by taking their radial pulse. Record the heart rate in the data table. 6. Place the occlusion cuff on the upper part of the exercising arm. Do not inflate. 7. The volunteer will then exert a force on the dynamometer approximately 30% of their maximum and maintain it for three minutes. 8. At one minute the blood pressure will be taken. The monitor will have to anticipate this reading and inflate the cuff prior to the time mark so that the reading is as close to one minute as possible. 9. A pulse reading should be taken at immediately following the blood pressure reading. 10. Repeat the readings of blood pressure and pulse rate at the two- and three-minute marks. 11. Just following the three-minute reading, the occlusion cuff should be inflated to 200 mm Hg. This will cut off all blood flow to the arm. As soon as the pressure reaches 200, the volunteer should stop exercising. 12. At four minutes, check blood pressure and pulse. Deflate the occlusion cuff immediately. 13. Take a final blood pressure reading and pulse at 5 minutes. 14. Calculate MAP as you did in the first part of this activity. Record these values in the table. 15. Make a line graph of your results. You should have one line for each of the three values, systolic pressure, diastolic pressure, and MAP. Data Systolic Initial 1 Minute 2 Minutes 3 Minutes 4 Minutes 5 Minutes Diastolic MAP Heart Rate 2
5 Analysis 1. Describe what happened to the volunteer s MAP and heart rate during static exercise. How do these compare to values you obtained for dynamic exercise in the first part of this activity? How can you account for any differences? 2. How did heart rate and blood pressure change during the time the blood flow was occluded? Which of the two systems, Central Control or Feedback was most active at this time? Relate this information to your observations. 3. What was happening during the last minute? How do the data show this? 3
Blood Pressure. Blood Pressure (mm Hg) pressure exerted by blood against arterial walls. Blood Pressure. Blood Pressure
 Blood Pressure Blood Pressure (mm Hg) pressure exerted by blood against arterial walls Systolic pressure exerted on arteries during systole Diastolic pressure in arteries during diastole 120/80 Borderline
Blood Pressure Blood Pressure (mm Hg) pressure exerted by blood against arterial walls Systolic pressure exerted on arteries during systole Diastolic pressure in arteries during diastole 120/80 Borderline
Muscle Physiology. Lab 5. Human Muscle Physiology
 Lab 5 Human At the beginning of lab you will have the opportunity for 2 bonus points! You must guess which person in the class will have: 1) Maximum Grip Force 2) Longest time to half-max Force (longest
Lab 5 Human At the beginning of lab you will have the opportunity for 2 bonus points! You must guess which person in the class will have: 1) Maximum Grip Force 2) Longest time to half-max Force (longest
Circulation Stations
 Circulation Stations This worksheet corresponds with stations around the classrooms. Work in groups of 3 and do the stations in any order. Name: Station 1: Blood smear under a microscope Materials: - Microscope
Circulation Stations This worksheet corresponds with stations around the classrooms. Work in groups of 3 and do the stations in any order. Name: Station 1: Blood smear under a microscope Materials: - Microscope
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE
 MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology for the heart to work properly contraction and relaxation of chambers must be coordinated cardiac muscle tissue differs from smooth and skeletal muscle tissues
Evaluation copy. Blood Pressure. Project PROJECT DESIGN REQUIREMENTS
 Blood Pressure Project 9 Blood pressure is a measure of the fluid pressure within the circulatory system. This pressure is required to ensure the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to, and the removal of
Blood Pressure Project 9 Blood pressure is a measure of the fluid pressure within the circulatory system. This pressure is required to ensure the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to, and the removal of
A1 Reasons for taking part in activity. A2 Health, fitness, exercise and performance
 Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Candidate No. / Surname Signature Initials Paper Reference 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education End Of Unit Test SECTION 1: FITNESS A1 Reasons for taking
Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Candidate No. / Surname Signature Initials Paper Reference 1827/01 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education End Of Unit Test SECTION 1: FITNESS A1 Reasons for taking
INVESTIGATING HEART RATE AND BLOOD PRESSURE
 Hughes Undergraduate Biological Science Education Initiative HHMI INVESTIGATING HEART RATE AND BLOOD PRESSURE Learn how to measure heart rate and blood pressure. Learn the normal values for heart rate
Hughes Undergraduate Biological Science Education Initiative HHMI INVESTIGATING HEART RATE AND BLOOD PRESSURE Learn how to measure heart rate and blood pressure. Learn the normal values for heart rate
OEM MAXNIBP Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions Why does the monitor sometimes inflate the BP cuff, then shortly thereafter reinflate the cuff? How will I know if the monitor is experiencing motion artifact during a measurement?
Frequently Asked Questions Why does the monitor sometimes inflate the BP cuff, then shortly thereafter reinflate the cuff? How will I know if the monitor is experiencing motion artifact during a measurement?
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure. Vessel Elasticity Blood Volume Cardiac Output
 Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
Factors that Affect Pressure Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction pressure is affected by several factors:
Measuring Your Blood Pressure at Home. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Measuring Your Blood Pressure at Home A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor* has told you that you may have high blood pressure, also called hypertension.
Measuring Your Blood Pressure at Home A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, if: A doctor* has told you that you may have high blood pressure, also called hypertension.
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE
 MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
MEASURING AND RECORDING BLOOD PRESSURE INTRODUCTION The blood pressure, along with the body temperature, pulse, and respirations, is one of the vital signs. These measurements are used to quickly, easily,
Vtial sign #1: PULSE. Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation. Factors that influence pulse rate: Importance of Vital Signs
 Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation Elma I. LeDoux, MD, FACP, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Vtial sign #1: PULSE Reflects heart rate (resting 60-90/min) Should be strong and regular Use 2
Vital Signs: Assessment and Interpretation Elma I. LeDoux, MD, FACP, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Vtial sign #1: PULSE Reflects heart rate (resting 60-90/min) Should be strong and regular Use 2
How to measure blood pressure using digital monitors
 How to measure blood pressure using digital monitors What is high blood pressure? Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels. Systolic pressure is the blood
How to measure blood pressure using digital monitors What is high blood pressure? Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels. Systolic pressure is the blood
Section Two: Arterial Pressure Monitoring
 Section Two: Arterial Pressure Monitoring Indications An arterial line is indicated for blood pressure monitoring for the patient with any medical or surgical condition that compromises cardiac output,
Section Two: Arterial Pressure Monitoring Indications An arterial line is indicated for blood pressure monitoring for the patient with any medical or surgical condition that compromises cardiac output,
Plank 1 Tool: Hypertension Medical Assistant Training (Providence Medical Group)
 Plank 1 Tool: Hypertension Medical Assistant Training (Providence Medical Group) Task Qualification Training Packet Volume 1 Date Performing Blood Pressure Checks SUBJECT AREA Vital Signs EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
Plank 1 Tool: Hypertension Medical Assistant Training (Providence Medical Group) Task Qualification Training Packet Volume 1 Date Performing Blood Pressure Checks SUBJECT AREA Vital Signs EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Manual Blood Pressure Measurement
 Manual Blood Pressure Measurement 1 Peter Mahoney, CETL Clinical Skills Facilitator Measuring Blood Pressure manually can be difficult if not practised regularly. However it is important to be able to
Manual Blood Pressure Measurement 1 Peter Mahoney, CETL Clinical Skills Facilitator Measuring Blood Pressure manually can be difficult if not practised regularly. However it is important to be able to
Low Intensity Alternatives for Strength and Hypertrophy
 Low Intensity Alternatives for Strength and Hypertrophy Jacob M. Wilson, PhD, CSCS*D Human Performance laboratory University of Tampa, Tampa, FL Traditional Techniques The American College of Sports Medicine
Low Intensity Alternatives for Strength and Hypertrophy Jacob M. Wilson, PhD, CSCS*D Human Performance laboratory University of Tampa, Tampa, FL Traditional Techniques The American College of Sports Medicine
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness
 Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
Heart Rate and Physical Fitness The circulatory system is responsible for the internal transport of many vital substances in humans, including oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. The components of the
Effects of Caffeine on Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Stimulation: A Noninvasive Study Based on a Single Dose of Caffeine
 Effects of Caffeine on Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Stimulation: A Noninvasive Study Based on a Single Dose of Caffeine Physiology 435: Lab 601 Group 3 Dr. Lokuta Kira Arno, Logan Schlosser, Chris Boyd,
Effects of Caffeine on Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Stimulation: A Noninvasive Study Based on a Single Dose of Caffeine Physiology 435: Lab 601 Group 3 Dr. Lokuta Kira Arno, Logan Schlosser, Chris Boyd,
MICROGRAVITY EFFECTS ON HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration MICROGRAVITY EFFECTS ON HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Instructional Objectives Students will: analyze the effects of external stimuli on the physiological
National Aeronautics and Space Administration MICROGRAVITY EFFECTS ON HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Instructional Objectives Students will: analyze the effects of external stimuli on the physiological
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back
 Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Vascular System The heart can be thought of 2 separate pumps from the right ventricle, blood is pumped at a low pressure to the lungs and then back to the left atria from the left ventricle, blood is pumped
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Blood Vessels and Circulation
 13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
13 Blood Vessels and Circulation FOCUS: Blood flows from the heart through the arterial blood vessels to capillaries, and from capillaries back to the heart through veins. The pulmonary circulation transports
MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS
 BLOOD SUGAR MANAGEMENT GUIDE MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS Understanding and Tracking the ABCs of Type 2 Diabetes 1 BLOOD MY TYPE SUGAR 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT ABC NUMBERS GUIDE When you have type 2 diabetes,
BLOOD SUGAR MANAGEMENT GUIDE MY TYPE 2 DIABETES NUMBERS Understanding and Tracking the ABCs of Type 2 Diabetes 1 BLOOD MY TYPE SUGAR 2 DIABETES MANAGEMENT ABC NUMBERS GUIDE When you have type 2 diabetes,
Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus
 Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus When Key Points / Objectives Content Day 1 INTRODUCTION HOMEOSTASIS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Day 2 CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GENETICS Day 3 INTEGUMENTARY
Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus When Key Points / Objectives Content Day 1 INTRODUCTION HOMEOSTASIS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Day 2 CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GENETICS Day 3 INTEGUMENTARY
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations. Chapters 5 & 6
 Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Anaerobic and Aerobic Training Adaptations Chapters 5 & 6 Adaptations to Training Chronic exercise provides stimulus for the systems of the body to change Systems will adapt according to level, intensity,
Chapter 15. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes. general properties Anatomy. Autonomic effects on target organs
 Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 15 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Visceral Reflexes general properties Anatomy Autonomic effects on target organs Central control of autonomic function 15-1 Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Activity: Build Your Own Lung
 Activity: Build Your Own Lung Supplies per group: 2 liter pop bottle Scissors 2 straws 2 balloons 3 rubber bands clay piece of clear wrap paper binder clip Directions: 1. Carefully, cut the bottom off
Activity: Build Your Own Lung Supplies per group: 2 liter pop bottle Scissors 2 straws 2 balloons 3 rubber bands clay piece of clear wrap paper binder clip Directions: 1. Carefully, cut the bottom off
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
3 rd Russian-Bavarian Conference on Bio-Medical Engineering
 3 rd Russian-Bavarian Conference on Bio-Medical Engineering Blood Pressure Estimation based on Pulse Transit Time and Compensation of Vertical Position Dipl.-Inform. Med. Christian Douniama Dipl.-Ing.
3 rd Russian-Bavarian Conference on Bio-Medical Engineering Blood Pressure Estimation based on Pulse Transit Time and Compensation of Vertical Position Dipl.-Inform. Med. Christian Douniama Dipl.-Ing.
GRADE 11F: Biology 3. UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours. Human gas exchange system and health. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
Exchange solutes and water with cells of the body
 Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Chapter 8 Heart and Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Transport Blood Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Transport blood under high pressure Capillaries Exchange solutes and water with cells
Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex
 Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex Module Objectives: 1. Describe the anatomic pathway of a tendon tap reflex. 2. Explain how a tendon tap reflex assessment assists in diagnosis of a
Module 1: The Somato-Motor System: Tendon Tap reflex Module Objectives: 1. Describe the anatomic pathway of a tendon tap reflex. 2. Explain how a tendon tap reflex assessment assists in diagnosis of a
Chapter 12. Temperature Regulation. Temperature Regulation. Heat Balance. An Overview of Heat Balance. Temperature Regulation. Temperature Regulation
 Chapter 12 Body core temperature regulation Critical for: Cellular structures Metabolic pathways Too high Protein structure of cells destroyed Too low Slowed metabolism Cardiac arrhythmias Homeothermic
Chapter 12 Body core temperature regulation Critical for: Cellular structures Metabolic pathways Too high Protein structure of cells destroyed Too low Slowed metabolism Cardiac arrhythmias Homeothermic
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
4 Week Body Contour / Lipo Light Program
 Natural Health Solutions 14698 Galaxie Ave. Apple Valley, MN 55124 (952) 891-22225 4 Week Body Contour / Lipo Light Program Welcome and Congratulations! This is an important decision towards improving
Natural Health Solutions 14698 Galaxie Ave. Apple Valley, MN 55124 (952) 891-22225 4 Week Body Contour / Lipo Light Program Welcome and Congratulations! This is an important decision towards improving
MEASURING VITAL SIGNS TRAINING CHECKLIST
 Measuring Vital Signs A guide to help Direct Support Professionals learn how to measure, and report vital sign measurements. Outcomes: Know how to take each individual s vital signs. Demonstrate the correct
Measuring Vital Signs A guide to help Direct Support Professionals learn how to measure, and report vital sign measurements. Outcomes: Know how to take each individual s vital signs. Demonstrate the correct
Republic Polytechnic. Continuing Education & Training. Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology
 Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Republic Polytechnic Continuing Education & Training Course Structure: Anatomy & Physiology Module Anatomy and Physiology Description This module introduces the basic human anatomical organization, tissue
Tymikia S. Glenn, BS ACSM CPT Fitness and Membership Director Milan Family YMCA
 Tymikia S. Glenn, BS ACSM CPT Fitness and Membership Director Milan Family YMCA Benefits of Starting an Exercise Program 1. Helps build and maintain healthy bones, muscles and joints 2. Reduces feelings
Tymikia S. Glenn, BS ACSM CPT Fitness and Membership Director Milan Family YMCA Benefits of Starting an Exercise Program 1. Helps build and maintain healthy bones, muscles and joints 2. Reduces feelings
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR
 Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
Anatomy and Physiology: Understanding the Importance of CPR Overview This document gives you more information about the body s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology). This information will help
31.1 The Neuron. BUILD Vocabulary. Lesson Objectives
 Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Name Class Date 31.1 The Neuron Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart
Renal Blood Flow GFR. Glomerulus Fluid Flow and Forces. Renal Blood Flow (cont d)
 GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
GFR Glomerular filtration rate: about 120 ml /minute (180 L a day) Decreases with age (about 10 ml/min for each decade over 40) GFR = Sum of the filtration of two million glomeruli Each glomerulus probably
AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING QUICK START GUIDE
 C A R D I O P E R F E C T AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING QUICK START GUIDE UNDERSTANDING ERROR CODES ERROR CODE DESCRIPTION 1 Unknown error 2 This can indicate one of the following problems: After
C A R D I O P E R F E C T AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE MONITORING QUICK START GUIDE UNDERSTANDING ERROR CODES ERROR CODE DESCRIPTION 1 Unknown error 2 This can indicate one of the following problems: After
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11
 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
Clinical Care Program
 Clinical Care Program Therapy for the Cardiac Patient What s CHF? Not a kind of heart disease o Heart disease is called cardiomyopathy o Heart failure occurs when the heart can t pump enough blood to meet
Clinical Care Program Therapy for the Cardiac Patient What s CHF? Not a kind of heart disease o Heart disease is called cardiomyopathy o Heart failure occurs when the heart can t pump enough blood to meet
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE. Content Title: Methods of training. Practical Application/Explanation. Fartlek training. Continuous training
 Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
Content Title: Methods of training Key points GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION Different methods of training How to design specific training sessions How to design a training programme PE2 UNIT GUIDE Practical Application/Explanation
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3
 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper There are 25 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 18 out of 25 marks All questions are multiple
Automatic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor with
 Instruction Manual Automatic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor with Model HEM-609 ENGLISH ESPAÑOL CONTENTS Before Using the Monitor Introduction...................................... 3 Important Safety Notes.............................
Instruction Manual Automatic Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor with Model HEM-609 ENGLISH ESPAÑOL CONTENTS Before Using the Monitor Introduction...................................... 3 Important Safety Notes.............................
5TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE
 PHYSICAL EDUCATION 5 TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE PART I. Revised 5-13 DIRECTIONS: Review the following terms and concepts. Do not try to memorize the definitions, rather think about and understand: 1)
PHYSICAL EDUCATION 5 TH GRADE FITNESS STUDY GUIDE PART I. Revised 5-13 DIRECTIONS: Review the following terms and concepts. Do not try to memorize the definitions, rather think about and understand: 1)
Provided by the American Venous Forum: veinforum.org
 CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
CHAPTER 1 NORMAL VENOUS CIRCULATION Original author: Frank Padberg Abstracted by Teresa L.Carman Introduction The circulatory system is responsible for circulating (moving) blood throughout the body. The
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Direct Arterial Blood Pressure Monitoring Angel M. Rivera CVT, VTS (ECC) Animal Emergency Center Glendale, WI March 2003
 Direct Arterial Blood Pressure Monitoring Angel M. Rivera CVT, VTS (ECC) Animal Emergency Center Glendale, WI March 2003 Introduction Direct measurement of arterial blood pressure is obtained via a peripheral
Direct Arterial Blood Pressure Monitoring Angel M. Rivera CVT, VTS (ECC) Animal Emergency Center Glendale, WI March 2003 Introduction Direct measurement of arterial blood pressure is obtained via a peripheral
Heart Failure EXERCISES. Ⅰ. True or false questions (mark for true question, mark for false question. If it is false, correct it.
 Heart Failure EXERCISES Ⅰ. True or false questions (mark for true question, mark for false question. If it is false, correct it. ) 1. Heart rate increase is a kind of economic compensation, which should
Heart Failure EXERCISES Ⅰ. True or false questions (mark for true question, mark for false question. If it is false, correct it. ) 1. Heart rate increase is a kind of economic compensation, which should
Blood Pressure Guidelines and Screening Techniques
 Blood Pressure Guidelines and Screening Techniques Connie M. Kracher, PhD, MSD Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Taking patients blood pressure during dental examinations is critical to their overall
Blood Pressure Guidelines and Screening Techniques Connie M. Kracher, PhD, MSD Continuing Education Units: 1 hour Taking patients blood pressure during dental examinations is critical to their overall
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Experiment MP-1: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity and Muscle Strength
 Experiment MP-1: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity and Muscle Strength Calibrating the Hand Dynamometer 1. Collect 5 textbooks or use the barbell weight. Weigh the stack of books on the bathroom scale. Record
Experiment MP-1: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity and Muscle Strength Calibrating the Hand Dynamometer 1. Collect 5 textbooks or use the barbell weight. Weigh the stack of books on the bathroom scale. Record
3. Tunica adventitia is the outermost layer; it is composed of loosely woven connective tissue infiltrated by nerves, blood vessels and lymphatics
 Blood vessels and blood pressure I. Introduction - distribution of CO at rest II. General structure of blood vessel walls - walls are composed of three distinct layers: 1. Tunica intima is the innermost
Blood vessels and blood pressure I. Introduction - distribution of CO at rest II. General structure of blood vessel walls - walls are composed of three distinct layers: 1. Tunica intima is the innermost
Certificate in School of Applied Physiology
 Certificate in School of Applied Physiology The certificate program, as outlined below, satisfies the institutional requirement for 12 semester hours, with at least 9 being at the 3000 level or above.
Certificate in School of Applied Physiology The certificate program, as outlined below, satisfies the institutional requirement for 12 semester hours, with at least 9 being at the 3000 level or above.
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013
 Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Anatomy and Physiology Warm up questions Fall 2013 QUESTION POSSIBLE ANSWERS : Chapter 1 Introduction and Regions Chapter 2 Chemistry I can name systems of the I can identify regions of the I can describe
Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture
 1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
1 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 15 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture 2 THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and certain
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Chapter 7: The Nervous System Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways involved in a withdraw reflex Define
Anna M. Lamb DO FACOFP OMED 2010 San Francisco
 Anna M. Lamb DO FACOFP OMED 2010 San Francisco When we started; Solo practitioner One LPN, One MA, One Receptionist 3000 Patients Where we are now: One physician, one PA One RN, One LPN, One MA, One Receptionist
Anna M. Lamb DO FACOFP OMED 2010 San Francisco When we started; Solo practitioner One LPN, One MA, One Receptionist 3000 Patients Where we are now: One physician, one PA One RN, One LPN, One MA, One Receptionist
Indirect Blood Pressure Measurement
 P r o c e d u r e s P r o C A R D I O L O G Y Peer Reviewed Indirect Blood Pressure Measurement Maintenance of appropriate systemic arterial blood pressure is vital for survival. Because many common situations
P r o c e d u r e s P r o C A R D I O L O G Y Peer Reviewed Indirect Blood Pressure Measurement Maintenance of appropriate systemic arterial blood pressure is vital for survival. Because many common situations
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6
 Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Our Human Body On-site student activities Years 5 6 Our Human Body On-site student activities: Years 5-6 Student activity (and record) sheets have been developed with alternative themes for students to
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation
 Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
Diagram showing Systemic and Portal Circulation The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System comprises of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, nodes and ducts. Lymph fluid is not blood plasma, it contains
A&P Basics. a. 1,6,3,4,5,2 b. 2,4,5,6,1,3 c. 1, 3,6,5,4,2 d. 3,1,5,6,4,2 e. 1,6,3,2,5,4
 1. Which of the following disciplines is MOST likely to concentrate on the structure and function of organelles? a. Gross anatomy b. Histology c. Cytology d. Embryology 2. Which of the following disciplines
1. Which of the following disciplines is MOST likely to concentrate on the structure and function of organelles? a. Gross anatomy b. Histology c. Cytology d. Embryology 2. Which of the following disciplines
CHEM 1406 BSA/BMI Measurement Laboratory (revised 01/03//06) BSA, Body Surface Area
 CHEM 1406 BSA/BMI (revised 01/03//06) BSA, Body Surface Area See pages 105-110 of dosage text for equations, calculations and adult nomogram See pages 270-273 of dosage calculation text for pediatric nomogram
CHEM 1406 BSA/BMI (revised 01/03//06) BSA, Body Surface Area See pages 105-110 of dosage text for equations, calculations and adult nomogram See pages 270-273 of dosage calculation text for pediatric nomogram
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
Blood Pressure and Your Health
 Blood Pressure and Your Health YOUR GUIDE TO: Blood pressure basics The danger of high blood pressure Steps to avoid or lower high blood pressure I started measuring my blood pressure at home after I learned
Blood Pressure and Your Health YOUR GUIDE TO: Blood pressure basics The danger of high blood pressure Steps to avoid or lower high blood pressure I started measuring my blood pressure at home after I learned
Record this information about the person who will be doing the exercise. a Would you describe yourself as physically fit? No
 Heart rate, breathing rate, physical fitness Student sheet 1 Personal record Record this information about the person who will be doing the exercise. a Would you describe yourself as physically fit? No
Heart rate, breathing rate, physical fitness Student sheet 1 Personal record Record this information about the person who will be doing the exercise. a Would you describe yourself as physically fit? No
Please read chapter 15, The Autonomic Nervous System, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class.
 Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Please read chapter 15,, complete this study guide, and study this material BEFORE coming to the first class. I. Introduction to the autonomic nervous system: Briefly describe the autonomic nervous system.
Practical class 3 THE HEART
 Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
Practical class 3 THE HEART OBJECTIVES By the time you have completed this assignment and any necessary further reading or study you should be able to:- 1. Describe the fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium,
To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes.
 Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Circulatory system. Basic function: To provide the body (cells) with oxygen, and remove CO 2. To provide the body (cells) with nutrients and remove wastes. Not all organisms have a circulatory system -
Laerdal Patient Monitor Help Page 1 June 14, 2012, Rev E
 Laerdal Patient Monitor Help Page 1 Using the Laerdal Patient Monitor The Laerdal Patient Monitor software is used to simulate a typical Patient Monitor found in hospitals and ambulances. It is made available
Laerdal Patient Monitor Help Page 1 Using the Laerdal Patient Monitor The Laerdal Patient Monitor software is used to simulate a typical Patient Monitor found in hospitals and ambulances. It is made available
Cardiorespiratory Fitness
 Cardiorespiratory Fitness Assessment Purpose Determine level of fitness & set goals Develop safe & effective exercise prescription Document improvements Motivation Provide info concerning health status
Cardiorespiratory Fitness Assessment Purpose Determine level of fitness & set goals Develop safe & effective exercise prescription Document improvements Motivation Provide info concerning health status
Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels of the body form a closed delivery system that begins and ends at the heart.
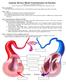 Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction The blood vessels
1.1.1 To include: Body language - facial expressions, gestures, eye contact and posture
 Unit 415 Delivering Personal Training Sessions Recommended Guided Learning Hours: 58 Credit value 9 QCF Unit Number J/600/9053 1. Understand how to instruct exercise during personal training sessions 1.1
Unit 415 Delivering Personal Training Sessions Recommended Guided Learning Hours: 58 Credit value 9 QCF Unit Number J/600/9053 1. Understand how to instruct exercise during personal training sessions 1.1
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE AND YOUR KIDNEYS
 HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE AND YOUR KIDNEYS www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney (NKF) Foundation offers guidelines and commentaries that help your healthcare
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE AND YOUR KIDNEYS www.kidney.org About the Information in this Booklet Did you know that the National Kidney (NKF) Foundation offers guidelines and commentaries that help your healthcare
CONSTRUCTION WORK and CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDERS
 Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
Connecticut Department of Public Health Environmental and Occupational Health Assessment Program 410 Capitol Avenue MS # 11OSP, PO Box 340308 Hartford, CT 06134-0308 (860) 509-7740 http://www.ct.gov/dph
PTA 210 PTA Technique. Vital Signs
 PTA 210 PTA Technique Vital Signs Review Last Lecture Why learn aseptic technique? 3 modes of infection transmission 3 levels of cleanliness Standard precautions (hand hygiene, PPE, respiratory hygiene,
PTA 210 PTA Technique Vital Signs Review Last Lecture Why learn aseptic technique? 3 modes of infection transmission 3 levels of cleanliness Standard precautions (hand hygiene, PPE, respiratory hygiene,
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack
 Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Year 2 Science: The Human Body Resource Pack Body Systems II Body Systems Digestion our bodies break down food and use Skeletal system the skeleton is made up of bones that support our the nutrients to
Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Information for patients Gina Wall Senior Physiotherapist
 Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis Information for patients Gina Wall Senior Physiotherapist What do Physiotherapists do? We conduct assessments by asking detailed questions about your symptoms, medical
Physiotherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis Information for patients Gina Wall Senior Physiotherapist What do Physiotherapists do? We conduct assessments by asking detailed questions about your symptoms, medical
Blood Pressure Assessment Program Screening Guidelines
 Blood Pressure Assessment Program Screening Guidelines Assessment Pre-Assessment Prior to/during assessment, explain to client the following: What is meant by high blood pressure; What are the effects
Blood Pressure Assessment Program Screening Guidelines Assessment Pre-Assessment Prior to/during assessment, explain to client the following: What is meant by high blood pressure; What are the effects
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology
 Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Level 2 Certificate in Fitness Instructing Unit 1: Anatomy and Physiology These questions have been compiled based on the information available for the above qualification and unit. This mock should be
Dr. Enas Elsayed. Brunnstrom Approach
 Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
Brunnstrom Approach Learning Objectives: By the end of this lab, the student will be able to: 1. Demonstrate different reflexes including stimulus and muscle tone response. 2. Demonstrate how to evoke
Chapter 13. The Nature of Somatic Reflexes
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
Chapter 13 The Nature of Somatic Reflexes Nature of Reflexes (1 of 3) A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in a gland or muscle tissue occur without our
What Are the Health Benefits Associated with Strength Training?
 Strength Training Program Necessary Basic information to obtain results. -- Most of the information contained in this handout is based on information gathered, researched, and presented by the National
Strength Training Program Necessary Basic information to obtain results. -- Most of the information contained in this handout is based on information gathered, researched, and presented by the National
Anatomi & Fysiologi 060301. The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) The circulation system transports; What the heart can do;
 The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
The cardiovascular system consists of; The cardiovascular system (chapter 20) Principles of Anatomy & Physiology 2009 Blood 2 separate pumps (heart) Many blood vessels with varying diameter and elasticity
Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate
 Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate Introduction Even before you were born, one of the first things your doctor did when you went for an office visit was listen to your heart. Your heart rate, the number of times
Project 4.2.1: Heart Rate Introduction Even before you were born, one of the first things your doctor did when you went for an office visit was listen to your heart. Your heart rate, the number of times
High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys
 High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys About 65 million Americans have high blood pressure, but as many as one third or three in 10 don't even know it. There are usually no signs or symptoms that your blood
High Blood Pressure and Your Kidneys About 65 million Americans have high blood pressure, but as many as one third or three in 10 don't even know it. There are usually no signs or symptoms that your blood
Fall Arrest System: A series of equipment components designed to stop the fall of individuals working at heights should they fall.
 Blog Back to Blog Listings Suspension Trauma 101 March 18, 2016 @ 10:37am Why are rescue at height plans so important? Why do we talk so much about knowing what to do when sh!t hits the fan? One of the
Blog Back to Blog Listings Suspension Trauma 101 March 18, 2016 @ 10:37am Why are rescue at height plans so important? Why do we talk so much about knowing what to do when sh!t hits the fan? One of the
Breathing and Holding Your Breath copyright, 2005, Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania 1
 Breathing and Holding Your Breath copyright, 2005, Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania 1 Introduction Everybody breathes all day, every day. Why?
Breathing and Holding Your Breath copyright, 2005, Dr. Ingrid Waldron and Jennifer Doherty, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania 1 Introduction Everybody breathes all day, every day. Why?
STAGE 5: Interacting Systems
 Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
Stage 5: In this stage, students will explore how systems interact with each other to maintain healthy and optimal body functioning, including how the body responds to changes in the environment such as
The EasySense unit can detect that the Smart Q Heart Rate Sensor is connected and the range it is set to.
 Heart Rate Sensor Heart Rate Sensor (Product No PC-3147) Pulse rate Range: 0 to 200 bpm Resolution: 1 bpm Waveform Range: -2000 to 2000 mv Resolution: 1 mv Introduction The Smart Q Heart Rate Sensor monitors
Heart Rate Sensor Heart Rate Sensor (Product No PC-3147) Pulse rate Range: 0 to 200 bpm Resolution: 1 bpm Waveform Range: -2000 to 2000 mv Resolution: 1 mv Introduction The Smart Q Heart Rate Sensor monitors
