DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to
|
|
|
- Peregrine Wilson
- 7 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
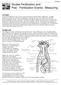
1 Flower Anatomy DID YOU KNOW that the plants most important to agriculture all produce flowers? Every major food crop is a flowering plant. We do not think about the flowers of wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans. Maybe it is because they are not as showy as the flowers of horticultural crops. Objective: Describe the parts of flowers and their functions, the types of flowers, and inflorescences. Key Terms: anther bract calyx carpel catkin complete flower corolla corymb cymes determinate dioecious filament head imperfect flower incomplete flower indeterminate inflorescence monoecious ovary panicle pedicel peduncle perfect flower perianth petals pistil pistillate pollen raceme receptacle sepals spadix spike stamen staminate stigma style tepals umbel Flowers Flowers are the most obvious part of many plants. In some cases, they are extremely showy. In other cases, they are not easily seen. Whether they are showy or not, the purpose of a flower is for a plant to be able to reproduce sexually. Page 1
2 FLOWER PARTS Flowers are made of many intricate and important parts. Most flowers contain male and female parts. Male Flower Parts The male part of the flower is called the stamen. It is made of the stalk-like filament that holds up the sack-like anther. The anther contains pollen, the grain released by flowers, which contains the sperm. Flowers that have male parts and no female parts are called staminate. Female Flower Parts The female part of the flower is called the pistil. The carpel is the basic unit of the female reproductive organ, and a pistil may consist of one or more carpels. The carpel is composed of a stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is a sticky tissue at the end of the pistil that is receptive to pollen. Located below the stigma is a rod-shaped middle part called the style and a swollen base (called the ovary) that contains eggs. Once the pollen reaches the stigma, it forms a pollen tube down through the style to the ovary where sperm is deposited. Flowers that have female parts and no male parts are called pistillate. Other Parts Pollen grains (contain sperm) Stigma Flowers have parts that are not classified as male or female. The petals, usually colorful leaf-like structures, attract animals and insects. Sometimes the petals are fused together and form a structure called a corolla. Beneath the petals are green leaf-like structures called sepals. The sepals support the petals and protect the flower before it opens; the sepals may be fused together to form a calyx. Together, the petals and the sepals are called the perianth. With some plants, a clear distinction between petals and sepals cannot be made. In these cases, the parts of the perianth are called tepals. Tulip flowers and many monocots have tepals. Some plants have modified leaves at the base of a flower or floral inflorescence called a bract. The bracts may be green, but in some cases (e.g., the poinsettia) the bracts are colorful. The flower stem is referred to as the pedicel, and the portion of the pedicel that holds the flower parts is the receptacle. Ovule Ovary Pollination Egg cell FIGURE 1. The transfer of pollen to the stigma. Style Page 2
3 TYPES OF FLOWERS Flowers come in many shapes, sizes, and colors. Not all of them have all of the structures mentioned previously. Plants may produce flowers that are perfect or imperfect. A flower with male and female parts is called a perfect flower. A flower that is missing male or female parts is an imperfect flower. Petal Anther Filament Stamen Pistil Stigma Style Sepal Ovary Receptacle Pedicel FIGURE 2. Parts of a perfect flower. Plants may have flowers that are complete or incomplete. If a flower has sepals, petals, pistils, and stamens, it is a complete flower. If a flower is missing one of those, it is an incomplete flower. Imperfect flowers are always incomplete, but incomplete flowers may or may not be imperfect. Plants may be classified as monoecious or dioecious. Monoecious plants have male and female flowers on one plant. Corn, cucumbers, and oaks are monecious. Dioecious plants have male and female flowers on separate plants. Soybeans, asparagus, kiwi, and hemp are examples of dioecious plants. A good way to tell the difference between a monocot and a dicot is to look closely at the flowers. Monocots have flowers with flower parts in multiples of three, and dicots have flowers with flower parts in multiples of four or five. TYPES OF INFLORESCENCES Flowers are borne on plant stems in one of two ways. Some plants have solitary flowers, such as the tulip, narcissus, and rose. Other plants have flower clusters, known as an inflorescence, which is the stem s branching system. The main stem of an inflorescence is known as the peduncle. Pedicels that branch from the peduncle support individual flowers. Page 3
4 Types of inflorescence can be classified by the sequence of flowering within the flower cluster. If the first flower to open is at the apex of the stem and the progression of flowering is downward or outward, the inflorescence is said to be determinate. Some examples of determinate flowers include liatris, kalanchoe, and the African violet. If the last flower to open is terminal on the main axis and the progression of flowering is inward or upward, the inflorescence is indeterminate. Indeterminate types of inflorescences are racemes, corymbs, heads, and umbels. Freesia, cineraria, snapdragon, and stock have indeterminate inflorescence. There a variety of inflorescence types. Some common types are cyme, spike, raceme, panicle, corymb, umbel, spadix, catkin, and head. The spike and the panicle types of inflorescence are the most common among monocot plants. Cymes take on several forms, but cymes are usually flat-topped inflorescences. Dichasium cymes bear terminal flowers on peduncles with a pair of branches that produce lateral flowers. Cymes may be simple or compound. Monochasium cymes have terminal flowers, and below it, monochasium cymes have one branch that produces a single lateral flower. The terminal flower is the oldest. Tomatoes, potatoes, and alstroemerias are cymes. Baby s breath is a compound dichasium cyme. Raceme Panicle Cyme Spike Spadix Corymb Umbel Catkin Head FIGURE 3. The arrangement of flowers on a stem. Page 4
5 A spike is an elongated inflorescence with a central axis where sessile flowers are attached. Wheat, barley, ryegrass, wheatgrass, gladioli, and liatris are spike inflorescences. A raceme is an elongated inflorescence with a central axis where simple pedicels of more or less equal length are attached. Examples of racemes include foxtail millet, snapdragon, delphinium, Scotch broom, and stock. A panicle is an elongated inflorescence with a central axis where there are branches that are themselves branched. Rice, oats, Sudan grass, Kentucky bluegrass, tall fescue, timothy, grain sorghum, astilbe, and begonia have a panicle inflorescence. A corymb is a short and broad, flat-topped indeterminate inflorescence with a main vertical axis and pedicels or branches of unequal length. The outer flowers open first. Yarrow is an example of a corymb. An umbel is an inflorescence with several branches arising from a common point. A simple umbel consists of flowers with single pedicels. Compound umbels have secondary branching in the form of pedicels at the end of a ray. Queen Anne s lace and amaryllis have umbels. A spadix is a spike with a thickened, fleshy axis, usually enveloped by a showy bract called a spathe. Floriculture crops with a spadix include the calla lily and anthurium. A catkin is a spike, raceme, or cyme composed of unisexual flowers without petals and falling as a unit. Catkins are found on willows, alders, oaks, and birch. A head is a rounded or flat-topped cluster of sessile flowers. Head inflorescences of the aster family resemble single flowers. These consist of centrally grouped flowers called disc flowers encircled by ray flowers. Some common plants that have a head inflorescence are gerbera daisy, chrysanthemum, sunflower, marigold, dahlia, strawflowers, and cineraria. Summary: The purpose of a flower is for a plant to be able to reproduce sexually. The male part of the flower (stamen) consists of a filament and an anther. The anther contains pollen. The female part of the flower (pistil) is composed of the stigma, style, and ovary. Other flower parts include petals, sepals, bracts, pedicels, and receptacles. Plants may produce flowers that are perfect or imperfect and may have flowers that are complete or incomplete. Plants may be classified as monoecious or dioecious. Monocots have flowers with flower parts in multiples of three. Dicots have flowers with flower parts in multiples of four or five. Flowers may be borne solitary, or they may be in flower clusters (inflorescence). An inflorescence may be determinate or indeterminate. Some common inflorescence types are cyme, spike, raceme, panicle, corymb, umbel, spadix, catkin, and head. Page 5
6 Checking Your Knowledge: 1. What is the purpose of a flower? 2. What are the male and female parts of a flower? 3. What are complete, incomplete, perfect, and imperfect flowers? 4. How do monocot flowers differ from dicot flowers? 5. What is an inflorescence? Expanding Your Knowledge: Obtain flowers from different plants. Using a forceps and scalpel, carefully dissect the flowers. Identify the floral parts, and then count the floral parts. Use a magnifying lens or microscope for a closer look at the structures. Web Links: The Basics of Flowers Corn (Maize) Flowers Flowers Flowers: Features of Flowering Plants Page 6
Dissect a Flower. Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens
 Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Huntington Library, Art Collections, and Botanical Gardens Dissect a Flower Overview Students dissect an Alstroemeria or similar flower to familiarize themselves with the basic parts of a flower. They
Biology 213 Angiosperms. Introduction
 Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Biology 213 Angiosperms Introduction The flowering plants, the angiosperms, are the most recent plants to evolve and quickly became the dominant plant life on this planet. They are also the most diverse
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) Key Concepts What are the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms? How does pollination
Plant Reproduction. 2. Evolutionarily, floral parts are modified A. stems B. leaves C. roots D. stolons E. suberins
 Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Plant Reproduction 1. Angiosperms use temporary reproductive structures that are not present in any other group of plants. These structures are called A. cones B. carpels C. receptacles D. flowers E. seeds
Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616)
 Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
Chapter 24 Reproduction of Seed Plants Section 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers (pages 609 616) This section describes the reproductive structures of gymnosperms and angiosperms. It also explains
What's in a Flower. Ages: 8 to 12. Contributor: Susan Jaquette, Cornell Plantations volunteer
 Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
Ages: 8 to 12 What's in a Flower Contributor: Susan Jauette, Cornell Plantations volunteer Main idea: Flowers are composed of several distinct parts, each of which plays an important role in nature. Objective:
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview Objectives bold Part I Floral Anatomy . calyx sepals corolla, petals, stamens, filament
 Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and Seeds Overview In this lab you will observe assorted flowers, fruits, and seeds to better understand the unique adaptations of and the life cycle of angiosperms.
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS
 PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
PLANT BITS 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS-NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 11: PLANTS There are four main parts to a plant. They are the root, stem, leaf and flower. Each part has an important task to do in the life of
Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds
 Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds Objectives of the Lab: 1) Explore the structure and function of flowering plant reproductive organs from flower development through fruit maturation. 2) Examine
Plant Anatomy Lab 2: Flowers, Fruits and Seeds Objectives of the Lab: 1) Explore the structure and function of flowering plant reproductive organs from flower development through fruit maturation. 2) Examine
Parts of a Flower and Pollination
 Science Unit: Lesson 3: Soils, Plants, and First Nations Parts of a Flower and Pollination School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Britannia Elementary School, Vancouver School District Developed by: Catriona
Science Unit: Lesson 3: Soils, Plants, and First Nations Parts of a Flower and Pollination School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Britannia Elementary School, Vancouver School District Developed by: Catriona
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions Sepals Anther Stamens (male) Filament Stigma Pistil Style (female) Ovary Petals sepals petals stamens pistil
 Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
Flower Model: Teacher Instructions In order to better understand the reproductive cycle of a flower, take a look at some flowers and note the male and female parts. Most flowers are different; some have
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
 Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
Biology 172L General Biology Lab II Lab 03: Plant Life Cycles and Adaptations II: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Introduction Vascular seed-bearing plants, such as gymnosperms (cone-bearing plants) and angiosperms
version if desired, and Teacher Preparation Notes are available at http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/sci_edu/waldron/.
 Using a Dichotomous Key to Identify Flowers (and the murderer) Adapted and Excerpted from Constructing a Dichotomous Key by Margaret Bankhead of Robert A. Black Magnet School, Making a Dichotomous Key
Using a Dichotomous Key to Identify Flowers (and the murderer) Adapted and Excerpted from Constructing a Dichotomous Key by Margaret Bankhead of Robert A. Black Magnet School, Making a Dichotomous Key
Vascular Plants Bryophytes. Seedless Plants
 plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
plant reproduction The Plants Vascular Plants Bryophytes Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses lack roots and specialized tissues grow in moist, shady areas All have sieve cells and tracheids Seedless Plants Ferns
Introducing the parts of a flower
 Parts of a flower Teacher Guidance Introducing the parts of a flower pollen petal stamen anther filament stigma style ovary carpel ovule sepal stem Figure 2. A half flower, showing the basic parts: sepal,
Parts of a flower Teacher Guidance Introducing the parts of a flower pollen petal stamen anther filament stigma style ovary carpel ovule sepal stem Figure 2. A half flower, showing the basic parts: sepal,
Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land,
 24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
24 1 Reproduction With Cones and Flowers Seed plants are well adapted to the demands of life on land, especially in how they reproduce. The gametes of seedless plants, such as ferns and mosses, need water
Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth?
 1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
1 Expt. How do flowering plants do it without flagella? The journey to find an egg. What causes pollen grain germination and tube growth? File: F12-07_pollen Modified from E. Moctezuma & others for BSCI
Chapter 38: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
 Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Name Period Concept 38.1 Flowers, double fertilization, and fruits are unique features of the angiosperm life cycle This may be a good time for you to go back to Chapter 29 and review alternation of generation
Can you see the difference between wind pollinated and insect pollinated flowers?
 Can you see the difference between wind pollinated and insect pollinated flowers? Age of Students 10 14 years Duration 1 hour Summary Pollination is a very effective factor in the evolution of plants and
Can you see the difference between wind pollinated and insect pollinated flowers? Age of Students 10 14 years Duration 1 hour Summary Pollination is a very effective factor in the evolution of plants and
Plant Parts. Background Information
 Purpose The purpose of this lesson is for students to learn the six basic plant parts and their functions. Time Teacher Preparation: 30 minutes Student Activity: 60 minutes Materials For the teacher demonstration:
Purpose The purpose of this lesson is for students to learn the six basic plant parts and their functions. Time Teacher Preparation: 30 minutes Student Activity: 60 minutes Materials For the teacher demonstration:
Topic 26. The Angiosperms
 1 Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant
1 Topic 26. The Angiosperms Domain Eukarya Kingdom Plantae The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant
Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator
 Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator Understanding the role and structure of a flower Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms. They are not simple structures,
Lab 9: The Reproduction of Angiosperms and the Role of the Pollinator Understanding the role and structure of a flower Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms. They are not simple structures,
Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring
 WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
WFP062298 Double Fertilization and Post - Fertilization Events: Measuring Concepts In plants fertilization is the event in sexual reproduction which follows pollination. In higher plants, two sperm are
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice
 10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
10B Plant Systems Guided Practice Reproduction Station 1 1. Observe Plant A. Locate the following parts of the flower: stamen, stigma, style, ovary. 2. Draw and label the parts of a flower (listed above)
8. Study the cladogram underline the derived characteristics and circle the organisms that developed from them.
 Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Answer the questions as you go through the power point, there are also paragraphs to read where you will need to hi-lite or underline as you read. 1. What are the
Robert G. Anderson, Extension Floriculture Specialist
 HortFacts 12-03 Production Statistics for Greenhouse Crops In Kentucky Robert G. Anderson, Extension Floriculture Specialist The statistics for greenhouse crop production in Kentucky offer a historical
HortFacts 12-03 Production Statistics for Greenhouse Crops In Kentucky Robert G. Anderson, Extension Floriculture Specialist The statistics for greenhouse crop production in Kentucky offer a historical
Chapter 3. Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction. Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos
 BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 13 Chapter 3 Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos Objectives Angiosperms. Understand alternation of generations.
BOT 3015L (Sherdan/Outlaw/Aghoram); Page 1 of 13 Chapter 3 Biology of Flowering Plants: Reproduction Gametophytes, Fruits, Seeds, and Embryos Objectives Angiosperms. Understand alternation of generations.
FORMS AND FUNCTIONS OF FLOWERS AND FOLIAGES USED IN FLORAL DESIGNS
 FLORAL IDENTIFICATION 8943-A FORMS AND FUNCTIONS OF FLOWERS AND FOLIAGES USED IN FLORAL DESIGNS You have been asked to design a floral arrangement for a customer. The customer has indicated the type of
FLORAL IDENTIFICATION 8943-A FORMS AND FUNCTIONS OF FLOWERS AND FOLIAGES USED IN FLORAL DESIGNS You have been asked to design a floral arrangement for a customer. The customer has indicated the type of
Bees and Flowers Partners in Pollination
 Bees and Flowers Partners in Pollination - Local Plant Community Investigation - Flower Dissection - Flower Collections - Build a Flower Build a Bee - Bee Collections - Making Pollen Slides Rural Science
Bees and Flowers Partners in Pollination - Local Plant Community Investigation - Flower Dissection - Flower Collections - Build a Flower Build a Bee - Bee Collections - Making Pollen Slides Rural Science
Geraniaceae geranium family
 Geraniaceae geranium family Long-known for the prized ornamentals and house plants obtained from South African species. Nova Scotia hosts two genera and a half-dozen species. Most are herbs with lobed
Geraniaceae geranium family Long-known for the prized ornamentals and house plants obtained from South African species. Nova Scotia hosts two genera and a half-dozen species. Most are herbs with lobed
most modern cladograms have Amborella and water lilies as a sister group (or groups) to the rest of the angiosperms
 Topic 7: Angiosperms, Flowers and Pollination Syndromes Phylum Anthophyta (Chs. 30, 38) Ι. Phylum Anthophyta flowering plants (antho flower) A. also known as angiosperms (angeion vessel or enclosure; sperma
Topic 7: Angiosperms, Flowers and Pollination Syndromes Phylum Anthophyta (Chs. 30, 38) Ι. Phylum Anthophyta flowering plants (antho flower) A. also known as angiosperms (angeion vessel or enclosure; sperma
The Parts of a Flower
 The Parts of a Flower Developed by Steve Cooke. The webaddress for this activity is: Last updated 7th November 2008 Teacher notes You might need to enlarge the diagram and the labels to A3 to make them
The Parts of a Flower Developed by Steve Cooke. The webaddress for this activity is: Last updated 7th November 2008 Teacher notes You might need to enlarge the diagram and the labels to A3 to make them
Kansas State University Agricultural Experiment Station and Cooperative Extension Service 1
 Kansas State University Agricultural Experiment Station and Cooperative Extension Service 1 2 Preparing Cut Flowers for Exhibit Exhibiting flowers in shows and fairs can be fun. You and others will enjoy
Kansas State University Agricultural Experiment Station and Cooperative Extension Service 1 2 Preparing Cut Flowers for Exhibit Exhibiting flowers in shows and fairs can be fun. You and others will enjoy
IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions. Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9. Chapter 6 Plant structure and function
 1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
1 IGCSE and GCSE Biology. Answers to questions Section 2. Flowering Plants. Chapters 6-9 Chapter 6 Plant structure and function Page 54 1. a Epidermis. Helps maintain shape, reduces evaporation, resists
Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the phylum Magnoliophyta. Angiosperms - Flowering Plants. Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms. Fungi?
 Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the phylum Magnoliophyta The Importance of Plant Collections Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants
Angiosperms or Flowering Plants the phylum Magnoliophyta The Importance of Plant Collections Land Plant Evolution: Algae to Angiosperms The greatest adaptive radiation... is the largest radiation of plants
Plant Growth & Development. Growth Stages. Differences in the Developmental Mechanisms of Plants and Animals. Development
 Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
Plant Growth & Development Plant body is unable to move. To survive and grow, plants must be able to alter its growth, development and physiology. Plants are able to produce complex, yet variable forms
PLANT DIVERSITY. EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae
 PLANT DIVERSITY 1 EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae Spores Leaf Ancestral green algae Flagellated sperm for reproduction Plenty of water Nutrients and CO 2 diffuse into tissues Holdfast Flagellated
PLANT DIVERSITY 1 EVOLUTION OF LAND PLANTS KINGDOM: Plantae Spores Leaf Ancestral green algae Flagellated sperm for reproduction Plenty of water Nutrients and CO 2 diffuse into tissues Holdfast Flagellated
2. Fill in the blank. The of a cell is like a leader, directing and telling the different parts of the cell what to do.
 1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
1. Plant and animal cells have some similarities as well as differences. What is one thing that plant and animal cells have in common? A. cell wall B. chlorophyll C. nucleus D. chloroplasts 2. Fill in
THE EARLY ITALIANS were the first to have
 Designing Vase Arrangements THE EARLY ITALIANS were the first to have arranged flowers in vases. They harvested flowers from their gardens to create the displays. Vase arrangements are a relatively easy
Designing Vase Arrangements THE EARLY ITALIANS were the first to have arranged flowers in vases. They harvested flowers from their gardens to create the displays. Vase arrangements are a relatively easy
And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All. Evolution of Plants
 And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All Around Evolution of Plants Adapting to Terrestrial Living Plants are complex multicellular organisms that are autotrophs they feed
And the Green Grass Grew All Around and Around, the Green Grass Grew All Around Evolution of Plants Adapting to Terrestrial Living Plants are complex multicellular organisms that are autotrophs they feed
II. Vegetative Propagation. Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting
 II. Vegetative Propagation Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting a. Use of Apomictic Seeds Apomixis = Development of seeds
II. Vegetative Propagation Use of Apomictic Seeds Use of Specialized Vegetative Structures Adventitious Root Induction (Cuttings) Layering Grafting a. Use of Apomictic Seeds Apomixis = Development of seeds
Flowers; Seeds enclosed in fruit
 Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Name Class Date Chapter 22 Plant Diversity Section Review 22-1 Reviewing Key Concepts Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following questions. 1. Describe the main characteristics of plants.
Tips on Flower Conditioning
 Tips on Flower Conditioning AGAPANTHUS - Cut 1" from the stems and place in 10"- 12" of cool water with amount of floral preservative. the correct ALLIUM Add a few drops of Bleach to the water to eliminate
Tips on Flower Conditioning AGAPANTHUS - Cut 1" from the stems and place in 10"- 12" of cool water with amount of floral preservative. the correct ALLIUM Add a few drops of Bleach to the water to eliminate
nucleus cytoplasm membrane wall A cell is the smallest unit that makes up living and nonliving things.
 1 In nature there are living things and nonliving things. Living things depend on three basic life processes: nutrition, sensitivity and reproduction. Living things are made up of cells. 1. Match the two
1 In nature there are living things and nonliving things. Living things depend on three basic life processes: nutrition, sensitivity and reproduction. Living things are made up of cells. 1. Match the two
Plants for primary pupils
 Plants for primary pupils Part 1: Parts of a flower Science and Plants for Schools (SAPS), an initiative launched in 1990, works with teachers to: develop new resources that support the teaching of plant
Plants for primary pupils Part 1: Parts of a flower Science and Plants for Schools (SAPS), an initiative launched in 1990, works with teachers to: develop new resources that support the teaching of plant
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout
 PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Name: TA and Section time Welcome to UCSC Greenhouses. This sheet explains a few botanical facts about plant reproduction that will help you through the display and handout.
Petite Collection. (3) mini red gerbera daisies and (2) stems spray roses with seasonal accents, hand tied with matching ribbon.
 FLORAL BROCHURE Petite Collection 1 (3) mini red gerbera daisies and (2) stems spray roses with seasonal Bouquet $30 2 3 (3) mini pink gerbera daisies and (2) stems spray roses with seasonal Bouquet $30
FLORAL BROCHURE Petite Collection 1 (3) mini red gerbera daisies and (2) stems spray roses with seasonal Bouquet $30 2 3 (3) mini pink gerbera daisies and (2) stems spray roses with seasonal Bouquet $30
Pollination and fertilisation
 Pollination and fertilisation Teacher Guidance Introducing pollination and fertilisation Pollination is the transfer of pollen, from the stamens to the stigma. The pollen is often carried by insects and
Pollination and fertilisation Teacher Guidance Introducing pollination and fertilisation Pollination is the transfer of pollen, from the stamens to the stigma. The pollen is often carried by insects and
Magnoliophyta - Angiosperms
 Magnoliophyta - Angiosperms Survey of Angiosperms using APG system Amborella trichopoda Magnoliophyta - Angiosperms Survey of Angiosperms using APG system What is the APG classification? Basal angiosperms
Magnoliophyta - Angiosperms Survey of Angiosperms using APG system Amborella trichopoda Magnoliophyta - Angiosperms Survey of Angiosperms using APG system What is the APG classification? Basal angiosperms
How Plants Are Identified
 3 How Plants Are Identified T he easiest method, and the one probably used the most often for learning the names of the plants of a particular location or region, or just the name of a particular plant,
3 How Plants Are Identified T he easiest method, and the one probably used the most often for learning the names of the plants of a particular location or region, or just the name of a particular plant,
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development. Chapter 35
 Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Plant Structure, Growth, and Development Chapter 35 PLANTS developmental plasticity = ability of plant to alter form to respond to environment Biological heirarchy Cell basic unit of life Tissue group
Introduction to Design Techniques
 Introduction to Design Techniques DESIGN TECHNIQUES Now that you have a good understanding of the elements and principles of design, the next step is to learn the techniques of floral design. When professional
Introduction to Design Techniques DESIGN TECHNIQUES Now that you have a good understanding of the elements and principles of design, the next step is to learn the techniques of floral design. When professional
(1) Hybrid Cucumber Seed Production. Samuel Contreras Departamento de Ciencias Vegetales Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Santiago, Chile
 (1) Hybrid Cucumber Seed Production Samuel Contreras Departamento de Ciencias Vegetales Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Santiago, Chile (2) Introduction Cucurbitaceae family The Cucurbitaceae
(1) Hybrid Cucumber Seed Production Samuel Contreras Departamento de Ciencias Vegetales Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Santiago, Chile (2) Introduction Cucurbitaceae family The Cucurbitaceae
3D Pumpkins Illinois Ag in the Classroom. 3D Pumpkins Illinois Ag in the Classroom
 Materials orange construction paper 2 paper fasteners for each pumpkin green construction paper for vines paper punch scissors 3D Pumpkins Illinois Ag in the Classroom Instructions Cut 3 strips about 1
Materials orange construction paper 2 paper fasteners for each pumpkin green construction paper for vines paper punch scissors 3D Pumpkins Illinois Ag in the Classroom Instructions Cut 3 strips about 1
ennessee is one of the top livestock producing states in the country. Much of the livestock in Tennessee is raised by smaller-scale, parttime
 T ennessee is one of the top livestock producing states in the country. Much of the livestock in Tennessee is raised by smaller-scale, parttime producers. No matter what size operation, good pasture management
T ennessee is one of the top livestock producing states in the country. Much of the livestock in Tennessee is raised by smaller-scale, parttime producers. No matter what size operation, good pasture management
Floral Biology and Pollination Biology of Cannabis sativa L.
 The International Journal of Plant Reproductive Biology 2(2) pp. 191-195, 2010 Floral Biology and Pollination Biology of Cannabis sativa L. Anita Rana and Namrta Choudhary 1 1 Academy of Life Sciences,
The International Journal of Plant Reproductive Biology 2(2) pp. 191-195, 2010 Floral Biology and Pollination Biology of Cannabis sativa L. Anita Rana and Namrta Choudhary 1 1 Academy of Life Sciences,
What Do Plants Need to Grow?
 Lesson #401 What Do Plants Need to Grow? Grades 2-4 Editors Mandi Bottoms Shaney Emerson Robin Satnick 2300 River Plaza Drive Sacramento, CA 95833 (916) 561-5625 (800) 700-2482 www.learnaboutag.org California
Lesson #401 What Do Plants Need to Grow? Grades 2-4 Editors Mandi Bottoms Shaney Emerson Robin Satnick 2300 River Plaza Drive Sacramento, CA 95833 (916) 561-5625 (800) 700-2482 www.learnaboutag.org California
2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents?
 2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents? offspring Offspring are young plants and animals. Offspring
2 nd Grade Science Unit B: Life Sciences Chapter 3: Plants and Animals in Their Environment Lesson 1: How are plants and animals like their parents? offspring Offspring are young plants and animals. Offspring
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers
 Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
Writing a Dichotomous Key to Wildflowers Objectives: 1. Understand how to use and make dichotomous keys. 2. Understand common terminology of plant morphology. 3. Learn to recognize some fall wildflowers.
Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education. April, 2006
 Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education April, 2006 Participant in Research Experience for Teachers (RET) Workshop at Western Michigan University 2005-06 Academic Year But
Beth Campbell Western Michigan University Senior, College of Education April, 2006 Participant in Research Experience for Teachers (RET) Workshop at Western Michigan University 2005-06 Academic Year But
The remarkable evolutionary success of flowering plants
 42 Plant Reproduction Concept Outline 42.1 Angiosperms have been incredibly successful, in part, because of their reproductive strategies. Rise of the Flowering Plants. Animal and wind dispersal of pollen
42 Plant Reproduction Concept Outline 42.1 Angiosperms have been incredibly successful, in part, because of their reproductive strategies. Rise of the Flowering Plants. Animal and wind dispersal of pollen
Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My!
 Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My! Objectives 1. The student will be able to identify parts of a plant. 2. The student will understand the function of plant parts. Grade Level 1-3 4-6 TEKS: 1.6B, 2.6C;
Roots and Stems and Leaves, Oh My! Objectives 1. The student will be able to identify parts of a plant. 2. The student will understand the function of plant parts. Grade Level 1-3 4-6 TEKS: 1.6B, 2.6C;
Pistillate Flower Abscission in Turkish Walnut Cultivars and Its Reduction by AVG
 Pistillate Flower Abscission in Turkish Walnut Cultivars and Its Reduction by AVG Ayşe Gün aysegun2000@hotmail.com Veli Erdoğan Ankara University, Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Horticulture Ankara,
Pistillate Flower Abscission in Turkish Walnut Cultivars and Its Reduction by AVG Ayşe Gün aysegun2000@hotmail.com Veli Erdoğan Ankara University, Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Horticulture Ankara,
Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II
 Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Text 2014 Andrea Garrison Plant Diversity II 2 Plant Classification Bryophytes
Kingdom Plantae Plant Diversity II Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Text 2014 Andrea Garrison Plant Diversity II 2 Plant Classification Bryophytes
Common Name: AMERICAN BARBERRY. Scientific Name: Berberis canadensis Miller. Other Commonly Used Names: none. Previously Used Scientific Names: none
 Common Name: AMERICAN BARBERRY Scientific Name: Berberis canadensis Miller Other Commonly Used Names: none Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Berberidaceae (barberry) Rarity Ranks: G3/S1 State
Common Name: AMERICAN BARBERRY Scientific Name: Berberis canadensis Miller Other Commonly Used Names: none Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Berberidaceae (barberry) Rarity Ranks: G3/S1 State
AG. 335 FLORAL DESIGN AND MARKETING
 AG. 335 FLORAL DESIGN AND MARKETING COURSE DESCRIPTION: A course designed to develop skills in floriculture and the techniques used to develop and complete a variety of retail items normally sold in a
AG. 335 FLORAL DESIGN AND MARKETING COURSE DESCRIPTION: A course designed to develop skills in floriculture and the techniques used to develop and complete a variety of retail items normally sold in a
Kindergarten Plants and Plant Growth Assessment
 Kindergarten Plants and Plant Growth Assessment 1a. Circle one thing that plants need to grow: 1b. Circle all of the things that plants need to grow: 1c. Name three things that plants need to grow: 2a.
Kindergarten Plants and Plant Growth Assessment 1a. Circle one thing that plants need to grow: 1b. Circle all of the things that plants need to grow: 1c. Name three things that plants need to grow: 2a.
3MNN Behavioral Outcomes Eat fruits and veggies, etc. SNAP-Education Nutrition Messages Eat fruits and veggies as healthy snacks, MyPyramid servings
 DRAFT 1 Lesson Plan Title: Phenomenal Plant Parts Grade Level: 3 Content Area: Science Setting: School garden, or classroom Instructional Time: 60 to 90 minutes Grade Level Expectations: Life Science L.OL.E3:
DRAFT 1 Lesson Plan Title: Phenomenal Plant Parts Grade Level: 3 Content Area: Science Setting: School garden, or classroom Instructional Time: 60 to 90 minutes Grade Level Expectations: Life Science L.OL.E3:
Cannabis-A Review. Written by Cannabis Training University (CTU) All rights reserved
 Cannabis-A Review Written by Cannabis Training University (CTU) All rights reserved Contents Uses of Cannabis:... 3 Varieties of Cannabis:... 7 Cannabis Sativa-... 7 Cannabis Indica-... 7 Cannabis Ruderalis-...
Cannabis-A Review Written by Cannabis Training University (CTU) All rights reserved Contents Uses of Cannabis:... 3 Varieties of Cannabis:... 7 Cannabis Sativa-... 7 Cannabis Indica-... 7 Cannabis Ruderalis-...
Fungi and plants practice
 Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Name: Period: Date: Fungi and plants practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the
Living things: Cells Living things:
 unit 1 The cell is the smallest unit capable of living an independent existence. Most cells contain a nucleus which controls the way they work; the only cells in the human body with no nuclei are the red
unit 1 The cell is the smallest unit capable of living an independent existence. Most cells contain a nucleus which controls the way they work; the only cells in the human body with no nuclei are the red
Honey Bee Background Information
 Honey Bee Background Information Honey bees are very important. Honey bees are the strongest link in the chain between the people who grow the food and the people who eat the food. Without honey bee pollination,
Honey Bee Background Information Honey bees are very important. Honey bees are the strongest link in the chain between the people who grow the food and the people who eat the food. Without honey bee pollination,
Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort
 The Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort Name Help Sheets: Things Plants Need There are certain things that every living thing needs in order to live and grow. Just like you, plants need
The Virginia Gardener http://www.hort.vt.edu/envirohort Name Help Sheets: Things Plants Need There are certain things that every living thing needs in order to live and grow. Just like you, plants need
PEACH TREE PHYSIOLOGY
 PEACH TREE PHYSIOLOGY David W. Lockwood Department of Plant Sciences & Landscape Systems University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN 37996 D. C. Coston Agricultural Experiment Station Oklahoma State University
PEACH TREE PHYSIOLOGY David W. Lockwood Department of Plant Sciences & Landscape Systems University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN 37996 D. C. Coston Agricultural Experiment Station Oklahoma State University
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
Introduction to Plants Unity and Diversity of Life Q: What are the five main groups of plants, and how have four of these groups adapted to life on land? 22.1 What are of plants? WHAT I KNOW SAMPLE ANSWER:
Tomato and Pepper. Samuel Contreras Departamento de Ciencias Vegetales Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Santiago Chile scontree@uc.
 (1) Hybrid seed production in vegetables (2) Introduction Solanaceae Family Tomato and Pepper Samuel Contreras Departamento de Ciencias Vegetales Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Santiago Chile
(1) Hybrid seed production in vegetables (2) Introduction Solanaceae Family Tomato and Pepper Samuel Contreras Departamento de Ciencias Vegetales Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Santiago Chile
Plant Nomenclature and ID
 Beginning Master Gardener Training January 15, 2013 Plant Nomenclature and ID Lydiae claytonii Horticulture Extension Agent lclayton2@alaska.edu Plant systematics and taxonomy Why classify? History of
Beginning Master Gardener Training January 15, 2013 Plant Nomenclature and ID Lydiae claytonii Horticulture Extension Agent lclayton2@alaska.edu Plant systematics and taxonomy Why classify? History of
Reproductive System. from the Human Body System Series. catalog # 3322. Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING
 Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Reproductive System from the Human Body System Series catalog # 3322 Published & Distributed by AGC/UNITED LEARNING 1560 Sherman Avenue Suite 100 Evanston, IL 60201 1-800-323-9084 24-Hour Fax No. 847-328-6706
Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones
 Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
Biology SAT II Review Sheet Plants Plant Classification, Structure, Growth and Hormones Multicellular autotrophs (organisms that use the energy of inorganic materials to produce organic materials) Utilize
EVERY LIVING THING has a number of
 Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Anatomy and Physiology of Animal Reproductive Systems EVERY LIVING THING has a number of organ systems operating to perform specific functions. If you were to examine one of these systems, you would observe
Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY
 Plant Diversity Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY Answer Key SECTION 20.1. ORIGINS OF PLANT LIFE 1. eukaryotic, photosynthetic, same types of chlorophyll, starch as storage product, cellulose in cell walls
Plant Diversity Unit 10- Plants /Study Guide KEY Answer Key SECTION 20.1. ORIGINS OF PLANT LIFE 1. eukaryotic, photosynthetic, same types of chlorophyll, starch as storage product, cellulose in cell walls
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns
 Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
Pre-lab homework Lab 2: Reproduction in Protists, Fungi, Moss and Ferns Lab Section: Name: 1. Last week in lab you looked at the reproductive cycle of the animals. This week s lab examines the cycles of
Dry Bean Types and Development Stages
 Dry Bean Types and Development Stages Two basic plant growth habits are found in dry edible bean: determinate (bush) or indeterminate (vining or trailing). Cultivars may be classified according to plant
Dry Bean Types and Development Stages Two basic plant growth habits are found in dry edible bean: determinate (bush) or indeterminate (vining or trailing). Cultivars may be classified according to plant
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1
 Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Reproductive System & Development: Practice Questions #1 1. Which two glands in the diagram produce gametes? A. glands A and B B. glands B and E C. glands C and F D. glands E and F 2. Base your answer
Table 3. List of descritors for maize
 Table 3. List of descritors for maize Descriptor Descriptor Descriptor state Recording stage Remarks number 1 Accession number 2 Total no. of leaves Record the total number of At flowering leaves per plant
Table 3. List of descritors for maize Descriptor Descriptor Descriptor state Recording stage Remarks number 1 Accession number 2 Total no. of leaves Record the total number of At flowering leaves per plant
Class Time: 30 minutes. Other activities in the Stem Cells in the Spotlight module can be found at: http://gslc.genetics.utah.edu/teachers/tindex/
 Teacher Guide: Color-Label-Learn: Creating Stem Cells for Research ACTIVITY OVERVIEW Abstract: Students color and label images on a worksheet and answer questions about the on-line content featured in
Teacher Guide: Color-Label-Learn: Creating Stem Cells for Research ACTIVITY OVERVIEW Abstract: Students color and label images on a worksheet and answer questions about the on-line content featured in
The Tiny Seed Written and Illustrated by Eric Carle 1987, Aladdin Paperbacks ISBN 0-689-84244-9
 Teacher s Guide to Third and Fourth Grade Reading and Writing Exercises for Written and Illustrated by Eric Carle 1987, Aladdin Paperbacks ISBN 0-689-84244-9 Developed by Jennifer A. Seitz For Florida
Teacher s Guide to Third and Fourth Grade Reading and Writing Exercises for Written and Illustrated by Eric Carle 1987, Aladdin Paperbacks ISBN 0-689-84244-9 Developed by Jennifer A. Seitz For Florida
How Insects Feed from Flowers
 The Pollinator Garden: www.foxleas.com How Insects Feed from Flowers The main insect groupings that include species that use flowers as a food source are: Butterflies and Moths (Lepidoptera), Bees and
The Pollinator Garden: www.foxleas.com How Insects Feed from Flowers The main insect groupings that include species that use flowers as a food source are: Butterflies and Moths (Lepidoptera), Bees and
Laboratory. Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs
 Laboratory 5 Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs 1 Laboratory 1: Leaves OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Describe and name leaf patterns 2. Identify the structural differences
Laboratory 5 Leaves: Specialized Plant Organs 1 Laboratory 1: Leaves OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Describe and name leaf patterns 2. Identify the structural differences
Plant Structure and Function
 NQF Level: 2 US No: 116057 Learner Guide Primary Agriculture Plant Structure and Function My name:. Company:. Commodity:.................... Date:............... The availability of this product is due
NQF Level: 2 US No: 116057 Learner Guide Primary Agriculture Plant Structure and Function My name:. Company:. Commodity:.................... Date:............... The availability of this product is due
Discovering cells. The fi rst drawing of cells
 Discovering cells Living things are made of cells. Just as bricks and planks of wood are the building blocks for houses, cells are the building blocks of living things. Cells, although they are very small,
Discovering cells Living things are made of cells. Just as bricks and planks of wood are the building blocks for houses, cells are the building blocks of living things. Cells, although they are very small,
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
 1.2 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Plant and animal cell structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells perform some similar functions,
1.2 Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Plant and animal cell structures are called organelles. Plant and animal cells perform some similar functions,
Chapter 13: Fibonacci Numbers and the Golden Ratio
 Chapter 13: Fibonacci Numbers and the Golden Ratio 13.1 Fibonacci Numbers THE FIBONACCI SEQUENCE 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, The sequence of numbers shown above is called the Fibonacci
Chapter 13: Fibonacci Numbers and the Golden Ratio 13.1 Fibonacci Numbers THE FIBONACCI SEQUENCE 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, The sequence of numbers shown above is called the Fibonacci
Total Income from Farming in the United Kingdom. First estimate for 2015
 28 April 2016 Total Income from Farming in the United Kingdom First estimate for 2015 This release presents the first estimate of Total Income from Farming for the United Kingdom for 2015. Total Income
28 April 2016 Total Income from Farming in the United Kingdom First estimate for 2015 This release presents the first estimate of Total Income from Farming for the United Kingdom for 2015. Total Income
SELL CUT FLOWERS FROM PERENNIAL SUMMER-FLOWERING BULBS Andy Hankins Extension Specialist-Alternative Agriculture, Virginia State University
 SELL CUT FLOWERS FROM PERENNIAL SUMMER-FLOWERING BULBS Andy Hankins Extension Specialist-Alternative Agriculture, Virginia State University Commercial producers of field-grown flower cut flowers generally
SELL CUT FLOWERS FROM PERENNIAL SUMMER-FLOWERING BULBS Andy Hankins Extension Specialist-Alternative Agriculture, Virginia State University Commercial producers of field-grown flower cut flowers generally
Landscape Plant Recognition Plant Descriptions Field Day #1
 CUPRESSACEAE cypress family Cosmopolitan Mostly scale like foliage or whorled in 3 s Resinous Cones, male & female Cone scales in pairs, peltate or basally attached Cones generally smaller than Pinaceae
CUPRESSACEAE cypress family Cosmopolitan Mostly scale like foliage or whorled in 3 s Resinous Cones, male & female Cone scales in pairs, peltate or basally attached Cones generally smaller than Pinaceae
Class Insecta - The insects
 A Introduction 1. Very species rich 2. Characteristics a. 3 pairs of legs b. 2 pairs of wings (most) except flies (1 pair of wings - Diptera) B. Distribution 1. All habitats except saltwater - replaced
A Introduction 1. Very species rich 2. Characteristics a. 3 pairs of legs b. 2 pairs of wings (most) except flies (1 pair of wings - Diptera) B. Distribution 1. All habitats except saltwater - replaced
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum
 Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
Assignment Discovery Online Curriculum Lesson title: In Vitro Fertilization Grade level: 9-12, with adaptation for younger students Subject area: Life Science Duration: Two class periods Objectives: Students
PLANT PURPOSE: WATERING SPRAY OTHER
 Revised 24th February, 2016 The Smiling Worm product you have purchased has a wide range of applications. However, dilution rates and methods of application differ. Below you will find a list of the many
Revised 24th February, 2016 The Smiling Worm product you have purchased has a wide range of applications. However, dilution rates and methods of application differ. Below you will find a list of the many
7A The Origin of Modern Genetics
 Life Science Chapter 7 Genetics of Organisms 7A The Origin of Modern Genetics Genetics the study of inheritance (the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles) Heredity: the
Life Science Chapter 7 Genetics of Organisms 7A The Origin of Modern Genetics Genetics the study of inheritance (the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles) Heredity: the
